M6 - mutations and DNA repair
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
what are mutations?
heritable changes in genome
what are point mutations?
alteration of - of nucleotides, can be - (two options) of a nucleotide pair
single pair, addition/deletion
what are larger mutations?
- (four options) of nucleotide sequence
they are - (less/more) common
deletions, inversions, duplications and translocations
less
how do mutations occur?
spontaneous and induced
spontaneous mutations arise occasionally in all cells, they - (are/aren’t) caused by an agent
aren’t
induced mutations are due to exposure to a - or - mutagen
chemical, physical
mutations can be classified using - or -
genotypic change, phenotypic consequences
spontaneous mutations result from
errors in -
base tautomerization
insertions/deletions due to slippage
spontaneous - in DNA
action of mobile genetic elements such as -
all spontaneous errors are corrected by the -
DNA replication, lesions, transposons
DNA repair systems
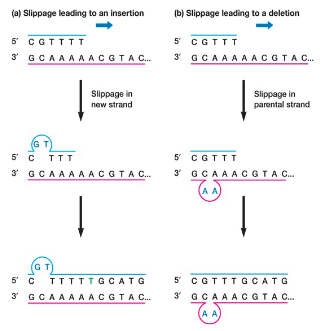
replication errors usually occur in stretches of - nucleotides
slippage in new strand results in -
slippage in parental strand results in -
repeated
insertion
deletion
base tautomerization is when the nitrogenous base of a nucleotide can shift to a - form
bases are usually in - form, but can shift to - or - forms
tautomeric forms have different - characteristics
tautomeric
keto, imino, enol
H-bonding
base tautomerization results in abnormal -
results in A binding with - and G binding with -
base pairing
C, T
base tautomerization results in - and -
transition: purine for - or pyrimidine for -
transversion: purine for - and vice versa
transition, transversion
purine, pyrimidine
pyrimidine
transversion mutations are - (less/more) common than transition mutations because it is sterically difficult to pair - or -
less, purine with purine, pyrimidine with pyrimidine
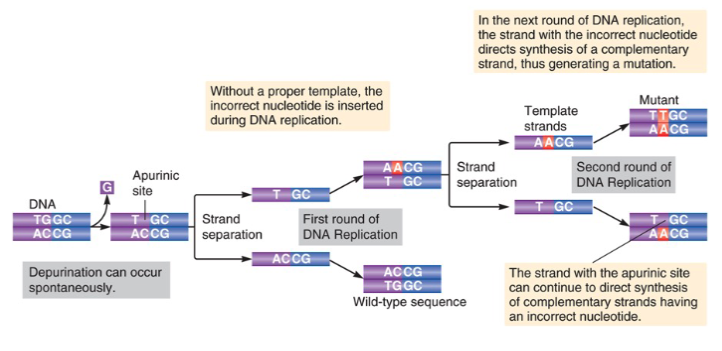
depurination is when purines lose their base to form - sites
depyrimidination is when pyrimidines lose their base to form - sites
apurinic
apyrimidinic
mutagens are any agent that - DNA, alters its -, or interferes with its function can induce a -
damages, chemistry, mutation
chemical mutagens are classified by mode of action (three things)
base analogues
DNA modifying agents
intercalating agents
physical mutagens include -
UV light
base analogs are chemicals that can substitute for -
example: - pairs with both A and G leading to -
nucleotide bases
5-BU, mutations
applications for base analogs (three)
BrdU labelling used to detect -
FACS
labelling -
cell proliferation, DNA/RNA
DNA-modifying agents change structure of - and therefore alter -specificity
example: MNNG is an alkylating agent that methylates -, causing it to base pair with -
base, base-pairing
G, T
intercalating agents insert into - causing distortion in the structure interfering with - introducing -
DNA, replication, mutations
UV radiation causes formation of - bonds between -
results in - → replication - → DNA can’t act as template
covalent, adjacent pyrimidines
thymine dimers, inhibition
wild type is the - form of gene
most prevalent
forward mutation is a mutation from - to - phenotype
wild, mutant
reversion mutation is a second mutation at the - (different/same) site that restores - phenotype
same, wild type
suppressor mutation is when - phenotype is restored by mutation at a - (different/same) site than original site
wild-type, different
Silent forward mutation: change in NT - (does/doesn’t) change the AA due to -
doesn’t, degeneracy
missense forward mutation: change in NT results in - (same/different) AA
different
conservative/neutral forward mutation: when AA change substitutes an AA with - (similar/different) properties
similar
nonsense forward mutation: converts sense codon to - codon
results in early - of translation and a - polypeptide
stop/nonsense
termination, shortened
frameshift forward mutation: insertion/deletion of one or two base pairs changes -, usually -
reading frame, deleterious
reversion mutation are any mutational process or mutation that restores - genotype to cells already carrying a phenotype-altering forward mutation
true reversions restore the wild-type -
pseudoreversions restore the wild-type - by a compensating gene sequence change
wild-type
gene sequence
phenotype
intragenic suppressor mutations restores - phenotype via a second mutation in the - (same/different) gene
wild-type, same
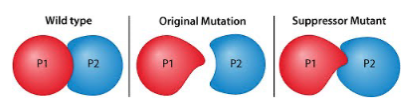
extragenic/intragenic suppressor mutations restores - phenotype via a second mutation -
wild-type, elsewhere
lethal mutations results in -
death
conditional mutations are only expressed under certain -
masked under - set of conditions and visible under - set of conditions
environmental conditions
permissive, restrictive
auxotrophic mutant results in inactivation of - → unable to make -
auxotrophic mutants have conditional phenotypes because if given correct -, pathway may -
biosynthetic pathway, essential macromolecules
intermediates, continue
wild-type strain that gave rise to auxotrophic mutant is called -
prototroph
resistance mutant has acquired - to some - or -
resistance, pathogen, chemical
regulatory sequences are responsible for controlling -
gene expression
mutations in operator site produce altered operator sequences not recognized by - → operon is always -
repressor, transcribed
Why are mutations important for organisms (microbes)?
Can enhance - during - environmental conditions
survival, changing
Why are mutations for important for microbial geneticists?
• Mutant strains are used to study - (such as DNA replication, flagellar rotation, etc.)
• use of - in recombinant DNA procedures
complex processes
selective markers
go through applications !
ok