Nucleic Acids
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
monomers of nucleic acids
nucleotides
examples of nucleic acids
DNA: carries instructions for making proteins
RNA; carry out and interpret the instructions coded in the DNA
what makes up nucleotides
pentose sugar - deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA (OH group on C2 so has extra oxygen)
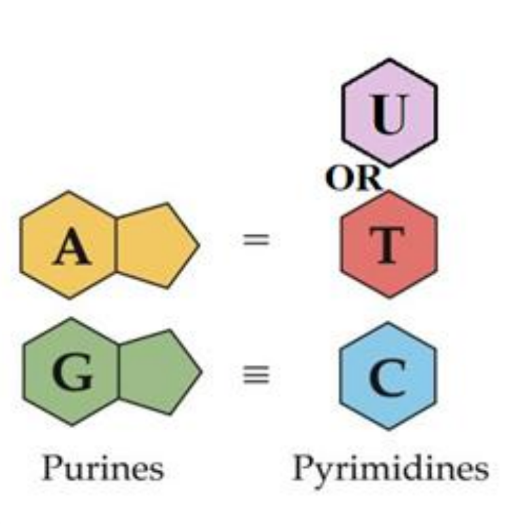
Nitrogenous Base - Adenine and Guanine - purines having two ring structure a hexagon and pentagon
Thymine , Uracil (RNA) or Guanine, they are pyrimidines having 1 ring - hexagon
phosphate group - makes nucleic acid acidic
acronyms
PURe As Gold
purine
in PYRamids U C Tombs
pyrimidine
purine structure vs pyrimidine structure
what do nucleosides consist of
pentose sugar and nitrogenous base only
bonds of nucleotides
phosphodiester bond between sugar and phosphate group of next one
via a CONDENSATION REACTION
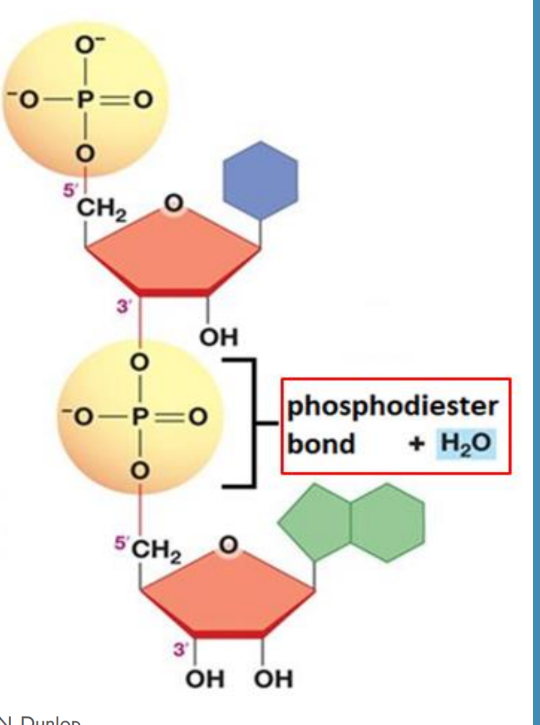
what makes up the sugar-phosphate back bone
alternating sugar molecules (deoxyribose in DNA) and phosphate groups. The sugar of one nucleotide connects to the phosphate of the next nucleotide by a phosphodiester bond
DNA full name
deoxyribonucleic acid
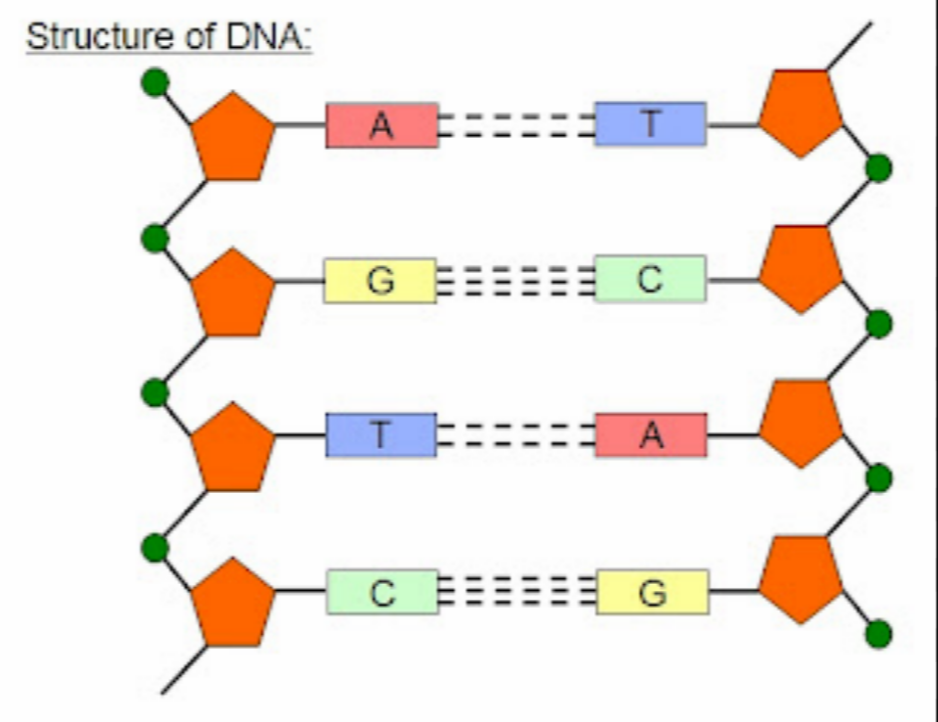
shape of DNA
double helix
draw DNA
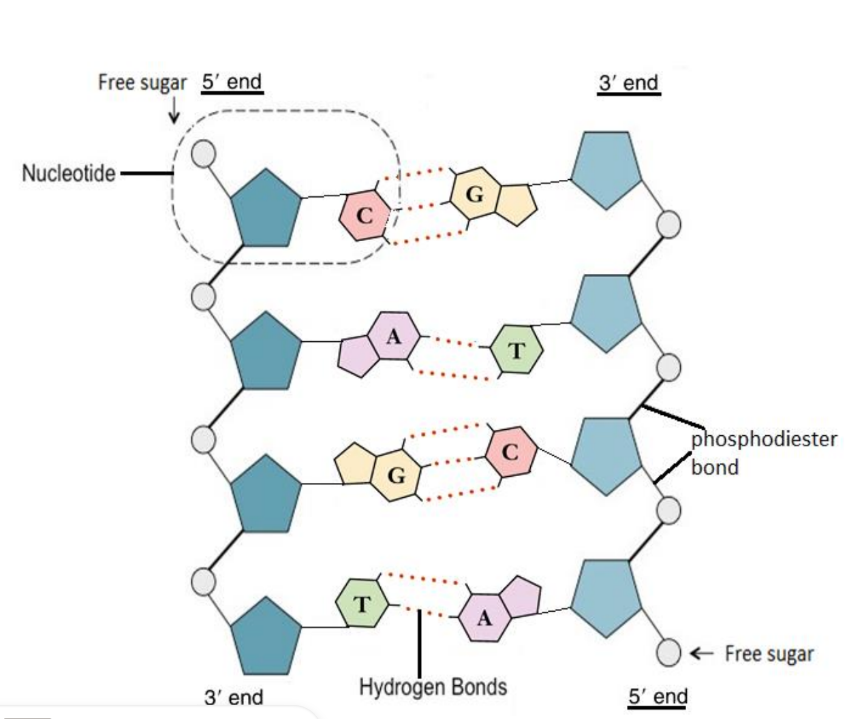
what makes it possible to copy DNA
complimentary base pairing - Complementary base pairing makes DNA copying easier because each base has a matching partner (A with T, C with G). When DNA splits, the matching bases help build a new, identical strand.
what is complimentary base pairing
Complementary base pairing is the way nitrogenous bases in DNA pair up with each other following specific rules
what are two complimentary polynucleotide strands held together by
hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases of adjacent nucleotides
A only bonds to T via 2 H bonds
C only bond to G via 3 H bonds
what does it mean by antiparallel
the two dna strands run in opposite directions 3’ to 5’ and the other 5’ to 3’
RNA full name
ribonucleic acid
what is RNA made up of
1 polynucleotide strand
does complimentary base pairing in RNA occur
yes
A binds to U
and c binds to G
types of rna
mRNA - messanger RNA takes DNA out of the cell and gives instructions
tRNA - transfer RNA; brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome
rRNA- ribosomal RNA, makes up ribosomes are helps form ribosomes structure and helps assemble proteins
(catalyzes peptide bond formation between amino acids)
How does complimentary base pairing make it possible to copy DNA with little errors
the way bases pair follow strict rules, only adenine can bond with thymine etc. etc.