Catalytic transfer hydrogenation (Midterm)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Catalytic transfer hydrogenation is used in processing of __ __.
Vegetable oils
Saturated fats do not contain __. They are __ at room temp.
Alkenes. Solid.
Vegetable oils contain __. They are typically __ at room temp, but can be made into __ by hydrogenation.
Alkenes. Liquids but can be made into solids.
Hydrogenation of an alkene pi bond
Reduction reaction. Increases hydrogen content, and changes physical and chemical properties.
Closing the loop
Using outputs of one process as inputs for another process, decreasing environmental impact of waste streams
Day 1 techniques of transfer hydrogenation
heating at reflux
filtration
‘workup’ on aqueous organic extraction
rotovap
Day 2 techniques for purification and characterization
recrystallization
purity: IR and melting point
identity: IR and melting point
Reduction at a carbon atom identified by…
Decreased number of bonds to electronegative atoms, increased hydrogen content
Purpose of rotovap
Separate solvent from the organic compound. Heat can boil off the solvent, lower pressure will not damage the organic solid. Rotation increases surface area for faster evaporation
Purpose of recrystallization, through vacuum filtration
Is a purification process in which the desired products forms crystals from solutions
What is the purpose of the wetted filter paper during vacuum filtration?
The wetted paper (with the solvent with the organic compound) get vacuumed over the funnels holes to provide a barrier to prevent the solid from draining into the flask with the solvent
Purpose of separation from extraction with separatory funnel
Allows separation of immiscible liquids (aqueous layer and organic layers)
Overlap of two hydrogens s-orbitals of opposite signs give __ __.
Destructive interference = a node between the atoms = antibonding
Overlap of two hydrogens s-orbitals of same signs give __ __.
Constructive interference = bonding
LUMO
Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital. Usually antibonding
HOMO
Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital. Usually bonding
Alkene pi bonds are reduced by __ __.
Catalytic hydrogenation
Catalyst purpose
Lowers energetic barriers (activation energy), but it is not consumed in the reaction
Homogeneous catalysis
Presence of Ni, Pd, or Pt in solution as catalyst
Catalyst we used in experiment
Heterogeneous catalysis, specifically the solid Pd cat.
Using the solid Pd catalyst allowed for the reactions steps to occur on __ __ __.
the surface of the metal
Where does the Pd catalyst obtain the H’s from?
From formate ions
Advantages of heterogeneous catalyst over homogeneous catalysis
A solid catalyst in heterogeneous catalysis can be reused/recycled, rather than dissolving in the organic solvents
When H2 adds across an alkene they are added by __ addition.
Syn addition
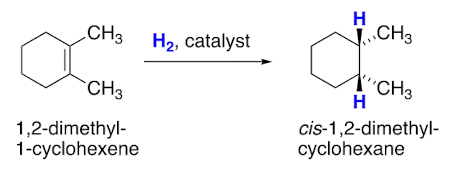
Enantioselective catalysis is if the product is __ and a reaction occurs in a __ environment, one enantiomer may be produced in greater quantity.
Chiral in a chiral environment
Our reaction __ occur in a chiral environment. The __ addition can occur on either face of the alkene = __ product.
Doesn’t. Syn addition. Racemic.
Purpose of heating at reflux
The reaction proceeds to an elevated, controlled temperature without losing solvent/reactants due to evaporation by continuous condensing and return of vapors