Medical Assistant Certification Exam
1/296
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
297 Terms
What are the 4 parts to a patient's medical history?
chief complaint (CC), history of present illness (HPI), Past, Family and Social History (PFSH), and review of systems (ROS)
Vital signs reflect the functions of what three body processes necessary for life?
body temperature, respiration and heart function
what are the 4 vital signs of body function?
temperature, pulse, respiration and blood pressure
Give the normal temp ranges for the following sites: rectal, oral, axillary and tympanic membrane?
rectal 98.6-100
oral 97.6-99.6
axillary 96.6-98.6
tympanic 9.8.6
febrile v afebrile
febrile is the presence of fever, afebrile is absence of fever
3 types of fever?
intermittent, remittent and continuous
oral temperature is not taken from which patients?
infants and children less than 6 yo, patients who had face, neck nose or mouth surgery, those receiving oxygen, patients w altered mental status and others
how long should you wait for patients who just finished eating drinking or smoking to take temp?
30 minutes
What method of taking temp is the least accurate?
axillary (underarm)
normal adult pulse range
60-100 BPM
what is the site most commonly used for taking pulse?
radial artery in wrist
normal range for adults respiration?
12-20 per minute
what are 3 respiration rate abnormalities?
apnea- temporary complete absence of breathing
tachypnea- rate > 40.min
bradypnea- decease in number of respirations
What are to abnormalities in respiratory rhythm?
Cheyne-Stokes- regular pattern of irregular breathing rate
Orthopnea- difficult to breathe unless in upwright position
what does depth of respiration refer to?
amount of air that is inspired and expired during respiration
what are three abnormalities in depth of respirations?
hypoventilation-reduced amt of air enters lungs
hypernea- abnormal inc in depth and rate of breathing
hyperventilation- increased amt of air entering lungs
Define blood pressure
measurement of the amt of force exerted by the blood on the peripheral arterial walls and is expressed in mmHg
BP consists of what 2 components?
highest (systole) and lowest (diastole) amt of pressure exerted during cardiac cycle
Name some common errors in blood pressure measurmens
improper cuff size, arm is not at heart level, cuff not deflated, improper cuff placement
anthropometric refers to what?
comparative measurements of the bdoy
What are the 4 principles of physical examination?
inspection, palpation, percussion, ausculatationq
to make a diagnosis the physician utilizes what 3 sources?
patient's health history, physical exam, and lab tests
horizontal recumbent position
used for most physical exams
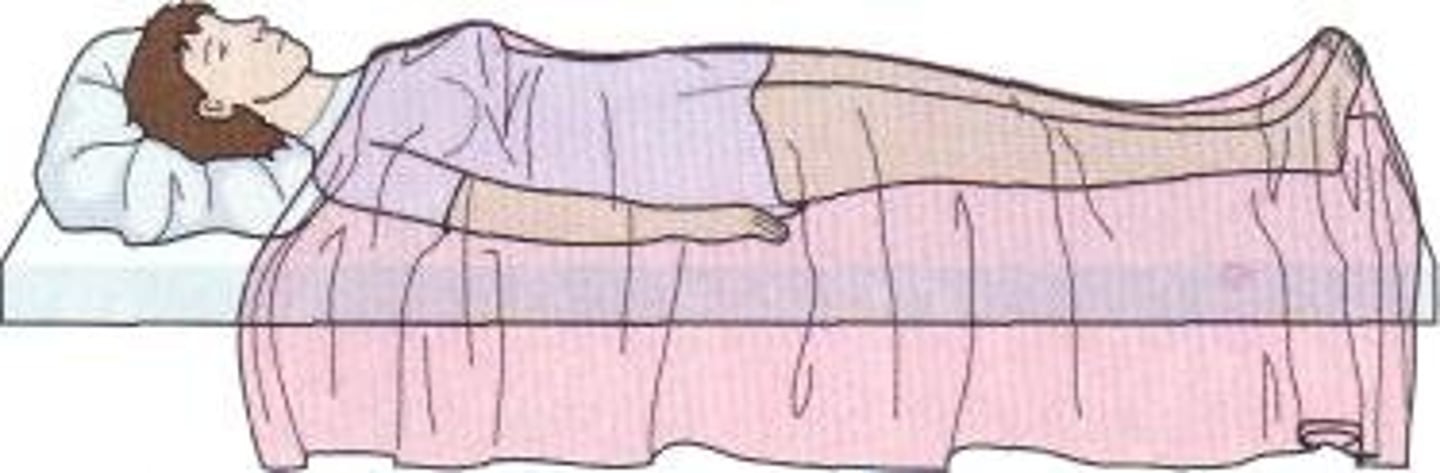
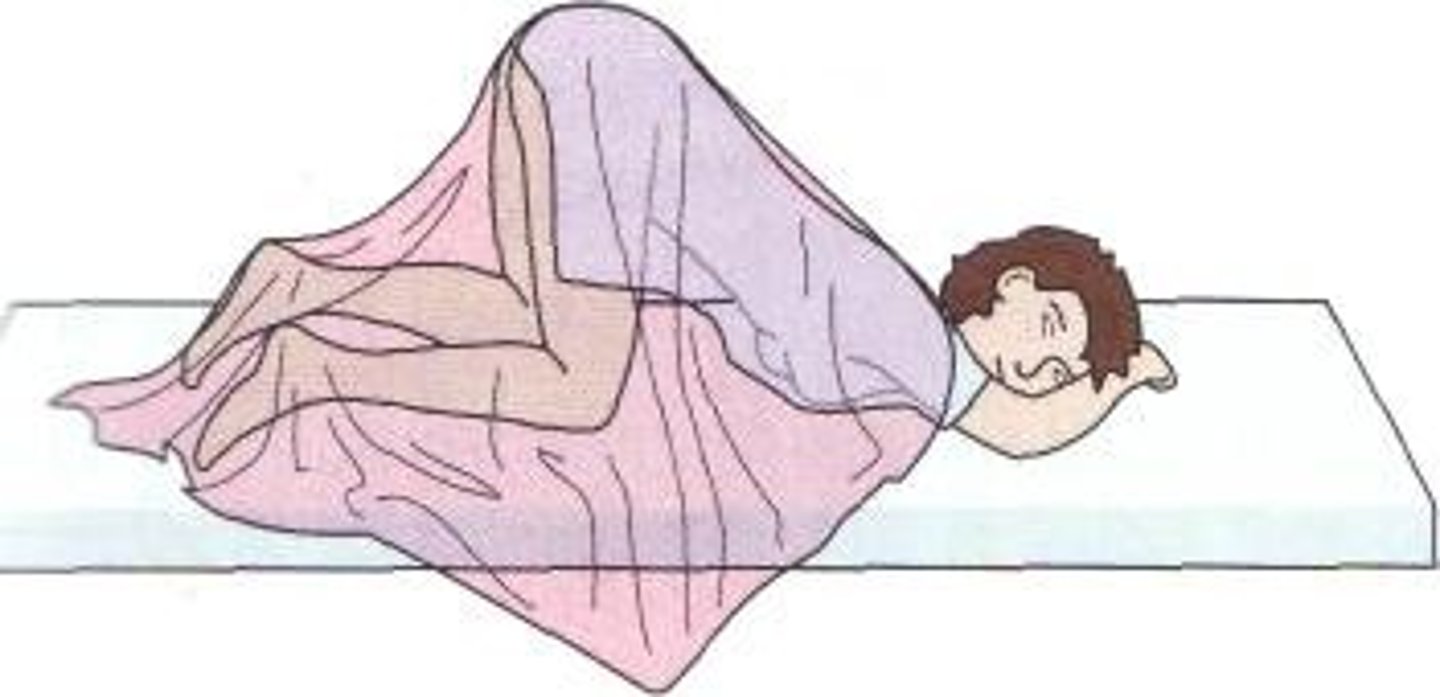
dorsal recumbent position
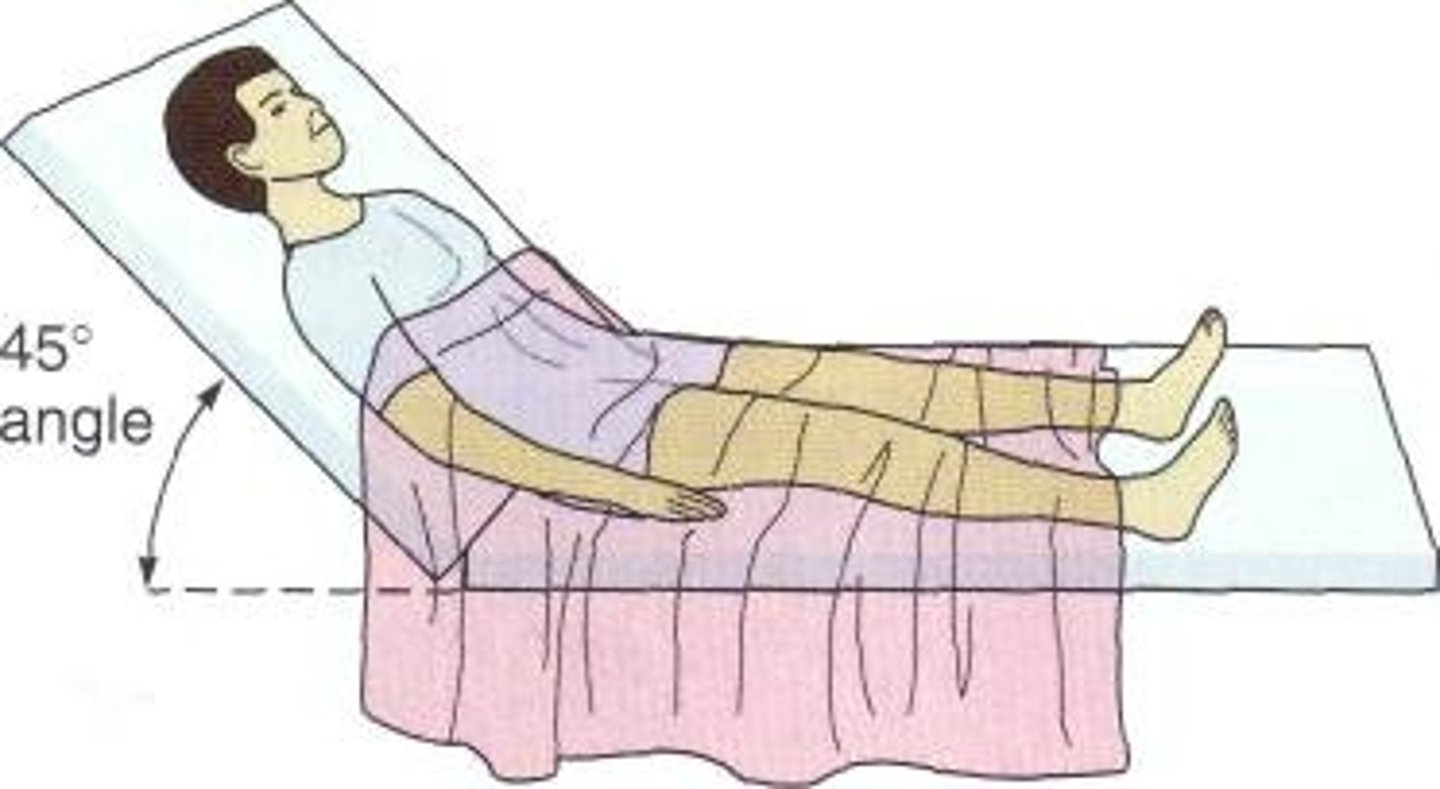
fowler's position
used to promote drainage or ease breathing
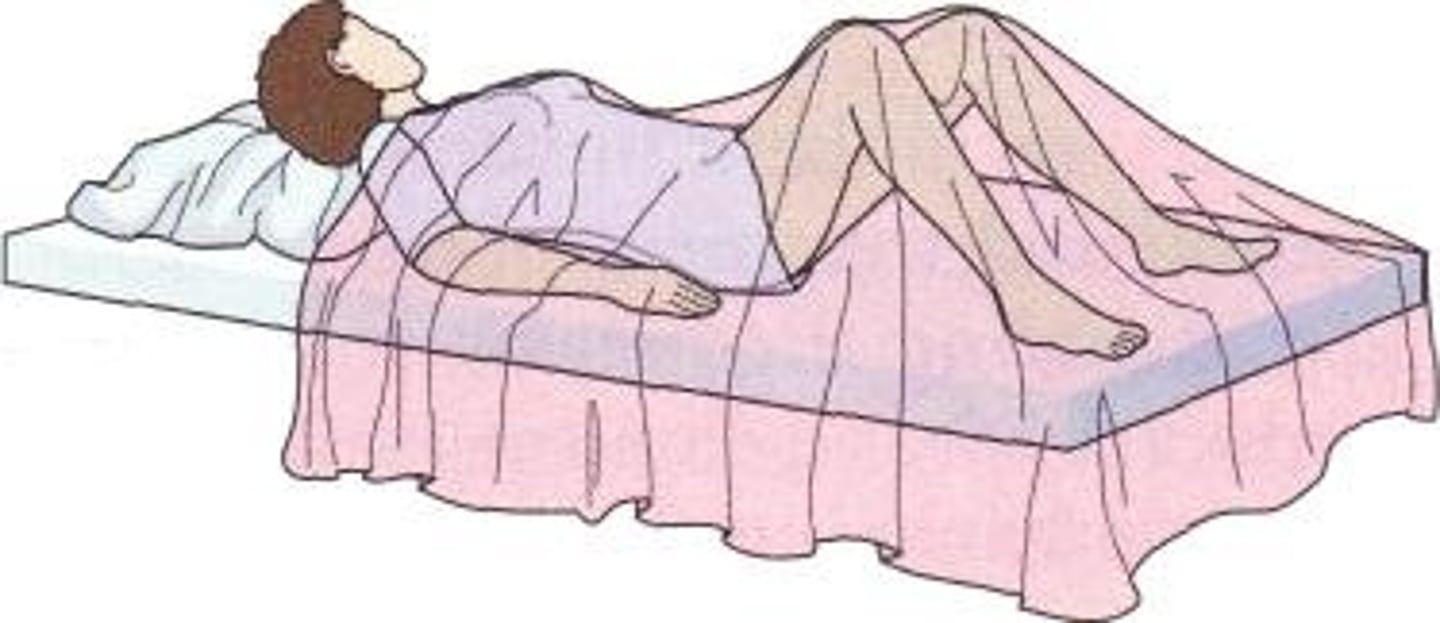
dorsal lithotomy position
used for exam of pelvic orgns
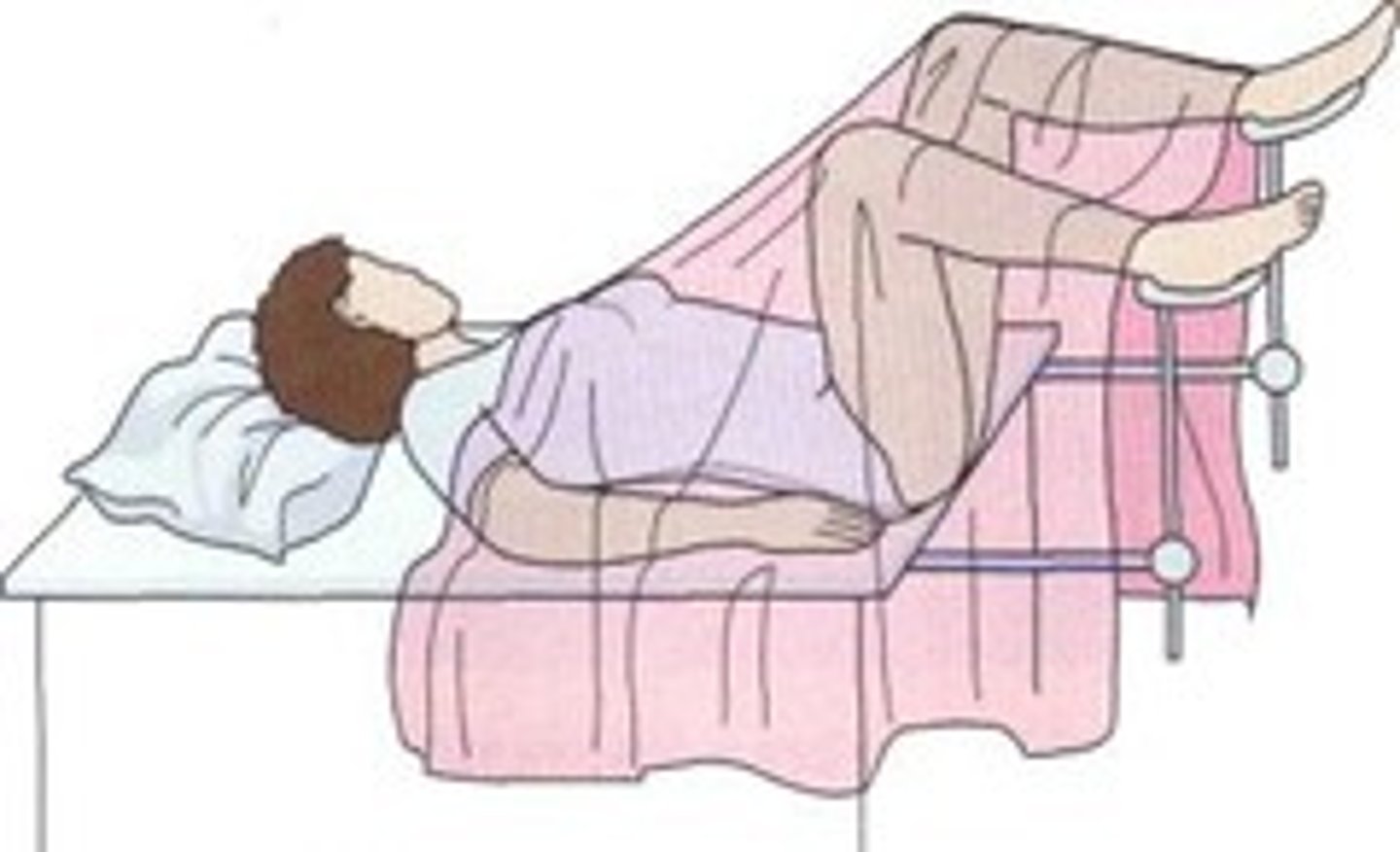
prone position
used to examine spine and back
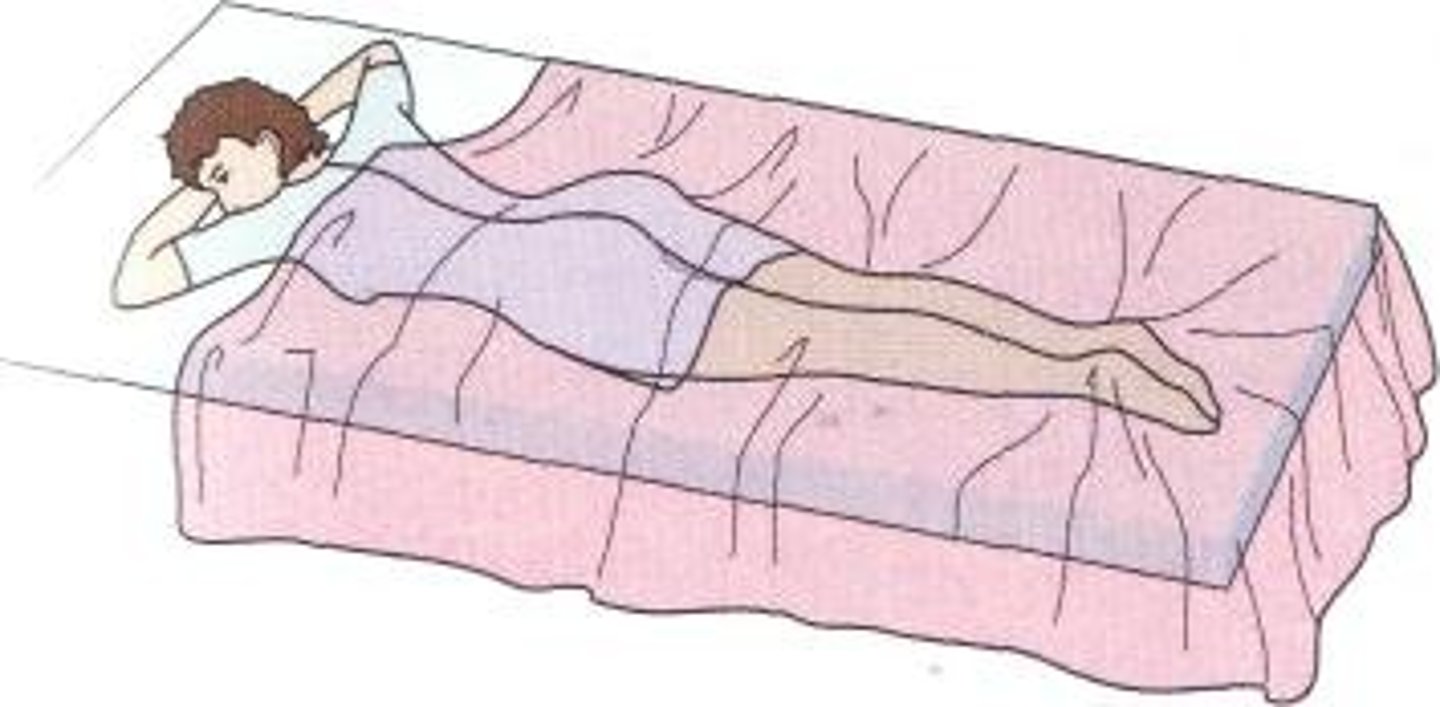
Sim's position
used for rectal examination
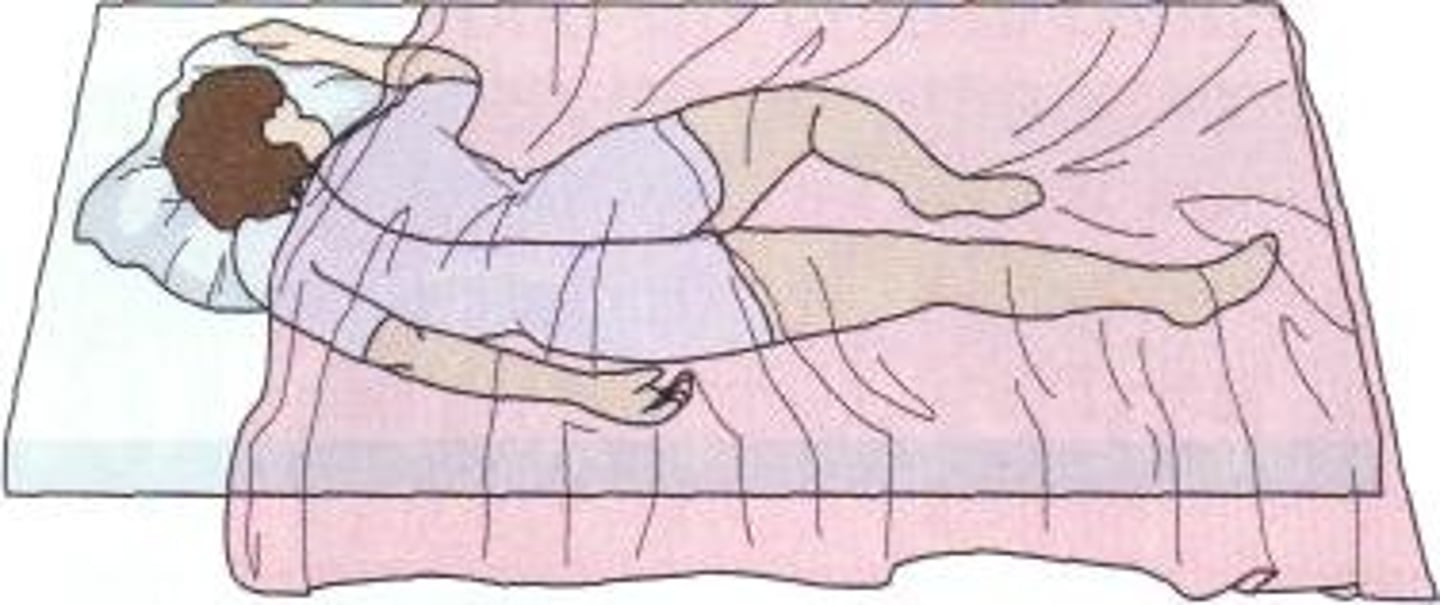
knee-chest position
used for rectal and vaginal exams
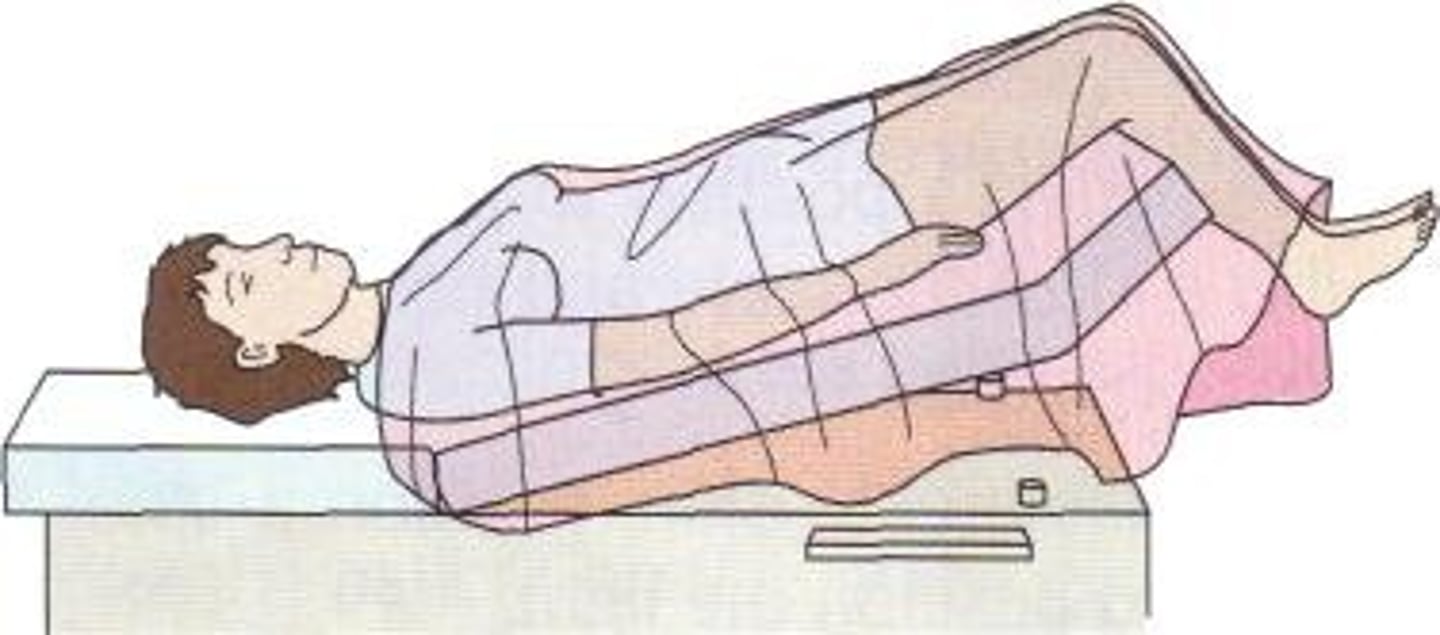
trendelenburg position
used for surgical procedures of pelvis and abdomen
Which organization is responsible for the identification of the various hazards present in the workplace and for the creation of rules and regulation to minimize exposure to hazards?
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
What are the 3 categories for safety hazards?
physical hazards, chemical hazards, biological hazards
for an external hemorrhage how is bleeding controlled?
elevating the affected part above heart level and applying direct pressure to the wound
when does shock occur?
when there is insuffcient return of blood flow to the heart, resulting in inadequate supply of oxygen
what are the common symptoms of shock?
pale, cold clammy skin, rapid weak pulse, increased shallow breathing rate, expressionless face
first aid for shcok
maintain an open airway, call for assistance, keep victim lying dow, attempt to control cause of shock
what are agents?
infectious microorganisms that can be classified into groups
portal of exit and portal of entry
portal of exit is the method by which infectious agent leaves its resevoir; portal of entry allows infectious agent access to suceptible host
mode of transmition
specific ways in which microorganisms travel from resevoir to susceptible host. 5 main types: contact, droplet, airborne, common vehicle and vectorborne
define medical asepsis
the destruction of pathogenic microorganisms after they leave the body
what procedure is used in medical aspesis using various chemicals that can destroy pathogenic microorganisms?
disinfection
what is the least expensive and most readily available disenfection?
a 1:10 solution of household beach
4 methods of sterilization
gas sterilization, dry heat sterilization, chemcial and steam (autoclave)
what is the most important means of preventing the spread of infection?
hand washing
what are the 3 categories of isolation?
contact precautions, airborne precautions and droplet percautions
po (abb)
by mouth/orally
pr (abb)
per rectum
sl (abb)
sublingual (under tongue)
SQ (abb)
subcutaneous
pc (abb)
after meals
qhs (abb)
each night
prn (abb)
as needed
The heart is located in the thoracic cavity between the lungs in what space?
mediastenum, just behind the sternum
give layers of heart deep to superficial
endocardium, myocardium, pericardium
what is the "heart skeleton" made of?
four rings of thick connective tissue
what are the layers of fluid separating the parietal pericardium and visceral pericardium?
pericardial sac
what structure in the middle of the heart divides the heart into two sides?
septim
what kind of blood does the left and right side of the heart pump?
right pumps deoxygenated blood w low pressure from veins into lungs (pulmonary circulation) and left pumps oxygenated blood with high pressure (blood pressure) toward the tissues through the arteries (systemic circulation)
What are the four heart chambers?
right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle
what are the only arteries in the body that carry oxygenated blood?
pulmonary arteries (efferent)
what are the only veins in the body that carry oxygenated blood?
pulmonary veins (afferent)
what is the largest artery in the body?
the aorta
be familiar with heart anatomy
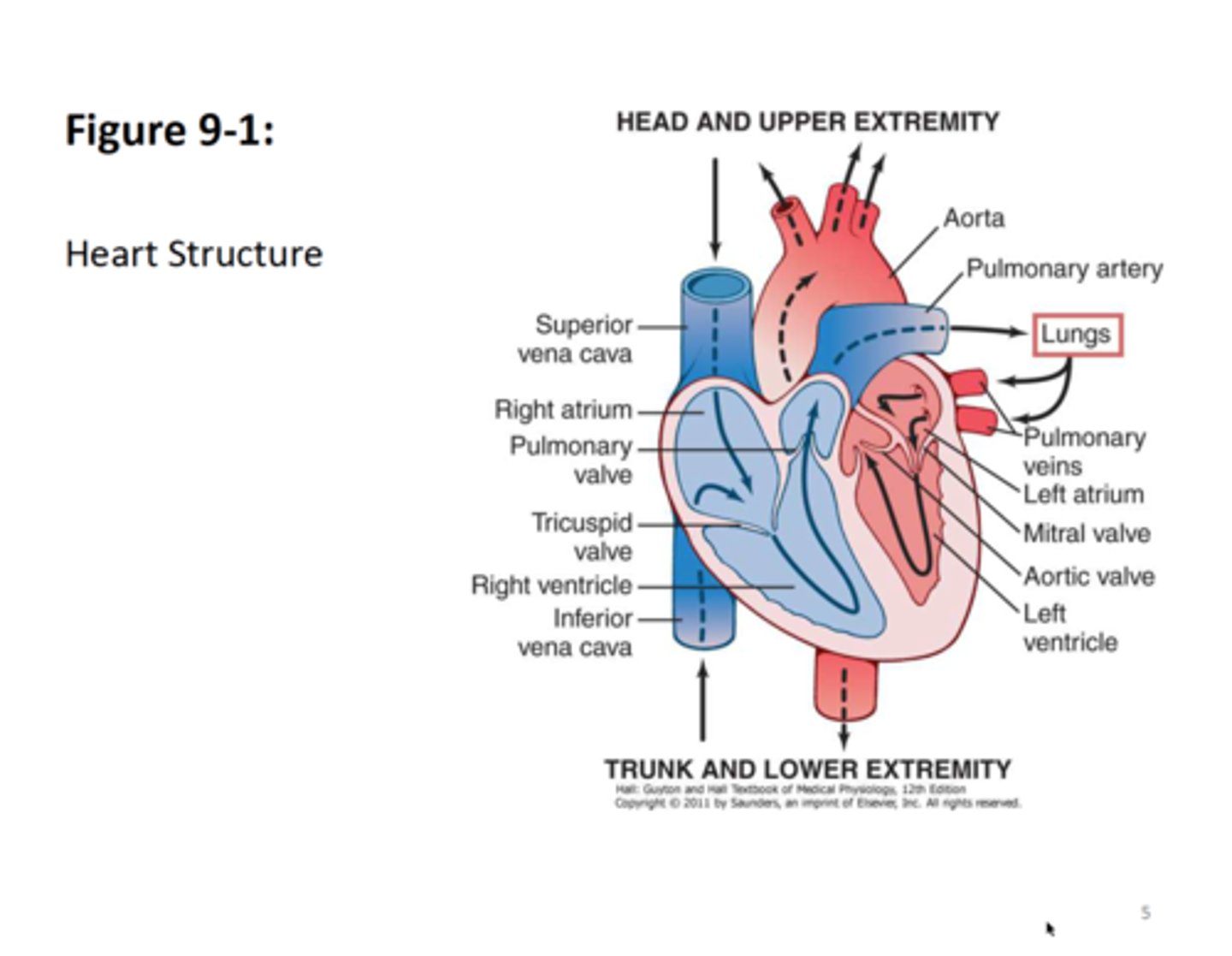
what is the purpose of heart vavles?
to prevent the backflow of blood therby assuring uni-directional flow through the heart
what are the subdivisions of the heart valves?
Atrioventricular valves (AV): Tricuspid + Bicuspid Mitral
semilunar valves: Pulmonic + Aortic
What are the AV cuspid valves characteristcs?
have tough fibrous rings, long and strong leaflets (cuspids), accessory organs (ie papillary muscles, chordae tendinae)
give the location of the AV cuspid valves?
tricuspid is btw the right atrium and right ventricle, bicuspid mitral is btw left atrium and left ventricle
characteristics of semilunar valves?
three leaflests, shallow in depth, no accessory organs
give location of semilunar valves?
pulmonic btq right ventricle and pulmonary trunk, aortic btw left ventricle and aorta
where are the coronary arteries located?
on the epidcardium
what are the two branches of the left coronary artery?
Left anterior descending (LAD) artery and Left Circumflex (LCX) artery
what is the main artery that supplies the right side of the heart?
Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
What is the period of contractions of both atria and ventricles?
systole
what is the period of relaxation and filling of all cardiac chambers?
diastole
heart sounds are caused by what?
closure of the heart vavles
when does the S1 first heart sound (Lubb) occur?
occurs during ventricle contraction and closure of AV valves
when does the S2 second heart sound (Dupp) occur?
occurs during ventricular relaxation when SL valves close
heart murmurs are caused by what?
diseases of the valves or other structural abnormalities
define heart rate
number of heart contractions per minute
what two things control heart rate?
chemo-receptors (chemical sensors) and Baro-receptors (pressure receptors) located in the aortic arch and carotid arteries
the heart is under the influence of which nervous system?
the autonomic nervous system which is subdivided into the sypathetic and parasypathetic
which division of the ANS has an inhibitory effect via acetylcholine?
parasympathetic (vagus nerve)
what division of the ANS has a excitatory effect via norepinephrine?
sypathetic
acetylcholine effects in body?
slows SA pacemaker and heart rate, slows conduction of electricity in AV node, decreases strength of atrial and ventricular contraction
norepinphrine effects in body?
increase HR, increases force of contraction, increases blood pressure, dopaminergic receptors increase the diameter of visceral blood vessels
True or false. the blood volume ejected outside the heart is equal to the blood volume returning back into the heart
TRUE
what is stroke volume (preload)?
the blood volume ejected outside the ventricle after each contraction; depends on volume of blood, force of myocardium contraction and vascular resistance
what is the Starling Law?
the greater the volume of blood inside the heart during diastole, the stronger the heart contraction force during systole.
the lower the resistance in the vessels, the MORE OR LESS easily blood can be ejected outside heart through circulation?
MORE
what is cardiac output?
the amount of blood ejected outside heart per minute
cardiac output equals (X) * (Y)
x- stroke volume
y- HRper/min
what is peripheral vascular resistance?
the force exerted against the blood flow determined by diameter of the vessel; lower the vascular resistance the less force needed to eject blood
define blood pressure
the force exerted by circulating blood volume on the walls of the artery during circulation
formula for BP
BP equals (cardiac output) * (vascular resistance)
define EKG
graphical presentation of heart electricity over time. electricity created by pacemaker cells
how is the electricity created by pacemaker cells?
elecrtical impulses created by passing of ions through the cell membrane
What are the 4 properties of cardiac cells?
automaticity
excitability
conductivity
contractility
when does depolarization occur?
when the postively charged ions rapidly move from outside the myocardial cell membrane to the inside, changing charge from negative to positive
depolarization results in what?
contraction
what is repolarization and when does it occur?
occurs immediately after depolarization and is the movement of positively charged ions back to the outside of the cell, returning cell back to original polarized state