BIO230 L9 Protein Sorting
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
post translational process of protein sorting
proteins fully synthesized in the cytosol before sorting
mitochondria, plasmids, nucleus, peroxisomes all fall under this category
co-translational process of protein sorting
endoplasmic reticulum falls under this category — proteins are associated with the ER during protein synthesis
what type of transport occurs between which organelles? (colour coded flowchart)
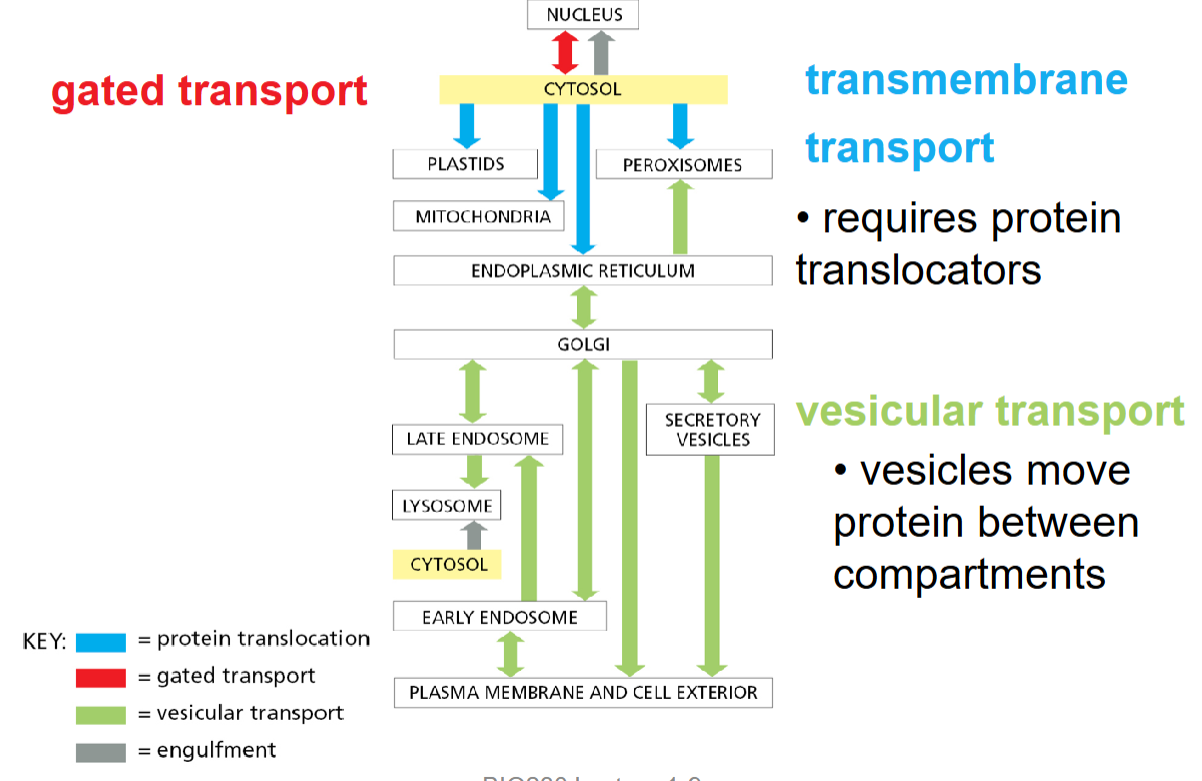
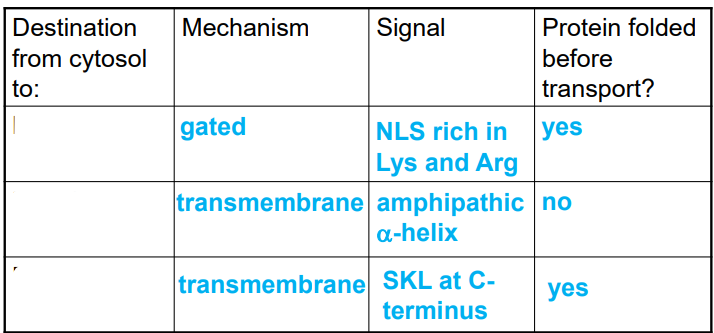
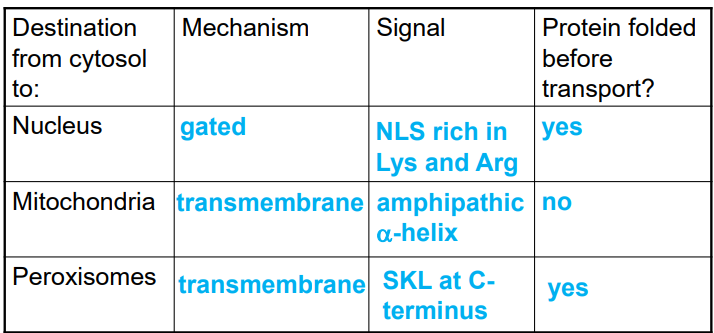
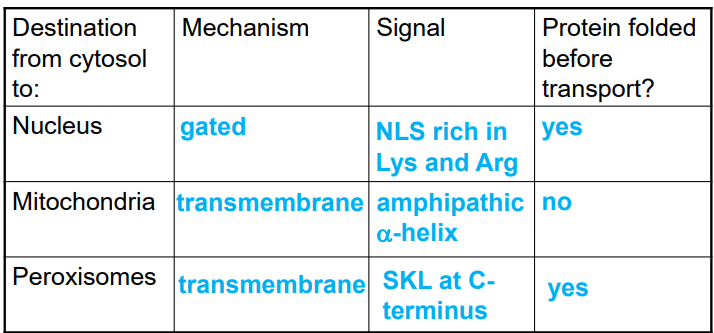
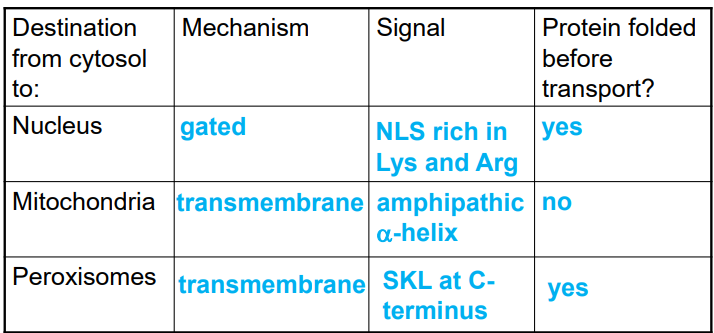
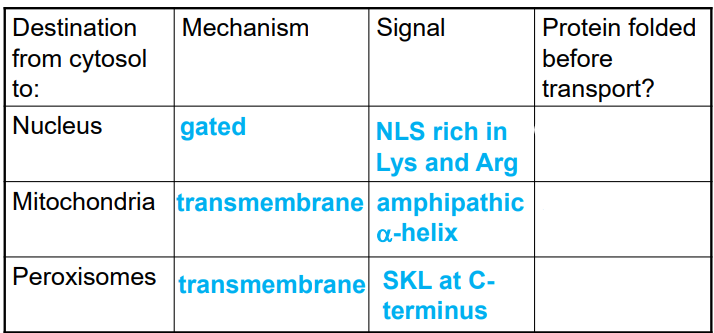
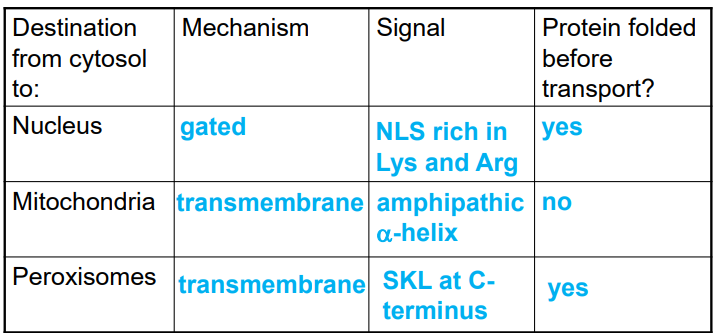
gated transport
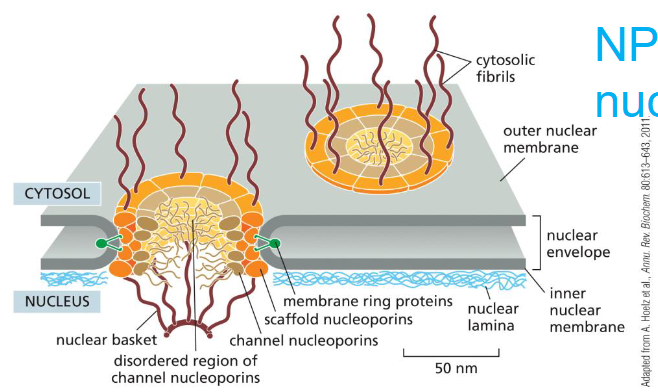
proteins moving between cytosol and nucleus through the nuclear pore complex
nuclear pore complex
selective transport of macromolecules
free diffusion of molecules <5000 daltons
transport of cargo occurs in both directions
made up of nucleoporins that facilitate transport with the nuclear import/export receptor
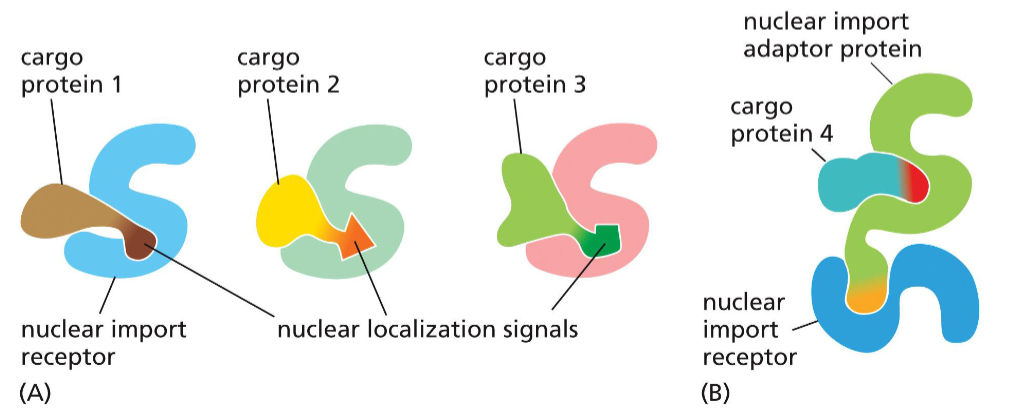
nuclear import receptor
a protein in the cytosol which binds to the nuclear localization signal in cargo (or with help from adaptor proteins)
once bound, binds to nucleoporins in the nuclear pore complex and transports into the nucleus
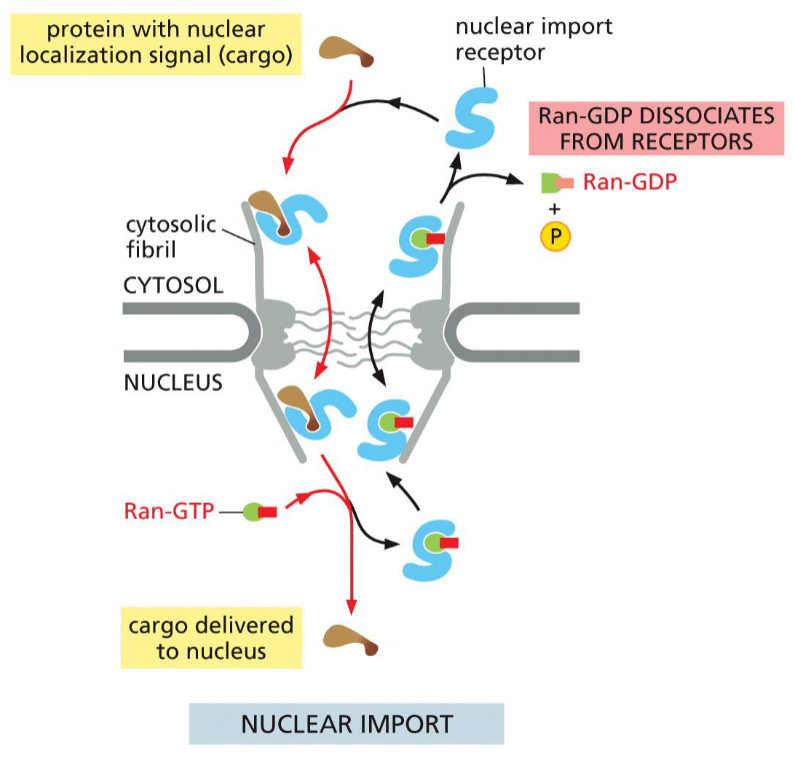
nuclear import of cargo proteins
Nuclear import receptor
binds cargo in cytosol
Receptor + cargo move to nucleus
Ran-GTP binding causes cargo release
Empty import receptor + Ran-GTP
move to cytosol
Ran Binding Protein and Ran-GAP
promote:
GTP hydrolysis
release of import receptor
nuclear export of cargo proteins
Nuclear export receptor
binds Ran-GTP + cargo in nucleus
Receptor + cargo + Ran-GTP move to cytosol
Ran Binding Protein and Ran-GAP promote:
GTP hydrolysis
release of cargo
release of export receptor
Empty export receptor returns to nucleus
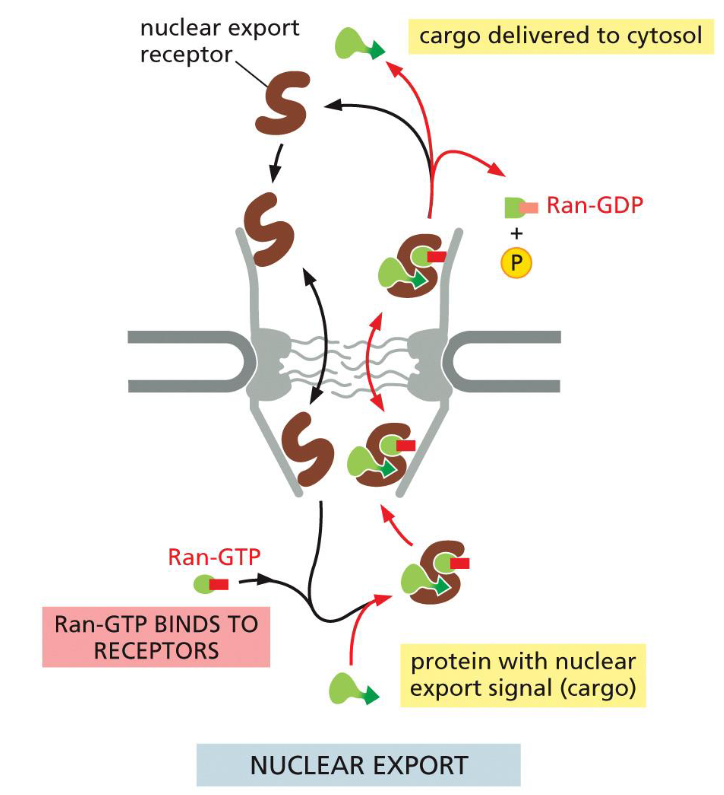
nuclear export receptor
a protein in the nucleus which binds to the nuclear export signal in cargo
once bound, binds to nucleoporins in the nuclear pore complex and transports into cytosol
newly assembled ribosomal subunits, RNA, or proteins with regulated nuclear import & export may be transported
nuclear localization signal
an amino acid sequence in a protein that binds to the nuclear import receptor
rich in Lys and Arg
Ran GTPase
an enzyme required for nuclear import and export
(GTP) causes cargo release by the NIR in the nucleus and (GDP) dissociates in cytosol
causes cargo binding to the NER in the nucleus and dissociates in cytosol
regulated by Ran-GAP (in nucleus) and Ran-GEF (in cytosol)
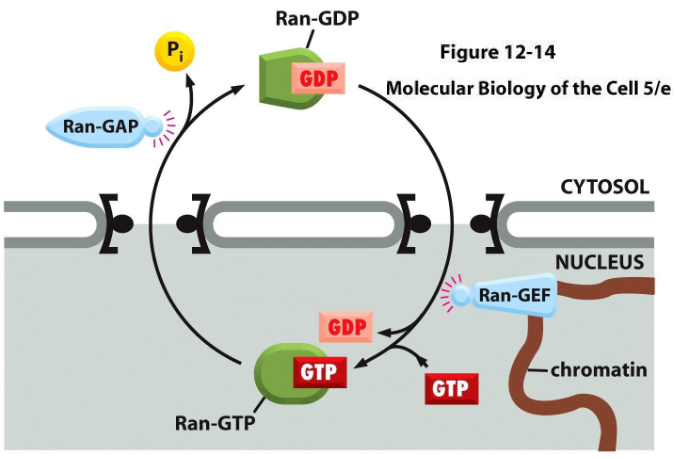
Ran-GAP (GTPase-Activating Protein)
an enzyme residing in the cytosol
promotes GTP hydrolysis by Ran and release of cargo and export receptor in nuclear export, import receptor in nuclear import
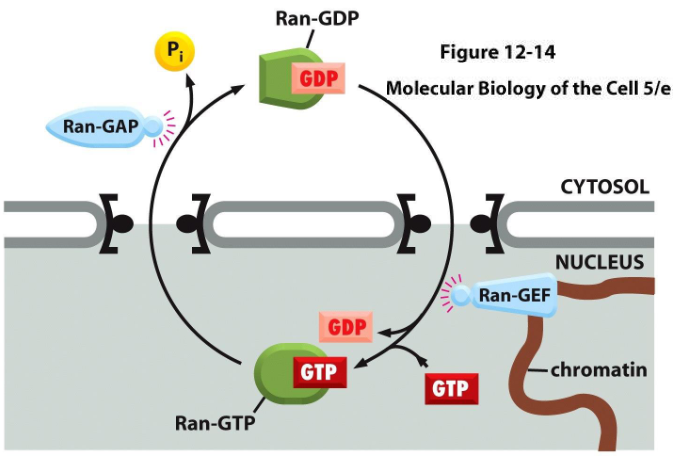
Ran-GEF (Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor)
an enzyme residing in the nucleus
promotes exchange of GDP for GTP by Ran
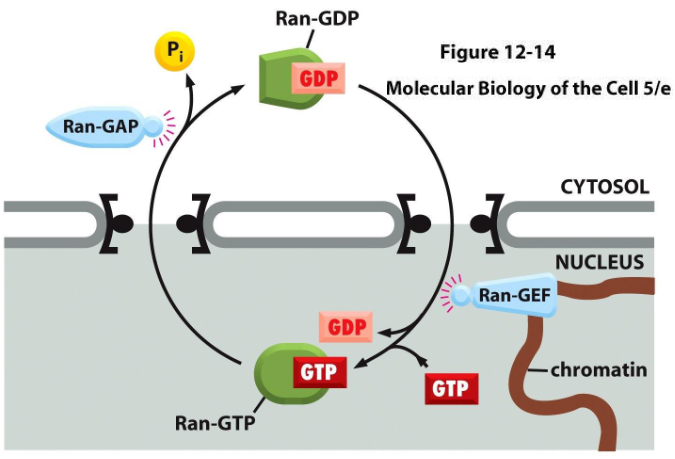
NTF2 (Nuclear Transport Factor 2)
transports Ran-GDP from the cytosol back into the nucleus
effectively creates directionality/a concentration gradient for Ran GTP/GDP
NFAT import/export cycle
high [intracellular Ca2+] → nuclear import
low [intracellular Ca2+] → nuclear export
![<p>high [intracellular Ca2+] → nuclear import</p><p>low [intracellular Ca2+] → nuclear export</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6f90e5f3-3ca1-4584-be40-bdcaab03bae3.png)
transmembrane transport
requires protein translocators — transports generally unfolded proteins across the membrane
occurs in ER, mitochondria, plastids, peroxisomes
why mitochondria and chloroplasts are special cases of transmembrane transport
mostly have their own genome and ribosomes but most proteins are nuclear encoded
have many membranes to pass through
importing proteins into the mitochondrial matrix
TOM and TIM23 complexes
protein remains unfolded in cytosol with use of cytosolic hsp70 chaperones
mitochondrial signal sequence is an N-terminal amphipathic alpha helix that binds receptor and is cleaved upon entry of the matrix
proteins can be further sorted
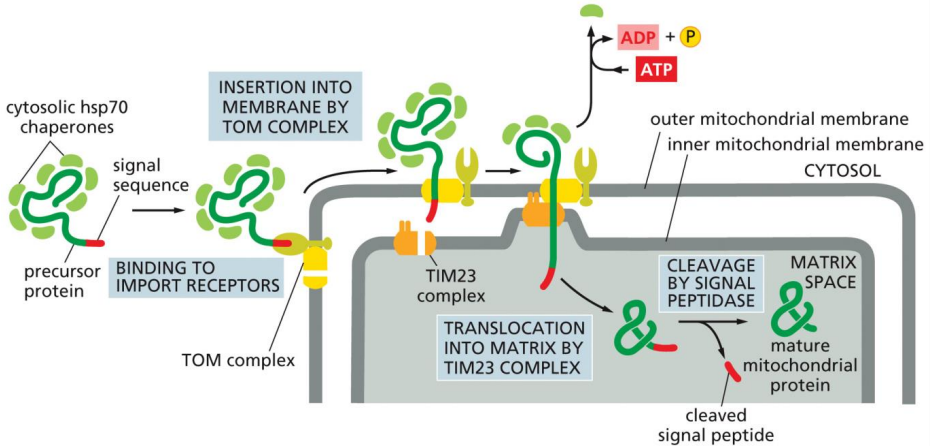
TOM complex
protein translocator in the mitochondria
on the outer membrane of the mitochondria
TIM23 complex
protein translocator in the mitochondria
on the inner membrane of the mitochondria
importing proteins to the chloroplast
TOC and TIC complexes
chloroplast signal sequence is an N-terminal amphipathic alpha helix that binds receptor in the TOC complex and is cleaved upon entry of the chloroplast
thylakoid signal sequence is a hydrophobic signal sequence unmasked when first signal is cleaved
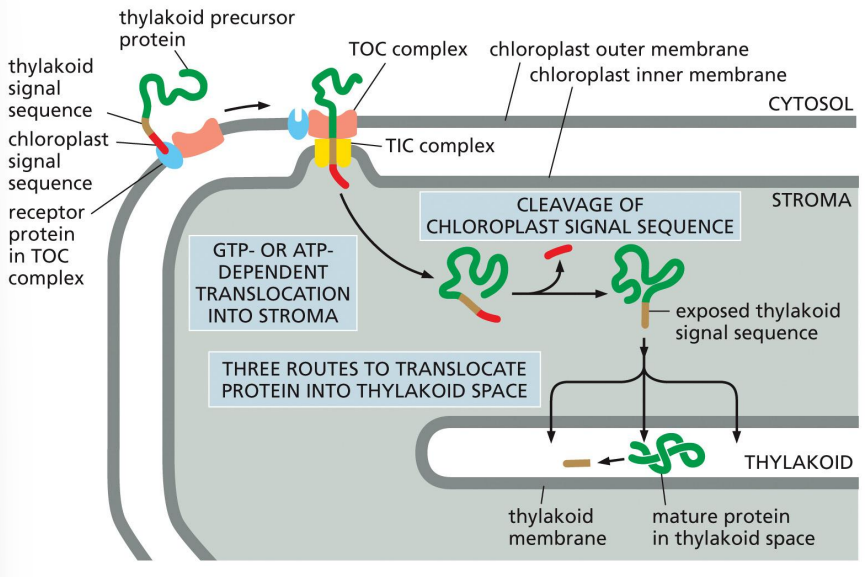
TOC complex
protein translocator in the chloroplast
has a separate receptor protein that binds precursor
on the outer membrane of the chloroplast
TIC complex
protein translocator in the chloroplast
on the inner membrane of the chloroplast
uses GTP or ATP dependent translocation into the stroma
importing proteins into the thylakoid
hydrophobic thylakoid signal sequence is unmasked when chloroplast signal sequence is cleaved
three different routes to translocate protein into thylakoid space
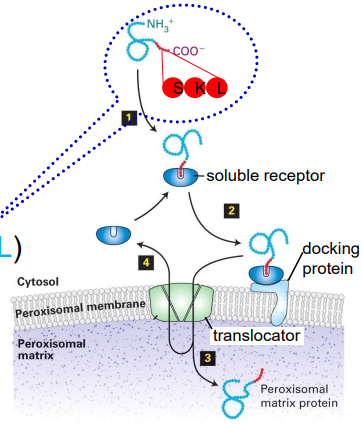
sorting proteins to the peroxisome
peroxisomal targeting signal contains 3 amino acids at C terminus (SKL)
protein is folded
transported across membrane by a large translocator complex
vesicular transport
vesicles move protein between compartments