Bio 2 Exam 3
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
good luck guys 🤟🏽
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms

Porifera (main features
have a simple anatomy
have 2 layers, around 15 cell types
choanocytes
spicules
not true tissues (cells are not determined)
no symmetry in adult (but yes in larvae)

Adult and Larvae Symmetry (Porifera)
adults - have no symmetry
essentially retain genes to be symmetrical but just don’t do it
larvae - can have radial or bilateral symmetry
larva disperses
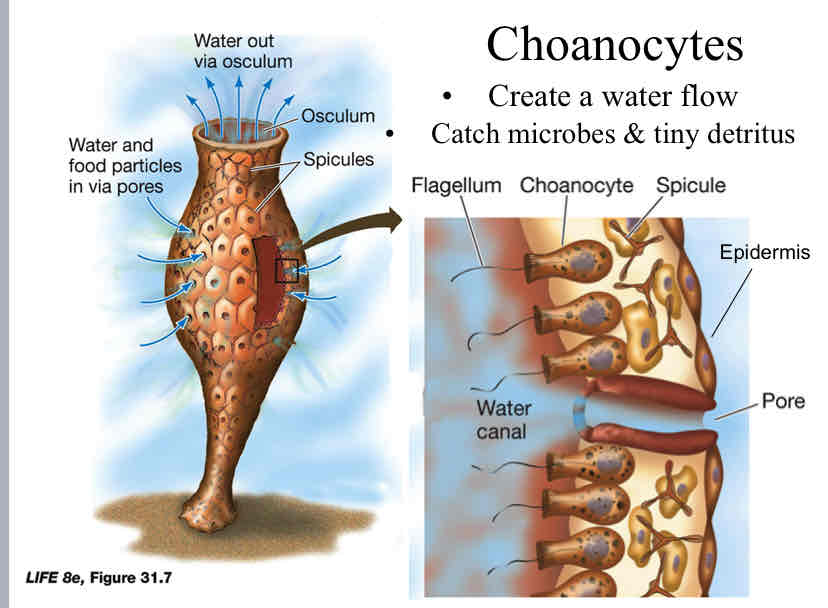
Choanocytes (collar cells)
create a water flow
catch microbes and tiny detritus
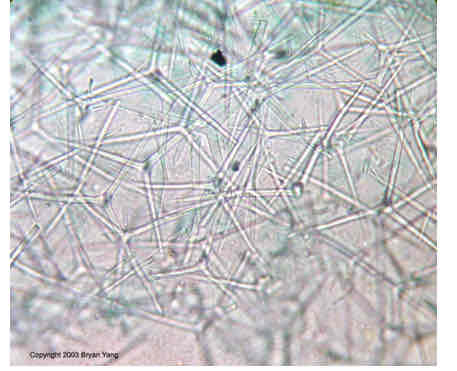
Spicules
are interlocking spikes made of calcium material
act as support
help deter feeding from other animals

Practice Question (Phylogenetic Trees) - According to Wang et al. (2010) the oldest fossil sponges, recently found in S. China, had silica (glass) spicules. This discovery
does not support the tree here
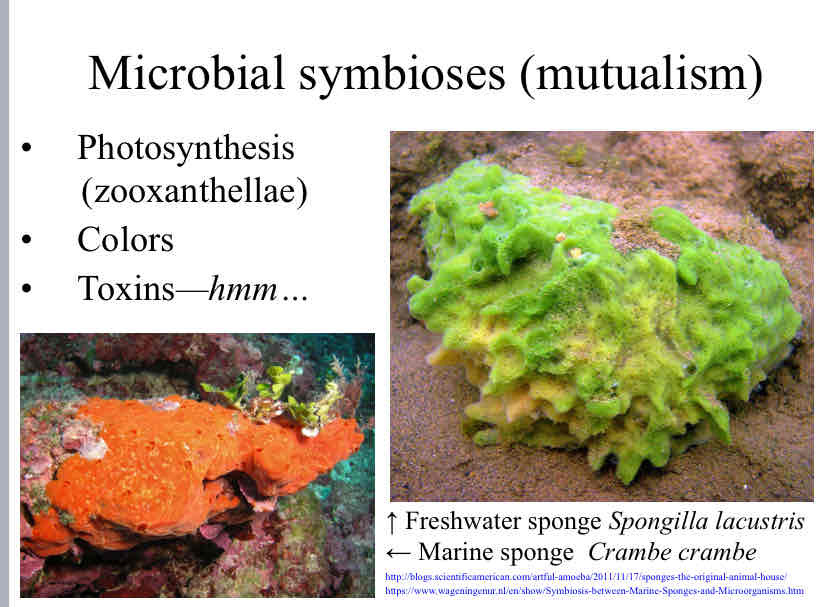
Microbial Symbioses (mutualism)
photosynthesis (zooxanthellae)
colors
toxins

Medicinal Sponges
can be used to treat diseases
e.g. the rope sponge picture here (Aplysina cauliformis) , can be used to treat tuberculosis
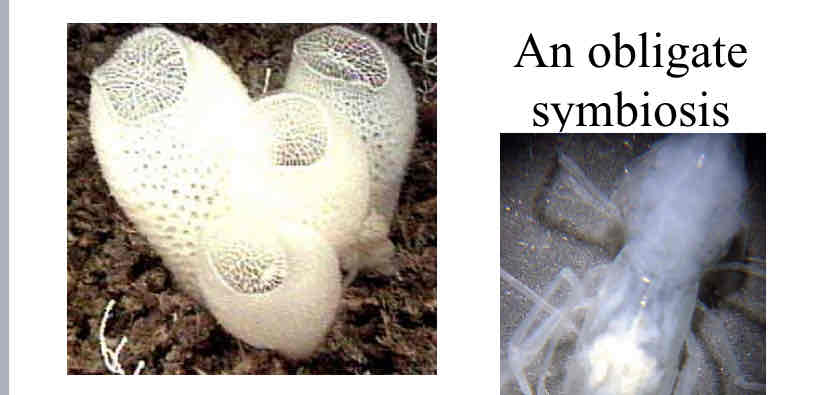
obligate symbiosis
the sponge - provides housing for the shrimp
the shrimp - provides cleaning service , and eats uneaten microscopic food

Kairou-Douketsu
young male shrimp enters sponge first
then female shrimp enters sponge
shrimp couple mate for life
they grow together and cannot leave

Cnidaria
radial symmetry in adult
2 “true” tissue layers
epidermis, gastrodermis, mesoglea between
cnidocytes
medusa and polyp
incomplete gut - they eat macroscopic food
organismal integration :
nerves
muscle
planula larva
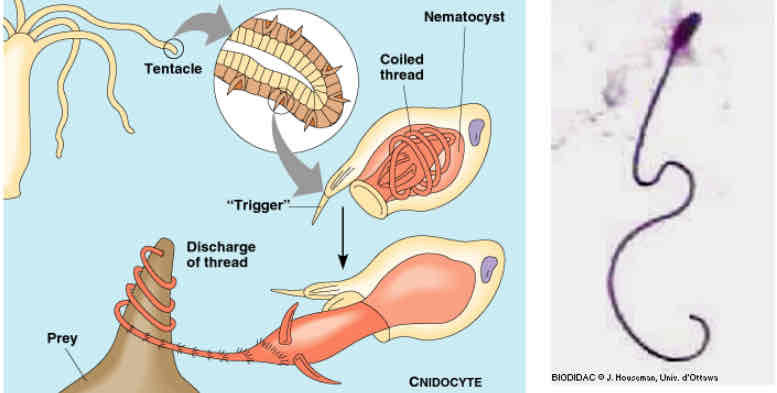
Cnidocytes
are stinging cells
discharged from cnidaria to immobilize prey
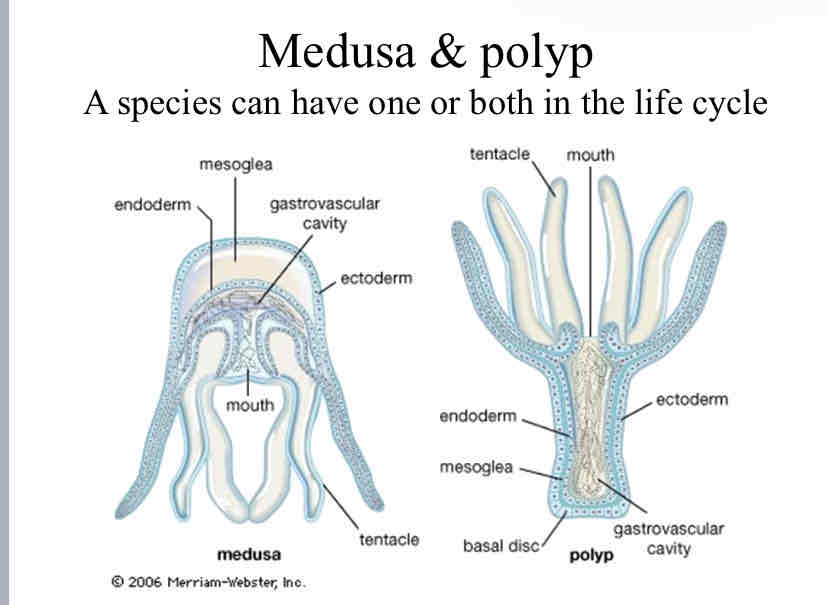
Medusa & Polyp
a species can have either one or both of them in their life cycle
medusas are free flowing
polyps are often attached to a surface or other polyps
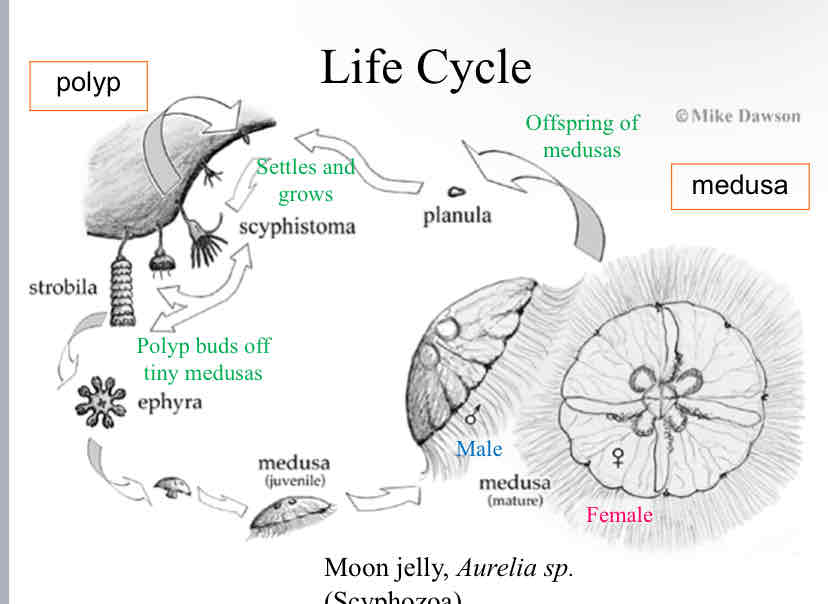
Cnidarian Sample Life Cycle
both medusa mate and produce an offspring called a planula
the planula settles and grows and becomes a polyp
the polyp produces tiny stacks of medusas and eventually buds them off
the medusas grow until they are mature enough to mate and the cycle begins again
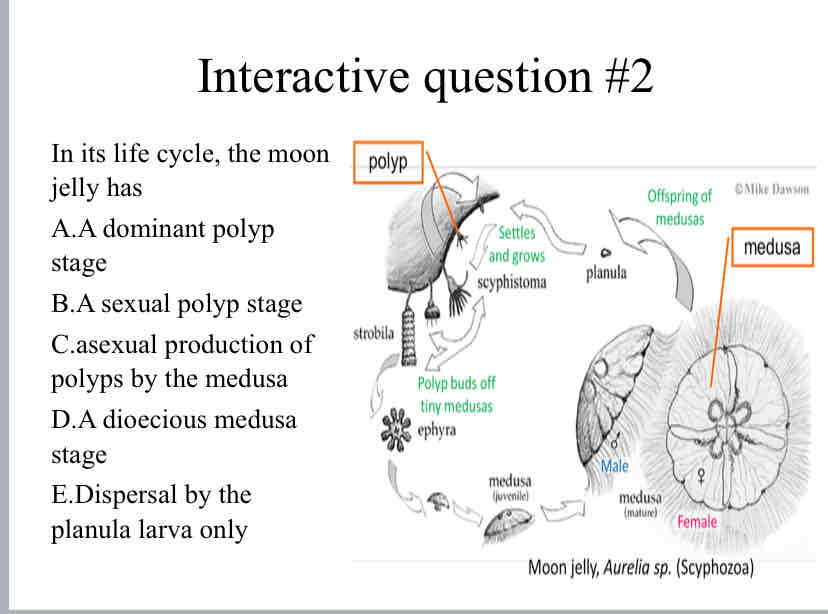
Practice Question (Life Cycle) - In its life cycle, the moon jelly has
A dioecious medusa stage
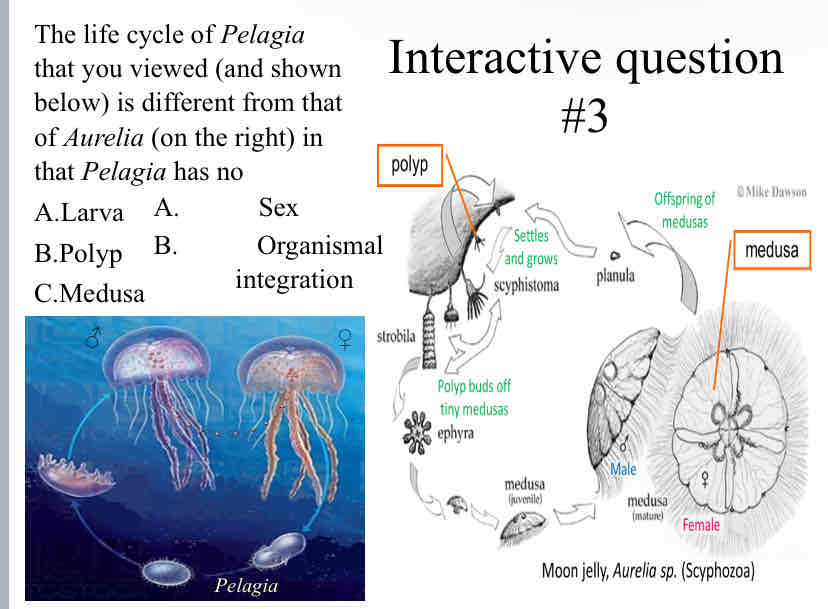
Practice Question (Life Cycle) - The life cycle of Pelagiathat you viewed (and shown below) is different from that of Aurelia (on the right) in that Pelagia has no
Polyp
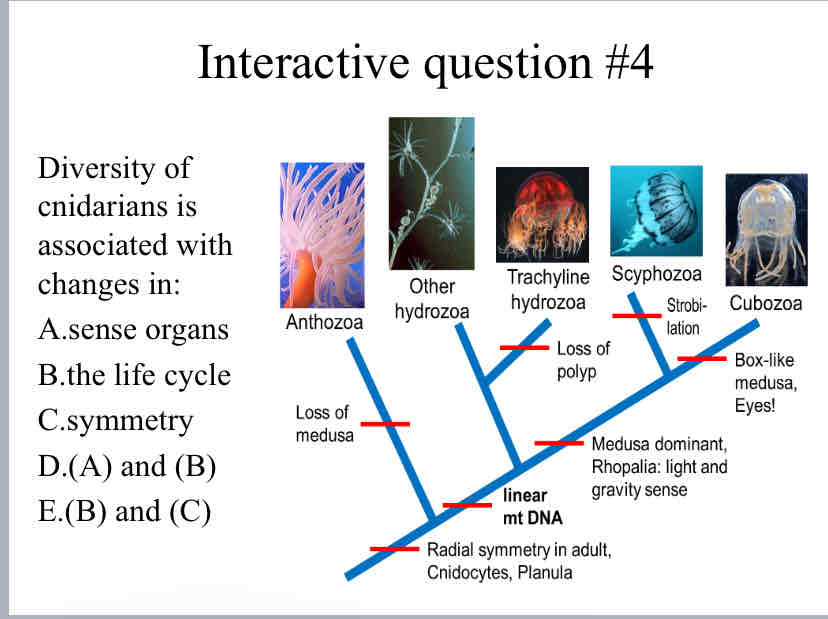
Practice Question (Cndiarian Phylogeny) - Diversity of cnidarians is associated with changes in:
sense organs & the life cycle
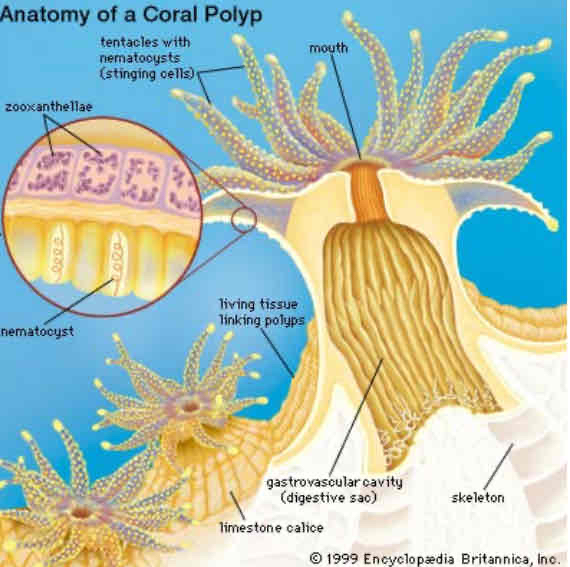
Corals with colonial polyps
these polyps have zooxanthellae (dinoflagellates) which :
are mutualistic photosynthetic protists
they produce most of the food used by coral

Coral Reefs
coral polyps secret limestone to build the reef, they are essentially ecosystem engineers
the reefs provide food and protection for fish

Coral bleaching (loss of zooxanthellae)
hypotheses of what causes it :
contagious disease
higher ocean
temperatures —> heat stress on symbiont
adaptation ?
gamble to obtain better symbiont strain ?

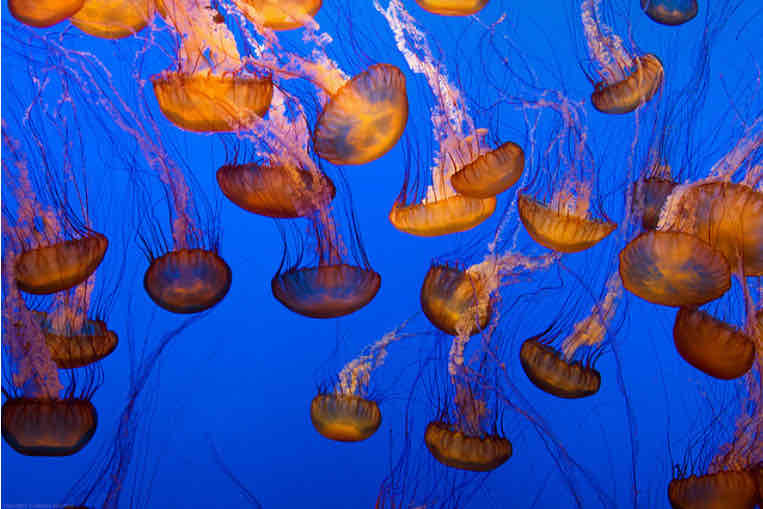
Sea Jellies (jellyfish)
most are predators
prey of sea turtles
look similar to plastic bags

Box Jellies (cubozoa)
perform a courtship dance
have image-forming eyes
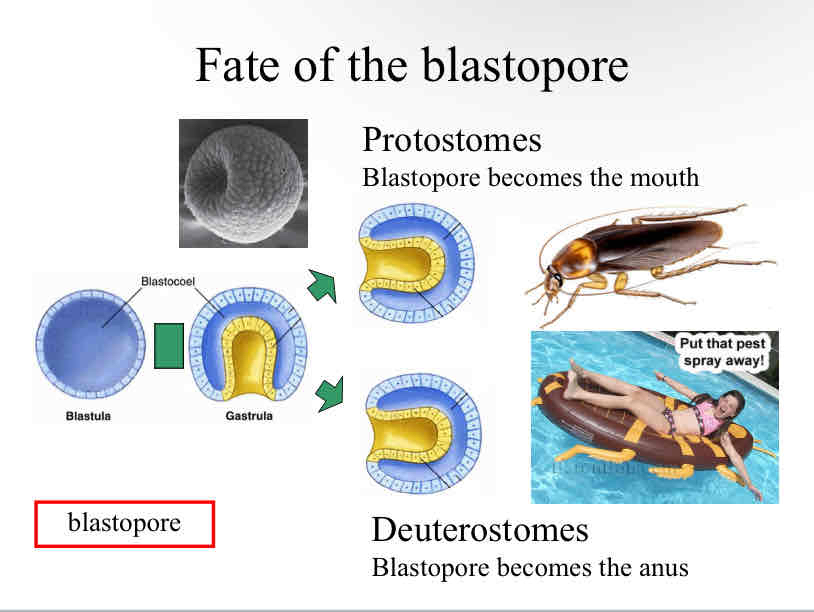
Fate of blastospore
in protosomes :
blastospore becomes the mouth
in deuterostomes :
blastospore becomes the anus
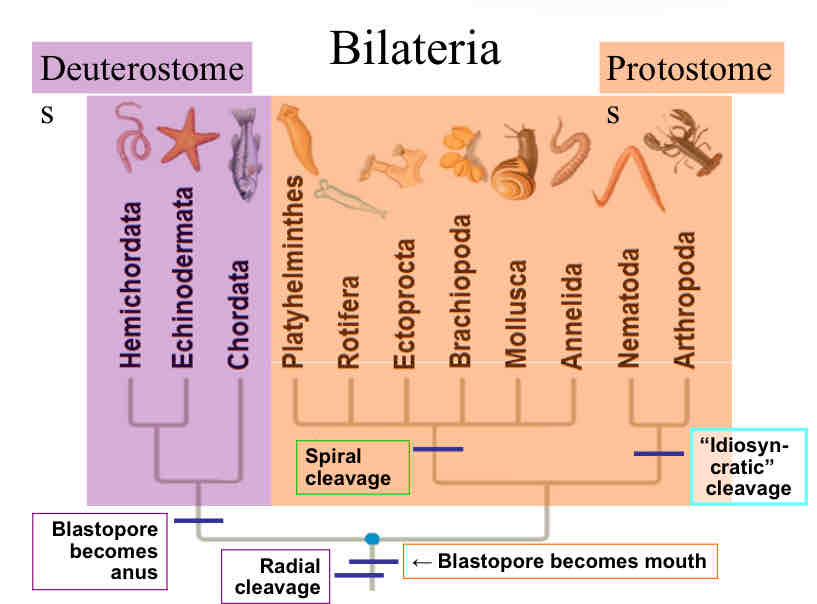
Bilaterians
Deuterostomes
radial cleavage
blastopore becomes anus
Protostomes
can have either spiral cleavage or idiosyncratic cleavage
blastopore becomes mouth
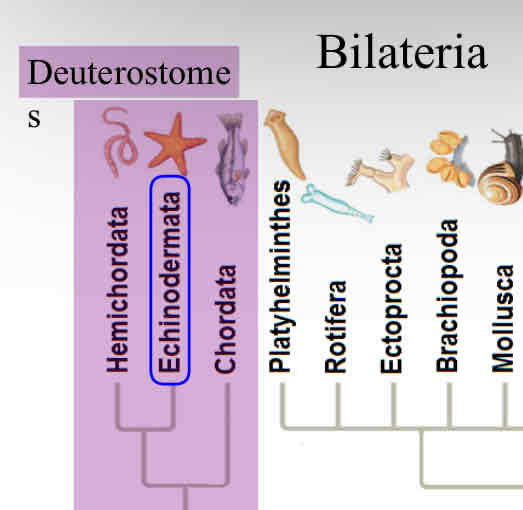
Echinoderms
habitat : all marine
pentaradial symmetry as adult
larva bilateral symmetry
endoskeleton
water vascular system
simple organ systems
no head or brain

Echinoderm Symmetry
larvae : bilateral
adults : pentaradial
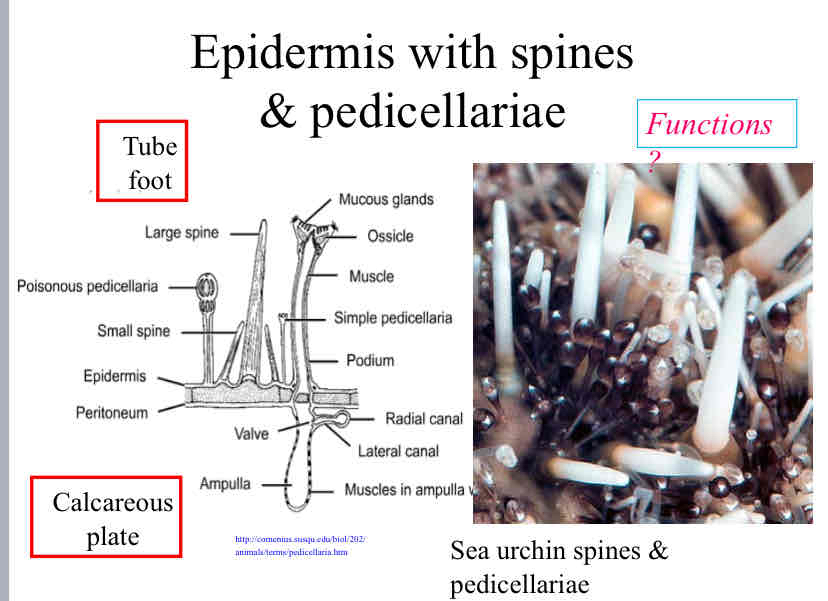
Epidermis with Spines & Pedicellariae
tube foot : movement , feeding, respiration
calcareous plate : provide protection
spines : provide sea urchins protection against predators, locomotion , sensing
pedicellariae : tube foot of sea urchins
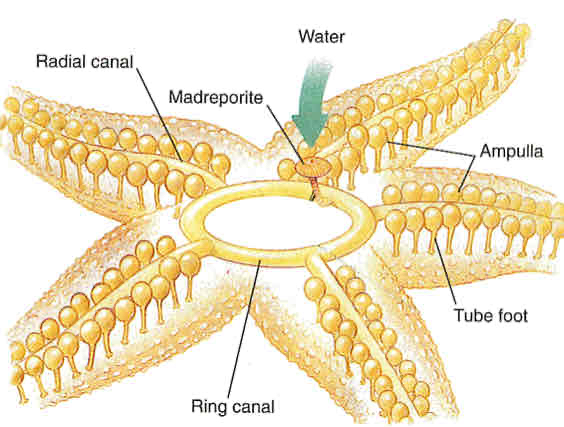
Echinoderms unique water vascular system
movement
feeding
defense
“circulation”
gas exchange
uses sea water as blood & as hydraulic fluid
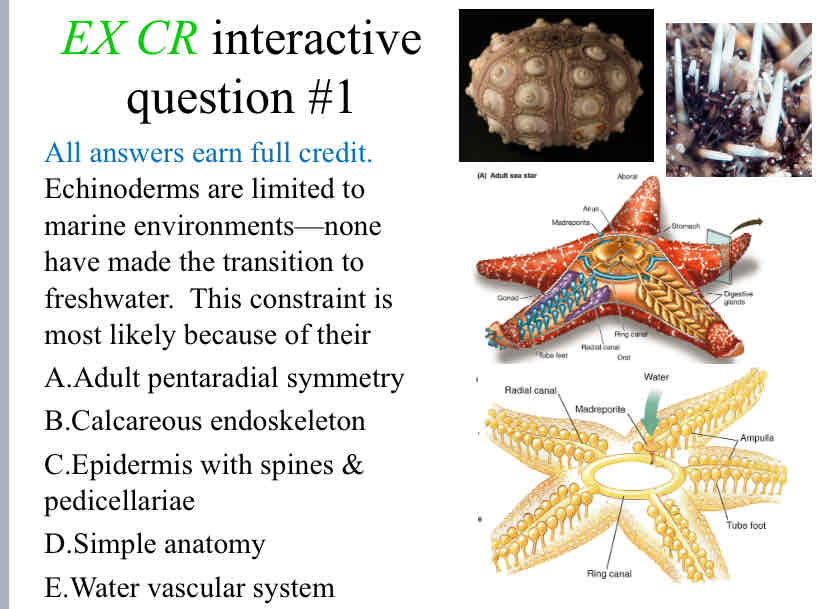
Practice Question (Echinoderm Evolution) Echinoderms are limited to marine environments—none have made the transition to freshwater. This constraint is most likely because of their
Water Vascular System
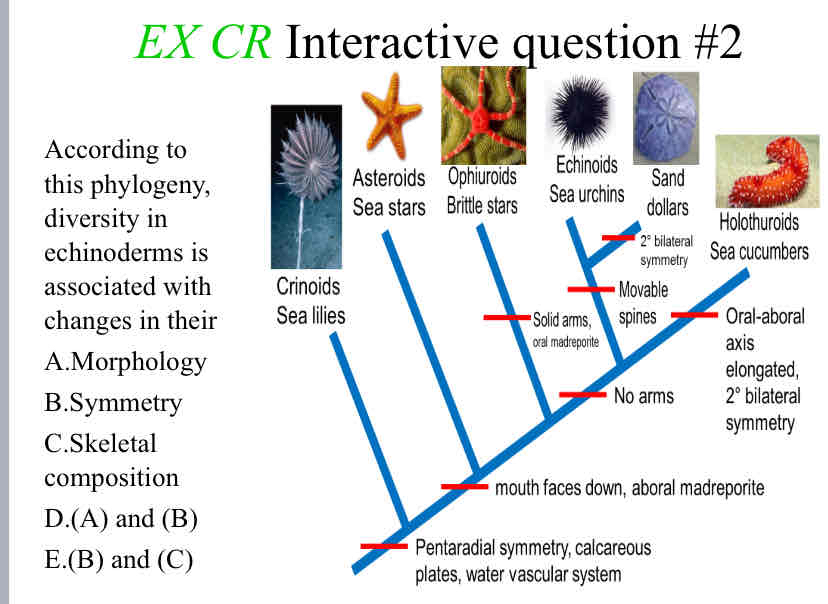
Practice Question (Echinoderm Phylogeny) - According to this phylogeny, diversity in echinoderms is associated with changes in their
Morphology and Symmetry
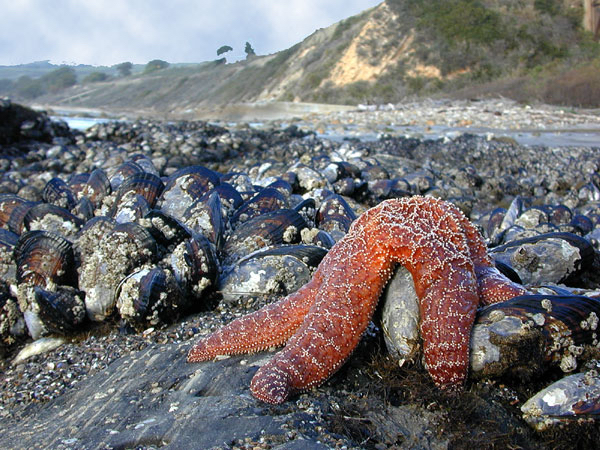

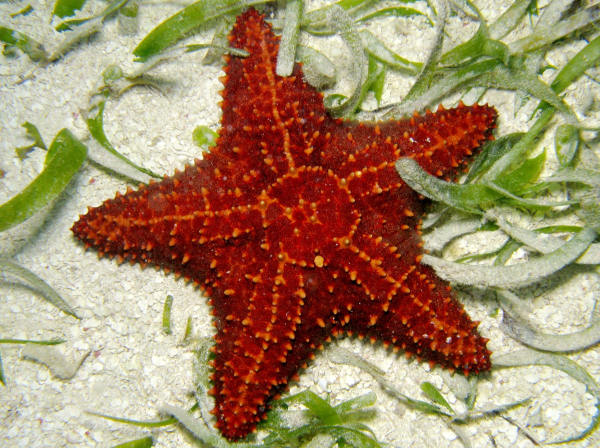
Sea Stars
very common
are predators
evert stomach , digest prey before ingesting

Crown of thorns
great barrier reef
coral predator up to 25cm
prey of triton’s trumpet snail
trumpet snails are sold as bags or ashtrays to tourists , this allows for the sea star to continue destroying the coral reef since there is no predator to stop it.

Practice Question (Great Barrier Reef) - You can help conserve the Great Barrier Reef by doing all of the following except:
Biocontrol of the Triton’s trumpet snail

Sea Urchins (Echindoidea)
no arms
spines
solid test (fused skeleton)
omnivores , graze algae

Practice Question (Fertilization) - Sea urchins are ____ and achieve fertilization by ____.
Dioecious; spawning w/o mating
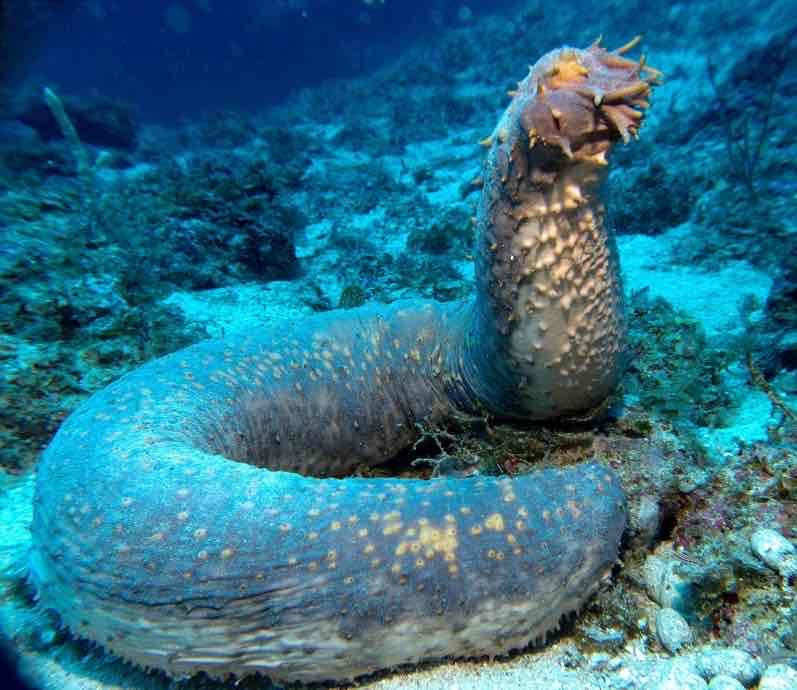

Sea Cucumbers (Holothuroidea)
are soft-bodied
1° pentaradial
secondarily 2° bilateral
sediment, filter feederd
are often toxic, which they use as a defense strategy to not be eaten
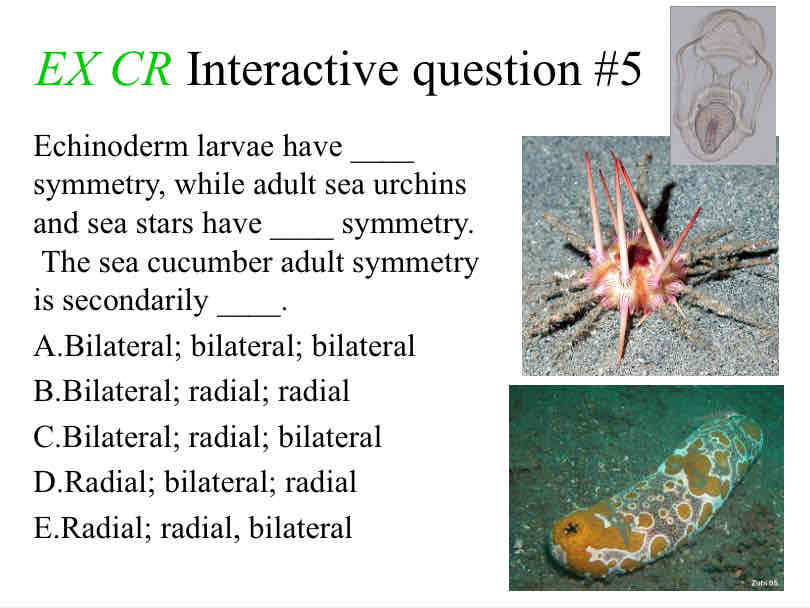
Practice Question (Symmetry) - Echinoderm larvae have ____ symmetry, while adult sea urchins and sea stars have ____ symmetry. The sea cucumber adult symmetry is secondarily ____.
Bilateral; radial; bilateral
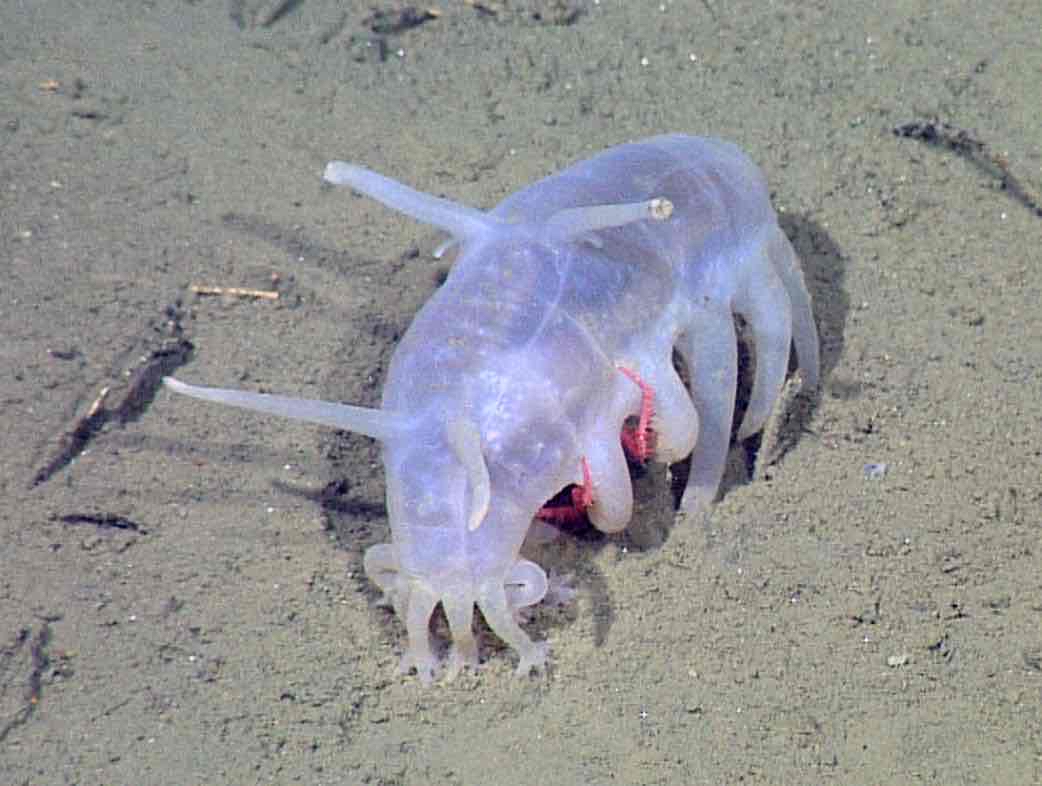

Sea Pig
abyssal (100m underwater)
detritus (decaying matter) feeders
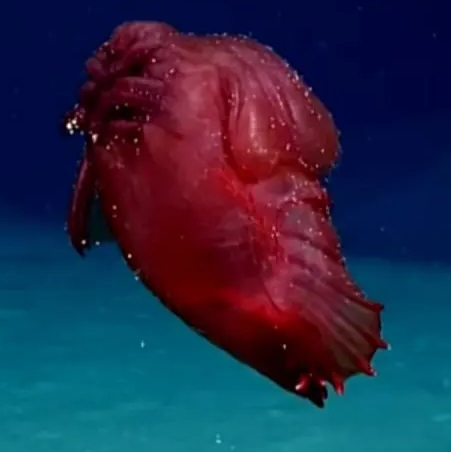

Headless Chicken Monster
abyssal
feeds on detritus (decaying matter)
swims to escape predators (theory)
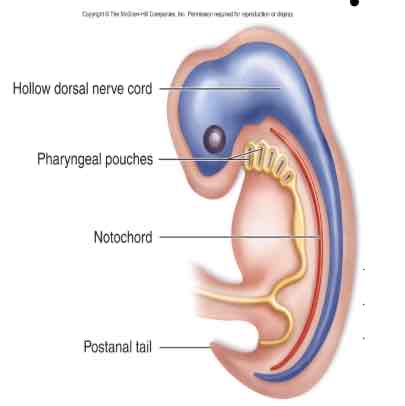
Chordates
notochord
dorsal hollow nerve cord
post-anal tail
Pharyngeal slits (homology with hemichordates)
segmentation - convergent with annelids and arthropods phyla
closed circulatory system
are dioecious
habitat
marine
water-to-land transition
land-to-water transition
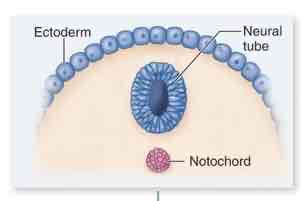
Notochord
flexible rod
collagen
muscle attachment
function (allowing for movement)
maybe be replaced by bone (derived)
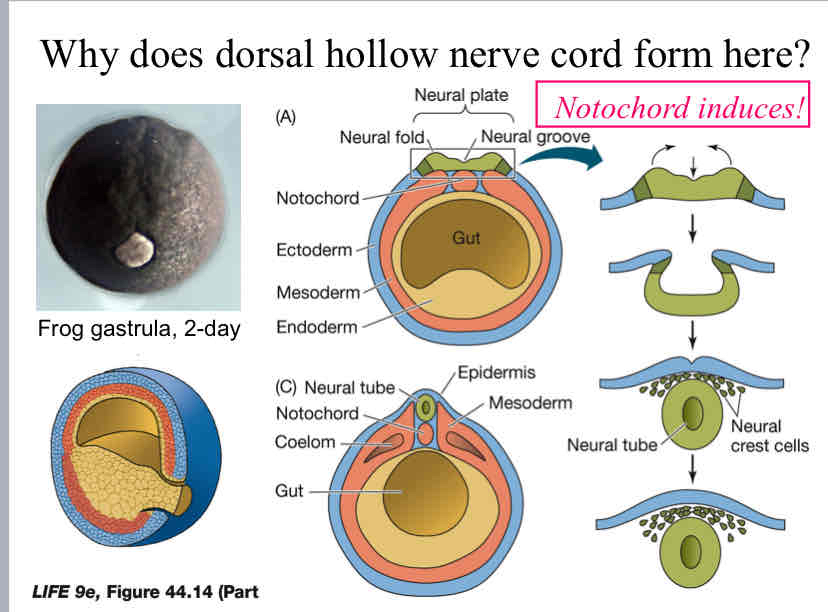
Practice Question (Nerve Cord) - Why does dorsal hollow nerve cord form here?
it happens as a result of different layers talking to each other telling each other what to do
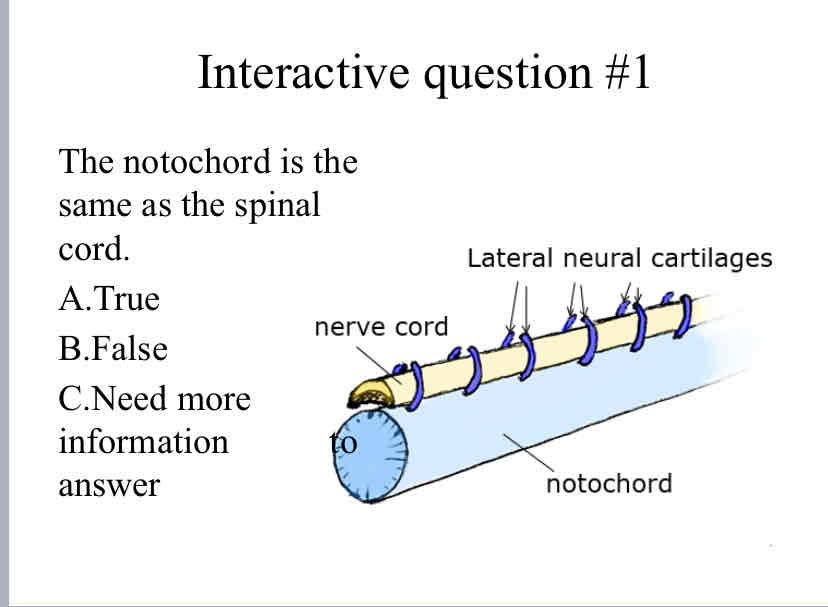
Practice Question (Notochord) - The notochord is the same as the spinal cord.
False (they are different)
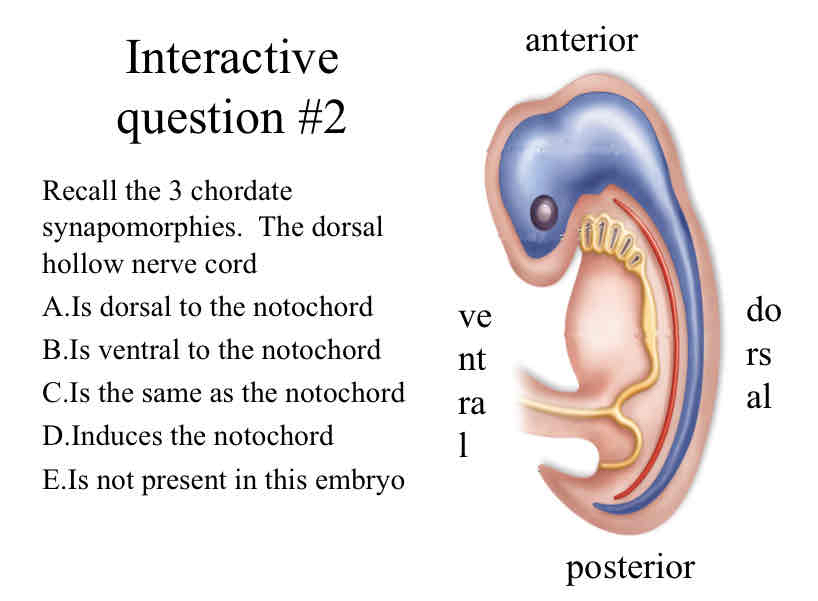
Practice Question (Nerve Chord) - Recall the 3 chordate synapomorphies. The dorsal hollow nerve cord
is dorsal to the notochord
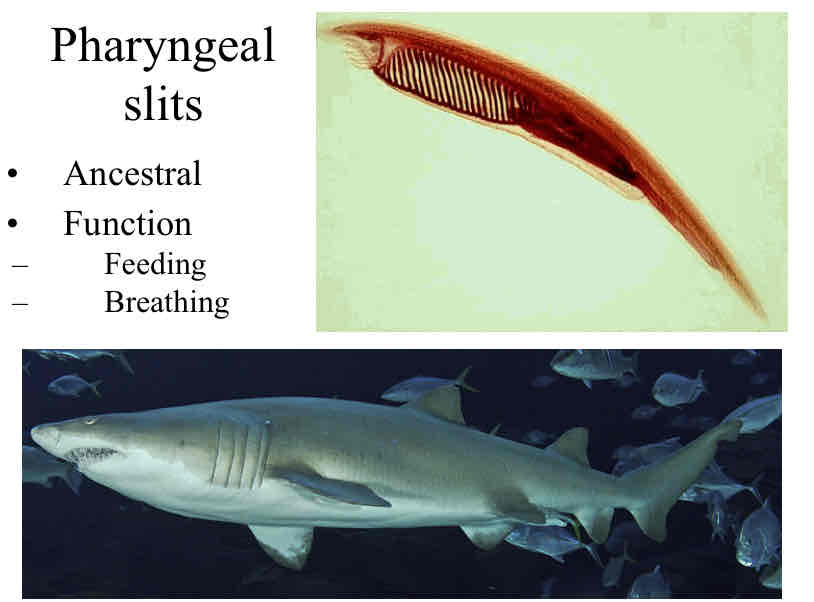

Pharyngeal slits
ancestral
function
feeding
breathing
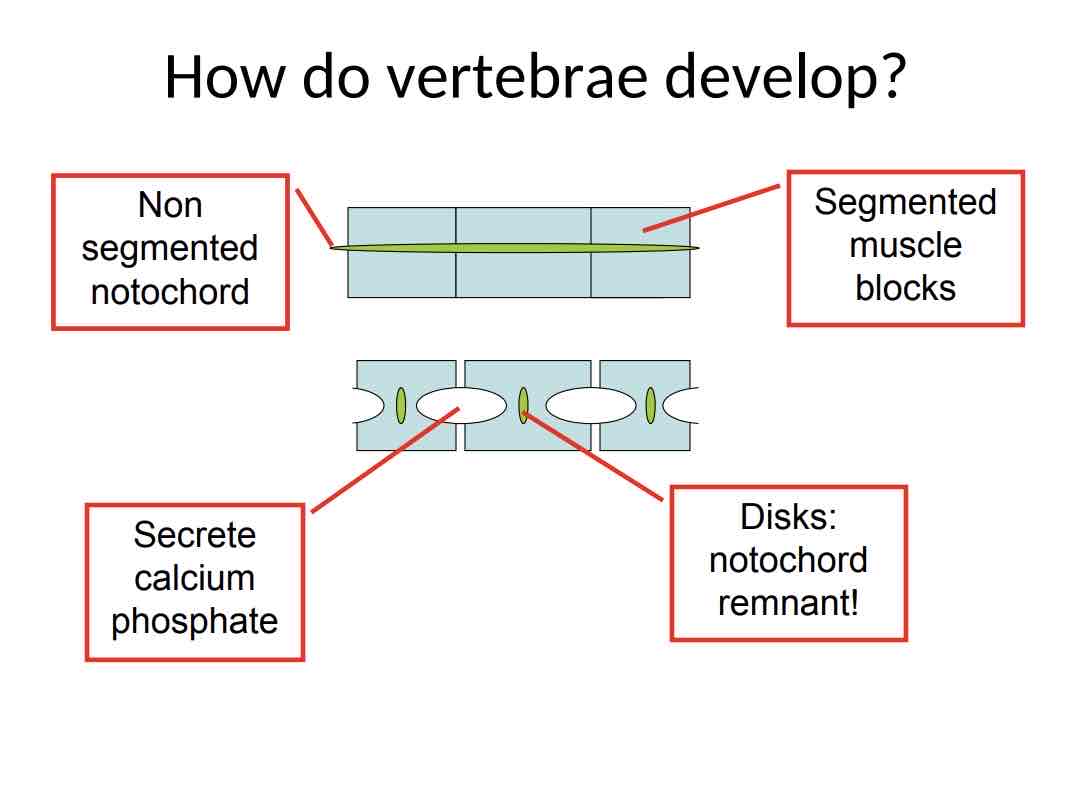
Practice Question (Vertebrae) How do vertebrae develop ?
the non segment notochord seperates into disks
the segment muscle block secret a calcium phosphate
Practice Question (Notochord) - Do you have a notochord?
yes, because it becomes the intervertebral discs
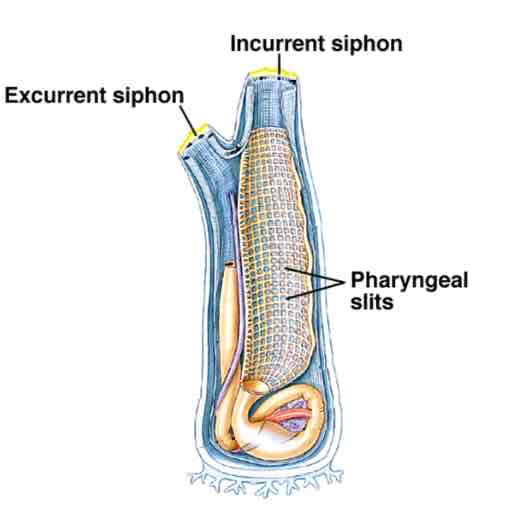
Urochordate (Sea Squirt) anatomy
siphons
filter : pharynx
slits
muscus
stomach
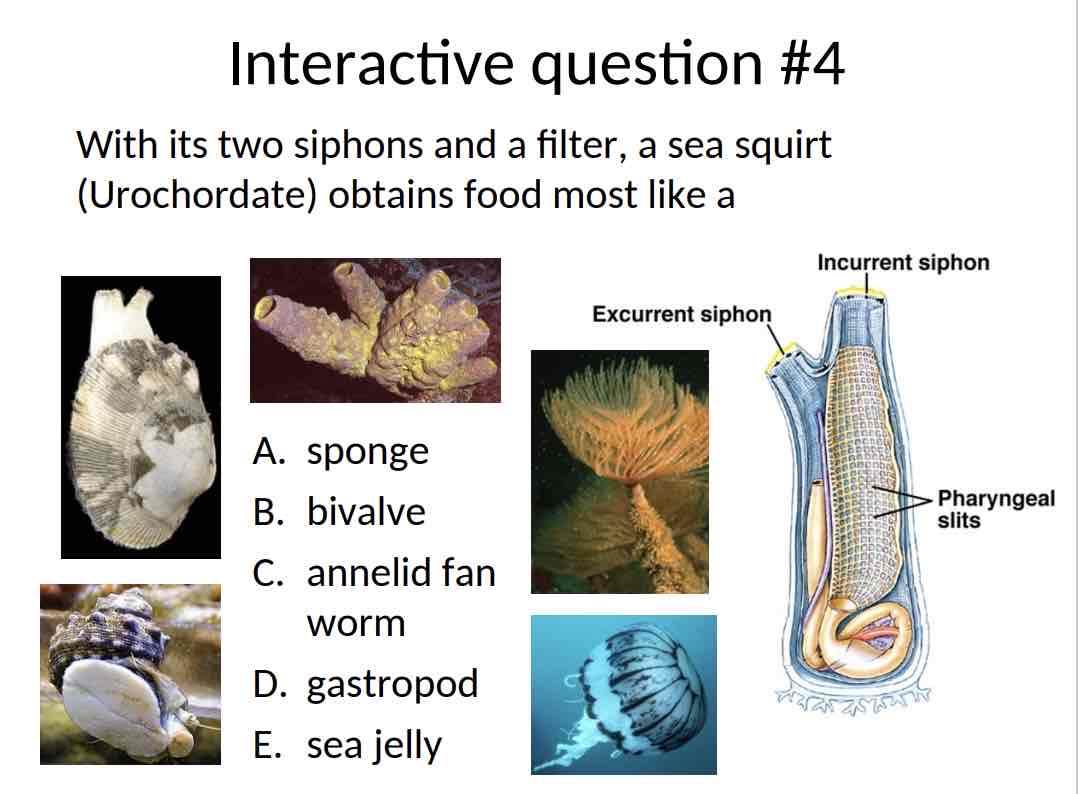
Practice Question (Sea Squirt) - With its two siphons and a filter, a sea squirt (Urochordate) obtains food most like a
Bivalve
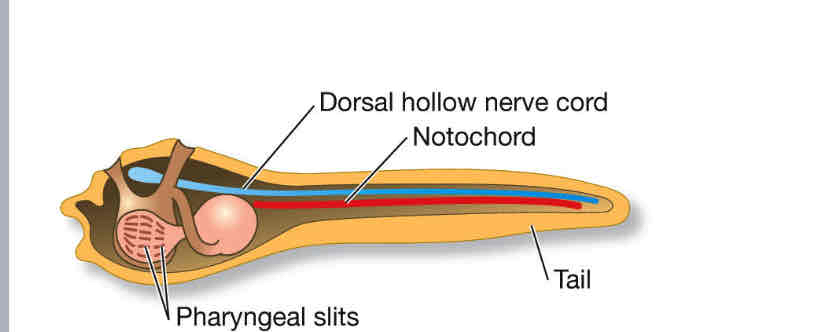
Urochordate larva has chordate features
they have a :
dorsal hollow nerve cord
notochord
tail
pharyngeal slits
larvaceans : adults retain larva-like features

Ray-Finned fishes
have complex jaws : two sets of them
oral (protrude) - used for suction feeding and grazing
pharyngeal (grind)
have vast diversity (because they are the right size for it)
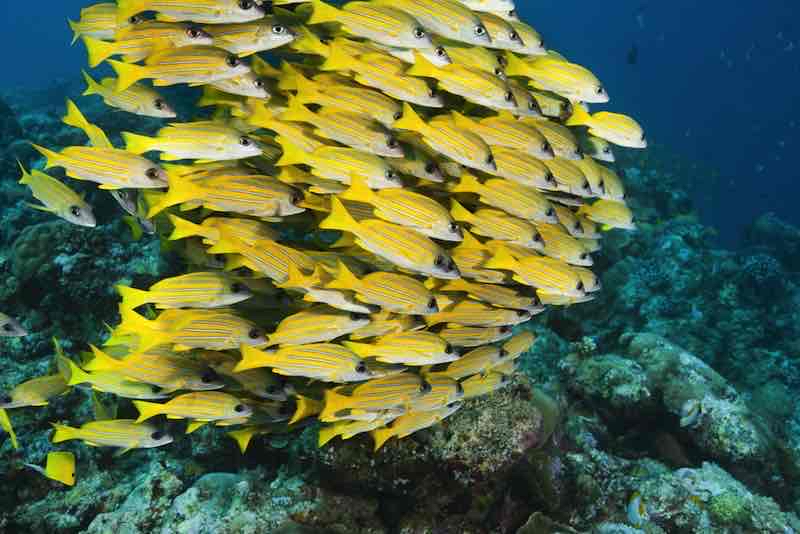

Innovation of Ray-finned fishes
eyes + lateral line - senses
fins - ability to maneuver
swim bladder - helps with buoyany
schooling - helps with behavior
Tetrapods (amphibians, mammals, reptiles) - Adaptations to Land
Earliest
lungs
limbs
Later
tough skin
internal fertilization
amniotic egg
flight

Land First - shrinking waterhole hypothesis
limbs and lungs may have evolved from the necessity of having to find new bodies of water as old waterholes dried up.

Limbs First - Woodland Hypothesis
limbs and necks were selected for by scavenging and hunting in shallow-flooded woodlands

Practice Question (Tetrapods) - Paleontologists have calculated that the legs of early tetrapods could not have supported their weight on land. This mostly supports
The “shrinking waterhole hypothesis”
Reptile Adaptations to Land
egg shell + internal membranes
used for protection, nourishment, gas exchange, and wasted
keratin scales
derived later : feathers and haie
internal fertilization
amniotic egg
parental care
clade (crocs/dinos/birds)
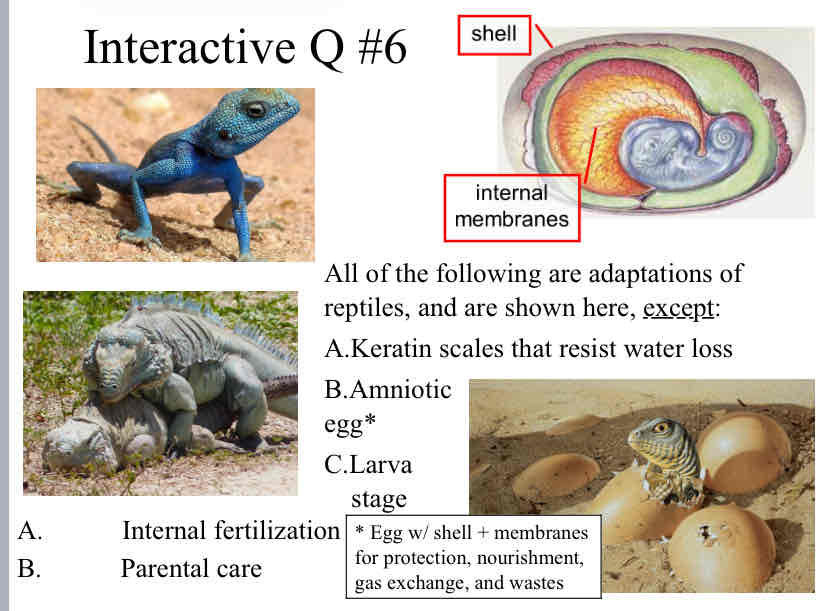
Practice Question (Reptiles) - All of the following are adaptations of reptiles, and are shown here, except:
larva stage
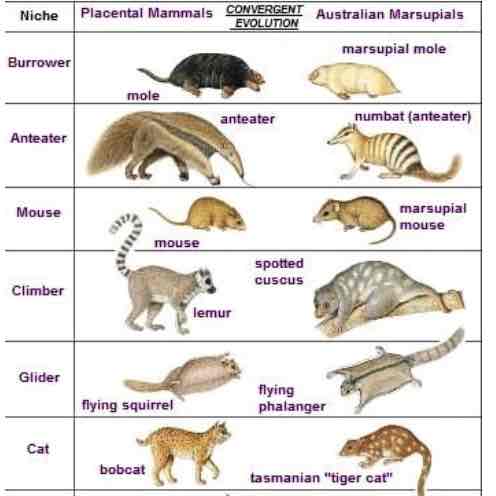
Convergent Evolution
Australia isolated for 40 million years
Placental and Marsupial animals
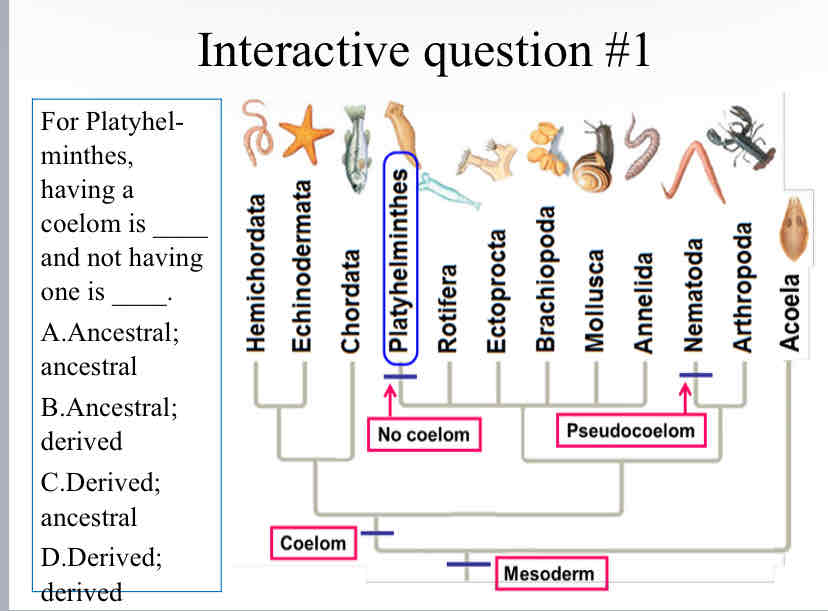
Practice Question (Flatworms) - For Platyhelminthes, having a coelom is ____ and not having one is
Ancestral ; derived
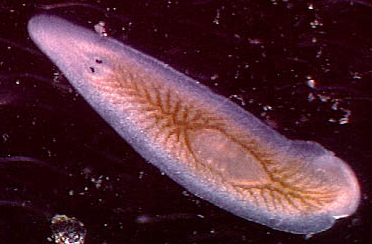
Platyhelminthes : main features
3 tissue layers
No coelom
Incomplete gut
branched
Little or no cephalization
Organ systems
nervous
excretory
Monoecious (hermaphroditic)
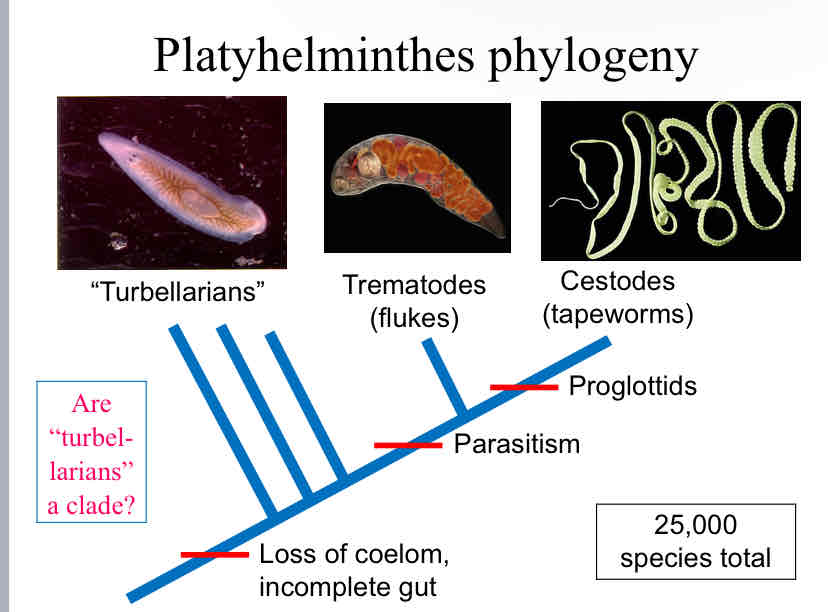
Platyhelminthes Phylogeny
turbellarians
trematodes (flukes)
cestodes (tapeworms)
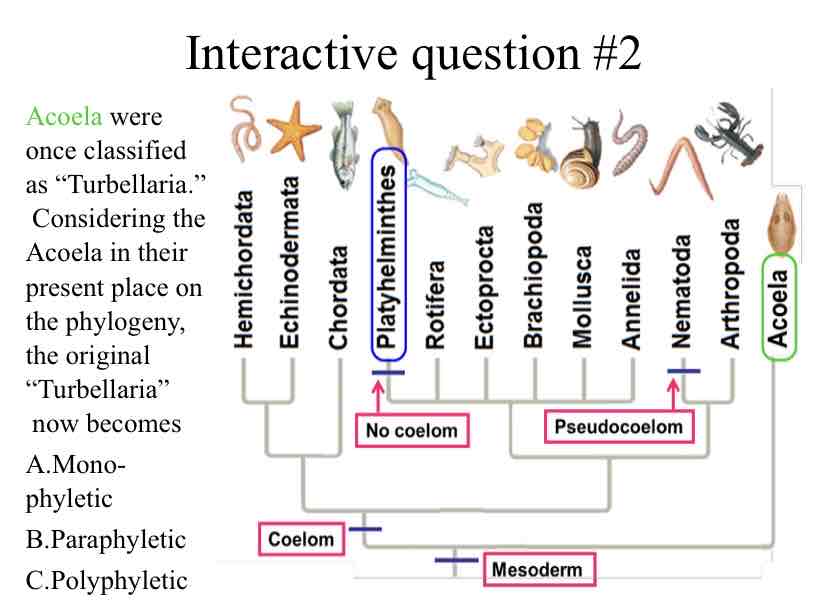
Practice Question (Acoela) - Acoela were once classified as “Turbellaria.” Considering the Acoela in their present place on the phylogeny, the original “Turbellaria”
Polyphyletic
Adaptations of Parasitism
Cephalization (decrease)
Digestive System (decrease)
Reproductive (decrease)
Pork Tapeworm (Cestoda)
functions
anterior end attached to wall of gut
posteriorly repeated sections
1) produce gametes
2) fill with fertilized eggs (embryos)
3) are shed in feces

A head is formally defined by
anterior head
sense organs
brain
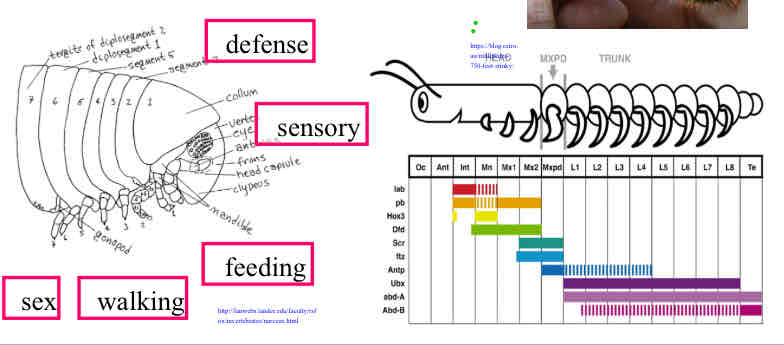
Segmentation in 3 animal phyla
distinct, repeated body modules
specialized for different functions
developmentally patterned by Hox genes
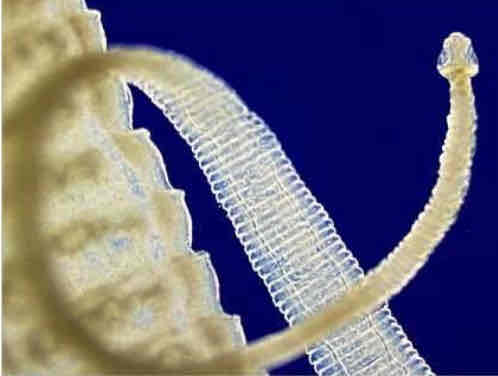
Pork tapeworm (cestoda) parts
scolex : hooks and suckers for attachment to gut wall
proglottids : detachable “packets” of eggs

Practice Question (Tapeworm) - Although it has no sense organs, the scolex of a tapeworm is its head (T/F), and its body shows “true” segmentation: patterned special-ization of body segments for various functions (T/F).
False; false
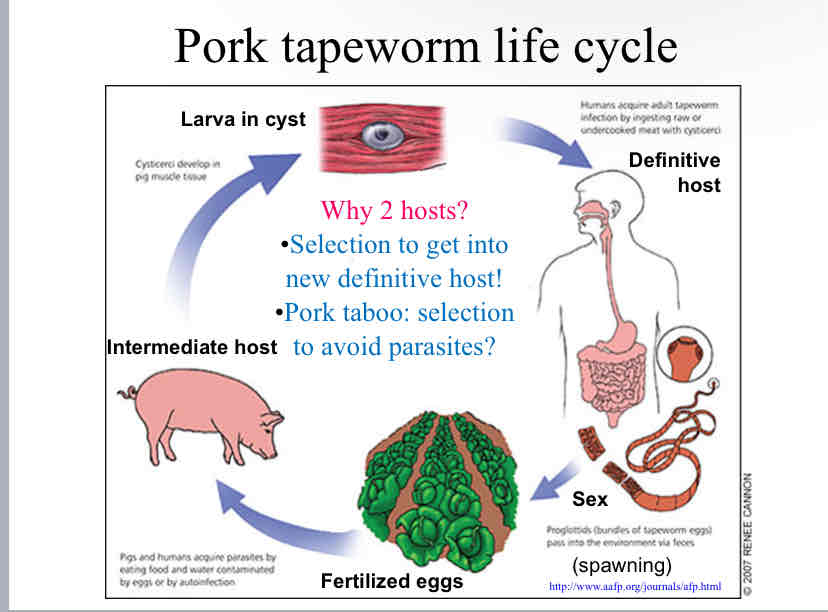
Pork Tapeworm Life Cycle
Pigs become infected by eating contaminated food or water containing tapeworm larvae, and they act as the intermediate host allowing the larvae to develop in a cyst inside their tissue.
Eventually the larva hatches inside the tissue becoming an adult tapeworm, and if we eat this meat raw or undercooked, we will get the tapeworm. We are now the definitive host to the adult tapeworm who lives inside our intestines and steals our nutrients.
Humans also help the tapeworm reproduce by passing its eggs into the environment through our poop, starting the cycle over again.
The advantage of an internal parasite having more than one host in their life cycle is that it ensures their survival, if something happens to their first host (the pig) they can just attach to another one and live off them instead (the human).
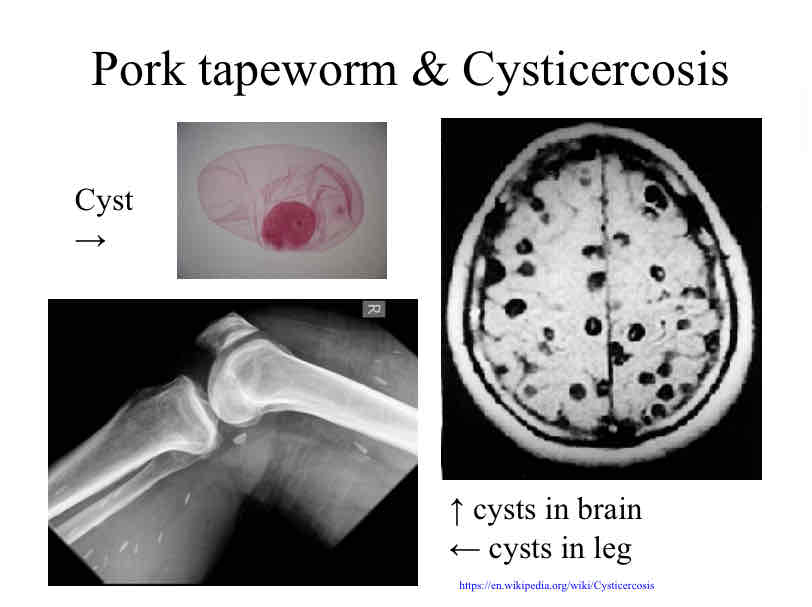
Tapeworm and Cysticercosis
If humans ingest the egg directly from contaminated water or food instead of the already adult worm from the pig tissue, the larvae will develop a cyst inside our tissues like the brain or eyes
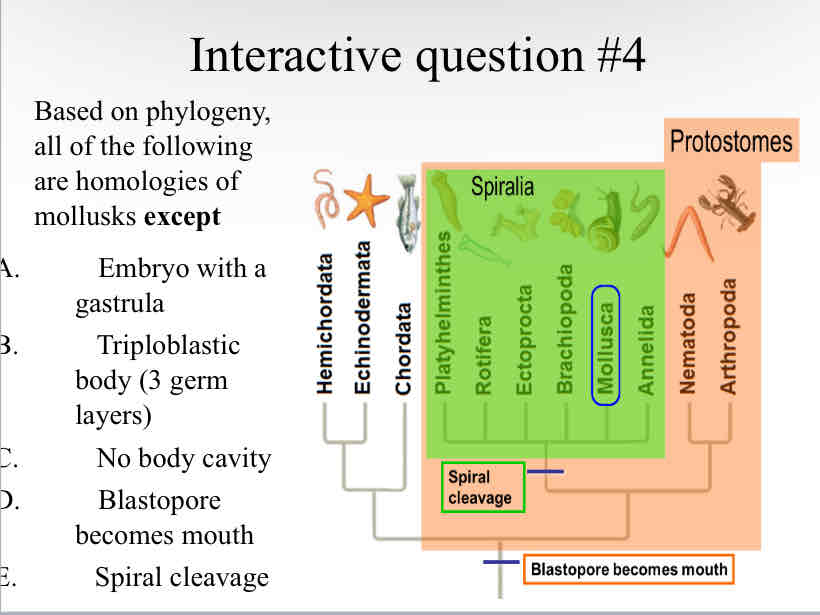
Practice Question (Mollusks) - Based on phylogeny, all of the following are homologies of mollusks except
No body cavity

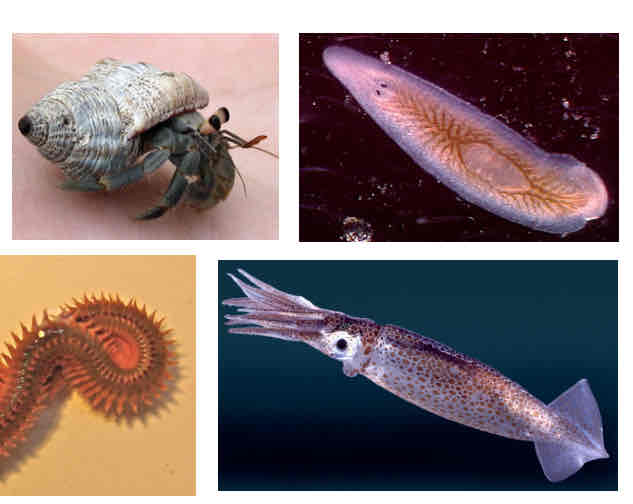
Mollusks : Main Features
Mantle
Muscular Foot
Radula
Cephalization in some
Reduced coelom
nervous
excretory
Well developed organ systems
Trochophore Larva
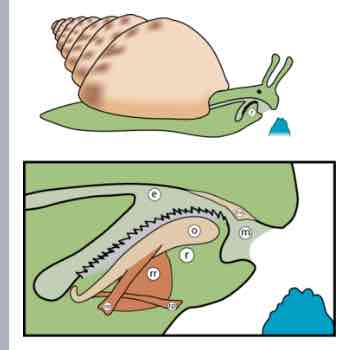
Mollusks (Radula)
used for grazing plants, algae, or animal tissue
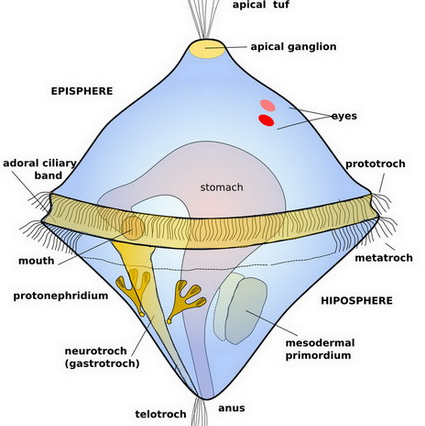
Trochophore Larva
feeding : complete gut
marine plankton
no larva : freshwater, land
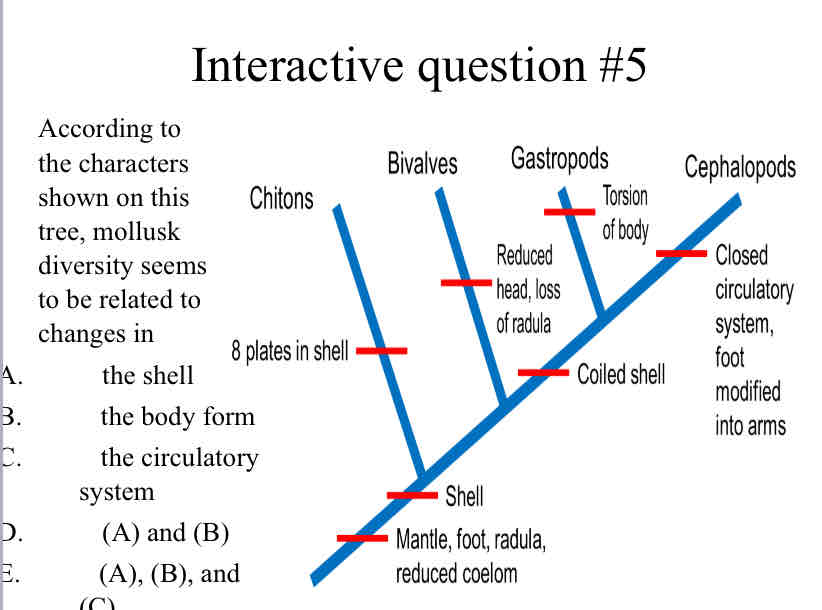
Practice Question (Mollusk Phylogeny) - According to the characters shown on this tree, mollusk diversity seems to be related to changes in
the shell, the body form, the circulatory system
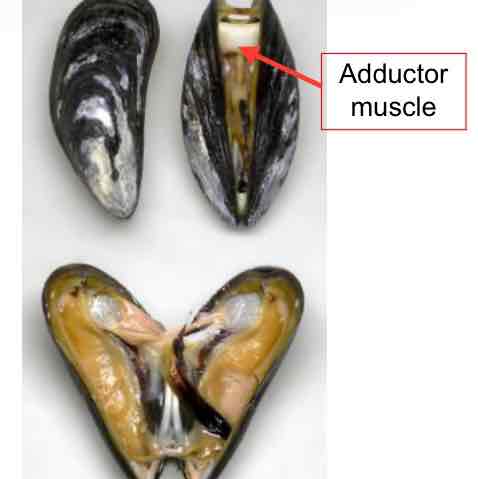
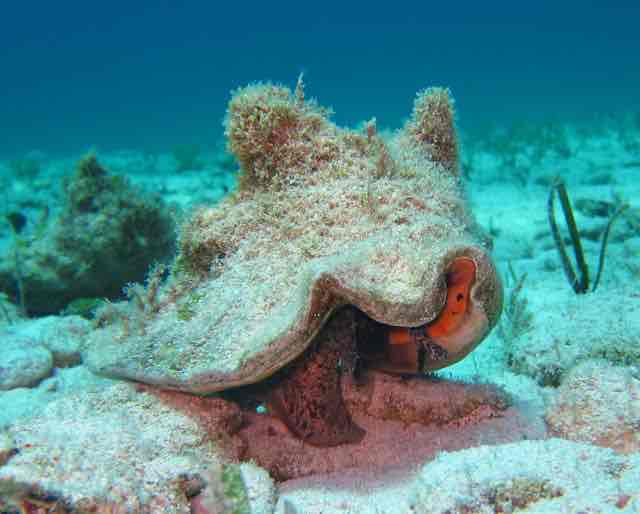
Bivalves
have 2 shells
abductor muscles
shucking cuts
huge in “scallops” they swim by opening and closing their shell
no radula
not cephalized
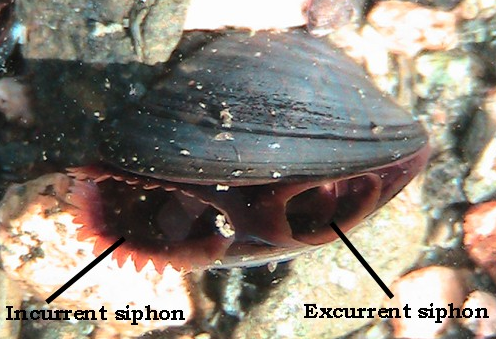
Bilvaves : filter feeders
have an incurrent siphon
use gills as filter
excurrent siphon
Gastropods
herbivores
grazers

Solar powered sea slug
chloroplasts from Vaucheria
litorea
has v. litorea genes
can maintain chloroplasts
Triton’s trumpet snail
found in great barrier reef
eats crown of thorns sea star
sea star eats coral

Cephalopods
are active predators
avoid predation themselves by camouflage

Squid social & communication
color
body language

Practice Question (Mollusks) - The mollusk clade with the most diversity (disparity = difference among them) in how they obtain food is
Gastropods

Chitons
weird mollusks
wandering meatloaf
8 plates in shell
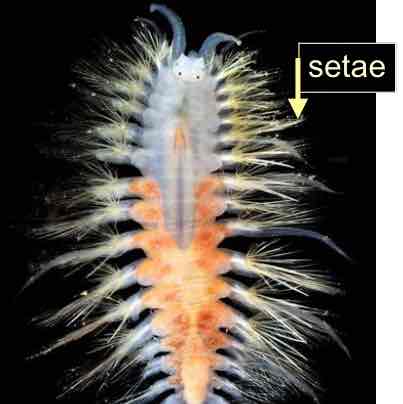

Annelida (segmented worms)
unique segmentation with septa
setae
hydrostatic skeleton
complete processing gut
well developed systems
closed circulatory system
ventral nervous system
complex musculature
trochophore larva
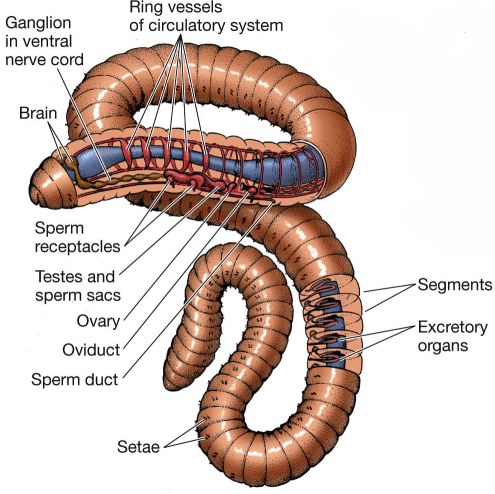
Segmentation + complex musculature
segments divide coelom into fluid filled compartments
complex muscles can squeeze in different directions
elongate
contract
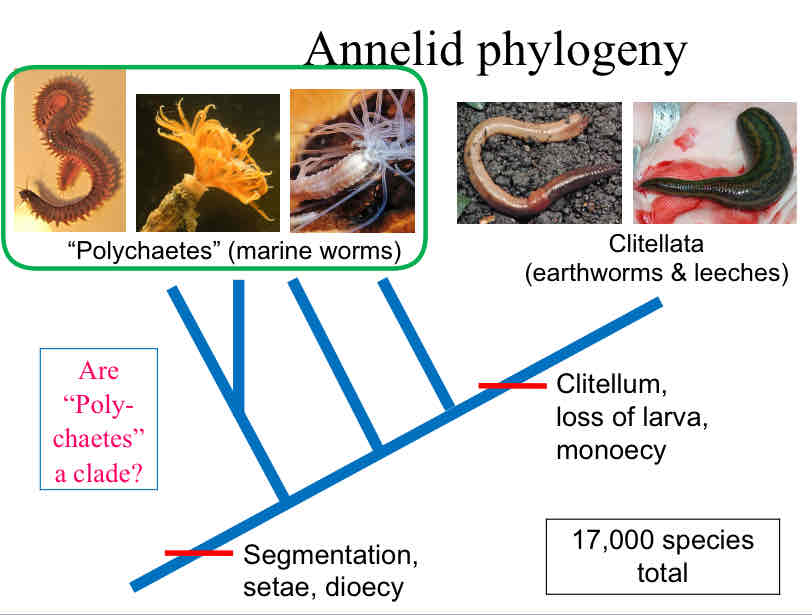
Are Polychaetes (marine worms) a clade ?
NO

Bobbit Worm
predator “polychaete” with cephalization
parapodia : locomotion
sit and wait

Earth Worms : ecosystem engineers
mixing
organic matter
aeration