ochem rxns
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
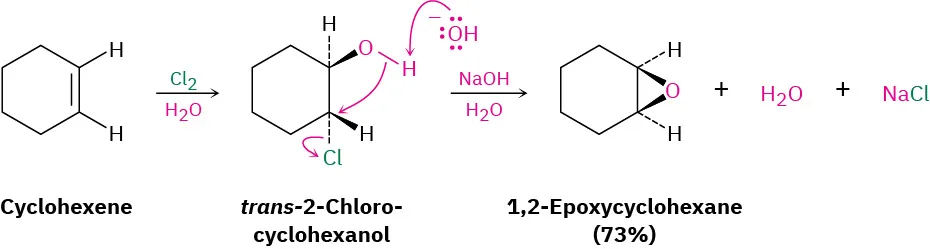
1) Cl₂, H₂O 2) NaOH, H₂O
Alkene to Epoxide
has halohydrin intermediate (where OH goes to the MORE substituted carbon & Cl goes to the LESS substituted carbon)
stereochem: anti addition in the halohydrin step, followed by an SN2 inversion, then epoxide
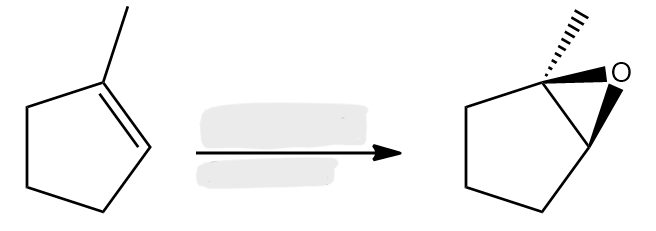
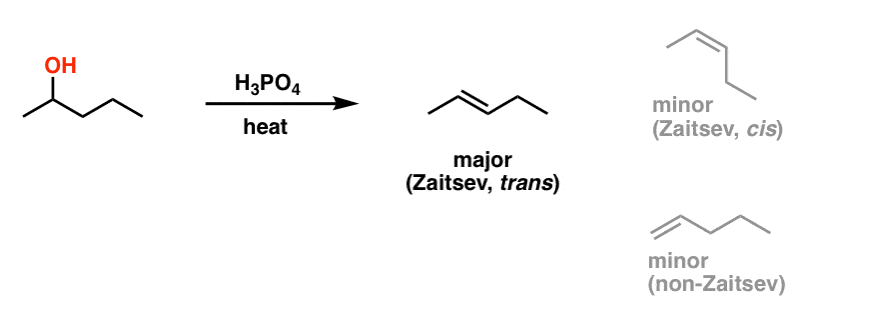
H3PO4
Alcohol to Alkene
2° or 3° alcohols
Gives Zaitsev alkene (more substituted)
Proceeds via E1
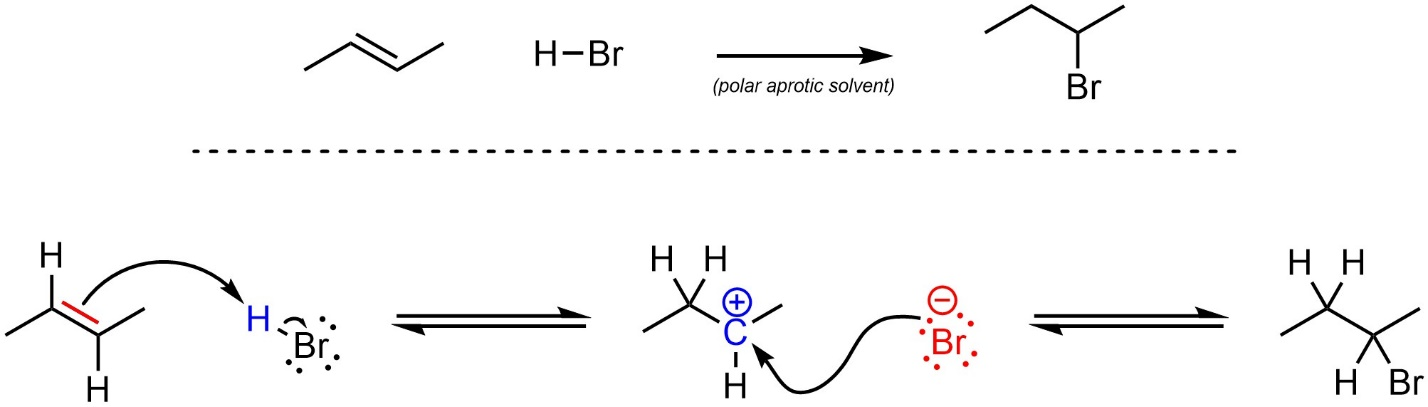
HX
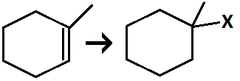
Alkene to Haloalkane
regiochem: Addition of X at MarkovNikov position
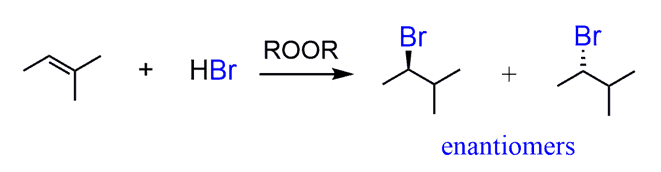
HBr, ROOR (peroxide)
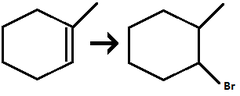
Alkene to Haloalkane
regiochem: Anti-MarkovNikov additon to pi bond
Br adds to the LESS substituted carbon
H adds to the MORE substituted carbon
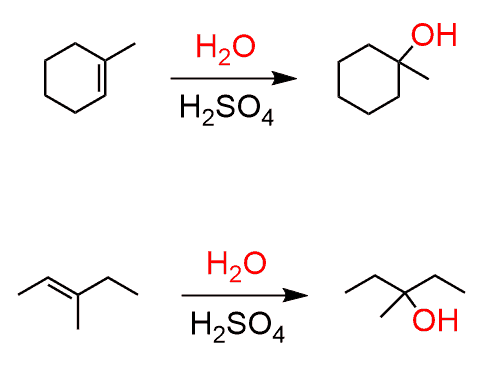
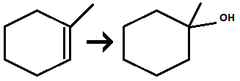
H₃O⁺/H₂O
Alkene to Alcohol
regiochemistry: markovnikov addition to a pi bond
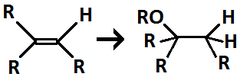
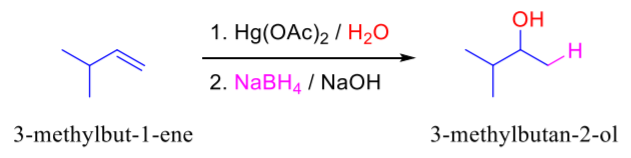
1)Hg(OAc)₂, H₂O 2)NaBH₄
Alkene to Alcohol
regiochem: addition of Alcohol at MarkovNikov
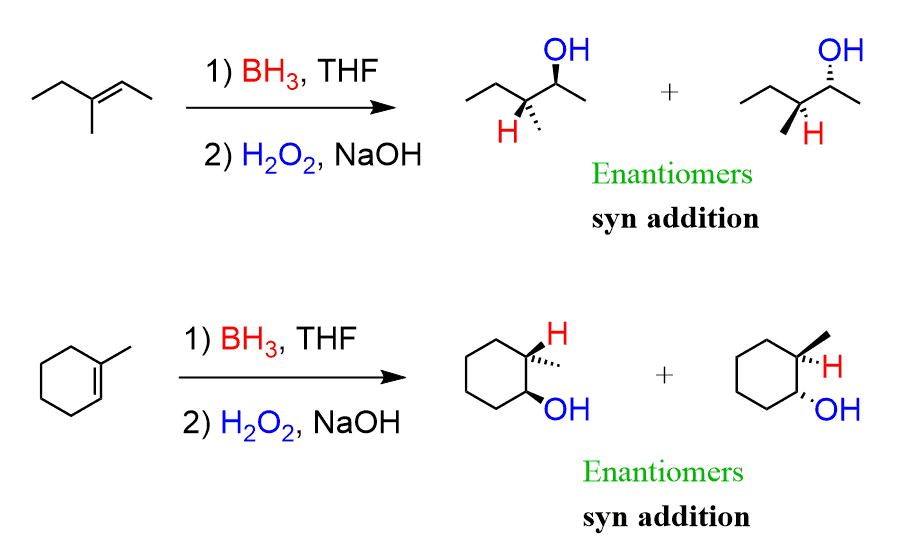
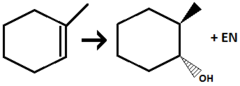
1) BH₃ 2) H₂O₂, NaOH
Alkene to Alcohol
regiochemistry: anti-MarkovNikov addition to pi bond
stereochem: syn-addition
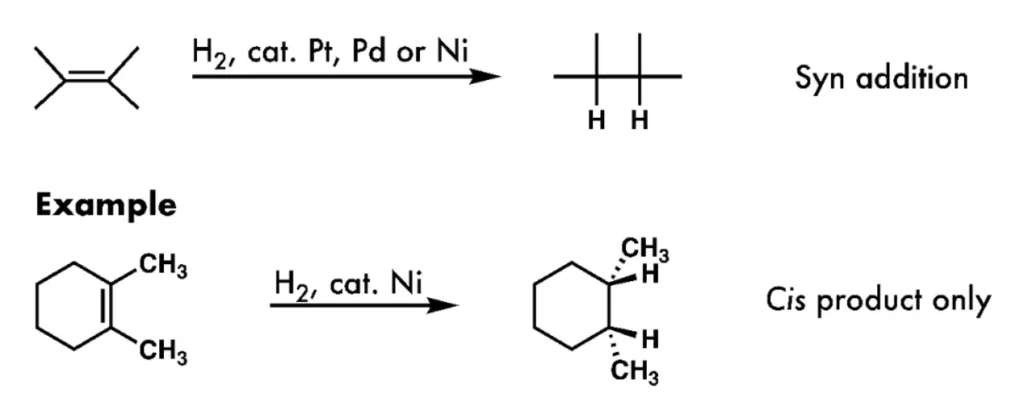
H₂/Pd, Pt, Ni
Alkene to Alkane
stereochemistry: syn-addition
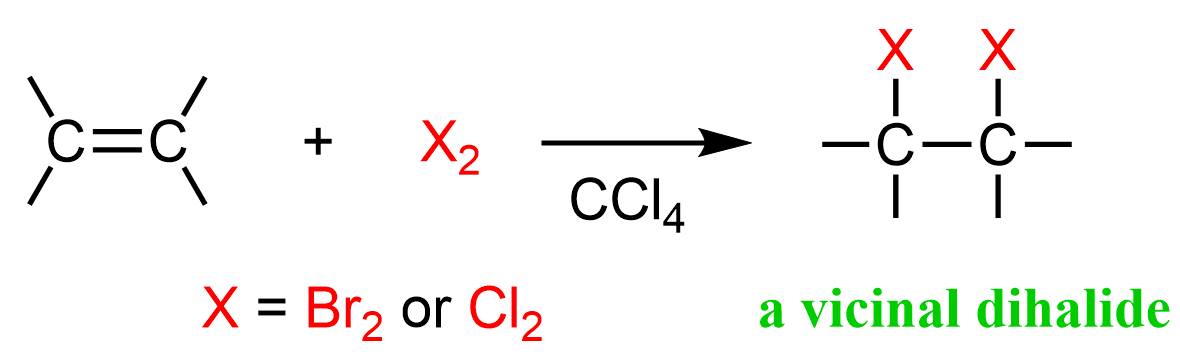
X₂ (ex. Br₂)
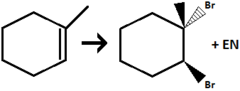
Alkene to Vicinal Dihaloalkane
halogenation to both double bond positions
stereochem: anti-addition (the two halogens end up on opposite faces of the alkene)
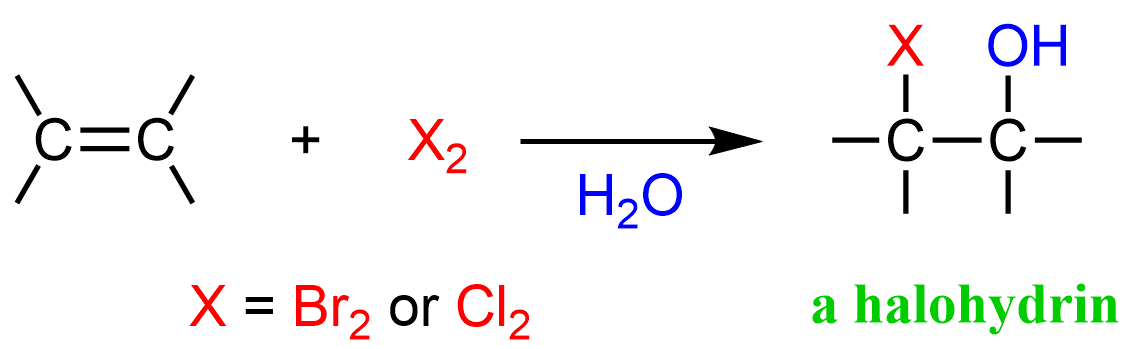
X₂, H₂O (ex. Br₂)
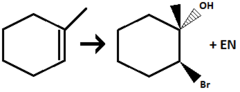
Alkene to Halohydrin
halogenation at Anti-MarkovNikov Position (X goes to the LESS substituted carbon)
adds Alcohol at MarkovNikov Postion (OH goes to the MORE substituted carbon)
stereochem: anti-addition (OH and X end up on opposite faces)
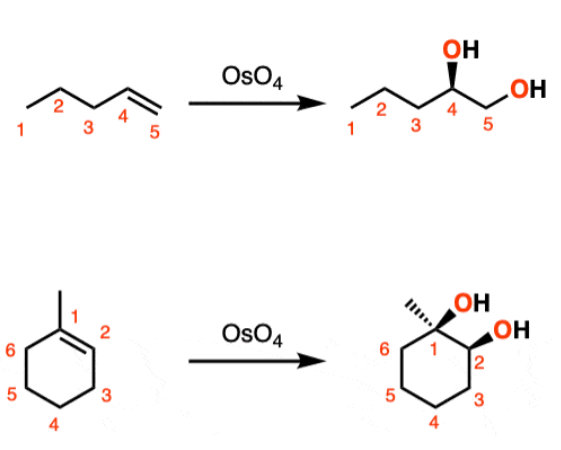
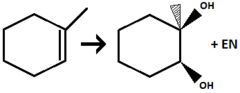
1) OsO₄ 2) NaHSO₃
Alkene to Vicinal Diol
regiochem for first step: syn-addition
Adds Alcohol to both double bond positions
will always give a vicinal diol with the two OH groups on the same face (same stereochem)
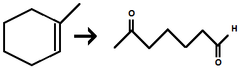
![<p>1) O₃ 2) DMS [same as (CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>S ]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/75026e8b-4f2d-414a-b4dc-83dd9582b72f.png)
1) O₃ 2) DMS [same as (CH3)2S ]
Alkene to Aldehyde/Ketone
cleave carbon carbon bond at Double Bond site and adds Oxygen to both openings
If an alkene carbon has at least one H → it becomes an aldehyde
If an alkene carbon has no Hs (only carbons attached) → it becomes a ketone
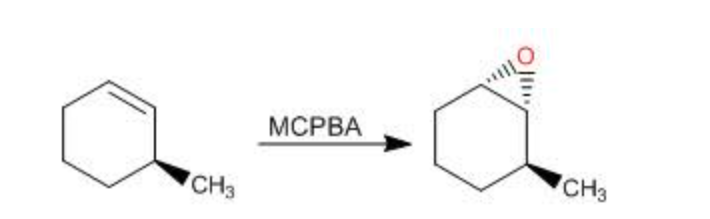
MCPBA
Alkene to Epoxide
stereochem: syn addition
preserves alkene geometry:
cis alkene → cis epoxide
trans alkene → trans epoxide
H₂SO₄, HgSO₄
Alkyne to Ketone
regiochem: Adds Ketone at MarkovNikov Position
only forms aldehyde in the case of acetylene (ethyne, HC≡CH)
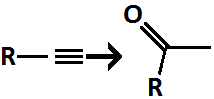
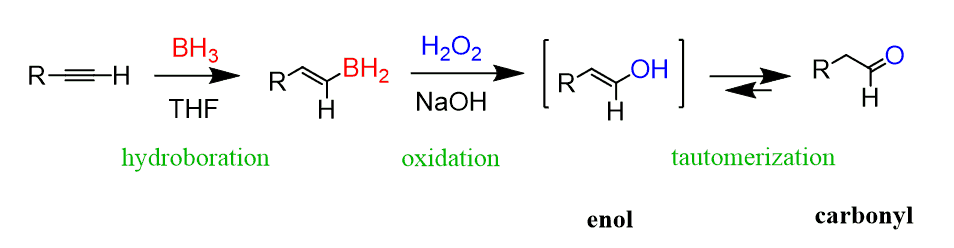
1) BH3 2)H₂O₂, NaOH
Alkyne to Aldehyde/Ketone
Terminal alkyne (R–C≡CH) → Aldehyde
Internal alkyne (R–C≡C–R′) → Ketone(s)
PCC or DMP or Swern Oxidation = 1) oxalyl chloride, DMSO; 2) tertiary amine
Alcohol to Aldehyde/Ketone
for 1° alcohol → aldehyde
for 2° alcohol → ketone
for 3° alcohol → no reaction
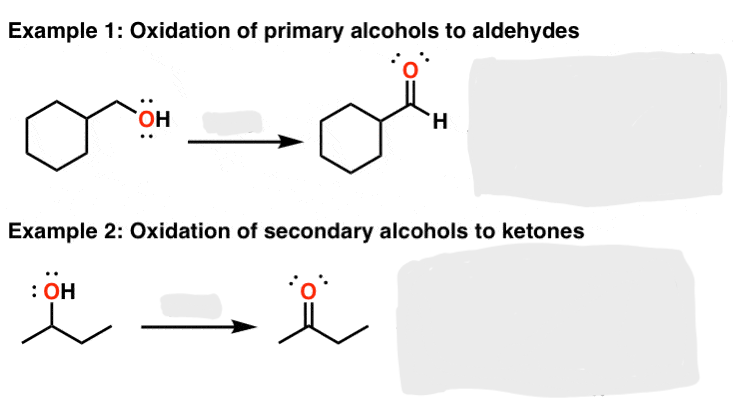
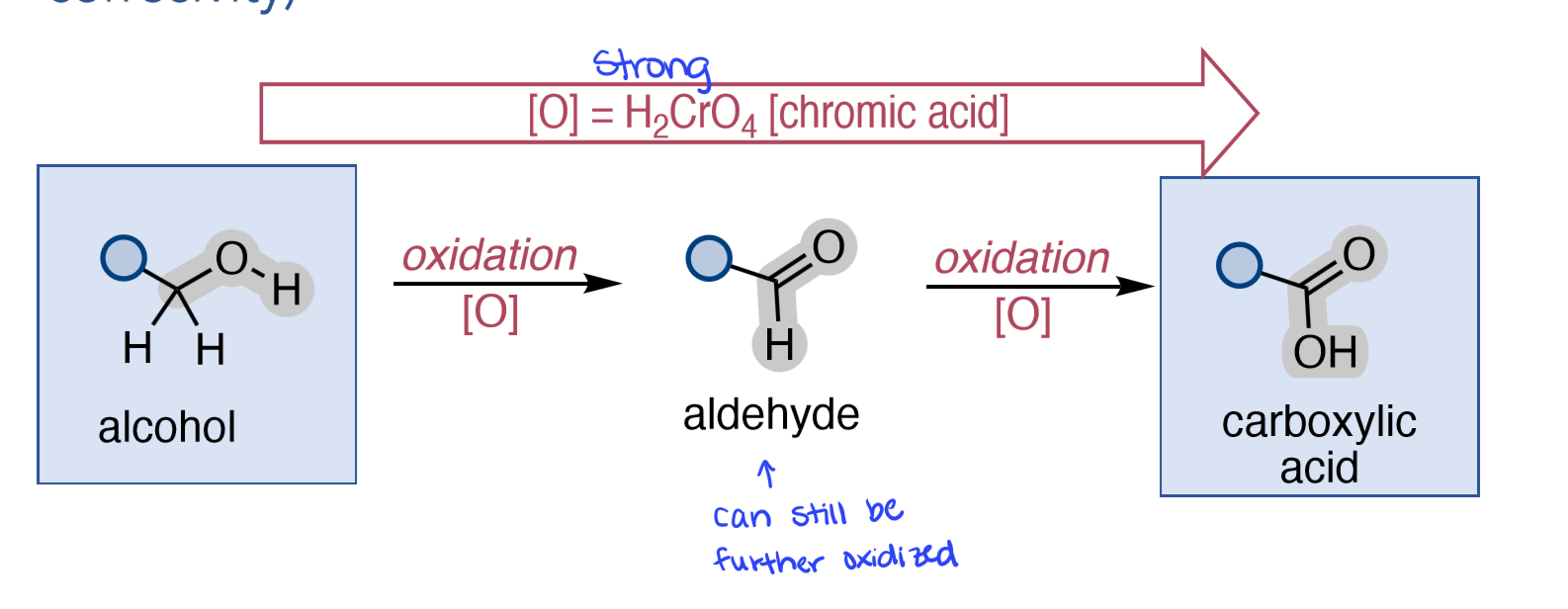
H₂CrO₄
Alcohol to Aldehyde to Carboxylic Acid
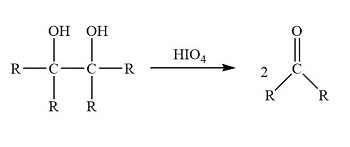
HIO4
Vicinal Diols into Aldehyde/Ketone
cleaves CC bonds
The two OH groups must be vicinal AND syn (cis)
If a diol carbon has at least one H → aldehyde
If it has no H (only carbons attached) → ketone
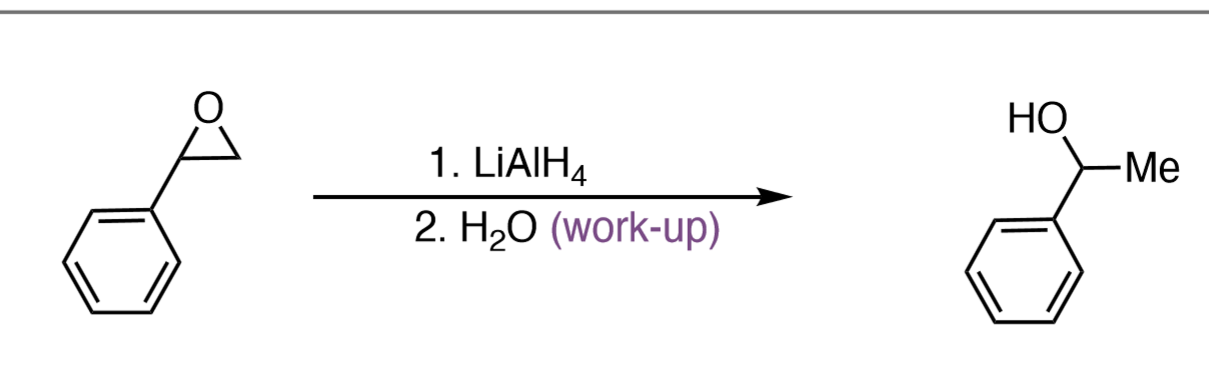
1) LiAlH₄ 2) H₂O
Epoxide to Alcohol
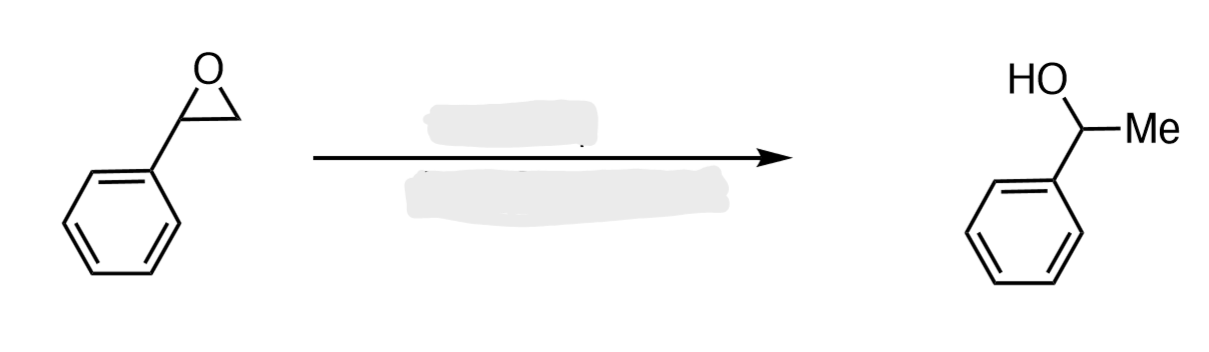
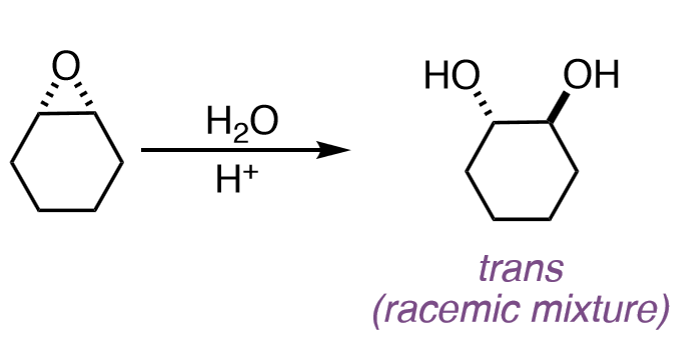
H₂O/H3O+
Epoxide to Vicinal Diol
The two OH groups end up anti (trans) to each other
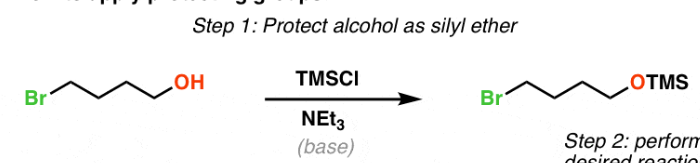
TMSCl + pyr
Alcohol to Silyl Ether
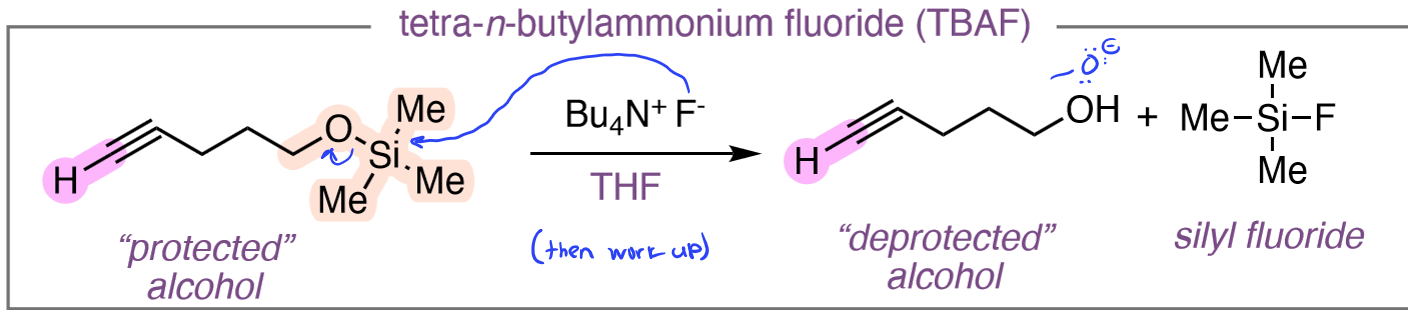
TBAF
Silyl Ether to Alcohol
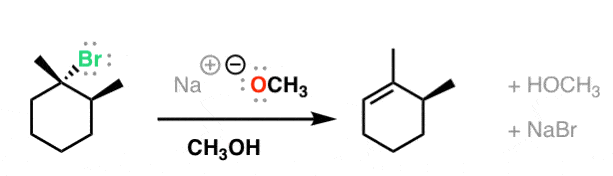
NaOR
Haloalkane to Alkene
works w 2° or 3° haloalkane
Regiochemistry: follows Zaitzev’s rules so the more substituted alkene predominates
Stereochem: requirement for the X and H to be eliminated with anti-periplanar geometry (E2 rxn)
works for all haloalkanes except methyl, but a bulky (non-nucleophilic) base must be used for 1° haloalkane
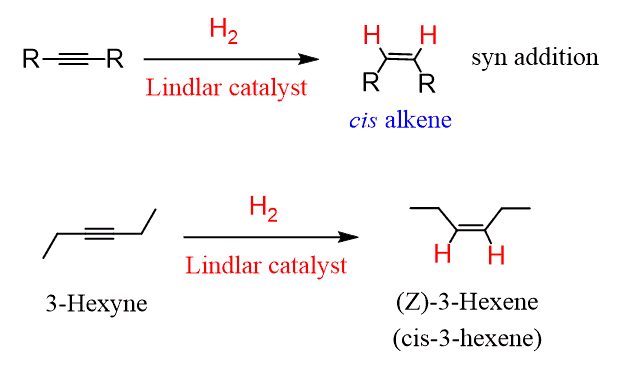
H2/Lindlars cat.
Alkyne to Alkene
Stereochemistry: gives cis-alkenes as products
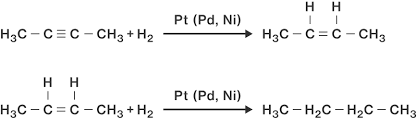
H₂/Pd, Pt, or Ni
Alkyne to Alkane
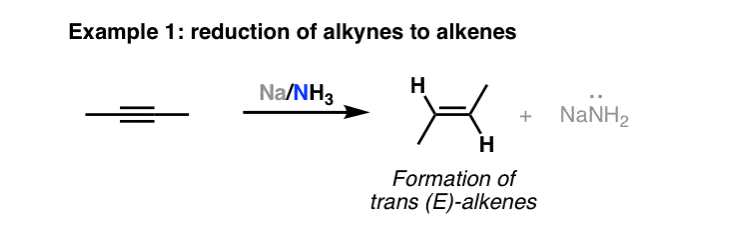
Na/NH3
Alkyne to Alkene
Stereochemistry: gives trans-alkenes as products
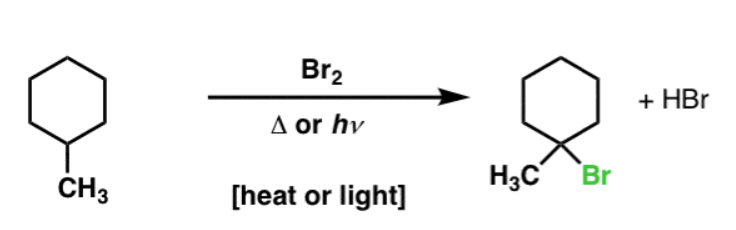
X2, hv or heat
Alkane to Haloalkane
regiochem: Reactivity of C–H bonds follows 3° > 2° > 1°
stereochem: Racemic if chiral
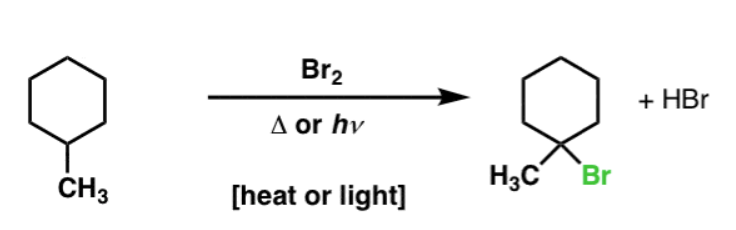
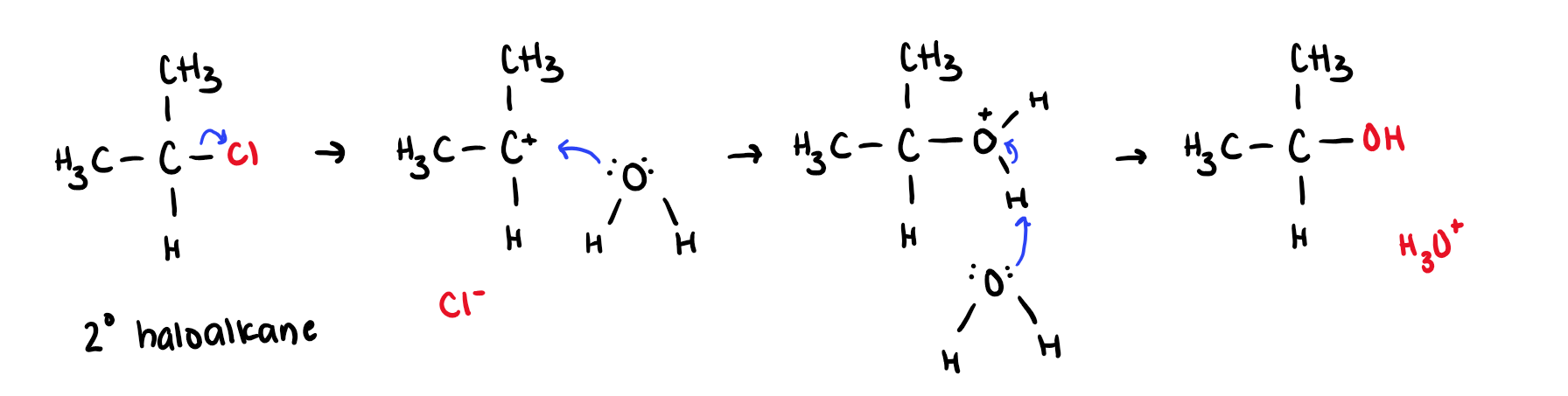
H2O, acid
Haloalkane into Alcohols
Works for 2° and 3° haloalkanes
stereochem: racemic if chiral
SN1 mechanism
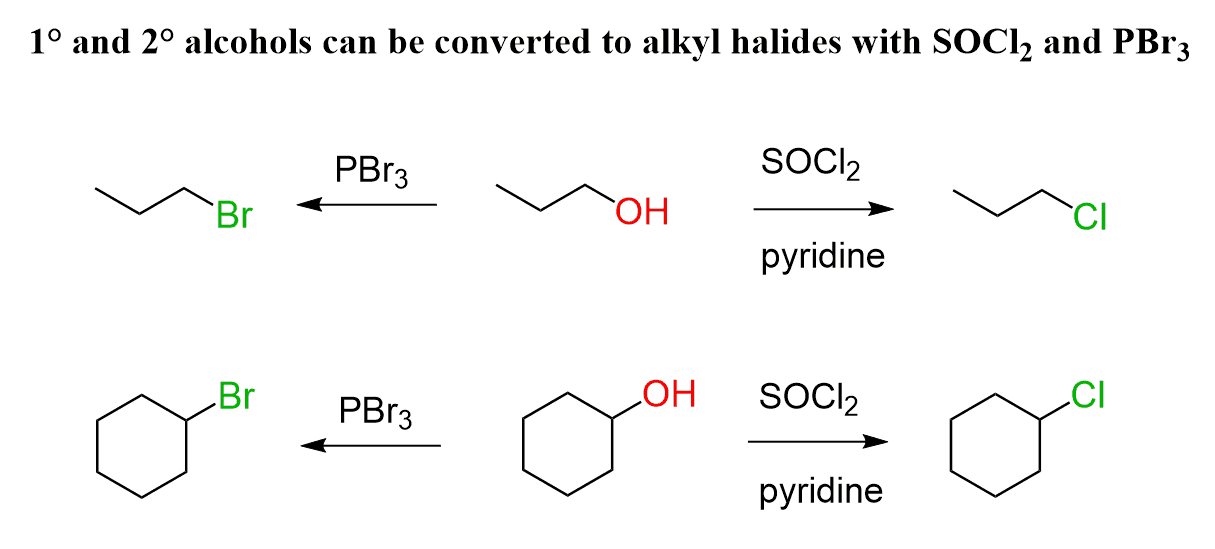
HX or SOCl2 (+ base) or PBr3
Alcohol to Haloalkane
works for methyl, 1°, and 2° haloalkanes
mechanism: SN2 → inversion
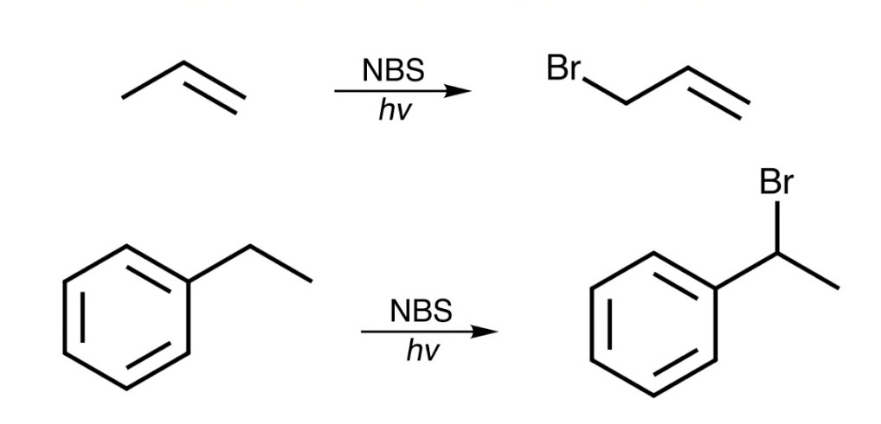
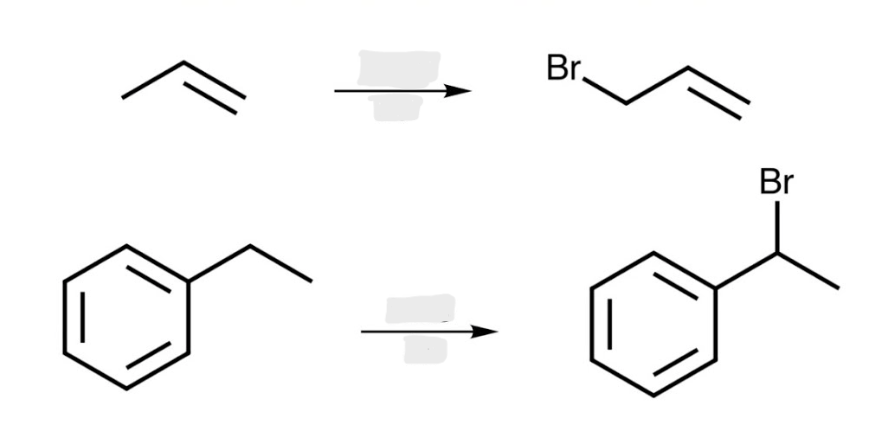
NBS
Alkene to Allylic Halides
Regiochemistry: the product with the more substituted alkene predominates
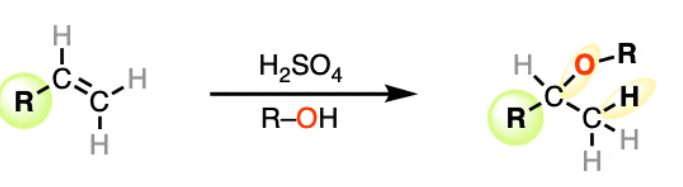
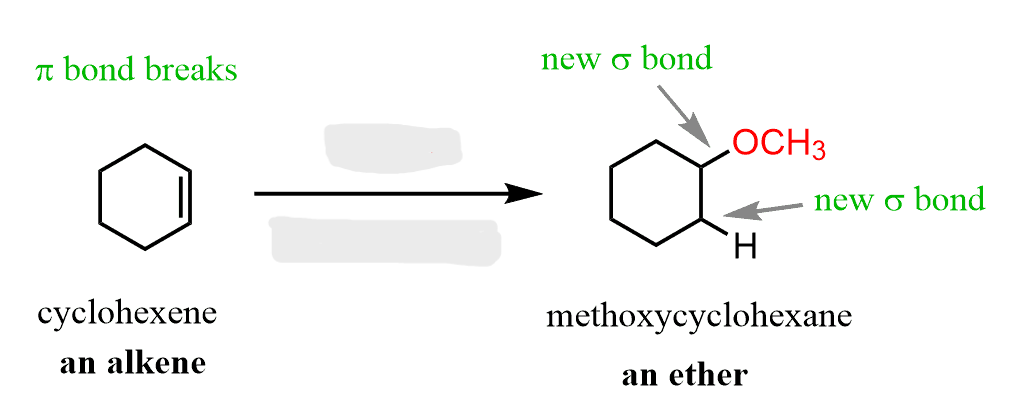
ROH/acid
Alkene to Ethers
Works for 2° and 3° haloalkanes
regiochem: Markovnikov addition
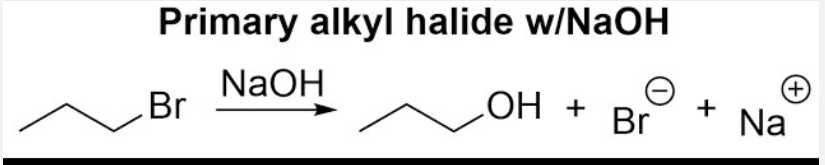
NaOH
Haloalkane to Alcohol
Works well for methyl and 1° haloalkanes
Inversion (SN2)
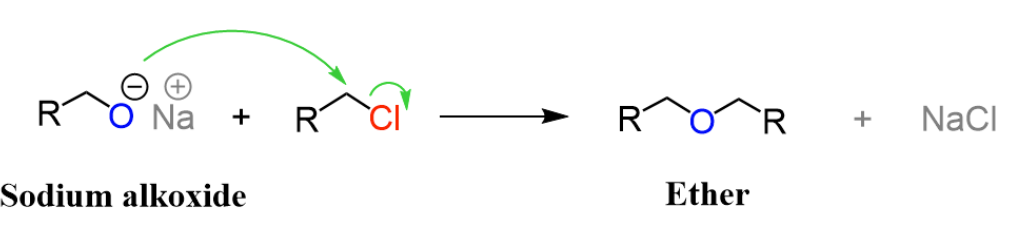
NaOR
Haloalkane to Ether
Works well for methyl and 1° haloalkanes
Inversion of configuration at that carbon (SN2)
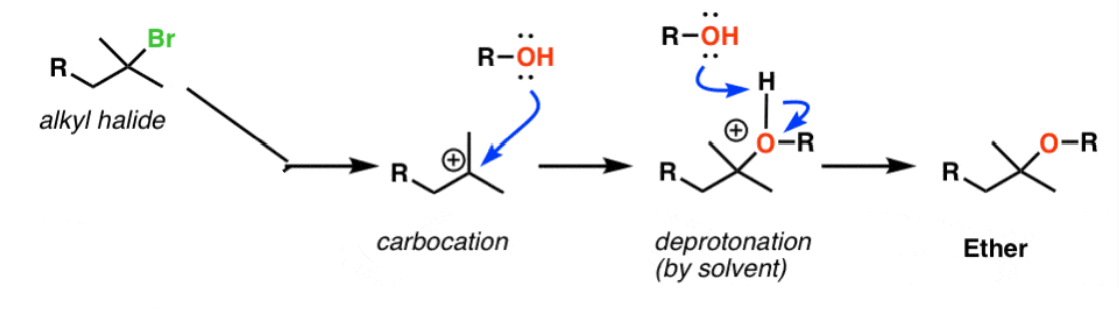
ROH
Haloalkane to Ether
Works for 2° and 3° haloalkanes
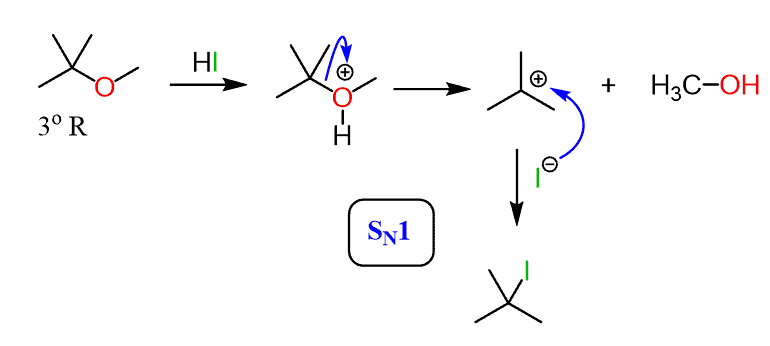
HI
Ether to Haloalkane
The ether oxygen is protonated
Makes a good leaving group (ROH⁺)

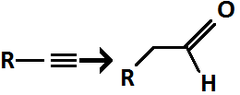
1) (sia)2BH, 2) H2O2, NaOH
Alkyne to Aldehyde/Ketone
regiochem: anti-Markovnikov addition to pi bond
Terminal alkyne (R–C≡CH) → Aldehyde
Internal alkyne (R–C≡C–R′) → Ketone(s)
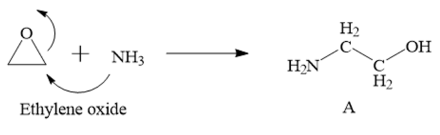
NH3; result: NH₂ on the less substituted carbon & OH on the more substituted carbon
Epoxide to Vicinal Aminoalcohol
regiochem: Attack at the LESS substituted carbon
NH₃ is a nucleophile
SN2-like behavior dominates
NaNH2/NH3
Vicinal Dihaloalkane to Alkyne
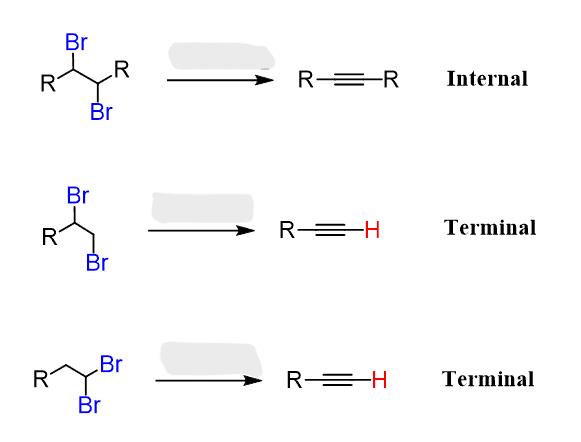
2X2
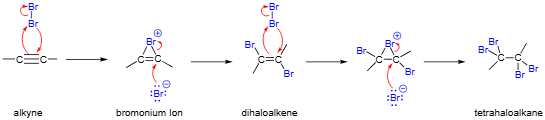
Alkyne to Vicinal Tetrahaloalkane
1 equivalent X₂ → trans dihaloalkene
2 equivalents X₂ → tetrahaloalkane
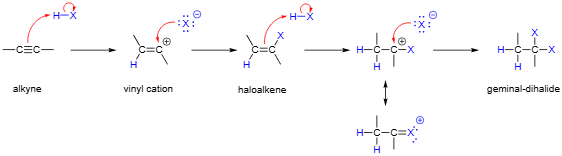
2HX; result:
X adds to the more substituted carbon
H adds to the less substituted carbon
The second HX adds the same way as the first
Alkyne to Geminal Dihaloalkane
regiochem: markovnikov addition to pi bond
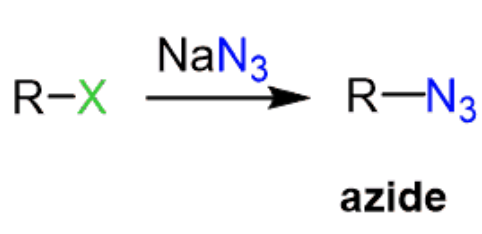
NaN3
Haloalkane to Alkyl Azides
works for methyl, 1°, and 2° haloalkanes
reaction type: SN2
stereochem: inversion
result: N₃ replaces X at the same carbon
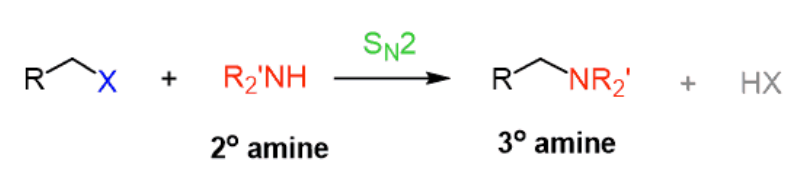
NHR2
Haloalkane to Amine
works for methyl, 1°, and 2° haloalkanes
rxn type: SN2 → inversion

NaSR
Haloalkane to Thioether
works for methyl, 1°, and 2° haloalkanes
rxn type: SN2 → inversion
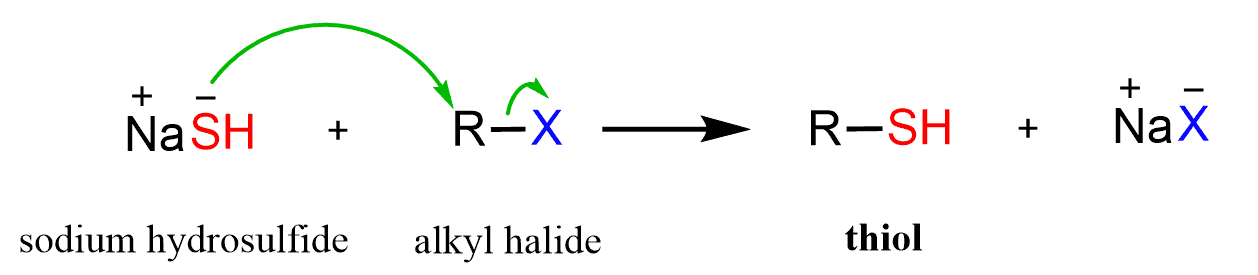
NaSH
Haloalkane to Thiol
works for methyl, 1°, and 2° haloalkanes
rxn type: SN2 → inversion
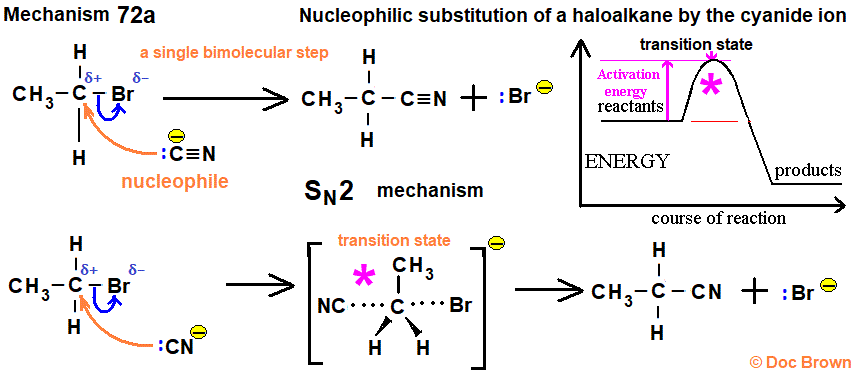
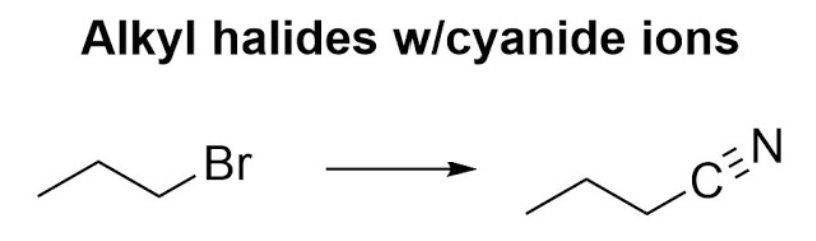
NaCN
Haloalkane to Nitrile
works for methyl, 1°, and 2° haloalkanes
carbon carbon bond forms
rxn type: SN2 → inversion
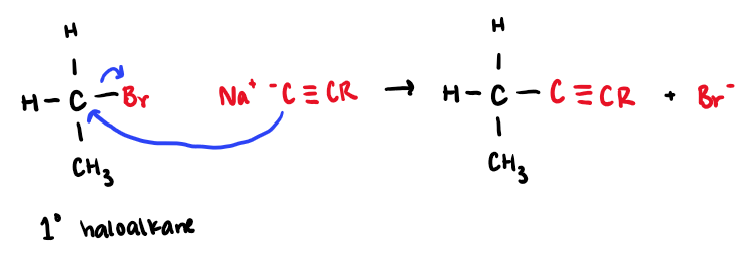
NaC≡CR
Haloalkane to Alkyne
works for methyl and 1° haloalkanes
carbon carbon bond forms
rxn type: SN2 → inversion