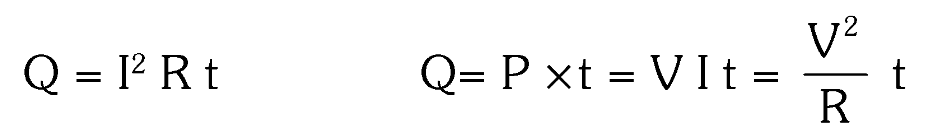Electric Current [INCOMPLETE]
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
In Progress
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What is the formula for Instantaneous Current?
I_{inst}=\dfrac{dq}{dt}
What is the formula for average current? there are two
I_{avg}=\dfrac{\Delta Q}{\Delta t}
I_{avg}=\dfrac{\int I\ dt}{\int\ dt} (with limits)
What is the formula for free electron density in terms of total number of free electrons?
n=\dfrac{N}{V}
What is the formula for current in terms of free electron density?
I=neAv_d
What is the formula for current in terms of drift velocity?
I=neAv_d
In a circular wire with frequency of rotation f, what is the formula for current through the wire?
I=qf
If a charge is moving in a circular path of radius r and speed v, what is the time period of the motion? What is the formula for equivalent current through the path?
T=\dfrac{2\pi r}{v}
I=\dfrac{q}{T} = \dfrac{qv}{2\pi r}
What is the formula for current density in terms of current?
J=\dfrac{I}{A}
What is the direction of current density?
Along the direction of current
What is the formula for current in terms of current density? (vector form)
I=\overrightarrow{J}\cdot\overrightarrow{A}
What is relaxation time?
\tau is the average time interval between two consecutive collisions of electrons
What is mean free path?
\lambda is the average distance travelled by an electron during its relaxation time
What is drift velocity really?
v_d is the average velcity acquired by an electron during relaxation time
What is the formula for drift velocity in terms of relaxation time?
v_d=\dfrac{eE\tau}{m}
where
e is the charge of an electron
E is the electric field at that point
\tau is the relaxation time
m is the mass of an electron
What is the formula for Resistance, in terms of relaxation time?
R=\dfrac{ml}{ne²\tau A}
where
m is the mass of an electron
l is the length of the conductor
n is the free electron density
e is the charge on an electron
\tau is the relaxation time
A is the cross-sectional area of the conductor
What is the formula for current density in terms of electric field?
\overrightarrow{J}=\dfrac{1}{\rho}\overrightarrow{E}
What is the formula for current density in terms of potential difference?
J=\dfrac{V}{l\rho}
where
V is potential difference
l is the length of the conductor
\rho is the resistivity of the conductor
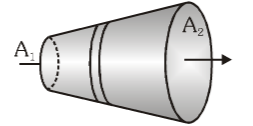
In this conductor, what is the comparison between the current passing through A_1 and A_2?
I_1=I_2
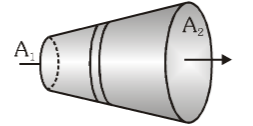
In this conductor, what is the comparison between the current density at A_1 and A_2?
J_1 > J_2
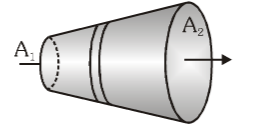
In this conductor, what is the comparison between the resistance at A_1 and A_2?
R_1 > R_2
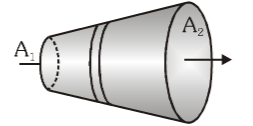
In this conductor, what is the comparison between drift velocity at A_1 and A_2?
v_{d1} > v_{d2}
What is the formula for current density in terms of drift velocity?
J=nev_d
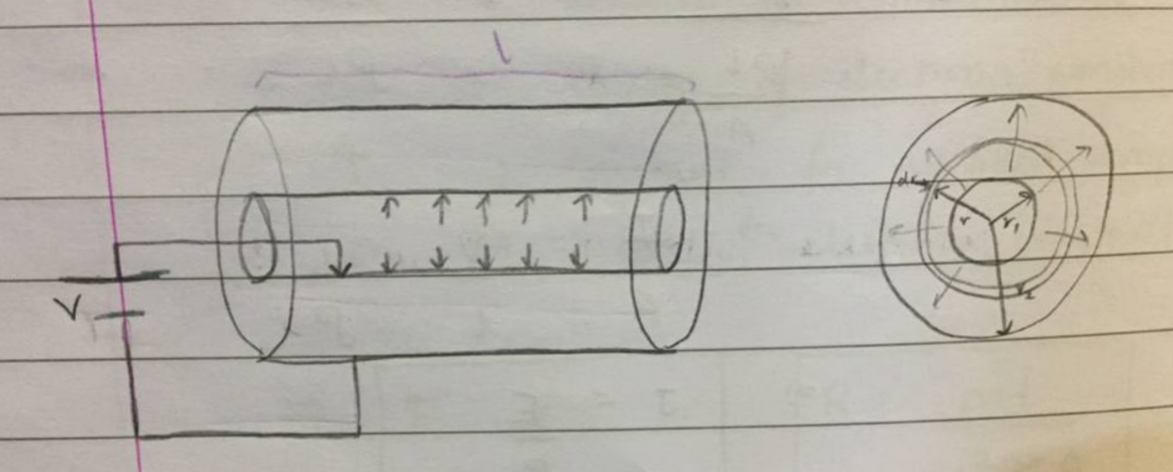
What is the formula for resistance in a 2D current?
R=\dfrac{\rho}{2\pi l}\ln\dfrac{r_2}{r_1}
When a wire is stretched, What is the relationship between the initial resistance and the final resistance? (in terms of both length and cross sectional area)
\dfrac{R_1}{R_2}=\dfrac{(l_1)²}{(l_2)²}=\dfrac{(A_2)²}{(A_1)²}
The coefficient of thermal resistivity is the fractional change in resistivity per unit change in temperature. Its definition is \alpha=\dfrac{\frac{d\rho}{\rho}}{dT}. How do you obtain an equation for the relationship between initial and final resistivity from this?
\alpha\ dT=\dfrac{d\rho}{\rho}
integrate both sides, rearrange
What is the formula for the relationship between initial and final resistivity, when the change in temperature is greater than 100 kelvin?
\rho=\rho_0e^{\alpha\Delta T}
What is the formula for the relationship between initial and final resistivity, when the change in temperature is less than 100 kelvin?
\rho=\rho_0(1+\alpha\Delta T)
What is the formula for the relationship between initial and final resistance, when the change in temperature is less than 100 kelvin?
R=R_0(1+\alpha\Delta T)
When a battery discharges, internal resistance of the battery increases or decreases?
increases.
What is the formula relating potential difference, electromotive force, current, and internal resistance (when battery is being discharged)?
V_A-V_B=\varepsilon -Ir
What is the formula relating potential difference, electromotive force, current, and internal resistance (when battery is being charged)?
V_A-V_B=\varepsilon +Ir
What is the formula for current in terms of electromotive force, internal resistance, and external resistance?
I=\dfrac{\varepsilon}{R+r}
What is the formula for Power in terms of current and external resistance?
P=I²R
What is the formula for Power (dissipated in the circuit) in terms of electromotive force and internal and external resistances?
P=\dfrac{\varepsilon²R}{(r+R)²}
The formula for Power (dissipated in the circuit) is
P=\dfrac{\varepsilon²R}{(r+R)²}
What is Power a function of?
External resistance (R)
The formula for Power (dissipated in the circuit) is
P=\dfrac{\varepsilon²R}{(r+R)²}
From this, how do you obtain the values of resistance for which the power is maximum?
Differentiate with respect to R, equate to 0 (finding the stationary point).
The formula for Power (dissipated in the circuit) is
P=\dfrac{\varepsilon²R}{(r+R)²}
What is the formula for the maximum value of Power?
P=\dfrac{\varepsilon²}{4r}
What is the formula for efficiency of a battery?
\eta =\dfrac{\text{output power}}{\text{input power}} =\dfrac{I²R}{I²(R+r)} = \dfrac{R}{R+r}
What is the value of efficiency of a battery when max power dissipates?
50%
The amount of current leaving the battery should be equal to the amount of current entering the battery.
Okay.
What is the formula for equivalent resistance in a series combination of resistances?
R_{eq}=\Sigma R
What is the formula for equivalent resistance in a parallel combination of resistances?
\dfrac{1}{R_{eq}}=\Sigma\dfrac{1}{R}
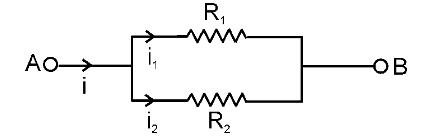
What is the formula for determining I_1?
I_1=\dfrac{IR_2}{R_1+R_2}
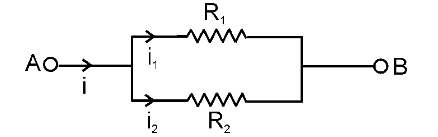
What is the formula for determining I_2?
I_2=\dfrac{IR_1}{R_1+R_2}
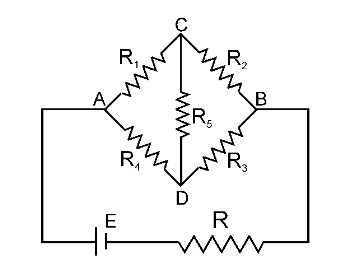
This is a Wheatstone Bridge.
Under what condition is it a BALANCED Wheatstone Bridge?
\dfrac{R_1}{R_2} = \dfrac{R_4}{R_3}
OR
\dfrac{R_1}{R_4} = \dfrac{R_2}{R_3}
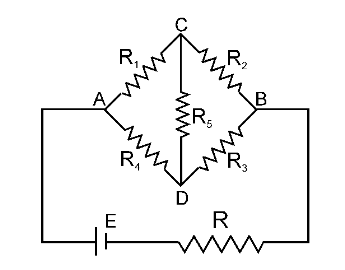
This is a Wheatstone Bridge.
If it is a balanced Wheatstone Bridge, What are the two things we can infer? (one about the current, one about the potential differences)
There is no current through R_5.
The potential difference between point C and point D is 0.
What is the Symmetry Rule?
If you can divide a circuit into 2 identical parts such that each part is a mirror image of the other, then all the points lying on the line of symmetry have equal potential (and if there is a wire along that line, then the wire carries no current)
Does EMF depend on nature of electrolyte?
yes
Does EMF depend on metal of electrodes?
yes
Does EMF depend on area of electrode plates?
no
Does EMF depend on distance between electrode plates?
no
Does EMF depend on quantity of electrolyte?
no
Does EMF depend on size of cell?
no
How does the distance between the electrodes affect the internal resistance of the cell?
increase of distance increases the internal resistance
How does area of electrode plates affect the internal resistance of the cell?
increase of area decreases the internal resistance
How does concentration of electrolyte affect the internal resistance of the cell?
increase in concentration increases the internal resistance
How does temperature affect the internal resistance of a cell?
incraease in temperature decreases the internal resistance.
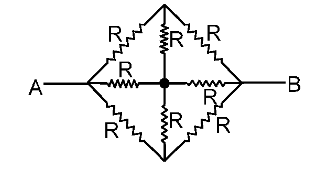
How would you use folding to solve this question?
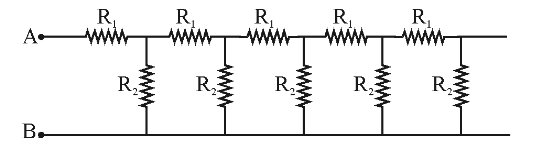
This is an infinite ladder problem. How would you approach this?
The equivalent resistance after each rung remains the same, so you can equate them and shit i guess
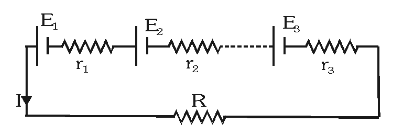
What is the formula for the equivalent EMF of batteries connected in series?
\varepsilon_{eq}=\Sigma\varepsilon
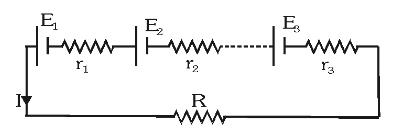
What is the formula for the equivalent internal resistance of batteries connected in series?
r_{eq}=\Sigma r
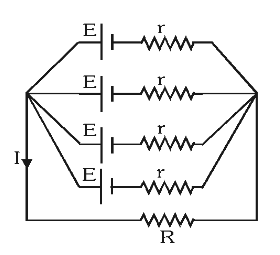
What is the formula for equivalent EMF of batteries connected in parallel? (when EMFs are different)
\varepsilon_{eq}=\dfrac{\frac{\varepsilon_1}{r_1}+\frac{\varepsilon_2}{r_2}…}{\frac{1}{r_1}+\frac{1}{r_2}…}
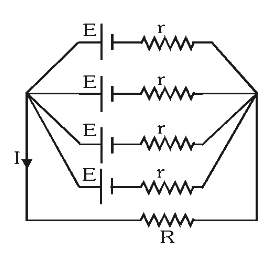
What is the formula for equivalent internal resistance of batteries connected in parallel? (when resistances are different)
same as normally parallel resistances
When is the coefficient of thermal resistivity positive? When is it negative?
\alpha is positive for conductors.
\alpha is negative for semiconductors and non-conductors.
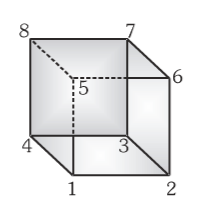
If a circuit is connected at nodes 1 and 7, what is the equivalent resistance of the cube? Assume all edges of the cube have the same resistance R.
R_{eq}=\dfrac56R
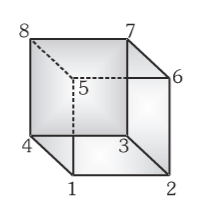
If a circuit is connected at nodes 1 and 6, what is the equivalent resistance of the cube? Assume all edges of the cube have the same resistance R.
R_{eq}=\dfrac34R
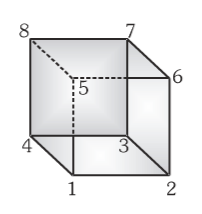
If a circuit is connected at nodes 1 and 2, what is the equivalent resistance of the cube? Assume all edges of the cube have the same resistance R.
R_{eq}=\dfrac{7}{12}R
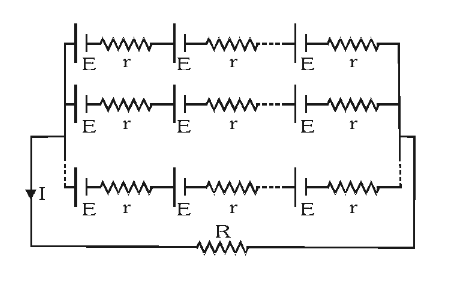
What is the equivalent EMF in this circuit?
\varepsilon_{eq}=n\varepsilon
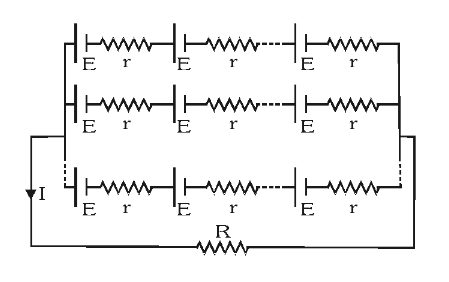
What is the equivalent internal resistance in this circuit?
r_{eq}=\dfrac{nr}{m}
Where
n is the number of resistances in series
m is the number of resistances in parallel
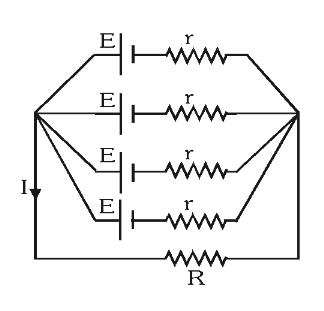
In this circuit, if there were no internal resistances, and the values of EMF were different for each cell, what would be the equivalent EMF?
\varepsilon_{eq}=\varepsilon_L
where \varepsilon_L is the EMF value of the cell with the least EMF out of all the cells ygwim?
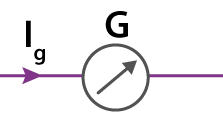
This is a galvanometer. I_g is the current through the galvanometer which causes a full scale deflection. What happens when the current through the galvanometer is greater than I_g?
the needle breaks.
What is the formula for sensitivity of a galvanometer?
S=\dfrac{\Delta\theta}{\Delta I}
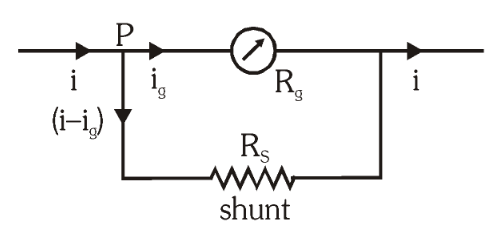
This is an ammeter. What is the formula for calculating the shunt resistance in this ammeter?
R_s=\dfrac{I_gR_g}{I-I_g}
Where I is the maximum current that can be measured by this ammeter.
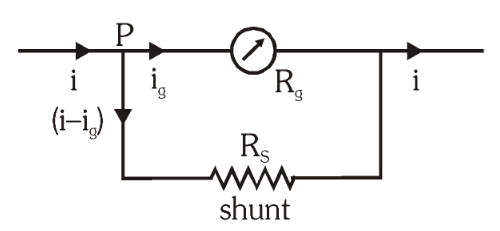
This is an ammeter. The shunting resistance should be minimum or maximum, for the ammeter to be as accurate as possible?
minimum
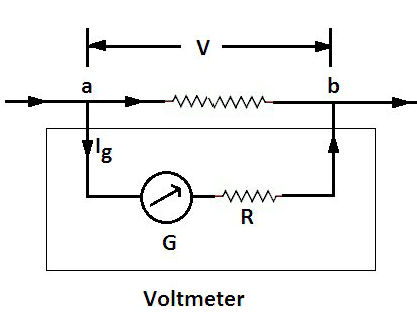
This is a voltmeter. What is the formula for calculating the large resistance?
R = \dfrac{V}{I_g}-R_g
where
V is the maximum potential difference measured (range of voltmeter)
I_g is the limiting current of the galvanometer
R_g is the resistance of the galvanometer
This is a voltmeter. Should R be maximum or minimum, for the voltmeter to be as accurate as possible?
maximum
What is the formula for heat produced due to current?