gcse biology
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
What type of cell are bacterial cells classified as? (1 mark)
Prokaryotes/prokaryotic cells
Some plant cells can produce glucose. Suggest why yeast cannot. (1 mark)
No chloroplasts/chlorophyll
What are the functions of permanent vacuoles in plant cells? (2 marks)
To store cell sap
To maintain turgor pressure
Why do muscle cells contain a lot of mitochondria? (3 marks)
Muscle cells require a lot of ATP to function
Mitochondria are the site of aerobic respiration
That release ATP from the breakdown of glucose
What are human gametes? (1 mark)
Haploid
Is a virus larger or smaller than a bacteria? (1 mark)
Smaller
What is an organelle? (2 marks)
A specialised structure in a cell performing a specific function for cellular processes
What is a cell? (2 marks)
The basic structural functional unit of all living organisms
What is a tissue? (2 marks)
A group of cells with similar structure and function
What is an organ? (3 marks)
A group of tissues performing specific physiological functions in a living organism
What is an organ system? (3 marks)
A group of organs performing functions necessary to survival of an organism (e.g the circulatory and respiratory system)
Give 4 examples of membrane bound organelles (4 marks)
Nucleus
Vacuole
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts
What are 3 characteristics of plants? (3 marks)
Cellulose cell wall
Multicellular
Usually photoautotrophic nutrition
What is a pathogen? (2 marks)
A microorganism incurring disease in another organism
What is an example of a virus and the disease it causes? (2 marks)
Influenza virus, causing influenza
What is an example of a fungi and the disease it causes? (2 marks)
Trichophyton rubrum, causing athlete’s foot
What is an example of a protist and the disease it causes? (2 marks)
Plasmodium, causing malaria
What is an example of a bacteria and the disease it causes? (2 marks)
Streptococcus pyogenes, causing strep throat
What is the cell wall of a bacteria made from? (1 mark)
Peptidoglycan
What is the cell wall of a fungi made from? (1 mark)
Chitin
What is the cell wall of a plant cell made from? (1 mark)
Cellulose
Where may adult stem cells be found? (1 mark)
In vascularised tissue
What are two examples of how stem cells can be used in medicine? (2 marks)
Replacing damaged cells instead of treating them
Regenerating missing tissue
Why are some people against stem cell research? (2 marks)
Taking totipotent and pluripotent cells from zygotes and blastocysts destroys them, which may be seen as killing babies.
What is a disease? (2 marks)
A pathological condition of a living organism disrupting bodily functions
What is the difference between a flaccid and plasmolysed cell? (2 marks)
A flaccid cell loses some of its shape and its vacuole shrinks, while a plasmolysed cell’s plasma membrane/cytoplasm has pulled away almost completely from the cell wall
Define the term diploid (3 marks)
Having two sets of chromosomes in the nucleus of the cells, one from the male parent and one from the female
What is cellulose? (1 mark)
A polysaccharide
Around what size is a bacteria? (1 mark)
A micrometer
What can make a bacteria gastro-resistant? (2 marks)
The slime capsule being able to protect the bacteria from gastric acid and immune cells
Do bacteria have DNA? (1 mark)
Yes, but it is not enclosed in a nucleus.
What is additional DNA in a bacteria stored as? (1 mark)
A plasmid.
What is the function of a cell membrane? (1 mark)
To control the passage of substances through the cell
What is the role of the cytoplasm? (1 mark)
To host chemical reactions
What is the role of a chloroplast? (1 mark)
To act as the site of photosynthesis
What substance do plants store short term and long term energy as? (2 marks)
Sucrose (short term) and starch (long term)
What type of metabolism do plants undergo? (1 mark)
Photosynthesis/photoautrophic nutrition
What is a ribosome? (1 mark)
The site of protein synthesis
What role do mitochondria serve? (1 mark)
Acting as the site of aerobic respiration
What are the two functions of the nucleus? (2 marks)
To control cell growth and division
To contain DNA
What bacteria is used in yoghurt and cheesemaking? (1 mark)
Lactobacillus
What type of nutrition do humans carry out? (1 mark)
Heterotrophic nutrition
What type of nutrition do prokaryotes primarily conduct?
Photosynthesis, and saprophytic nutrition
What do fungi store glucose as?
Glycogen
What and where do humans store glucose as? (2 marks)
Glycogen (a polysaccharide) in liver and muscles
What does ‘unicellular’ mean?
A unicellular organism
Where does anaerobic respiration happen in a cell?
Outside mitochondria (if present) and in the cytoplasm
What is an example of a unicellular fungi? (1 mark)
Yeast
What is an example of a multicellular fungi? (1 mark)
Mucor
What is the name for multiple hyphae?
A mycelium
Two examples of animals (2 marks)
Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly)
Homo sapiens (humans)
What structure helps fungi feed? (1 mark)
The hypha
What is the difference between nutrition and metabolism? (1 mark)
Nutrition refers to the process of obtaining and utilising food. Meanwhile, metabolism refers to all processes undergone to maintain life.
What do cells around the perimeter of a hypha share? (2 marks)
A vacuole and cell wall
How do fungi digest their food? (1 mark)
Extracellularly (extracellular digestion)
How do fungi regain their enzymes after releasing them to digest food with? (1 mark)
Diffusion; the concentration of enzymes outside the fungi would now be higher.
What is heterotrophic nutrition? (1 mark)
Nutrition in which the food is other organisms.
Why are viral teguments not present in all viruses? (1 mark)
Some viruses can effectively function without requiring an extra layer of protein
What do all viruses share in common? (2 marks)
The capsid, and the genetic material which it contains
What does the term ‘undifferentiated’ mean? (1 mark)
Able to conduct cell renewal/division and differentiation
Why are viruses not classified as living? (3 marks)
They cannot reproduce without a host cell
They lack sensitivity
They cannot excrete
They have no cellular structure
They do not grow
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in plants and fungi? (1 mark)
Glucose → energy + carbon dioxide + ethanol
What is the full definition of diffusion? (3 marks)
The net movement of particles down a concentration gradient, from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
What is the chemical equation for aerobic respiration? (3 marks)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6H2O + 6CO2 + ATP
Describe an experiment proving that respiration produces heat. (3 marks)
Put germinating and dead seeds in separate identical thermos flasks
Measure the temperature of the flasks with a thermometer
After a set period of time, measure the temperature of each flask once again.
Since dead seeds do not respire, the hotter germinating flask proves that respiration produces heat.
Why do humans predominantly use aerobic respiration? (2 marks)
It provides more energy over time than anaerobic respiration, and since humans are large organisms, they require more ATP.
Why is diffusion passive transport? (1 mark)
It does not use metabolic energy.
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in humans? (2 marks)
glucose → lactic acid + ATP
Will taking away a divider in a diffusion experiment involving gases decrease particle speed, given that there are no external factors, and heat is not involved? (3 marks)
The pressure decreases, and the gas expands into a vacuum. Kinetic energy is used up in the process. There is also no heat to transfer more kinetic energy, and so the gas’ speed changes, slowing down.
Why does increasing temperature cause an increase in diffusion rate? (2 marks)
High temperature increases kinetic energy, and thus particles will move faster, diffusing at a higher rate too.
Why does a larger surface area lead to faster diffusion into the same inner space? (2 marks)
The larger the surface area, the more opportunities there are for the particles to diffuse through/permeate the membrane, as there will be more particle collisions.
What absorbs CO2 during an experiment? (1 mark)
Potassium hydroxide, or sodalime.
What are the four things that increase diffusion rate? (4 marks)
A larger surface area, higher temperature, lower diffusion distance, and a larger concentration gradient.
How does a manometer work? (4 marks)
Air flows towards an area of lower concentration
Air concentration decreases when absorbed
Air will diffuse into the area of lower concentration
The bubble moves
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in plants and fungi? (3 marks)
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide + ATP
Why is gaining resources from the outside world easy for unicellular organisms? (3 mark)
100% of the cell is in contact with the environment
Thus they have a large SA:V, making diffusion faster and efficient
Concentration of resources in the outside environment is also higher than that of the cell’s internal region
These factors make diffusion rate increase, making gaining resources passive.
Name 3 activities requiring ATP within a human (3 marks)
Any 3 from:
Active transport
Breaking actin myosin bonds
Synthesis of large molecules
Mitosis
Homeostasis
What are villi and alveoli, and why are they good at their jobs? (2 marks)
They are specialised exchange surfaces
They have a large SA:V ratio.
What is Fick’s law? (3 marks)

Why do elephants struggle to manage their internal temperature? (1 mark)
They have a tiny SA:V ratio, so they overheat easily → this is why their ears are long and thin, with a large SA:V to compensate.
Why do mice struggle to maintain their internal temperature? (1 mark)
They have an incredibly large SA:V ratio, so they lose heat easily → this is why they have faster metabolism to generate more heat
What is the definition of osmosis? (3 marks)
The net movement of water molecules from a region of high water potential to a region of low water potential across a selectively permeable membrane
What chemical is used to test for carbon dioxide, and what is its positive result? (2 marks)
Limewater. It turns cloudy/mily white from clear.
What chemical tests for water, and what is a positive result? (2 marks)
Cobalt chloride paper. It will turn from blue into pink.
What is oxygen debt? (1 mark)
The volume of oxygen required to oxidise lactic acid from anaerobic respiration.
What is active transport? (3 marks)
The net movement of molecules ‘up’ a concentration gradient, from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration (requires ATP)
Why would a molecule not be absorbed by active transport (e.g xylose?) (3 marks)
Active transport is selective, there would be no transporter protein specific to the molecule, and transport proteins in cell membranes can distinguish between molecules.
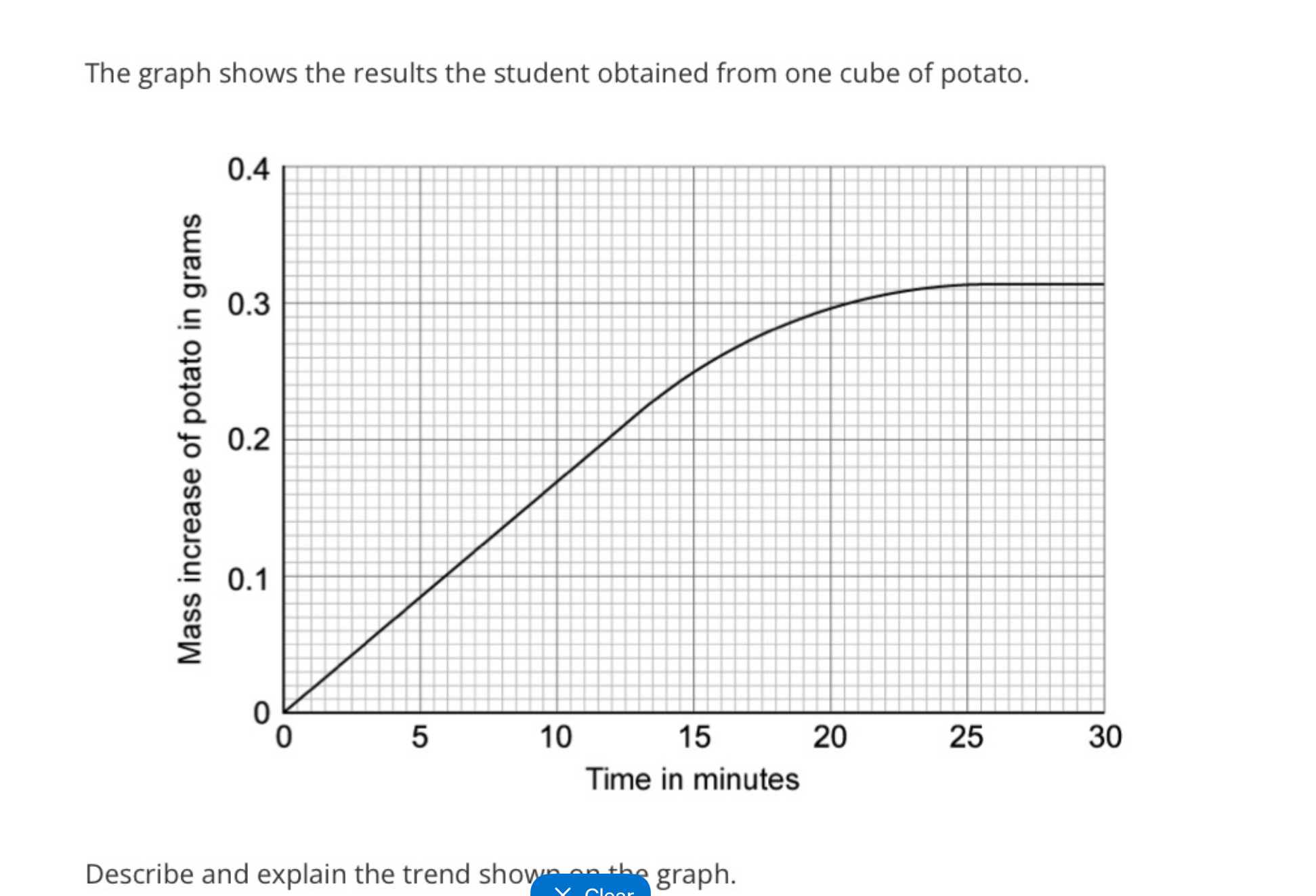
Describe and explain the trend shown on the graph (5 marks)
The water potential outside the potato is higher than the inside
Water moves into the potato cells by osmosis
The rate occurs more quickly when the water potential gradient is steepest, between 0 and 15/20 minutes
The rate of increase slows and the graph levels off because there is no longer a water potential gradient, and the water potential inside the potato is the same as/similar to the water potential outside the potato.
The graph levels off when the cell is turgid and cannot absorb any more water.
Human body temperature is approximately 37*C, providing the optimum temperature for the activity of protein molecules such as enzymes. Suggest why a temperature of 37*C maximises the rate of transport of substances across the cell membrane. (3 marks)
Temperatures less than 37*C would result in less kinetic energy of particles being transported
Causing a slower rate of diffusion/osmosis/active tramsport
Temperatures higher than 37*C would damage carrier proteins/cell membranes
Reducing the rate of/preventing the transport of molecules across the membrane.
Why would a student calculate a percentage change in mass as well as a change in mass in grams in an osmosis experiment? (1 mark)
Any one of the following:
To allow the results to be compared to each other
Because they had different start masses
What are two ways to measure the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction? (2 marks)
Measuring how long it takes for the reactant to be used up
Measuring the rate of production of the product
Define the term ‘catalyst’ (2 marks)
A chemical that speeds up a chemical reaction without being used up itself
What does the enzyme catalase break down? (1 mark)
Hydrogen peroxide
Why would an experiment involving showing that respiration produces heat require cleaning of the apparatus before the start of the experiment? (2 marks)
To kill any microorganisms that would respire and produce heat, interfering with the experiment.
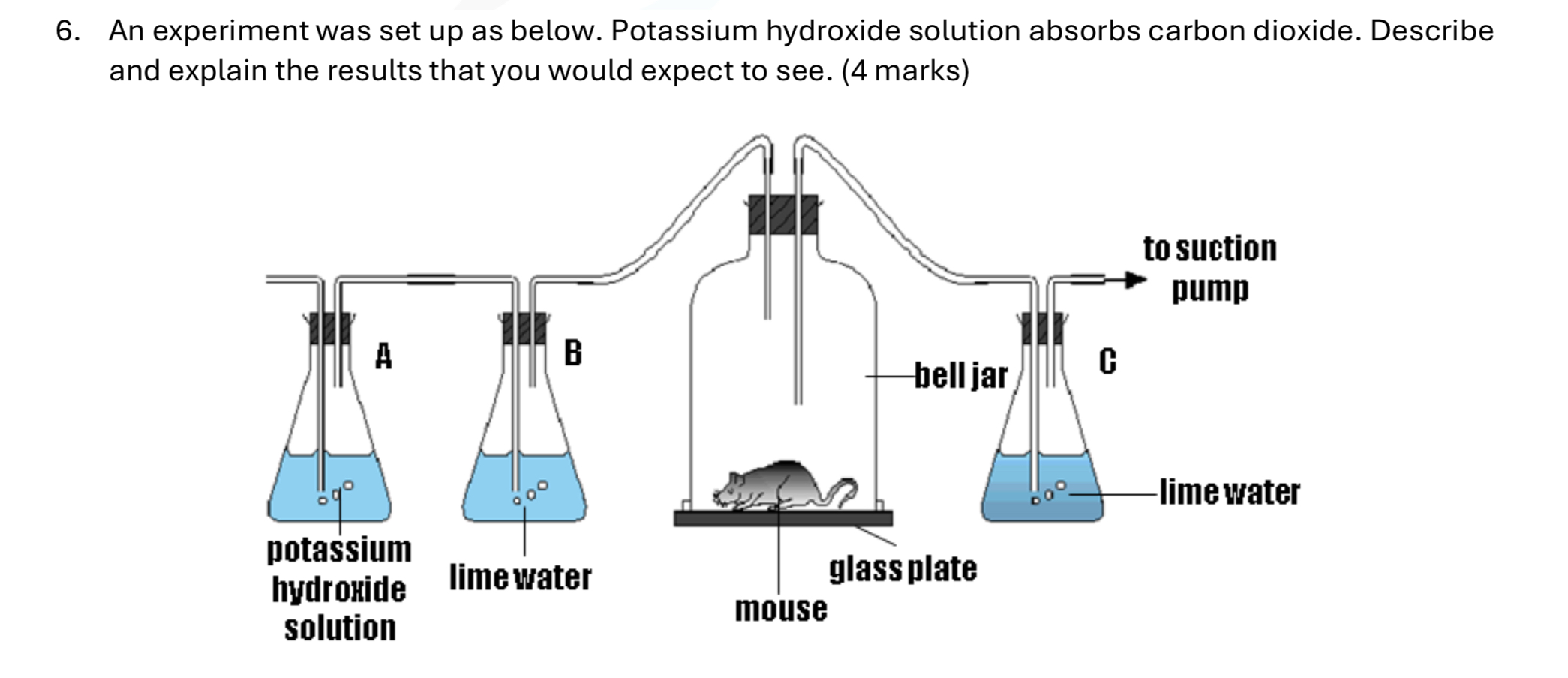
The mouse is living. Describe and explain the results expected. (4 marks)
A absorbs the CO2 from the air
B proves that no CO2 enters the bell jar by testing for it. It will be clear, to show a negative result
The mouse respires aerobically using the O2 content passing through the bell jar, producing CO2 and heat
C will thus turn cloudy, as there is CO2 passing through the limewater.
The suction pump bubbles the air through one direction, ensuring smooth passage and creating bubble shapes.
What is the GCSE definition of a balanced diet? (2 marks)
A diet providing all the necessary nutrients required for good health.
What are the nutrients required in a balanced diet/ what does a balanced diet consist of? (7 marks)
CPFFVMW (carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fibres, vitamins, minerals, water)
Where can you find carbohydrates? (2 marks)
Bread, rice, pasta, cereal, potatoes etc
What foods are good sources of protein? (2 marks)
Meat, fish, eggs, pulses, and nuts
What foods are a good source of dietary fibre? (2 marks)
Veggies and wholegrain.