Biology IB SL1 Final 2025
1/765
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
766 Terms
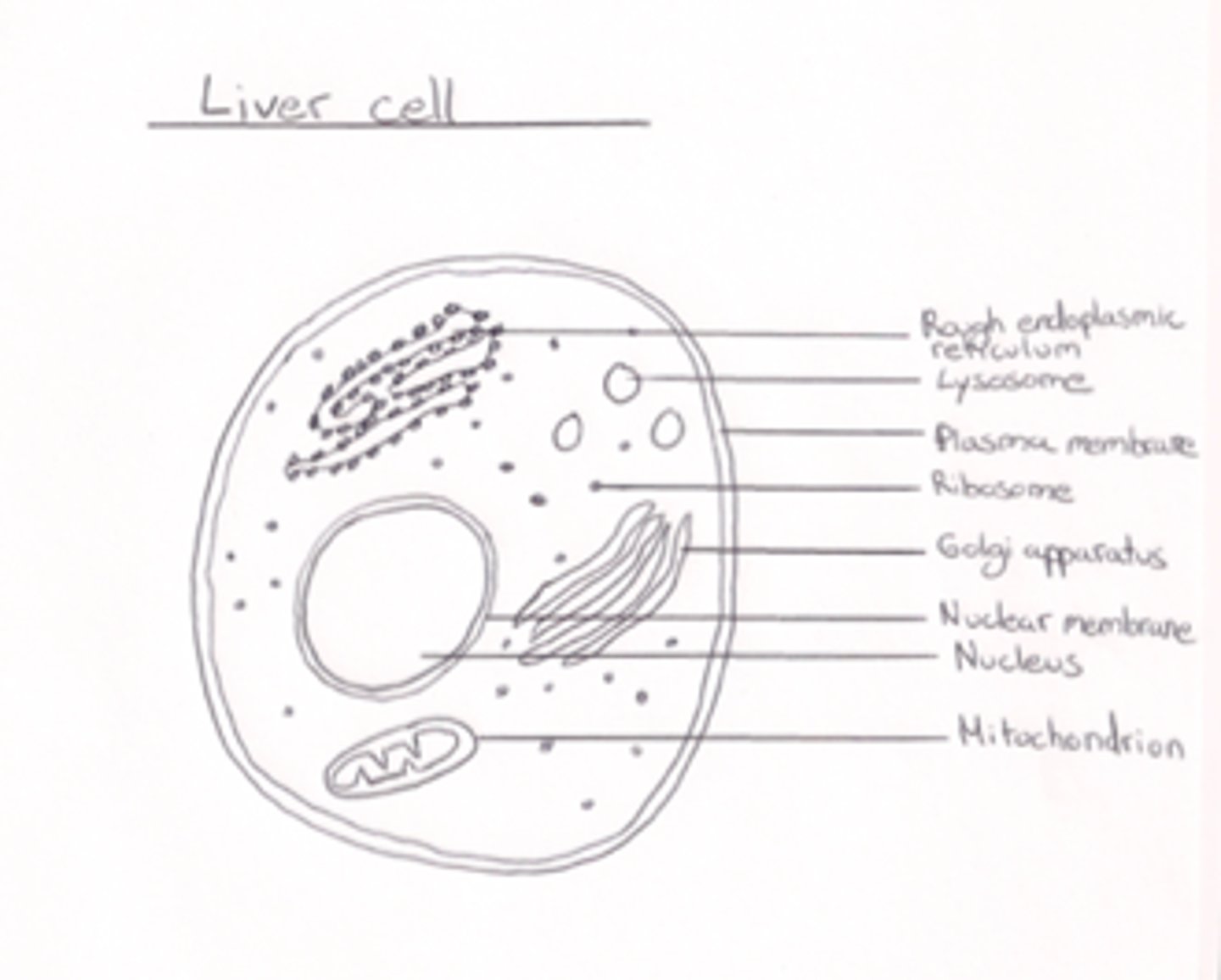
Eukaryote Cell
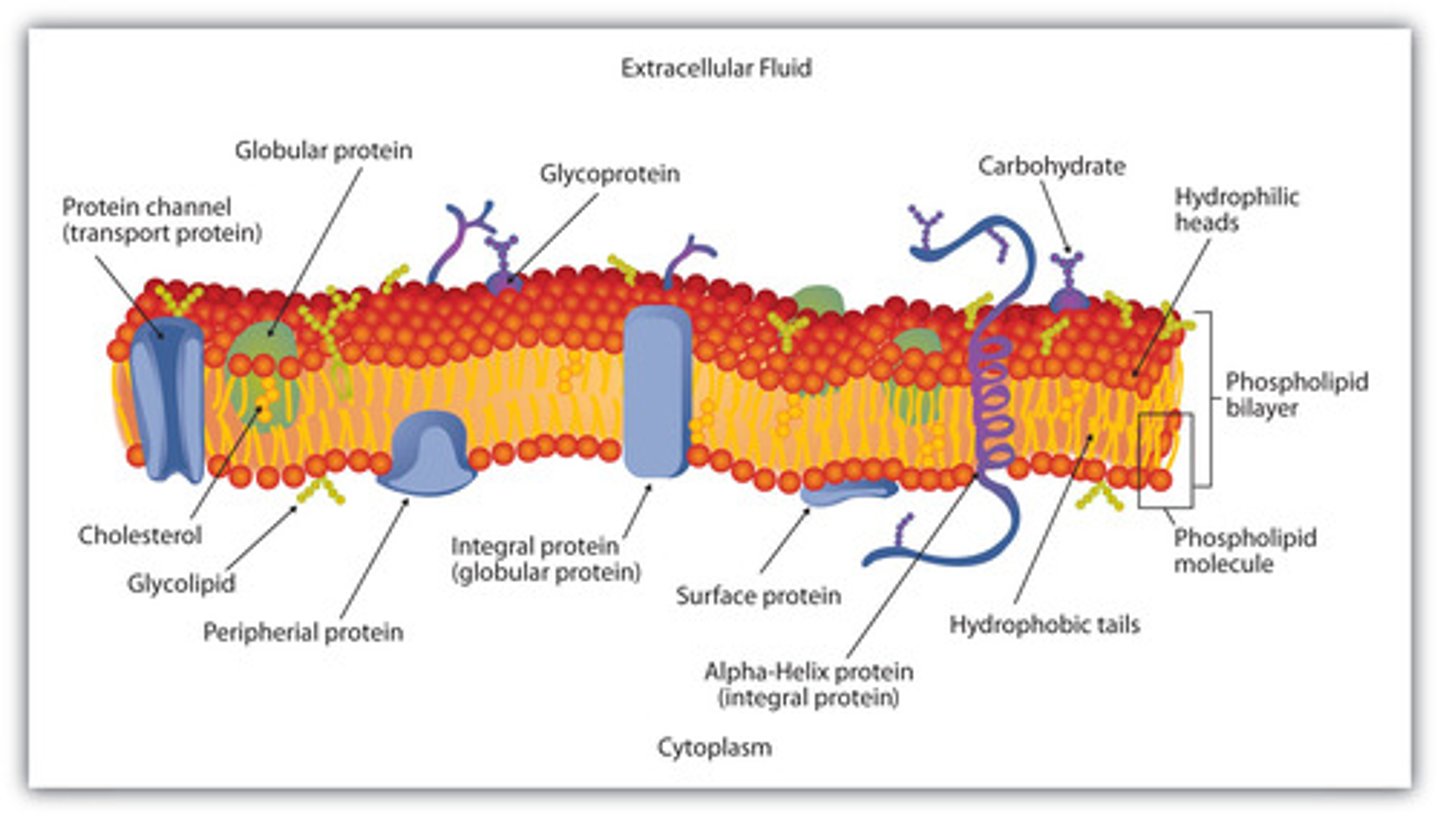
Phospholipid Bilayer
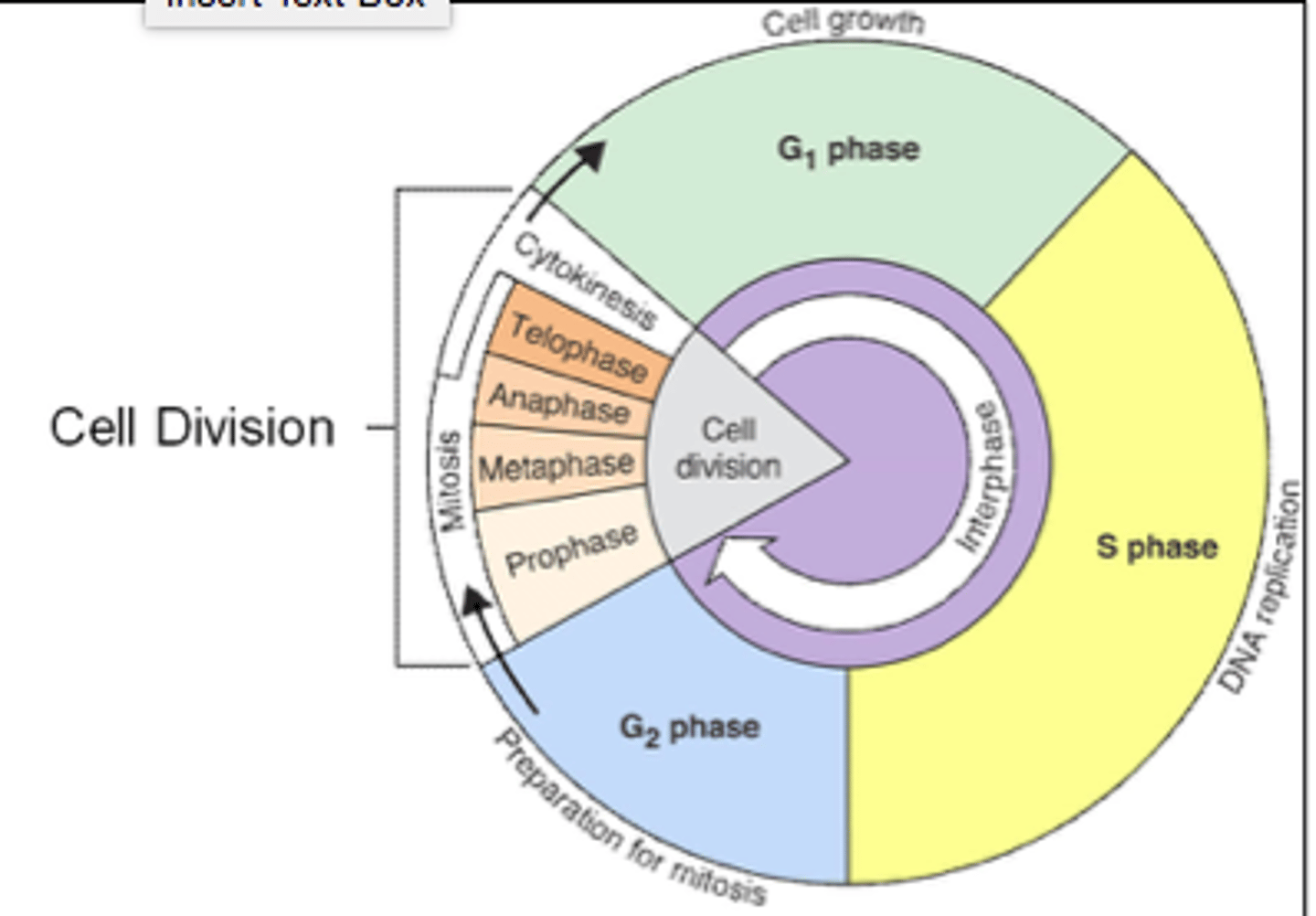
Stages of Cell Division
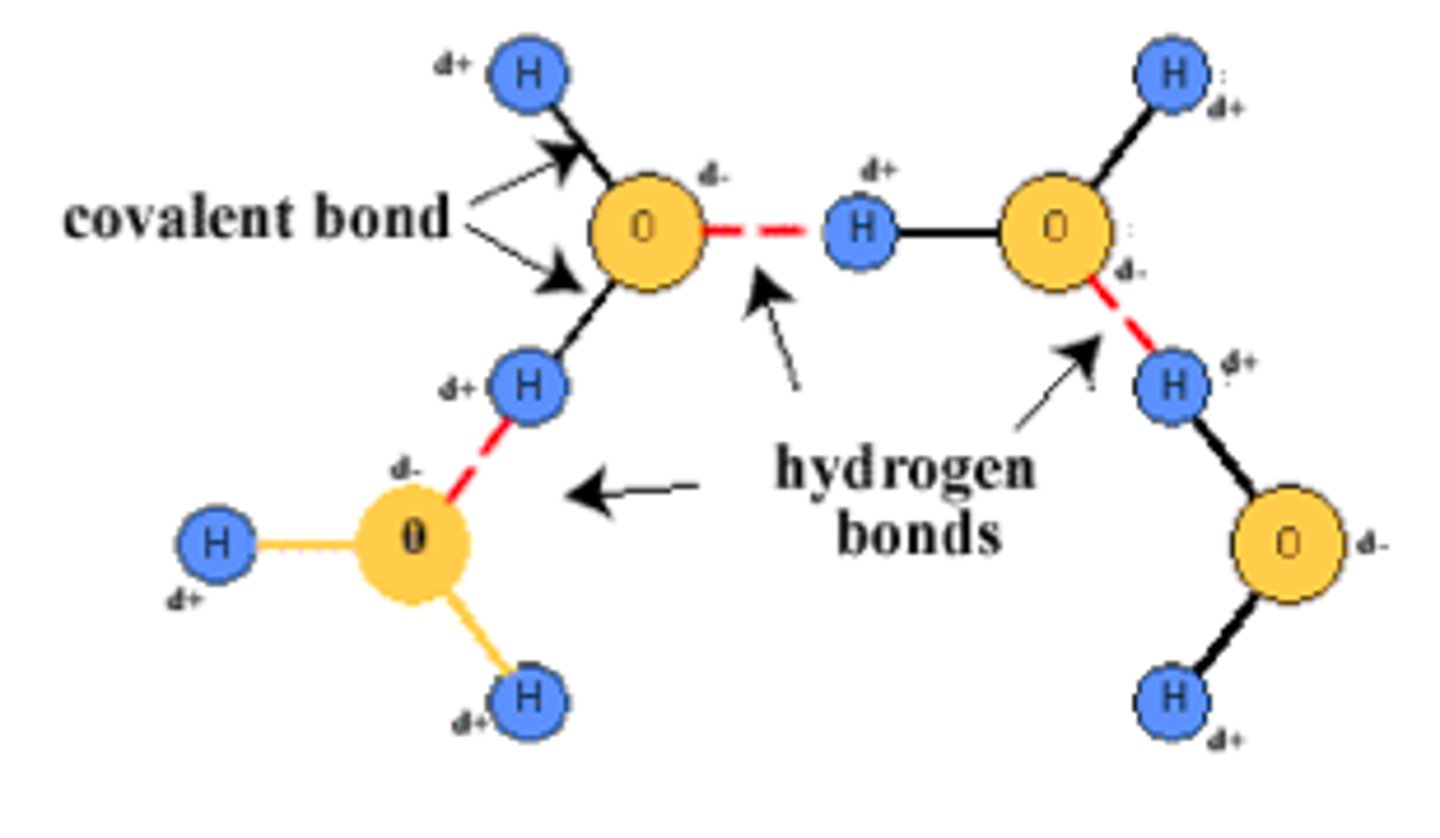
Structure of Water Molecules (polarity and hydrogen bond formation)
Glucose Molecule
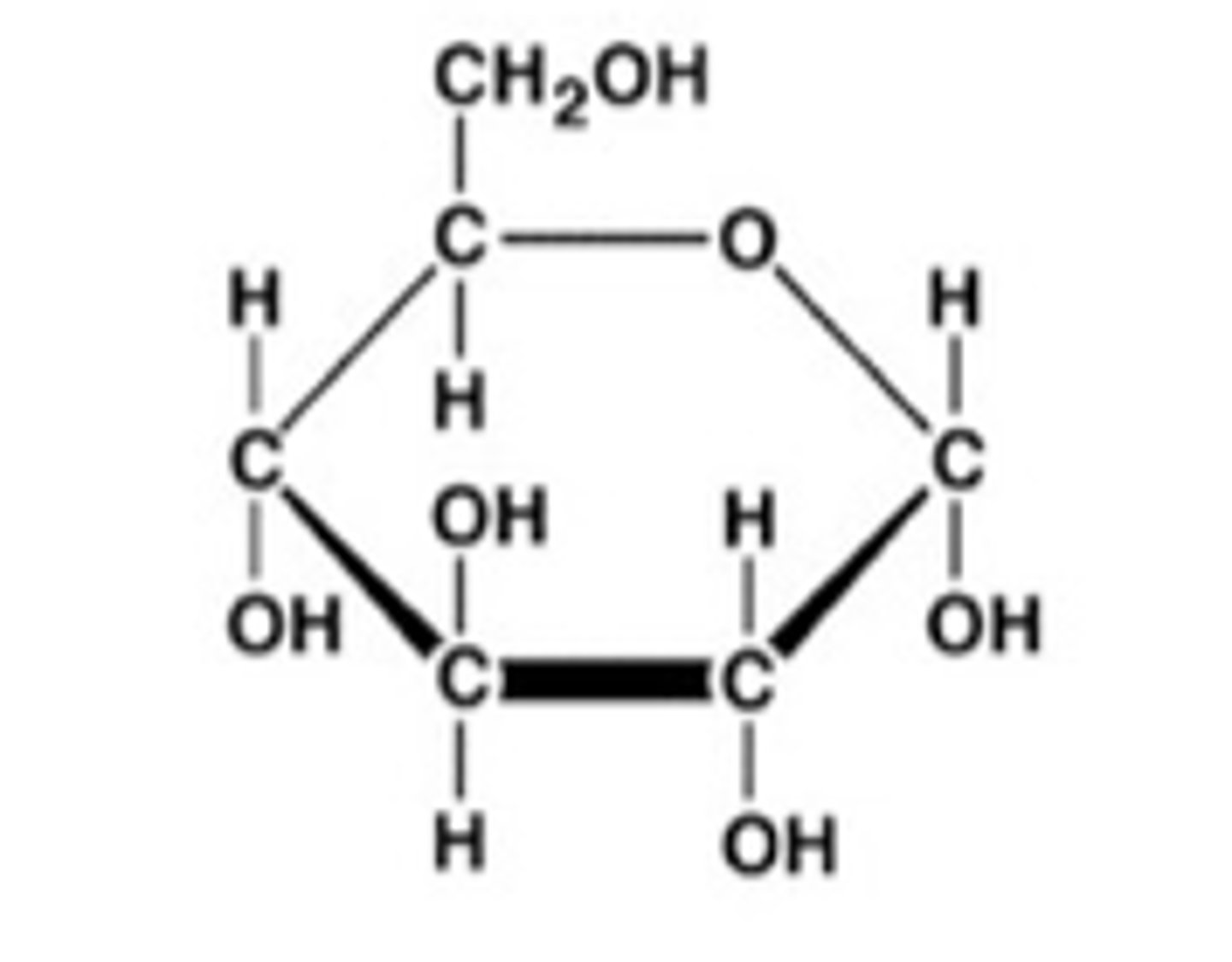
Ribose Molecule
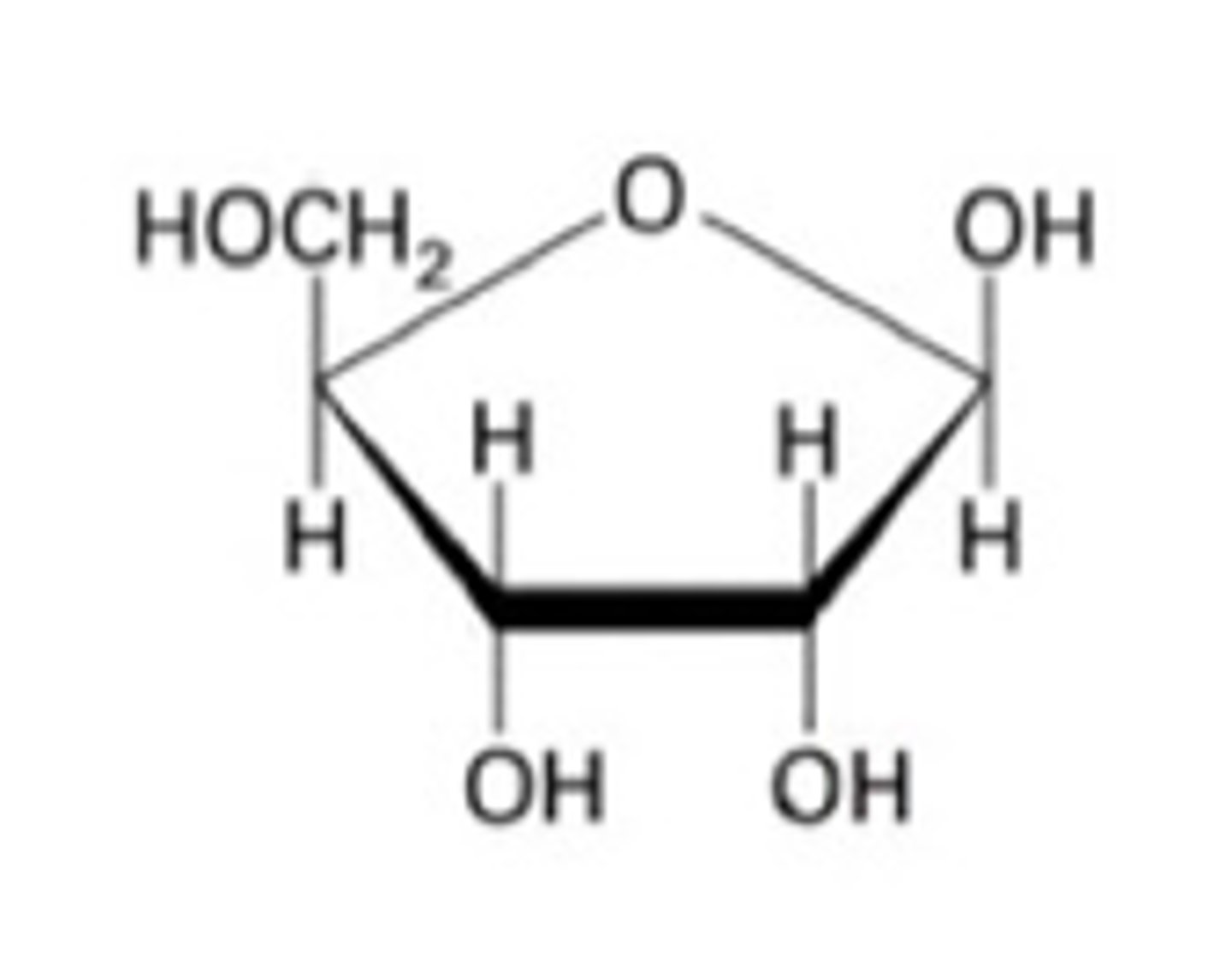
Amino Acid
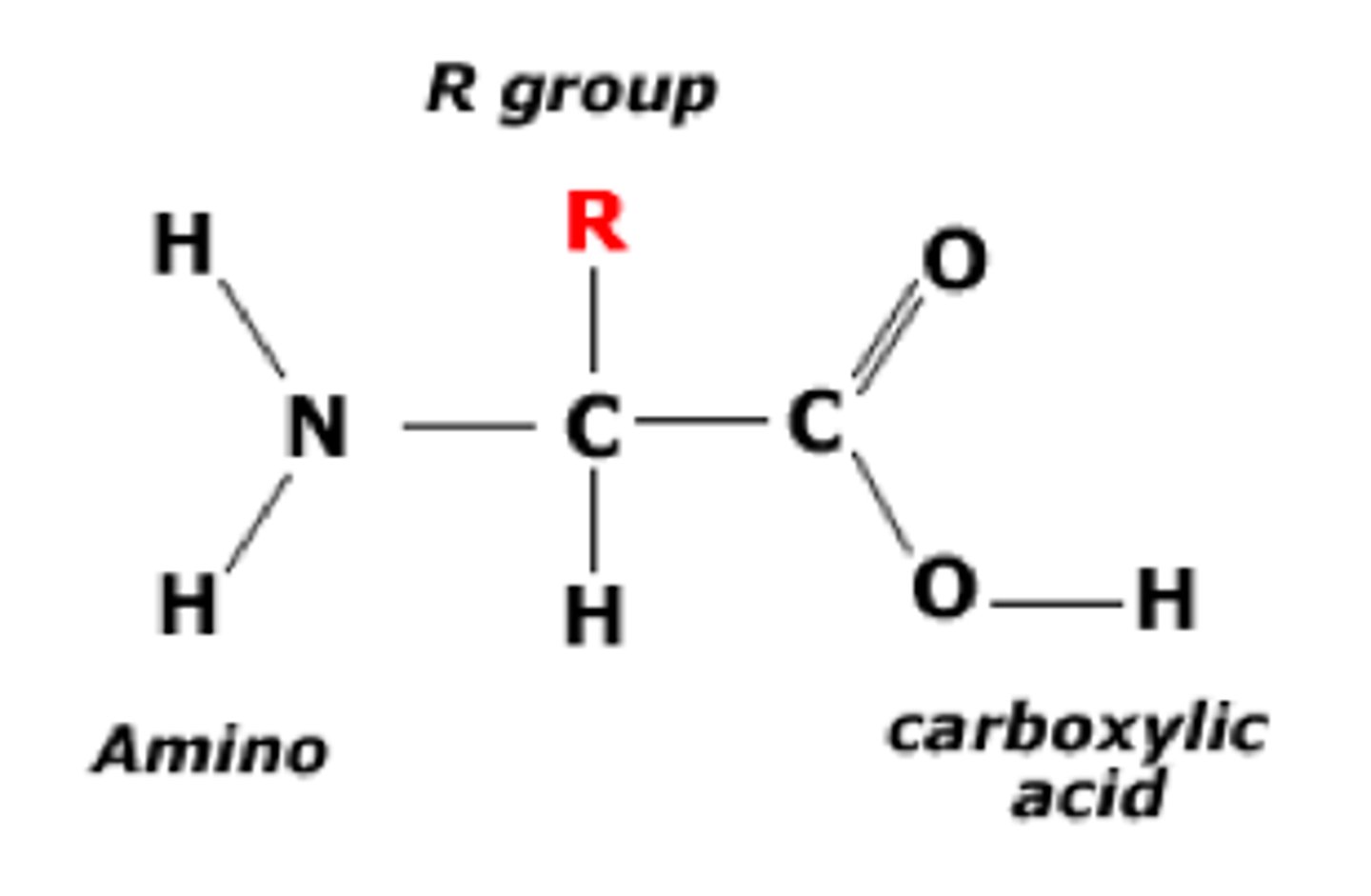
Fatty Acid
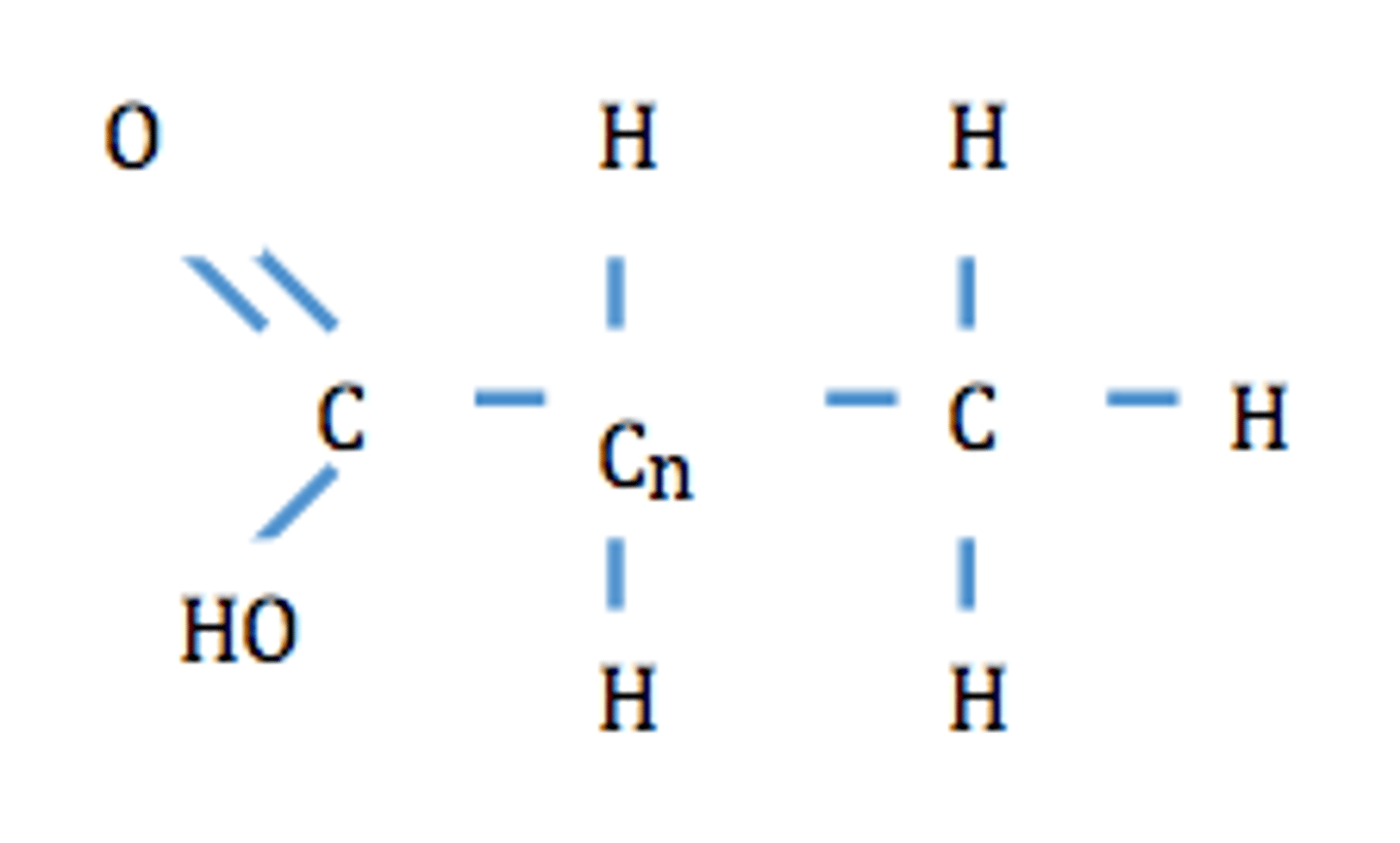
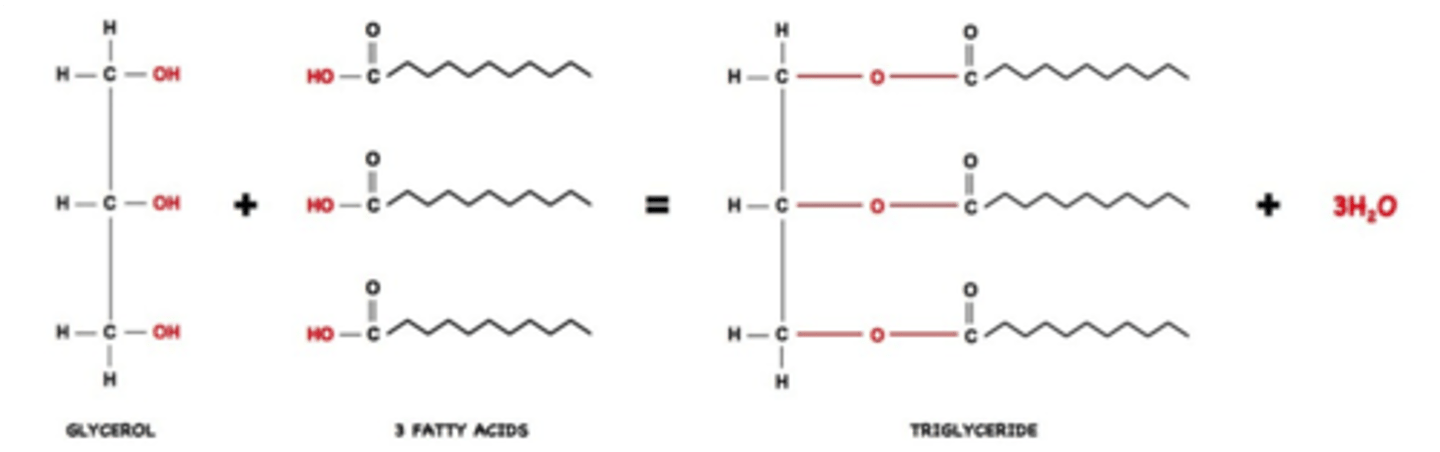
Glycerol
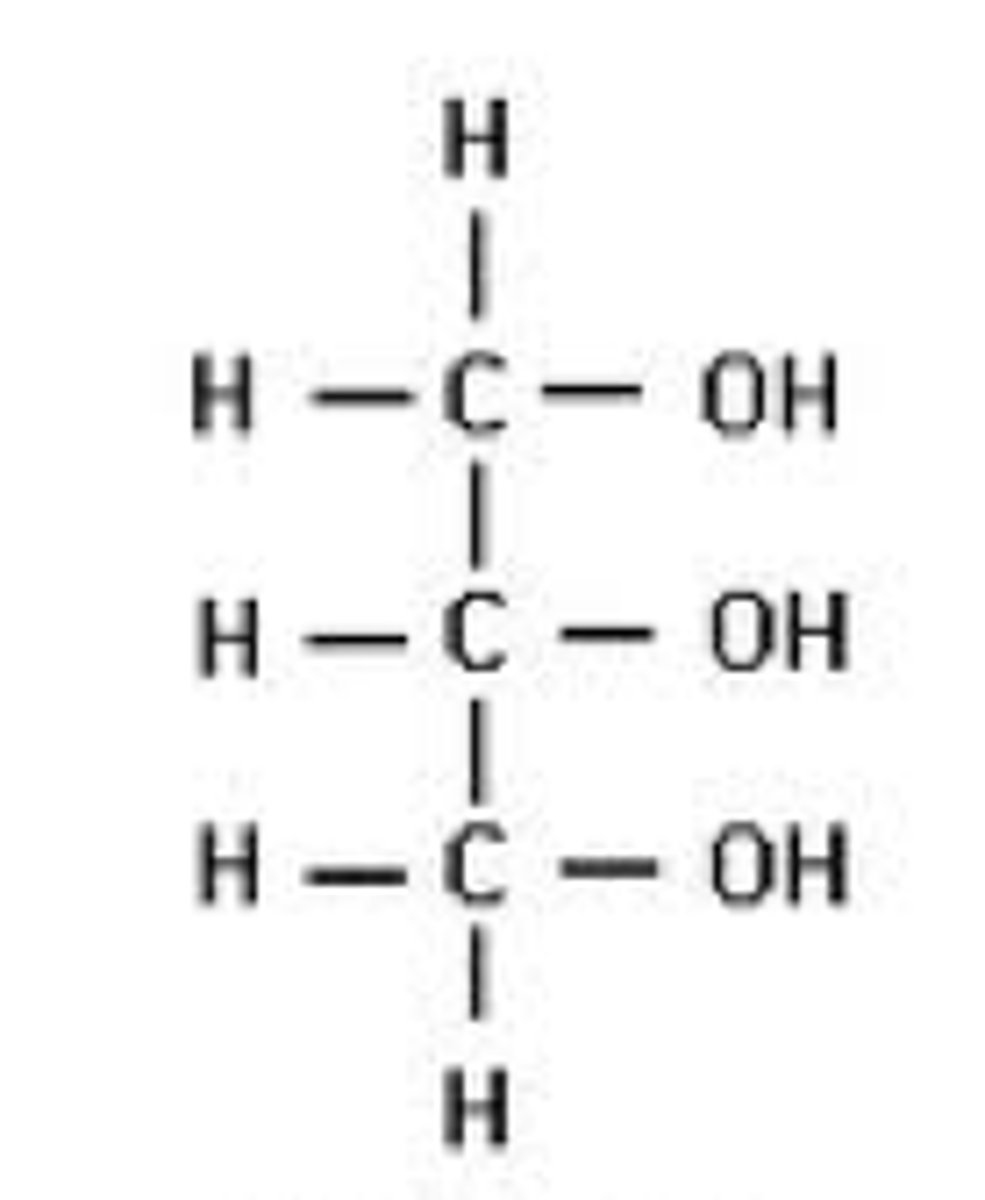
Condensation and Hydrolysis (Monosaccharides to Disaccharides)
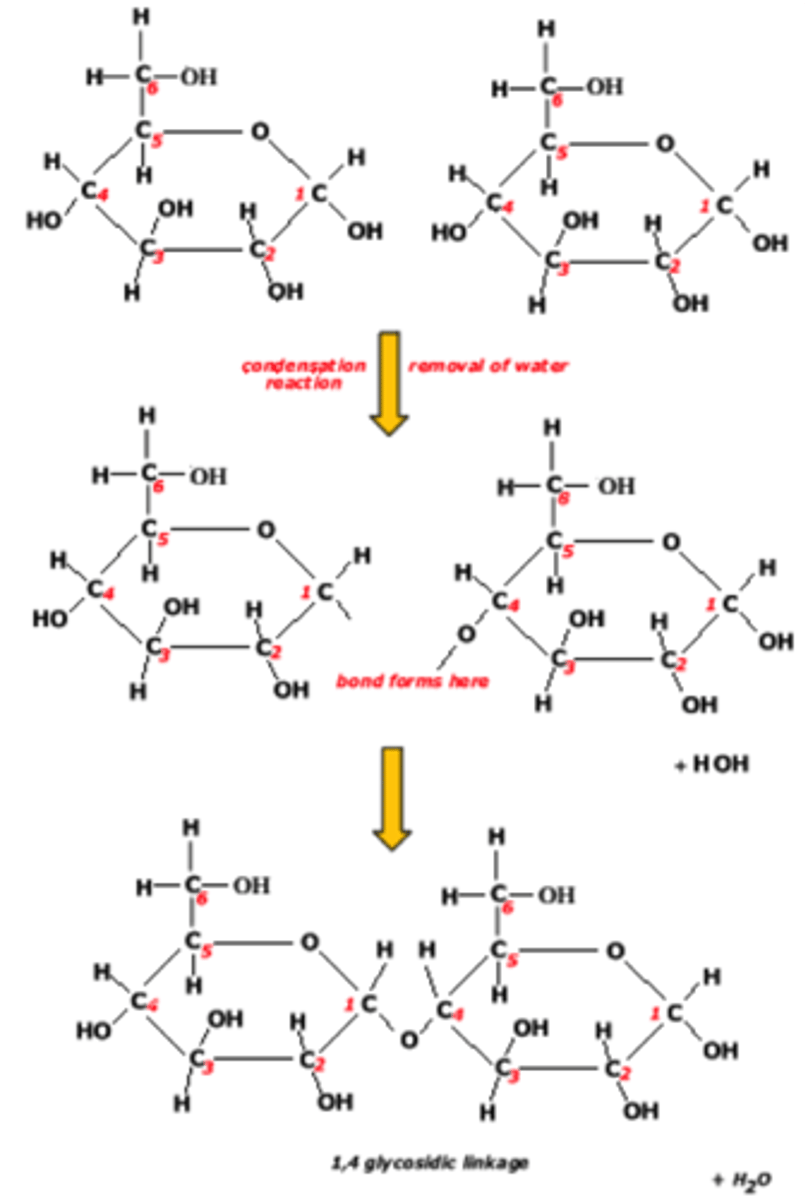
Condensation and Hydrolysis (Amino acids to Polypeptides)
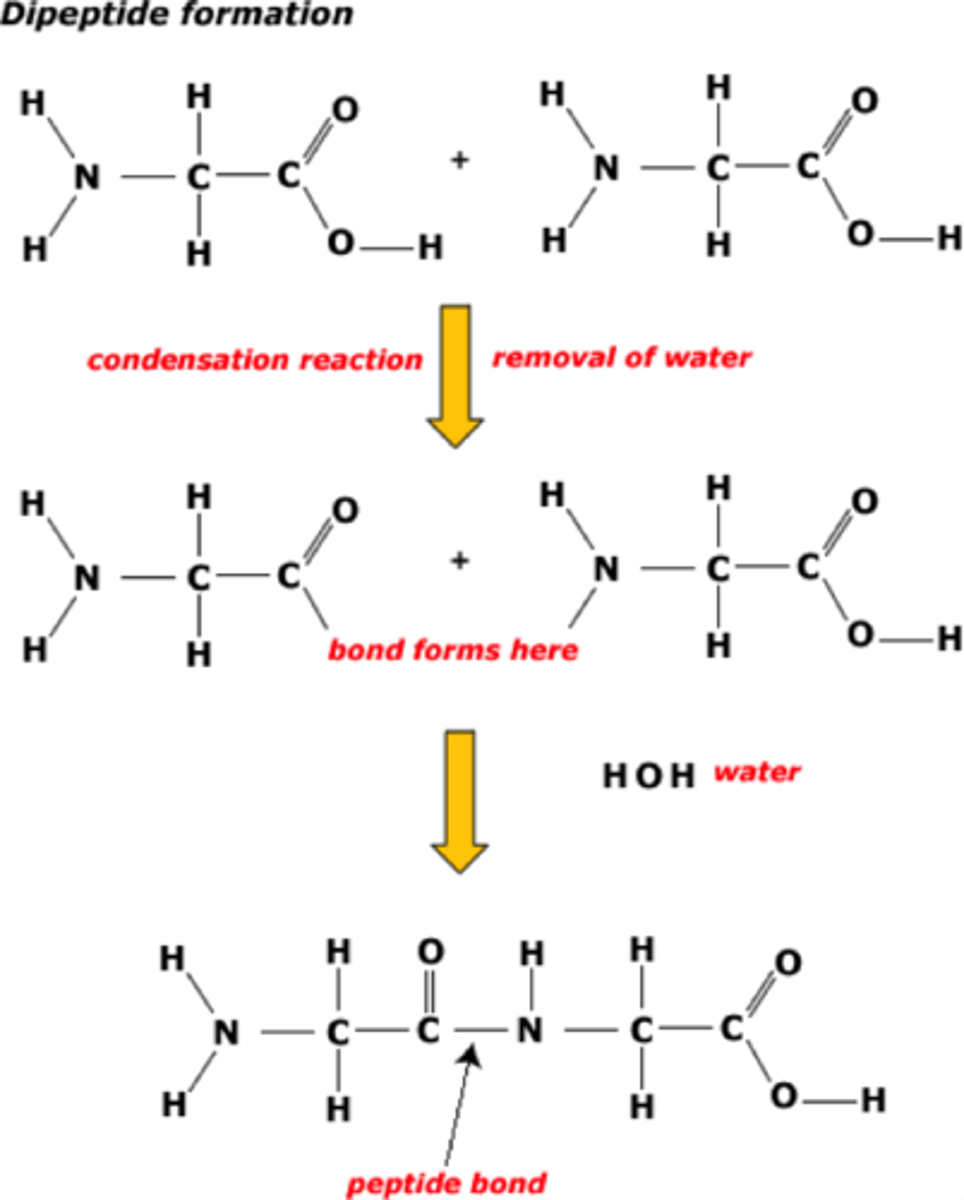
Condensation and Hydrolysis (Fatty Acids, Glycerol and Triglycerol)
Nucleotide Structure (sugar, base and phosphate)
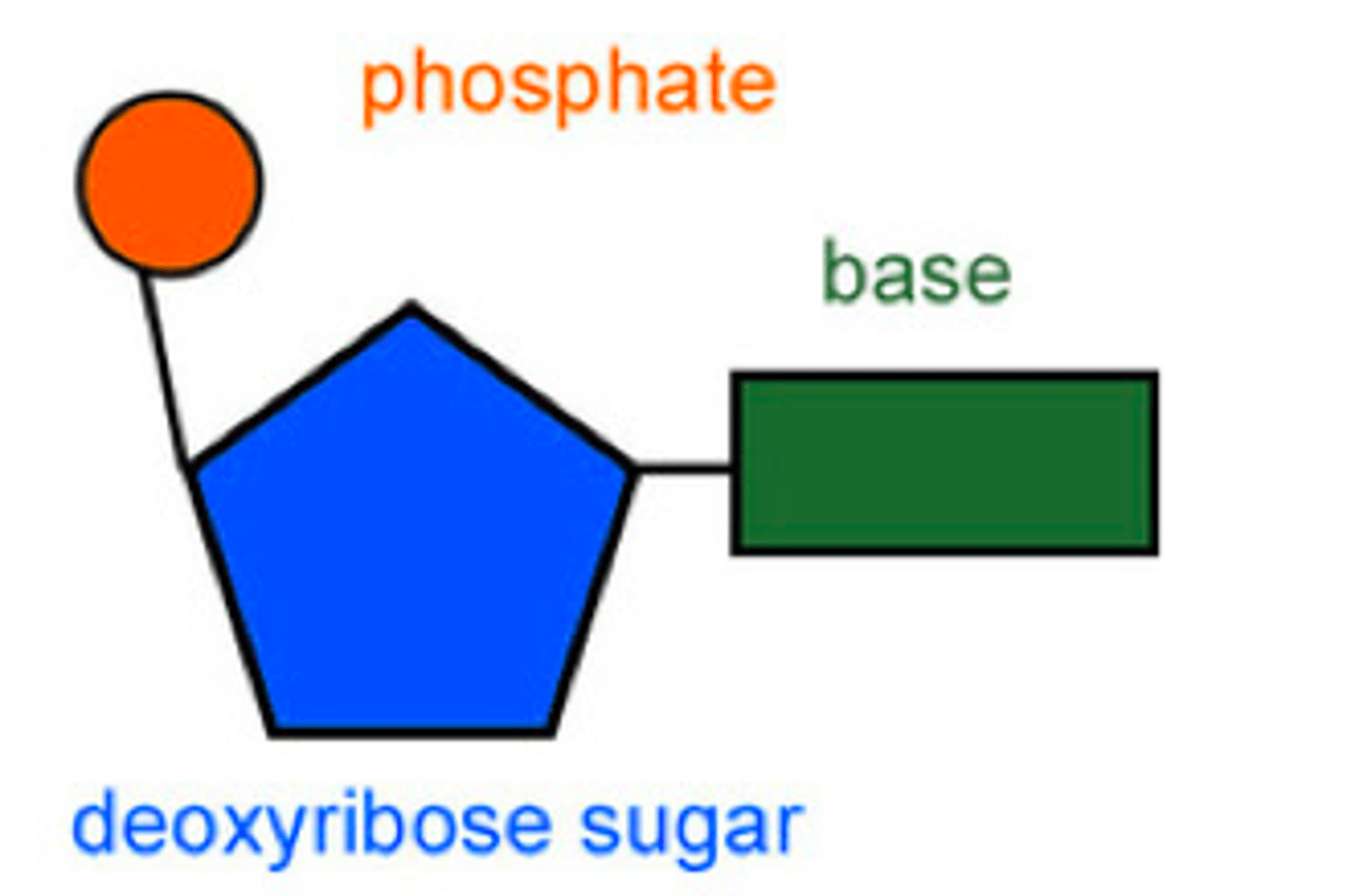
Linking of DNA Nucleotides with Covalent (phosphodiester) Bonds
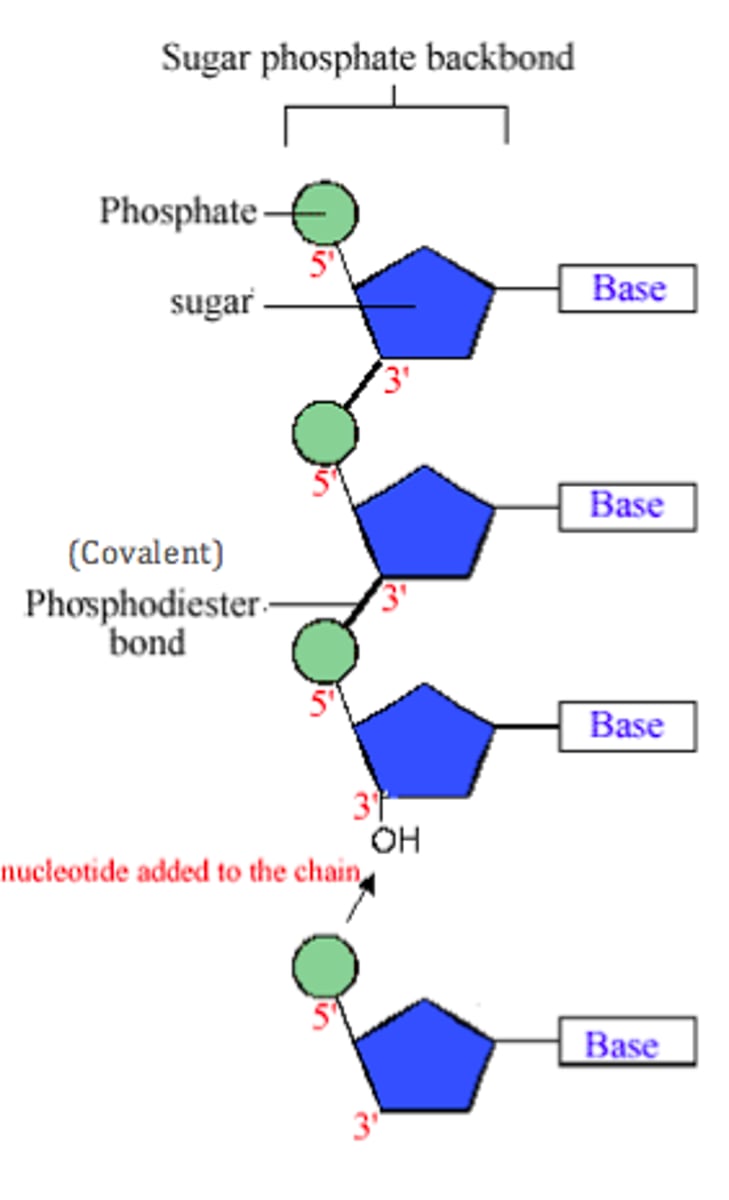
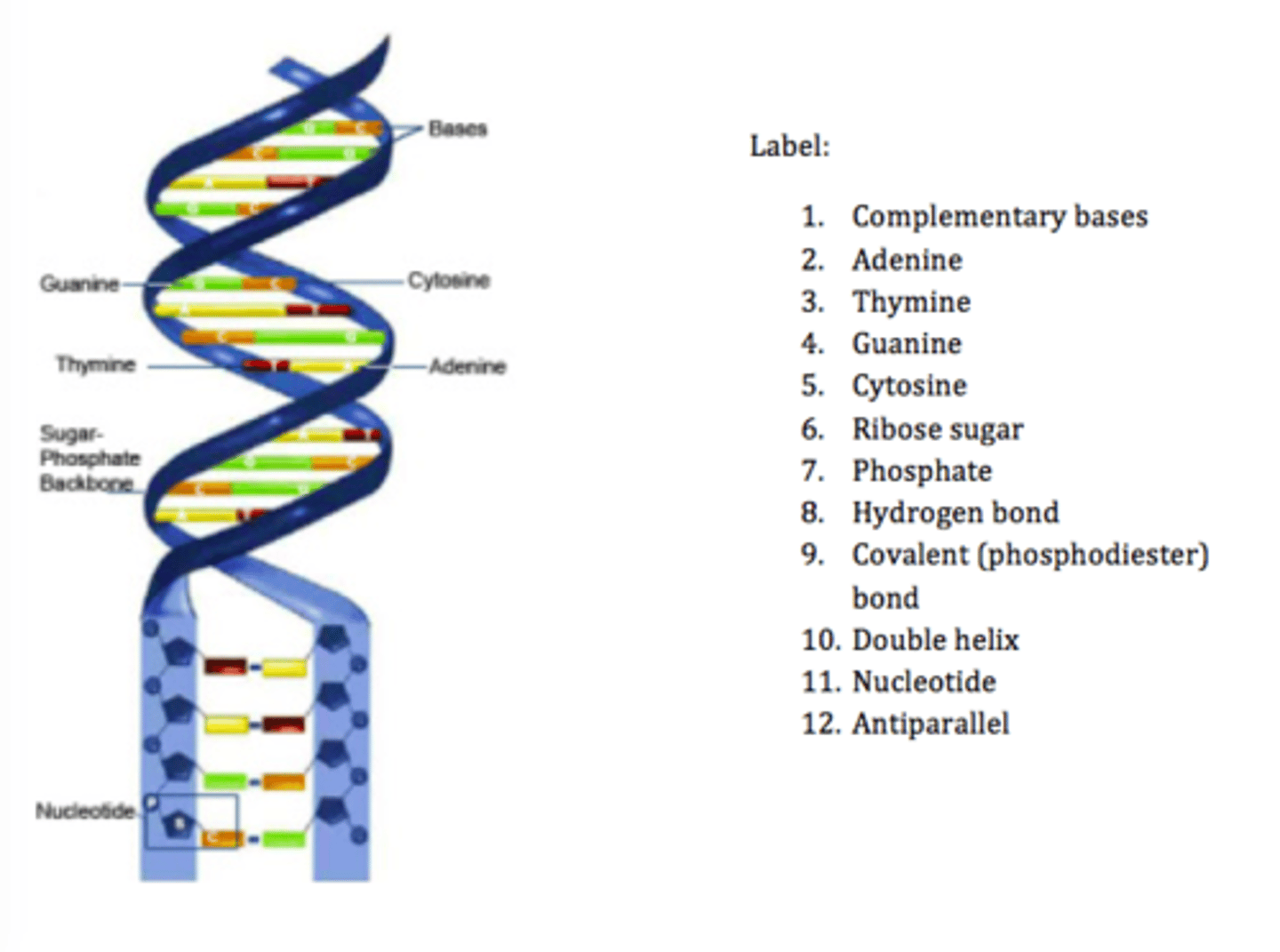
Molecular Structure of DNA (double helix)
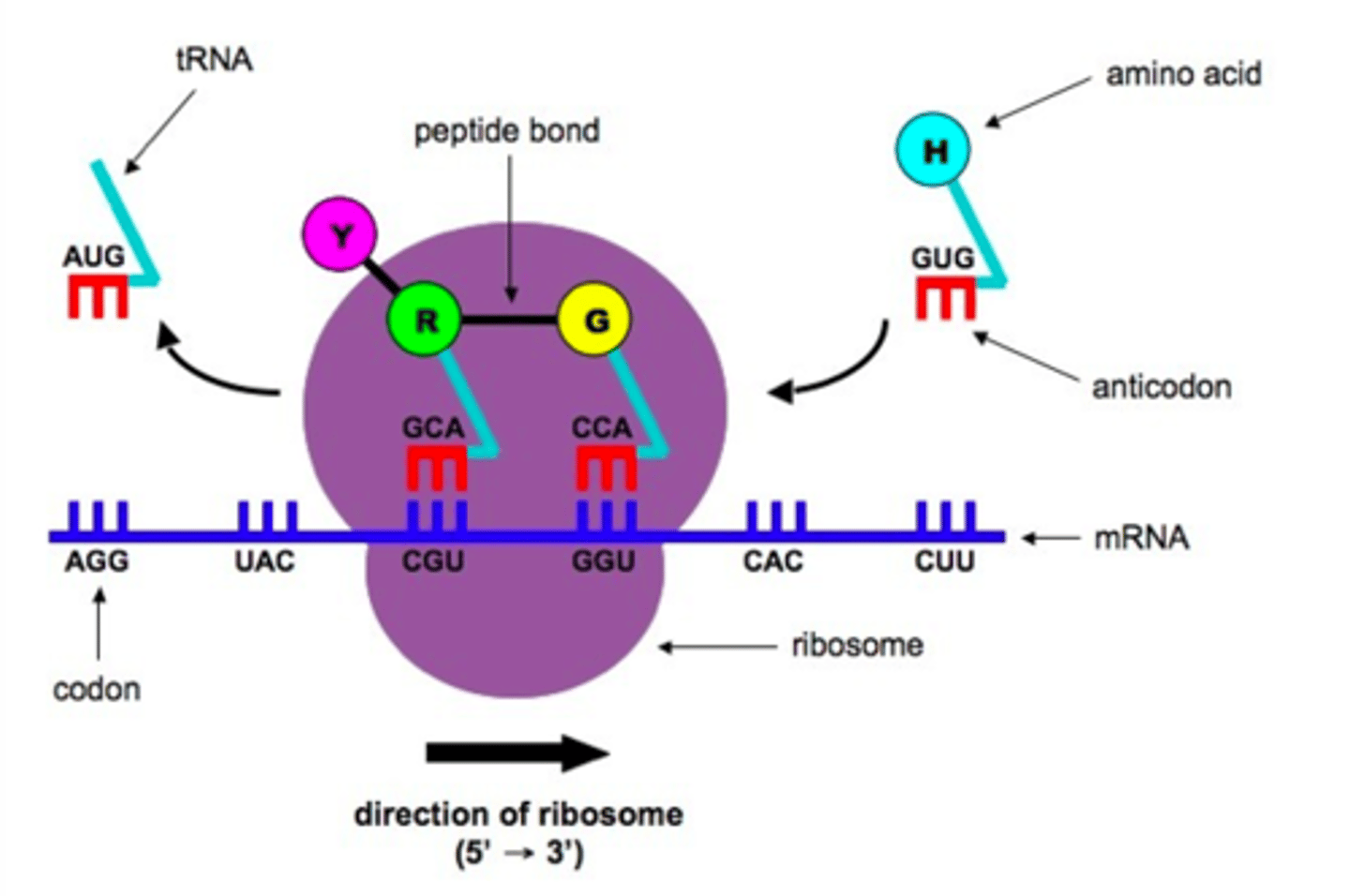
Process of Translation
Effects of Temperature on Enzyme Activity
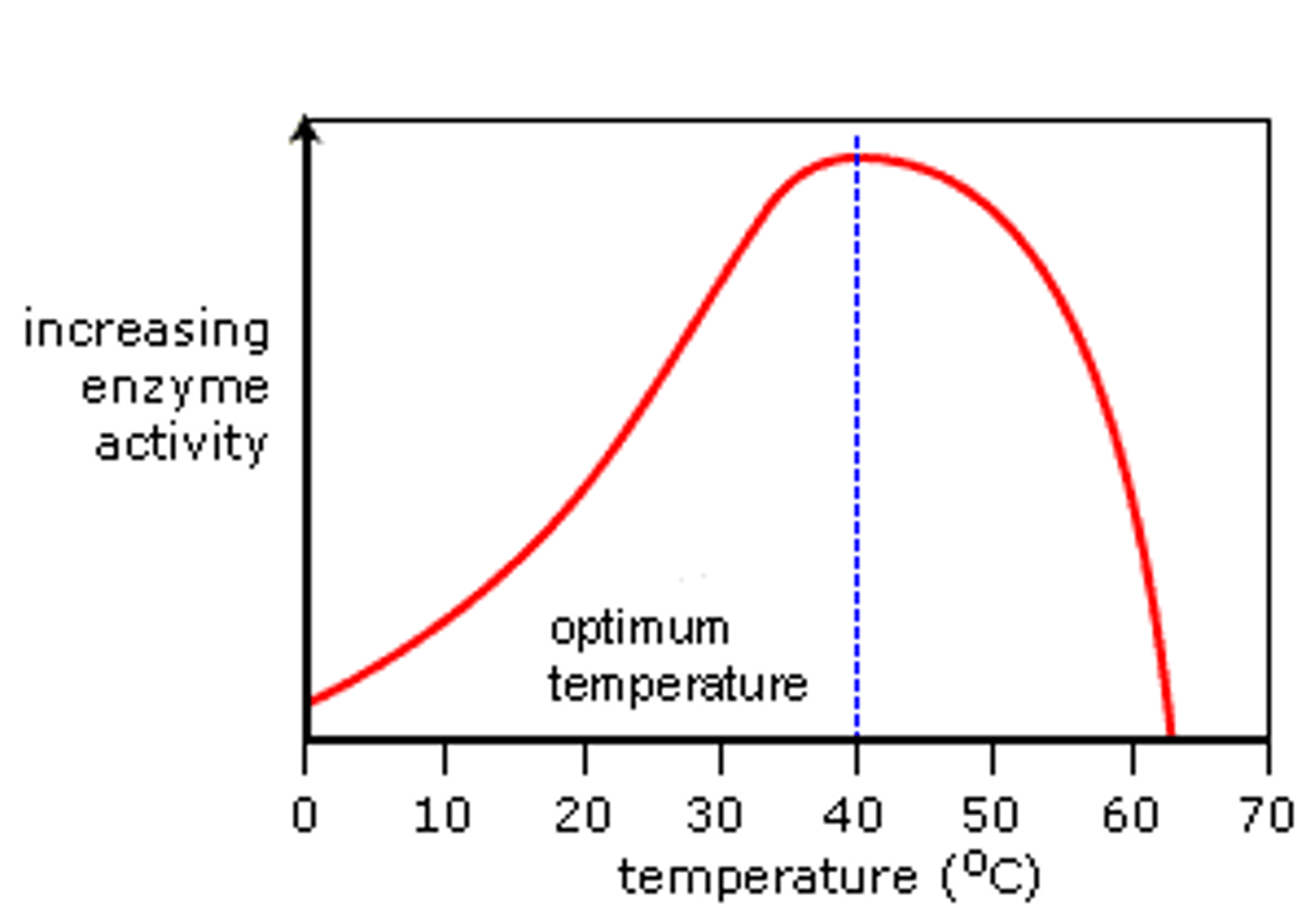
Effects of pH on Enzyme Activity
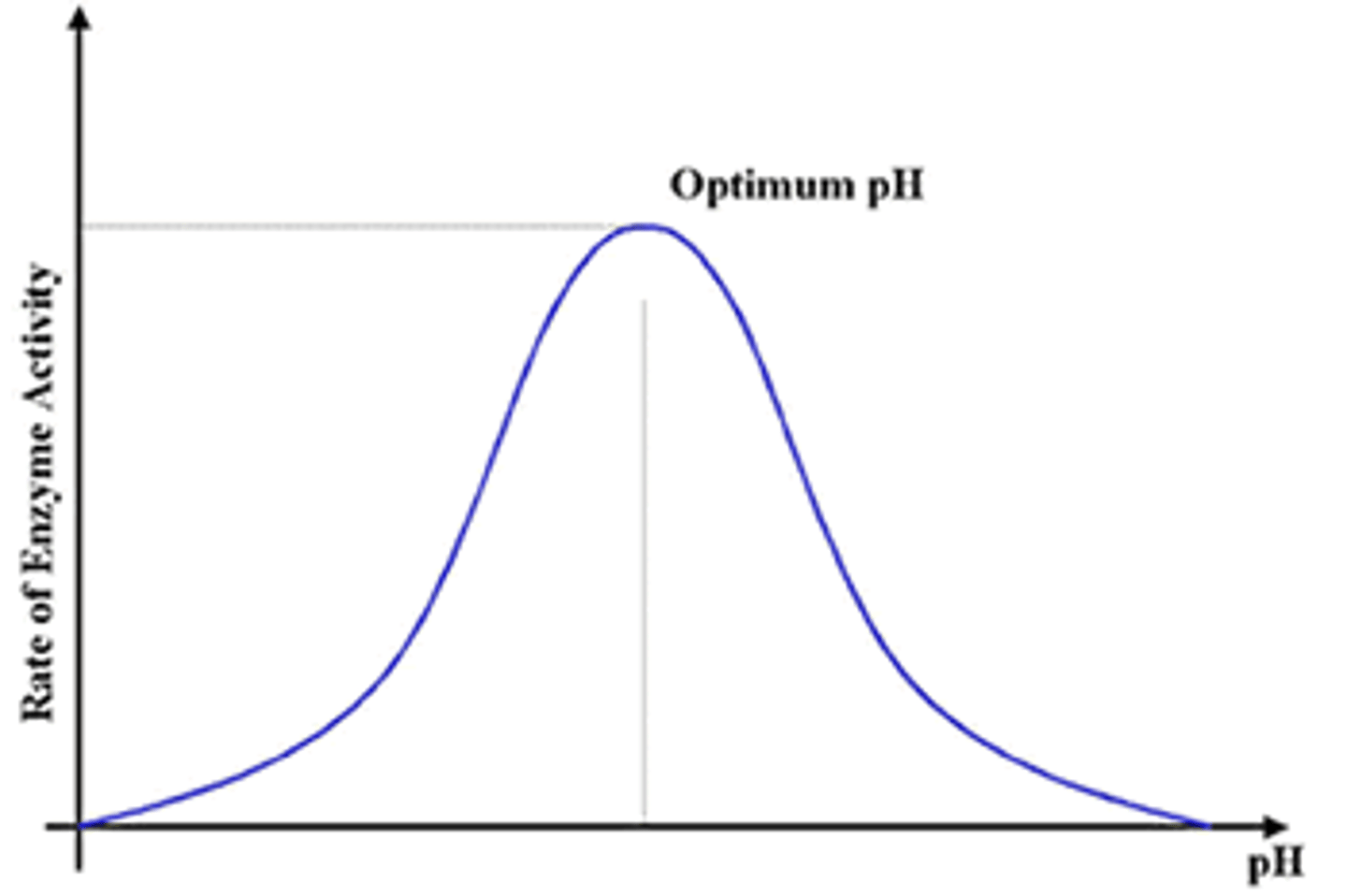
Effects of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity
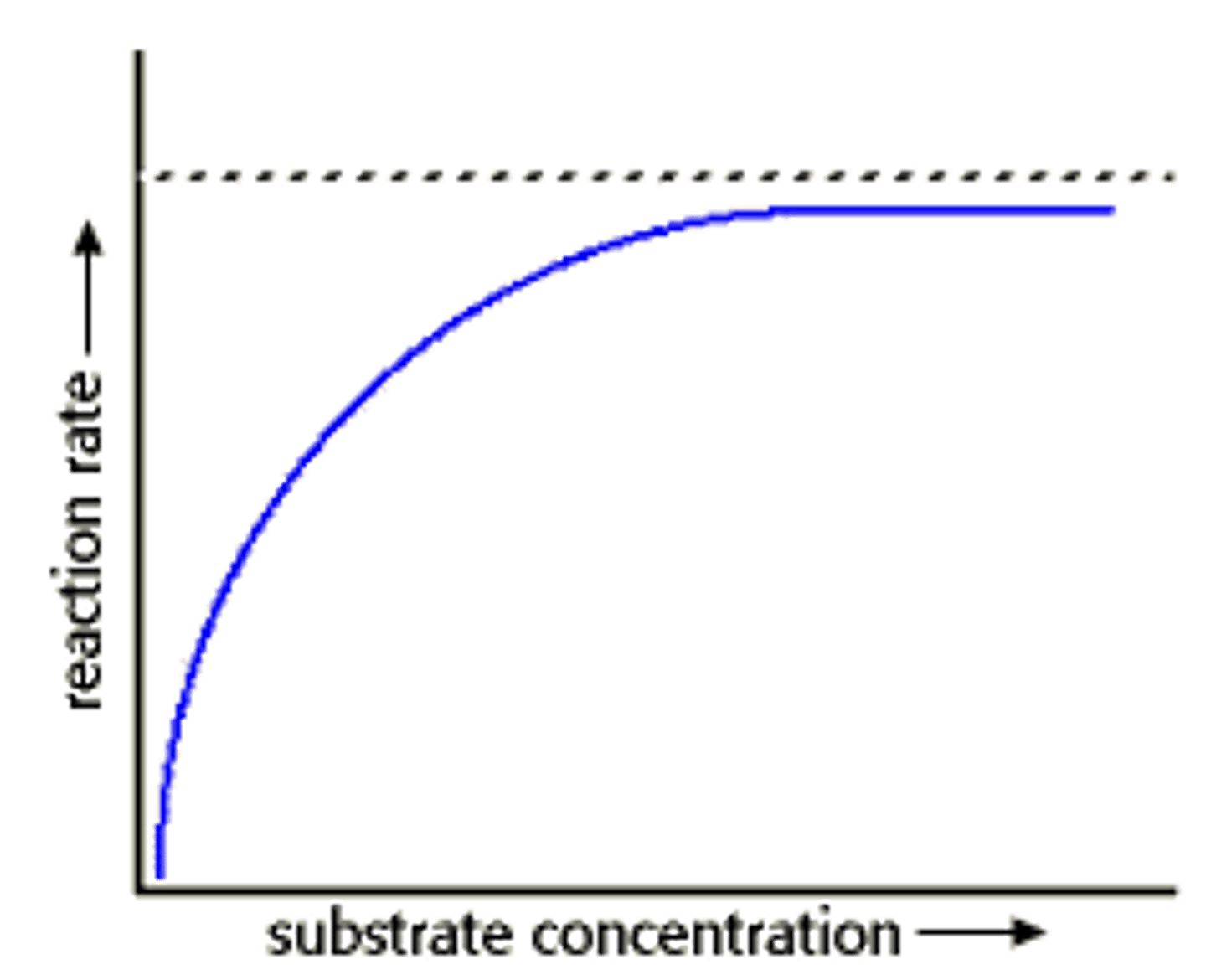
Production of Lactose-Free Milk
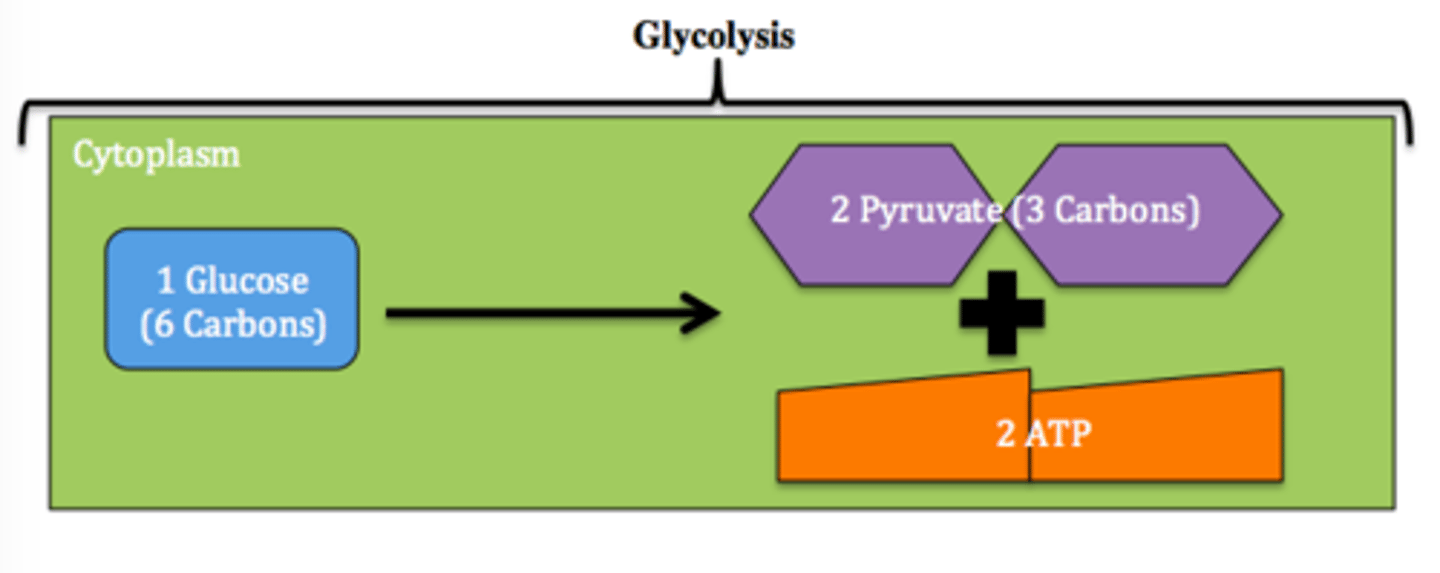
Glycolysis
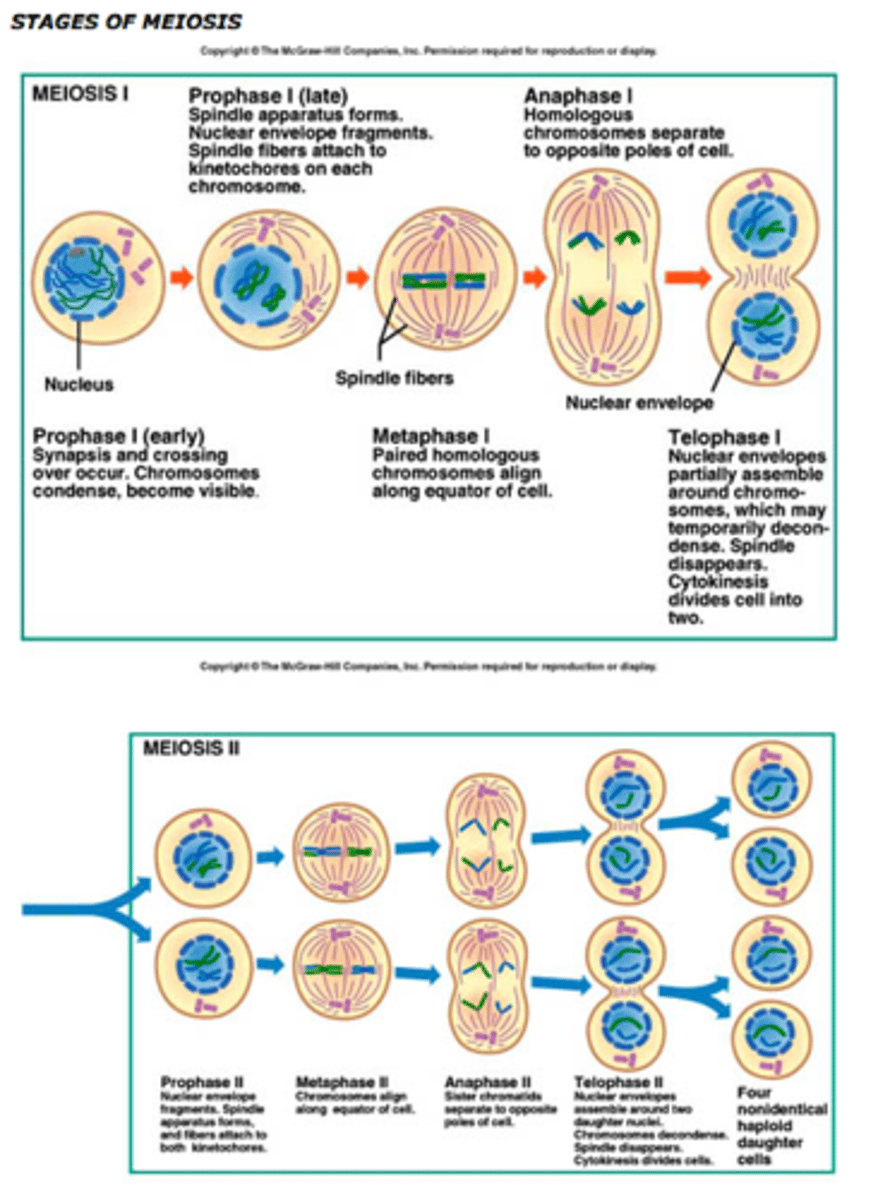
Process of Meiosis
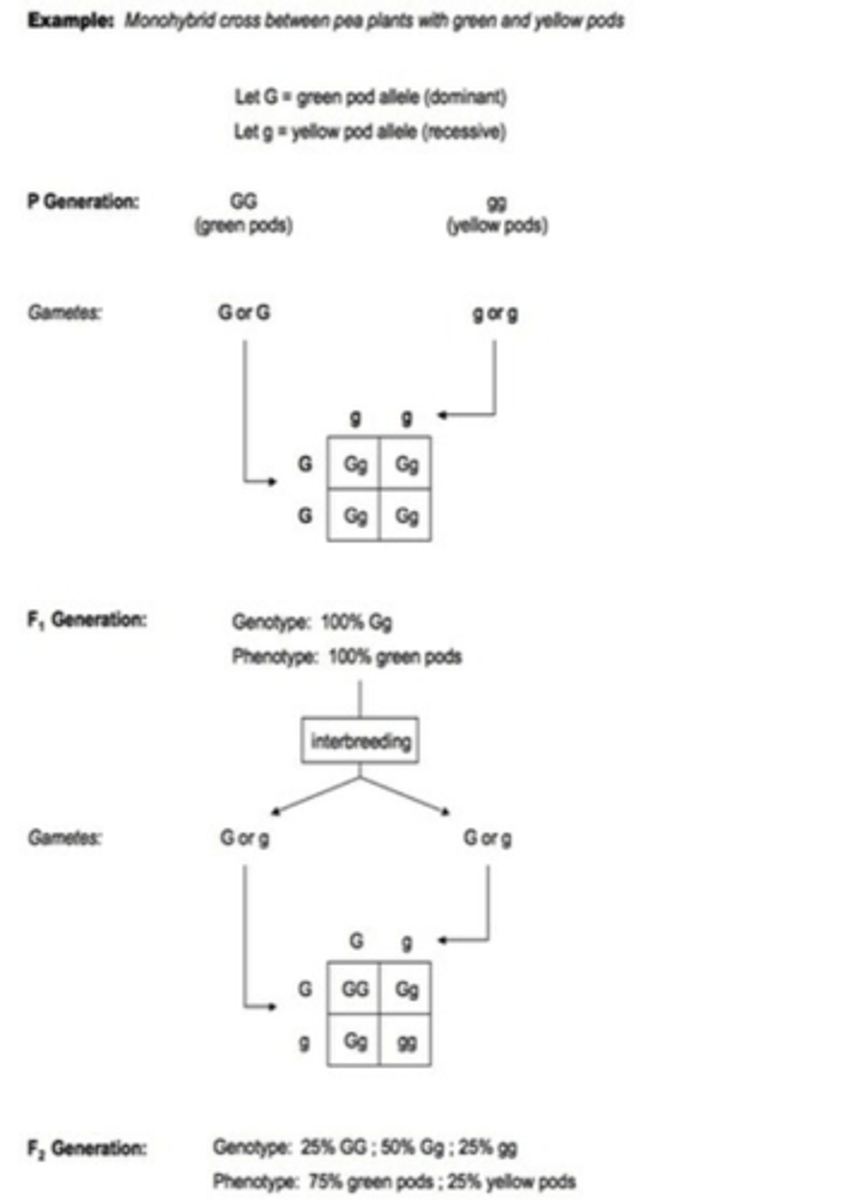
Monohybrid Cross
Gene Transfer
...
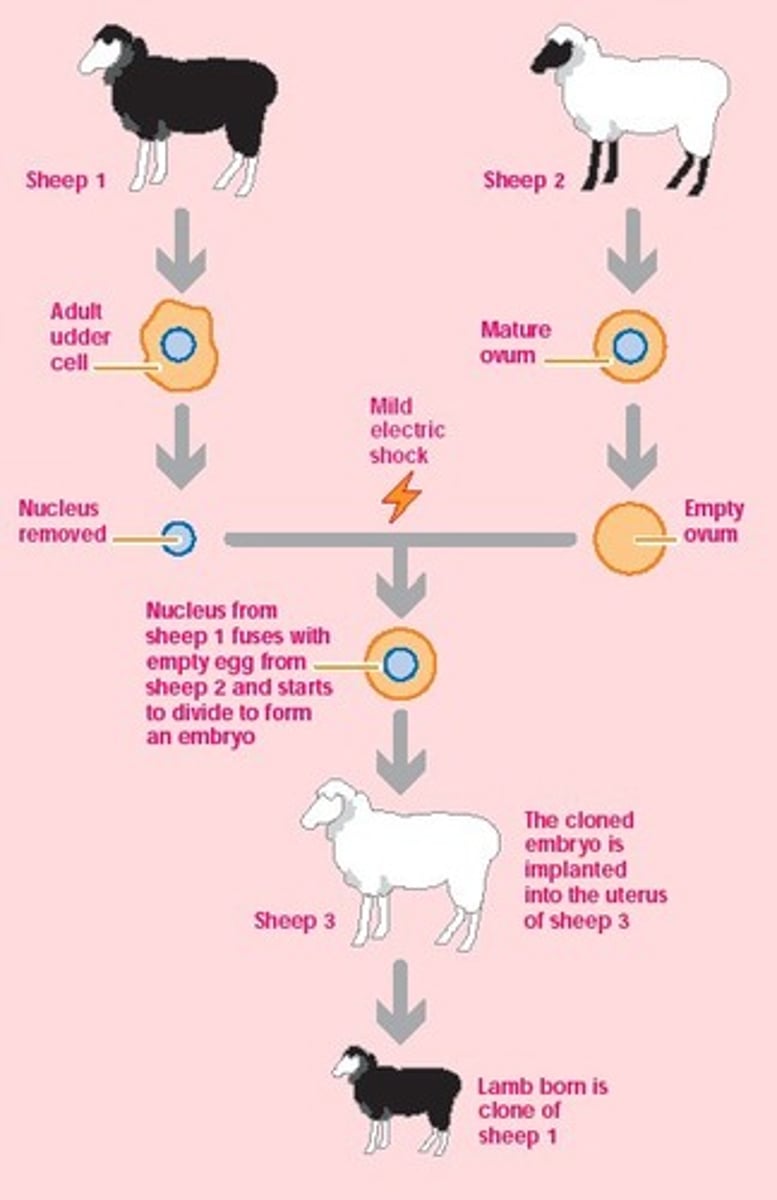
Somatic Nuclear Transfer-Cloning (enucleation, somatic cells)
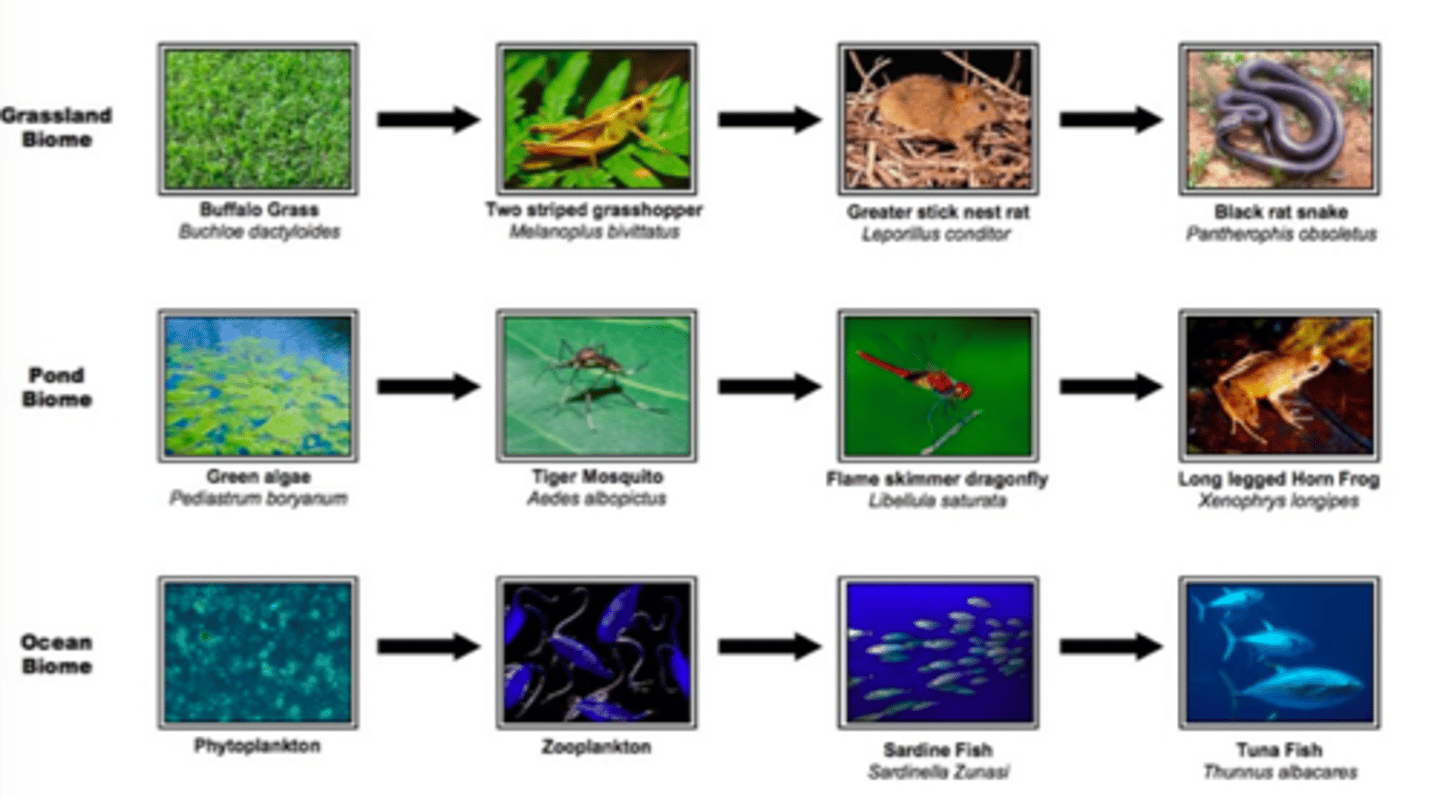
3 Examples of a Food Chain
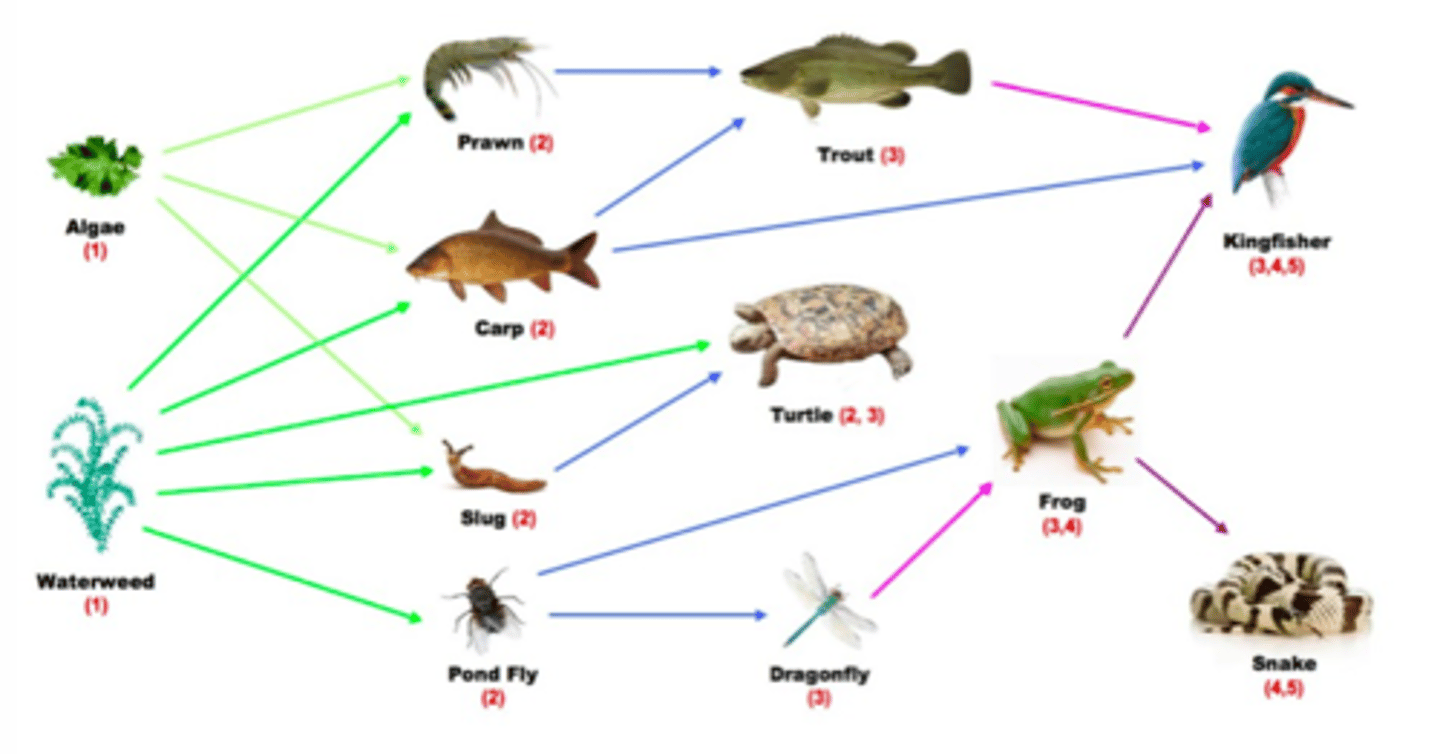
Food Web
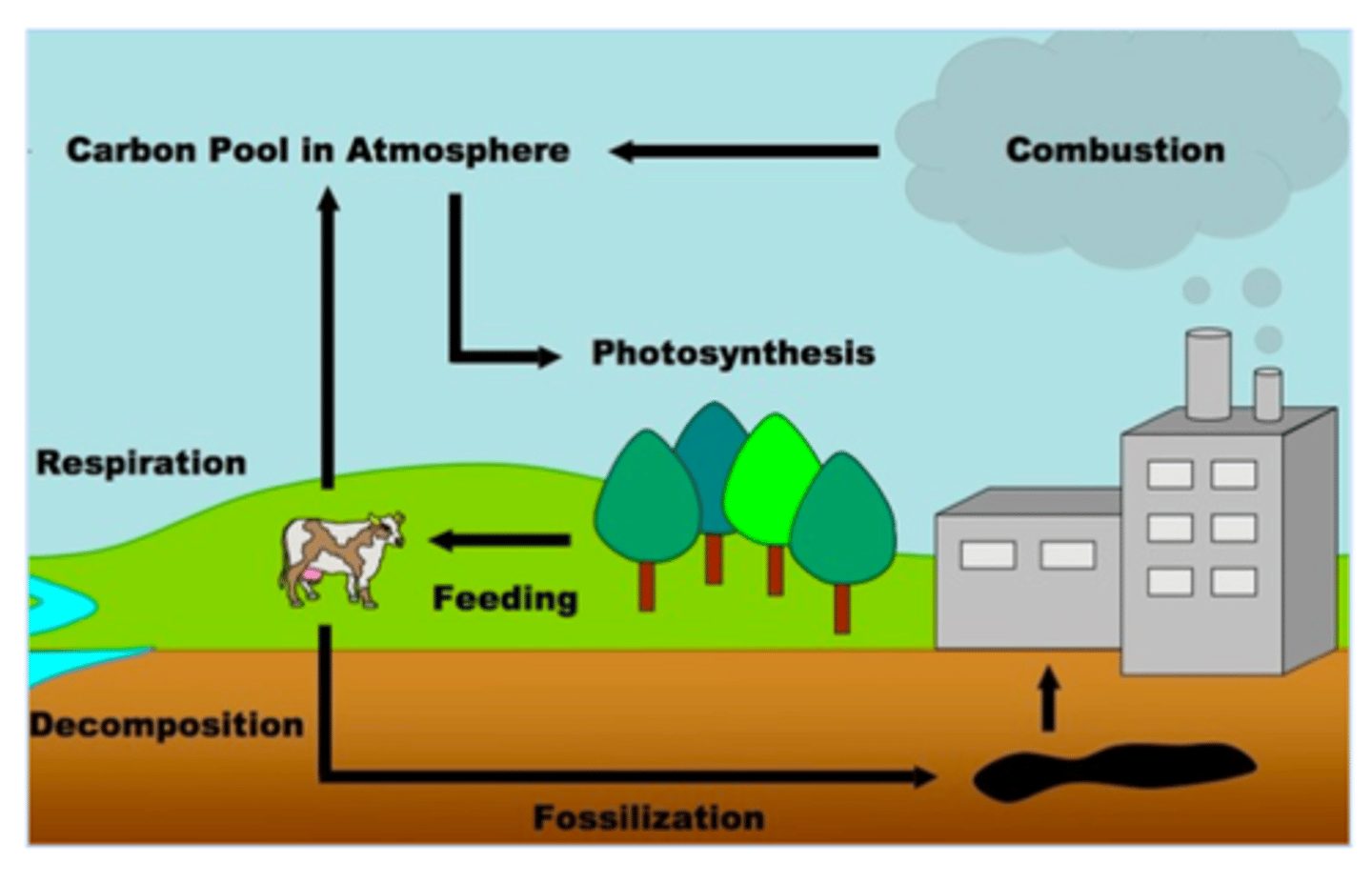
Carbon Cycle
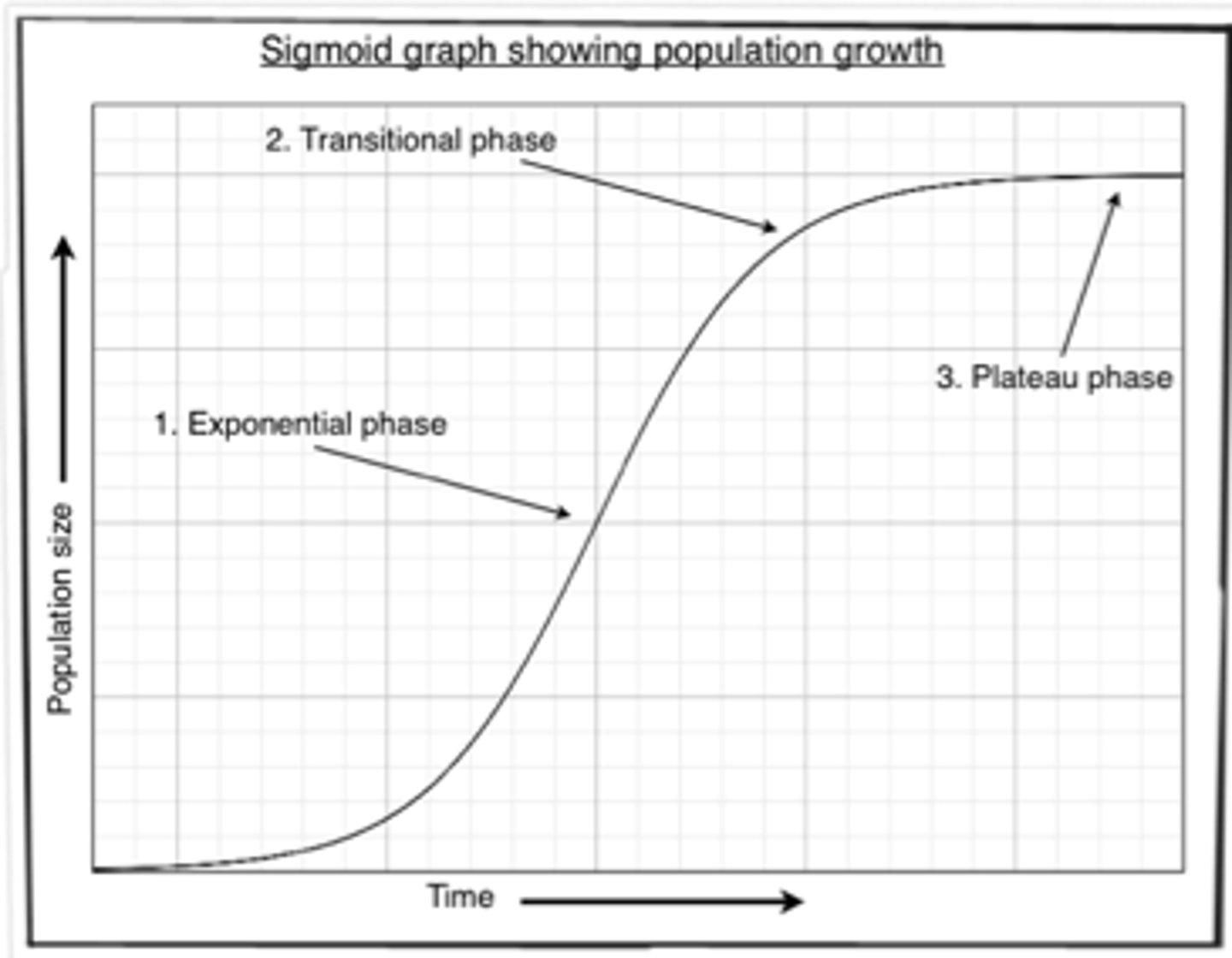
Sigmoid Population Growth Curve
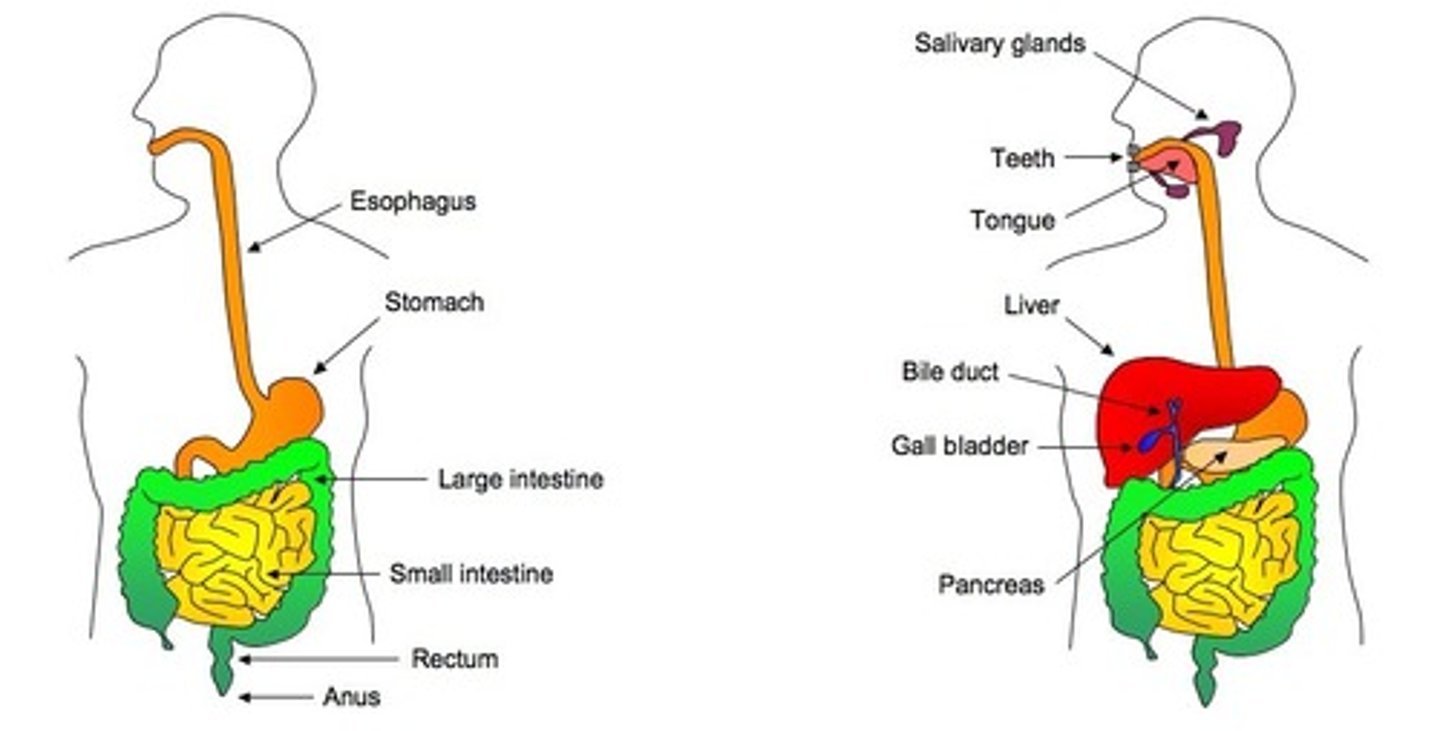
Human Digestive System
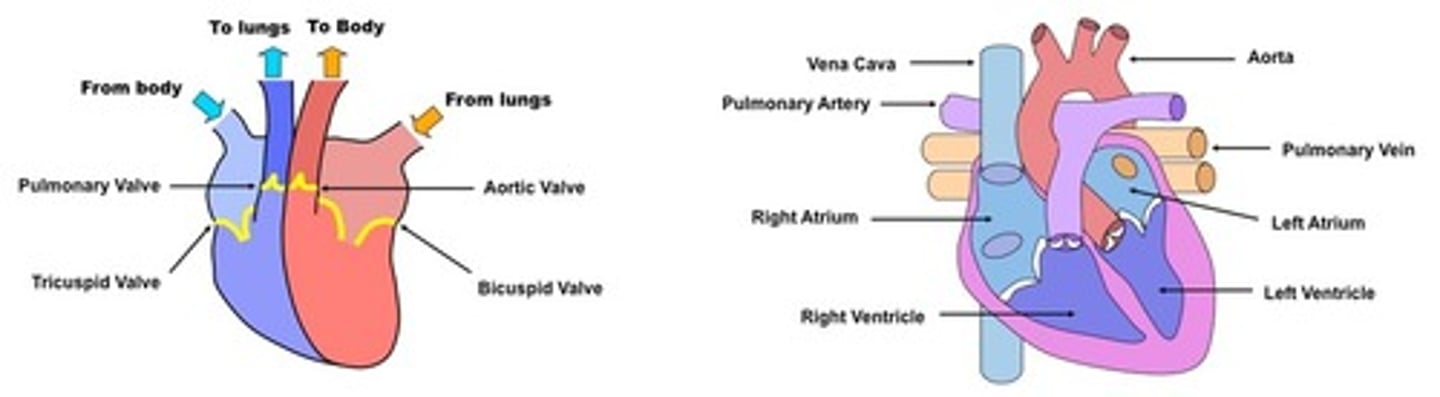
Heart
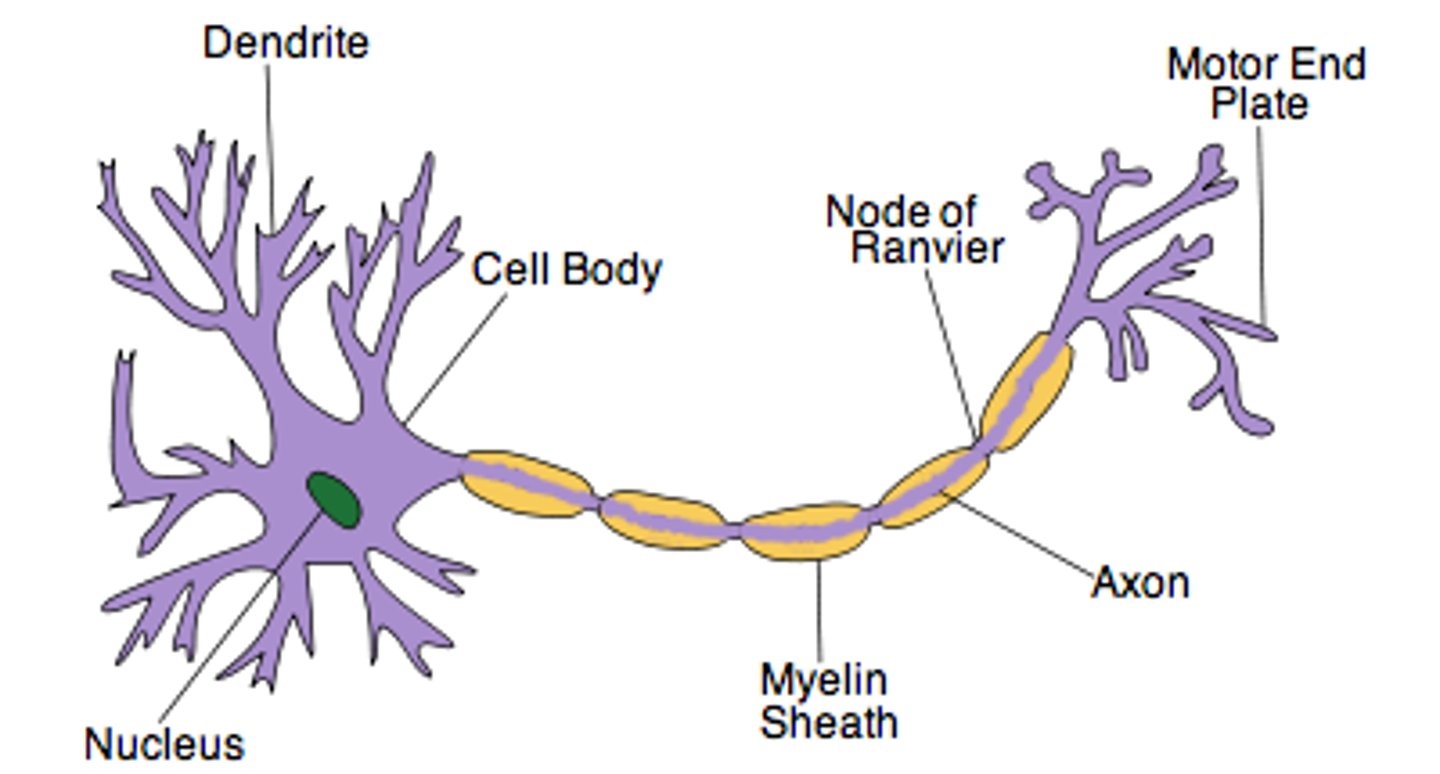
Motor Neuron
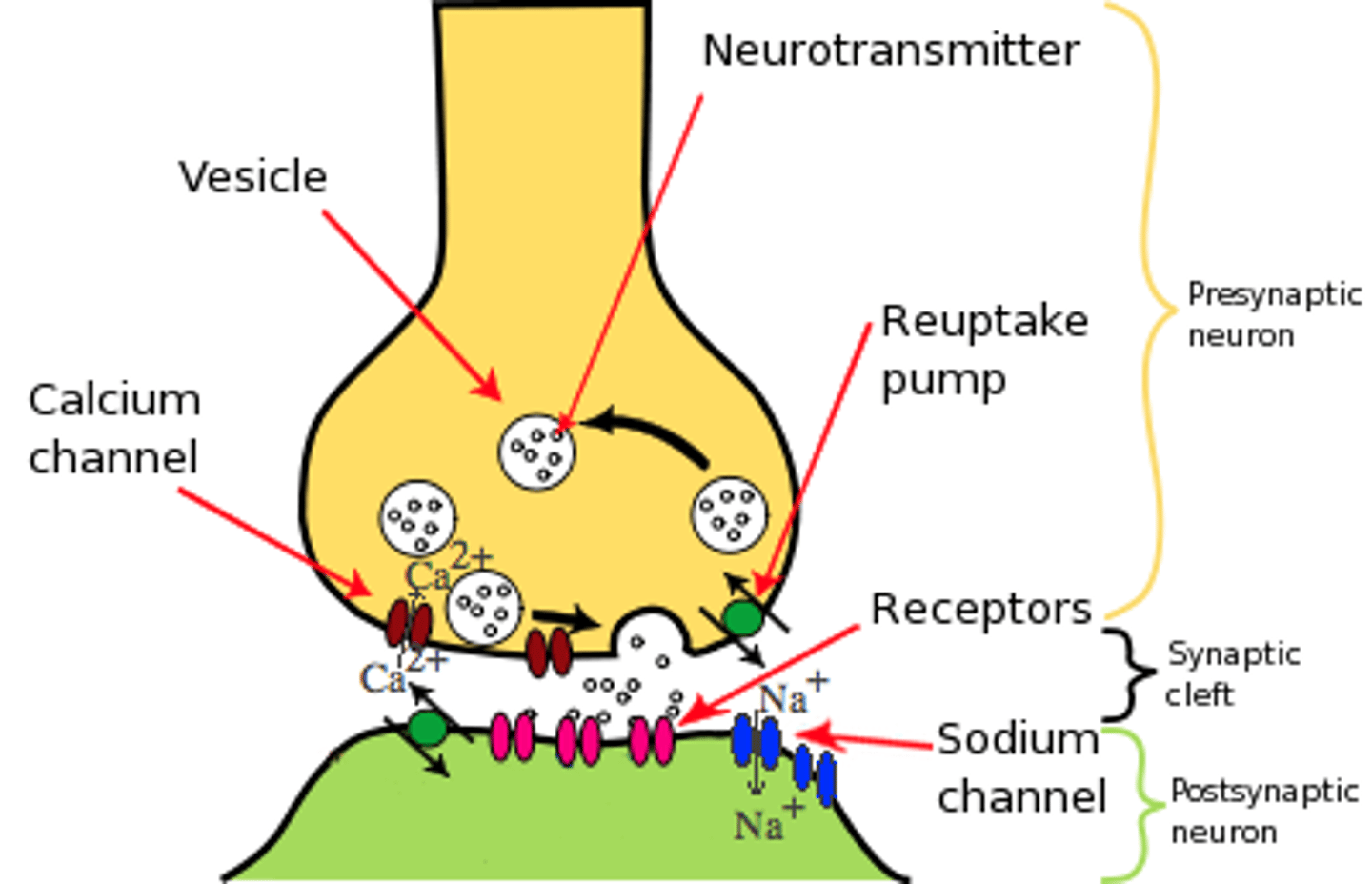
Synaptic Transmission
Prokaryote Cell
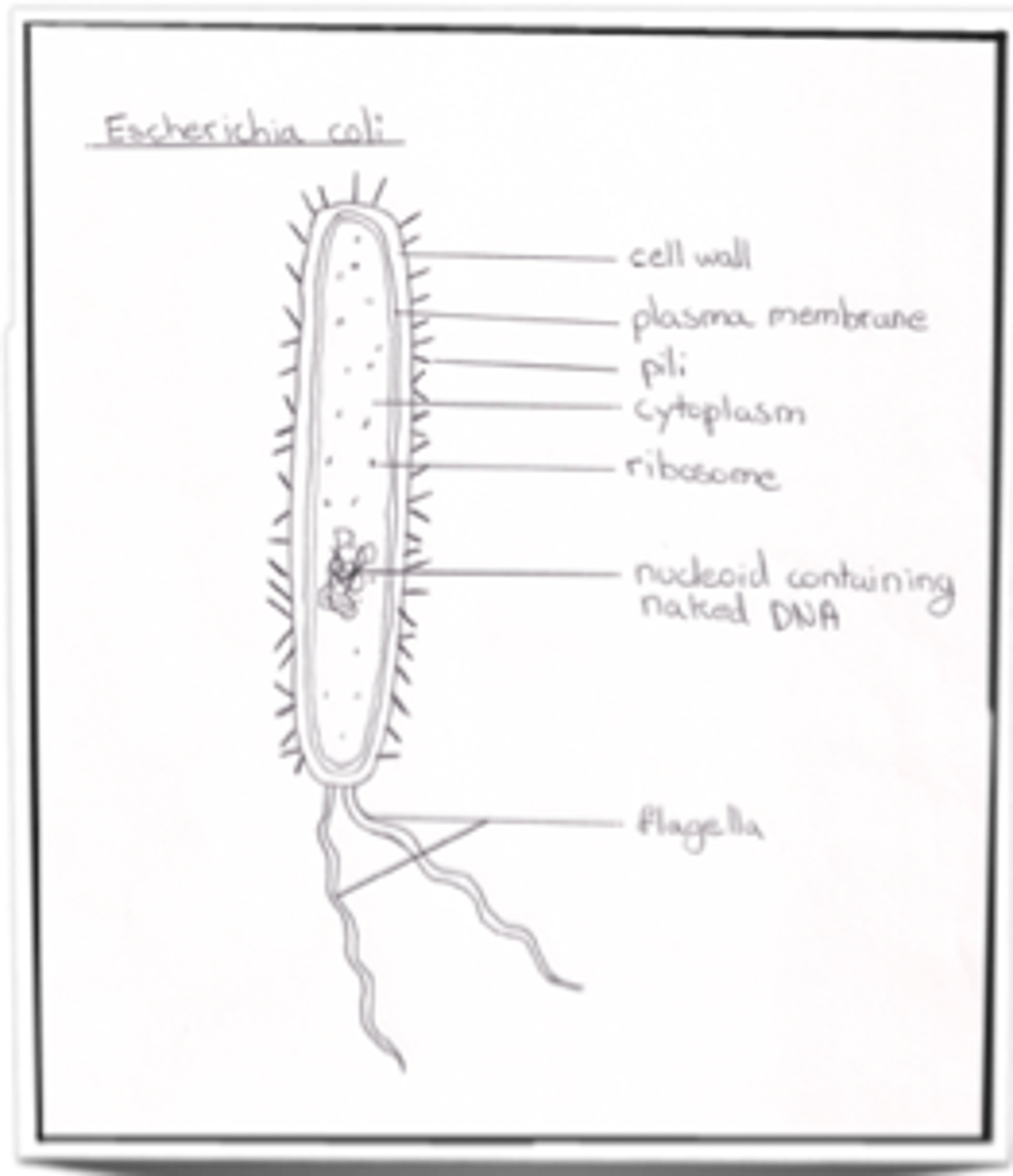
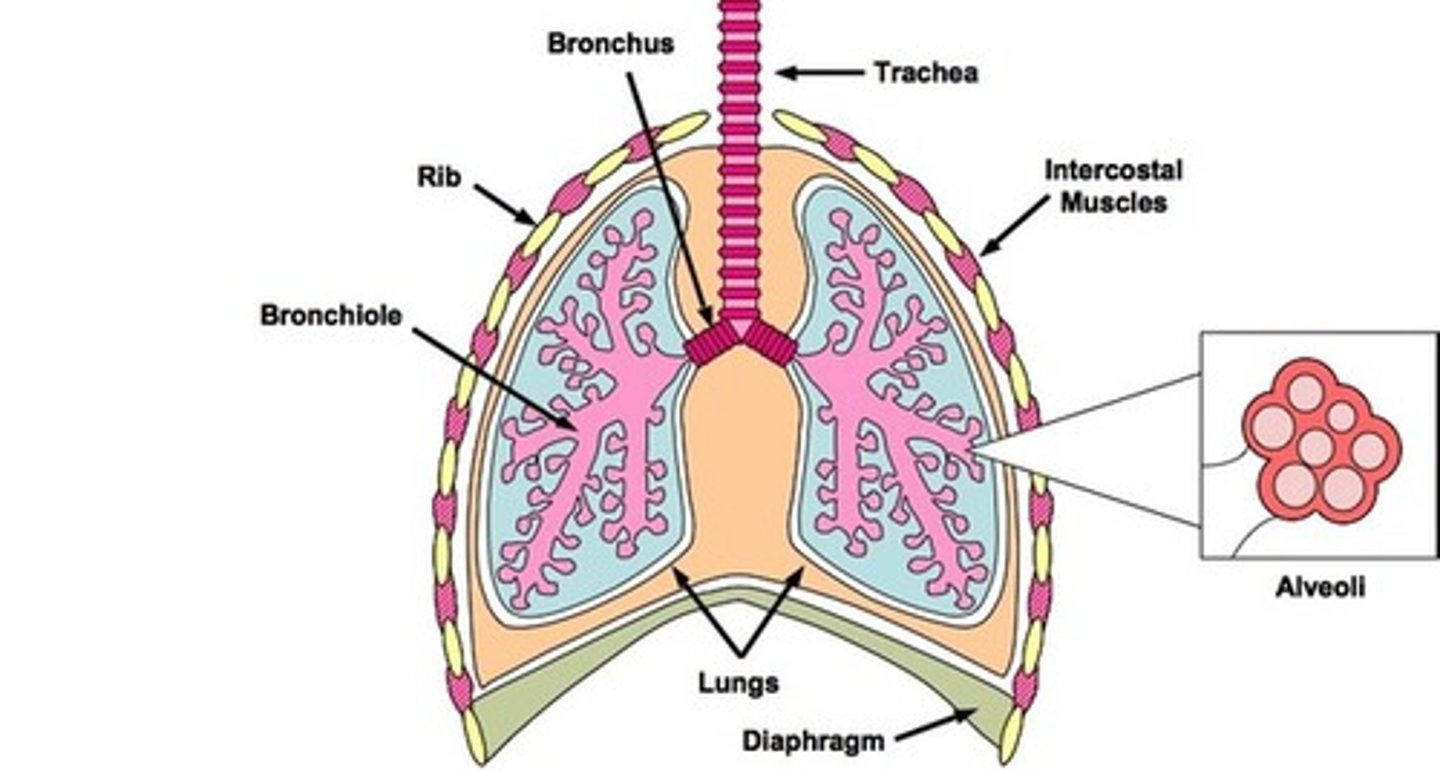
Lungs
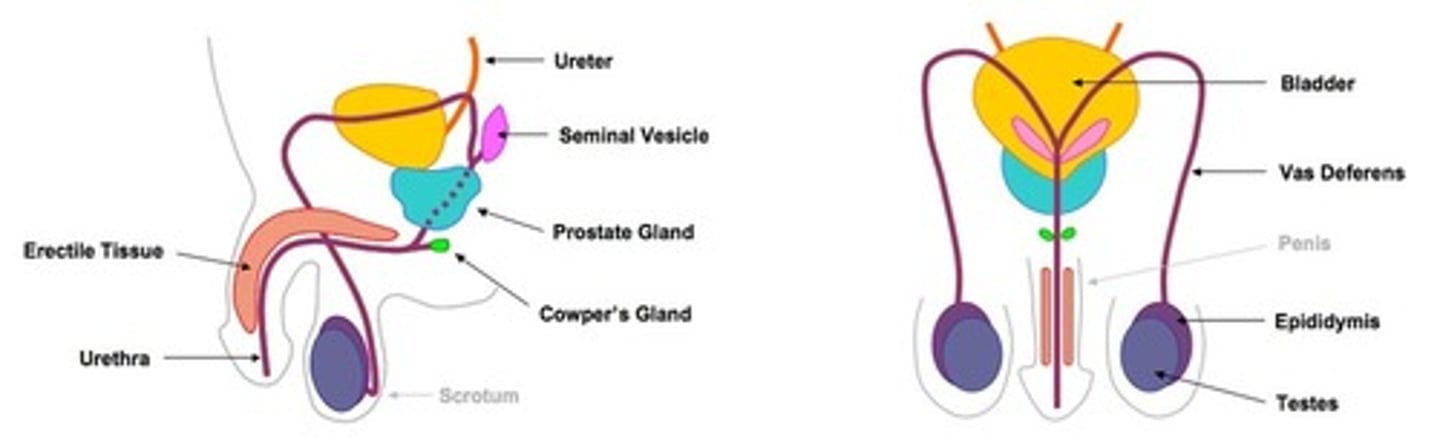
Male reproductive system
Female reproductive system

Genotype
The combination of the alleles on an organism's genes expressed in letters
Phenotype
The expression in traits of a genotype, which is described in words rather than represented by letters.
Dominant Allele
The part of a genotype allele which overrides recessive genes, and is always expressed in the phenotype, and represented by a capital letter.
Recessive Allele
The part of the genotype which can be overrided and not expressed in the presence of a dominant allele, and only expressed in a homozygous recessive allele combination.
Co-dominant Allele
A special circumstance in which both parts of an allele are expressed in the phenotype.
Homozygous
When two parts of the allele are the same as each other (Both dominant or both recessive).
Test-Cross
A test used to determine genotype of an unknown parent crossed with a homozygous recessive parent.
Punnet Square
A tool used to find the potential outcomes of a cross.
Pedigree Chart
A tool used to track a specific trait throughout the history of a particular organism.
Sex Linkage
Describes that a trait is carried through a particular sex, such as through mothers or through the fathers
Polymerase Chain Reaction
A process used to amplify small samples of DNA to use for genetic profiling, research and recombination
Gel Electrophoresis
A form of DNA Profiling which uses electrophoresis gel to put samples of amplified DNA into to produce a genetic profile.
DNA Profiling
A process which compares sections of DNA to determine patterns or paternity
Plasmid
Circles of DNA found in bacteria
Restriction Enzyme/ endonucleases
An enzyme required in gene transfer which cuts the any desired gene from the genome to be replaced.
Transgenic
An organism made by inserting a gene into an embryo so that it will develop the trait for that gene
Species
A classification unit in biology which describes a set of organisms which can reproduce together producing fertile offspring.
Habitat
The physical environment in which an organism lives.
Population
Population refers to the collective group of a particular species living in the same environment at the same time.
Community
A group of populations which live in the same environment at the same time and interact with each other.
Ecosystem
made up of the communities and the physical environment.
Autotroph
Any organism which can produce its own food out of organic molecules, like Carbon Dioxide.
Heterotroph
Any organisms which derive energy from other living organisms.
Consumers
Organisms which get their energy by eating other living organisms, or recently killed organisms.
Detritivores
Heterotrophs which derive energy by eating non-living organic matter.
Saprotrophs
Organisms which live in non-living organic matter and derive energy from it by secreting enzymes into it.
Trophic Level
Trophic levels represent the feeding status of organisms in a food chain or web.
Carbon Cycle
The natural/artificial processes through which carbon is exchanged through the earth and recycled and reused.
Keeling Curve
The curve developed over 40 years since 1960 by Charles Keeling which shows the significant increase in Carbon Dioxide levels in the earth's atmosphere since 1960.
Greenhouse Effect
The naturally occurring process of the greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, and water vapor, being trapped into the troposphere, raising temperatures on earth.
Precautionary Principle
The principle developed by environmentalists that corporations or operations should have to prove that their project will not harm the environment before they start.
Natality
The rate of birth in a population.
Sigmoid Shaped Population Curve
The graph of population increase which demonstrates how populations increase exponentially, gradually slowing as competition increases, then eventually plateau as the competition evens out the population.
Exponential Growth
A phase of the sigmoid shaped population curve which shows the initial rapid increase in population as members of a species produce more offspring than the environment can support.
Transitional Phase
Phase on the sigmoid shaped population curve in which the scarcity of resources causes a slow in population increase.
Plateau
The point on the sigmoid shaped population curve in which the population stops increasing and levels out as competition eliminates the rapid growth, and the population of the population reaches it's carrying capacity (K)
Evolution
The small changes over generations in the heritable traits of a population
Natural Selection
The process of a species preserving and passing down helpful traits and rejecting unhelpful traits.
Artificial Selection
The process of humans interfering by choosing to breed those organisms which display the traits we want.
Homologous Structure
Structures in various species designed for a specific task which are very similar. Provides evidence for Evolution.
Natural Variance
The variation in genes which occurs naturally from the random alignment or combination of chromosomes.
Adaptive Behavior
A behavior change carried out in response to environmental change which helps thr organism survive the change.
Mutation
Accidental changes in DNA sequence sometimes caused by a virus.
Sexual Reproduction
The combining of the genetic material of two organisms within a species to produce offspring.
Resistance
The gradual development of genes which enable organisms to resist an environmental change that could kill off the species.
Adaptation
A trait which serves a use to the organism and is passed on through natural selection.
Binomial Nomenclature
A two-part naming system for organisms which uses the capitalized genus name followed by the uncapitalized species name in order to identify a specific organism.
Taxa
The individual levels of classification for organisms
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Dichotomous Key
A series of binary questions which can be used to identify an organism based on physical characteristics.
Hiearchy
Refers to the classification of organisms in the various ranks, which descend down in specificity.
Bryophyta
A group of plants which are very simple and have no roots or stem, and small leaves and a furry appearance.
Filicinophyta
A group of plants with roots, leaves, and short stems. They have no lignin, and leaves are divided up into small sections and are often curled.
Coniferophyta
A group of plants with lignin in their trunks, and have pine needles for leaves.
Angiospermophyta
A group of plants with roots, stems, and leaves, which produce flowers.
Porifera
A phylum of the kingdom Animalia, which is characterized by no symmetry, no mouth or anus, no segmentation, and are porous filter feeders. (sponges)
Cnidaria
A phylum of the kingdom Animalia which is characterized by radial symmetry, a mouth but no anus, no segmentation, and stinging tentacles surrounding the mouth.(jellyfish)
Platyhelminthes
A phylum of the kingdom Animalia which is characterized by bilateral symmetry, a mouth but no anus, no segmentation, and a ribbon shaped body. (worms)
Annelida
A phylum of the kingdom Animalia which is characterized by bilateral symmetry, a mouth and an anus, very segmented bodies, and possibly with bristles and visible blood vessels. (earthworms)
Mollusca
A phylum of the kingdom Animalia which is characterized by bilateral symmetry at the foot, but no symmetry in the shell, a mouth and anus, but no visible segmentation. Often have shells but not always. (octupus, squid)
Arthropoda
A phylum of the kingdom Animalia which is characterized by bilateral symmetry, a mouth and anus, with segmentation and joints. They also have an exoskeleton, and jointed appendages. (crabs)
Digestion
The breakdown of food and macromolecules using enzymes to make it able to absorbed by the body.
Ingestion
The process of taking in macromolecules as food to be digested
Egestion
Getting rid of any substances which cannot be absorbed by the digestive system, such as fibers and dead cells.