structure of neuronal synapses
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
what is a synapse
point of connection between 2 neurones
what is a neurotransmitter
endogenous chemical that transmits signals across synapse from one neurone to another ‘target neurone, muscle cell or effector cells
what is a neuromodulator
endogenous chemical that is released from one neurone but if affects groups of neurones or effector cells that have appropriate receptor
differences between neurotransmitters (NT) and neuromodulators (NM)
NM acts through second messengers vs NT act directly on postsynaptic cells
NM produces long lasting effects vs NT have fast immediate response
NT is released at synapses vs NM not always released at synapses
NT = rapid, localised communication at synapses vs NM more longer duration responses
name if these are NT and/or NM:
acetylcholine
monoamines
catecholamines (dopamine, noradrenaline)
indolamines (serotonin)
amino acids - glutamate, GABA, glycine
peptides - endorphins
lipid substances
nucleosides - adenosine
acetylcholine = NT
monoamines = NT and NM
catecholamines (dopamine, noradrenaline)
indolamines (serotonin)
amino acids - glutamate, GABA, glycine = NT and NM
peptides - endorphins = NT and NM
lipid substances = NT
nucleosides - adenosine = NM
summary of the different ways drugs can modify neurotransmitter system in brain
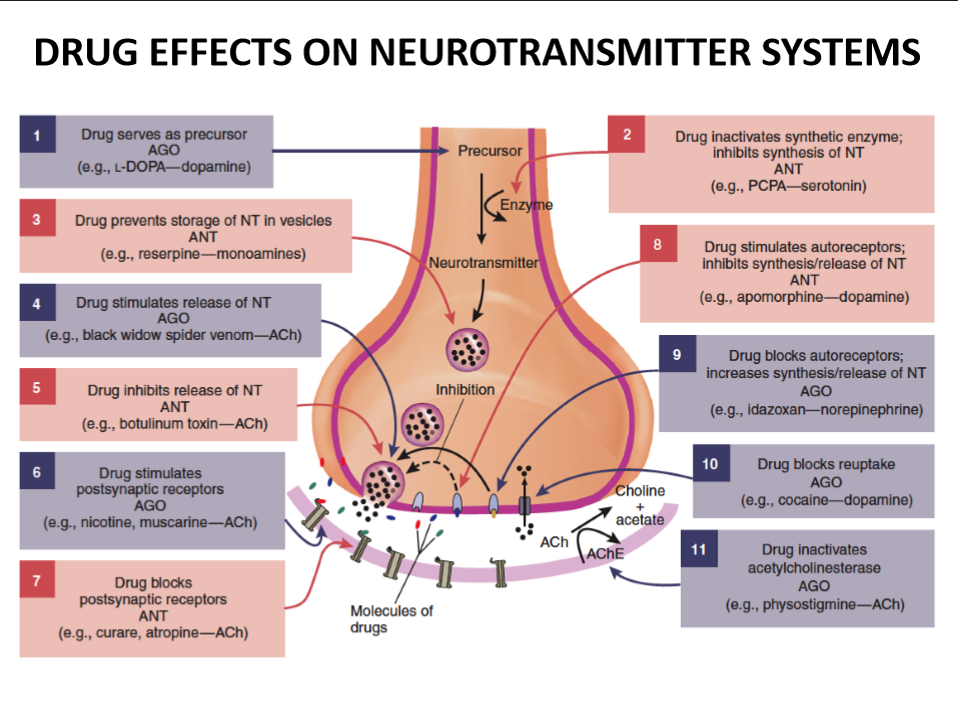
what is a presynaptic autoreceptor
Receptor on a neuron that binds the same neurotransmitter it releases → typically inhibits further release
what is presynaptic heteroreceptor
receptor on a presynaptic neuron that binds a different neurotransmitter → can inhibit or facilitate release of the main neurotransmitter
how can drugs affect presynaptic receptors
they can block or enhance autoreceptors or heteroreceptors to modify neurotransmitter release
how can presynaptic heteroreceptors produce presynaptic inhibition
inhibit release of neurotransmitter e.g. glutamate release by GABA b receptors so this causes reduction in postsynaptic activity