L4 - Prototyping
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is a task?
Set of activities required to achieve particular goal
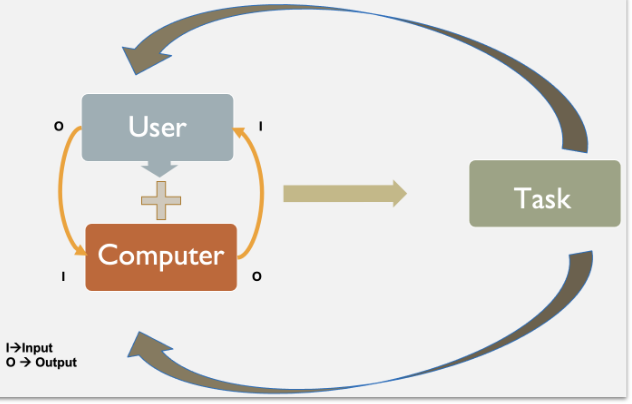
What are 2 ways to analyze a task?
GOMS
Cognitive task analysis (CTA)
“Task analysis is the process of learning about users by observing them in action to understand how they perform their tasks and achieve their intended goals.”
Identify user goals
Create a copy of stick note
Observe user actions to reach those goals
Mouse clicks, keyboard shortcuts
Analyze environmental and system influences
Workspace setup, distractions
Extract insights for design
Reduce unnecessary steps
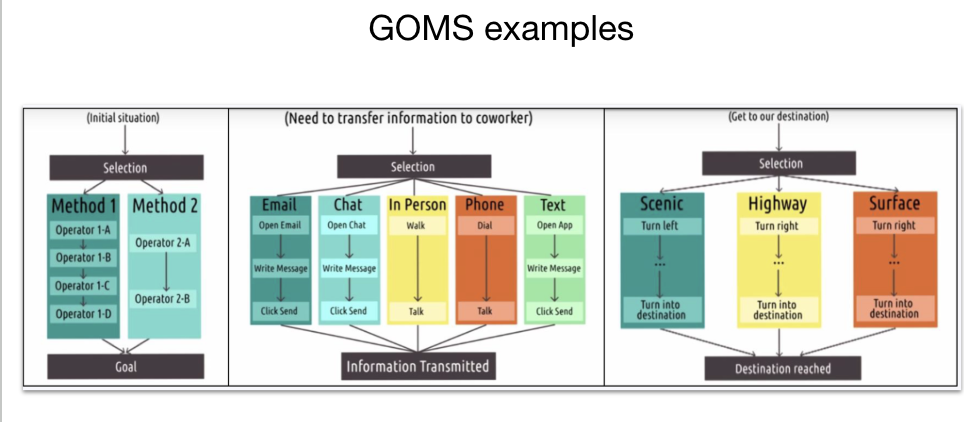
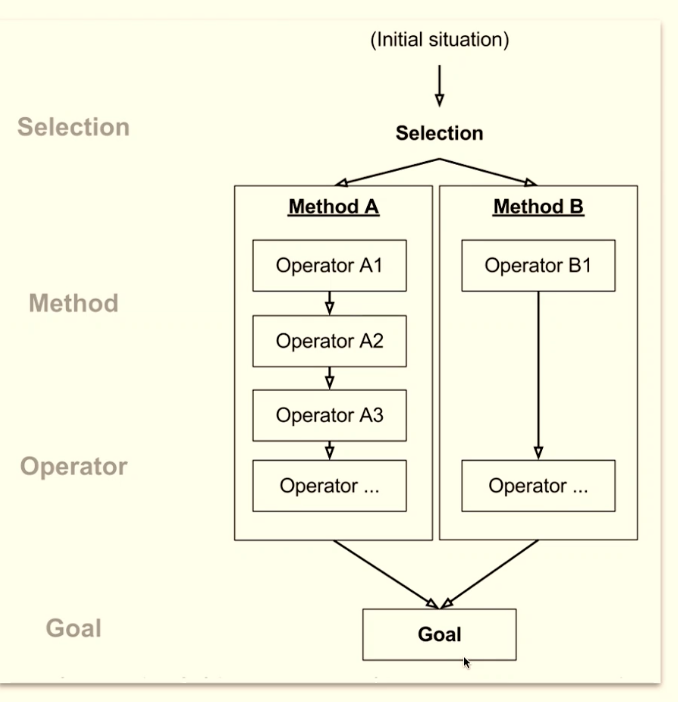
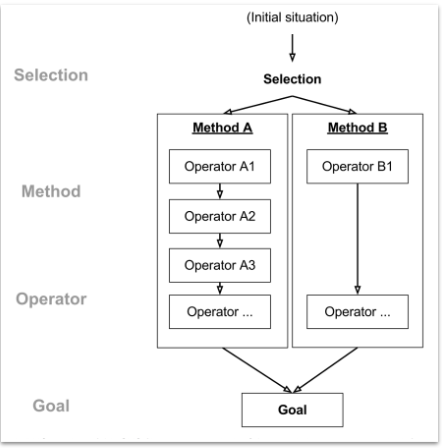
What is the GOMS approach?
GOMS approach considers humans as input/output systems, partially including cognitive and motor skills.
Goals → single or multiple to use HCI product
Operators → series of operations to execute the selected method
Methods → series of operations to achieve the goal
Selection rules → to select which method to use
Methods can be compared using: Number of steps, Execution time (keystroke vs. tap), etc.
Select the method that minimizes the number of steps.
What are 2 advantages of using GOMS?
It can predict interaction behavior (e.g., task completion time) of the users to aid our design
It can provide structured approach to quantify the interaction among different design alternatives
What are 2 disadvantages of using GOMS?
Cognitive processes are not part of GOMs
Oftentimes, we are discarding the novice users
What is missing in GOMS?
cognitive processes
GOMS considers humans as Input/Output machine, but do not include what is happening in between. For instance, some people might prefer email over in person meetings.
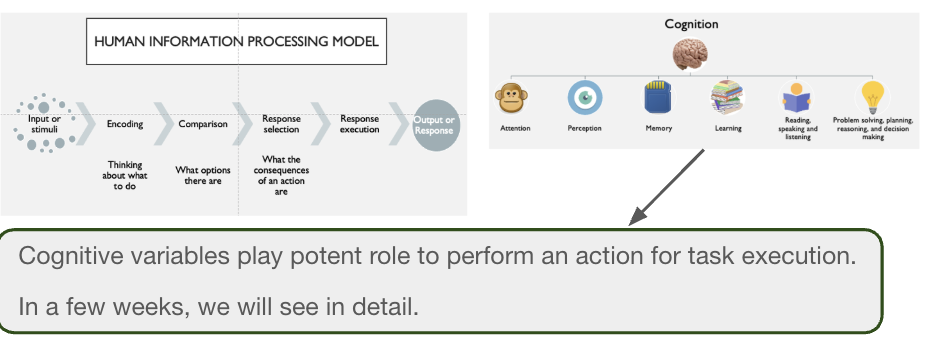
What is cognitive task analysis (CTA)?
more emphasis on cognitive aspects of the tasks. this approach aims at analyzing and understanding cognitive processes to perform the task
some factors:
memory
attention
cognitive load
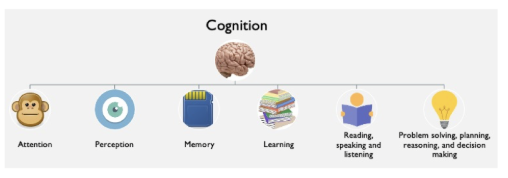
What are pros of CTA?
less formalism yet good enough to design interfaces
considers cognitive aspects of task
how easy to perform?
less/more cognitive load
attention hungry or seamless
recognition over recall
What are cons of CTA?
needs collaboration with different field
time
hard to carry out if you are new in desiging interfaces

What is prototyping?
“Prototyping is an experimental process where design teams implement ideas into tangible forms from paper to digital.”
With prototyping your team will diminish, prevention, correction, and failure costs.
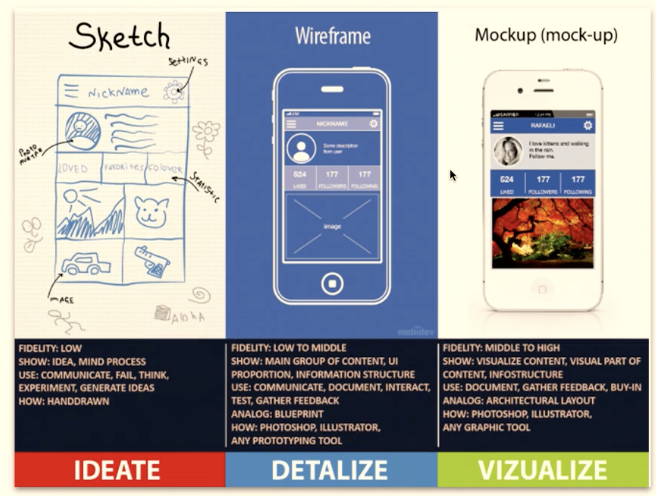
Why is it good to prototype?
a clear picture of the potential benefits, risks and costs to stakeholders
adapt changes early to avoid commitment to a single, falsely-ideal version
users’ feedback to help pinpoint which elements/variants work best
improve time-to-market by minimizing the number of errors to correct before product release.
Describe the low fidelity prototype, paper prototypes
Cheap and quick iteration
Pieces serve as documentation [this is important for your project]
Good for team building
Honest feedback by user [Low emotional and time investment]
[-] Paper prototypes lacks realism and requires in person testing.
What can you learn with low-fi paper prototypes?
conceptual model
functionality
navigation & task flow
terminology
screen contents

What can’t you learn with low-fi paper prototypes?
look
feel
response time
are small changes noticed?
exploration vs deliberation


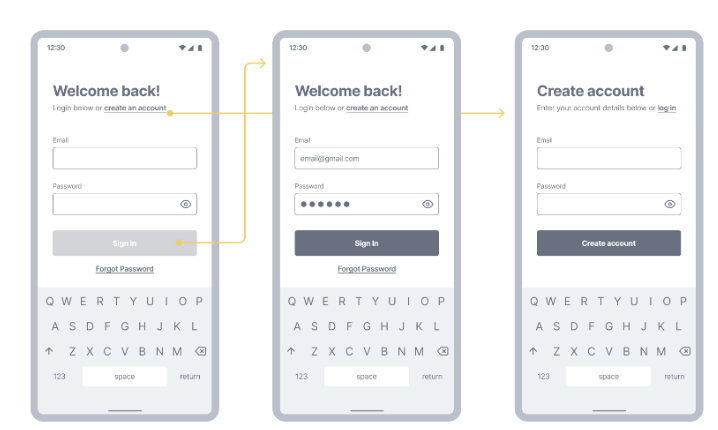
Describe the medium fidelity prototype, clickable wireframes
“Just like paper prototypes, clickable wireframes often don’t look like the finished product, but they do have one significant advantage over paper prototypes — they don’t require a separate person to work as a facilitator during the testing session.”
You can interact with prototype
Content and visual design are less emphasized
Mostly designed with wireframe software, e.g. figma.
Content is static but allows (clickable) interactions
You can view and interact on a device
More on wireframes
Interactive storyboard
Placement of items
No real content
All pages available
Good guideline for developers
Architecture and layout
Flow of the interaction with UI
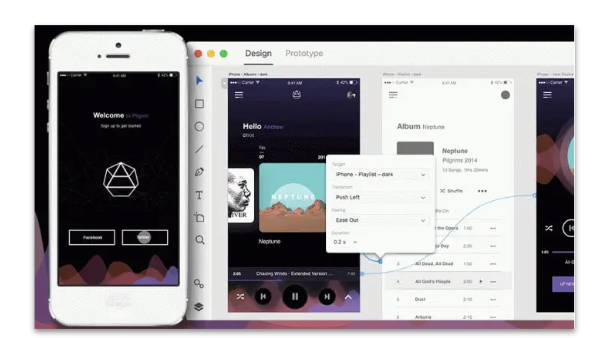
Describe the high fidelity prototype
“High-fidelity (hi-fi) prototypes appear and function as similar as possible to the actual product that will ship.”
Visual design: Realistic and detailed design — all interface elements, spacing, and graphics look just like a real app or website.
Content: Designers use real or similar-to-real content. The prototype includes most or all of the content that will appear in the final design.
Interactivity: Prototypes are highly realistic in their interactions.
Hi-fi prototypes will be created with a software tool, e.g. Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD.
[+] You will get meaningful feedback during usability test
[+] UI element level details (test affordance and animations)
[+] Good demonstration to stakeholders
[-] time demanding
[-] costly to build
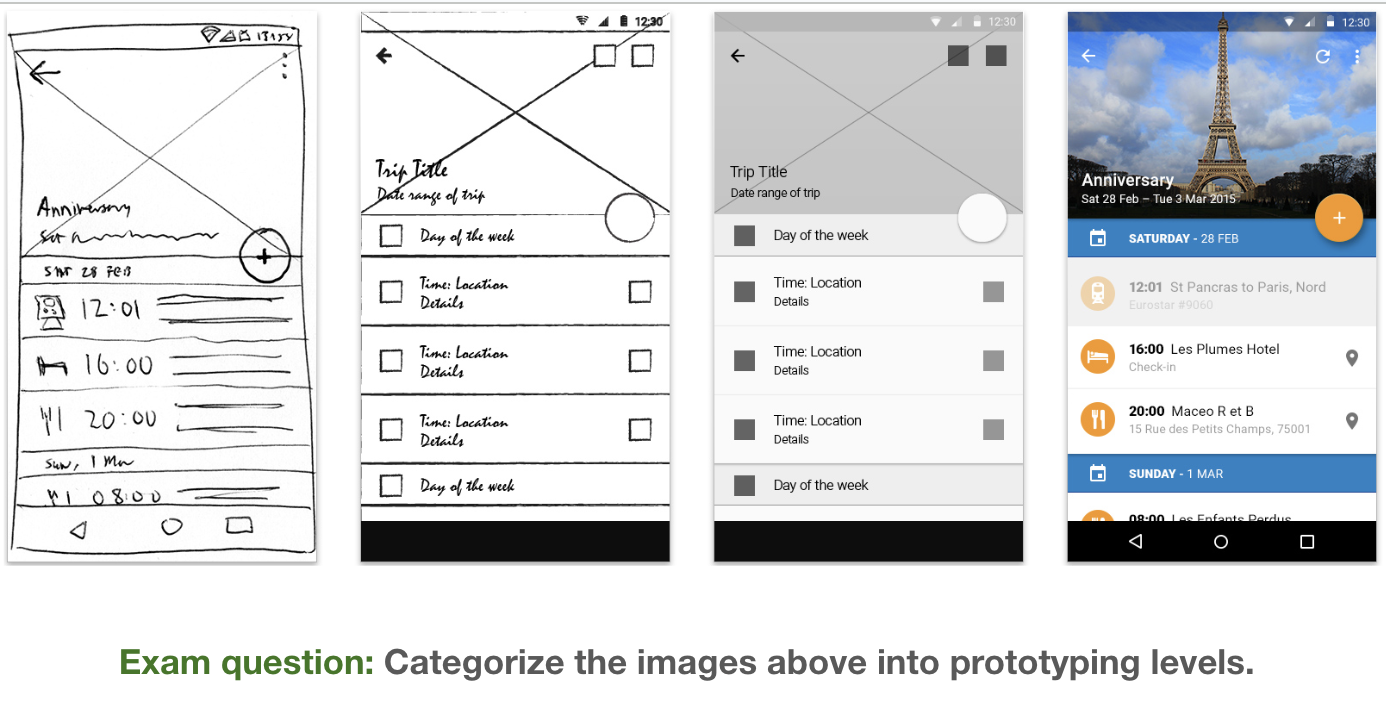
Analyze in content, interaction, and visual
P1: low fidelity = 1+2
P2: medium fidelity = 3
P3: high fidelity = 4
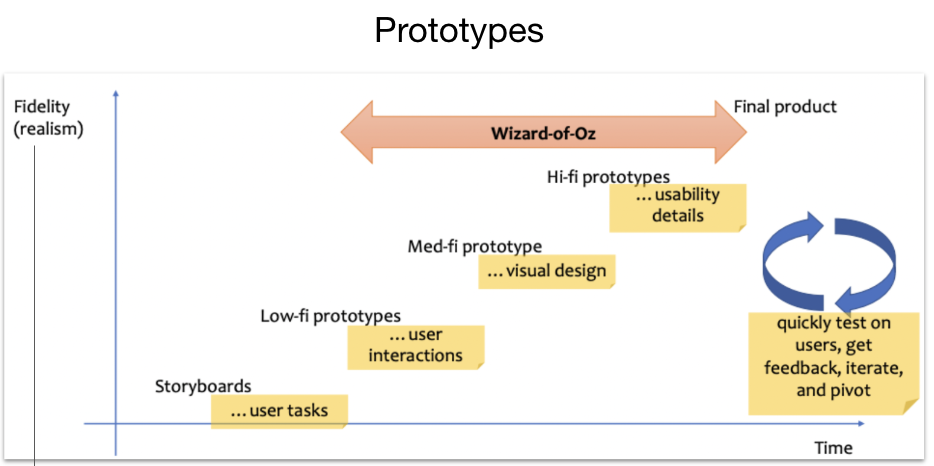
What does fidelity refer to?
Fidelity refers to the level of detail and functionality you include in your prototype. [Visual design, content, and interactivity]
![<p><span style="background-color: transparent; font-family: "Helvetica Neue", sans-serif;"><strong>Fidelity</strong> refers to the level of detail and functionality you include in your prototype. [Visual design, content, and interactivity]</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/21f05a94-2152-4466-a84a-9b744c448fe9.png)