Psych Finals - Operant & Classical Conditioning
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Operant Conditioning
(also called instrumental conditioning) an animal or human performs some behavior, and the following consequence increases or decreases the chance that they will preform the same behaviour
law of effect
behaviors followed by positive consequences are strengthened, while behaviors followed by negative consequences are weakened
operant response
a response that can be modified by its consequences and is a meaningful unit of ongoing behavior that can be easily measured
shaping
an experimenter successively reinforces behaviors that lead up to or approximate the desired behavior
superstitious behaviour
a behavior that increases in frequency because its occurrence is accidentally paired with the delivery of a reinforcer
2 kinds of consequences
Reinforcement - increases the chance that the behavior will occur again
Punishment - decreases the chance that the behavior will occur again
Positive reinforcement
a stimulus increases the probability that a behavior will occur again
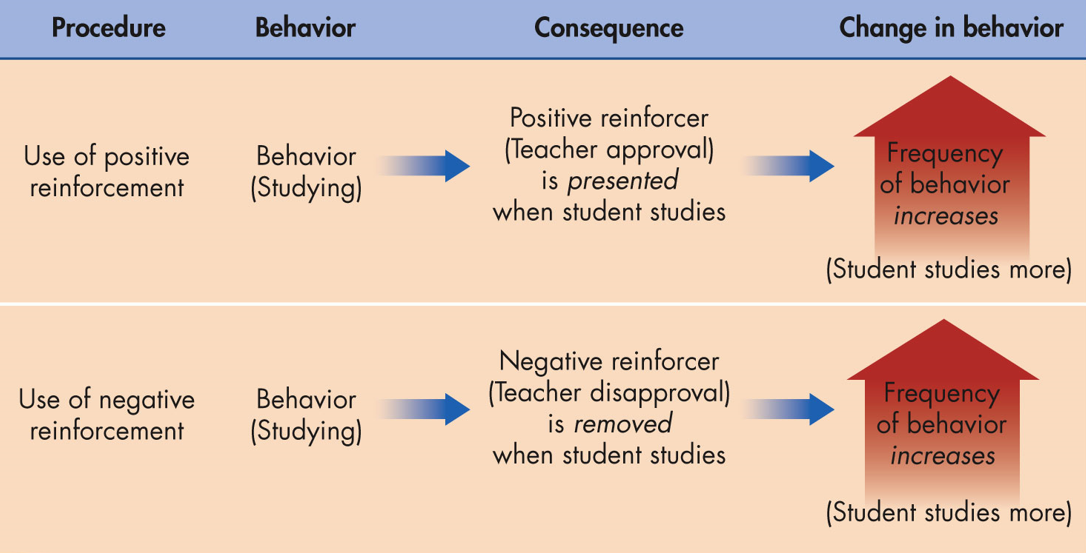
Negative reinforcement
an unpleasant stimulus whose removal increases the likelihood that the preceding response will occur again
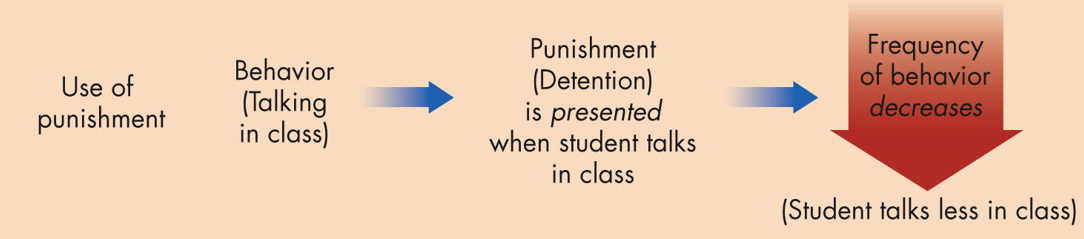
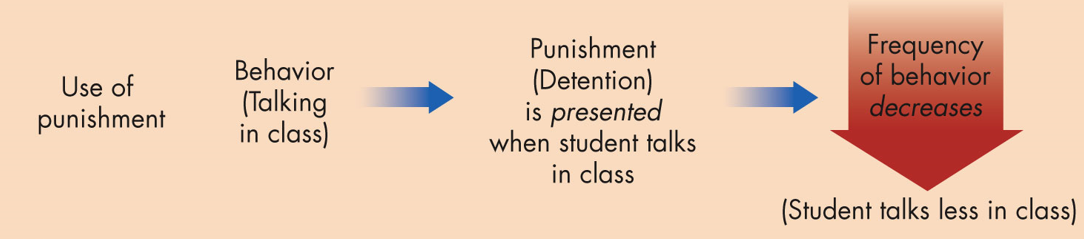
Positive Punishment
an unpleasant stimulus decreases the chances that the response will recur (ex: electric shocks)
Negative Punishment
removal of stimulus decreases the chances that the response will recur (removing one’s allowance)
Reinforcements & Punishments Concept chart
Schedule of reinforcement
a program or rule that determines how and when the occurrence of a response will be followed by a reinforcer
Continuous reinforcement
means that every occurrence of the operant response results in delivery of the reinforce
Partial Reinforcement
refers to a situation in which responding is reinforced only some of the time
Fixed Ratio Schedule
a reinforcer occurs only after a fixed number of responses are made by the subject
ex: If factory workers are paid after packing six boxes, quota and going home, SM advantage card points
Fixed Interval Schedule
a reinforcer occurs following the first response that occurs after a fixed interval of time
ex: payday is on Saunday so faculty gets more excited the closer to the weekend.
Variable Ratio Schedule
a response is reinforced after an unpredictable number of responses
ex: In slot machines, there’s always a possibility the next coin will be the winning one. In Call centers, more calls for a high chance of a bonus
Variable Interval Schedule
response is rewarded after an unpredictable amount of time has passed
ex: Checking cell phone for text messages when phone is on silent.
Your teacher gives pop quizzes
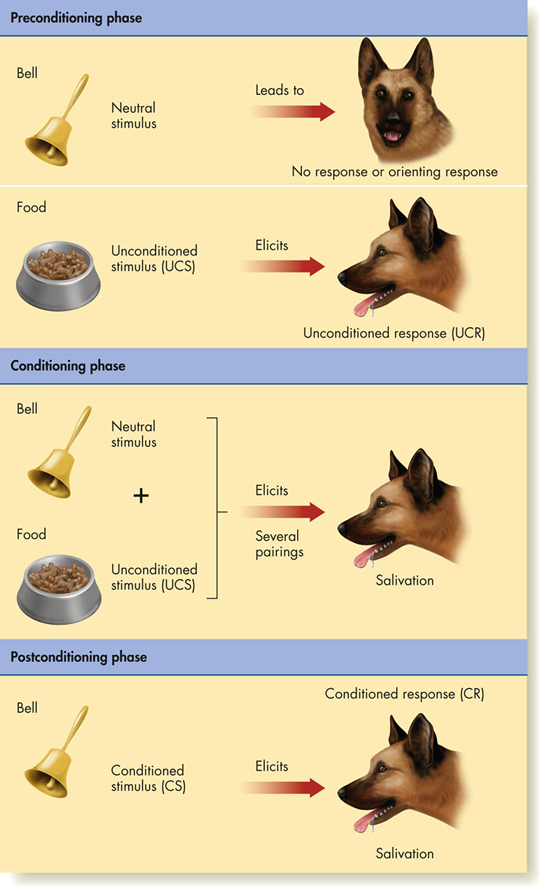
Classical Conditioning
a neutral stimulus acquires the ability to produce a response that was originally produced by a different stimulus
Cognitive learning
a kind of learning that involves mental processes, such as attention and memory; may be learned through observation or imitation
Neutral Stimulus
some stimulus that causes a sensory response, such as being seen, heard, or smelled, but does not produce the reflex being tested
Unconditioned Stimulus - UCS
some stimulus that triggers or elicits a physiological reflex, such as salivation or eye blink
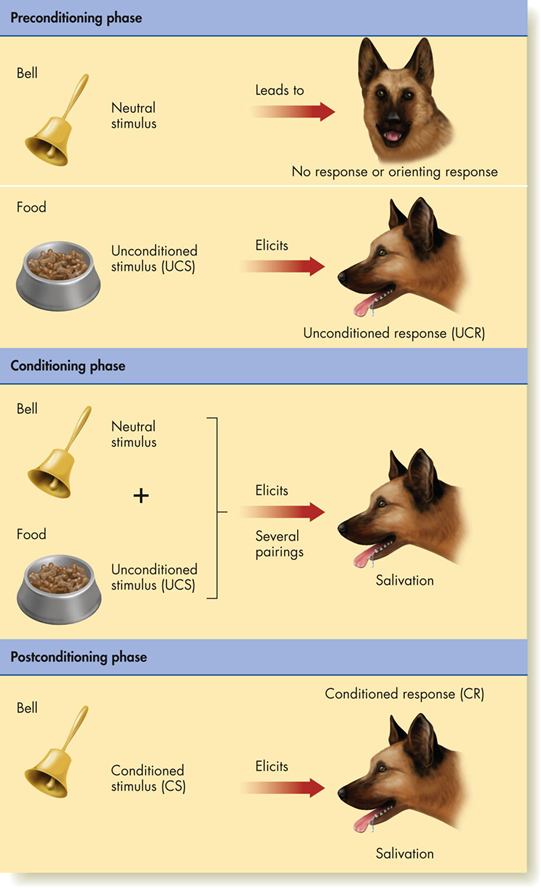
Unconditioned Response - UCR
an unlearned, innate, involuntary physiological reflex that is elicited by the unconditioned stimulus
Conditioned Stimulus - CS
a formerly neutral stimulus that has acquired the ability to elicit a response that was previously elicited by the unconditioned stimulus
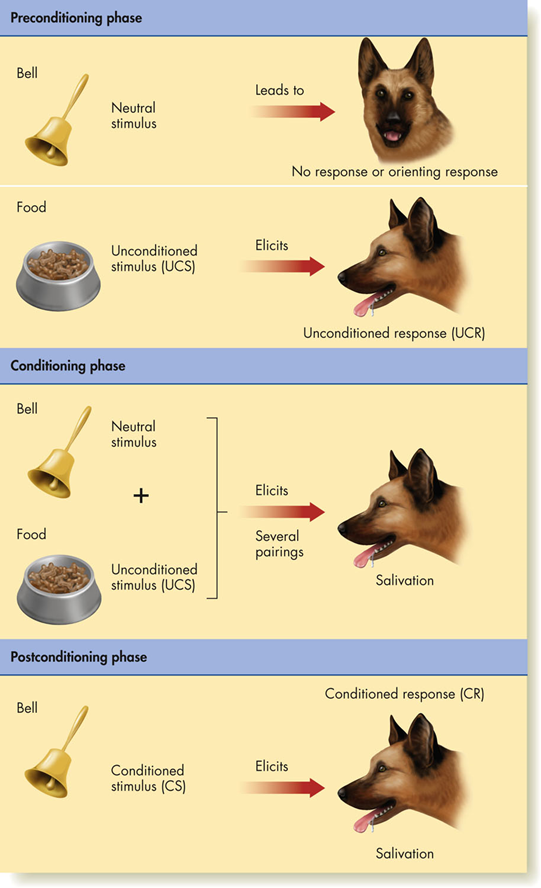
Conditioned Response - CR
elicited by the conditioned stimulus, is similar to, but not identical in size or amount to, the unconditioned response
Generalization
the tendency for a stimulus that is similar to the original conditioned stimulus to elicit a response that is similar to the conditioned response
Discrimination
occurs during classical conditioning when an organism learns to make a particular response to some stimuli but not to others
Extinction
a procedure in which a conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus and, as a result, the conditioned stimulus tends to no longer elicit the conditioned response (CS no longer followed by an UCS - no longer elicits CR)
Spontaneous Recovery
the tendency for the conditioned response to reappear after being extinguished even though there have been no further conditioning trials
Adaptive Value
the usefulness of certain abilities or traits that have evolved in animals and humans and tend to increase their chances of survival, such as finding food, acquiring mates, and avoiding pain and injury
Taste Aversion Learning
associating a particular sensory cue (smell, taste, sound, or sight) with getting sick and thereafter avoiding that particular sensory cue in the future
ex: rat poison, food, alcohol, etc
Conditioned emotional Response
feeling some positive or negative emotion, such as happiness, fear, or anxiety, when experiencing a stimulus that initially accompanied a pleasant or painful event
ex: injections, needles, and fear
Stimulus Substitution
a neural bond or association forms in the brain between the neutral stimulus (tone) and unconditioned stimulus (food). After repeated trials, (tone) and acts like a substitute for the UCS the neutral stimulus becomes the conditioned stimulus ned stimulus (food)
Contiguity Stimulus
classical conditioning occurs because two stimuli (neutral stimulus and unconditioned stimulus) are paired close together in time (are contiguous)
ex: seeing a pizza is paired closely in time with eating it, the sight alone begins to elicit salivation
Systematic Desensitization
a person imagines or visualizes fearful or anxiety-evoking stimuli and then immediately uses deep relaxation to overcome the anxiety / a form of counterconditioning because it replaces, or counters, fear and anxiety with relaxation