Stats Textbook Terms
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Cases
Objects described in a set of data. Ex: customers, companies, study subjects, units
Label
Special variable distinguished in different cases
Variable
Characteristics of a case
Values
Different cases have different values
Categorical variable
Places a case into several groups or categories
Quantitative Variable
takes numerical variables for which arithmetic operations such as adding and averaging make sense
key characteristics of data set
who what and why
Explanatory Data Analysis
Examine data and describe their main features
Distribution of a categorical variable
Lists the categories and gives either the count or the percent (or proportion) of the cases that fall in each category
mean x̅
x1+x2+…./n
median M
(n+1)/2 (to find location of median)
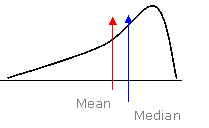
Median versus mean
Median is more resistant to the mean
If shape is symmetric, median = mean
Shape
Skewed where the tail is
Quartiles
25%, 50%, 75%
IQR (Interquartile range)
Q3-Q1
Outlier IQR
1.5 x IQR
Q1- (1.5 x IQR) = lower bound
Q3 + (1.5 x IQR) = upper bound
S (Standard Deviation) Formula
√[ Σ(xi - x̄)² / (n-1) ]
S² (Variance) Formula
∑ (xi - x̄)² / (n - 1)
Degrees of Freedom formula
n-1
What does s measure?
spread about the mean
s=0
No spread
When are variables associated?
If knowing the valuable of one tells you something about the values of the other
Responsive Variable
Measures an outcome of a study
Explanatory Variable
Explains or causes changes in the response variable
Independent Variable
the factor that a researcher manipulates or changes to see how it affects another variable
Dependent Variable
a variable (often denoted by y ) whose value depends on that of another.
Scatterplot
Shows the relationship between two quantitative variables measured on the same cases
Positively Associated
two things are positively associated when above-average values of one tend to accompany above-average values of the other and below-average values tend to occur together
Negatively Associated
Two variables are negatively associated when above-average values of one tend to accompany below-average values of the other, and vice versa
Correlation (r ) formula
Causation
x → y
Common Response
z→x and y
Confounding
x→ y
z→ y
Sample Space S
The set of all possible outcomes
Event
An outcome or a set of outcomes of a random phenomenon. Subset of the sample space
ex: exactly four heads
Probability rules
Rule 1. The probability P(A) of any event A satisfies 0 ≤ P(A) ≤ 1.
Rule 2. If S is the sample space in a probability model, then P(S) = 1.
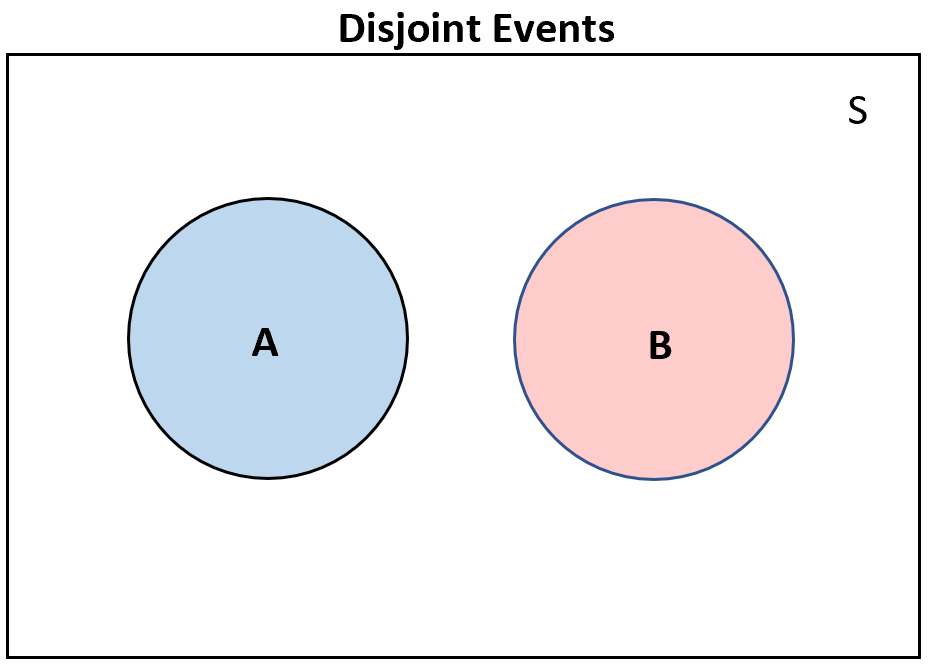
Rule 3. Two events A and B are disjoint if they have no outcomes in common and so can never occur together. If A and B are disjoint,
P (A or B) = P (A) + P (B)
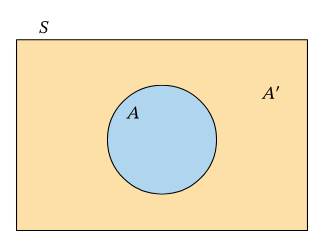
Rule 4. The complement of any event A is the event that A does not occur, written as Ac. The complement rule states that
P (Ac) = 1 − P (A)
Rule 5. Two events A and B are independent if knowing that one occurs does not change the probability that the other occurs. If A and B are independent,
P (A and B) = P (A) P (B)
Disjoint events
Complement A^c
Multiplication rule for independent events
P (A and B) = P (A) P (B)
Independent in probability
The outcome of one event is not influenced by the outcome of another event
Additional Rule
If A and B are disjoint events, then
P (A or B) = P (A) + P (B)
Complement Rule
For any event A,
P (Ac) = 1 − P(A)
RULE FOR UNIONS OF TWO EVENTS
any two events A and B,
P (A or B) = P (A) + P(B) − P (A and B)
Conditional Probability
When P(A) > 0, the conditional probability of B given A is
P(B|A)= P(AandB)/ P(A)
Intersection of events
When P(A) > 0, the conditional probability of B given A is
P(B|A)= P(AandB) P(A)
Independent Events
Two events A and B that both have positive probability are independent if P(B|A) = P(B)
Density Curve
A density curve is a curve that
Is always on or above the horizontal axis.
Has area exactly 1 underneath it.
A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. The area under the curve and above any range of values is the proportion of all observations that fall in that range.
symmetric normal density, right skewed/left skewed
Normal distribution density curve
Right skewed density curve
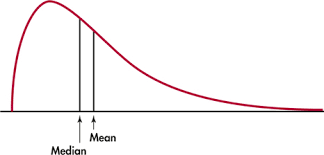
Left skewed density curve
What does the standard deviation control in a curve
the spread of the curve
The 68-95-99.7 Rule
In the Normal distribution with mean μ and standard deviation σ:
Approximately 68% of the observations fall within σ of the mean μ. Approximately 95% of the observations fall within 2σ of μ. Approximately 99.7% of the observations fall within 3σ of μ.
N(μ, σ)
mean μ and standard deviation σ
z score
z = x–μ / σ
Random Variable
a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random process.