Horizontal Determinants of Occlusion
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
what is the ideal occlusion in lateral excursive movement
we want ideal force distribution in excursive movements so either on canines (mutually protected) or on all posterior teeth (group function)
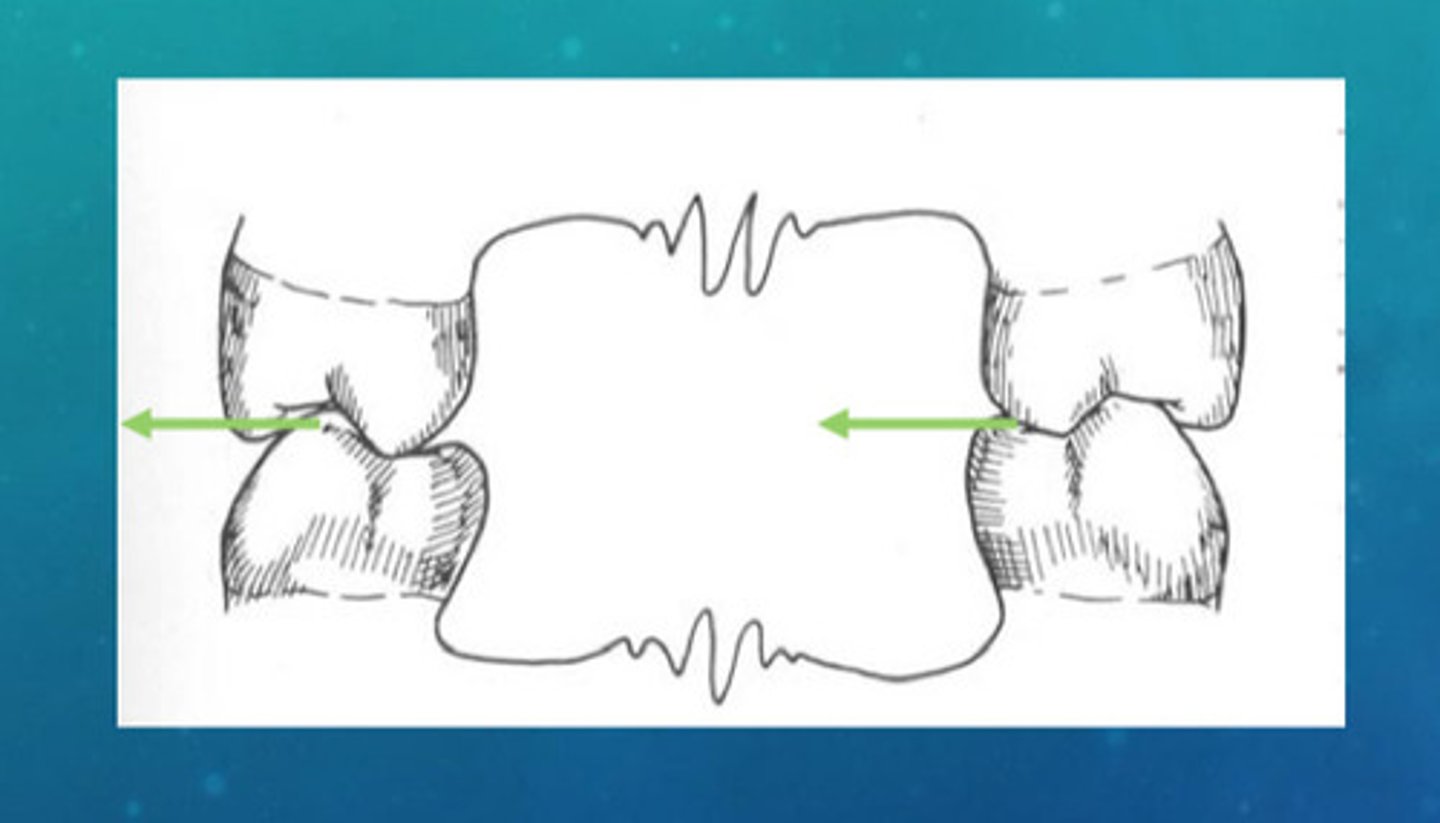
in excursive movements in posterior teeth, we want no _________ tooth contact
no isolated tooth contact
an optimal angle between what movements can limit occlusal interferences in ideal occlusion of lateral excursive movements
optimal angle between W and NW movements
in ideal occlusion, we want minimal "___________" of maxillary anterior incisors with excessive anterior or mesialized lateral movement
bumping
most lateral force in ideal occlusion should be on the _________ rather than the ___________
canines; incisors
incisor "bumping" can interfere with what and is detrimental to what
can interfere with canine guidance; detrimental to periodontium
_______ movement of the mandible reduces interferences
vertical
in border mandibular movements, the mandible moves forward ______ mm
5-10 mm
in border mandibular movements, the mandible moves laterally ____ mm
15 mm; total left to right movement is 30 mm
sagittal and horizontal pathways start from what position
CO
frontal pathways start from what position
MI
what 3 things determine posterior tooth contact and tooth morphology in the horizontal plane
1) ridge and groove direction
2) cusp position
3) cusp height (lesser degree)
anterior "bumping" can lead to trauma to maxillary incisors due to what
due to more anteriorly directed forces
why should canines absorb the lateral forces more?
they have longer roots
what are the 4 horizontal determinants of occlusion
1) A-P distance from condyle
2) lateral distance from mid sagittal plane
3) intercondylar distance
4) Bennett Movement (immediate side shift and progressive side shift)
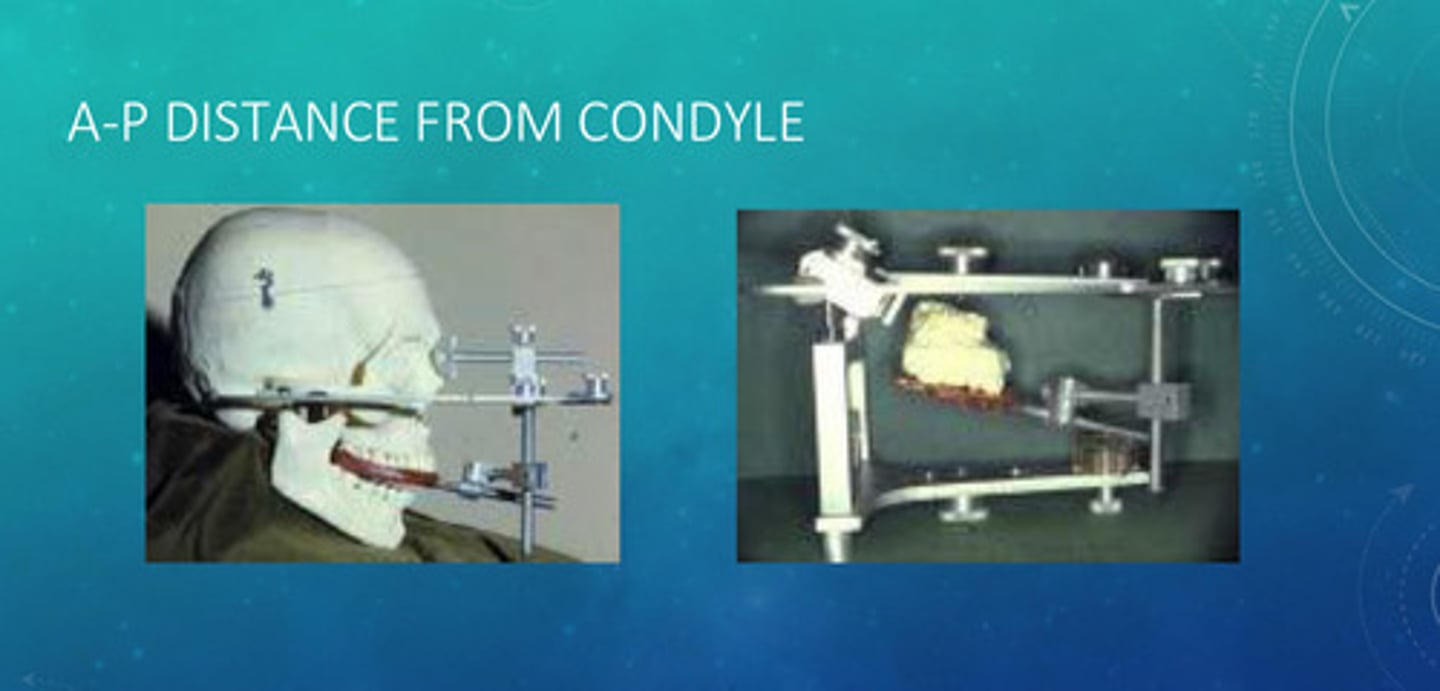
A-P distance from condyle examples
average distance is 100 mm
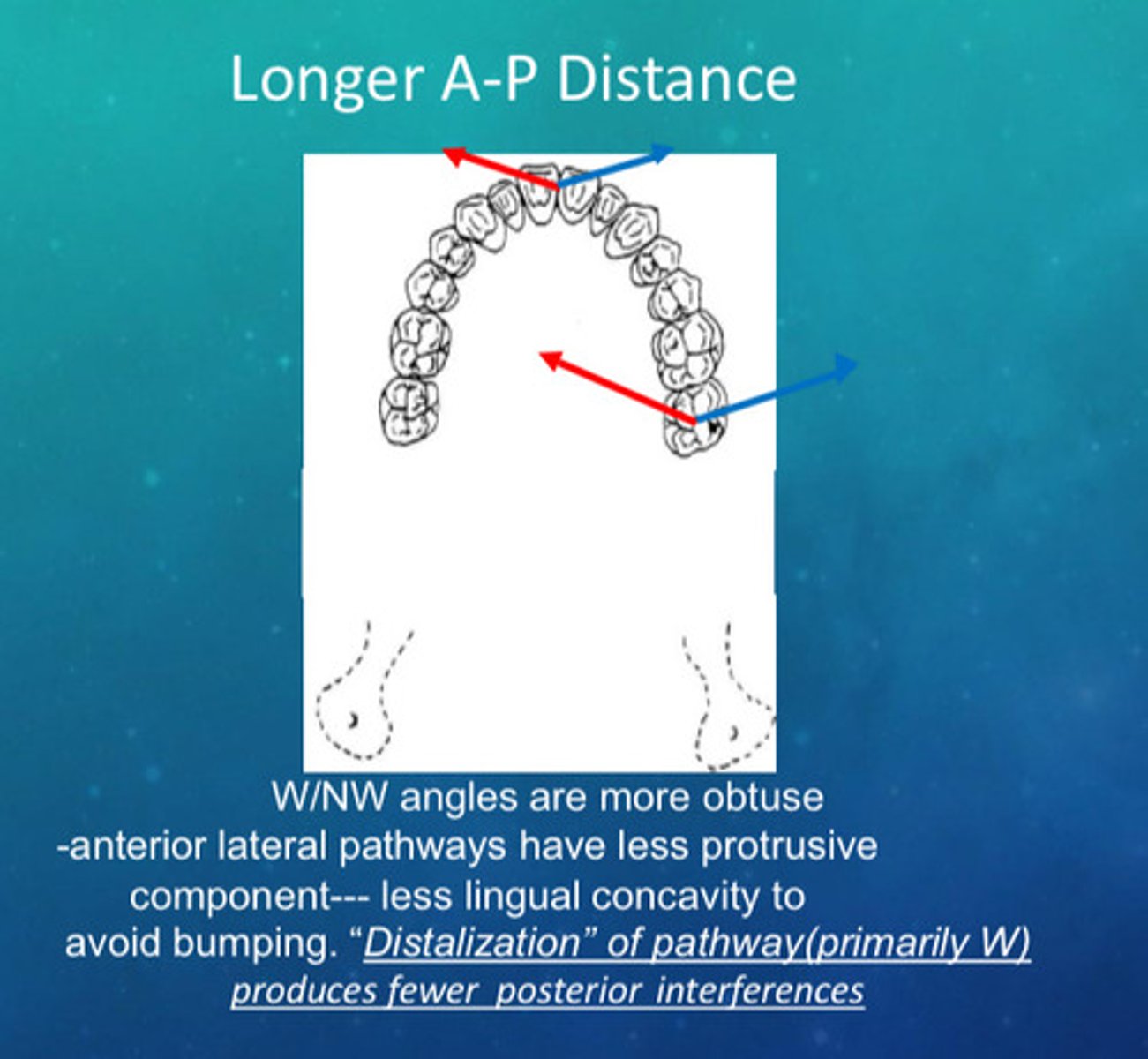
in longer A-P distance, what 4 things do you see
1) W/NW angles are more obtuse
2) anterior lateral pathways have less protrusive component
3) less lingual concavity to avoid bumping
4) distalization of pathway (primarily W) produces fewer posterior interferences
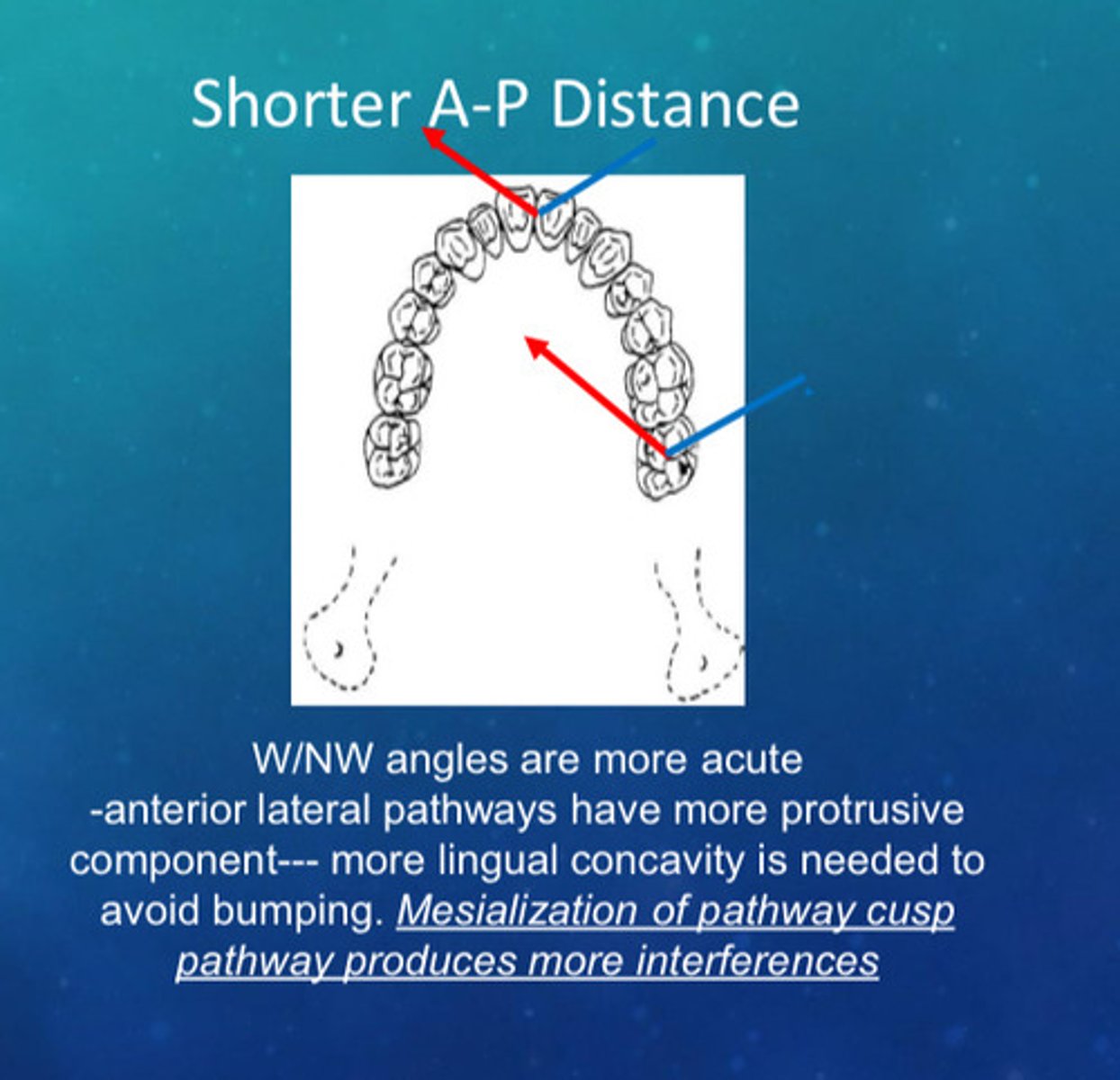
in shorter A-P distance, what 4 things do you see
1) W/NW angles are more acute
2) anterior lateral pathways have more protrusive component
3) more lingual concavity is needed to avoid bumping
4) mesialization of cusp pathway produces more interferences
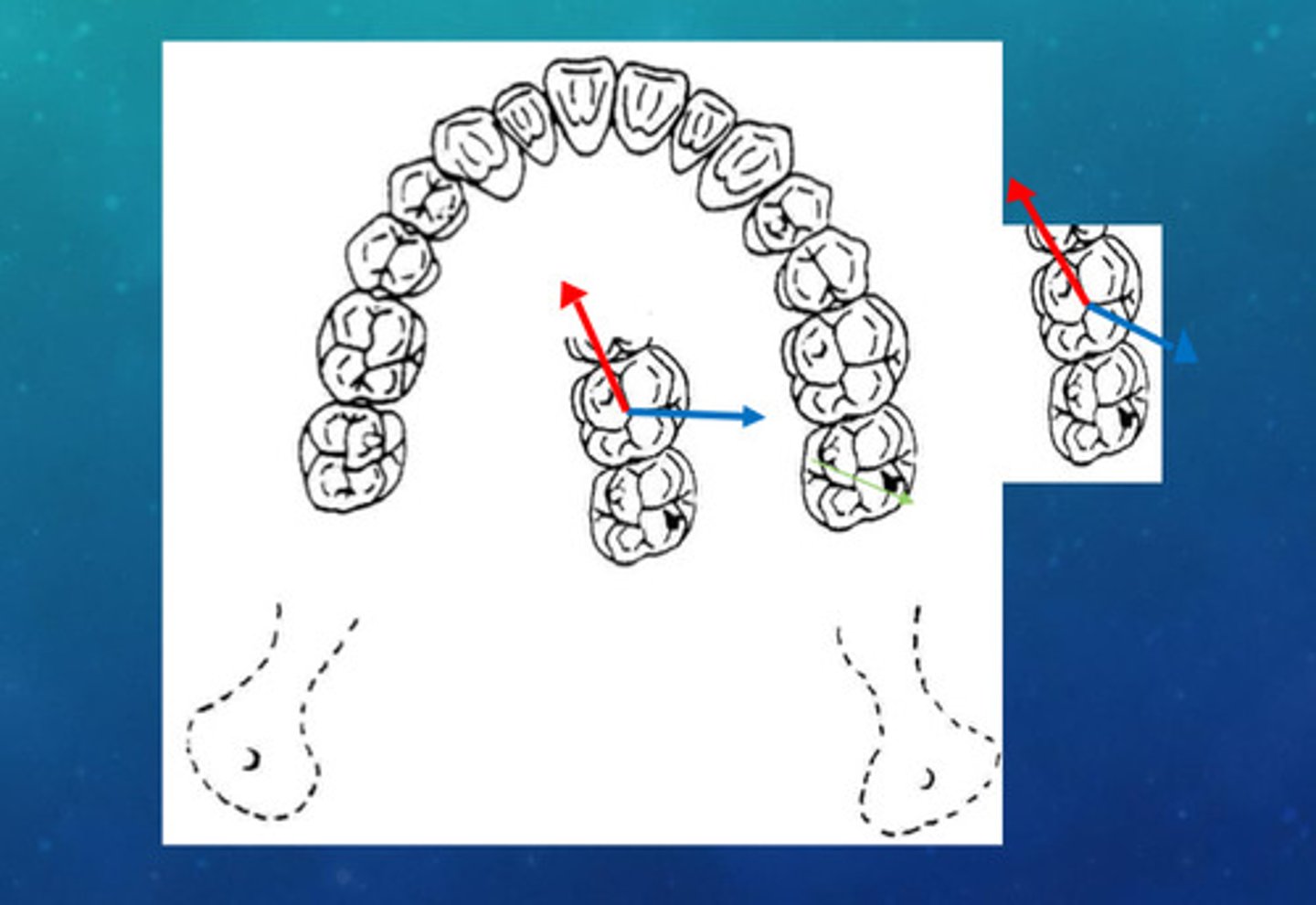
when the horizontal distance from the mid sagittal plane (mediolateral distance) is relatively short, what 3 things do you see
1) narrow arch
2) maxilla is narrow relative to intercondylar width
3) W/NW angles are more acute
when the horizontal distance from the mid sagittal plane (mediolateral distance) is relatively long, what 4 things do you see
1) wide arch
2) maxilla is wide relative to intercondylar width
3) W/NW angels are more obtuse
4) the NW pathway is affected the least, so we say that the W pathway is "distalized"
example of distance from midsagittal plane
intercondylar distance is _______ programmable on pantadent semi adjustable articulator
NOT
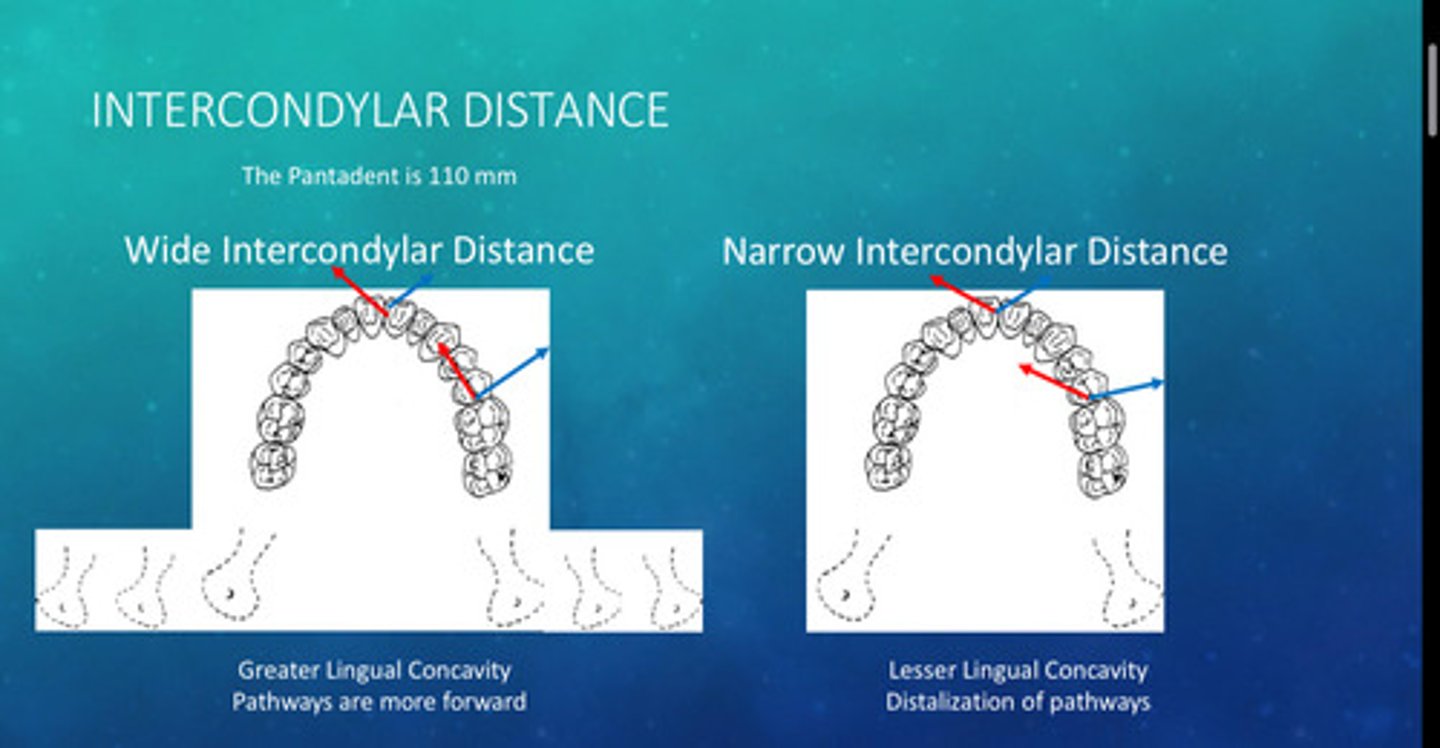
the average width of the intercondylar distance is
110 mm
if the intercondylar distance is narrow relative to maxilla, what 3 things do you see
1) W/NW angles are more obtuse
2) maxillary is more distalized (primarily W)
3) anterior bumping is lower risk
if the intercondylar distance is wide relative to maxillary, what 3 things do you see
1) W/NW angles are more acute
2) maxillary is more mesialized
3) anterior bumping is higher risk
examples of intercondylar distance
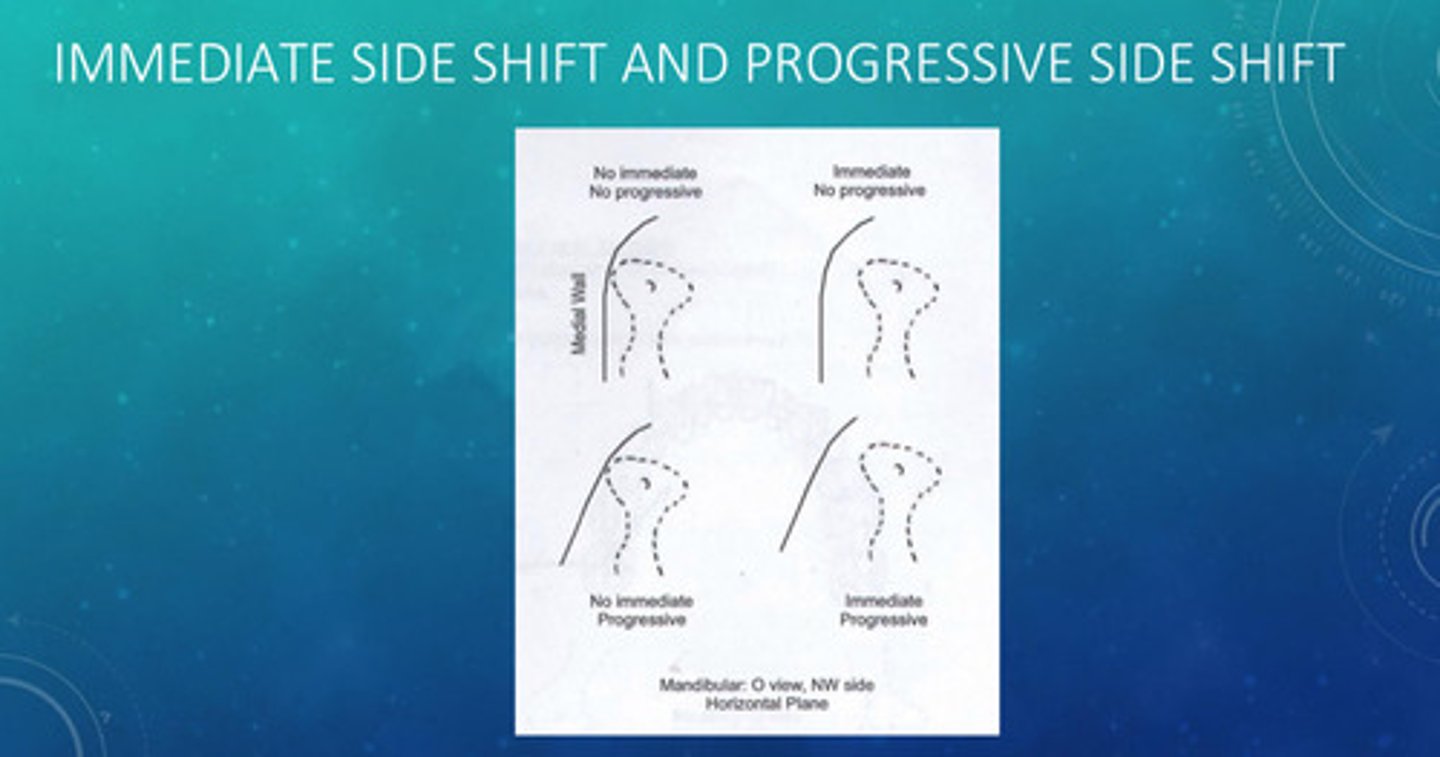
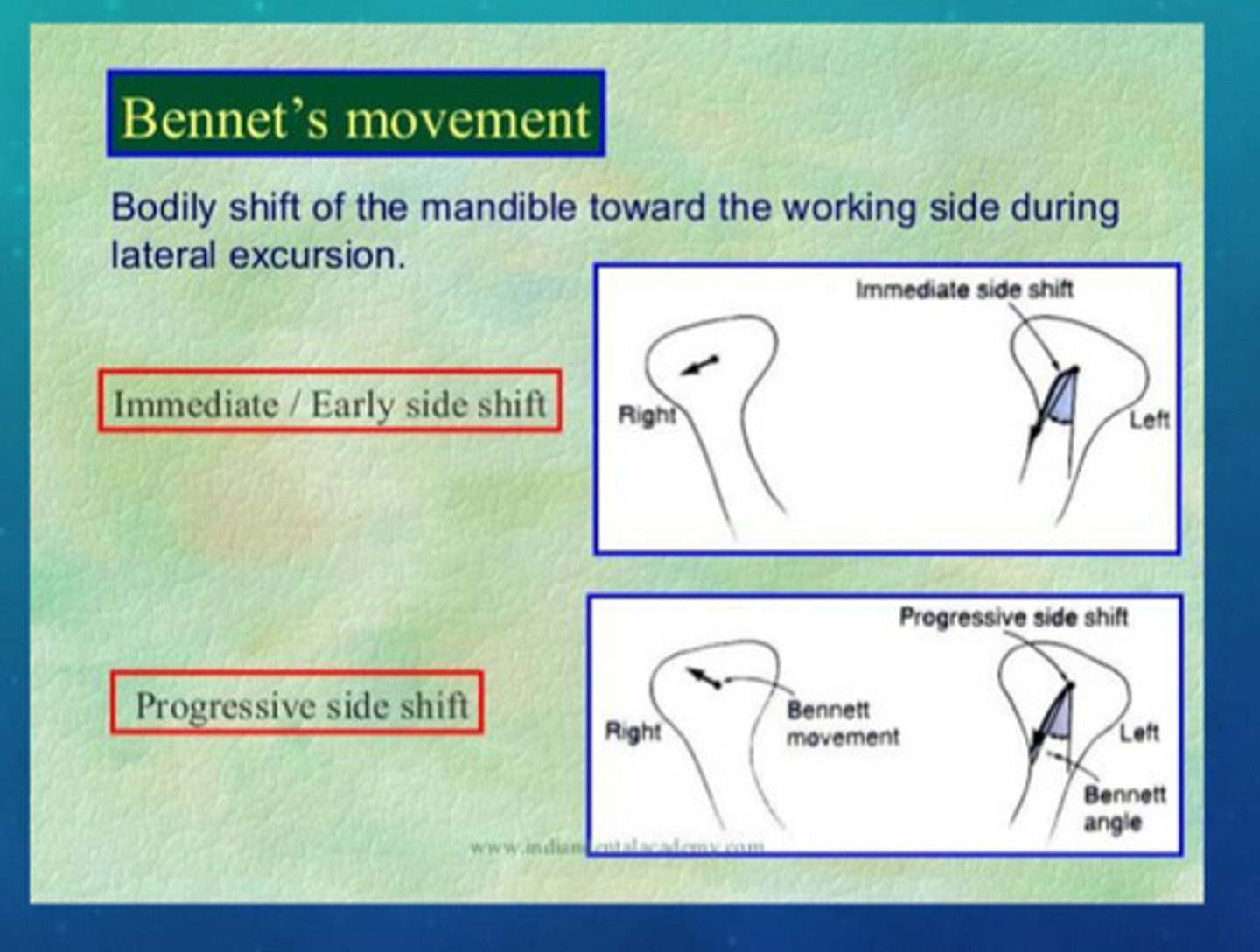
what is bennett movement (immediate side shift)
the movement in which the mandible moves (less than 1mm) laterally prior to translation
bennett movement (immediate side shift) results in _______ excursive interferences
greater
with more bennett movement (immediate side shift), what is required?
greater lingual concavity
in bennett movement (immediate side shift), retrusive movement ______ effects but requires ____ lingual concavity
accentuates; less
in bennett movement (immediate side shift), protrusive movement ______ effects but requires _____ lingual concavity
mitigates; more
the panadent semi adjustable articular has no immediate side shift, but has a preprogrammed progressive side shift; what is the preprogrammed measurements
0.5 medial shift for every 3mm protrusive movement
examples of immediate and progressive side shifts
more explanation of bennett's movement
what things of cusp morphology affect the frontal determinants of occlusion
1) cusp height
2) cusp M-D placement
what things of fossa morphology affect the frontal determinants of occlusion
fossa width
what are the 4 frontal determinants of occlusion
1) AP proximity to condyle (ex: premolar vs molar)
2) ML proximity to condyle (ex: wide vs narrow arch)
3) intercondylar distance
4) bennett movement (side shift: laterotrusive movement, latero-surtrusive movement which is upward, and latero-detrusive movement which is downward)
excursive movements in the frontal plane will affect the morphology of which cusps
non-functional cusps
the occlusal determinants of the frontal plane will affect which movements
the excursive movements
in order to compensate for the occlusal interferences in bennett movement, the teeth need what?
shorter cusps and broader fossa
bennett movements
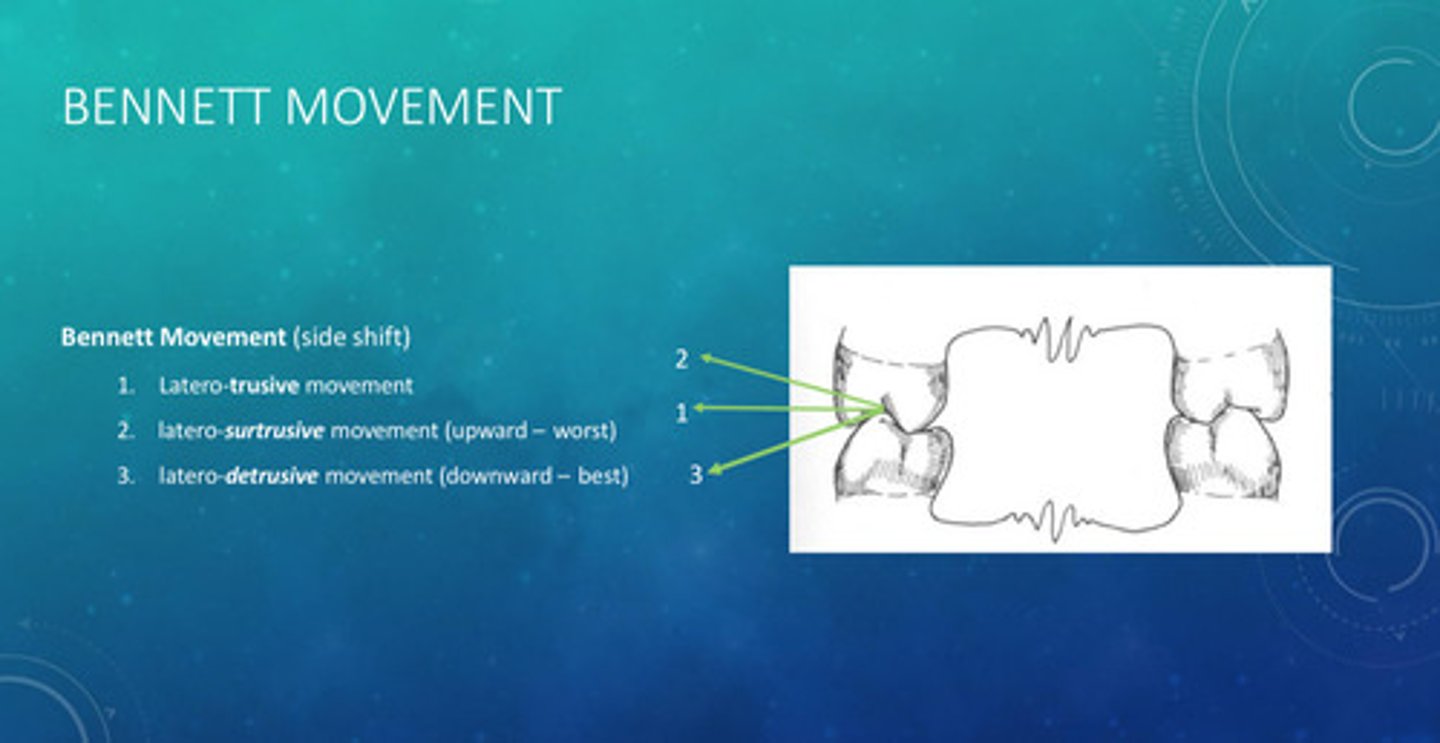
bennett movement in the vertical plane are directly related to ________ movement before what?
immediate movement before translation; the mandible will not disclude in a vertical direction, therefore will result in occlusal interferences before the teeth separate