Biology - carbohydrates + polymers + lipids
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topic one - carbohydrates + polymers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
How is water a polar molecule? What does this mean it can do?
It is charged because there is an uneven distribution of electrons. O is delta negative because there are unbonded electrons in the atom, H is delta positive because the bonded electrons are concentrated on one side.
This means water can form hydrogen bonds
Fill in the gaps
Water has a very high ________ ______ _________ this means lots of energy is needed to change the _____. When heated heat energy goes towards _________ or breaking __________ ______ rather than increasing the molecule’s __________ _______ so water act as a ______ against rapid _______ change. This makes it an ideal _______ for __________ ____________.
Water has a very high specific heat capacity this means lots of energy is needed to change the temperature. When heated heat energy goes towards weakening or breaking hydrogen bonds rather than increasing the molecule’s kinetic energy so water act as a buffer against rapid temperature change. This makes it an ideal habitat for aquatic organisms.
What are the benefits of water having a high specific latent heat of vaporisation?
It means a large amount of energy is needed to evaporate the water so organisms can cool down without losing lots of water. E.g. sweating - heat energy used to evaporate water from surface of the skin cooling the body down.
How is ice still beneficial.
Ice is less dense than water so it floats and can be a habitat for a number of organisms. Ice also insulate the water below preventing it from freezing so organisms can still live in the water.
Why is water a good solvent?
A lot of important substances are ionic, so because water is dipolar, one end will be attracted to the negative ion and the other will be attracted to the positive ion so the ions will be completely surrounded in the water - they’ll dissolve.
What does cohesive and adhesive mean?
Cohesion - attraction between water molecules of the same type (due to hydrogen bonds) because water is dipolar it is very cohesive. Adhesion - the ability of water to stick to other surfaces (e.g. water allows columns of water to travel up xylem tube)
What are the benefits of water being an excellent solvent?
Pro/Eukaryotic cells contain a large amount of dissolved substances e.g. chemical involved in metabolic reactions and enzymes needed to carry out reactions (proteins, glucose, NaCl, urea), Bodies of water also contain dissolved oxygen used by organism living in water to carry out respiration.
What property of water means it can transport substances e.g blood plasma
The fact that it is a good solvent
What property does cohesion give to water molecules and what is the benefit of this?
It causes surface tension - allows the surface of water to act as a habitat - pond skaters.
What are examples of water being useful in metabolic reactions?
Hydrolysis, photosynthesis. water produced in: condensation reactions aerobic respiration
What is a polymer
A pattern of repeating units made up of many identical monomers
What is a monomer
A small repeating unit
Give one example of a biologically important polymer other than starch or protein
DNA
What is glucose and what is its structure?
A hexose monosaccharide - contains 6 carbon atoms
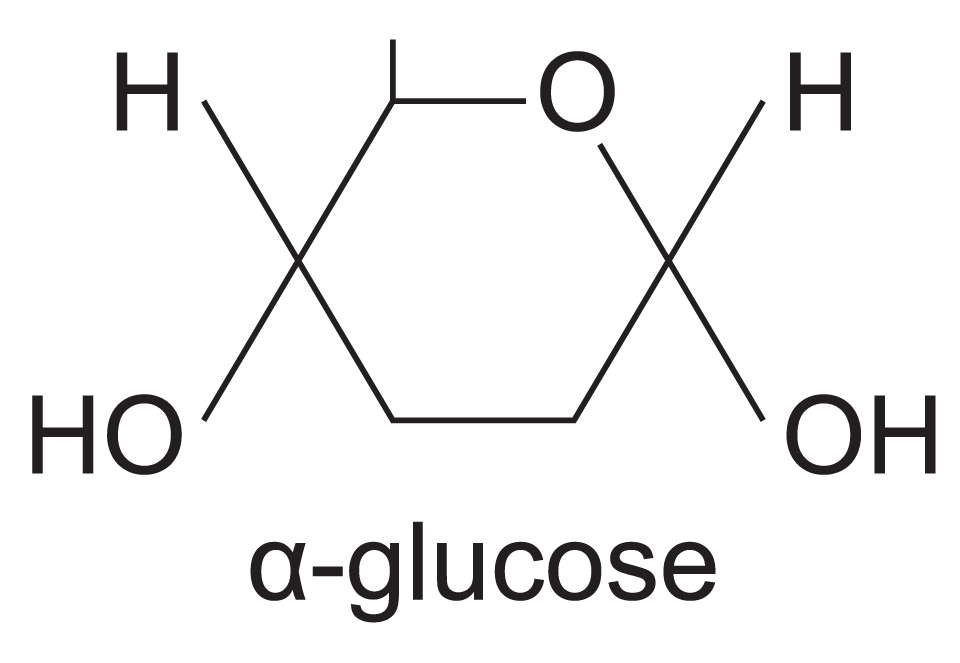
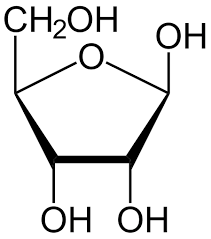
What is ribose and what is its structure?
A pentose monosaccharide (contains 5 carbon atoms)
What is the formulas for:
Glucose
ribose
Glucose - C6H12O6
Ribose - C5H10O5
why are monosaccharides soluble in water?
Because they have a large number of OH groups - hydroxyl groups - (which are polar) and can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules - hydrophillic
What is alpha glucose
An isomer of glucose that can bond together to form starch or glycogen
What does alpha glucose look like?
H on top. Hydroxyl below the ring.
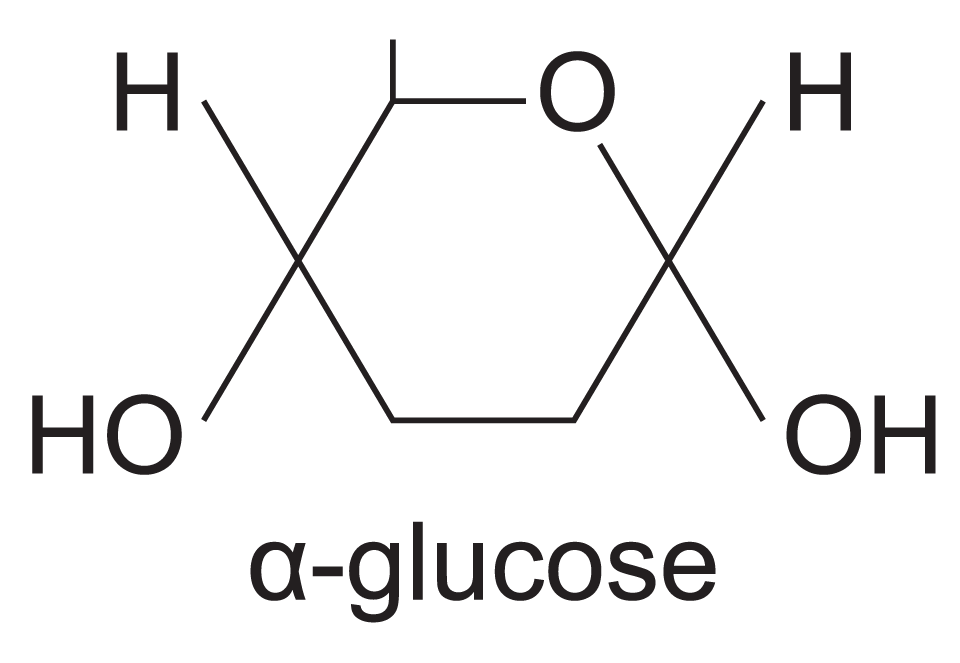
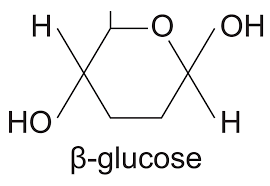
What is beta glucose
An isomer of glucose that can bond together to form starch or protein
What does beta glucose look like?
H on bottom. Hydroxyl above the ring.
What is the same about both isomers of glucose
Alpha and beta: both bonded to H atom and OH (hydroxyl) group.
What is a glycosidic bond?
Covalent chemical bond - It forms by a condensation reaction. One hydrogen and one hydroxyl group forms water.
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
How is this done in cells?
If water added to disaccharides we can break the glycosidic bonds - converting back to original monosaccharides.
Done in cells by enzymes.
What are three monosaccharides to learn
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
What is Maltose
Is it reducing or non - reducing?
A disaccharide with two alpha glucose molecules 1,4 glycosidic bond.
Reducing
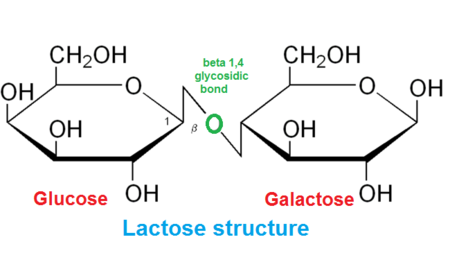
What is Lactose
Is it reducing or non - reducing?
A disaccharide made up of glucose and galactose (1,4) glycosidic bond
Reducing
What is Sucrose
Is it reducing or non - reducing?
A disaccharide made up pf glucose and fructose
Non - reducing
What is the problem with glucose’s solubility?
What is the solution to this?
if cells contained large amounts of dissolved glucose then it can cause water to enter the cells by osmosis.
So plants cells can store glucose as starch - which can be found in starch grains
What is starch?
A polysaccharide which consists of two molecules - amylose and amylopectin
What is amylose?
Unbranched polymer of alpha glucose joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds
What does the structure of amylose look like
The amylose molecule twists into a compact helix with hydrogen bonds forming between glucose molecules along the chain. This structure helps make starch a compact molecule
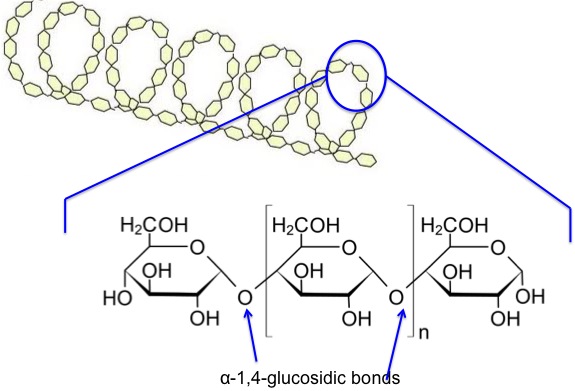
How is the helix of amylose held in place?
Is amylose soluble (answer with reference to amylopectin)
With hydrogen bonds
No it is not soluble, second most soluble to amylopectin
What is amylopectin?
A branched polymer of alpha glucose joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds, there are branches every 25,30 glucose molecule
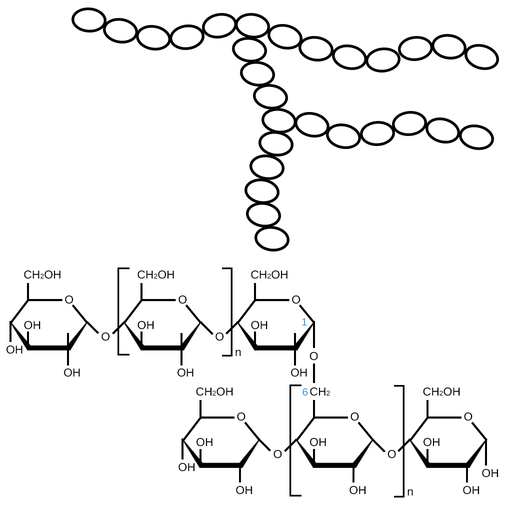
How is a branch bonded to amylopectin?
Joined to main chain by glycosidic bonds =, bond between carbon 1 of alpha glucose and carbon 6 of alpha glucose - 1,6 glycosidic bond
Is starch soluble in water
No
Can amylose and amylopectin diffuse out of cell and why
No because they are polymers so they are too big to diffuse through cell membrane.
What does a plant cell do when the cell needs glucose?
Enzymes break glycosidic bonds in starch - hydrolysis.
The enzymes act as the ends of the moelcules amylopectin has many branches so many ends so enzymes can break starch down rapidly.
Describe and explain features of starch that make it a good storage molecule (E)
It is in soluble in water so it doesn’t affect water potential
It is branched/coiled so makes the molecule compact/helix can fit many molecules in a small area
Branched ends for faster break down
large molecule so can’t cross cell membrane
Explain one way in which starch molecules are adapted for their function in plant cells. (E)
Insoluble so don’t affect water potential
Helical so are compact
Large molecules so cannot leave the cell
What is glycogen?
Animals glucose storage molecule
What is glycogen - strucure
A polymer of alpha glucose which is joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds. Glycogen also contains lots branches joined by 1,6 glycosidic bonds.
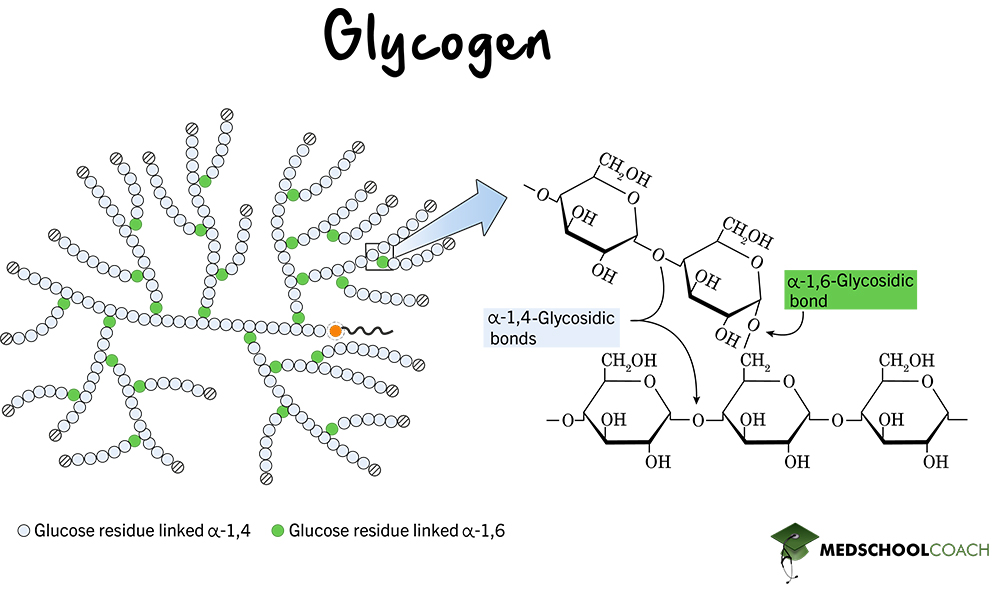
How is glycogen adapted for its role
It has many branches which make it a compact molecule, because it has a large number of branches it has lots of free ends so enzymes can convert glycogen back to glucose very rapidly. This is important as animals often have a high rate of respiration and energy needs can change rapidly.
What features of glycogen make it an ideal glucose storage molecule in animal cells?
it is insoluble in water so will not draw water into cells by osmosis
It is a large molecule so cannot diffuse out of a cell
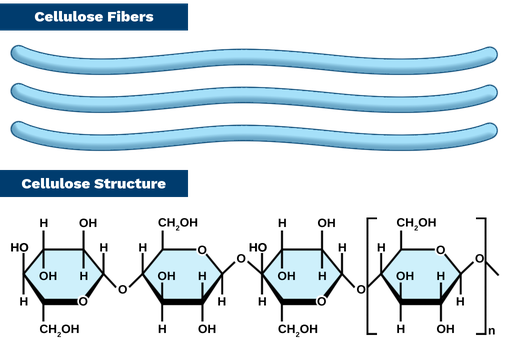
What is cellulose a polymer of
Beta glucose
How do beta glucose monomers bond
OH is above the ring so to form 1,4 glycosidic bond hydroxyl groups point in different directions. So when molecules of cellulose formed, every second beta glucose molecule flips.
True or false: cellulose is a branched polysaccharide
False
Fill in the gaps
As cellulose forms a straight _______ without any branches, this allows cellulose molecules to get _____ together. ___________ _______ can form between neighbouring chains. Because many _____________ ______ form this makes cellulose extremely ______.
As cellulose forms a straight chain without any branches, this allows cellulose molecules to get close together. Hydrogen bonds can form between neighbouring chains. Because many hydrogen bonds form this makes cellulose extremely strong.
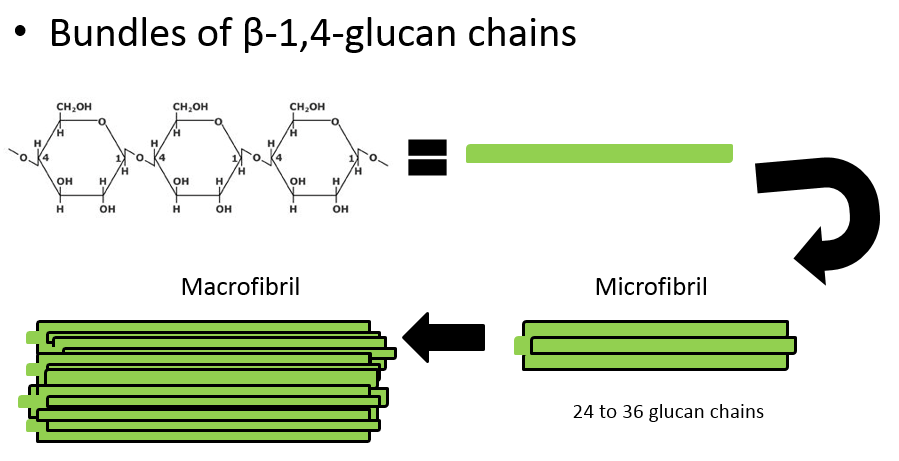
What is made when cellulose chains group together?
Microfibrils
What is made when microfibrils group together
Macrofibrill
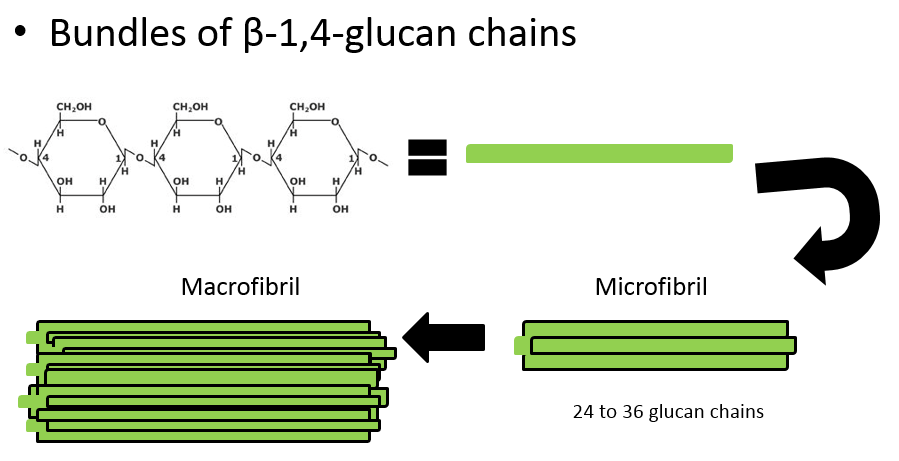
What is made when macrofibrils group together
Cellulose fibres
What does cellulose fibres form?
The cell wall in plants
How does cellulose being very strong and permeable help the cell?
Under normal conditions plants cells contain a lot of water as water moves in by osmosis plant cells contents push outwards against cell wall but the strength of the cellulose means it can resist the outwards pressure due to the cell’s contents preventing the plant cell from bursting.
What does it mean if a plant cell is turgid? What feature do turgid plant cells give plants?
When it is full of water
Turgid plant cells make the plant upright
Explain how cellulose molecules are adapted for their function in plant cells (E)
They have long and straight chains
They become linked together by many hydrogen bonds to form fibrils
They provide strength to the cell wall
What are the polysaccharides to learn?
Starch - amylose and amylopectin
Glycogen
Cellulose
Describe the structure of glycogen
Polysaccharide of alpha glucose
branched structure
What two categories can sugars be divided into?
Reducing sugars
non reducing sugars
True all false all mono and di saccharides are reducing sugars
False
all monosaccharides are reducing sugars
some disaccharides are reducing sugars - maltose and lactose
What is a reducing sugar
One that reduces another molecule and oxidised itself
Which disaccharide is a non-reducing sugar
Sucrose
How would you test for reducing sugars?
Grind food with distilled water + filter away solid food particles
Place 3cm3 of food solution in boiling tube + add 3cm3 of benidicts solution
Place boiling tube in beaker of water + leave for 5 mins
How could you tell if something had reducing sugars - from practical
Benidict’s solution contains copper ions Cu2+ which makes the solution blue. If reducing sugar is present this adds an electron to the Cu2+ ion to form a Cu1+ which is a red precipitate.
What do the colours mean in the benidicts test
Small amount of reducing sugar - green
Higher amount - yellow
Higher amount - orange
Lot of reducing sugar - brick red
What are the limitations of the benidicts test
It only gives a very approximate amount of reducing sugar because it only shows a narrow range of colour changes and all humans perceive colour differently. So it is semi-quantitative
How would you test for non reducing sugars if they can’t be tested directly? (not method)
Break glycosidic bonds releasing monosaccharides because all monosaccharides reducing sugars they can be tested using benidicts
How do you test for non - reducing sugars
check if solution contains reducing sugars - carry out benidicts test + note any colour change that takes place.
take fresh boiling tube + add 3cm3 of unknown solution
then add 3cm3 HCl and gently boil solution in water bath for 5 mins
If non - reducing sugar present then acid hydrolyses glycosidic bonds releasing monosaccharides
next add 3cm3 of dilute alkali e.g. sodium hydroxide solution and use pH paper to check solution is alkali - because benidicts test doesn’t happen under acid conditions
Add 3cm3 of benidicts solution and heat in boiling water for 5 mins and note any colour change.
Reducing and non - reducing test what is present
if 1st green and 2nd red
If 1st blue and 2nd orange
If 1st red 2nd not possible
both reducing and non reducing sugar present
no reducing sugar present, non - reducing sugar present
large amount of reducing sugar, non-reducing sugar test not possible because colour change would not be seen past red.
What groups do reducing sugars have
Free aldehyde or ketone groups
Explain how the structures of amylopectin and glycogen make them suitable for storing energy. (E) (3)
Branched therefore can be rapidly hydrolysed to release glucose (1)
Compact so more energy/glucose can be stored (1)
Insoluble so does not affect osmosis (1)
Molecules too large to diffuse across cell surface membrane (1)
What is an organic molecule?
A molecule that contains a carbon-carbon bond or a carbon-hydrogen bond
What is a lipid?
and what are the two types of lipid?
An organic molecule which is a large complex molecule (macromelecule)
Triglycerides and Phosolipids
Why are lipids not polymers?
Because each unit is not a monomer, because it is a long complex molecule but doesn’t have units you can break it down into.
What are triglycerides?
One of the two types of fat which is a source of energy found in oily foods, butter and certain facts.
What are phospholipids?
One of the two types of fat which have a structural role in building up cell membranes - they are the main component in cell membranes.
What is the structure of a triglyceride?
Formed from one molecule of glycerol and 3 fatty acids
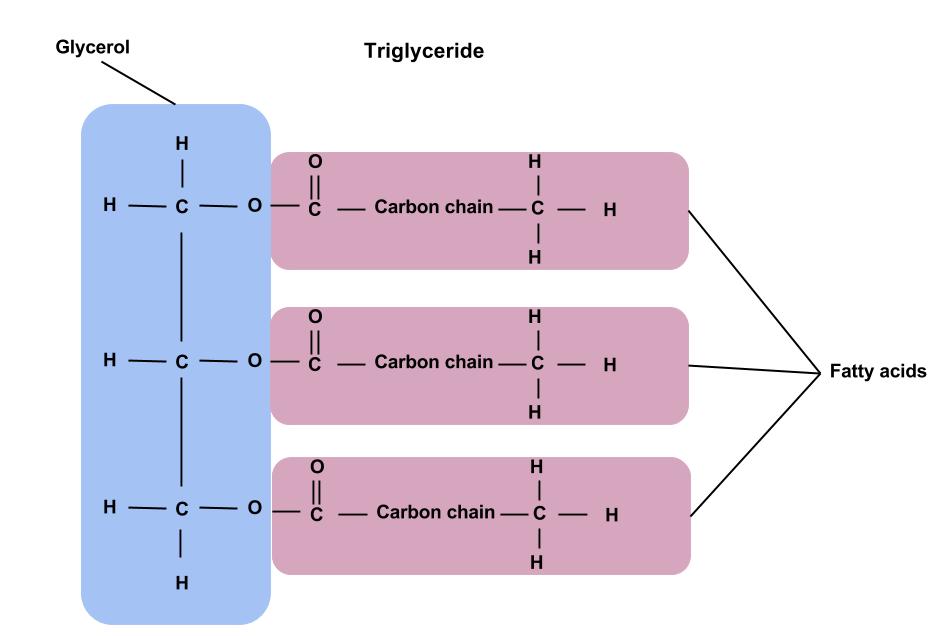
What is glycerol?
An organic alcohol which has 3 hydroxyl (-OH) groups
3 carbons long and 3 hydroxyl groups
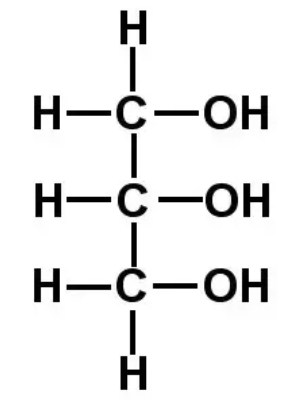
What are fatty acids?
why are fatty acids not polymers?
Organic acids (which means they can lower the pH of things) they have a carboxyl (-COOH) group joined to a hydrocarbon tail - they are a type of carboxylic acid.
Not a polymer because it doesn’t have the same units repeating itself.
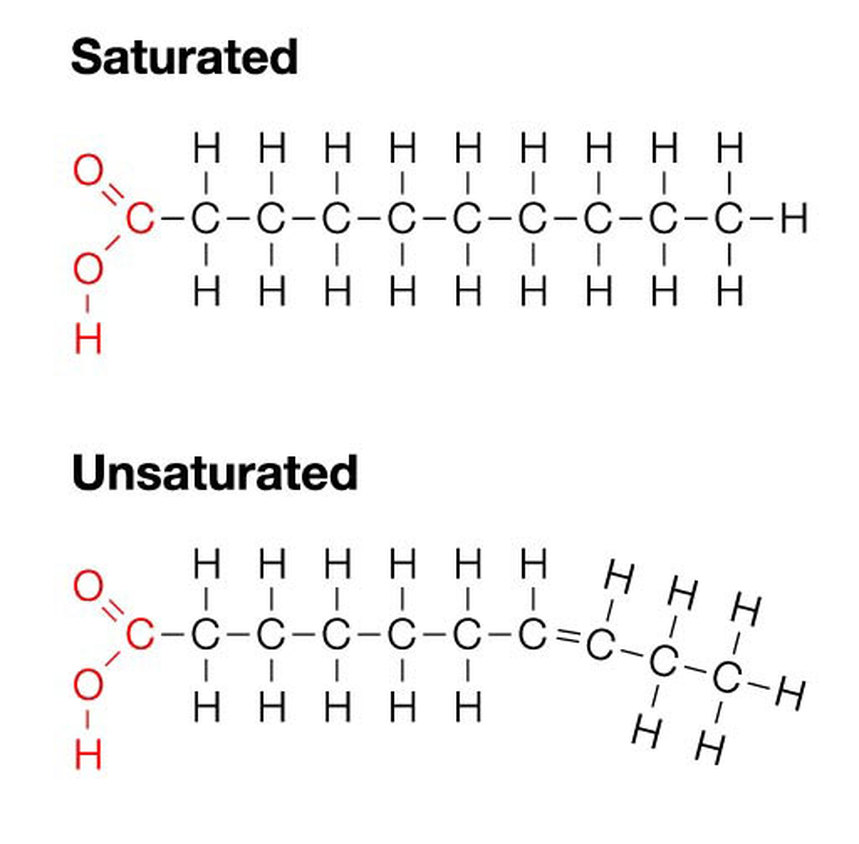
How can you make it easier to write out the hydrocarbon tail on fatty acids?
Replace the hydrocarbon tail with the letter ‘R’
How does the glycerol molecule join to 3 fatty acids?
It is a covalent - ester bond formed by condensation reaction between -OH group of carboxylic acid and -OH group of an alcohol.
How many ester bonds and so molecules of water does a triglyceride contain?
3
How can triglycerides be broken down into glycerol and fatty acids?
With 3 hydrolysis reactions which requires 3 molecules of water.
What is a phosphate ester bond
The joining of a phosphate group onto glycerol in a condensation reaction between hydroxyl group (-OH)
What is the structure of a phosopholipid?
Phosphate group and glycerol molecule is the head and the 2 fatty acid chains are the tails.
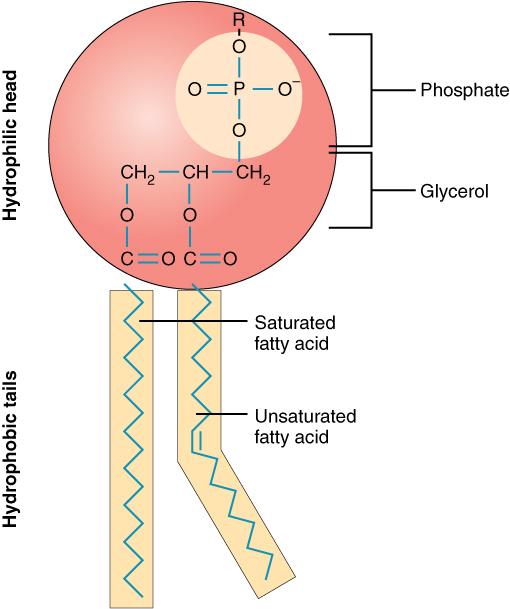
True or false a phospholipid is a polar molecule
True
What happens when a phospholipid is surrounded by water?
The hydrogen ions (found in the phosphate group) dissociate form the phosphoric acid
What happens when the hydrogen ions in a phospholipid dissociate from the phosphoric acid
they give off hydrogen ions so the phosphate group now has a negative charge
What does the phosphate group being negatively charged mean?
The phospholipid is hydrophilic so it is attracted to water due to having a charge
Why are the fatty acid tails in the phospholipid hydrophobic - a molecule repelled by water
Because they are non polar so they don’t have a charge and a hydrophobic molecule is a molecule that is repelled by water due to not having a charge
What is unique about the behaviour of phospholipids in water?
They have hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends so phospholipids may form a layer on the surface of the water, so the hydrophilic heads face the water and the hydrophobic tails face away form the water.
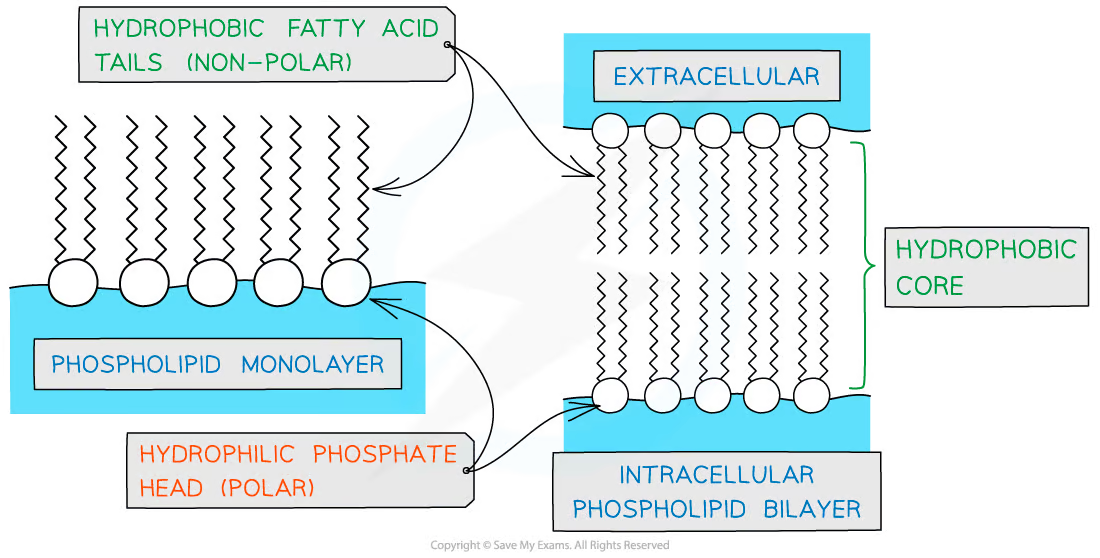
What is a micelle
A monolayer of phospholipids

What is a phospholipid bilayer?
Where the hydrophilic heads form 2 rows on the outside while the hydrophobic tails are sheltered in the middle.
There is an aqueous environment on either side.
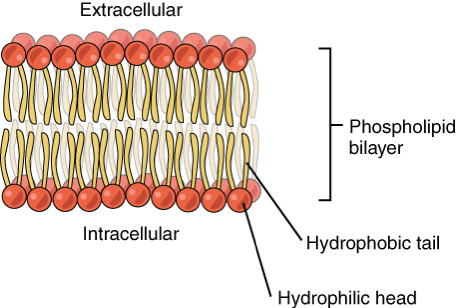
Complete the sentence:
The phospholipid bilayer is an integral part of all
Membranes in a cell (including organelle’s own membranes)
What about the phospholipid bilayer allows cells to become more fluid and change shape?
How are they still kept stable though?
The phospholipids can move past each other which keeps the membrane a fluid environment. Overall they are still attracted to each other but they can move around each other and dance closely and together meaning cells can become more fluid and change shape.
They will never expose their tails to the water so the membrane is kept stable and in the same general shape all the time.
What are the 2 ways the structure of the phospholipid bilayer allows for it to carry out its roles?
It is a barrier so it controls substances entering and exiting the cell.
Electrical insulation - it can prevent certain ions from leaving keeping ion and charge concentrations correct in and outside the membrane.
How does the structure of the phospholipid bilayer control electrical insulation?
The area in the middle is a non-aqueous environment because fatty acid tails almost force water to be excluded from the environment creating a barrier to charged molecules which are dissolved in water.
What are the molecules that can pass through a phospholipid bilayer?
only small, non-polar (not surrounded by water), molecules like O2 (to enter the cell when needed for respiration)and CO2 (to leave the cell as a waste product) can easily pass through the membrane
What is a membrane that controls what enters and leaves the cell called?
A partially permeable membrane
Why is it important to have a partially permeable cell membrane?
The cell’s contents - e.g. ions, concentration and solutes needs to be kept the same.
It needs to keep the two environments -inside and outside the cell- separate
Complete the sentance:
Partially permeability allow membranes to act as……
………An electrical insulator