chapter 13 - media violence
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
You observe Kris punch Laura in the nose and immediately you explain this as due to Kris having a very aggressive personality. You have just committed the
a. self-serving error
b. fundamental attribution error
c. consistency- consensus error
d. self-fulfilling prophecy
e. inconsistent information error
b. fundamental attribution error
What are some social influences?
Norms, conformity, and creates conflict
social influence: norms
Conventions, customs & laws that apply to a group’s behaviour
social influence: conformity
A change in attitude, behaviour or belief brought about by the real or imagined pressure from others
conflict
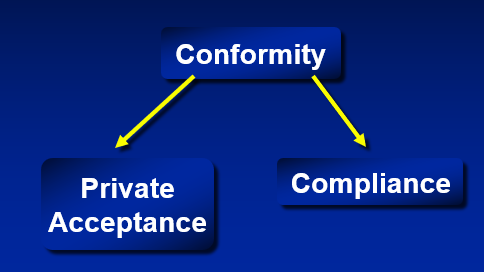
social influence flow chart - conformity
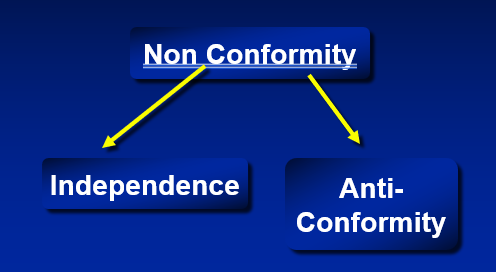
social influence flow chart - non-conformity
subtle influence: models
Our behaviour may be shaped by models, even in absence of direct intentional influence
subtle influence: response disinhibition
Model performs desired, but prohibited act
disinhibition refers to
a loss of control over one's behaviors, thoughts, or emotions, leading to actions or expressions that are inappropriate or socially unacceptable.
subtle influence: examples
crossing on red
media violence
Increase in suicides following 35 highly publicized suicides in 1950-1969 (Phillips, 1989)
200 after M. Monroe in 1962
Response Facilitation
Model performs “legal” behaviour... then we copy
e.g. - Yawning & head nodding
Candid Conformity
Trivial?
Wells & Petty (1980)
Conforming to group pressure
Informational Vs. Normative
Conforming to group pressure: Informational
Group gives information that individual can use for rational decision
Private Acceptance
Conforming to group pressure: Normative
Pressure to maintain group consensus... “don’t rock the boat”
Compliance
Asch's Conformity Studies
Solomon Asch conducted experiments in the 1950s to explore conformity in group settings. Participants were asked to match line lengths, but actors in the group purposely chose incorrect answers. Results showed that individuals often conformed to the group's wrong decision, highlighting the powerful influence of social pressure on behavior.
Compliance with Serious Requests
Milgram’s Studies
Subjects recruited by ads
“Teacher - Learner” Paradigm
Milgram’s Studies
Subject gives feedback with shock generator
Experimenter “prods” subject to continue
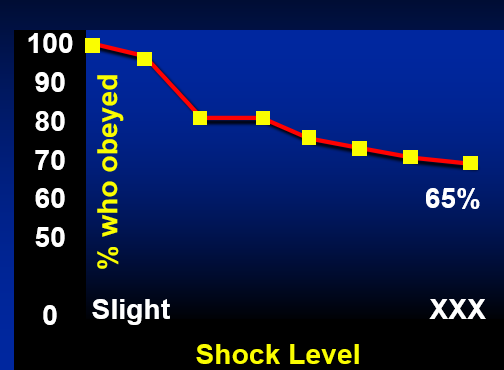
Psychiatrists predict 2% will complete the
shock series
Milgram’s Study of Obedience
What are factors are influencing obedience?
status, proximity, generality
factors influencing obedience: status
“Low” status setting 50% complete
factors influencing obedience: proximity
Authority figure
Proximity of Learner
Remote
Hear
See and hear
touch → 30% complete
factors influencing obedience: generality
certain subject? no
Lab only? no
Hofling et. al. (1966)
Rank & Jacobson (1977)
what are ways to counteracting obedience?
Personal Responsibility, disobedient models,
counteracting obedience: personal responsibility
Obedience drops dramatically
counteracting obedience: Disobedient Models
2 confederates refuse
Obedience drops to 10%
Television: by the age of
By the age of:
5 2 - 3 Hours per day
10 4 - 6 Hours per day
16 Witnessed more than 40,000 murders
18 More time watching TV than in school
Television
99% of households have at least one TV set
more than households with bathtub or telephone
On average, set is on 7 hours per day
Who watches more?
women, preschoolers, retired people
TV CONTENT: Barker & Ball (1969), Waters & Malamud (1975)
1. 8 out of 10 shows contain violence
2. Act of violence occurs every 16 minutes
3. Murder every 31 minutes
4. 93.5% of cartoons
5. "Good-Guys" as violent as "Bad-Guys"
6. Pain and suffering rarely shown
7. About 50% of killers do not suffer
8. Most people believe that there is to much violence
TV Images:
1. Violence more likely from minorities
2. Strangers should not be trusted
3. Whites do not get killed as often as nonwhites
4. Police are frequently violent
5. Violence and killing are painless
6. Violence often goes unpunished
7. Both good and bad people use violence
8. Violence is a successful means to an end
CBS (1980)
Prime Time: Average of 1.6 violent acts
6.4 acts per day
2,336 acts per year
Signorielli et al. (1982)
80% of all TV shows contain some violence
71% of prime time shows
94% of “children’s” weekend shows
Average of 5.2 violent acts per hour
Gerber (1993)
67% of Prime Time contains some kind of violence
National TV Violence Study (1997)
10,000 programs
60% contain violence
Parent’s Television Council (2009)
monitored prime time programming during “sweeps” (Feb. and May)
A total of 3929 acts of violence, average of 23.39 per hour
Parent’s Television Council (2013)
gun or bladed weapon every 3 min.
2017 → 61% of sweeps
Criminal Minds:
average of 52.8 acts of violence per episode ( 1 every 68 seconds )
Does TV violence cause aggression?
Does TV violence influence aggression?
Research Evidence
1. modelling studies
2. laboratory studies
3. long-term field studies
Modelling Studies: Bandura (1971)
Children can acquire new aggressive responses not previously at their disposal.
However, acquisition not equal to performance.
Lab Studies
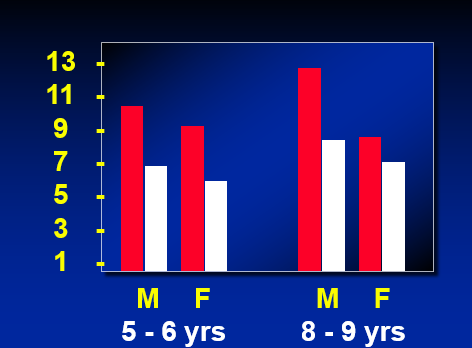
Libert & Baron (1972)
Kids (5-6, 8-9) watched either The Untouchables OR a track film
Then had opportunity to either help or hurt another child.
Time pressing Red "Hurt" button (y-axis)
red: violent
white: non-violent
Field Studies
Black & Bevan (1992)
Aggression scale to movie-goers before or after violent or nonviolent movie
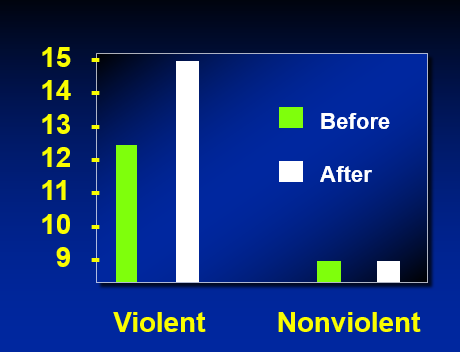
Long-Term Field Studies
Leyens et al. (1975) School boys exposed to steady diet of either aggressive or nonaggressive films.
Eron (1982) Three - year study with 748 children.
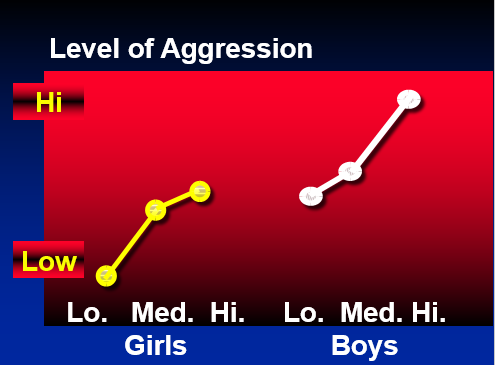
why do we get these media effects?
Social learning or modelling
Disinhibition
Desensitization to pain & aggression
Changes in the Brain
Wang et al. (2011)
fMRI before and after playing violent video game
Less activation in frontal lobe while completing emotional task… even 1 week after
Does TV violence cause aggression?
Does TV violence influence aggression?
maybe
definitely