Thermal Physics
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Molecular properties of solids:
A regular arrangement of all particles
Bonded together by electrostatic bonds
Vibrate in a fixed position
Not much kinetic energy compared to other states
Molecular properties of a liquid:
Heating up a solid causes the kinetic energy to break bonds
This allows molecules to move around and vibrate
Particle density may slightly decrease
More kinetic energy than a solid
Molecular properties of a gas:
Particle density decreases by a factor of 10 in each direction
Hence, they can take up the space of a container and be compressed
More free to move with lots of kinetic energy
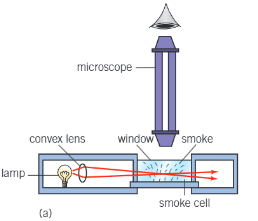
Brownian motion practical:
Particles of smoke are large enough to be seen under a microscope moving randomly
The random motion is caused by air molecules striking the smoke particles, of which are also in random motion
Triple point
On a pressure temperature graph, there exists a point where matter can be all 3 states
Can only exist in 1 temperature
Absolute zero
The temperature where a substance has minimum internal energy
Particles are theoretically stationary at this temperature
0K
Triple point of water (temperature)
0.01°C = 273.16K
Kelvin
Absolute temperature scale from absolute zero to the triple point of water
0K - 273.15K
0th law of thermodynamics
If two objects are in thermal equilibrium with a third, then all three are in thermal equilibrium
Internal energy formula:
The sum of all randomly distributed kinetic energy and potential energy in a system
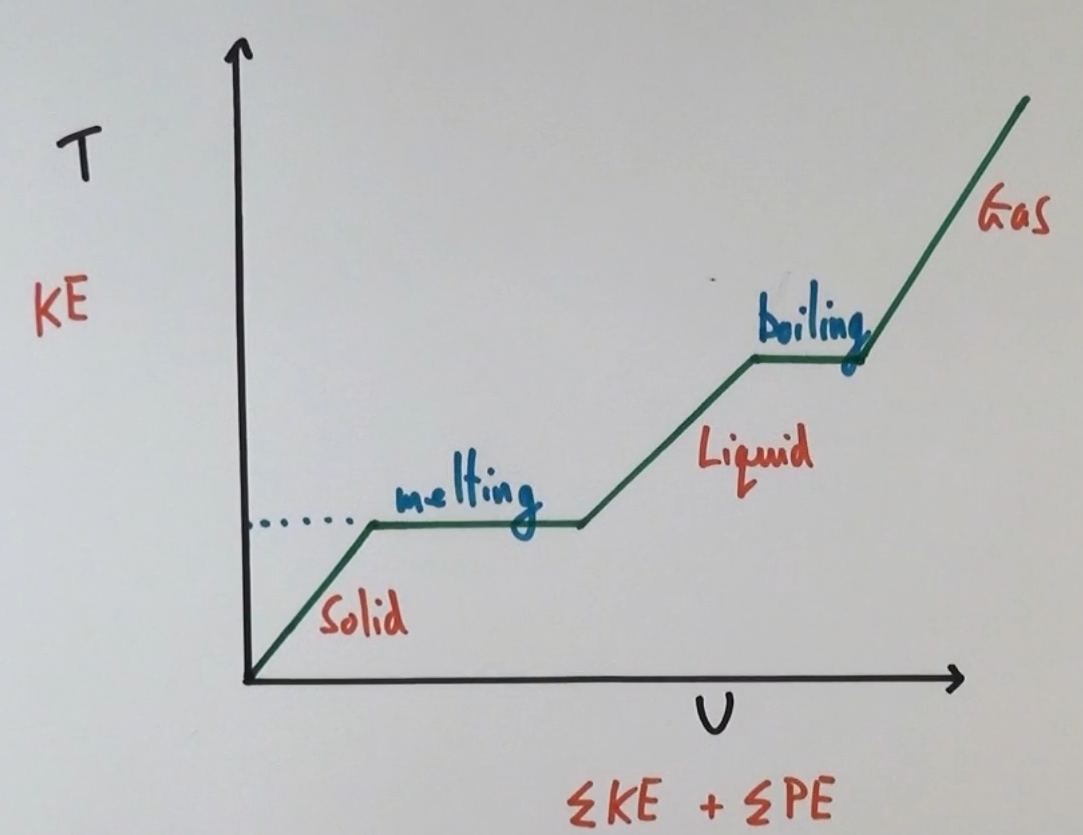
Phase change
When a substance changes state, a phase change occurs
The internal energy increases but the temperature stays constant
Temperature against potential energy graph
Specific heat capacity of a substance
The energy required per unit mass to change the temperature by 1K
Specific heat capacity equation:
c = E/(mΔθ) implies E = mcΔθ
c = specific heat capacity
E = energy supplied to the substance
Δθ = change in temperature
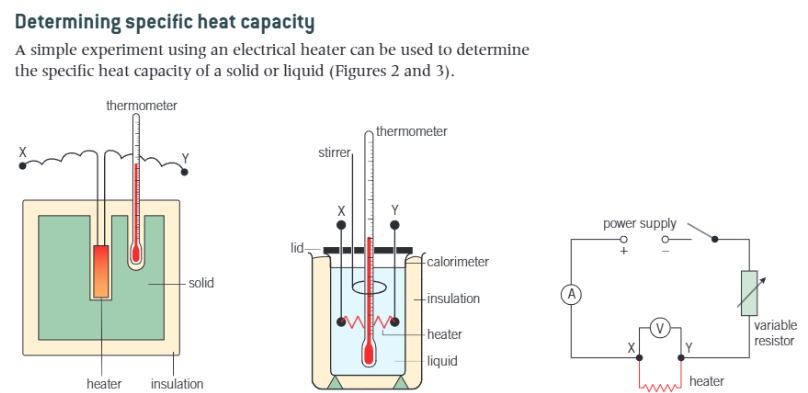
How can you determine the specific heat capacity of a substance?
Use c = IVt/(mΔθ)
Convert kelvin to celcius
K(x) = C(x) + 273.15
Which factors affect the time taken for two objects to reach thermal equilibrium?
The difference in temperature, area of contact and material.
Brownian motion
The random motion of particles suspended in a fluid
Describe the motion of smoke particles
Particles are always moving
Moving in random directions
In a jittery motion
Follows a zigzag path
Explain the motion of smoke particles
Air consists of a larger number of molecules which have a small mass compared to the smoke particles
They are continuously moving randomly, therefore causing elastic collisions
They have a range of speeds from 0 to high
What are some key features of a graph of temperature against time of a solid being heated up?
Goes through the origin
Linear
Higher gradient means lower specific heat capacity
What happens to the kinetic energy and potential energy as the temperature of a substance increase?
Only KE increases
What happens to the kinetic energy and potential energy as the substance changes state?
Only the potential energy increases
Latent heat of fusion
The energy required to change a solid to a liquid
Latent heats of vaporisation
The energy required to change a liquid into a gas
Compare the typical values of the SHL and SHV of a substance
SHF < SHV
Energy transfers of water being turned into steam, which is used to heat a coffee
Latent heat to condense the steam, energy lost by steam heat the coffee, energy gain by coffee