microbio clinical cases NOT FINISHED
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
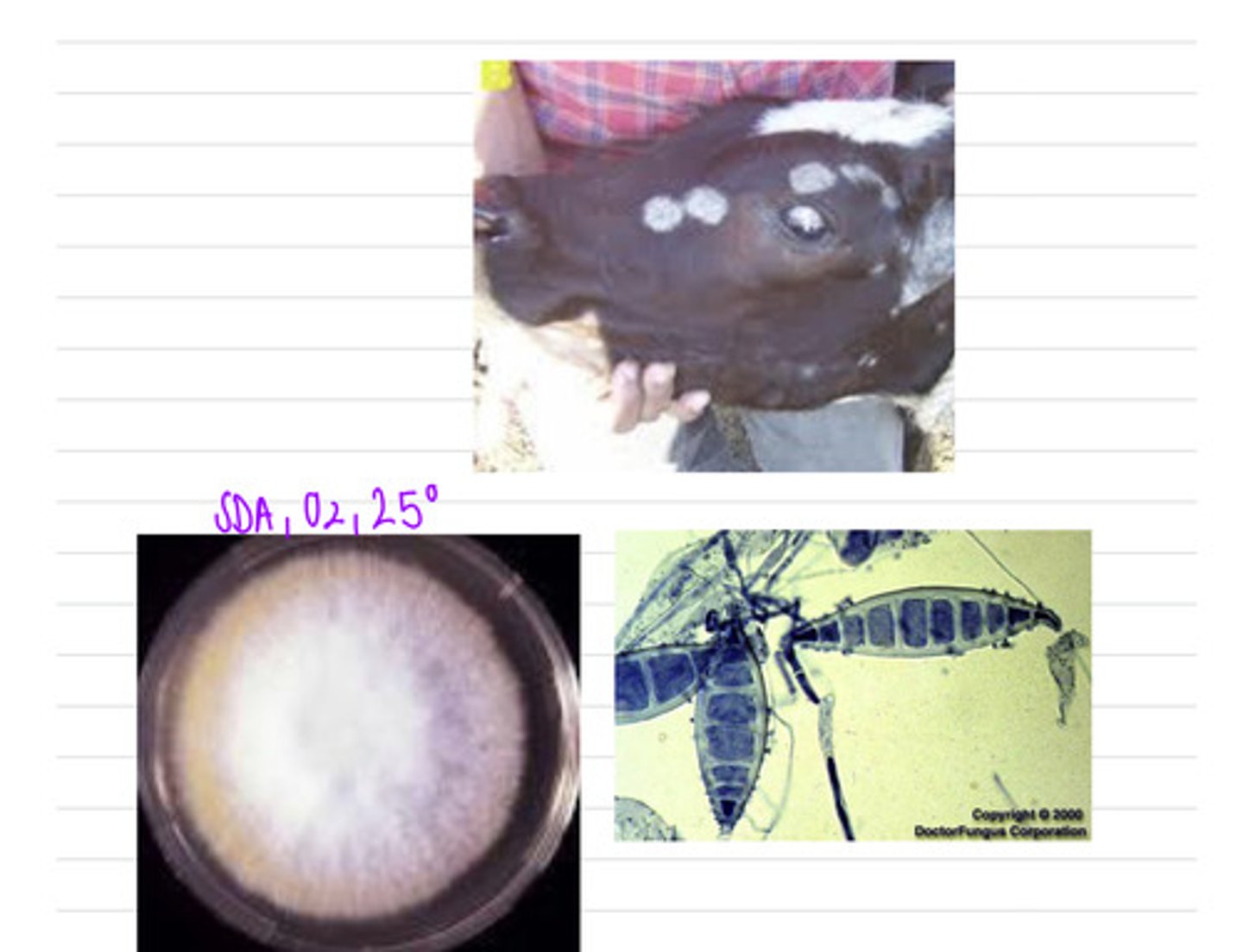
we could take a skin scraping. this cow has ringworm, caused by the species Microsporangium canis, a species of dermatophyte.
this cow is showing these cutaneous lesions on its face. after we take a sample, we grow the cells on SDA at 25 and also look under a microscope and see these results.
what sample should we take?
what is the diagnosis?
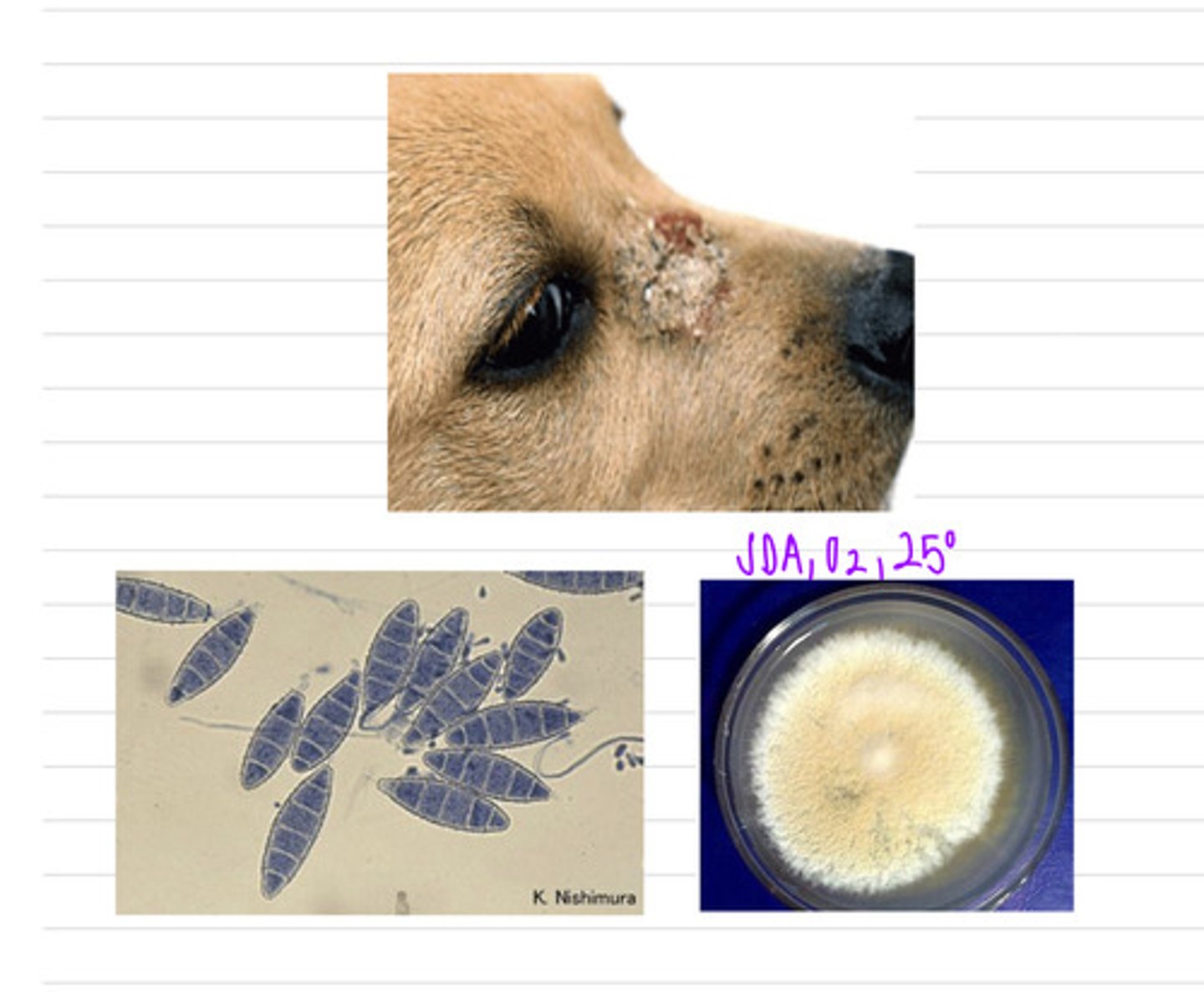
we could take a skin scraping. this dog has ringworm, caused by the species Microsporangium gypseum, a species of dermatophyte
this dog came into the vet with this facial lesion. we take a sample and isolate it on SDA at 25 degrees and see these microscopic results.
what sample should we take?
what is the diagnosis?
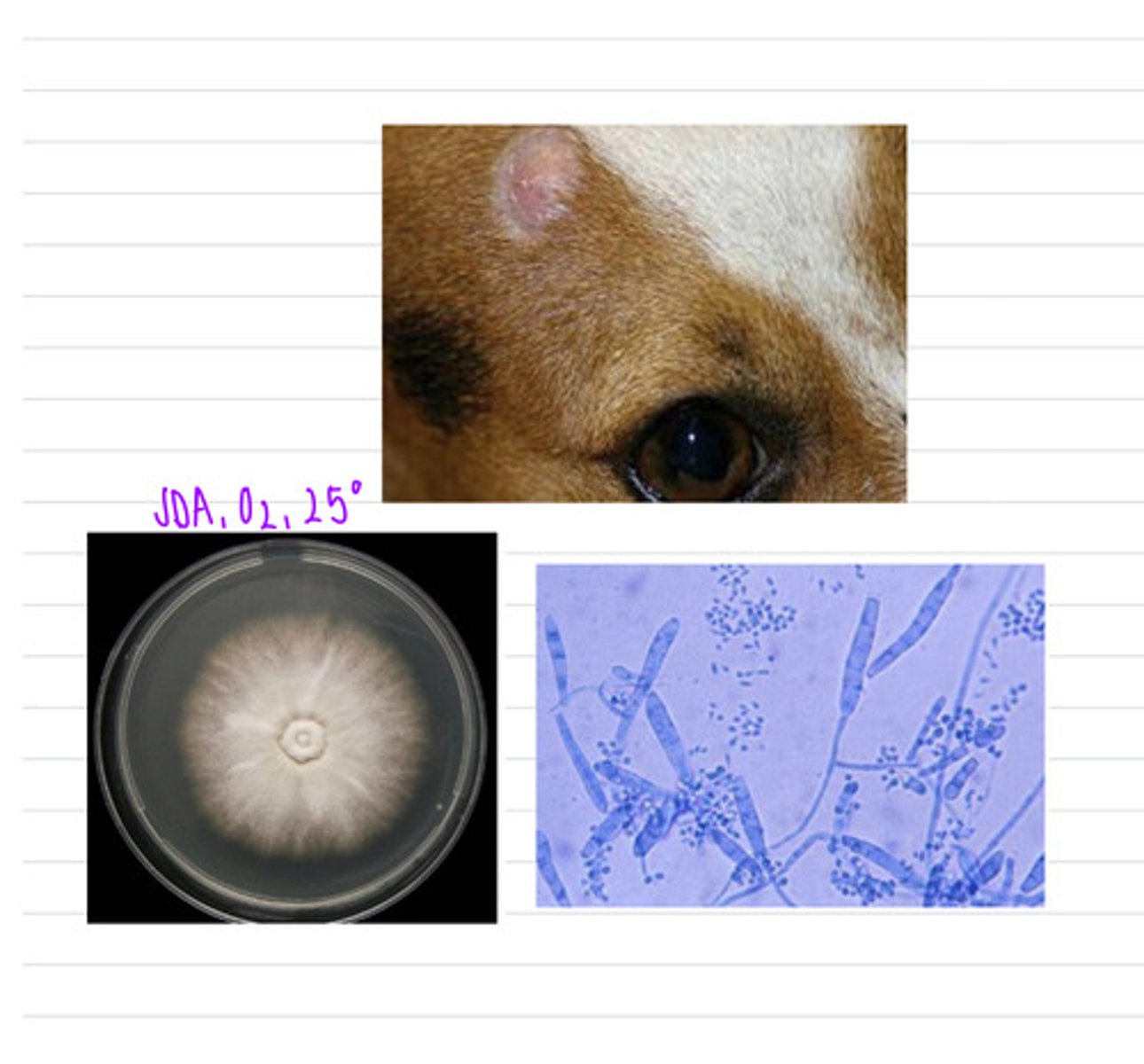
we could take a skin scraping. this dog has ringworm, caused by the species Microsporangium nanum, a species of dermatophyte
this horse came into the vet with these cutaneous lesions. we take a sample and isolate it on SDA at 25 degrees and see these microscopic results.
what sample should we take?
what is the diagnosis?
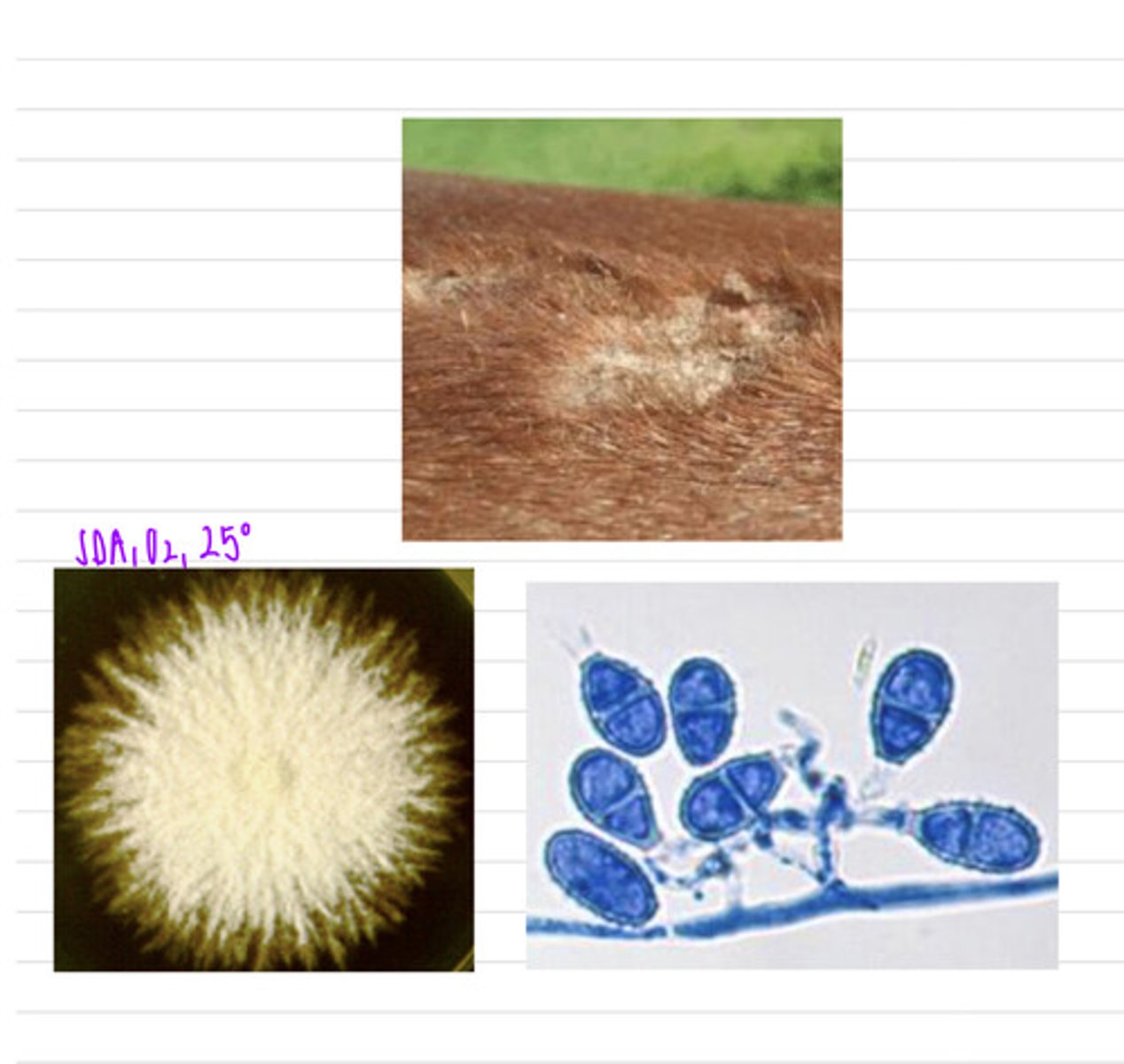

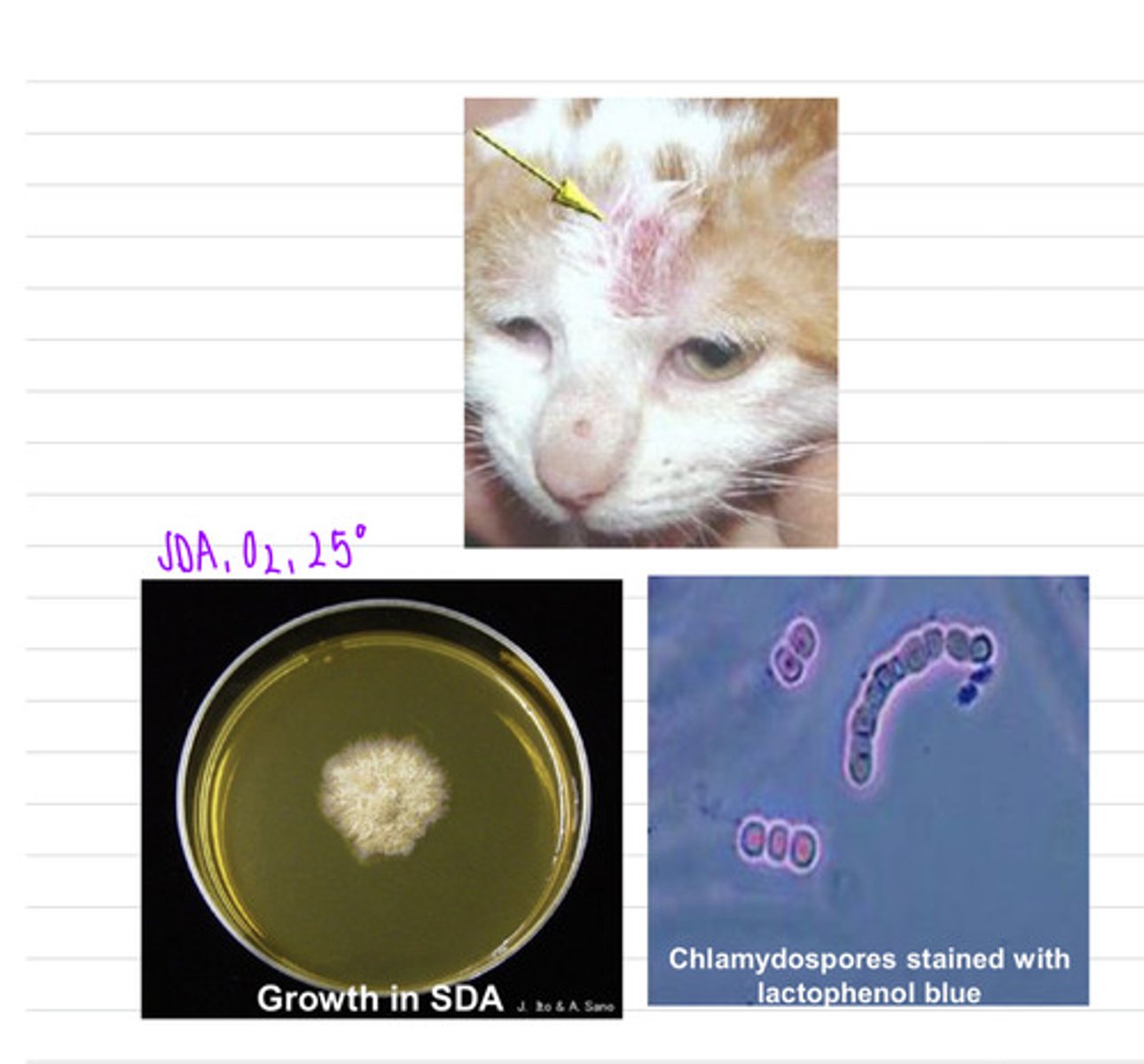
we could take a skin scraping. this dog has ringworm, caused by the species Microsporangium verrucosum, a species of dermatophyte
this cat came into the vet with this face lesion. we take a sample and isolate it on SDA at 25 degrees and see these microscopic results.
what sample should we take?
what is the diagnosis?
we could take a skin biopsy because it is subcutaneous . this dog has ringworm, caused by the species Microsporangium metagrophytes, a species of dermatophyte
this dog came into the vet with this face lesion. we take a sample and isolate it on SDA at 25 degrees and see these microscopic results.
what sample should we take?
what is the diagnosis?
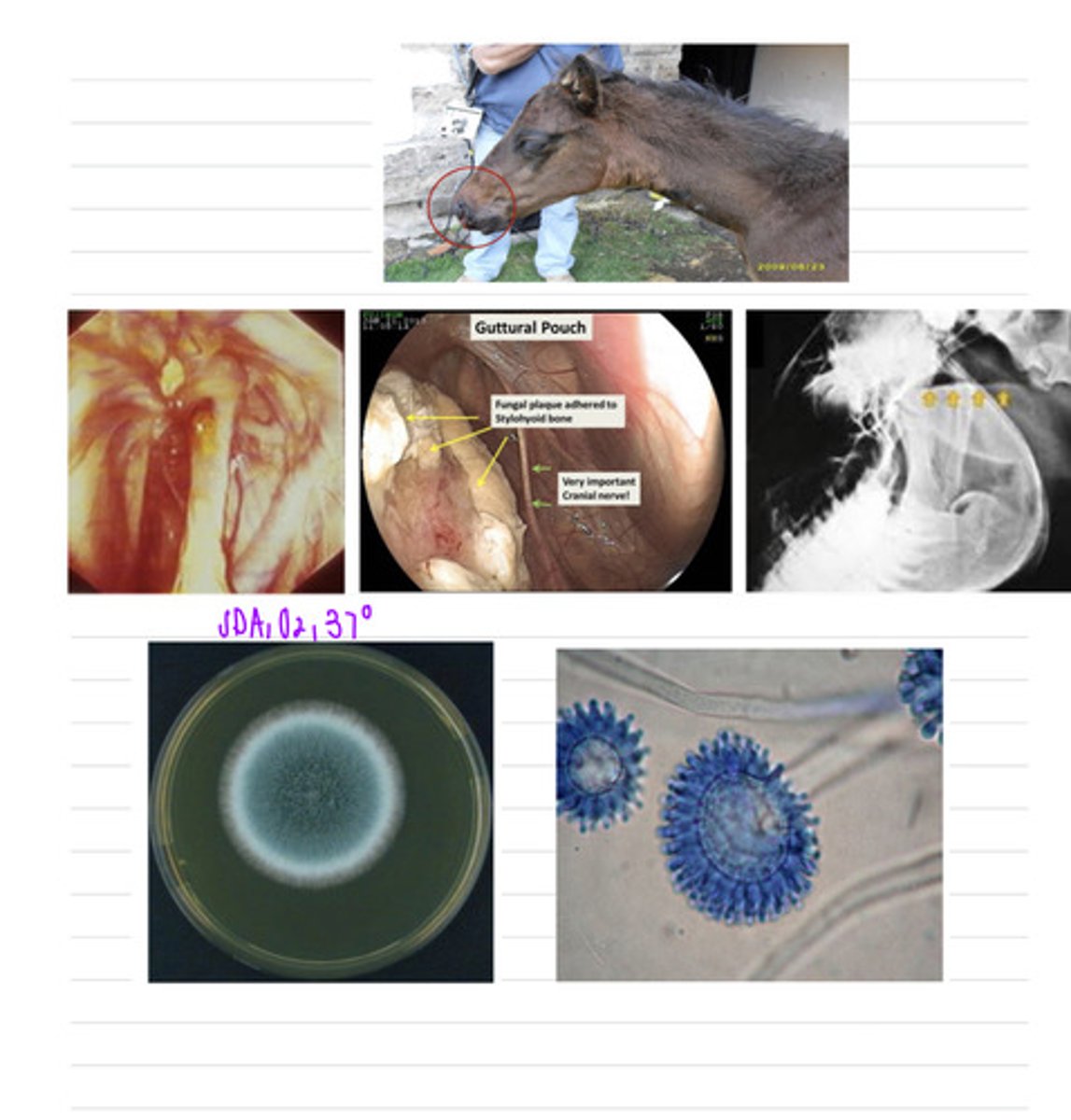
this horse has the disease guttural pouch mycosis, caused by the fungi Aspergillus fumigatus
this horse came into the vet showing epistaxis, dyspnea, and dysphagia. we take an Xray, an endoscopy, and stain a tissue sample with PAS. we take a biopsy and isolate it in SDA at 37 degrees.
what is the diagnosis?
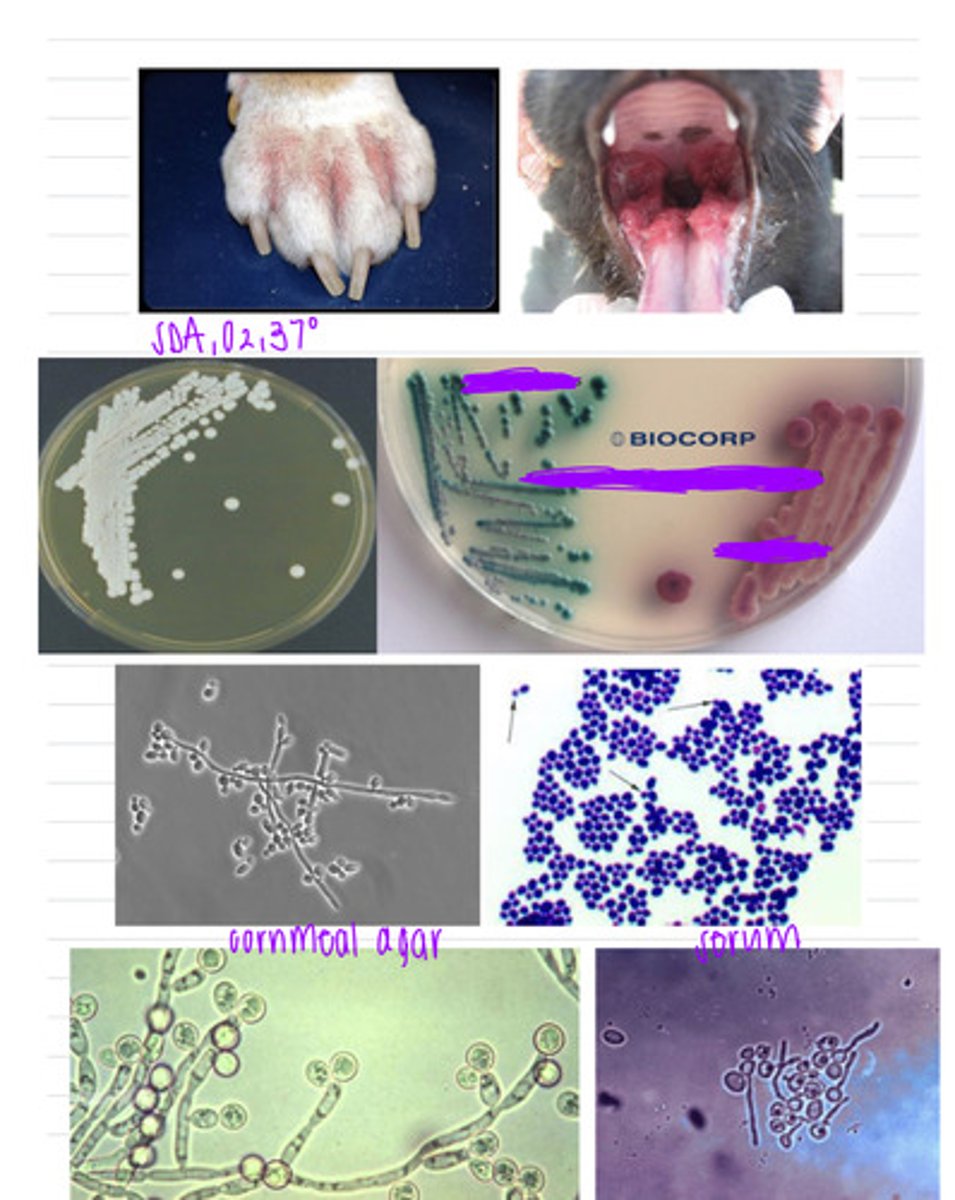
this dog was infected with Candida albicans and has oral candidiasis
this dog came into the vet with mucocutaneous lesions in its mouth. we isolate samples in SDA at 37 degrees, in a selective indicator media, in cornmeal agar, and in serum. we also look under a microscope. we see these results.
what is the diagnosis?
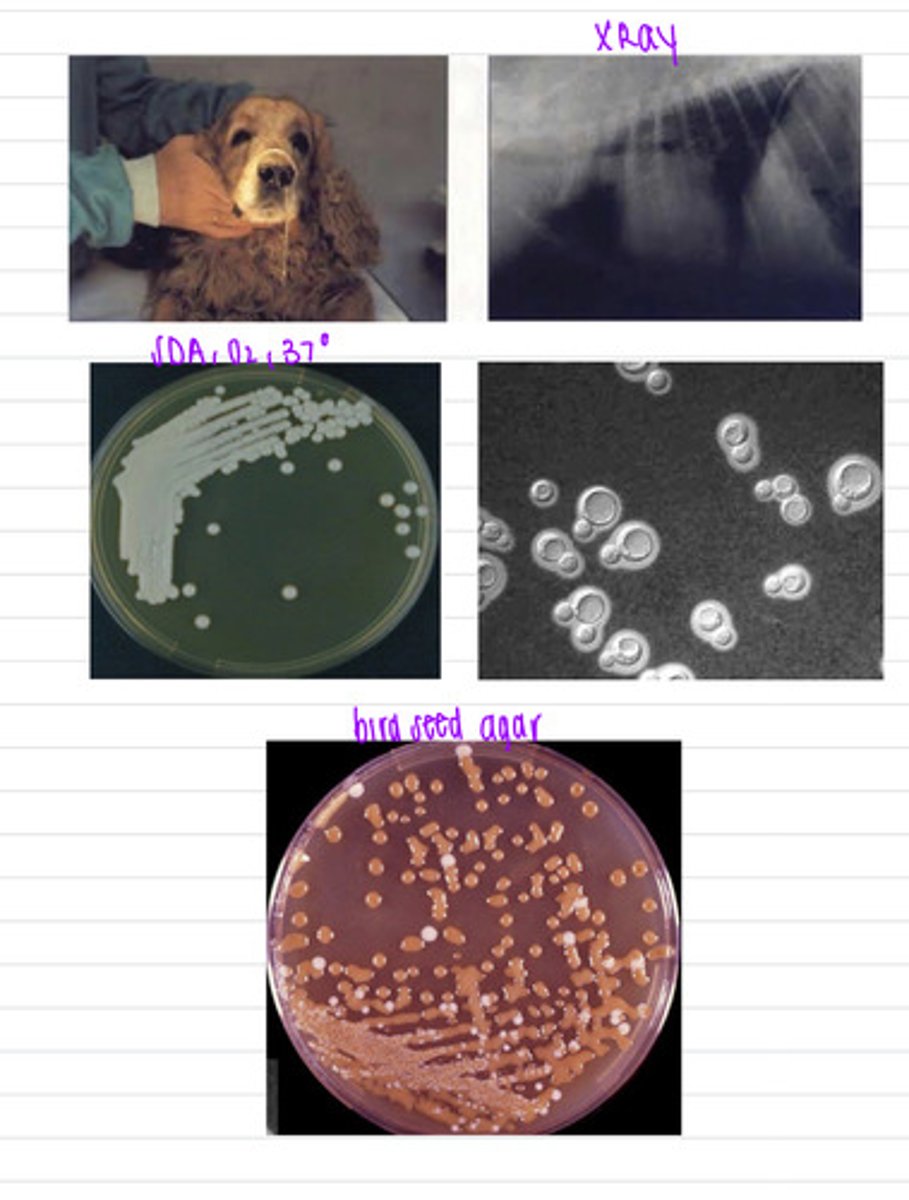
we should take a nose swab because the dog has nasal discharge. this dog was infected by Cryptococcus neoformans
this dog has neural and ocular signs and DIC. we isolate a sample at 37 degrees on SDA, and also on bird seed agar and take an Xray. these are the results.
what specimen should we take?
what is the diagnosis?
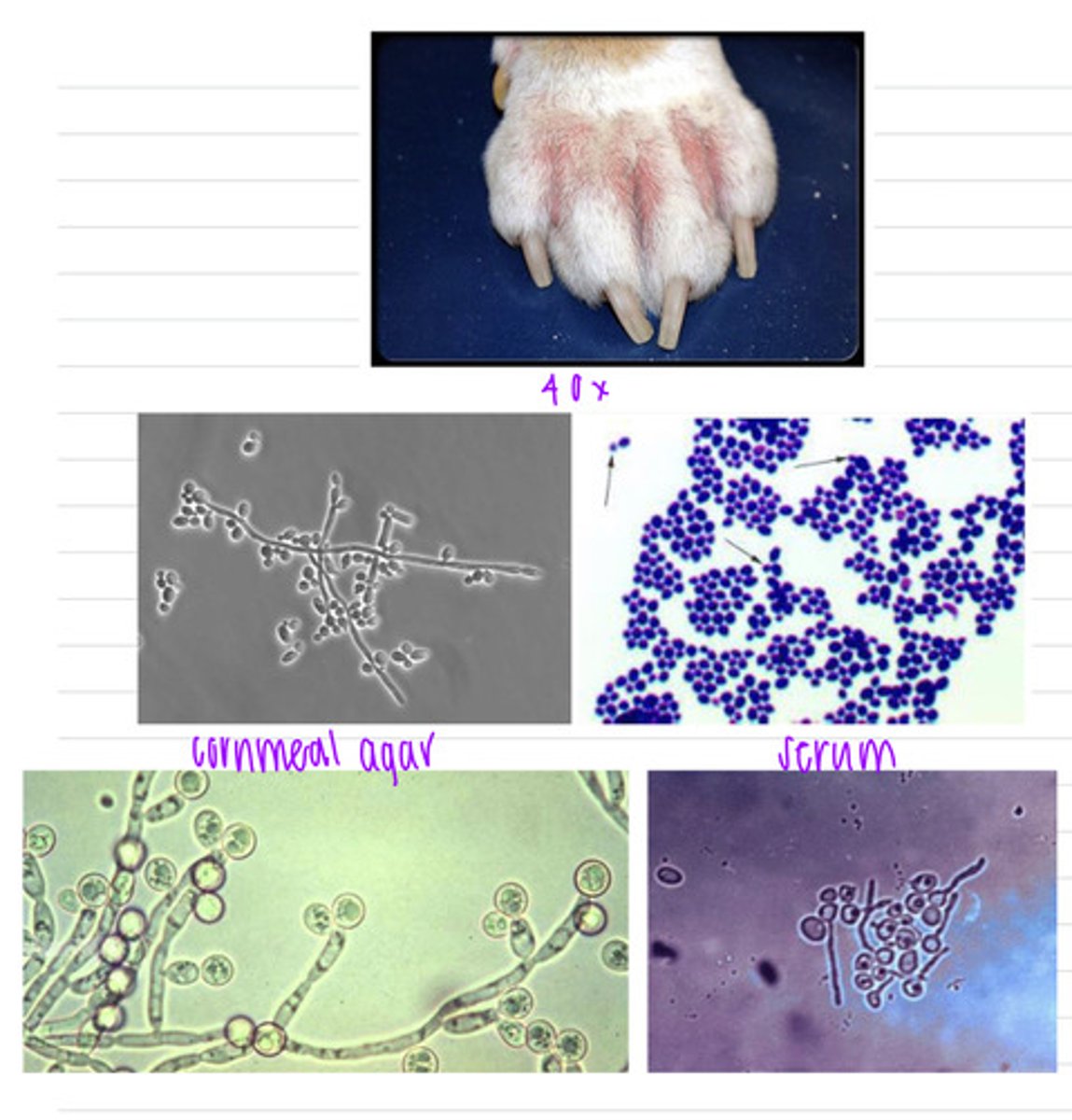
this dog was infected with Candida albicans, and has the disease cutaneous candidiasis
this dog has lesions between his toes. we take a sample, isolate it in cornmeal agar and serum, and look at it under a microscope, where we see these results.
what is the diagnosis?
we should take an ear canal swab. this dog has otitis externa, caused by Malasezzia pachydermatis
this dog came into the vet because he has an ear infection. we isolate a sample into SDA at 37 degrees and look under a microscope.
what sample should we take?
what is the diagnosis?
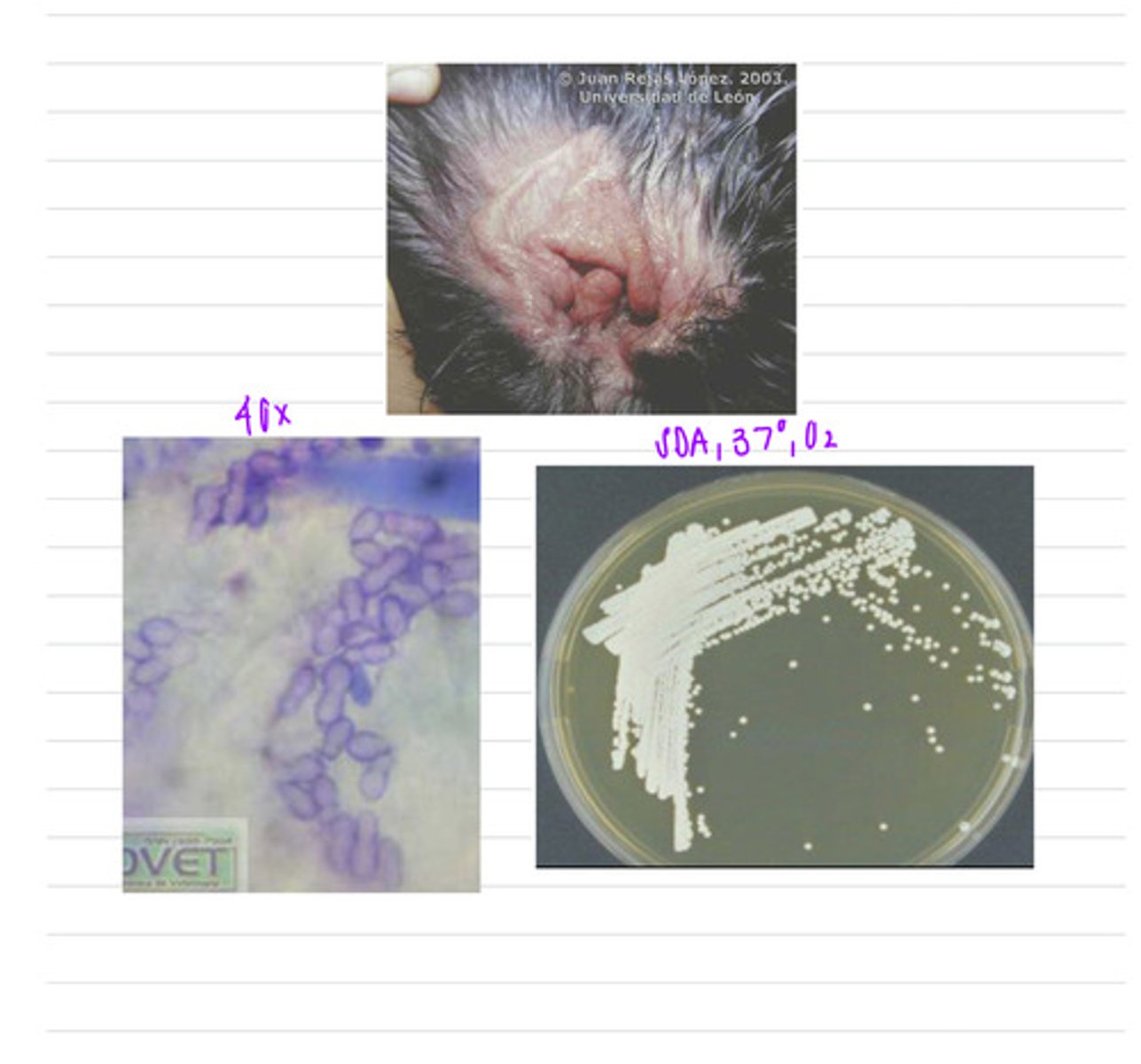
this dog has canine seborrheic dermatitis, caused by Malasezzia pachydermatis
this dog has superficial skin lesions. we take a sample, isolate it into SDA at 37 degrees, and look under a microscope.
what sample should we take?
what is the diagnosis?
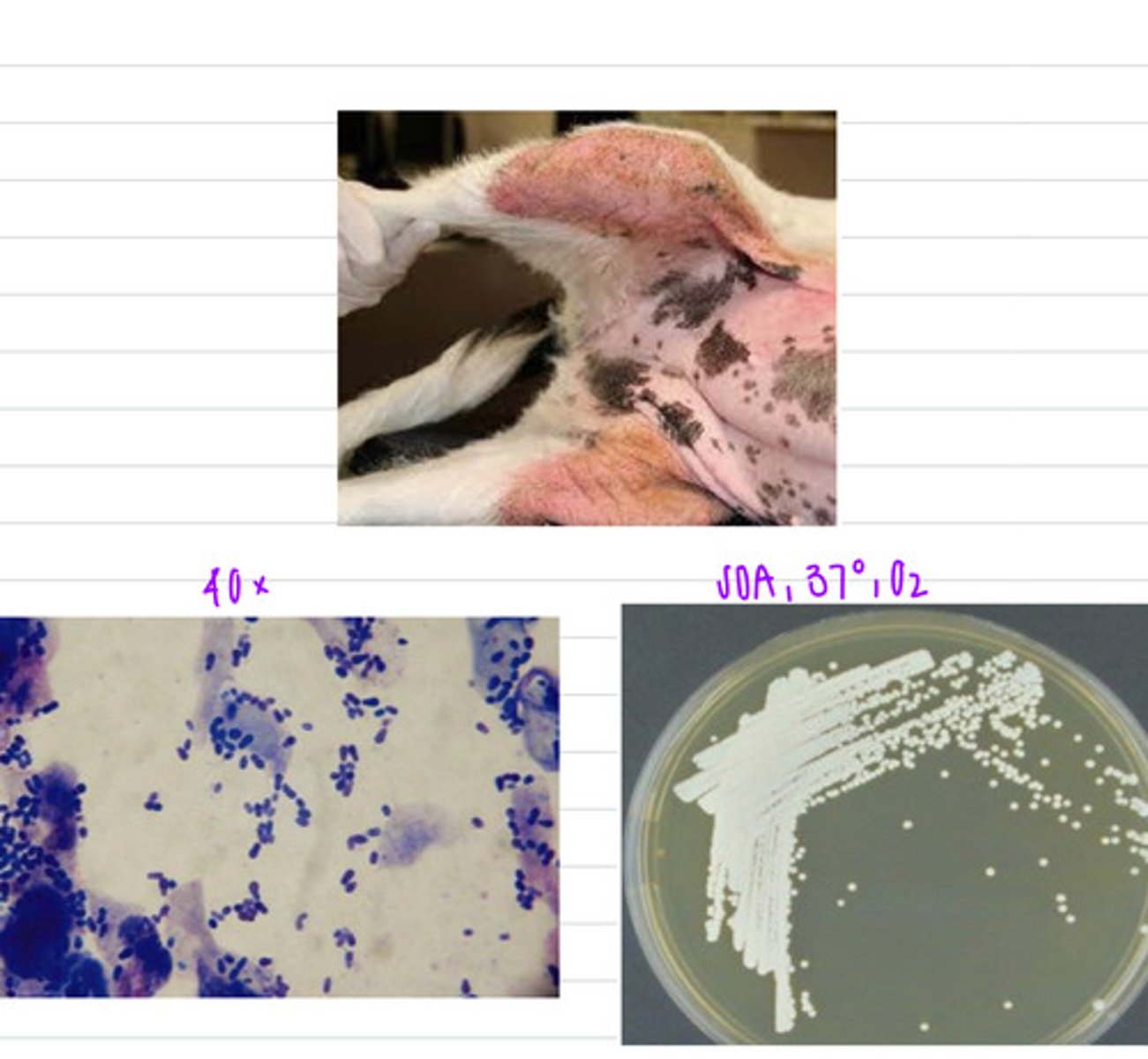
this cat has feline chin acne, caused by Malasezzia pachydermatis
this cat has these lesions on its chin. we take a sample, isolate it into SDA at 37 degrees, and look under a microscope.
what sample should we take?
what is the diagnosis?

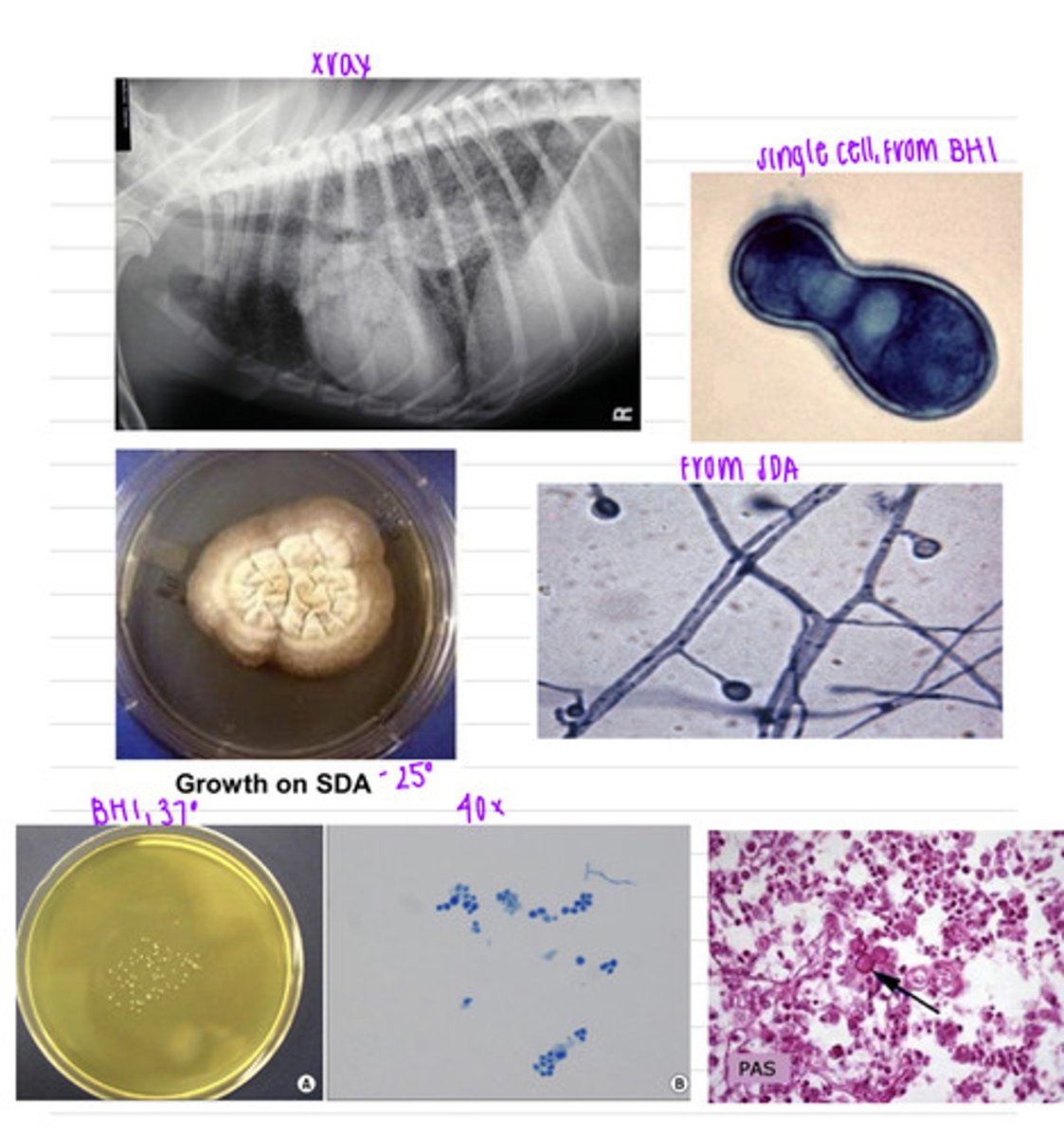
we should take a trachea biopsy (because this dog has no nasal secretions). he has blastomycosis, caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis
a dog came into the vet because he was coughing, having trouble breathing, and could not go on runs with his owner anymore, which was unusual. we take an Xray and isolate a sample on BHI at 37 degrees and on SDA at 37 degrees.
what sample should we take?
what is the diagnosis?
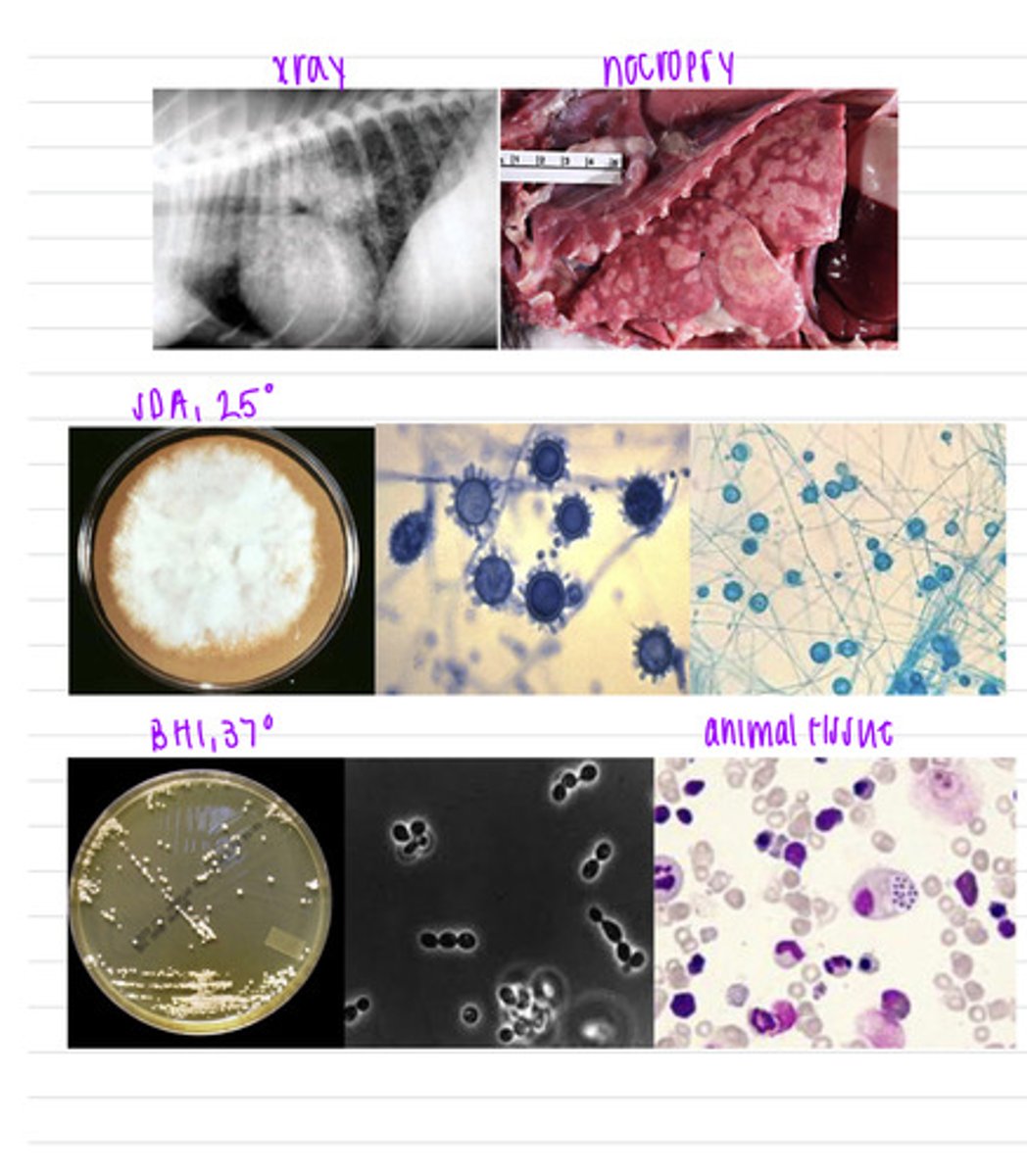
the cat had feline histoplasmosis, caused by Histoplasma capsulatum
a cat came into the vet because she had lost lots of weight and is having diarrhea. we notice it is also coughing and having trouble breathing. unfortunately, the cat passes away in the vet. we take an X ray, perform a necropsy of her thoracic cavity, and take samples to isolate in BHI at 37 degrees and in SDA at 25 degrees.
what is the diagnosis?
this horse has epizootic lymphangitis, caused by Histoplasma farciminosum
this horse was brought into the vet because he developed some lesions on its skin. we take samples and isolate them both on BHI at 37 degrees and SDA at 25 degrees.
what is the diagnosis?
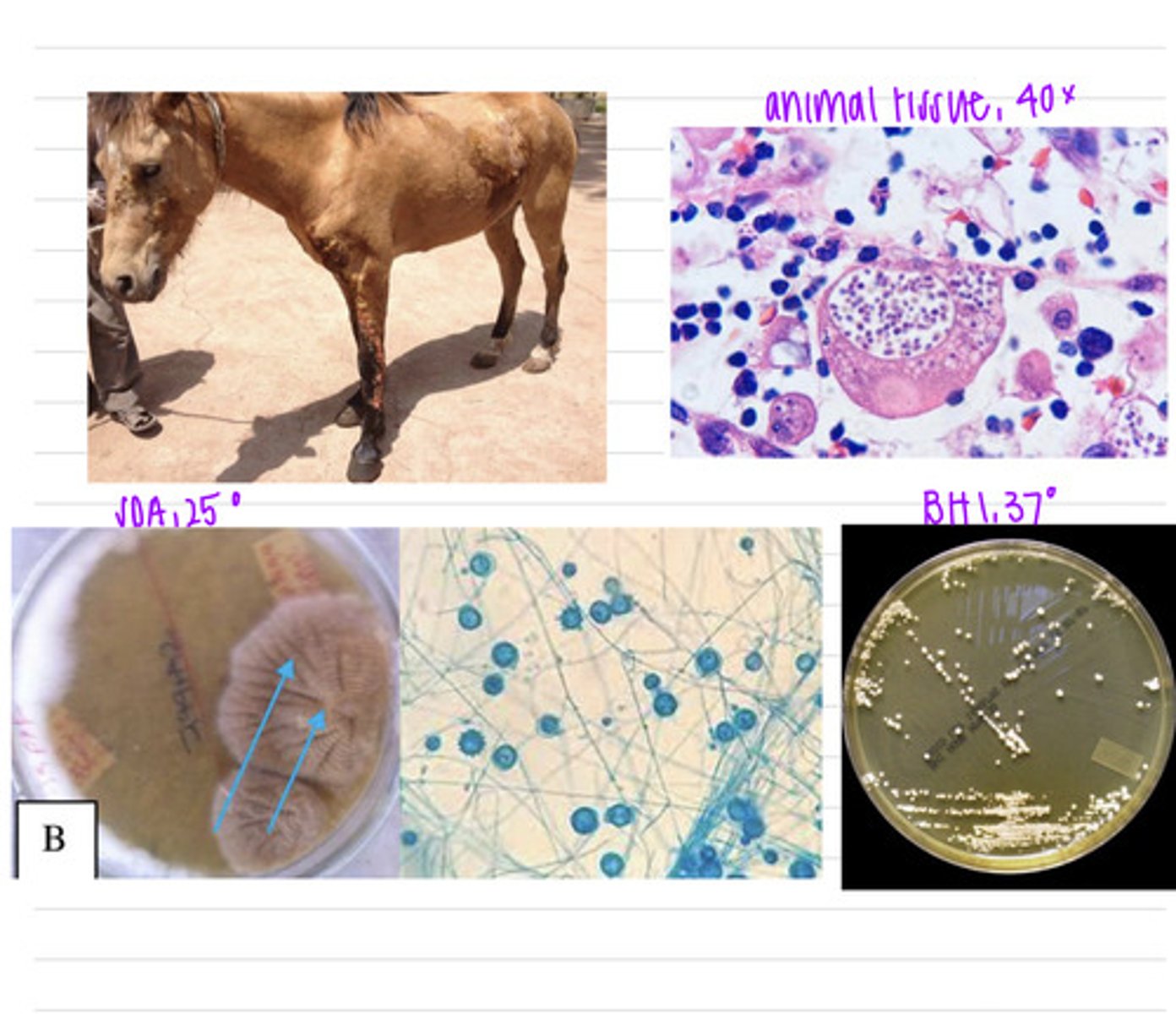
this horse has mycotic pneumonia caused and the disease coccidiomycosis caused by Coccidioides immitis
a horse's owner calls the vet because it is coughing, has a fever, has lost weight, and seems weak. we take samples and isolate them both on BHI at 37 degrees and SDA at 25 degrees.
what is the diagnosis?
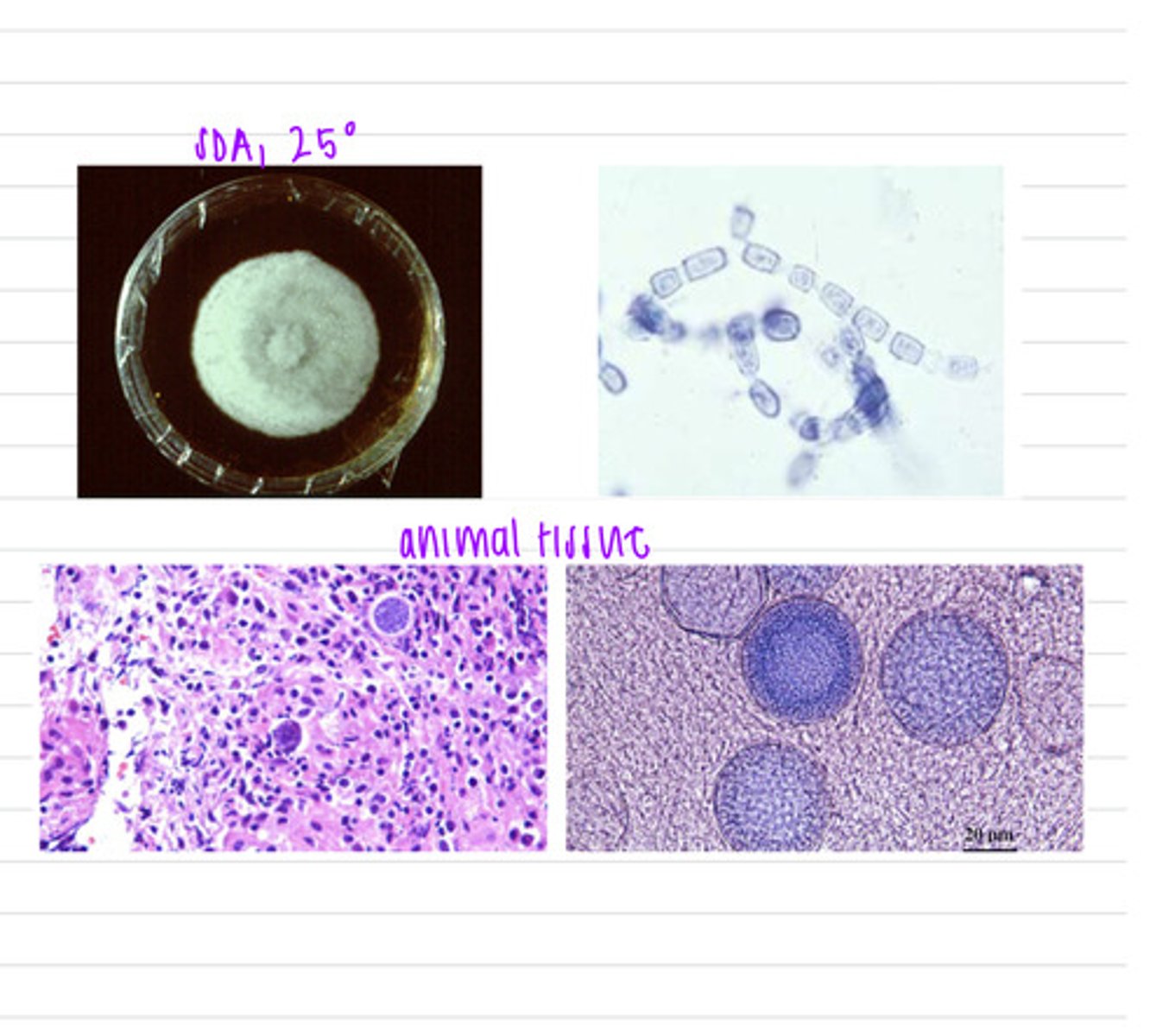
this dog has canine sporotrichosis, caused by Sporothrix schenckii
this dog has ulcerative, crusted lesions all over the skin of its head and trunk. we take samples and isolate them both on BHI at 37 degrees and SDA at 25 degrees.
what is the diagnosis?
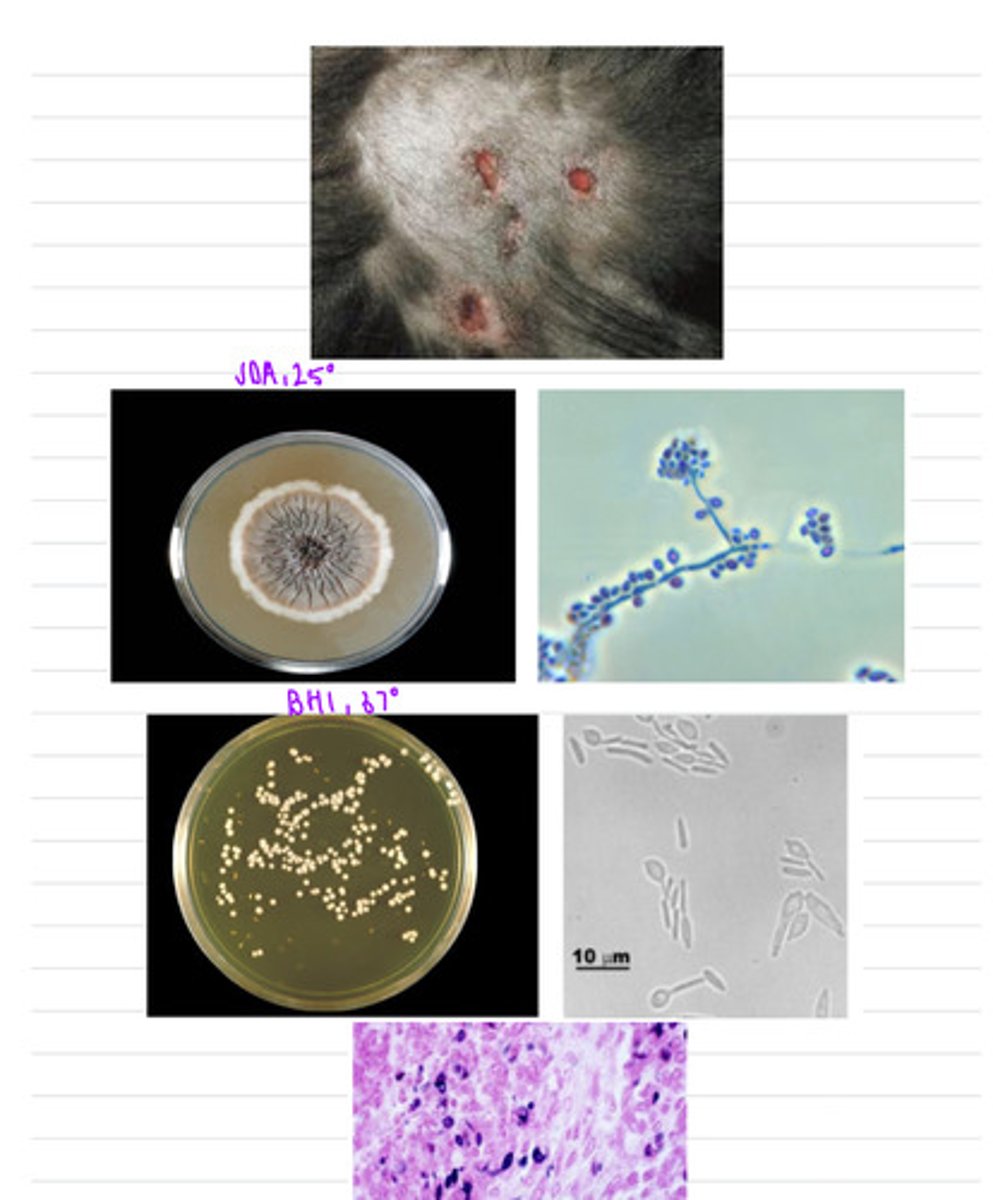
his cat has feline sporotrichosis, caused by Sporothrix schenckii
this cat came to the vet with lesions all over the skin of its head, tail, and extremities. we take samples and isolate them both on BHI at 37 degrees and SDA at 25 degrees.
what is the diagnosis?
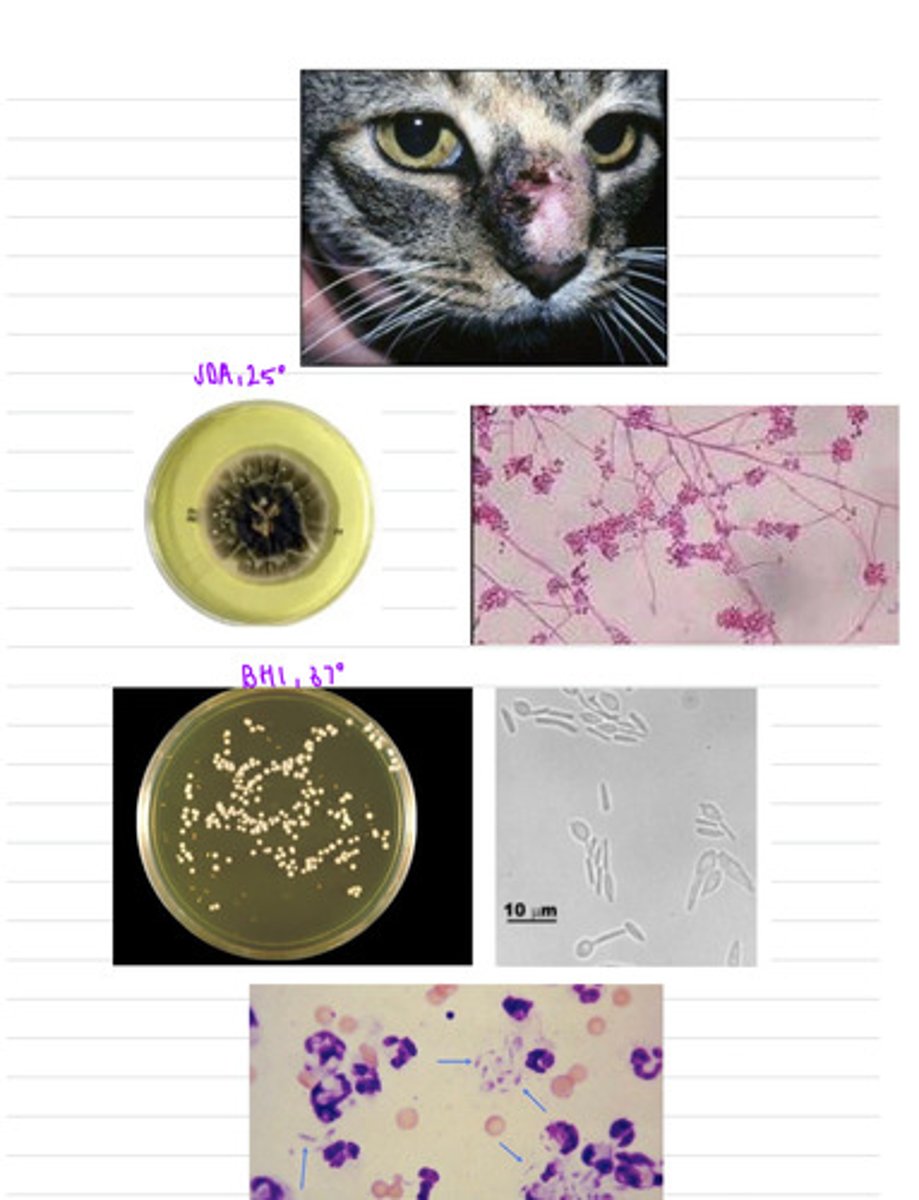
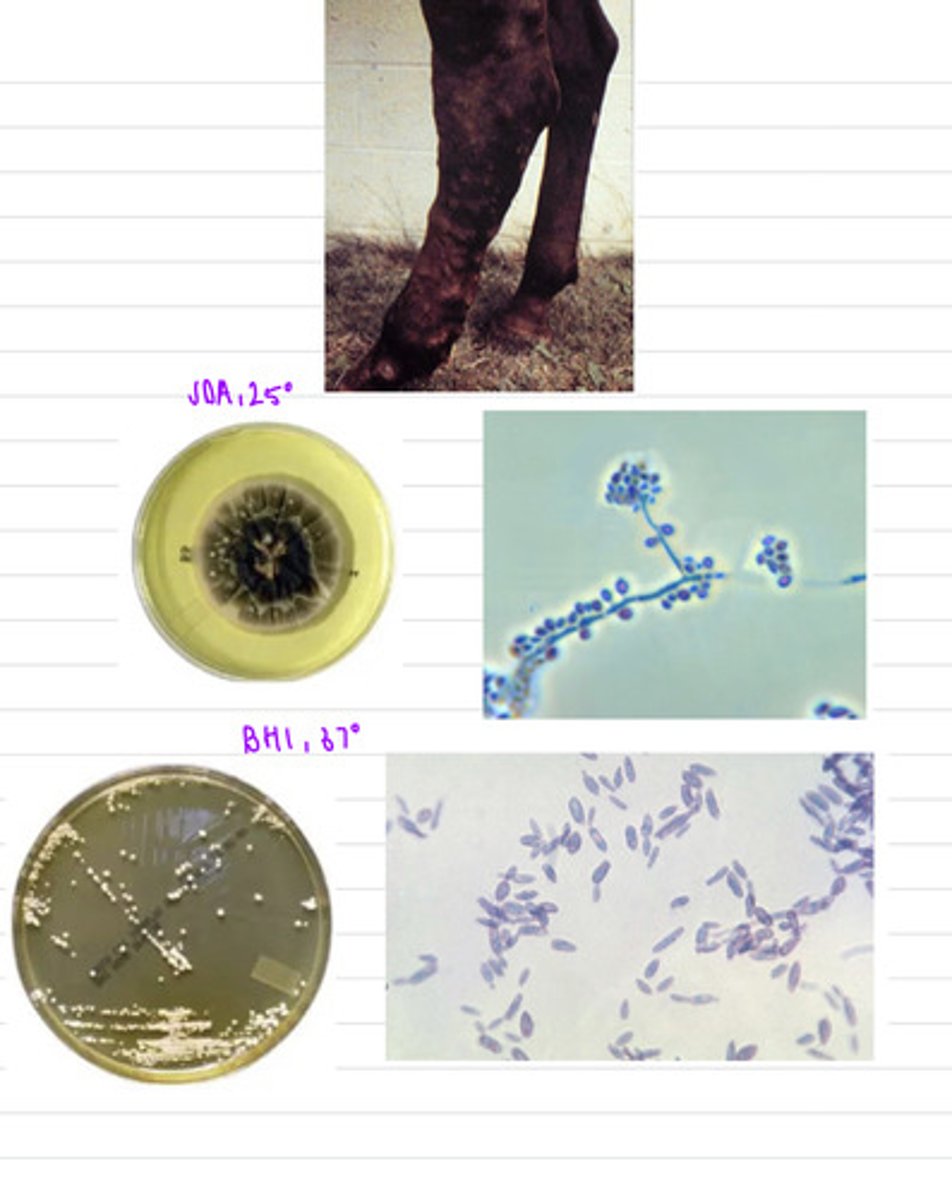
his horse has equine sporotrichosis, caused by Sporothrix schenckii
this horse came to the vet with lesions all over the skin and subcutaneous edema. we take samples and isolate them both on BHI at 37 degrees and SDA at 25 degrees.
what is the diagnosis?
the cow was infected by either the fungus Mucorales or Mortierellales. she has the disease mucormycosis (a type of zygomycosis)
a farmer calls because his cow just had an abortion. we take samples of the cotyledons of the placenta and isolate it on SDA and 37 degrees.
what is the diagnosis?
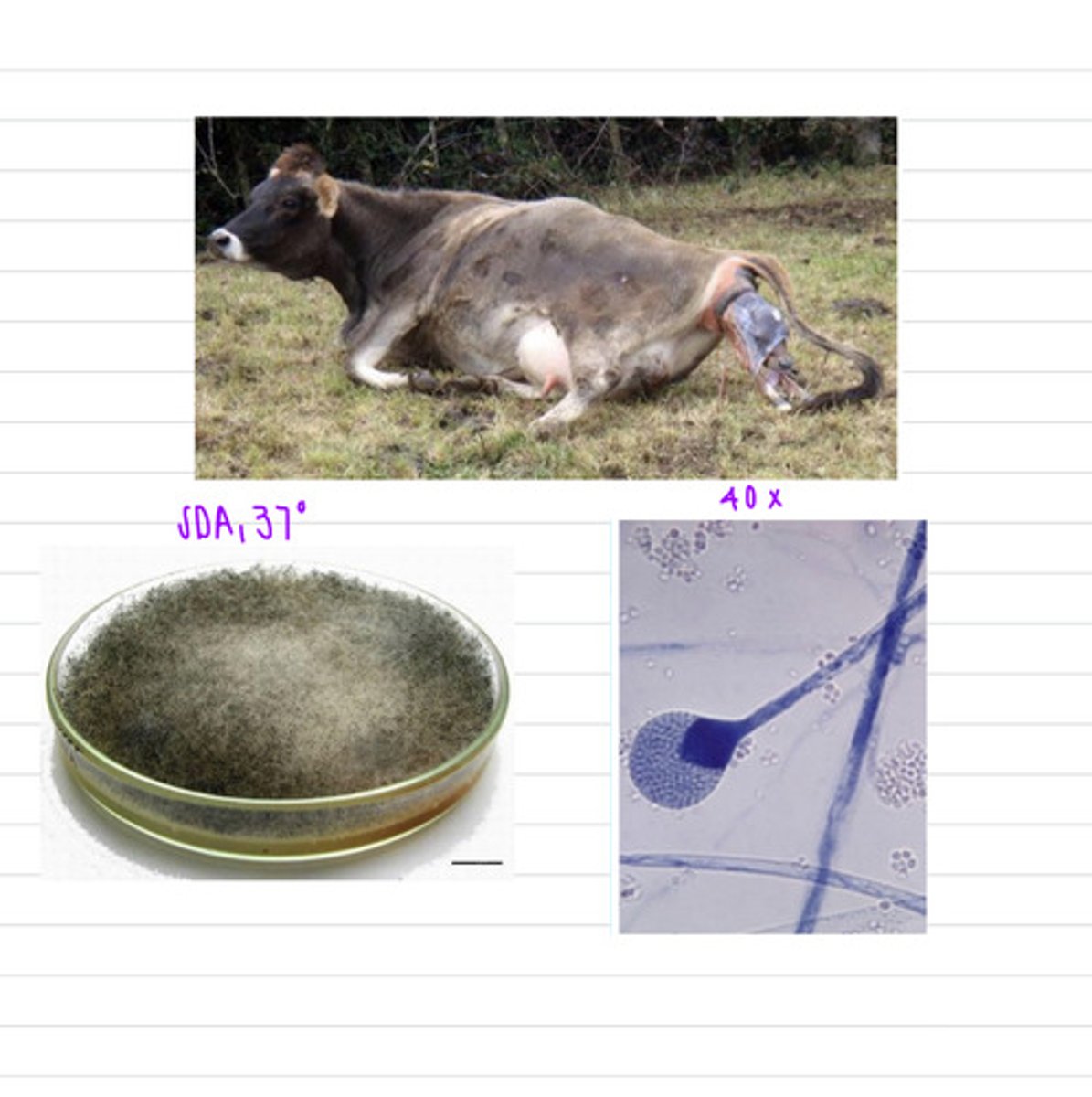

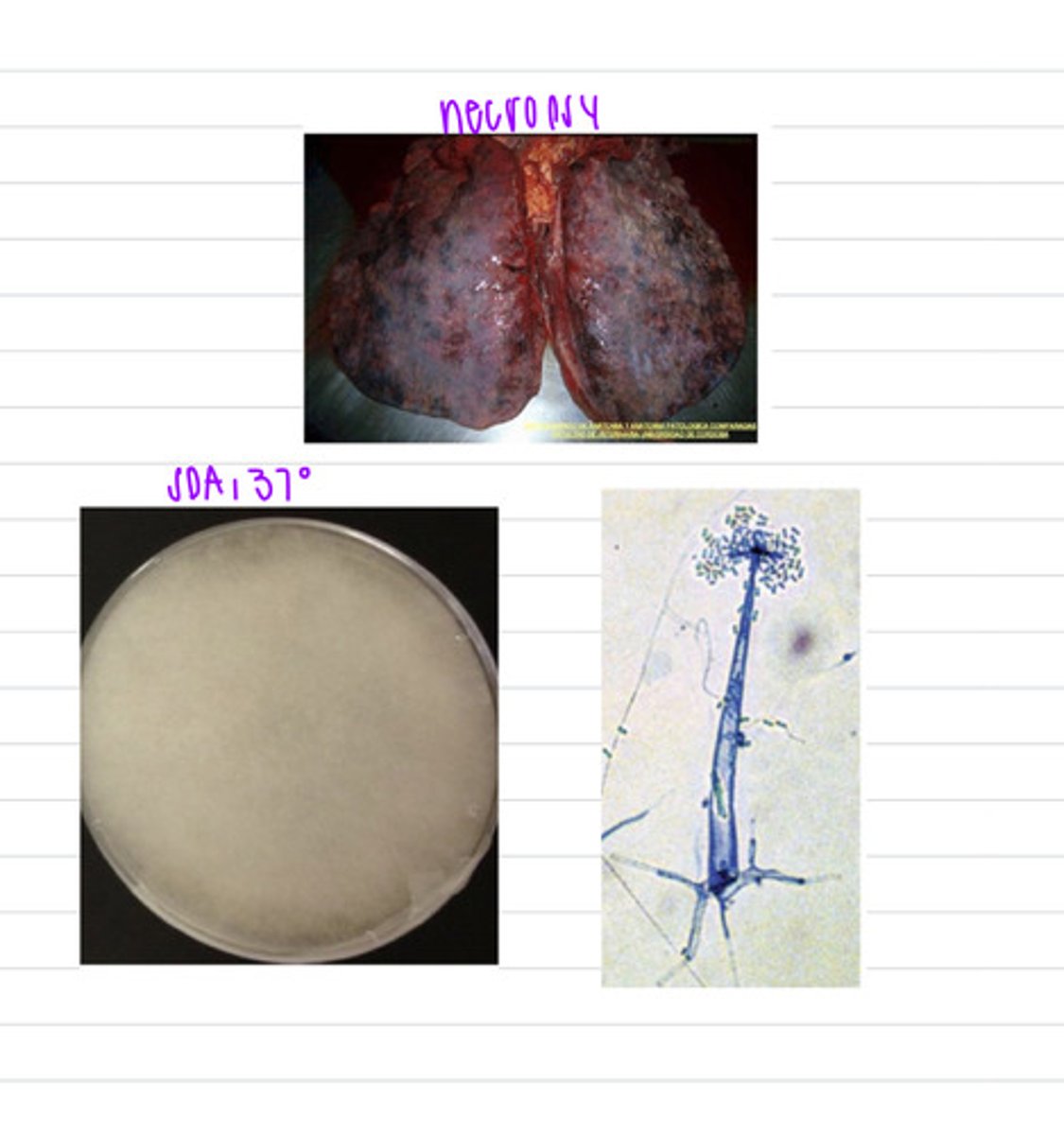
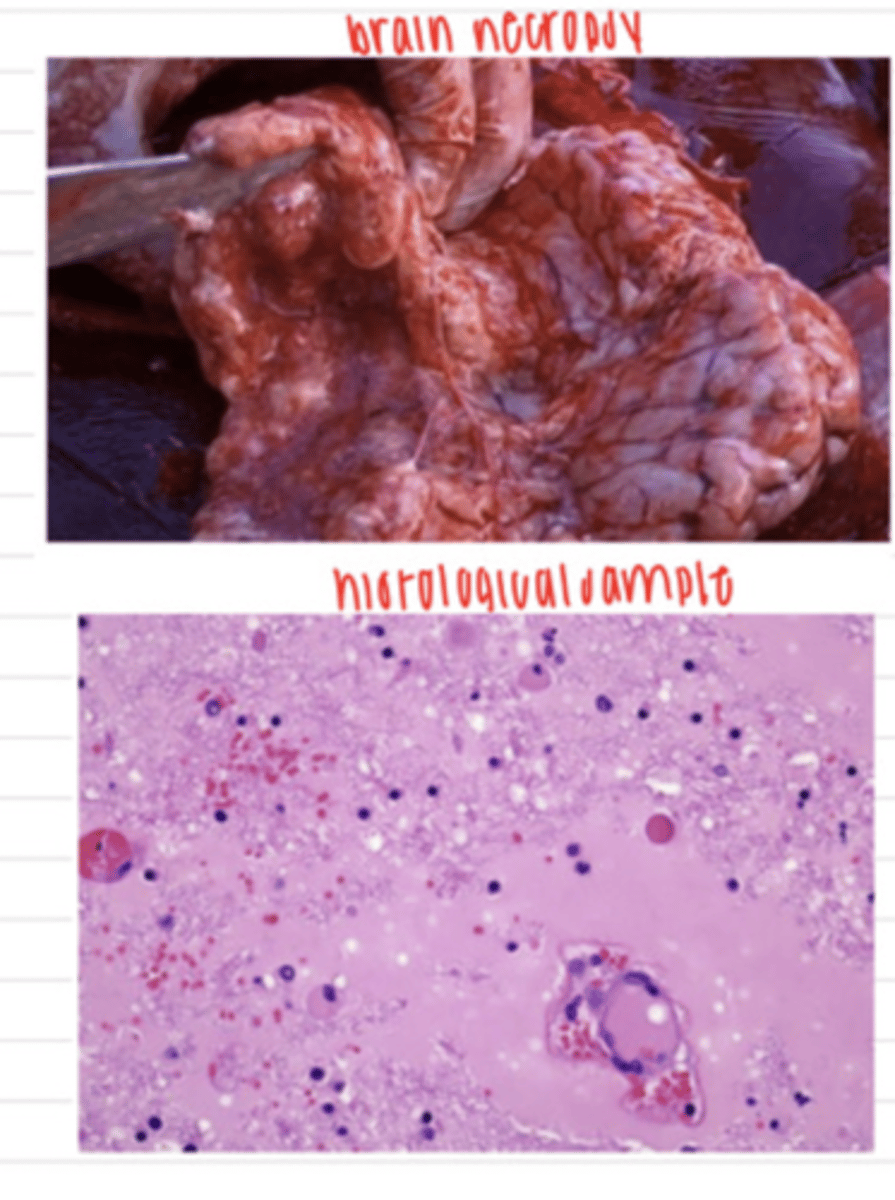
we should take samples of pneumonic exudate. The dog was infected by the fungus Mucorales or Mortierellales, and had the disease mucormycosis
a dog came into the vet with signs of pneumonia- coughing, fever, dyspnea,etc. it unfortunately dies, but we do a necropsy and find these lung lesions. we grow samples in SDA at 37 degrees and these are the results.
what samples should we take?
what is this diagnosis?
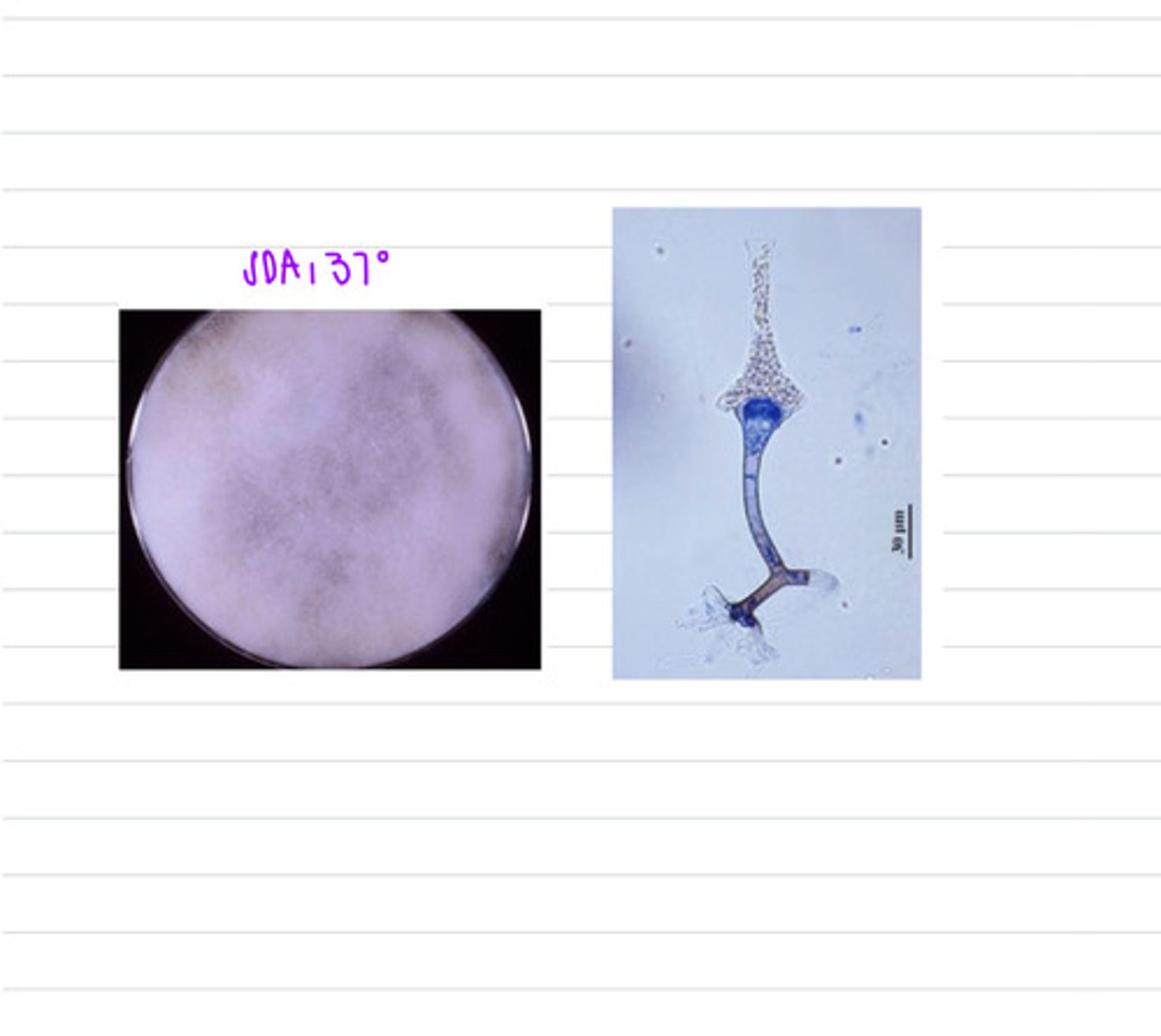
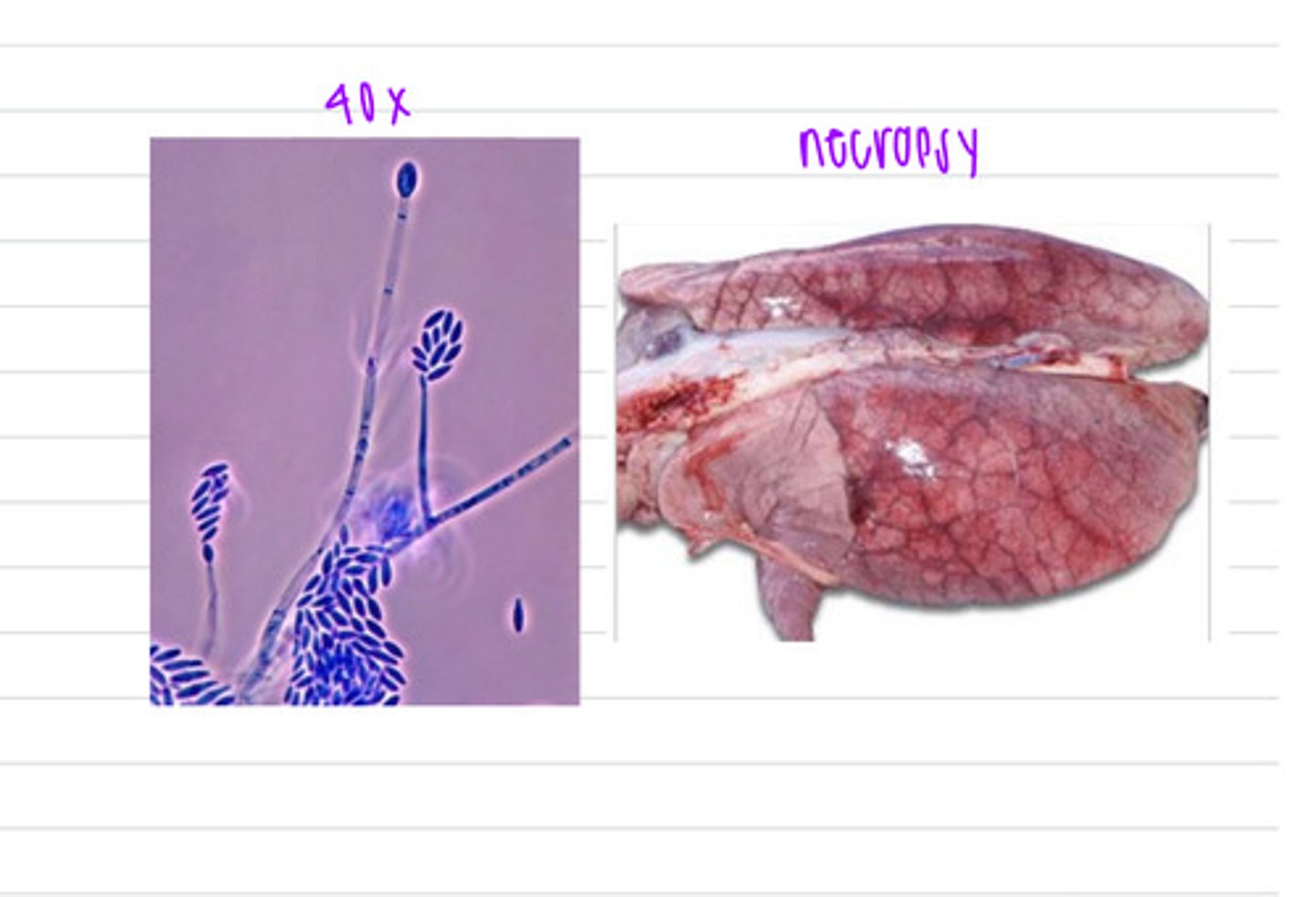
The pig was infected by the fungus Mucorales or Mortierellales, and had the disease mucormycosis
a pig is showing GI signs, including hemorrhage, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. we do an examination and notice enteritis and severe GI ulcers. we take samples from the GI organs and isolate at 37 degrees on SDA.
what is the diagnosis?
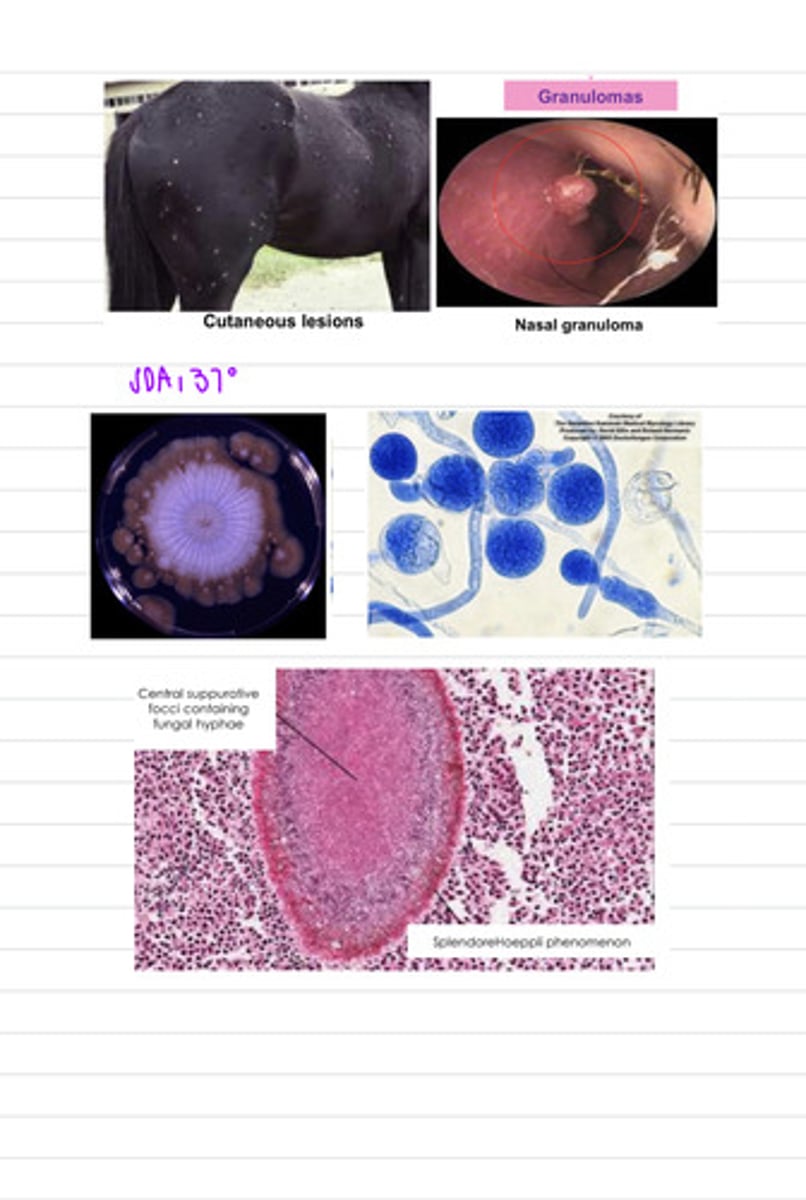
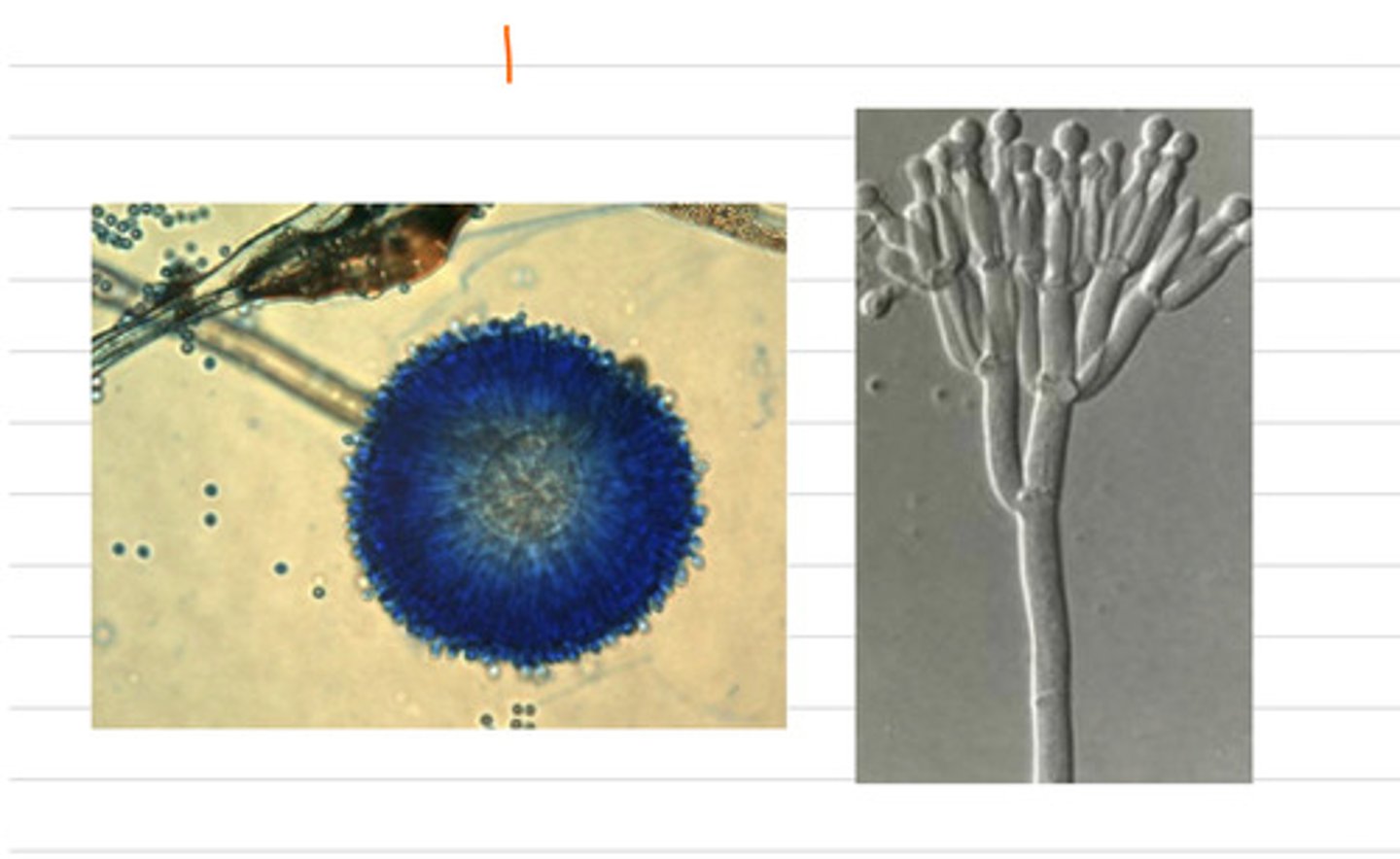
this horse has the disease Entomophthomycosis, caused by an infection by the fungus Entomophthorales
a horse is showing cutaneous and nasal granulomas, so we take a biopsy and grow the samples on SDA at 37 degrees. we also directly view a sample under a microscope. we find these results.
what is the diagnosis?
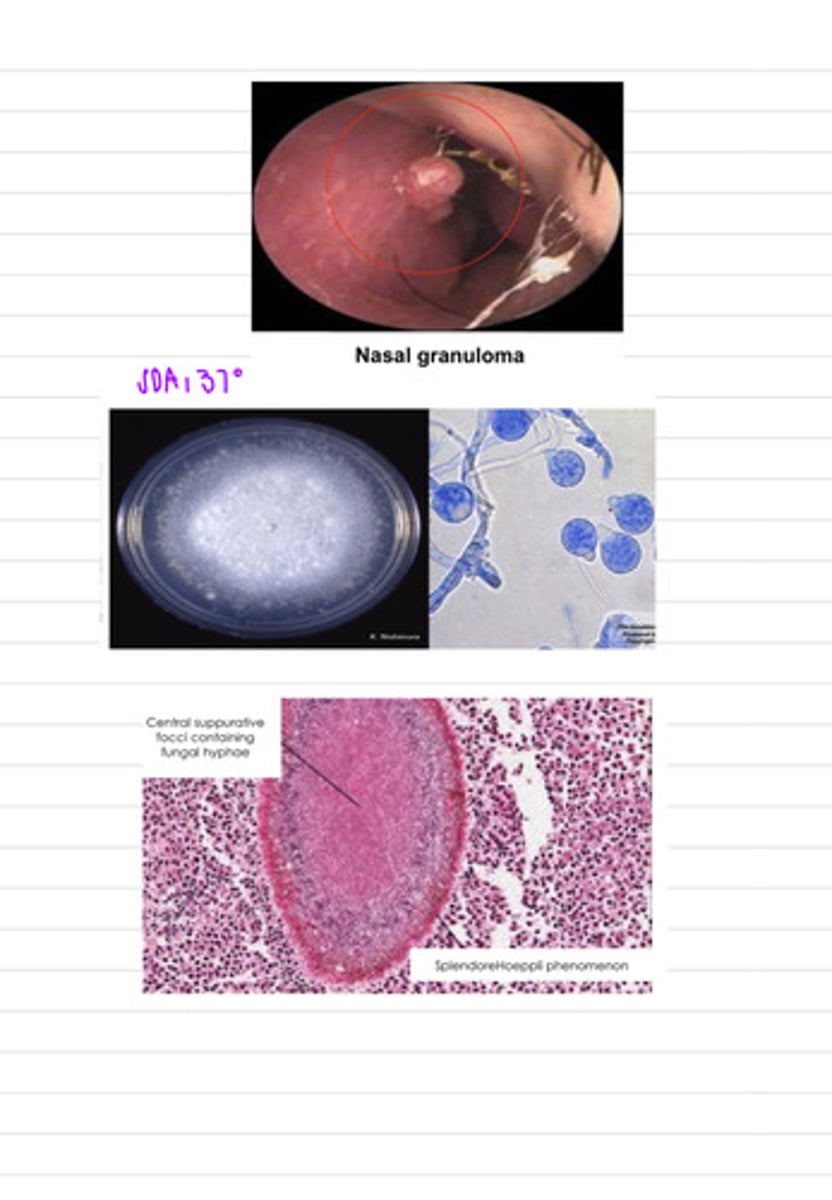
this sheep has the disease Entomophthomycosis, caused by an infection by the fungus Entomophthorales
a sheep is showing nasal granulomas, so we take a biopsy and grow the samples on SDA at 37 degrees. we also directly view a sample under a microscope. we find these results.
what is the diagnosis?
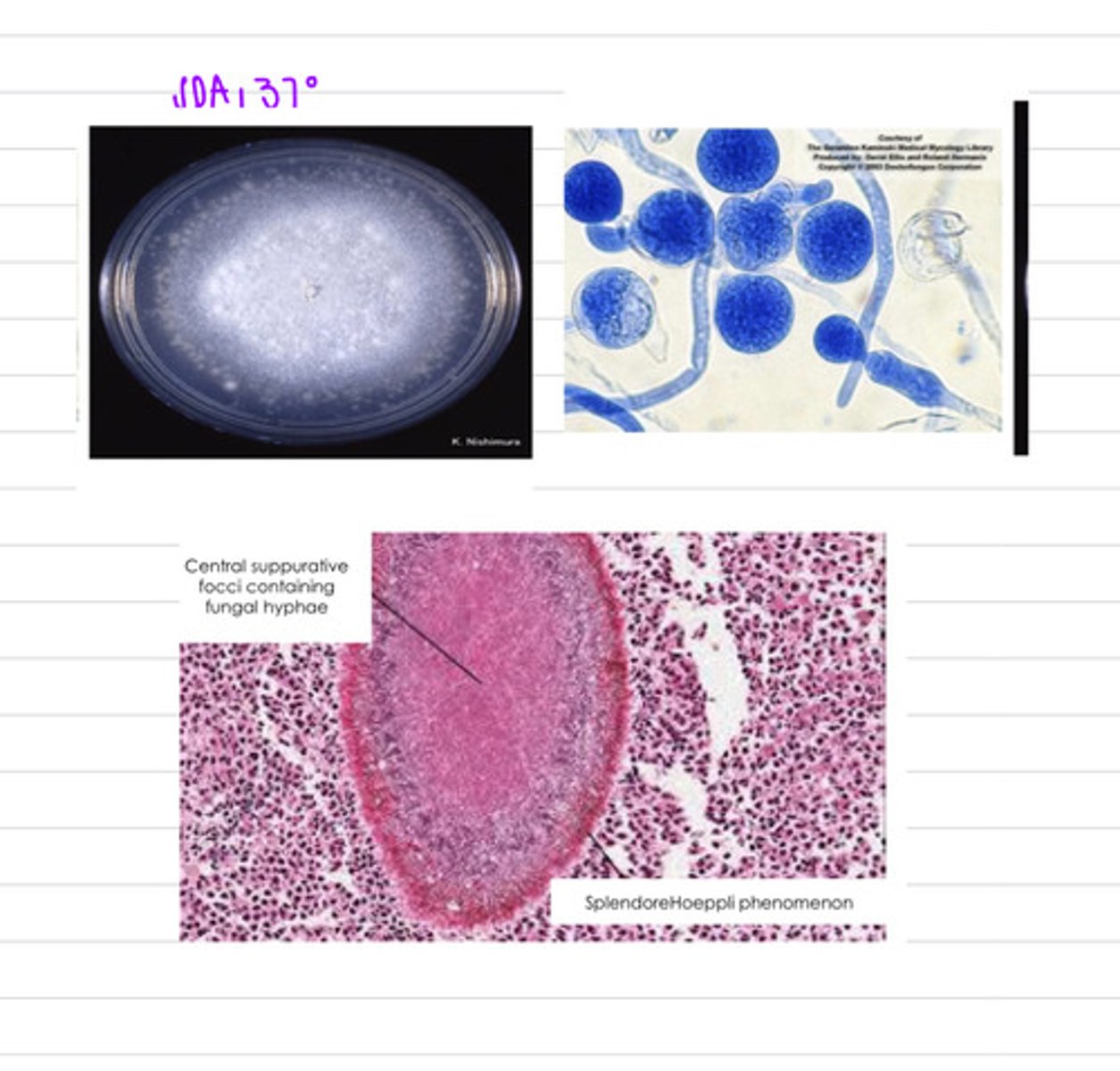
this dog has the disease Entomophthomycosis, caused by an infection by the fungus Entomophthorales
a dog is showing subcutaneous, GI, and pulmonary granulomas, so we take a biopsy and grow the samples on SDA at 37 degrees. we also directly view a sample under a microscope. we find these results.
what is the diagnosis?
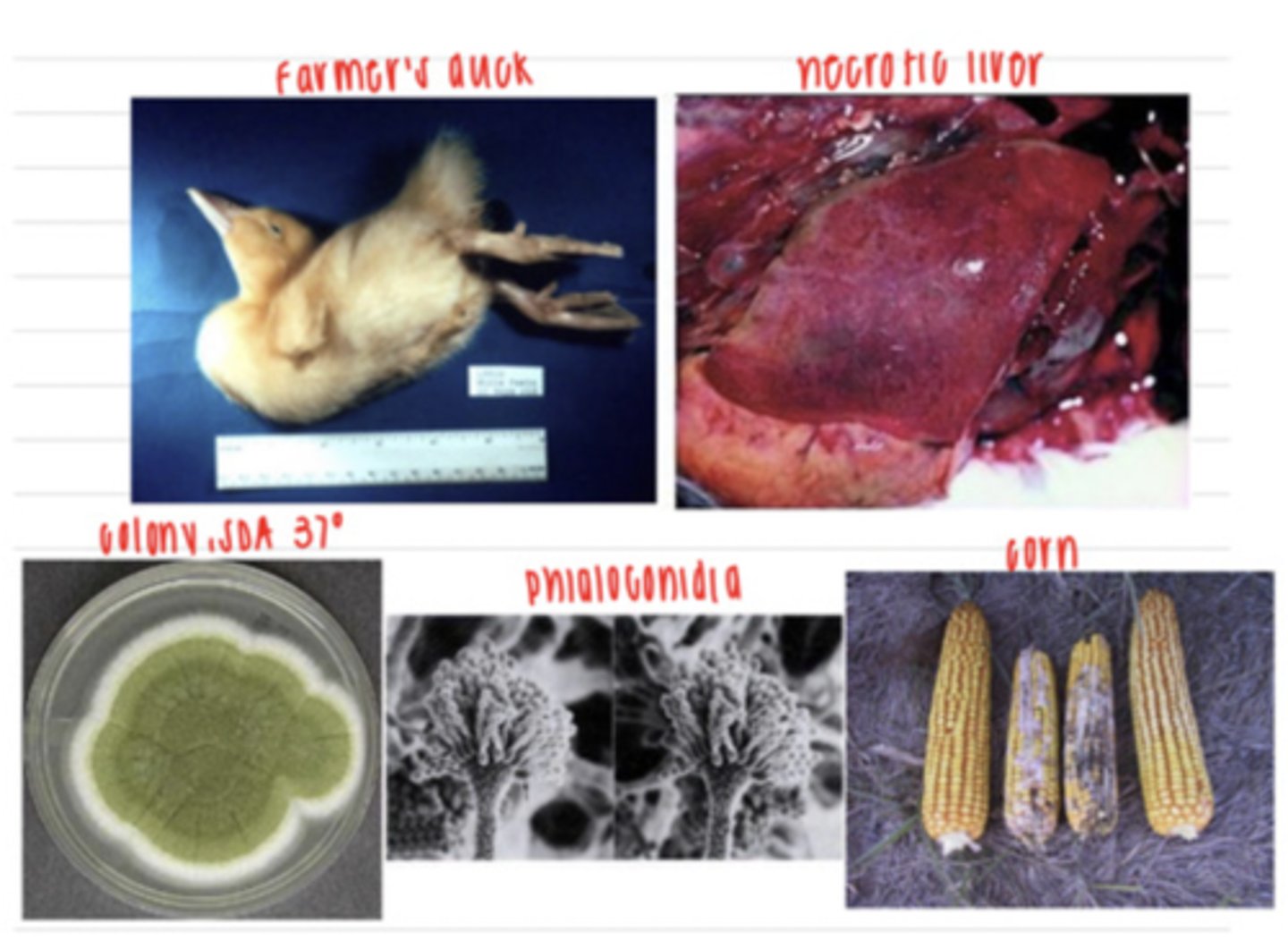
the duck has acute aflatoxicosis from ingesting the fungi Aspergillus flavus that contained aflatoxins
a farmer brings in a duckling on his farm that he noticed was experiencing ataxia, opisthotonos (muscle spasms), and then suddenly died. the vet does a necropsy and observes aplasia of the thymic cortex and necrosis of the liver. the farmer says that the corn that the animals have been eating does look a little moldy, so he brings in one for examination. the vet isolates some cells from the corn on SDA at 37 degrees and observes the colony and the phialoconidia that has grown. what is the diagnosis?
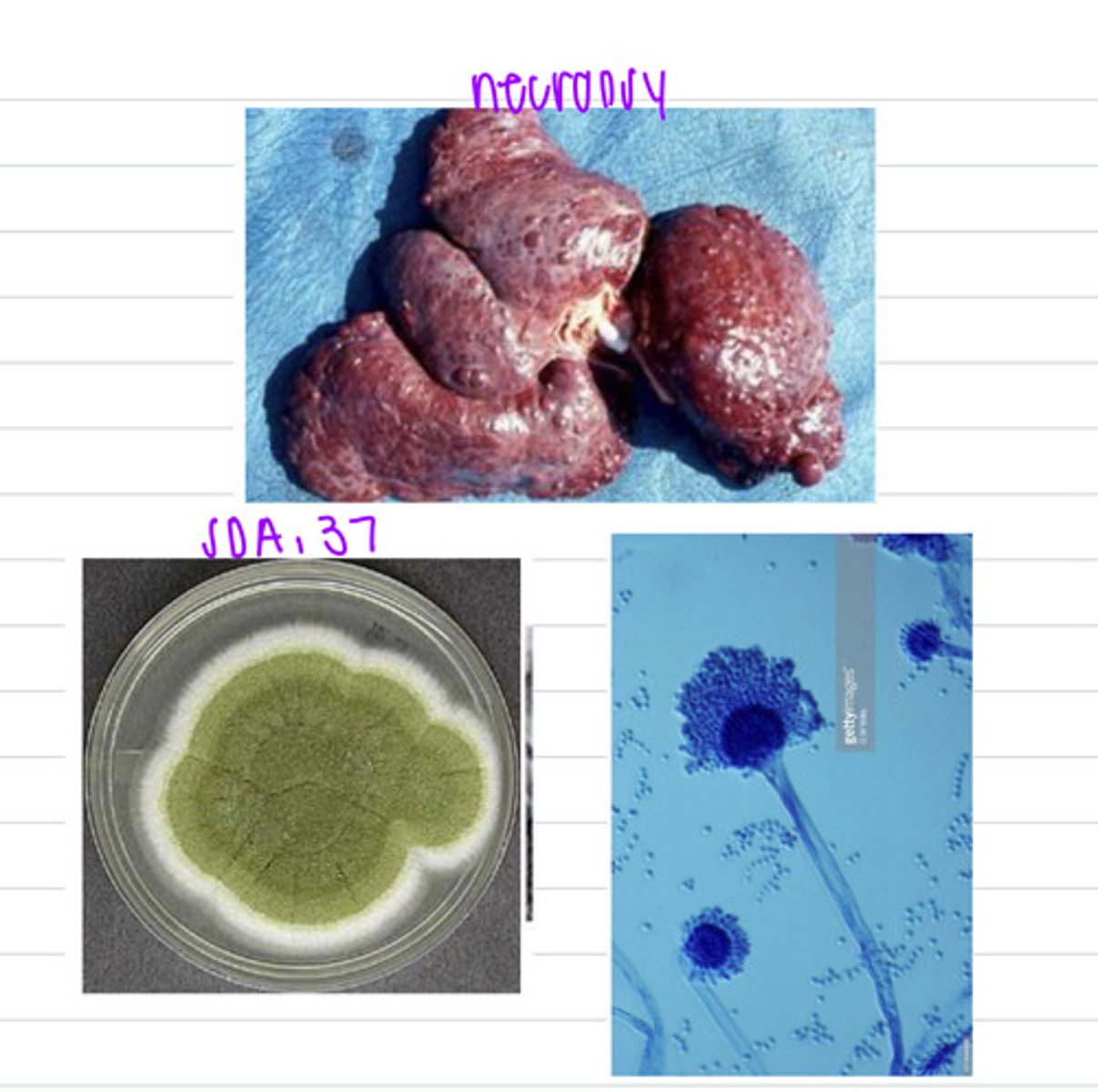
the dog has aflatoxicosis from ingesting the fungi Aspergillus flavus that contained aflatoxins
a vet does a necropsy on a dog and removes the liver. if we know the dog had eaten some fungus infected crops, what can we guess is the diagnosis?
the horse had mycotoxic leukoencephalomalacia (also known as equine encephalomalacia- ECEM) because it ate corn that had the fungal species Fusarium verticillioides, containing mycotoxin fumonisin
a man is concerned about his horse because it has been depressed, circling, weak, staggering, and cannot swallow his food. unfortunately, the horse dies before the vet can treat it, but the vet does a necropsy and finds areas of grey-brown malacia in the brain. he takes a sample and histologically observes liquefactive necrosis, congestion, and hemorrhages in the white matter of the cerebrum.
what is the diagnosis?
the disease is porcine pulmonary edema, which the pig contracted when it ate corn that had the fungal species Fusarium verticillioides growing on it. the mycotoxin is fumonisin.
a farmer brings in one of his pigs that has died. he says that the day before his death, he noticed the pig started to have trouble breathing, was weak, her mouth was turning blue, and she didn't want to stand up. the vet suspects a certain disease so takes out the pig's lungs to observe them and confirm his diagnosis because he sees interstitial pulmonary edema.
what is the diagnosis?
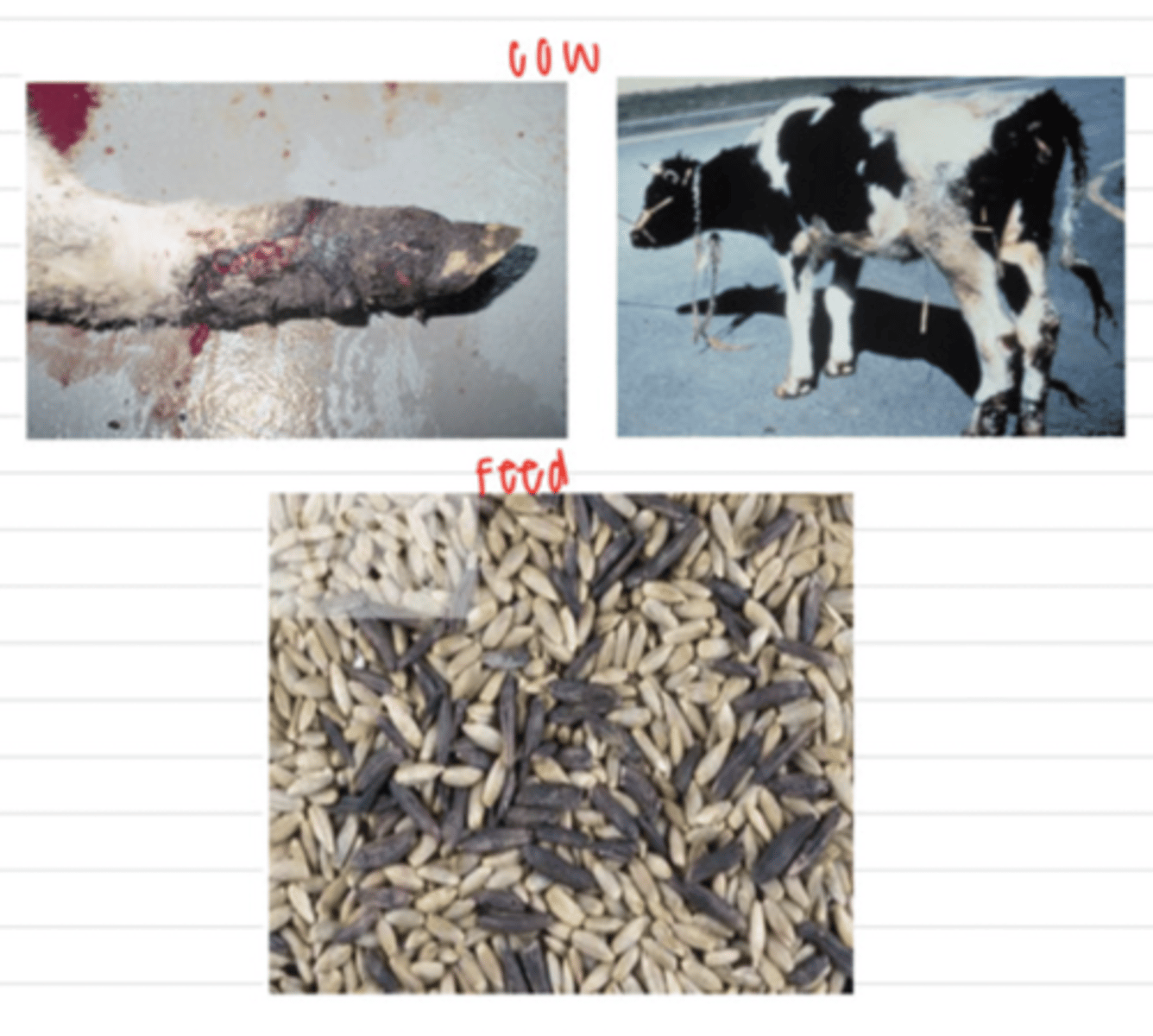
the cow has been eating seeds that have the fungus Claviceps purpurea growing inside, so it was infected by small amounts of the mycotoxin ergotamine/ergopeptide alkaloids. it has ergotism.
a cow comes to the vet with red, swollen, gangrene on its extremities. the farmer says it has been eating this feed:
what is the diagnosis?

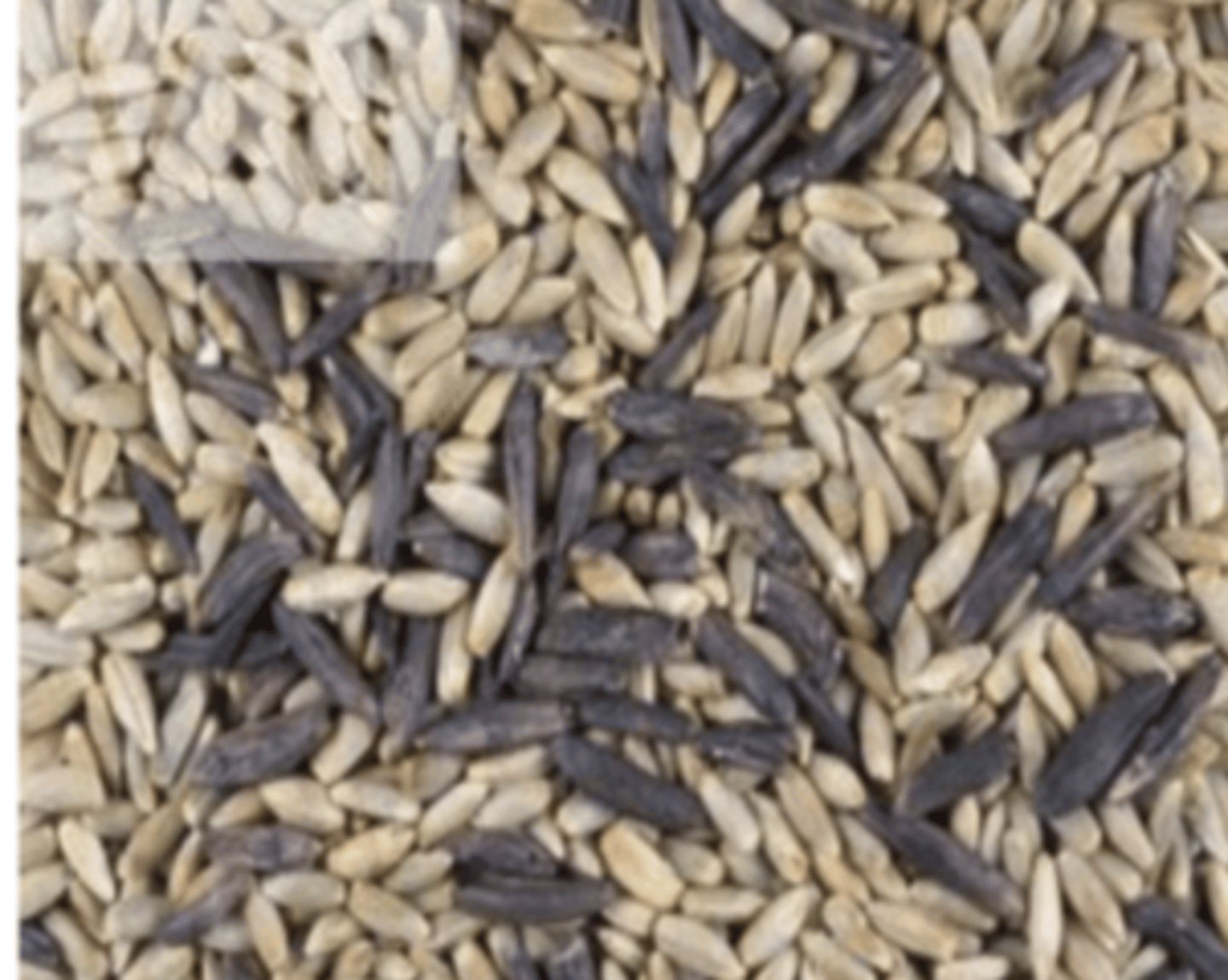
the dog ate seeds with the fungus Claviceps purpurea, which produces the mycotoxin ergotamine/ergopeptide alkaloids. the dog has ergotism.
a woman went on a walk with her dog, where it ate a large amount of black rye seeds. shortly after, the dog started staggering and having convulsive episodes. what can we assume is the diagnosis?

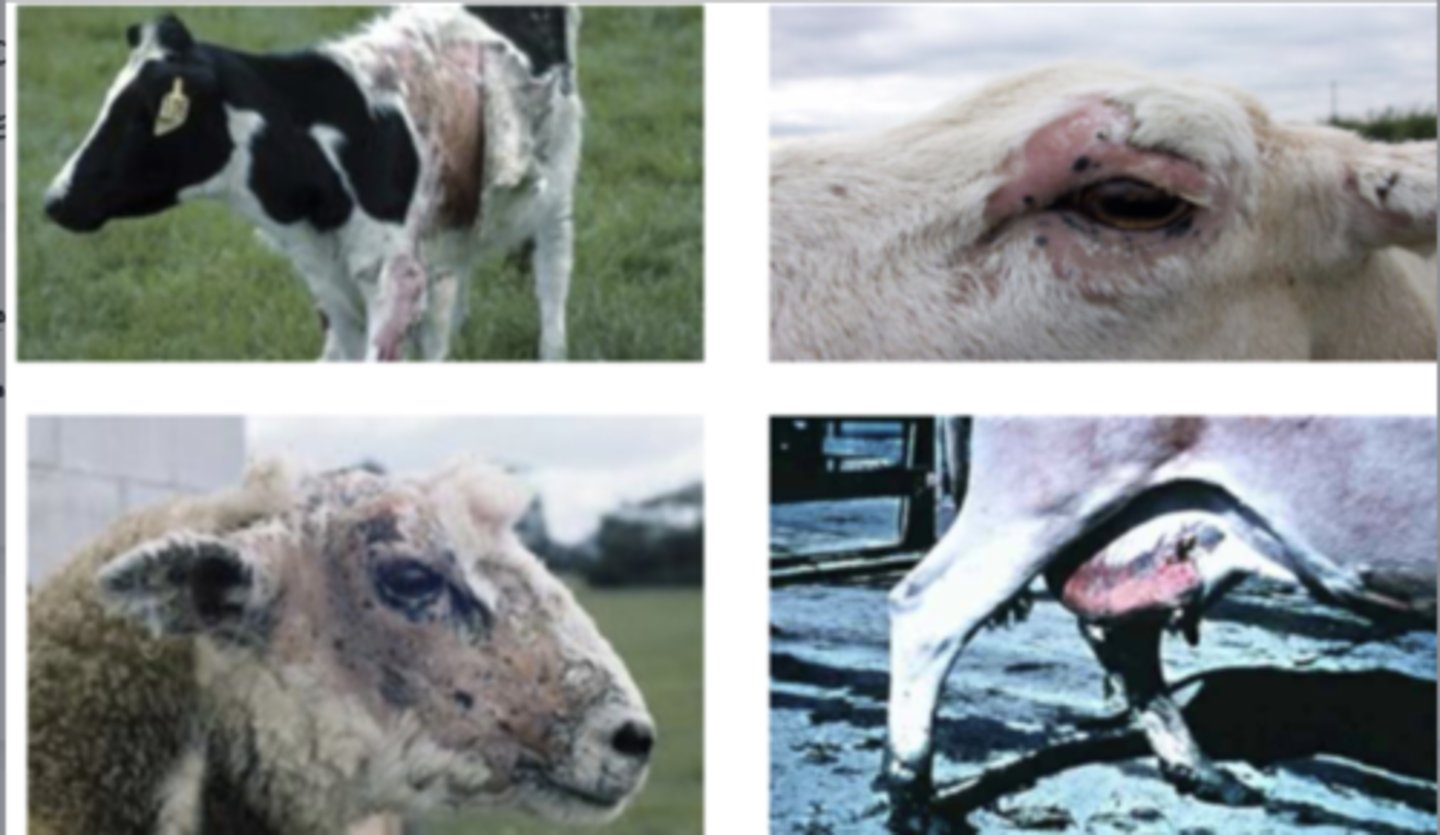
these animals possibly are eating feed with the fungus Pithomyces chartarum, which produces the toxin Sporidesmin (with the lesion-forming compound phylloerithryn)
a farmer notices his animals begin to show lesions on their skin- swelling, redness, alopecia, and they are itching a lot.
what is the possible diagnosis?

the pig has the disease ochratoxicosis, caused by ingesting ochatoxins that are produced by either the fungal species Aspergillus ochraceus or Penicillium viridicardium
a farmer notices his pig has lost his appetite, so he has lost lots of weight, and is also drinking and peeing a lot more than normal.
what could be the diagnosis?
infection by the fungus Fusarium graminearum, which produces the mycotoxin zealarenone, which causes the disease mycotoxic oestrogenism.
a farmer notices his pigs showing signs of prepubitral gilt- swollen vulva, hyperemia, hypertrophy of mammary glands and uterus, and some have vaginal and rectal prolapse.
what could be the fungal related diagnosis?
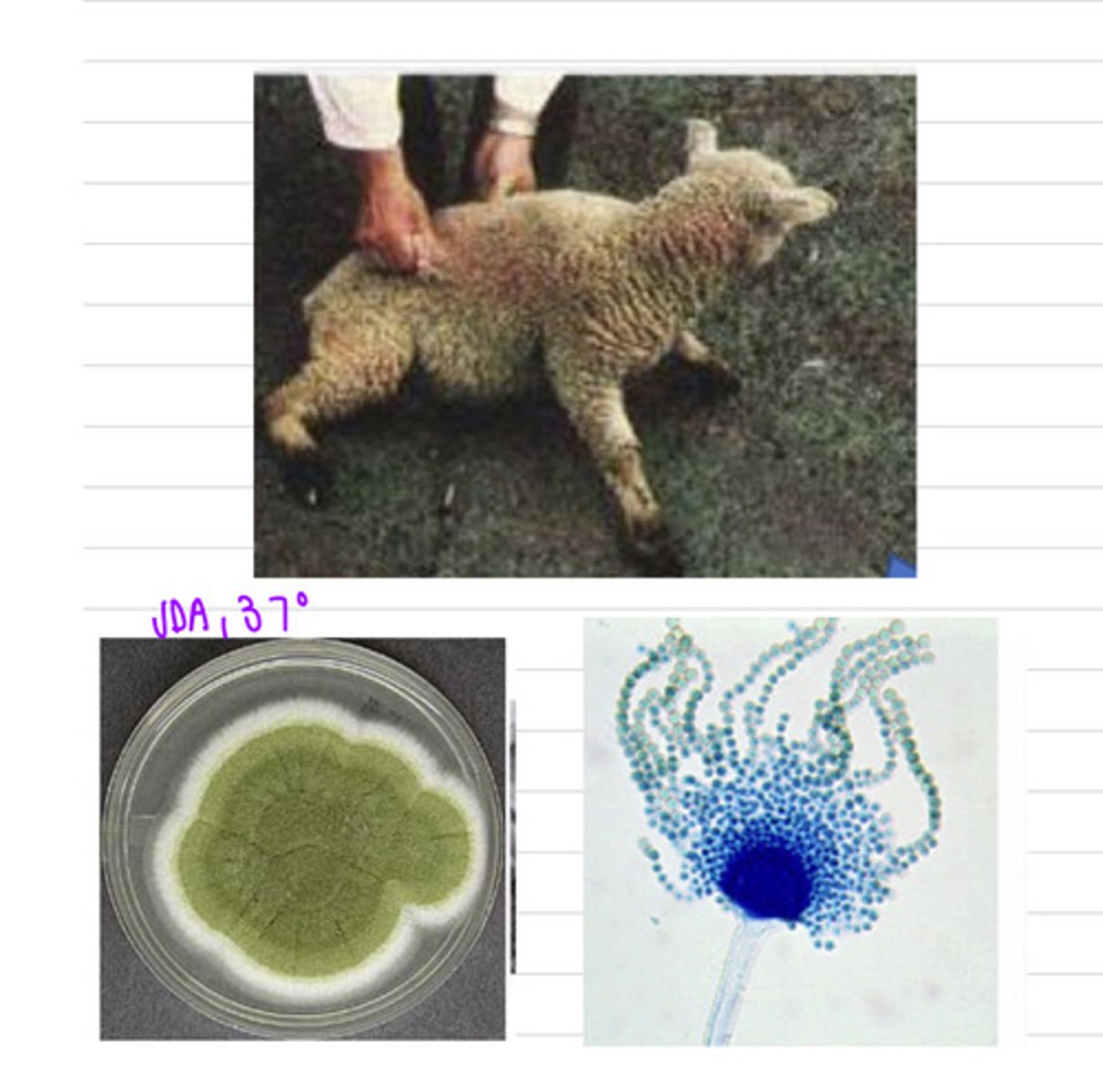
the sheep ingested the fungus Aspergillus flavus with the mycotoxin Penitrem A. he has the disease Tremorgenic mycotoxicosis
(the same disease can be caused by the fungal species Penicillium verrucosum)
a sheep beings to have neurological signs, such as muscle tremors, rigidity, seizures, recumbency, and fainting. we take a sample and isolate it on SDA at 37 degrees and see these results.
what is the diagnosis?

this cow was infected with the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. it has mastitis.
A farmer calls the vet because his female cows seem to have an infection on their udders. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media, blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?
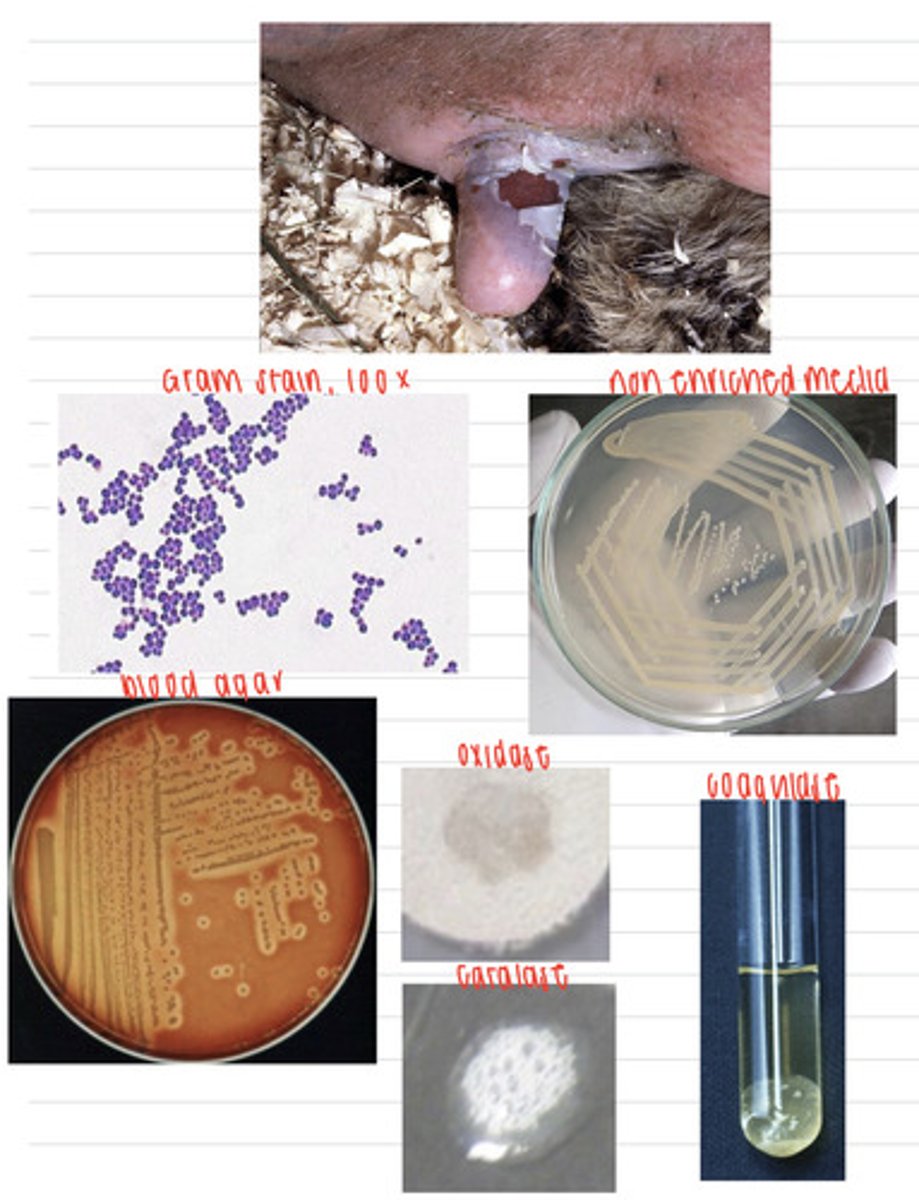
this rabbit was infected with the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus
A rabbit comes into the vet because of these skin lesions. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media, blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?
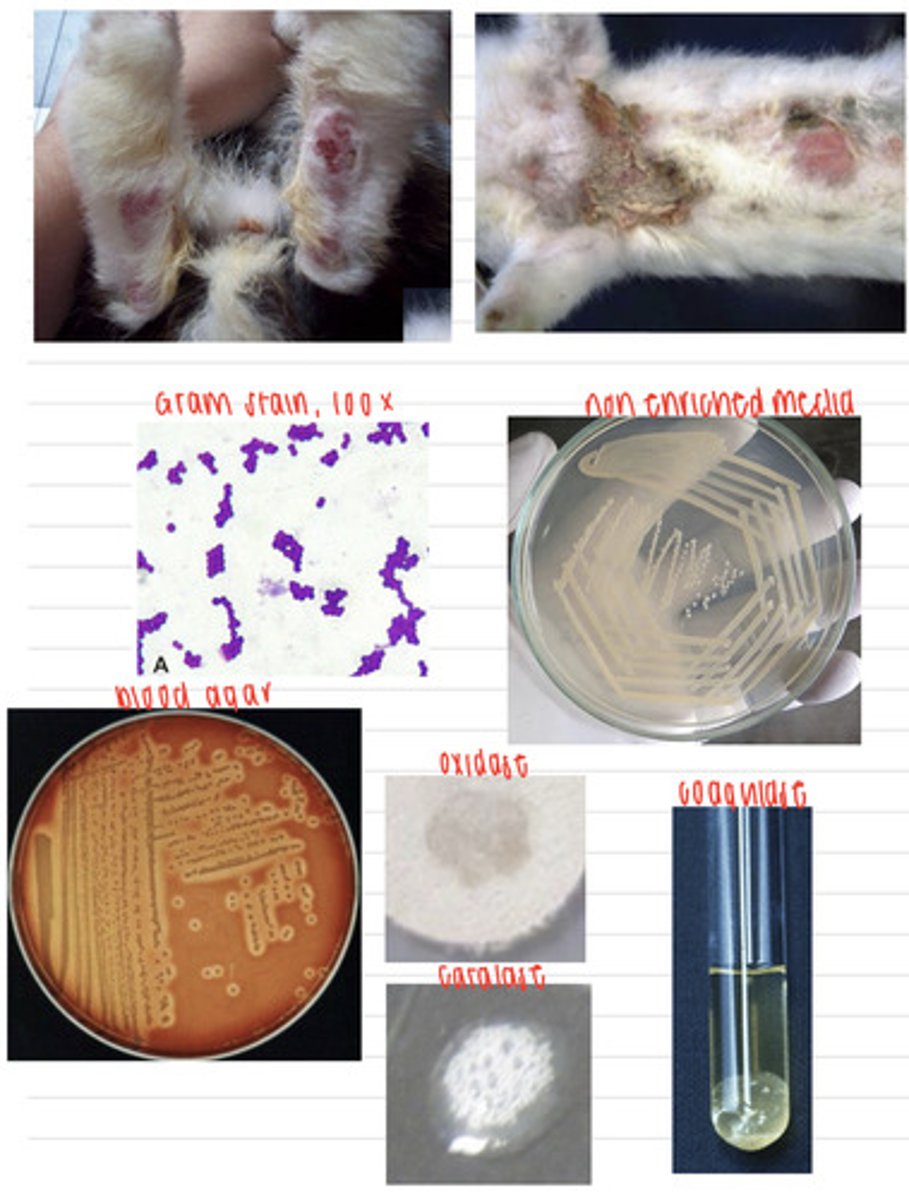
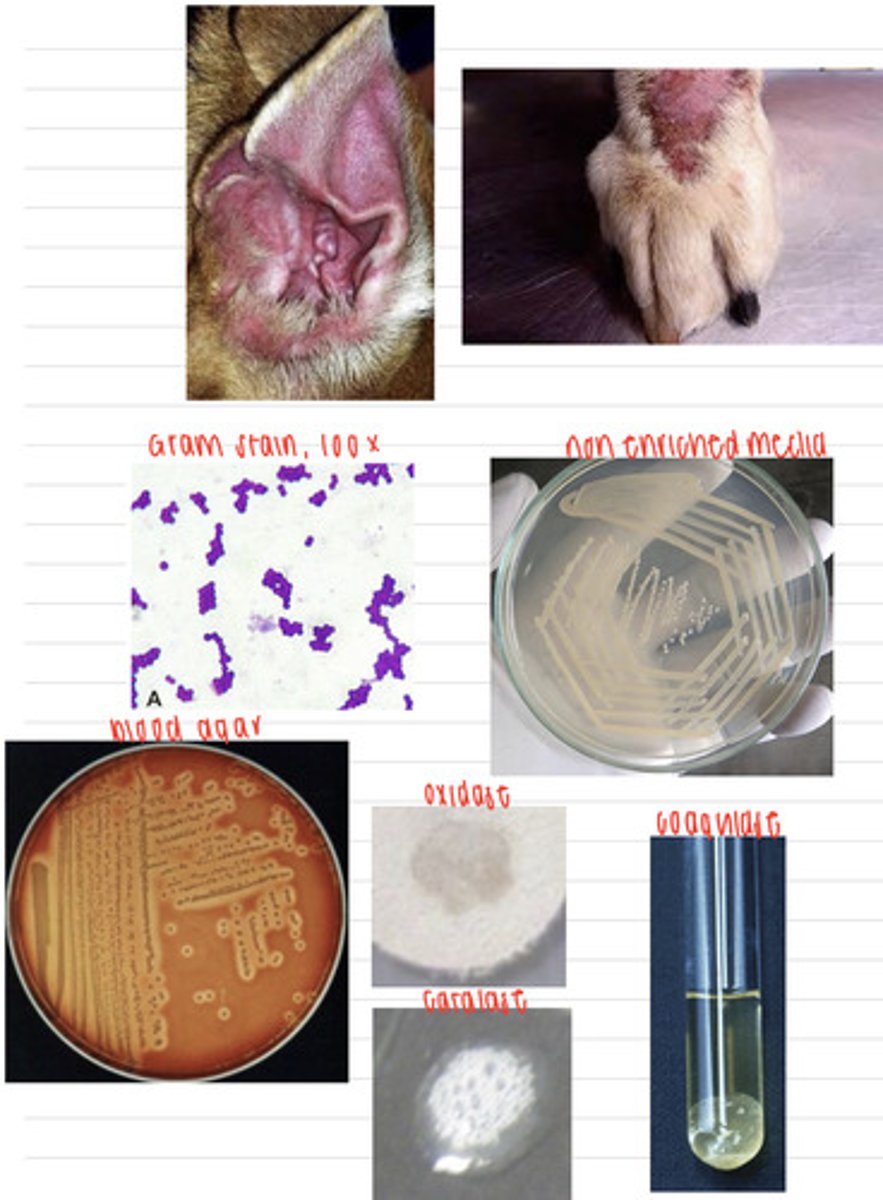
this dog was infected with the bacteria Staphylococcus pseudointermedius
A dog comes into the vet because of these skin lesions and ear infection. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media, blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?
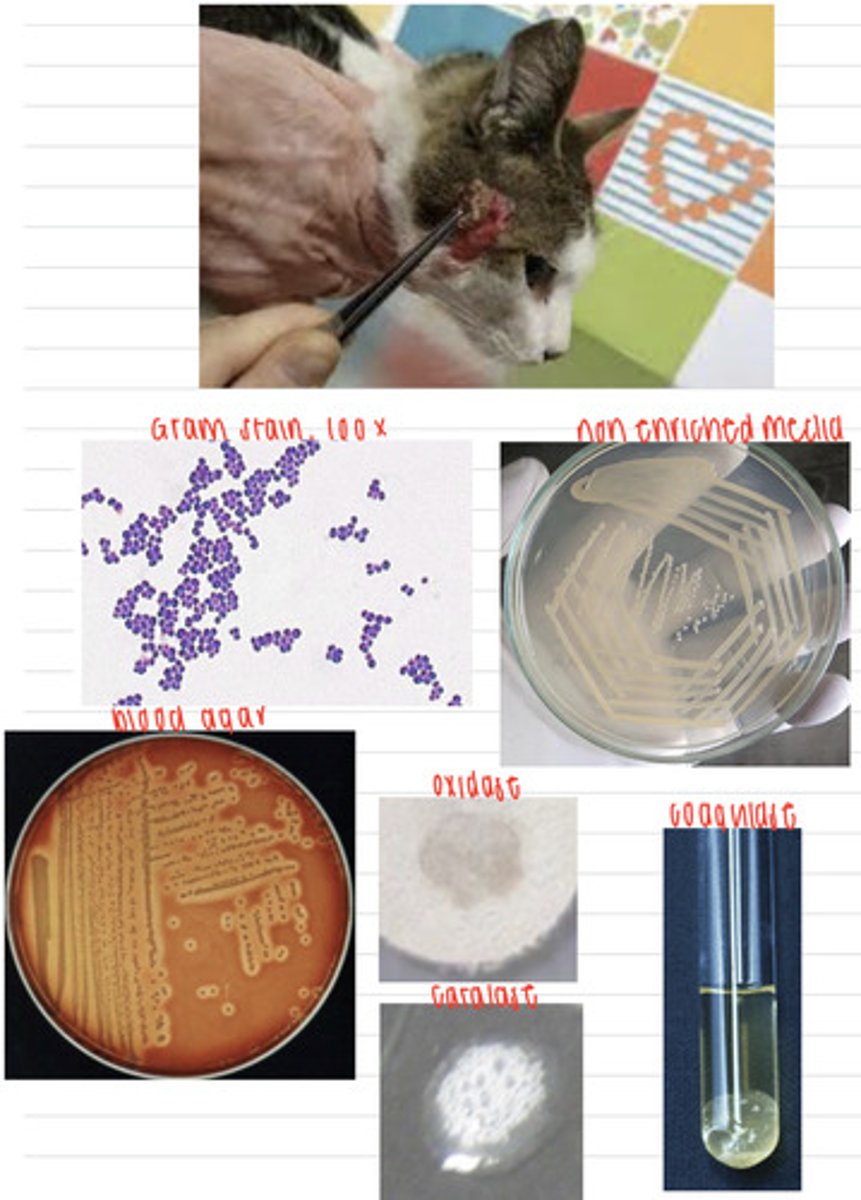
this cat was infected with the bacteria Staphylococcus pseudointermedius
A cat comes into the vet because of these skin lesions. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media, blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?
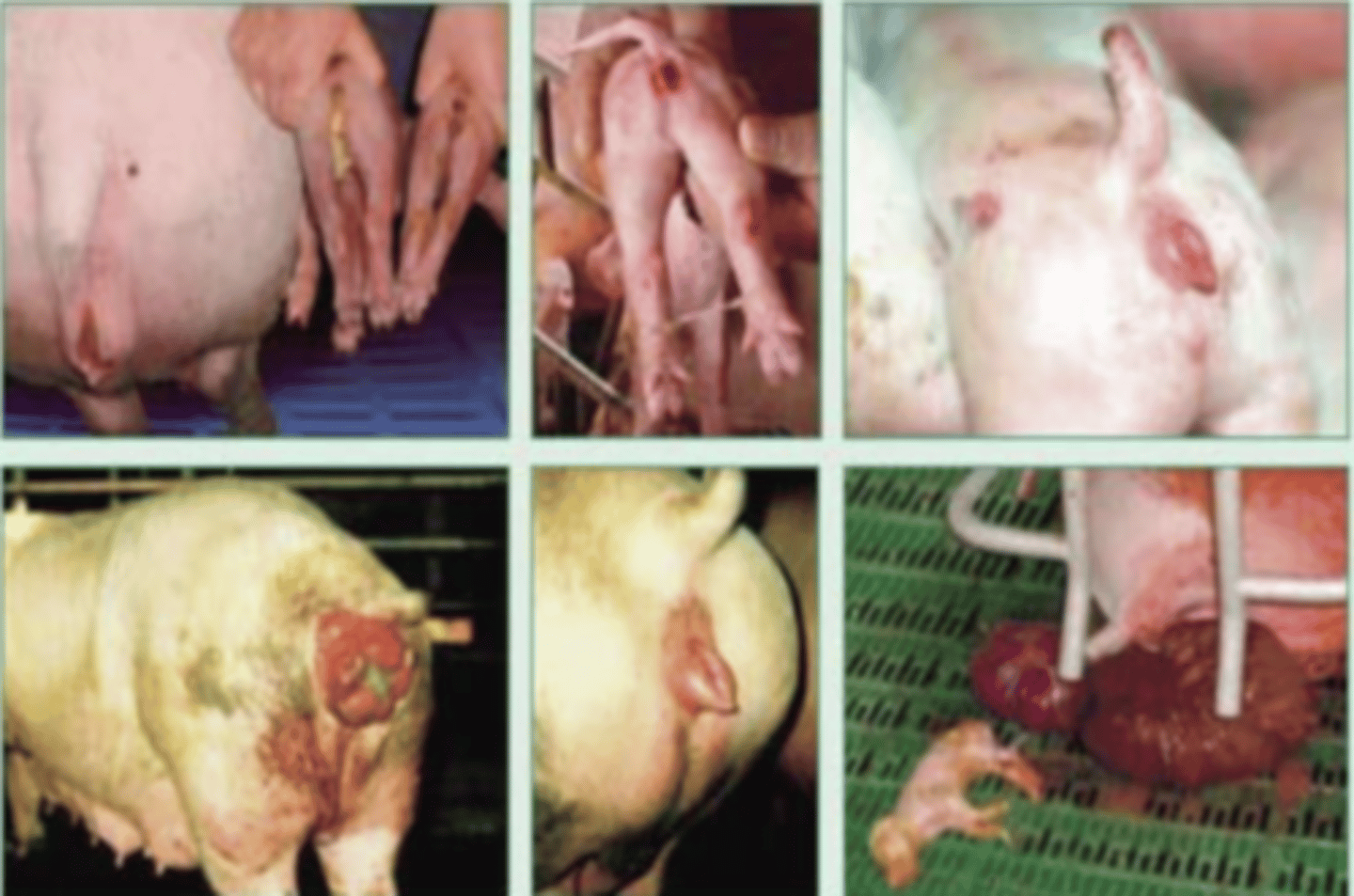
these pigs are infected with Staphylococcus hyicus and gave Greasy pig disease
A farmer notices his pigs have skin lesions that discharge. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media, blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?
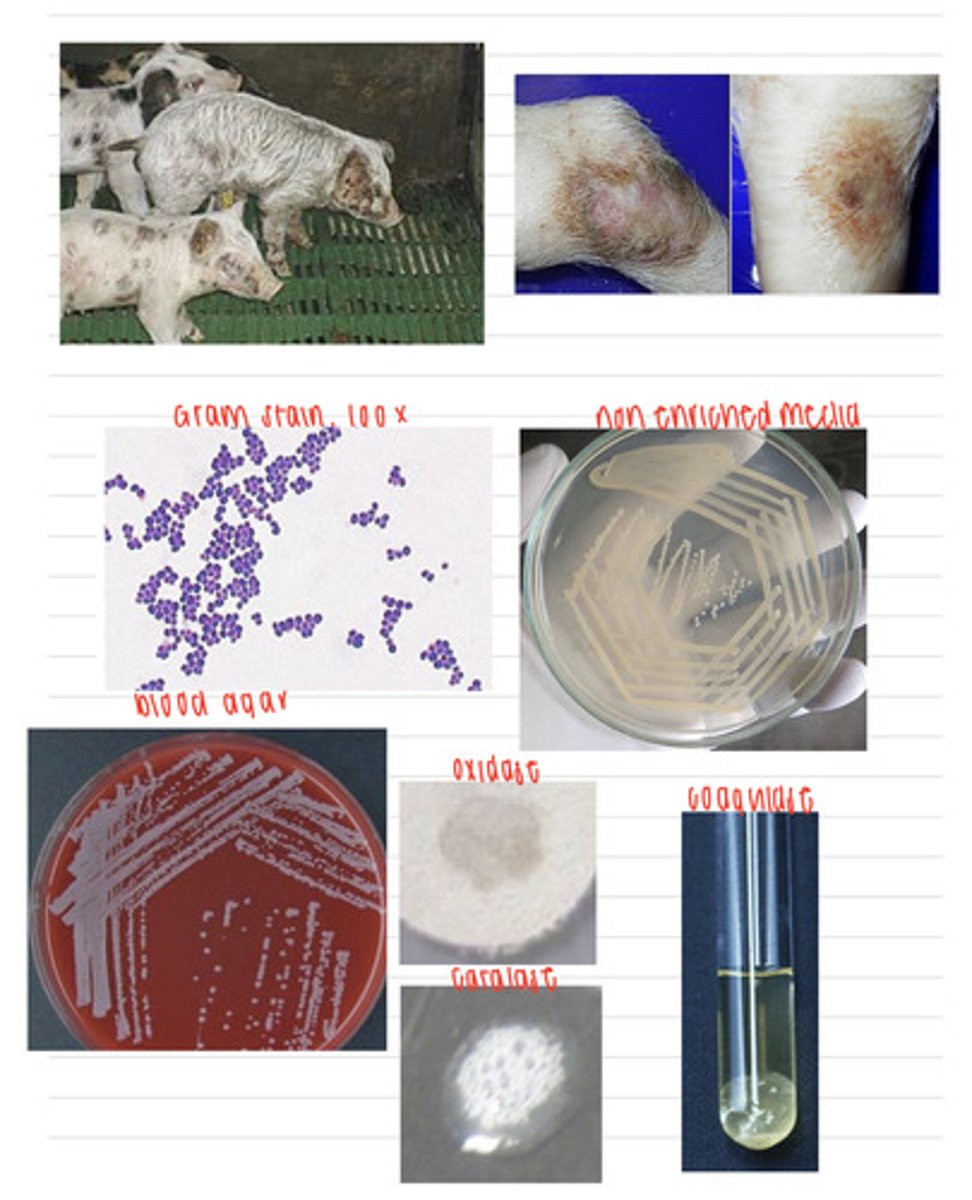
this cow has chronic mastitis and is infected with Streptococcus agalactiae
A cow is showing infection in its udders. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media (no growth), blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, CAMP, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?

the puppies had neonatal septicemia and were infected by Streptococcus agalactiae
a dog just had puppies, and some died before reaching 1 month because of septicemia. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media (no growth), blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, CAMP, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?
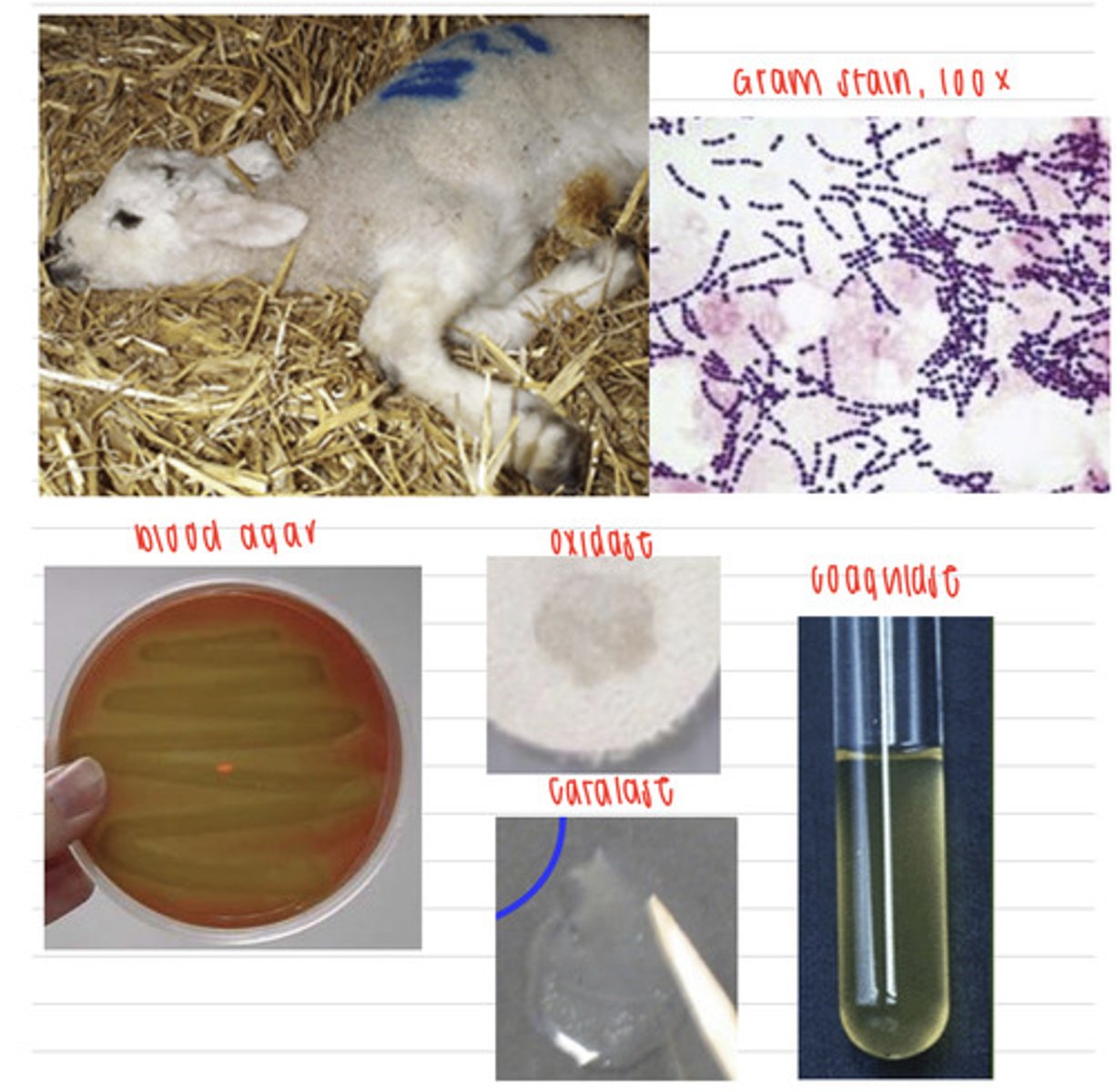
the lamb was infected by Streptococcus dysgalactiae
A farmer brings in his lamb with polyarthritis. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media (no growth), blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?
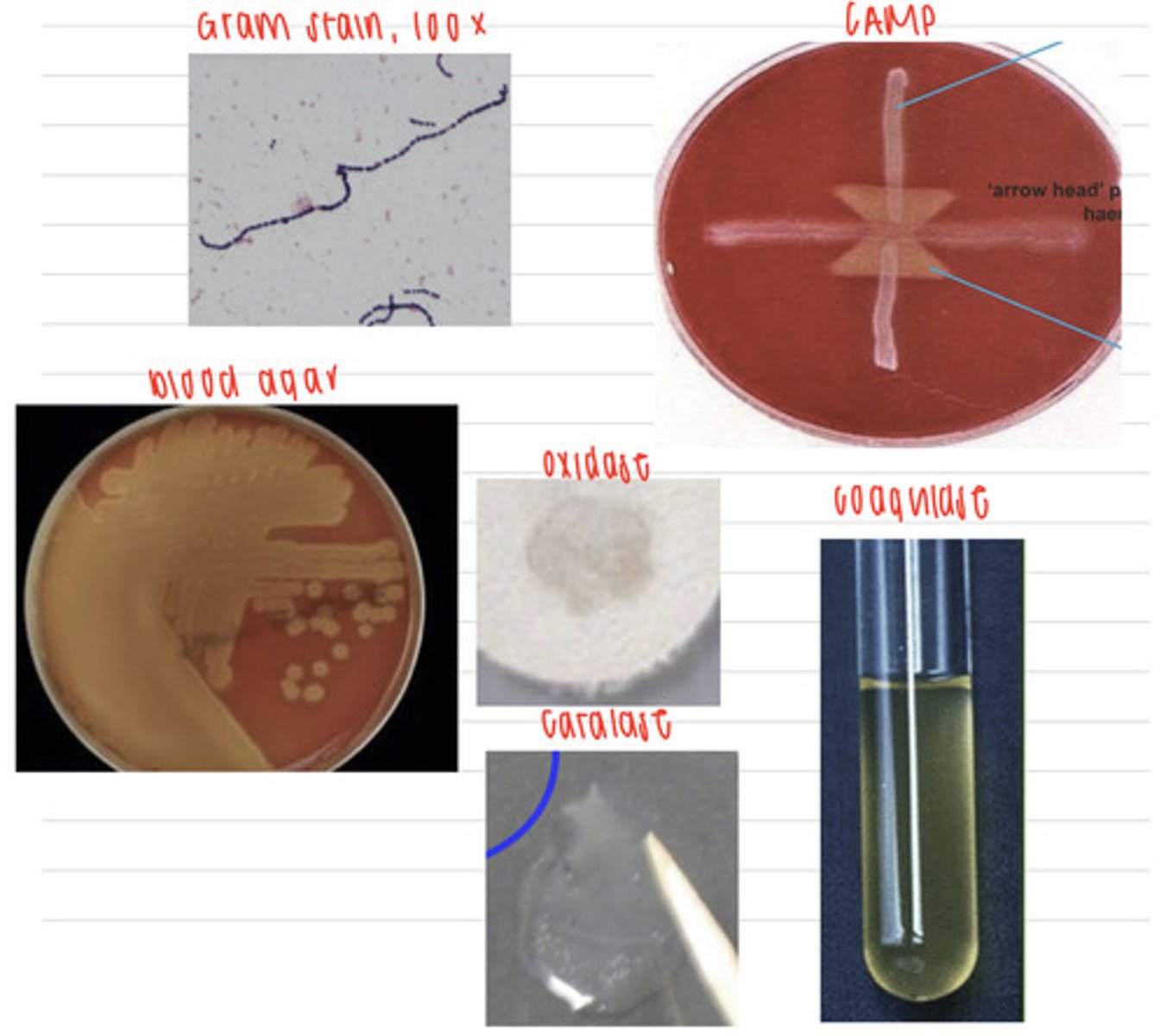
this horse has strangles, caused by a Streptococcus equi infection
an owner reports that his young horse has a fever, lesions on his lymph node area, and has nasal discharge. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media (no growth), blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?

the horse is infected by Streptococcus zooepidermicus
a horse is showing a navel infection as well as mastitis. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media (no growth), blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?
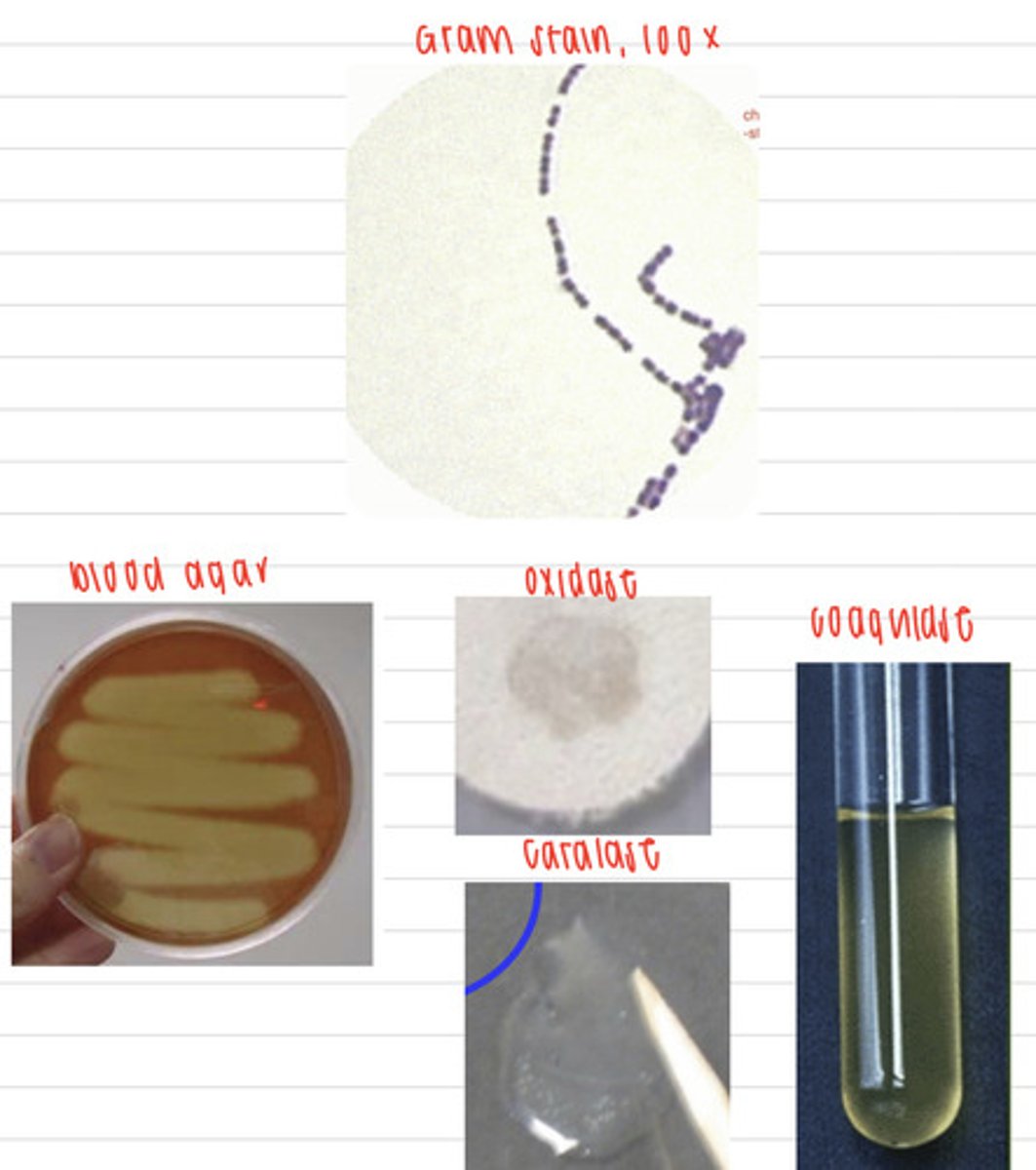
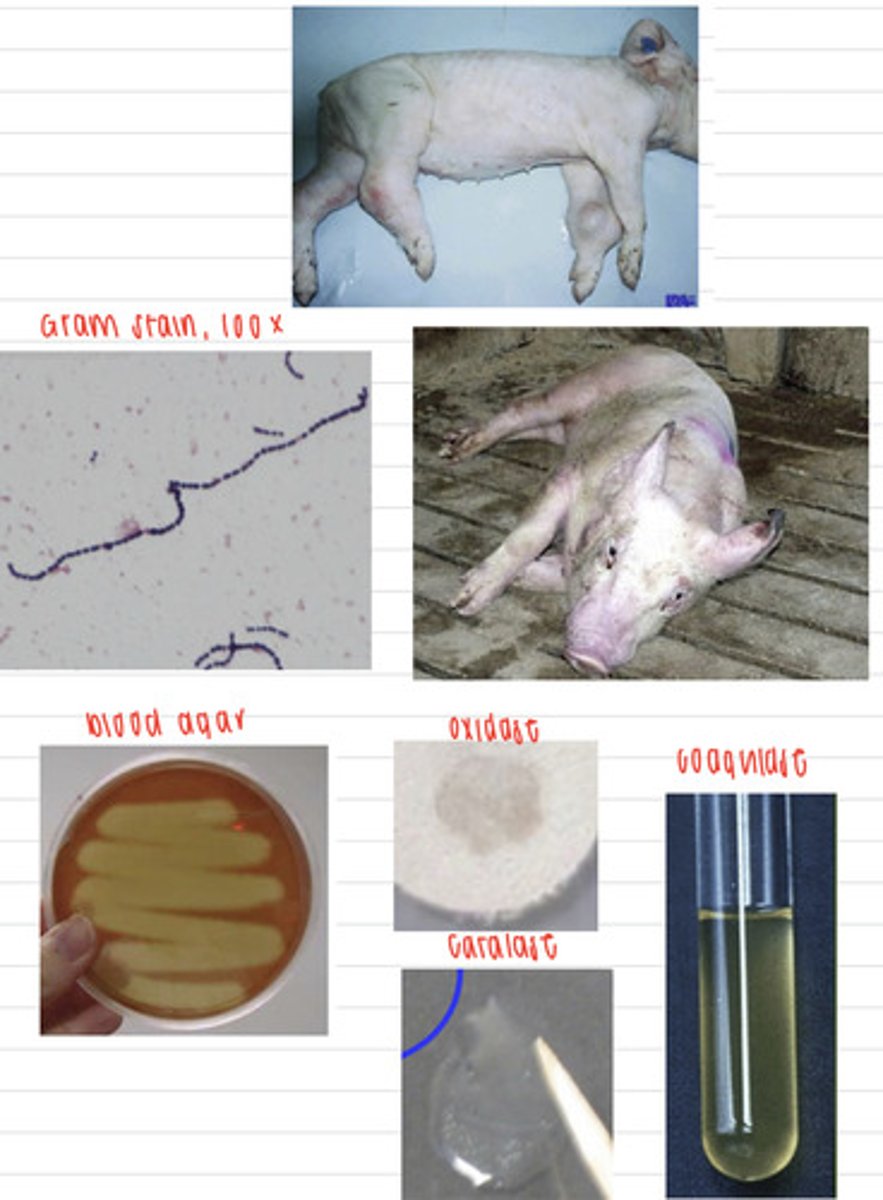
the pig has Porcine streptococcal meningitis, caused by Streptococcus suis
a pig comes into the vet showing these signs. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media (no growth), blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?
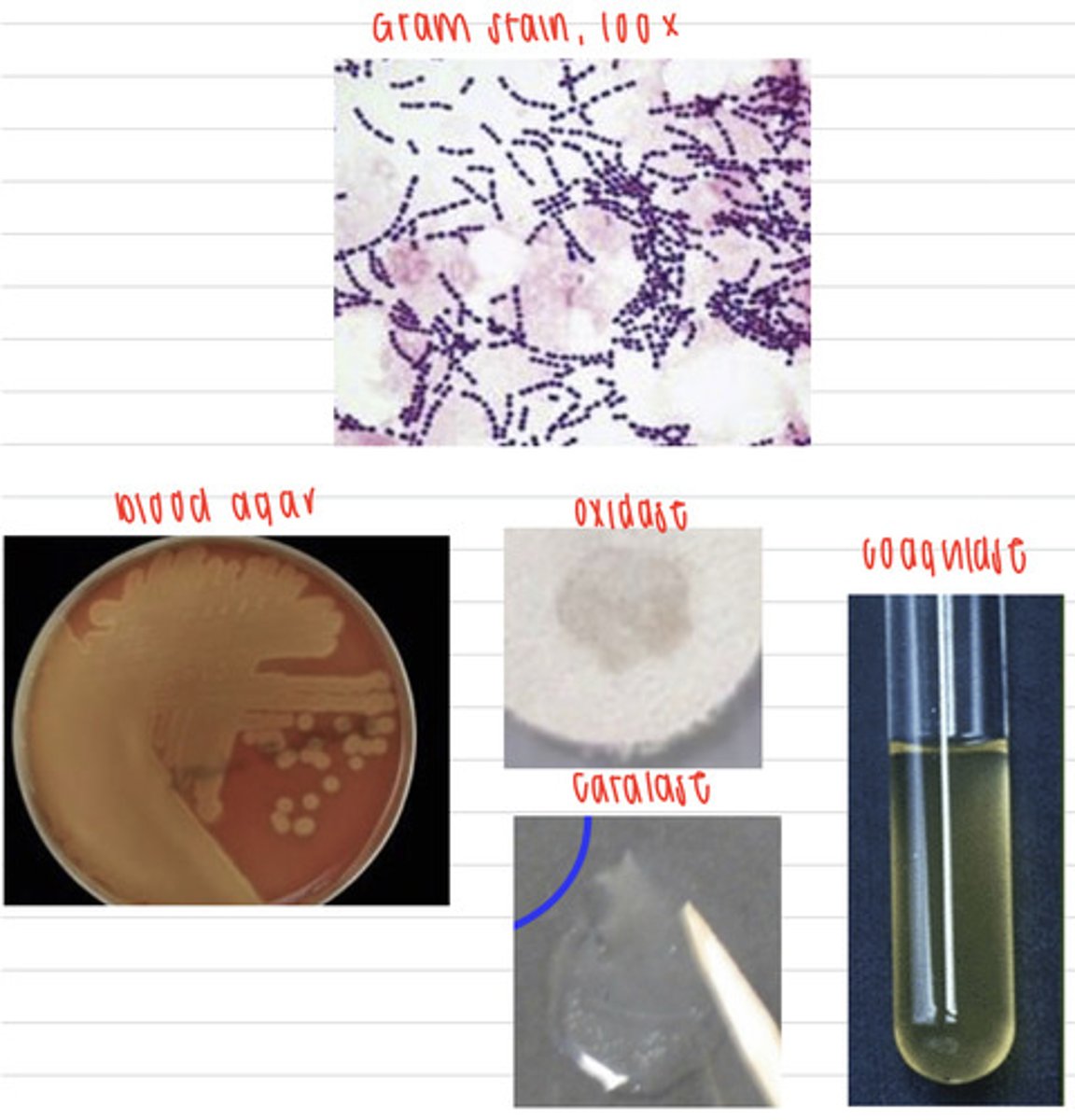
he is infected by Streptococcus suis
a human goes to the doctor and has septicemia and meningitis. We take samples, and isolate them on non-enriched media (no growth), blood agar, and MacConkey agar (no growth). we also stain using the gram method and perform oxidase, catalase, and coagulase tests. Here are the results.
What is the diagnosis?
he had tuberculosis, caused by an infected from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
a man dies and at the necropsy we find granulomas on his lungs. we take samples and inoculate onto non enriched media (no growth), blood agar, macconkey agar (no growth), and finally, egg enriched media. we stain the colonies with the ZN stain and perform coagulase, catalase, and oxidase tests. here are the results.
what is the diagnosis?
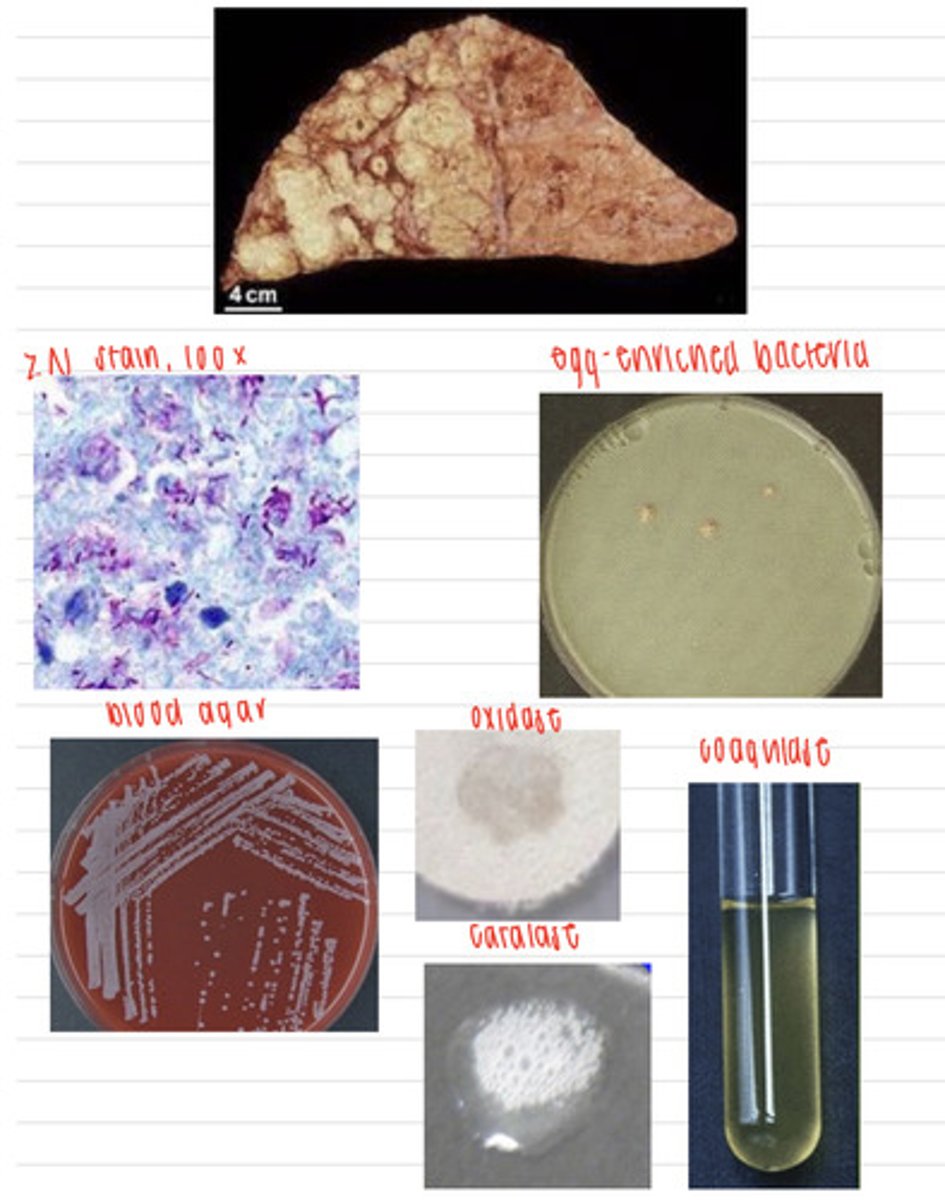
the cow had tuberculosis, caused by an infection by Mycobacterium bovis
a cow, after death, goes in for a necropsy, where we find these lesions on his liver and lungs. we take samples and inoculate onto non enriched media (no growth), blood agar, macconkey agar (no growth), and finally, egg enriched media. we stain the colonies with the ZN stain and perform coagulase, catalase, and oxidase tests. here are the results.
what is the diagnosis?
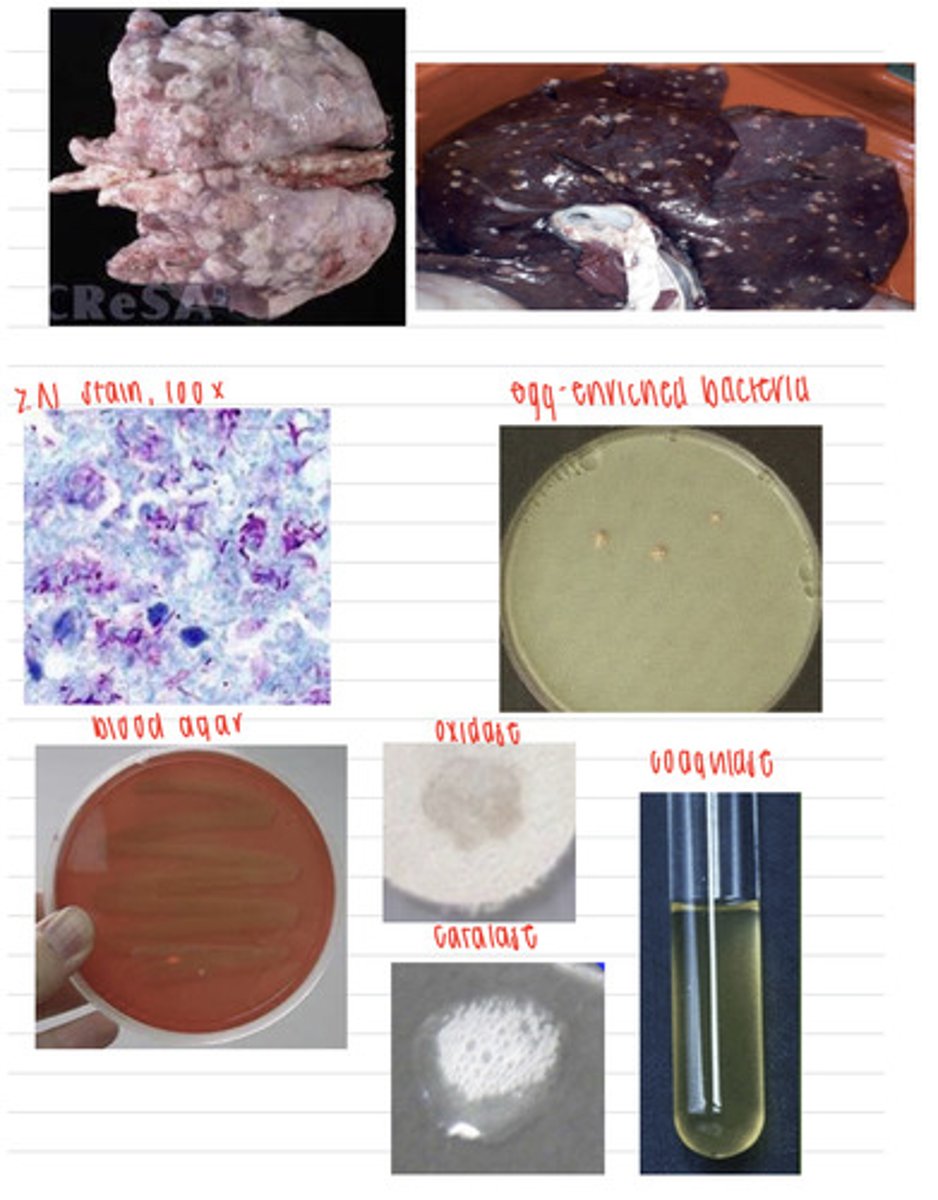
she has para tuberculosis/ johnes disease , caused by he bacteria Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis
a cow has lost a lot of weight and is having diarrhea. we take samples and inoculate onto non enriched media (no growth), blood agar, macconkey agar (no growth), and finally, egg enriched media. we stain the colonies with the ZN stain and perform coagulase, catalase, and oxidase tests. here are the results.
what is the diagnosis?
