Bones of the Lower Limb
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
How do lower and upper limbs rotate during development?
Upper limb rotates so thumb is lateral (anatomical position).
Lower limb rotates so big toe is medial (anatomical position).
(Important in functions of anterior/posterior compartments).
What forms the hip joint?
Head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis.
Which bones make up the hip bone?
Ilium, ischium, pubis.
What are the male and female Q angles?
Male - 12 degrees.
Female - 16 degrees.
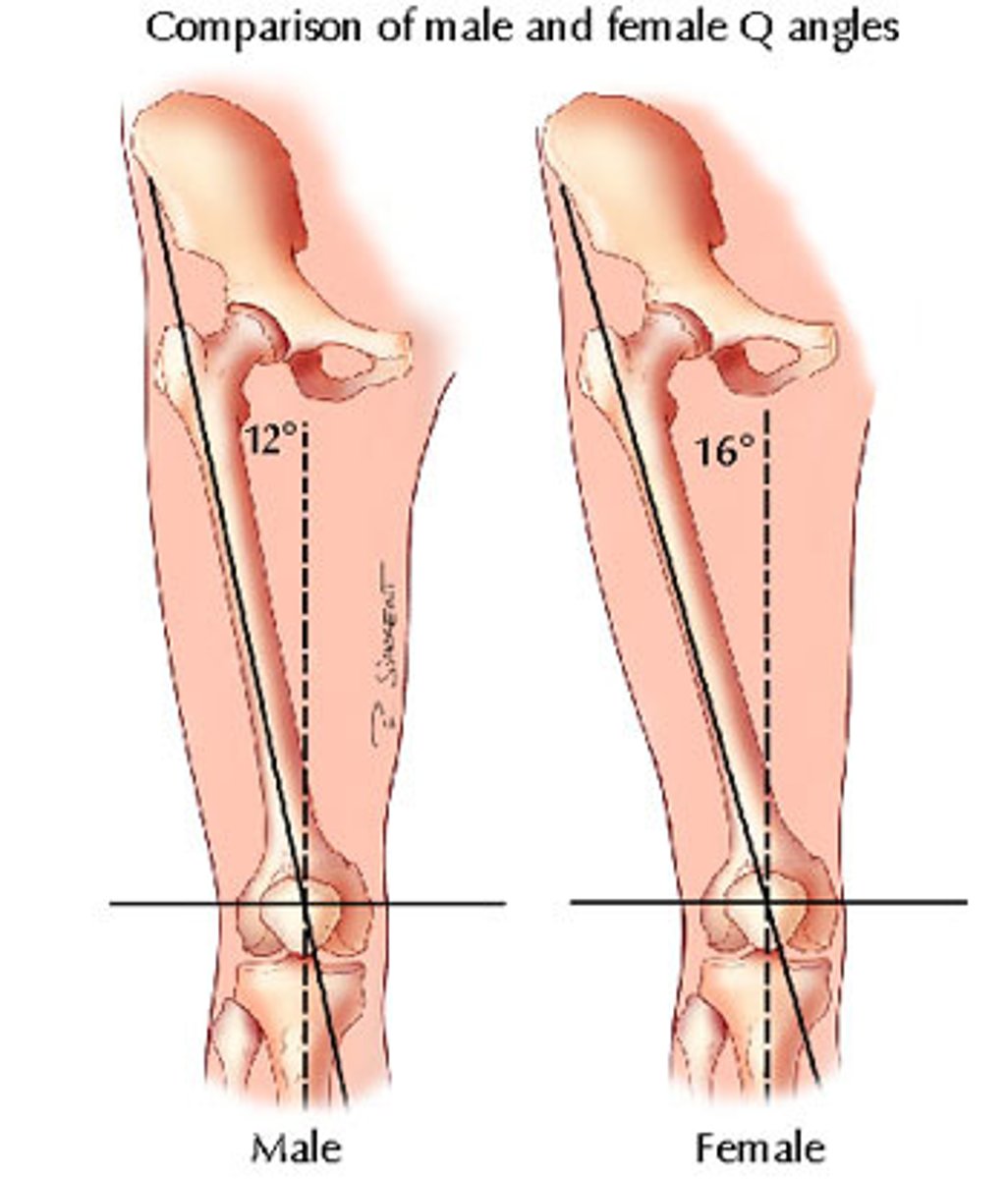
Why are females more susceptible to hip fractures?
Larger Q angle.
What is the head of the femur covered with?
Articular Cartilage
What is the function of the acetabular labrum?
Cartilaginous rim which increases depth and stability of hip joint.
What is the name of the small depression in the head of the femur? Why is it there?
The Fovea - site of attachment for ligamentum teres.
Which part of the femur is just inferior to the head?
Neck.
What are the 2 bony processes found on the proximal femur?
Greater and lesser trochanters.
Which muscles attach on the greater trochanter?
Muscles in the gluteal region. e.g. Gluteus Medius, Gluteus Minimus and Piriformis.
What originates from the greater trochanter?
Vastus Lateralis
What muscles attach on the lesser trochanter?
Iliopsoas.
What is the position of the 2 trochanters relative to the neck of the femur?
Greater Trochanter - lateral to the neck.
Lesser Trochanter - inferior to the neck.
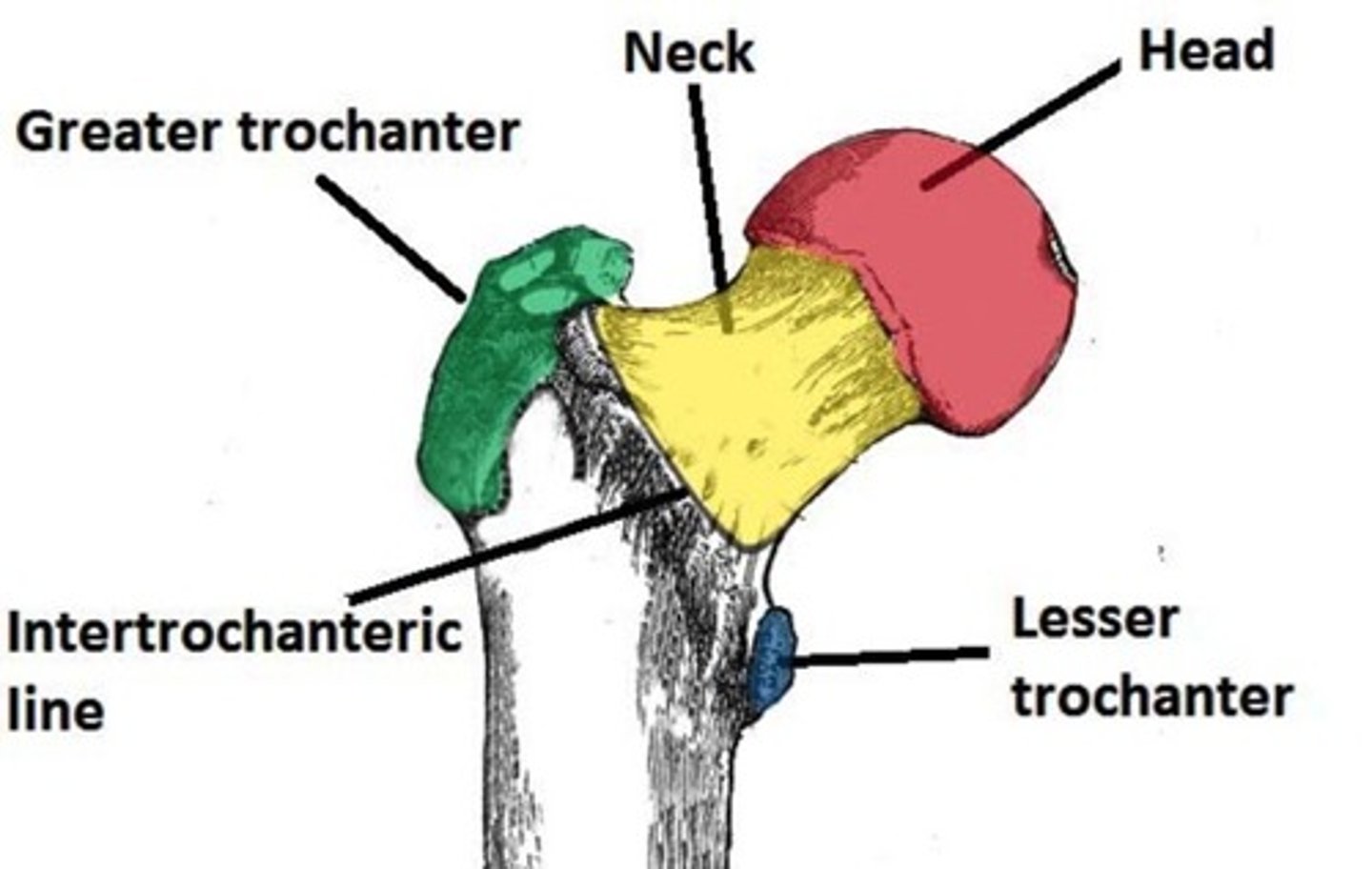
What is the name of the ridge of bone that runs between the 2 trochanters on the anterior surface?
Intertrochanteric Line
After the interochanteric line passes the lesser trochanter on the posterior surface, what does it become?
Pectineal Line
What is the name of the ridge of bone that runs between the 2 trochanters on the posterior surface?
Intertrochanteric Crest
Why is the intertrochanteric line important? (2 reasons)
Attachment for iliofemoral ligament.
Anterior attachment of the hip joint capsule.
How can proximal femur fractures be classified? How are they different?
Intracapsular - occurs within capsule of hip joint. Can cause damage to medial femoral circumflex artery - and cause avascular necrosis of the femoral head.
Extracapsular - blood supply to the femur is intact, so avascular necrosis is a rare complication.
What is avascular necrosis?
Bloodflow is disrupted to the fracture site and the resulting ischemia leads to tissue/bone necrosis.
What are the 2 roughened ridges of bone on the posterior shaft of the femur?
Linea Aspera
What do the linea aspera split to form?
Medial and lateral supracondylar lines.
Where does the medial supracondylar line end?
Adductor Tubercle - attachment site for Adductor Magnus.
Which neurovascular structures are at risk during a femoral shaft fracture?
Femoral nerve and artery.
Which parts of the distal femur articulate with the tibia and patella to from the knee joint?
Medial and Lateral Condyles.
Why is the lateral condyle more prominent?
Prevents excess lateral movement of the patella - could lead to dislocation the knee.
What are the bony elevations on the non-articular areas of the condyles?
Medial and Lateral epicondyles.
What is the notch on the posterior surface of the femur, which separates the 2 condyles?
Intercondylar Fossa
The intercondylar fossa contains 2 facets for attachment of which intracapsular knee ligaments?
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) - attaches to the medial aspect of the lateral condyle.
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) - attaches to the lateral aspect of the medial condyle.
Which bone is known as the kneecap?
Patella.
What type of bone is the patella?
Sesamoid.
What are the 2 surfaces of the patella?
Superior and Inferior.
What forms the superior and inferior aspects of the patella?
Superior - Base:
Attachment site for quadriceps tendon.
Inferior - Apex:
Connected to tibial tuberosity by patella ligament.
The posterior surface of the patella is marked with which 2 facets?
Medial Facet - articulates with medial condyle of the femur.
Lateral Facet - articulates with the lateral condyle of the femur.
What are the 2 main functions of the patella?
Leg Extension - Enhances the leverage that the quadriceps tendon can exert on the femur, increasing the efficiency of the muscle.
Protection - Protects the anterior aspect of the knee joint from physical trauma.
Which lower leg bone is known as the shin?
Tibia.
What is the proximal tibia widened by?
Medial and lateral condyles.
The flat surface formed proximally by the tibial condyles is known as what?
Tibial Plateau.
What region is located between the condyles of the tibia?
Intercondylar Eminence.
The intercondylar eminence projects upwards on either side as what?
Medial and Lateral Interoncdylar Tubercles.
What shape is the shaft of the tibia?
Prism-shaped.
3 borders and 3 surfaces.
The proximal aspect of the anterior border of the tibia is marked by what?
Tibial Tuberosity - attachment site for patella ligament.
Which ridge of bone on the posterior surface of the tibia marks the site of origin for the soleus muscle?
Soleal Line
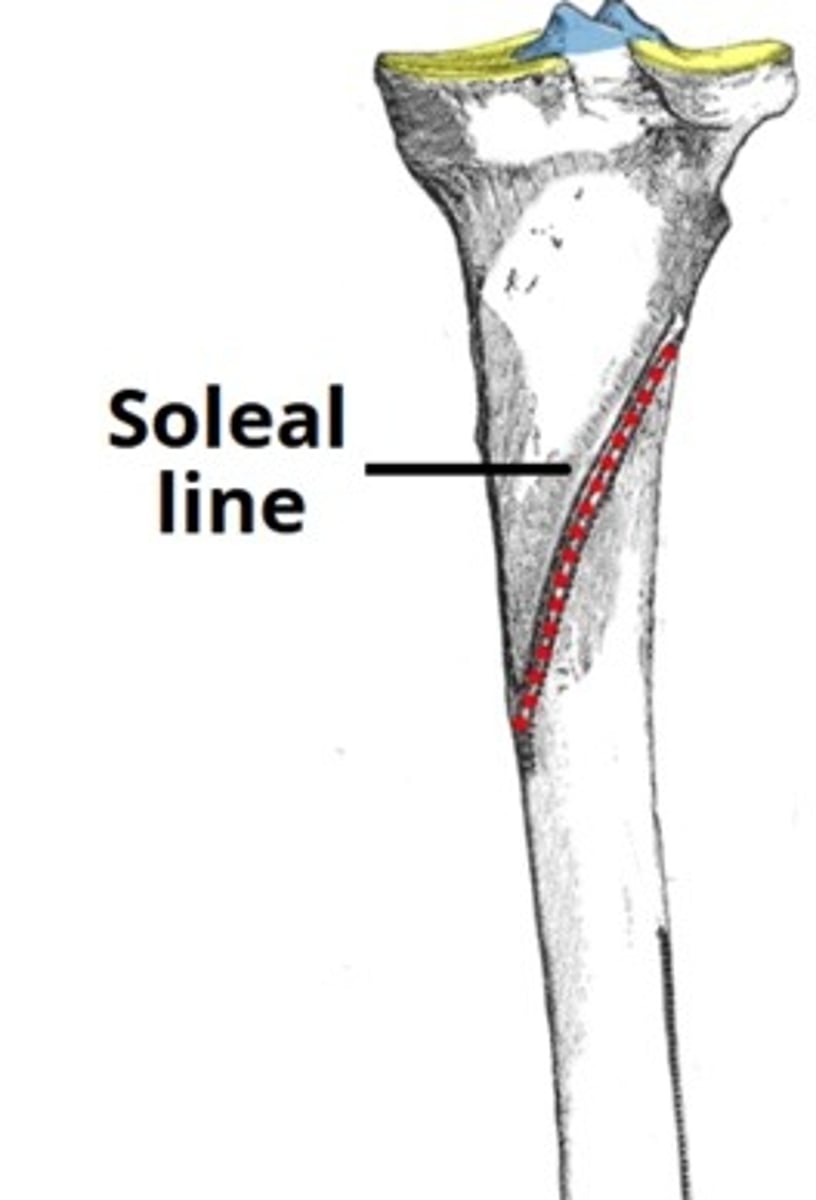
Why is the lateral border of the tibia significant?
Attachment site to the interosseous membrane that binds the tibia and the fibula together.
What is the bony projection continuing inferiorly on the medial aspect of the distal tibia?
Medial Malleous
On the posterior surface of the tibia, there is a groove through which which tendon passes?
Tendon of Tibialis Posterior
What is found on the lateral side of the distal tibia?
Fibular Notch - where fibula is bound to tibia, forming tibiofibular joint.
What are the 3 main articulations of the fibula?
Proximal tibiofibular joint – articulates with the lateral condyle of the tibia.
Distal tibiofibular joint – articulates with the fibular notch of the tibia.
Ankle joint – articulates with the talus bone of the foot.
On the posterior and lateral surface of the fibular neck, which nerve can be found?
Common Fibular Nerve
How many surfaces does the fibular shaft have?
3
Distally, the lateral surface of the fibula continues inferiorly to form what?
Lateral Malleolus
What are the 2 common methods of fracture of the lateral malloulus?
Forced external rotation of the ankle - this force of the talus against the bone causes a spiral fracture of the lateral malleolus.
Eversion of the foot - talus presses against malleolus, causing a transverse fracture.
How can the bones of the feet be divided?
Tarsals, Metatarsals, Phalanges.
What makes up the hindfoot, midfoot and forefoot?
Hindfoot - talus and calcaneus.
Midfoot - navicular, cuboid and cuneiforms.
Forefoot - metatarsals and phalanges.
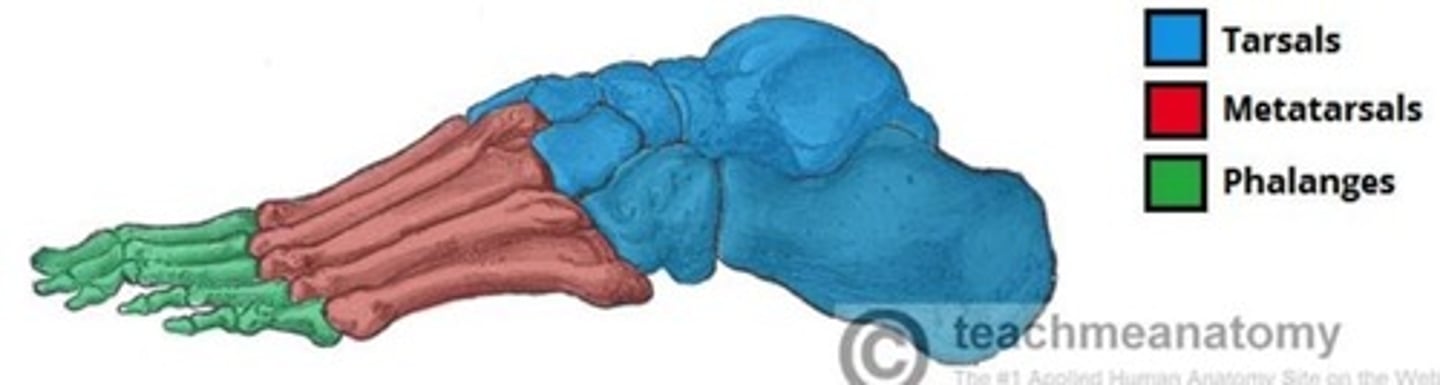
What are the 3 rows of tarsals?
Proximal, intermediate and distal.
What are the proximal tarsals?
Talus and Calcaneus.
What are the 3 articulations of the talus?
Superiorly - ankle joint - between the talus and the bones of the leg.
Inferiorly – subtalar joint – between the talus and calcaneus.
Anteriorly – talonavicular joint – between the talus and the navicular.
What are the 2 articulations of the calcaneus?
Superiorly - subtalar (talocalcaneal) joint – between the calcaneus and the talus.
Anteriorly - calcaneocuboid joint – between the calcaneus and the cuboid.
Where on the posterior aspect of the calcaneus does the Achilles tendon attach?
Calcaneal Tuberosity.
How many bones are in the intermediate group? What are they?
1 - Navicular.
What are the 3 articulations of the Navicular?
Posteriorly - articulates with the talus.
Anteriorly - all three cuneiform bones.
Laterally - cuboid bone.
Which bones make up the distal group?
Cuboid and 3 Cuneiforms.
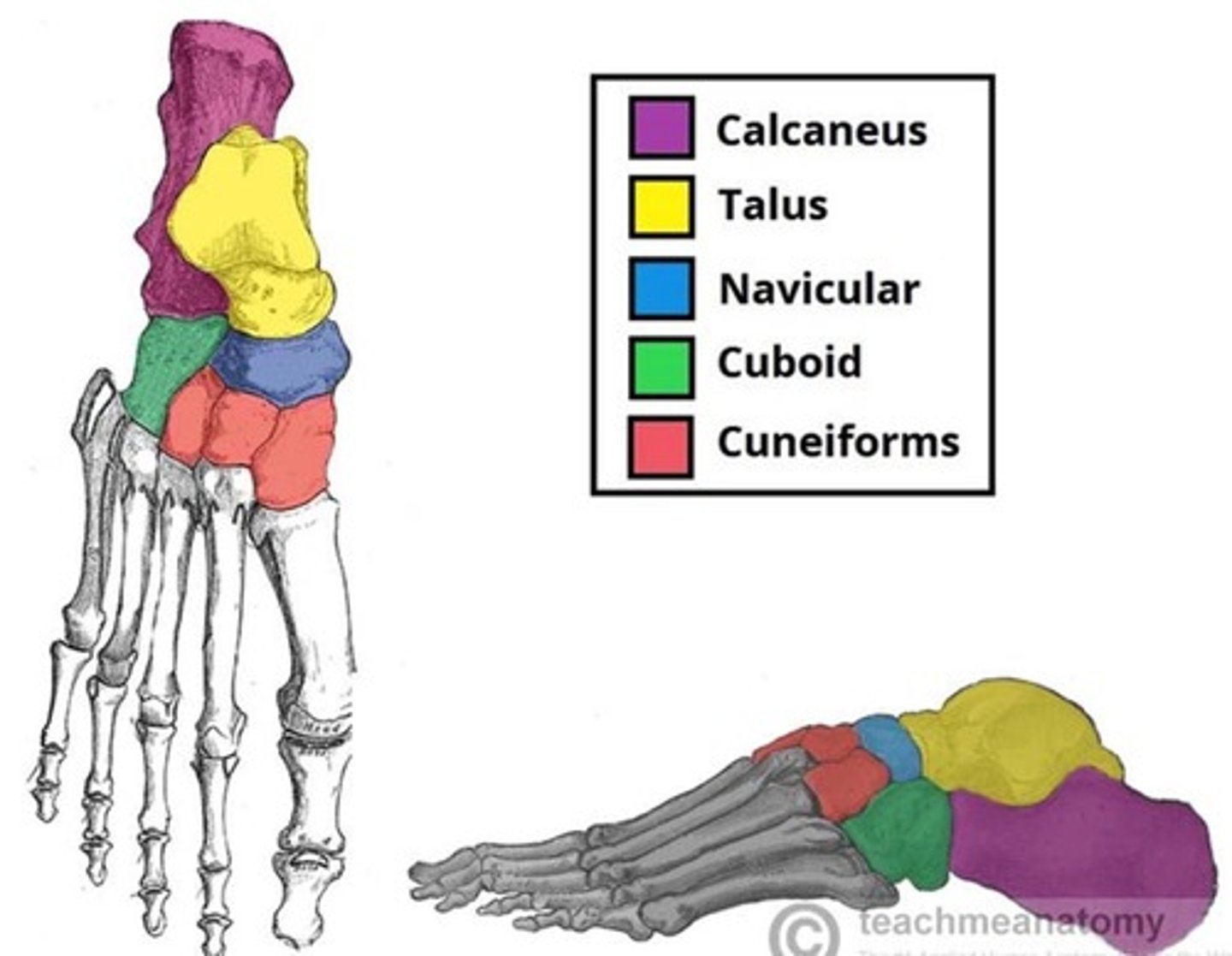
How does the cuboid lie in relation to the calcaneus and the metatarsals?
Anterior to calcaneus and behind the 4th and 5th metatarsals.
What are the 3 cuneiforms?
Medial, Intermediate and Lateral.
Which bones do the cuneiforms articulate with?
Articulate with the navicular posteriorly and the metatarsals anteriorly.
Which tarsals are most commonly fractured?
The Talus and Calcaneus.
How are the metatarsals numbered?
Medial to lateral, with the great or big toe (hallux) being digit 1.
What are the 3 articulations of the metatarsals?
Proximally – tarsometatarsal joints – between the metatarsal bases and the tarsal bones.
Laterally – intermetatarsal joint(s) – between the metatarsal and the adjacent metatarsals.
Distally – metatarsophalangeal joint – between the metatarsal head and the proximal phalanx.
What are the bones of the toes?
Phalanges
How many phalanges do the toes have?
Big Toe - 2.
Other Toes - 3.
Still learning (10)
You've begun learning these terms. Keep up the good work!