Small Intestines
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Appendicitis, diverticulitis, intussusception, SBO. neoplasms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
storage of intestinal flora, remnant of the past (vestigial)
Theoretical functions of the appendix
Appendix becomes obstructed → Increasing internal appendiceal pressure → inflammation from pressure -induced damage → fluid stasis and inflammation leads to gangrene and perforation
Appendicitis commonly affects people 10-30 y/o what is the pathogenesis?
fecalith, intestinal inflammation, foreign body, cancer/tumor
Common obstructions of the appendix
CBC (WBCs), UA (blood, pus), Hcg (if female - r/o pregnancy complications), CT with contrast, U/S (1st choice for peds and pregnant peeps - if neg get MRI)
17 y/o male presents to the ER for Abdominal pain, he states that it started in the middle of his stomach but now its right, lower part. He also reports N/V/D. Vitals are stable with the exception of 102.4 F temp. On physical exam, the patient is tender over McBurney’s point, + Rosving’s, and + obturator, heel tap is negative. What diagnostics you want girlie?
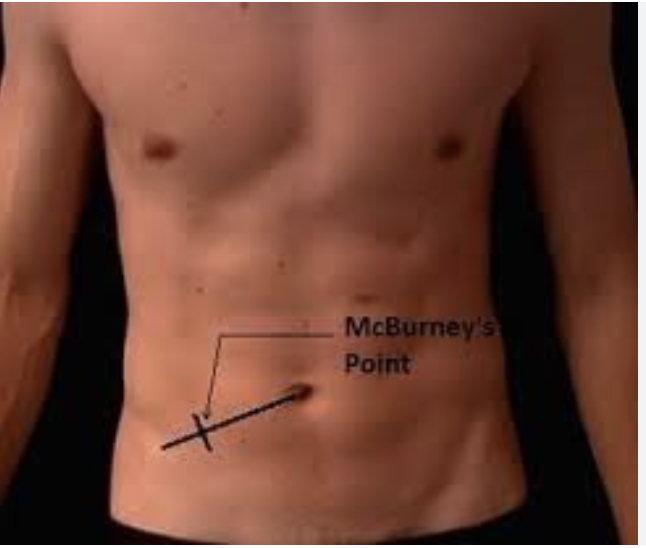
Rosving’s sign
indirect rebound test, the examiner presses on the left lower quadrant, away from the typical area of appendiceal pain.
Psoas Sign (retrocecal appendix)
manifested by right lower quadrant pain with passive right hip extension
Obturator sign
the clinician flexes the patient's right hip and knee, followed by internal rotation of the right hip, this elicits right lower quadrant pain - low sensitivity (8%) not really done anymore
pain in suprapubic region, urgency to urinate/defecate, tenderness with pelvic/rectal exam
If the appendix is in the pelvic region - what might we find?
RLQ, periumbilical, right subcoastal pain
For pregnant patients with appendicitis, what might we find on physical exam?
vague, less localized pain
For elderly patients with appendicitis, what might we find on physical exam?
Non-op with Abx (pip-taz or 2/3 G CPH + metro), Laprascopic appendectomy (peeps with no response, recurrence, elderly)
17 y/o male presents to the ER for Abdominal pain, he states that it started in the middle of his stomach but now its right, lower part. He also reports N/V/D. Vitals are stable with the exception of 102.4 F temp. On physical exam, the patient is tender over McBurney’s point, + Rosving’s, and + obturator, heel tap is negative. Labs reveal leukocytosis with hella bands, UA is positive for hematuria, U/S reveals a appendiceal diameter over 6mm, CT shows a appendiceal diameter over 6mm with surrounding fluid - consistent with appendicitis. What is your treatment plan?
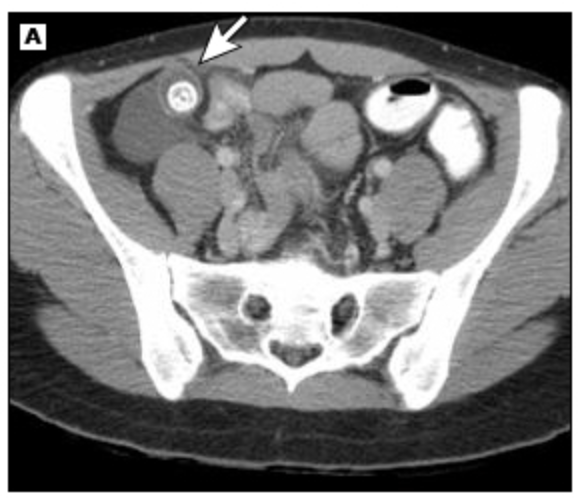
Drain the abscess, Abx (cover for psuedomonas), Appendectomy in 6 weeks
17 y/o male presents to the ER for Abdominal pain, he states that it started in the middle of his stomach but now its right, lower part. He also reports N/V/D. Vitals are stable with the exception of 102.4 F temp. On physical exam, the patient is tender over McBurney’s point, + Rosving’s, and + obturator, heel tap is positive. Labs reveal leukocytosis with hella bands, UA is positive for hematuria, U/S reveals a appendiceal diameter over 6mm, CT shows a appendiceal diameter over 6mm with abscess - consistent with perforated appendicitis. What is your treatment plan?
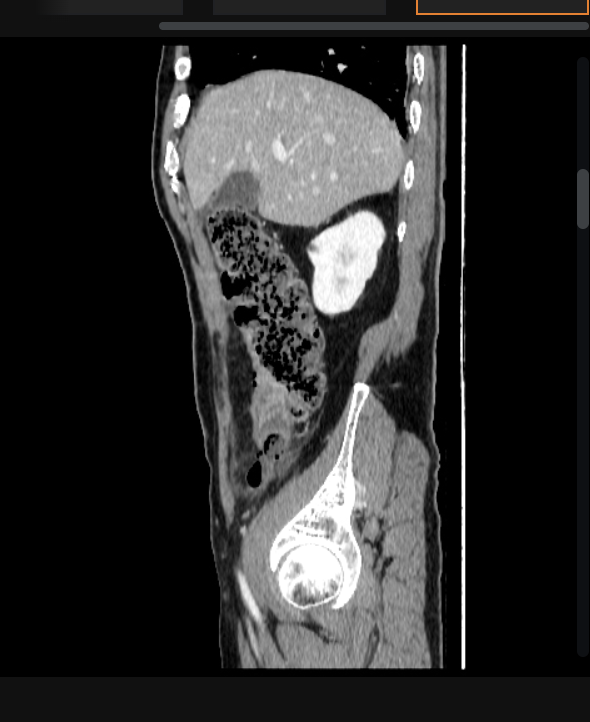
Immediate appendectomy with Abx, abdominal lavage
17 y/o male presents to the ER for Abdominal pain, he states that it started in the middle of his stomach but now its in the right, lower part. He also reports N/V/D. Vitals are stable with the exception of 102.4 F temp. On physical exam, the patient is tender over McBurney’s point, + Rosving’s, and + obturator, heel tap is positive. Labs reveal leukocytosis with hella bands, UA is positive for hematuria, U/S reveals a appendiceal diameter over 6mm, CT shows a appendiceal diameter over 6mm - consistent with free perforated appendicitis. What is your treatment plan?
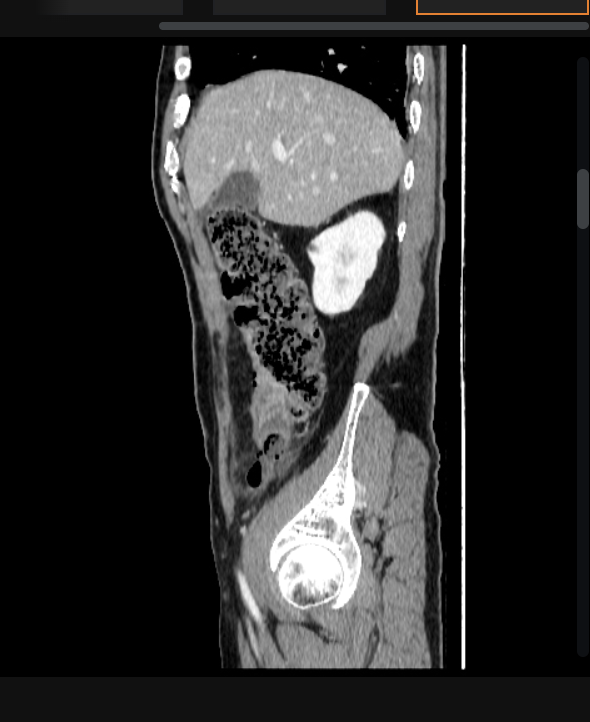
gastroenteritis, ovarian torsion, ecoptic pregnancy, tubo-ovarian cyst, ovarian cyst rupture, testicular torsion, diverticulitis, colon perforation, bowel perforation, renal stone
DDx for appendicitis
diverticulosis
Diverticulitis cannot happen without
Diverticulosis
An outpouching of the colon wall typically at well-defined points of weakness when the blood vessels penetrate (usually the sigmoid colon)
LGIB (usually painless)
Diverticulosis the the most common cause of
low dietary fiber (seeds and nuts don’t count), lack of exercise
Risk factors for Divertuculosis
uncomplicated diveriticulitis
inflammation of 1 or more diverticula that increases with age
micro-perforations
With any diverticulitis we assume
abscess, fistula, perforation (BIGGER than the micro - duh), bowel obstruction
Complicated diverticulitis includes:
CBC (WBCs), FOBT, CT with contrast (preferred!), DO NOT DO A COLONOSCOPY, CRP, UA (pyuria)
56 y/o male presents to the ER for abdominal pain with associated N/V/D. PMHx is positive for diverticuli. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp of 102.8. You note abdominal pain in the LLQ. What diagnostics you want?
Clear liquid diet, maybe Abx
56 y/o male presents to the ER for abdominal pain with associated N/V/D. PMHx is positive for diverticuli. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp of 102.8. You note abdominal pain in the LLQ. Lab work is as follows, leukocytosis, + FOBT, elevated CRP, UA reveals sterile pyuria. CT reveals localized bowel wall thickening (>4 mm) and an increase in soft tissue density within the pericolonic fat secondary to inflammation or fat stranding - consistent with diverticulitis. Let’s say its mild - what is your treatment plan?
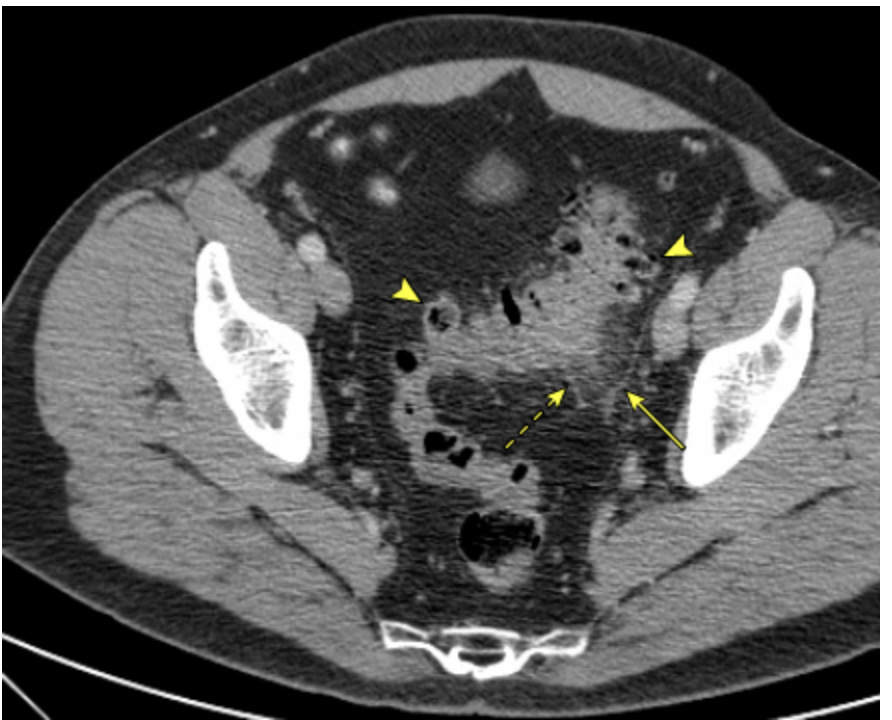
Cipro+metro OR Augmentin, clear liquid diet for 3 days, eat more fiber when symptoms resolve
56 y/o male presents to the ER for abdominal pain with associated N/V/D. PMHx is positive for diverticuli. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp of 102.8. You note abdominal pain in the LLQ. Lab work is as follows, leukocytosis, + FOBT, elevated CRP, UA reveals sterile pyuria. CT reveals localized bowel wall thickening (>4 mm) and an increase in soft tissue density within the pericolonic fat secondary to inflammation or fat stranding - consistent with diverticulitis. Let’s say its moderate - what is your treatment plan?
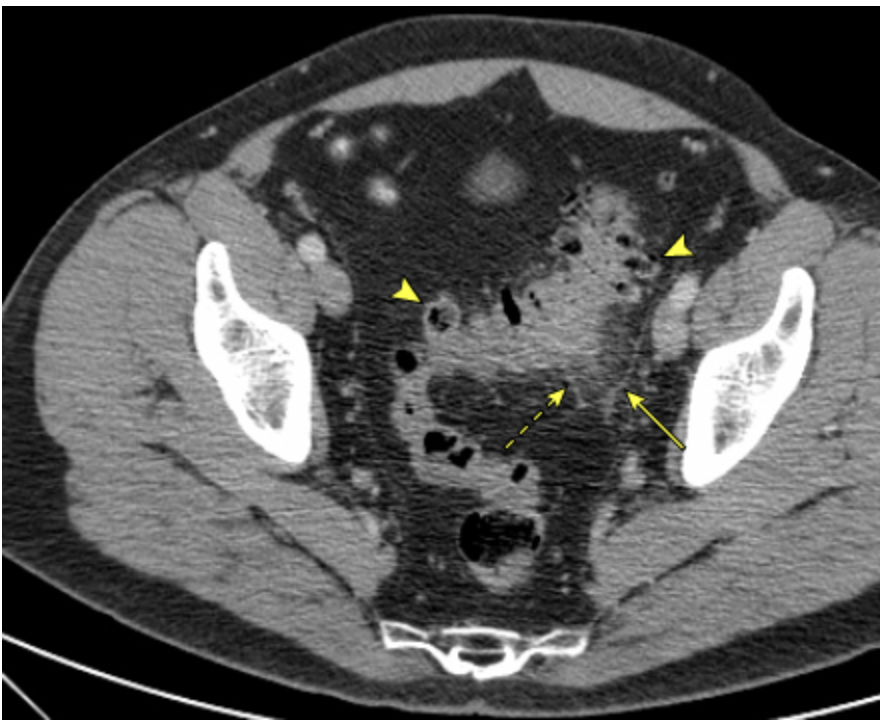
Call up gen surge, repeat CT, 72 hrs of abx, drain the abscess (if over 2 cm)
56 y/o male presents to the ER for abdominal pain with associated N/V/D. PMHx is positive for diverticuli. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp of 102.8. You note abdominal pain in the LLQ. Lab work is as follows, leukocytosis, + FOBT, elevated CRP, UA reveals sterile pyuria. CT reveals localized bowel wall thickening (>4 mm) and an abscess - consistent with complex diverticulitis. What is your treatment plan?
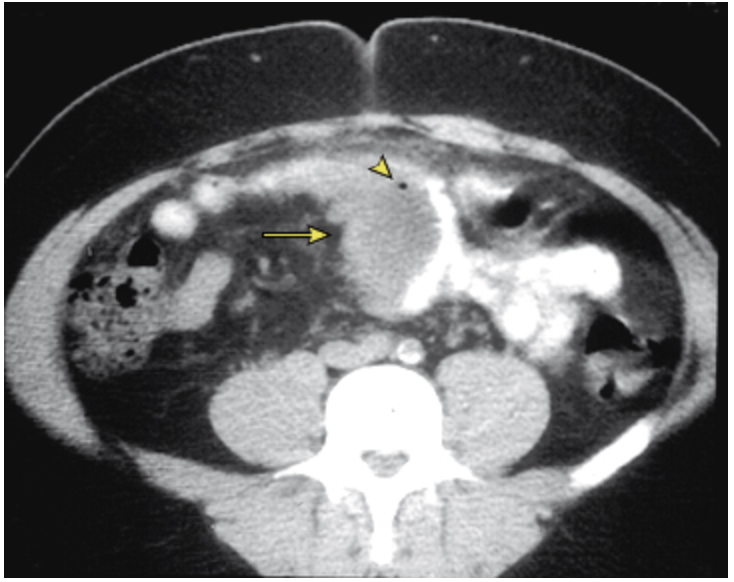
PO intolerant, severe pain, SIRs criteria, peritonitis (peritoneal signs), CT with signs of complex diverticulitis, failure to improve with outpatient, immuncomp, frail, older than 70, comorbidities
Which diverticulitis peeps are staying inpatient?
PO tolerant, symptoms are controllable with medications, no complicated findings or comorbidities, good support system
Which diverticulitis peeps can go outpatient?
10-30% will recur within 10-20 yrs (repeat attacks = elective bowel resection)
Prognosis of diverticulitis
appendicitis, IBD, colorectal cancer, infectious colitis, ischemic colitis, ovarian torsion, ecoptic pregnancy, tubo-ovarian cyst, ovarian cyst rupture, testicular torsion, renal colic, cystitis
DDX for diverticulitis
Intussusception
A segment of the bowel slides into the lumen of the proximal segment in a telescope like fashion lead to a bowel obstruction - usually in peds at the ileocecal junction (if adult think malignancy (50%))
U/S, ABD xray, CT scan
3 y/o presents to the ER with severe abdominal pain that the mother says must have started about 30 minutes ago. The child is laying on the exam table with legs drawn up to the abdomen and crying loudly. Mother states, “we just had to come in after his poop looked like currant jelly.” Vital are stable with the exception of a 103.6 temp. On a physical exam you note the abdomen is tender, distended, and you palpate a sausage shaped mass. What diagnostics you want?
Radiopaque contrast enema with xray (diagnostic AND treats children), Air enema (non-perf children only), Surgical resection (adults, perf children, unstable, enema is unsuccessful)
3 y/o presents to the ER with severe abdominal pain that the mother says must have started about 30 minutes ago. The child is laying on the exam table with legs drawn up to the abdomen and crying loudly. Mother states, “we just had to come in after his poop looked like currant jelly.” Vital are stable with the exception of a 103.6 temp. On a physical exam you note the abdomen is tender, distended, and you palpate a sausage shaped mass. U/S and CT show a target sign. Xray reveals a SBO with a meniscus sign. What is your treatment plan?
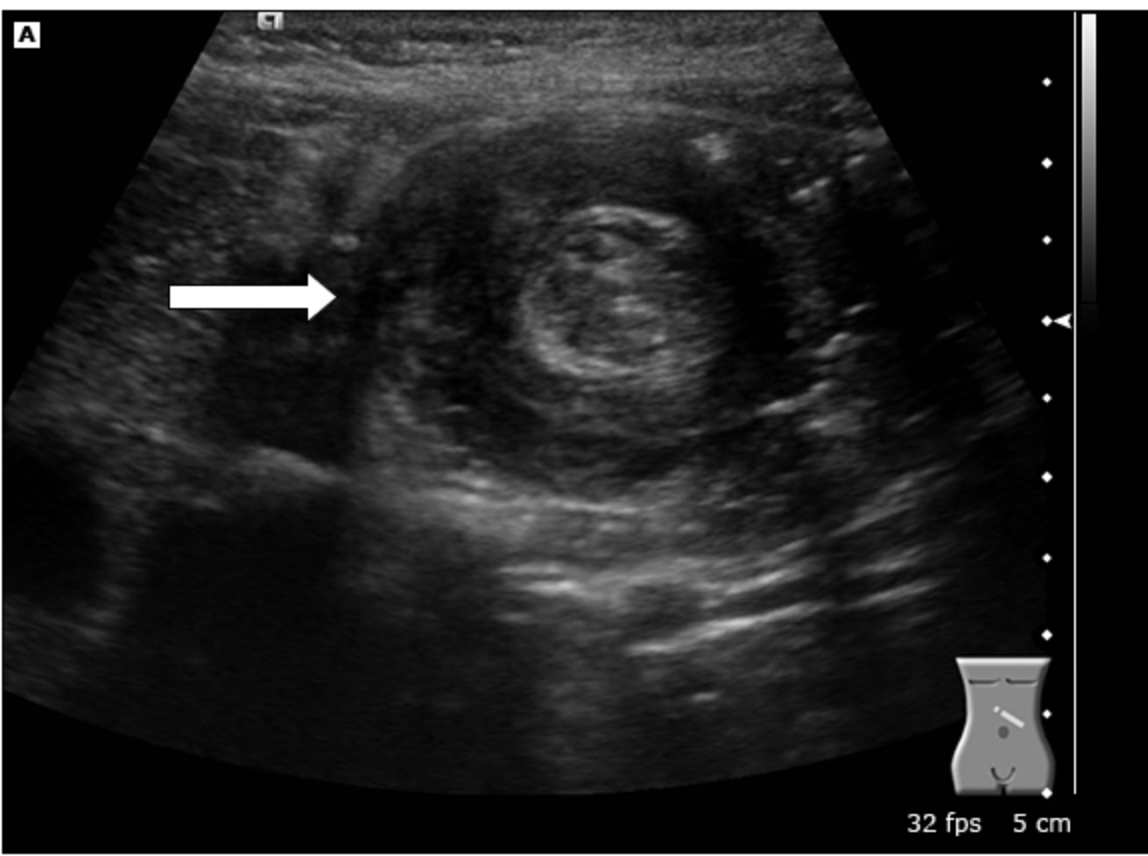
ischemic bowel, necrosis, perforation, infection (peritonitis), septic shock
Complications of intussuception
other bowel obstruction, LGIB, appendicitis, ischemic bowel disease, perforated ulcer, gastritis, ingested foreign body, AAA
DDX for intussusception
Food bolus activates excitatory neurons → moves forward → activates inhibitory neurons once it passes
Describe the motility of the small intestines
Bowel obstruction
A physical or functional blockage of the small or large intestines that prevents the forward movement of bowel contents leading to a buildup in pressure (gas, bloating, dilation reduces blood flow, rupture, strangulation)
Mechanical
What type of bowel obstruction is characterized by a physical object partially or completely blocking the movement of the bowel contents (tumor or twisting) - most common surgical disorder of the small intestine
surgical adhesions; neoplasms
Most common cause of SBO and LBOs
slower onset of symptoms, “pure liquid” diarrhea, flatulence
Partial obstructions allow for passage through a portion of the lumen - what does this look like?
abdominal/pelvic surgery/radiation therapy (adhesion), abdominal/groin hernia (bowel twists), inflammation (swelling of local bowel), neoplasms (obstructive or may cause intussusception), foreign body ingestion (if you’re brave enough)
Risk factors for mechanical obstructions
Ileus
a clinical syndrome in which intestinal motility is impaired in the absence of a mechanical obstruction that has the same signs as a mechanical obstruction and corrects as the inciting factors is normalized
anesthesia, physical bowel irritation during surgery, infection/inflammation, severe systemic illness, electrolyte abnormalities, meds
What may cause ileus?
ABD series (supine, upright abdomen, upright chest - preferred intitial), CT with contrast (#1 draft pick for definitive), CBC (leukocytosis or anemia if bad), CMP (elevated BUN and Creat if dehydrated)
59 y/o male presents to the ER for cramping abdominal pain and N/V. He states that the pain comes in waves but is a 9/10. He also reports that he had diarrhea all day but it stopped suddenly. Vitals are stable with the exception 114 bpm and 101.4 temp. On physical exam you note abdominal distention, hyperresonance on percussion and a palpable mass. The bowels sound hyperactive on one side and are absent on the other. What diagnostics you want?
IV hydration, Pain meds, NPO with NG tube for continuous evacuation, immediate surgical treatment, OR frequent serial exams for non-closed loop obstructions
59 y/o male presents to the ER for cramping abdominal pain and N/V. He states that the pain comes in waves but is a 9/10. He also reports that he had diarrhea all day but it stopped suddenly. Vitals are stable with the exception 114 bpm and 101.4 temp. On physical exam you note abdominal distention, hyperresonance on percussion and a palpable mass. The bowels sound hyperactive on one side and are absent on the other. Xrays reveal dilated loops of small bowel with air-fluid levels. CT allows for the visualization of the discrete transition from dilation to decompression. What is your treatment plan - its mechanical?

IV hydration, Pain meds (avoid opiates if possible), NPO with NG tube for continuous evacuation, treat the underlying, gradual progression of diet, Alvimopan (opiate-induced, post-op)
59 y/o male presents to the ER for cramping abdominal pain and N/V. He states that the pain comes in waves but is a 9/10. He also reports that he had diarrhea all day but it stopped suddenly. Vitals are stable with the exception 114 bpm and 101.4 temp. On physical exam you note abdominal distention, hyperresonance on percussion and a palpable mass. The bowels sound hyperactive on one side and are absent on the other. Xrays reveal dilated loops of small bowel with air-fluid levels. CT allows for the visualization of the discrete transition from dilation to decompression. What is your treatment plan - its functional?
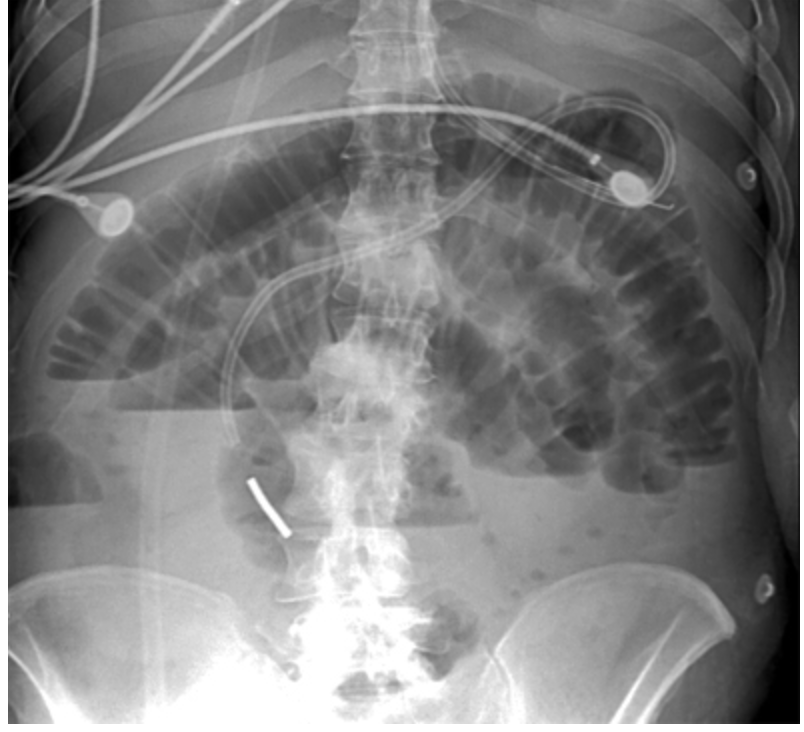
bowel ischemia, pancreatitis, gastritis, appendicitis, SBP, gastroenteritis, AAA
Bowel obstruction DDX
Ischemic bowel disease
Acute visceral artery insufficiency causing pain, tissue damage, and ultimately necrosis of the bowel due to embolism, thrombosis, or non-occlusive vascular insufficiency (like low CO)
CAD, PVD, HF, DM, tobacco use, OCP (hypercoaguable), DVT/thrombosis, cancer, recent intrumentation or surgery (especially aortoiliac or cardiopulmonary bypass), hypotension
Risk factors for ischemic bowel disease
Hx of post-prandial abd pain, avoidance of eating, weight loss
Signs of chronic ischemic bowel disease
CBC (WBC, anemia), Lactic, FOBT, CMP (albumin, phosphate), Coags, CTA or MRA (imaging of choice), colonoscopy (only if colon is affected), Xrays
70 y/o female presents to the ER for 10/10 abdominal pain like she is screaming. She states that is worse after she eats. PHMx of Vitals are stable with the exception of 100/66. On physical exam you note the patient is non tender on palpation even with this 10/10 pain as well as abdominal distention. What diagnostics you want?
Gen surg with immediate exploration and possible resection (Acute), Vascular surgery - angioplasty, vessels stenting, arterial bypass (chronic), NPO, O2, anticoags, Abx, NG tube, stabilize if in shock
70 y/o female presents to the ER for 10/10 abdominal pain like she is screaming. She states that is worse after she eats. PHMx of Vitals are stable with the exception of 100/66. On physical exam you note the patient is non tender on palpation even with this 10/10 pain as well as abdominal distention. Labs reveal MARKED leukocytosis, elevated lactate. Xrays reveal pneumatosis intestinalis. CTA reveals vessel occlusion and narrowing. What is your treatment plan - NO AMA OR SHE IS 100% DEAD?
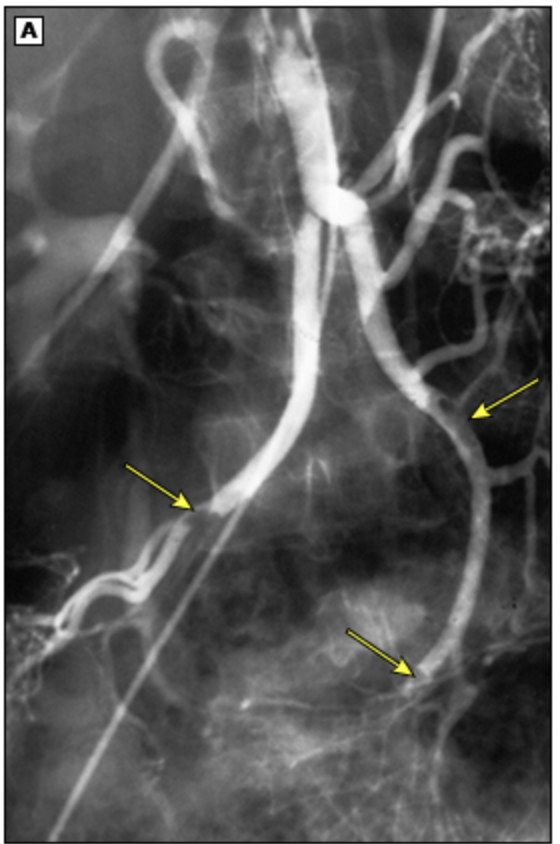
appendicitis, perforated hollow organ, intussusception, peptic ulcer, gastritis, diverticulitis, major vessel anuerysm, SBP, AAA
Ischemic bowel disease DDX
polyps (adenomatous polyps), lipomas
Benign tumors of the SI
adenocarcinoma (duodenum, proximal jejunum), lymphoma (usually Non-Hodkin’s, distal SI), Carcinoid (stomach and intestines)
Malignant tumors of the SI
FOBT + (early), abd pain, weight loss, N/V, distention, anemia, obstruction
For both adenocarcinoma and lymphoma what are you going to see in the S/Sx?
CT with contrast, biopsy (definitive)
For both adenocarcinoma and lymphoma what imaging do you want?
resection + chemo, maybe radiation
For both adenocarcinoma and lymphoma what is your treatment plan?
facial flushing, diarrhea, wheezing, lightheadness with tachycardia and hypotension
What are the signs of carcinoid syndrome - usually asymptomatic if the tumor is small?
local excision (if confine 85% success rate)
Treatment plan for carcinoid tumors - 5 yr is 80%