Blood Circulation and Heart Function Overview
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Deoxygenated Blood
Blood low in oxygen entering the right atrium.
Tricuspid Valve
Valve between right atrium and right ventricle.
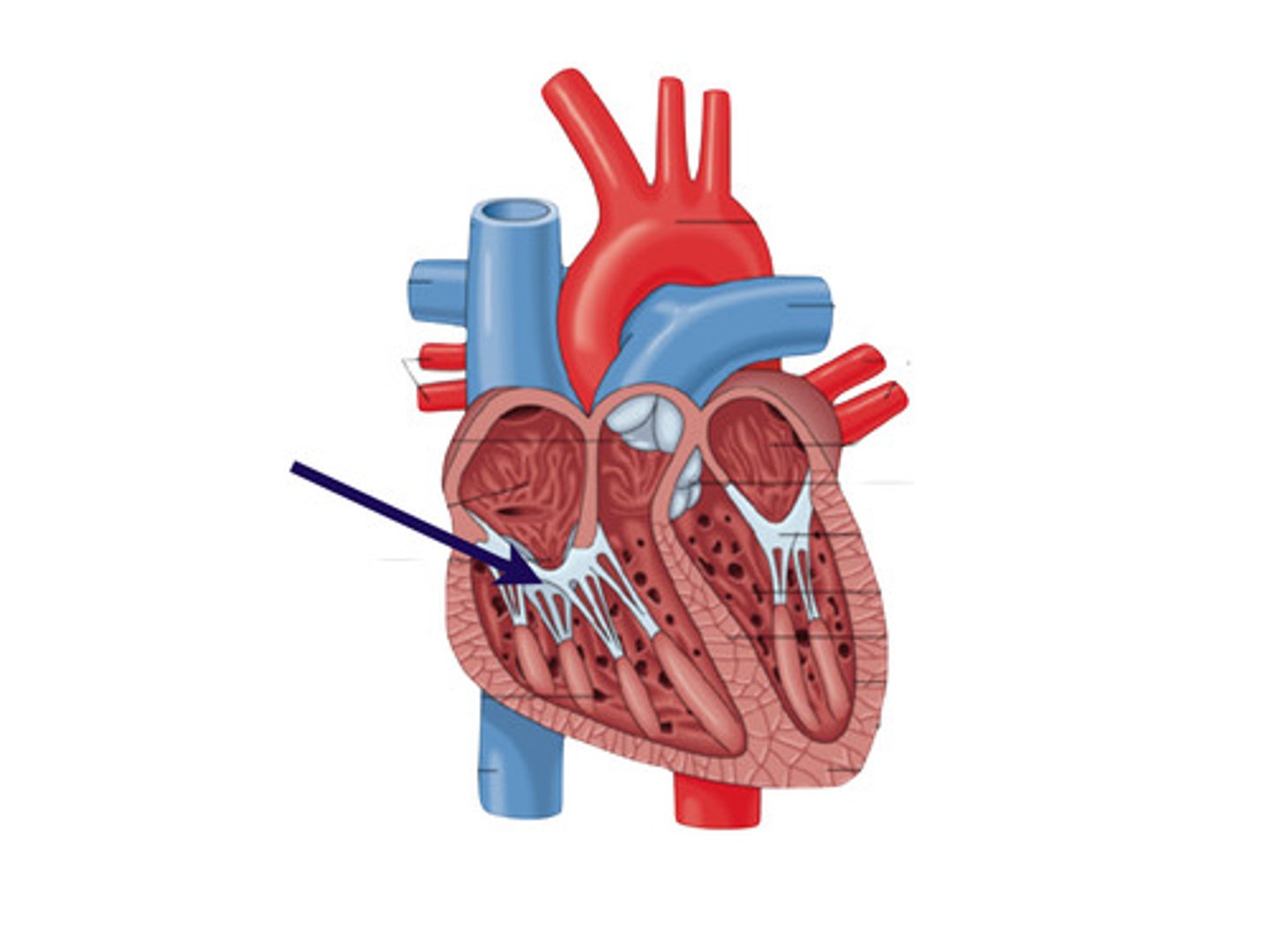
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
Valve between right ventricle and pulmonary arteries.
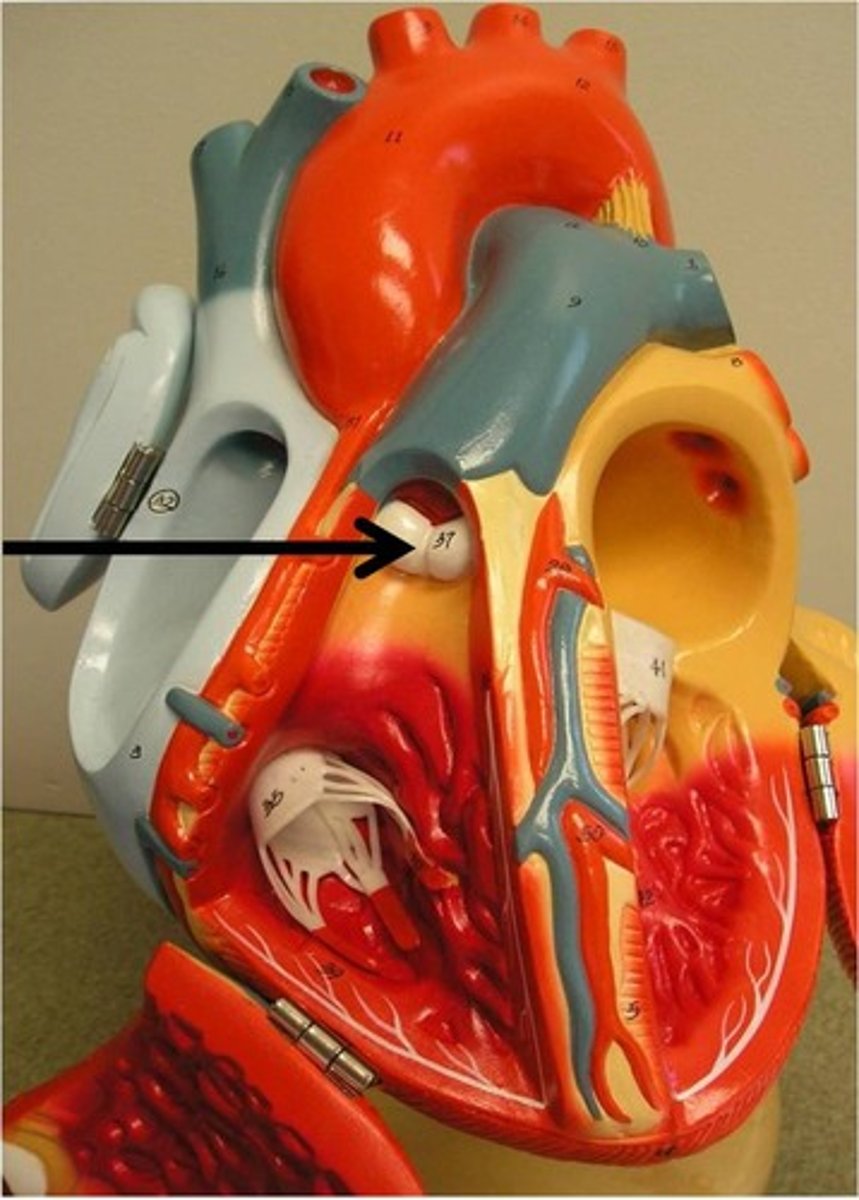
Oxygenated Blood
Blood rich in oxygen returning to the left atrium.
Mitral Valve
Valve between left atrium and left ventricle.
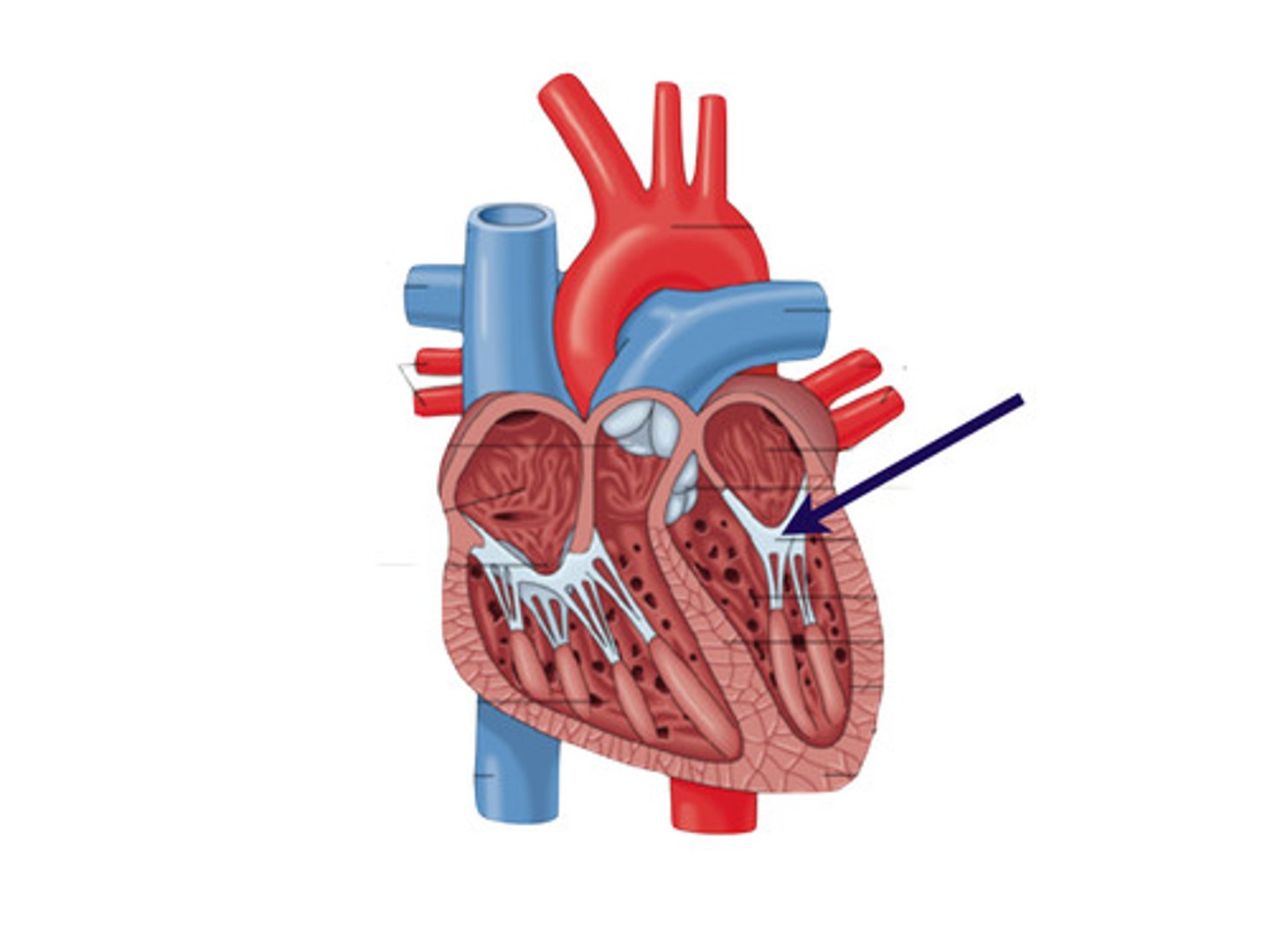
Aortic Semilunar Valve
Valve between left ventricle and aorta.
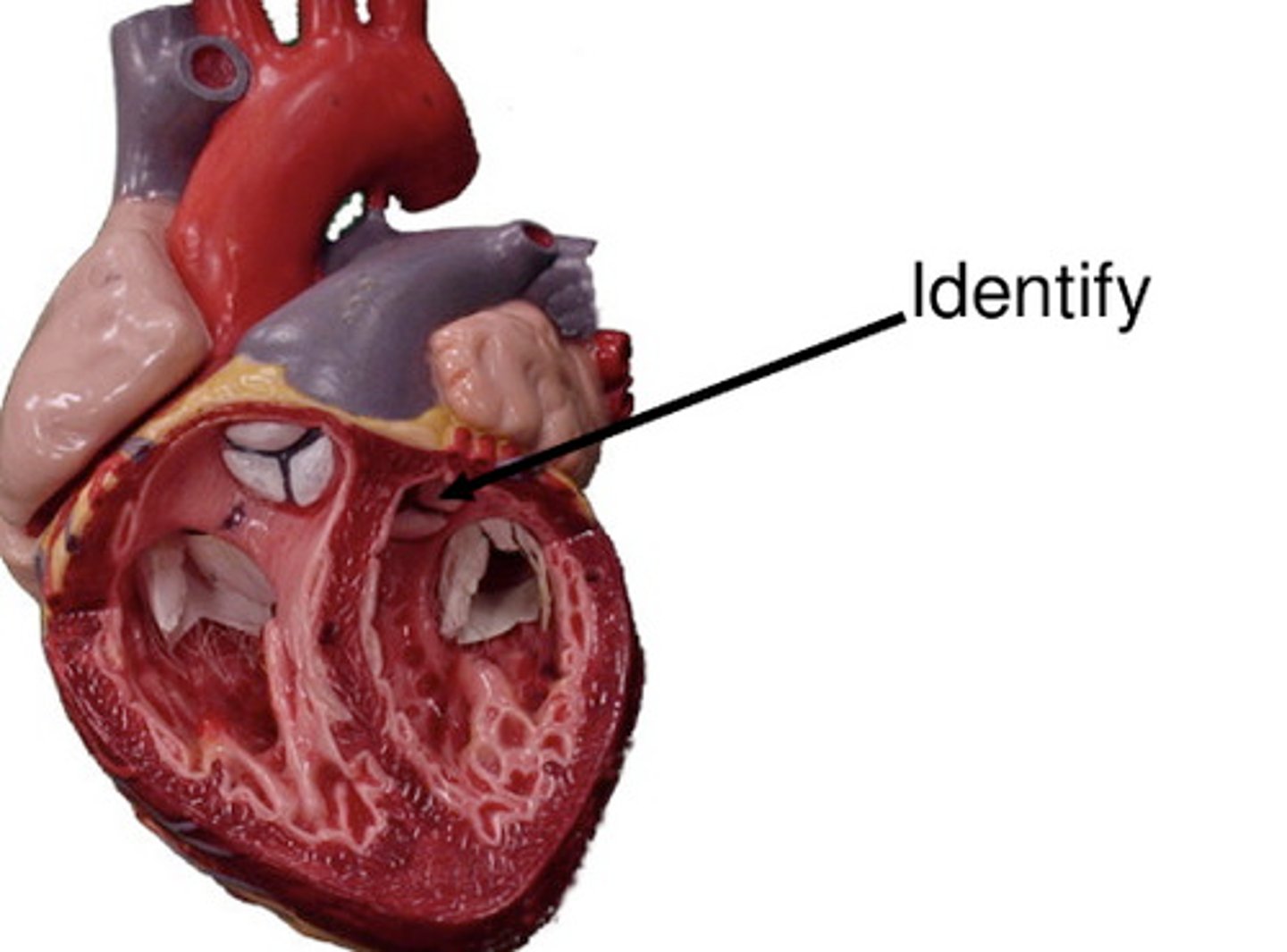
Pulmonary Circulation
Right heart to lungs and back to left heart.
Systemic Circulation
Left heart to body tissues and back to right heart.
Fibrous Pericardium
Tough outer layer surrounding the heart.
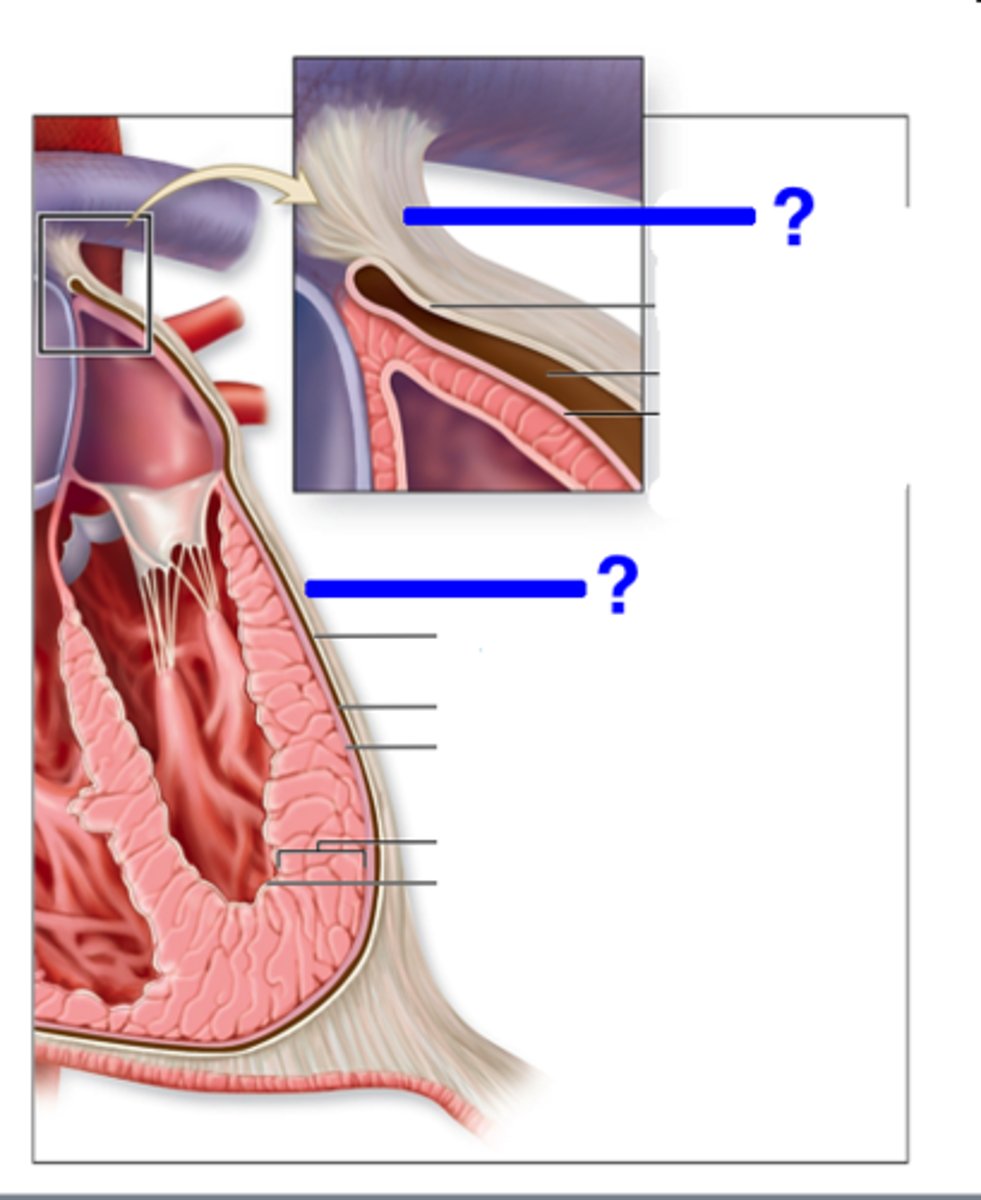
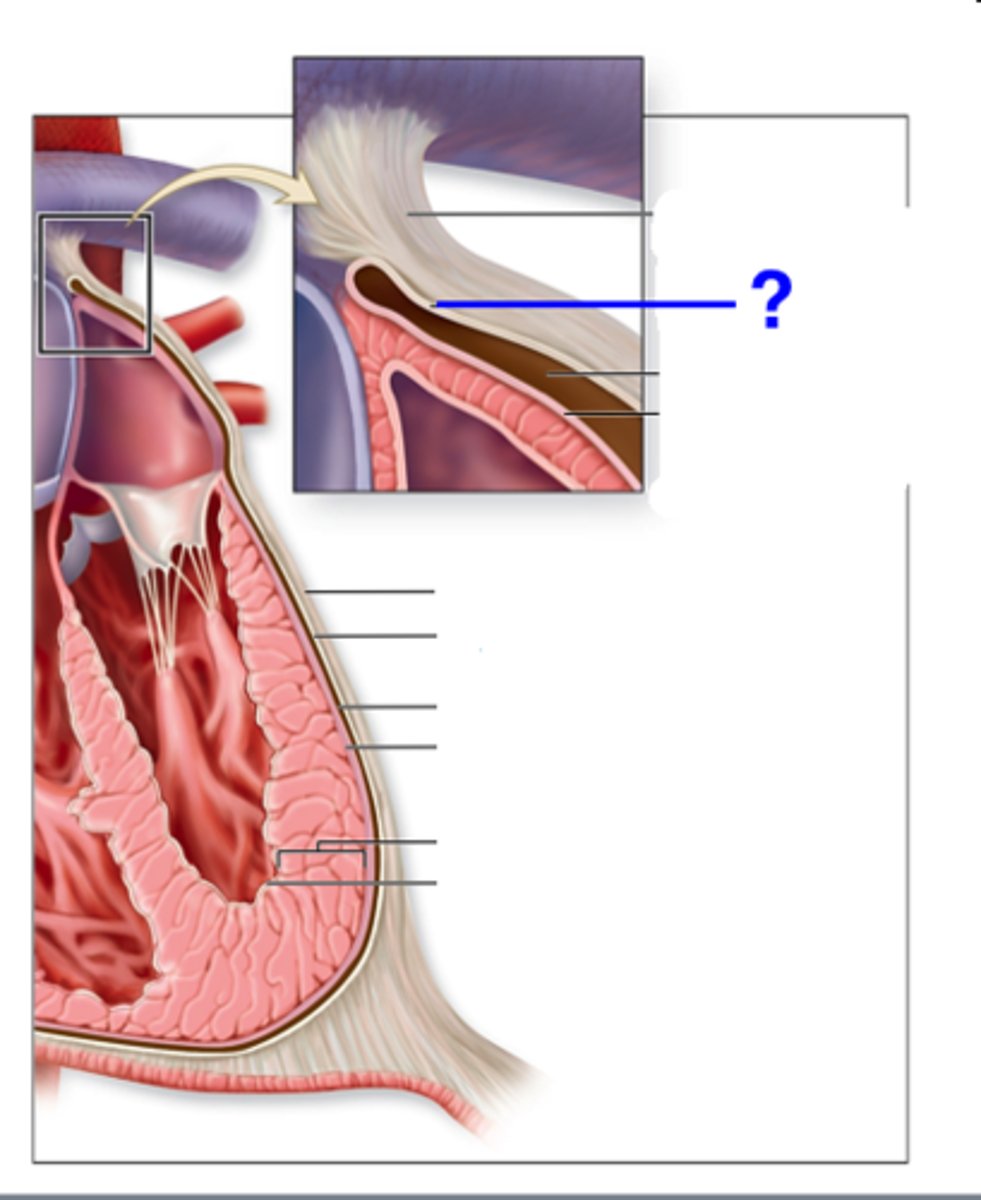
Serous Pericardium
Inner layer of the pericardium with two layers.
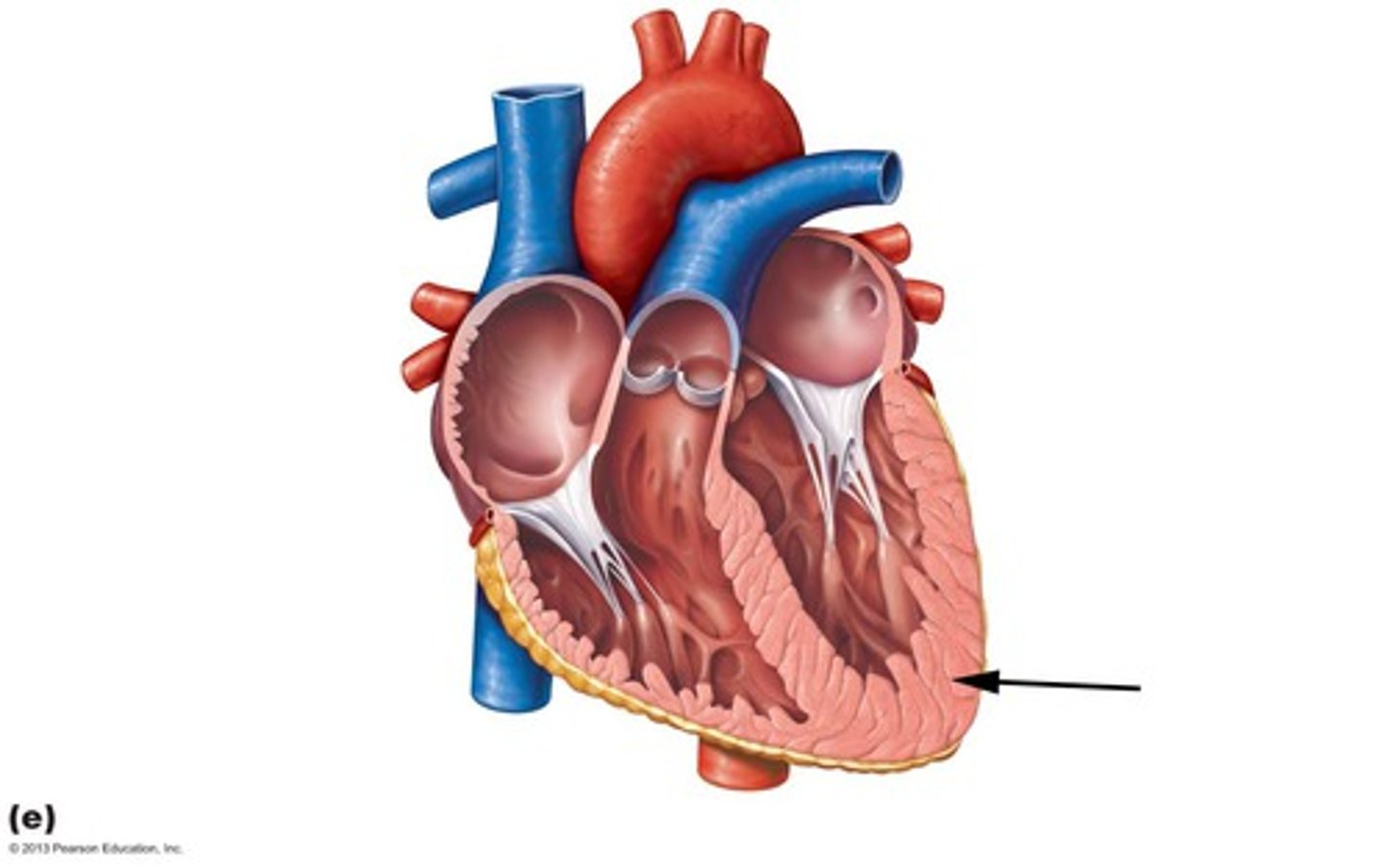
Epicardium
Outermost layer of the heart, also visceral pericardium.
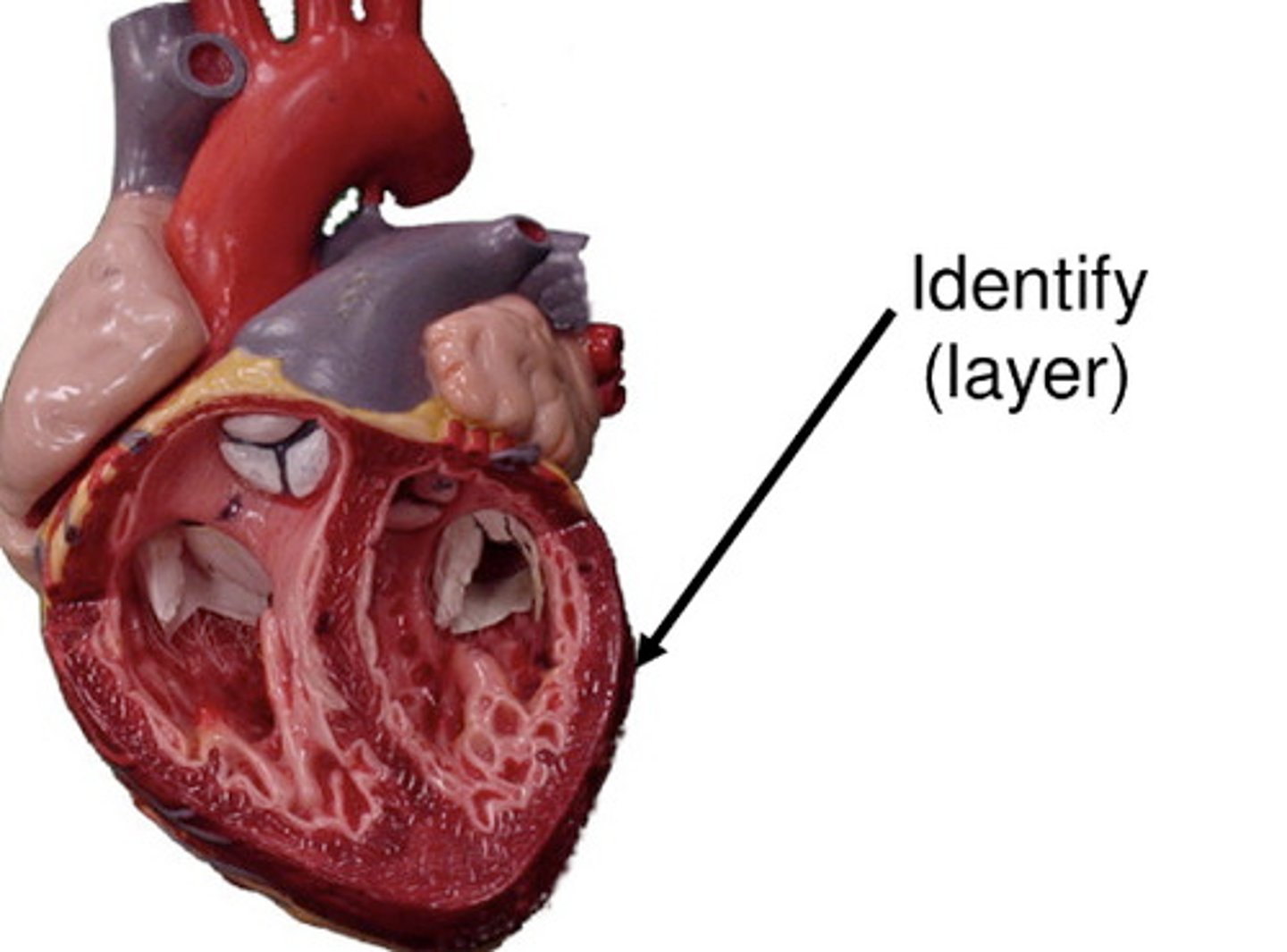
Myocardium
Muscular middle layer of the heart.
Endocardium
Smooth inner lining of the heart chambers.
Syncytium
Interconnected cardiac muscle cells for coordinated contraction.
Intercalated Disks
Structures allowing rapid electrical signal transmission.
Purkinje Fibers
Fibers transmitting impulses throughout the ventricles.
Graded Contractions
Variable strength contractions influenced by hormones.
Cardiac Cycle
Events occurring from one heartbeat to the next.
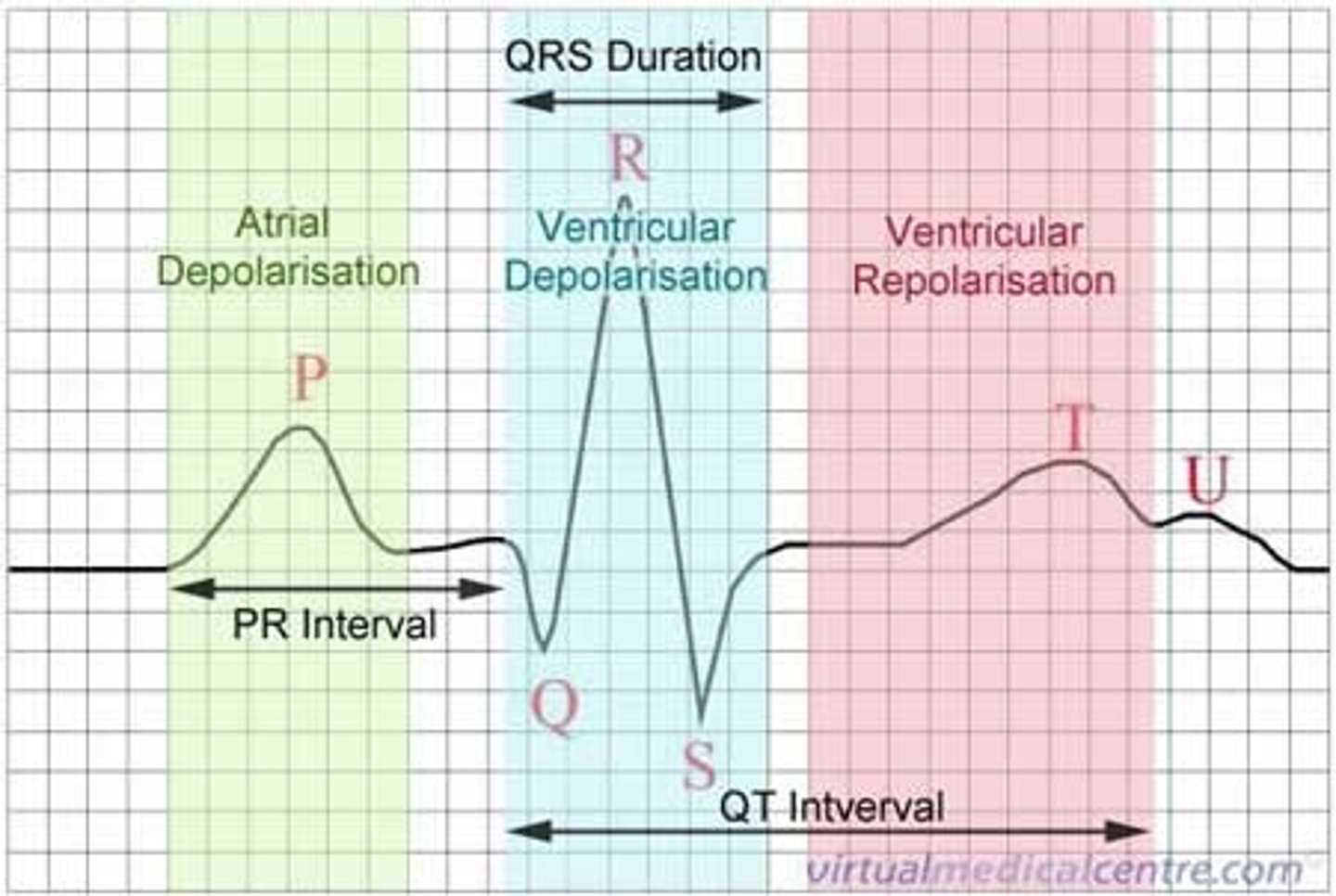
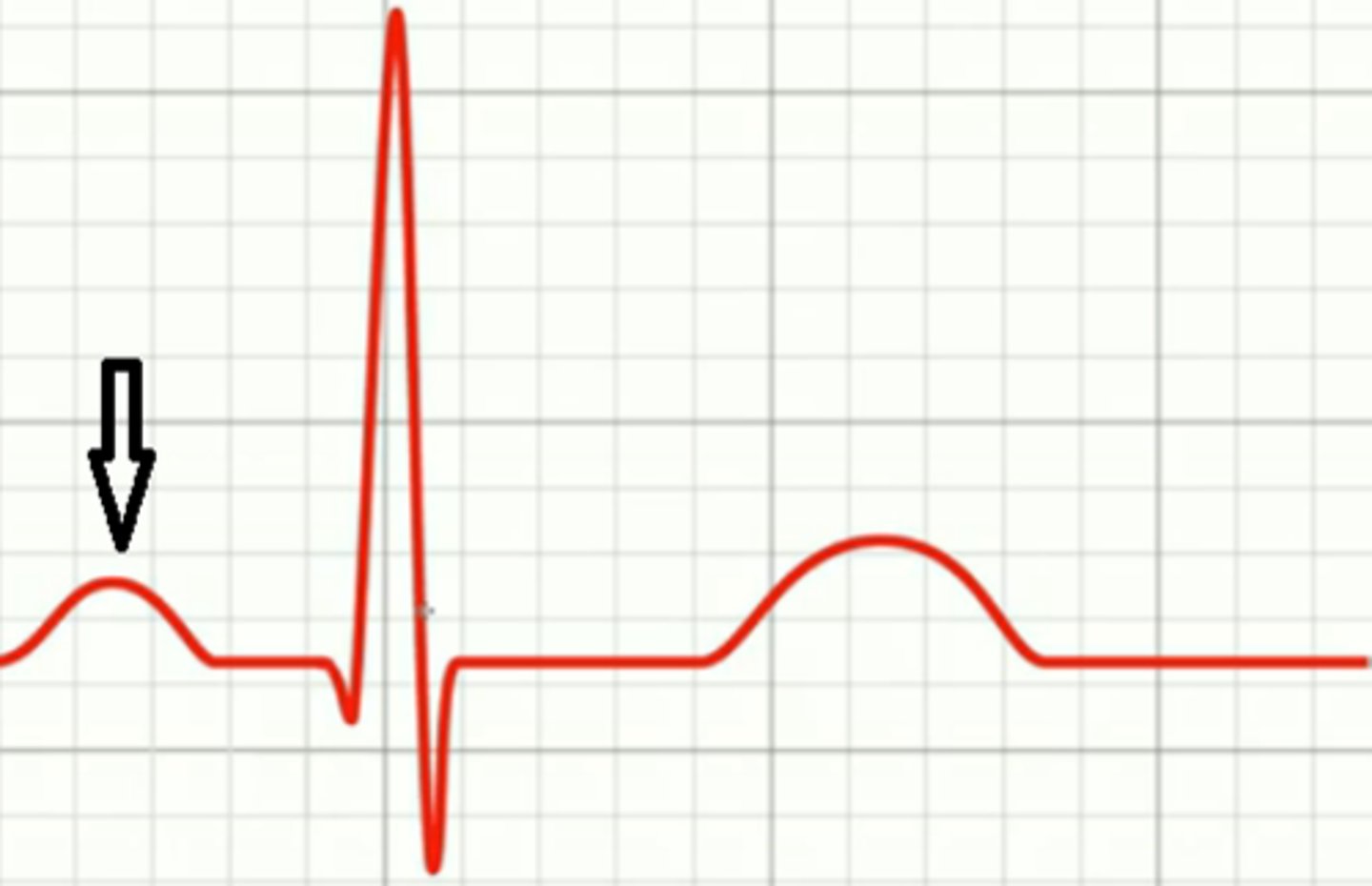
P Wave
Represents atrial depolarization in ECG.
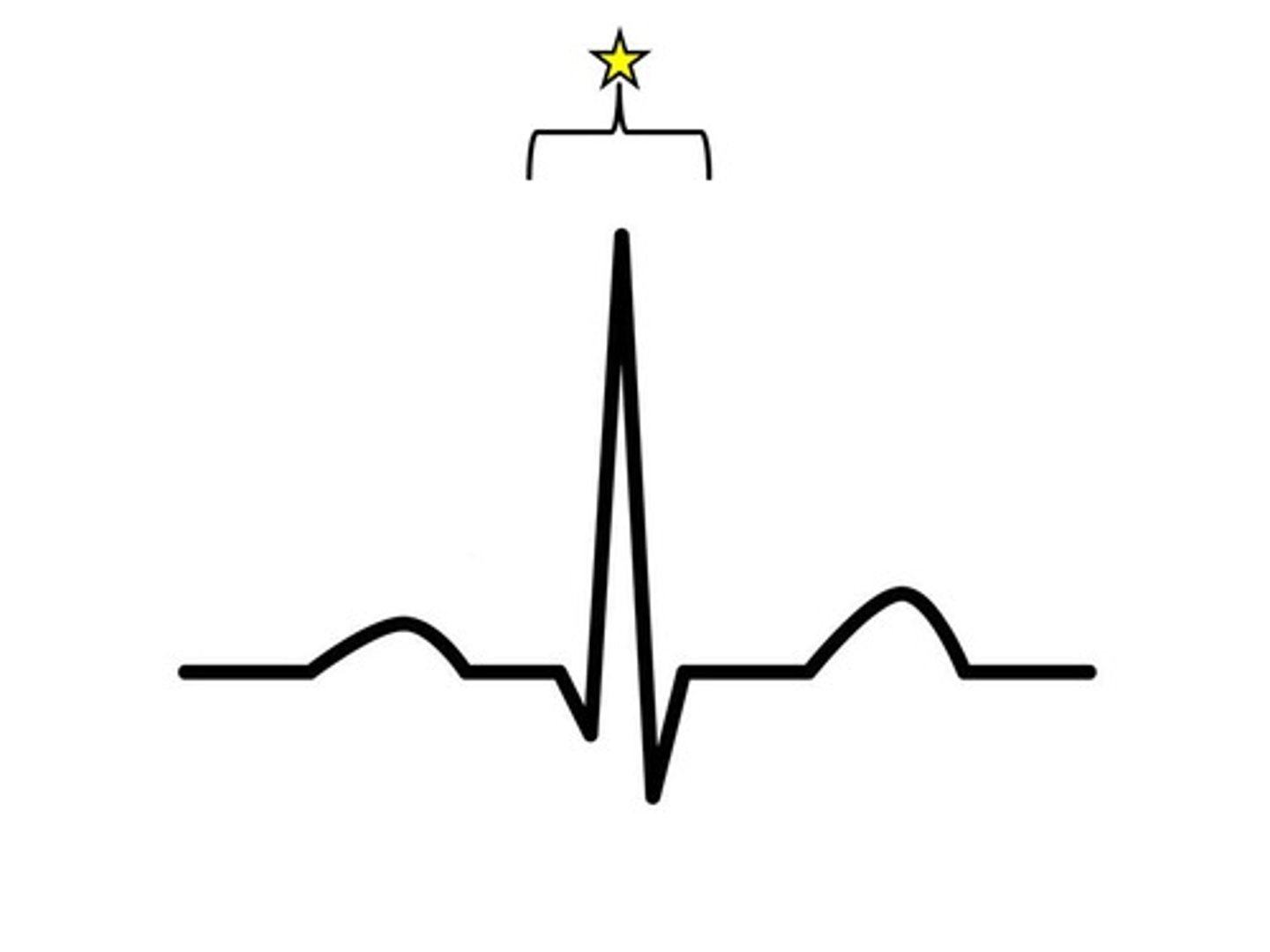
QRS Complex
Represents ventricular depolarization in ECG.
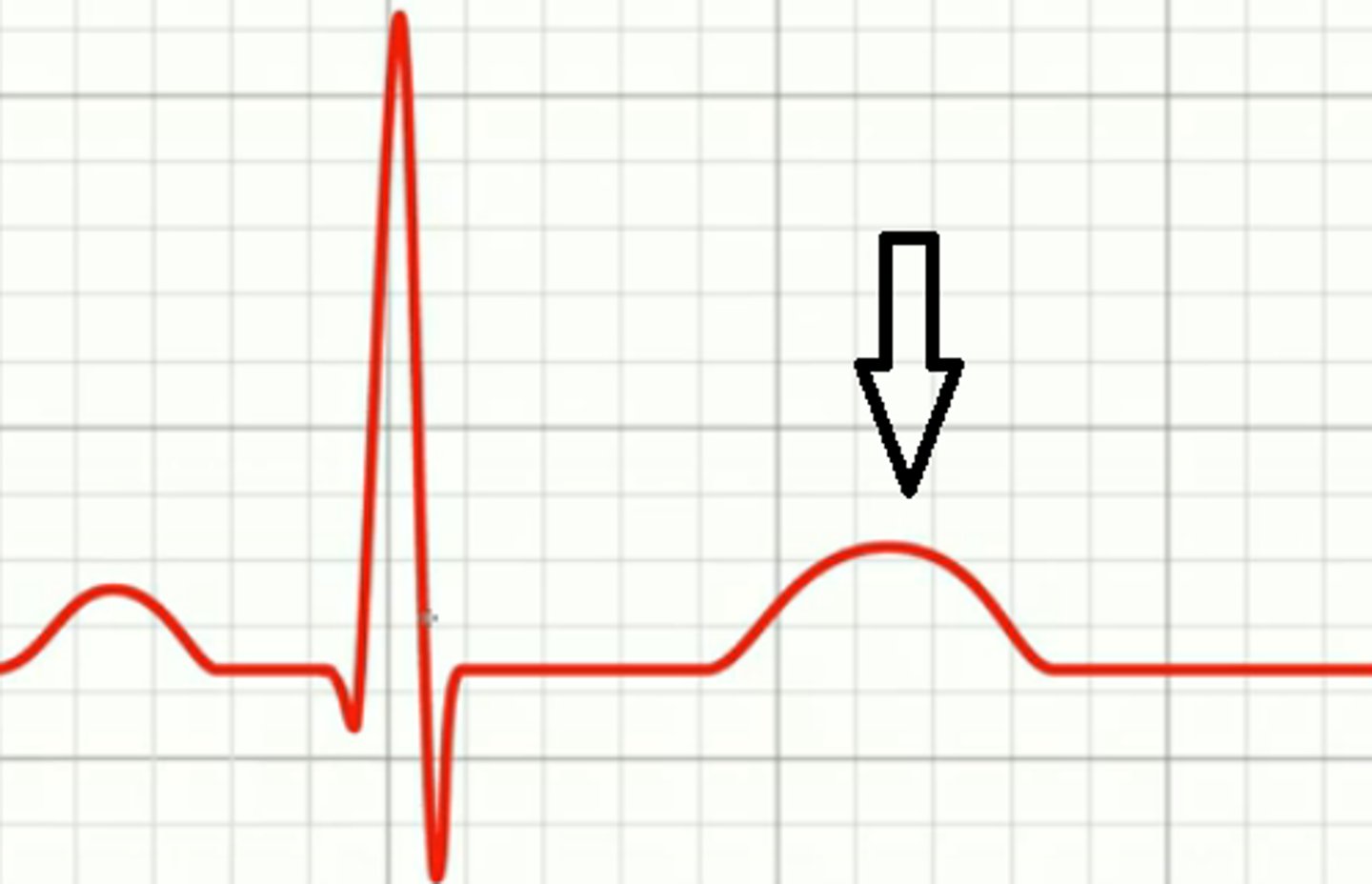
T Wave
Represents ventricular repolarization in ECG.
Cardiac Output (CO)
Volume of blood pumped by heart per minute.
End-Diastolic Volume (EDV)
Volume of blood in ventricles before contraction.
Baroreceptor Reflex
Regulates blood pressure through autonomic responses.
RAAS
System regulating blood volume and pressure via sodium retention.
ADH
Hormone increasing water reabsorption in kidneys.
Pressure Gradients
Differences driving blood flow through vessels.