2.1.5 Biological Membranes
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are the roles of membranes
Separates the components of the cell from their environments
Separates the different organelles within cells from each other and the cytosol
Acts as the interface for communication
Uses diffusion, osmosis and active transport to move substances across it
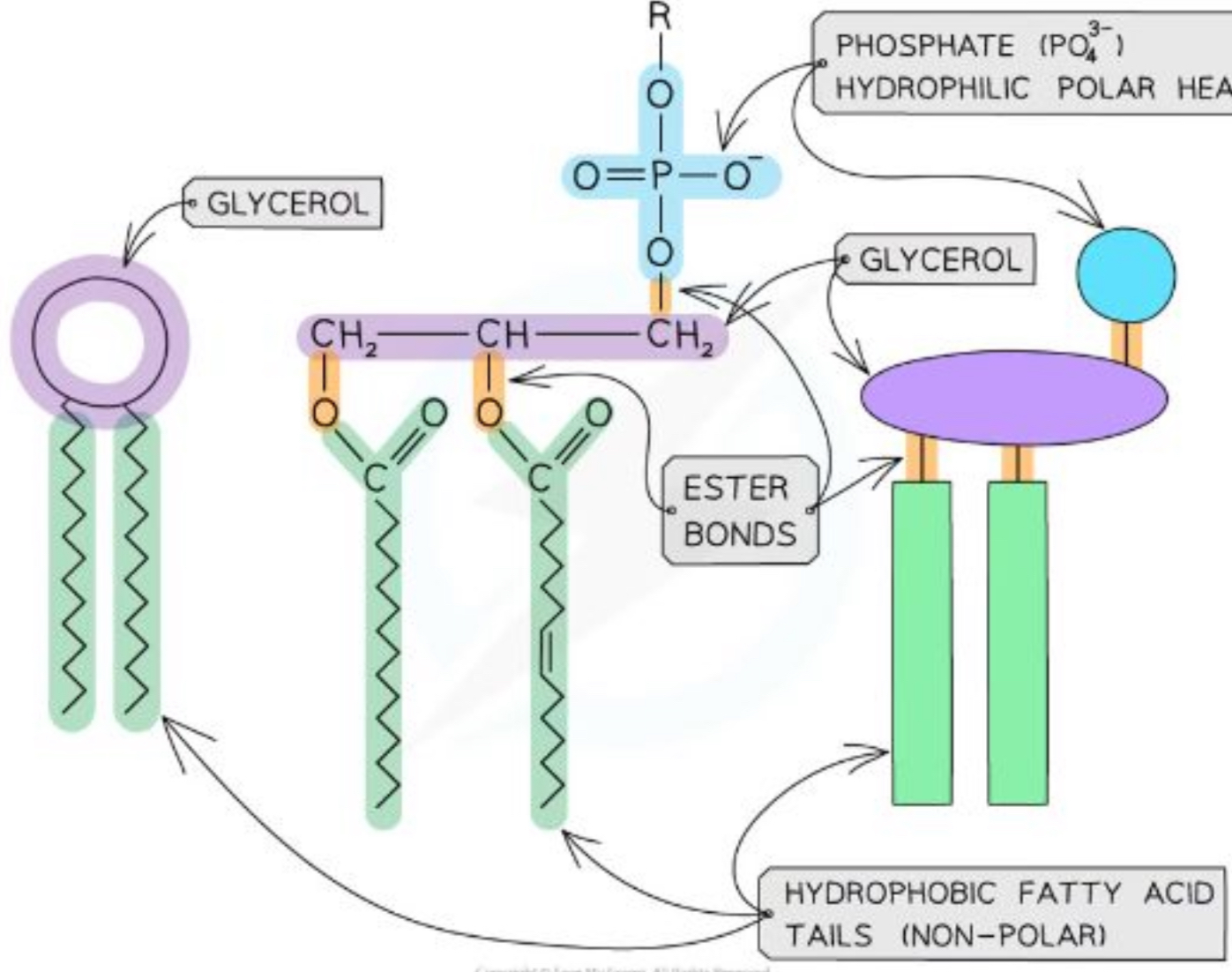
What is the structure of phospholipids
Only 2 fatty acids (the third has been replaced by a phosphate ion)
Contains a phosphate group, glycerol and 2 fatty acid tails
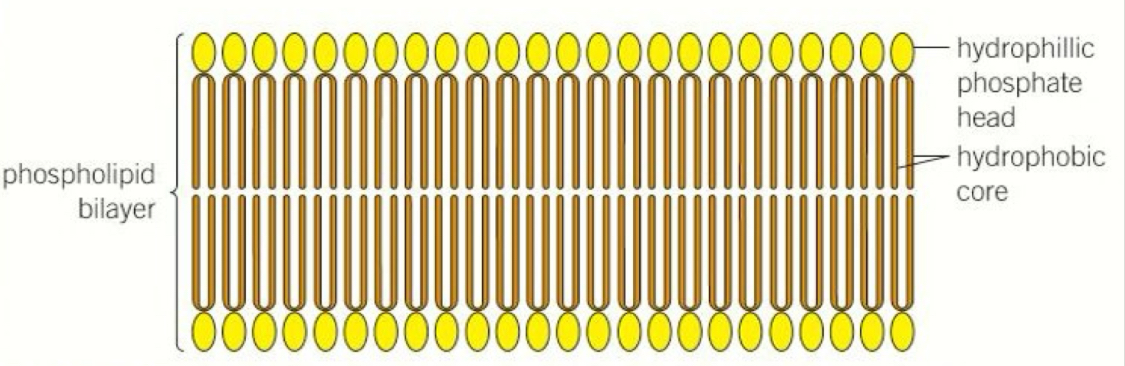
What is the structure of the plasma membrane
Formed by a phospholipid bilayer
The hydrophilic phosphate heads of the phospholipids form both the inner and outer layer of the membrane
The hydrophobic fatty acid tails form the hydrophilic centre
Fluid - phospholipids and proteins are free to move within the layer (mostly sideways) via diffusion
Mosaic - The proteins embedded in the layer vary in shape, size and position (in the very same as the tiles of the mosaic
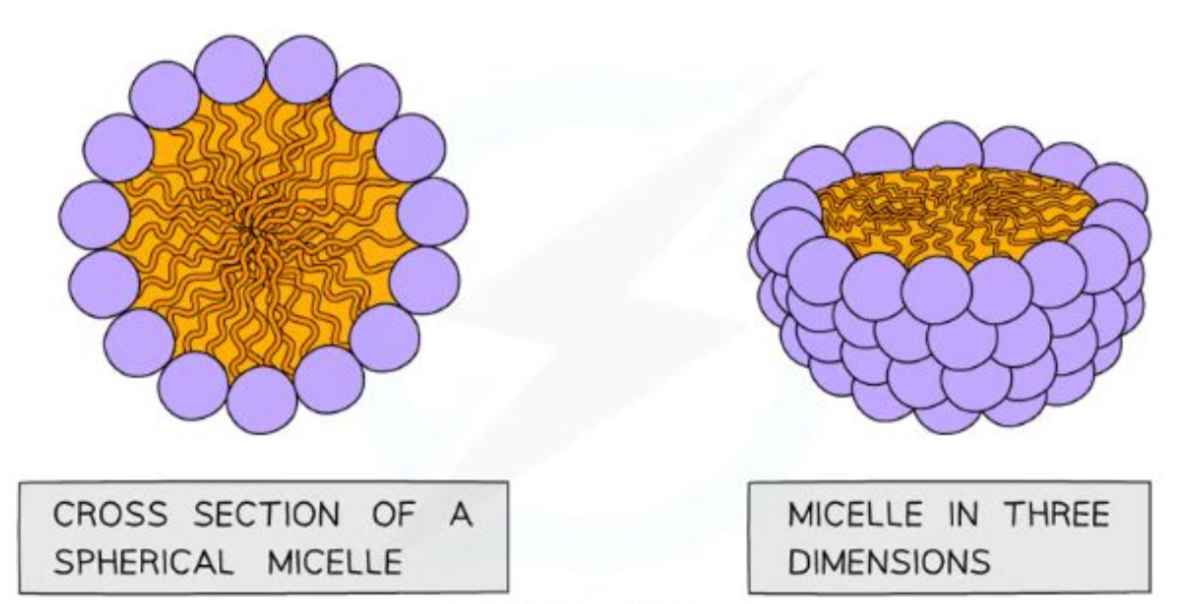
What is a micelle
If a phospholipid is mixed/shake with water they form spheres called a micelle
Hydrophilic head faces outwards
Hydrophobic fatty acid tails face inwards
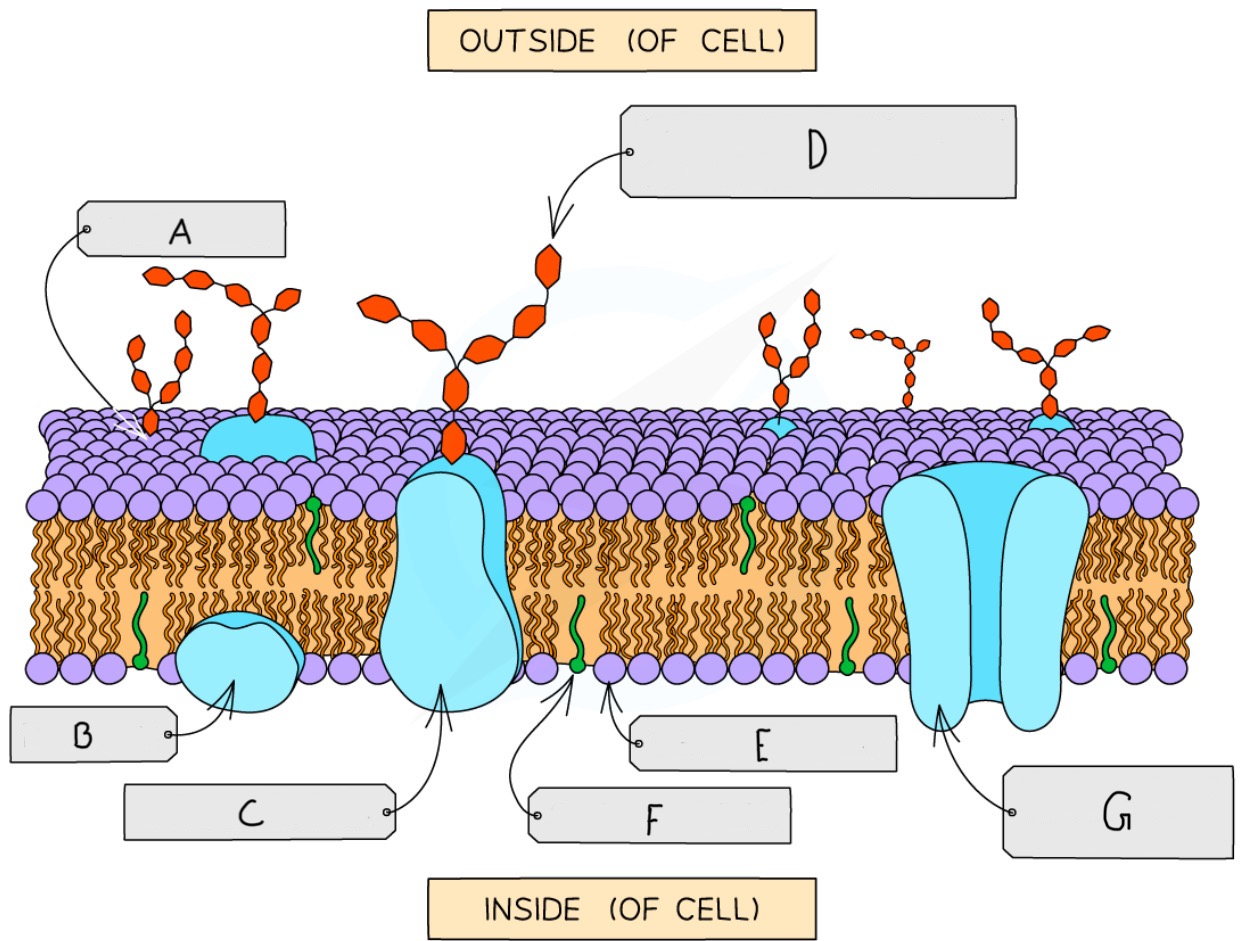
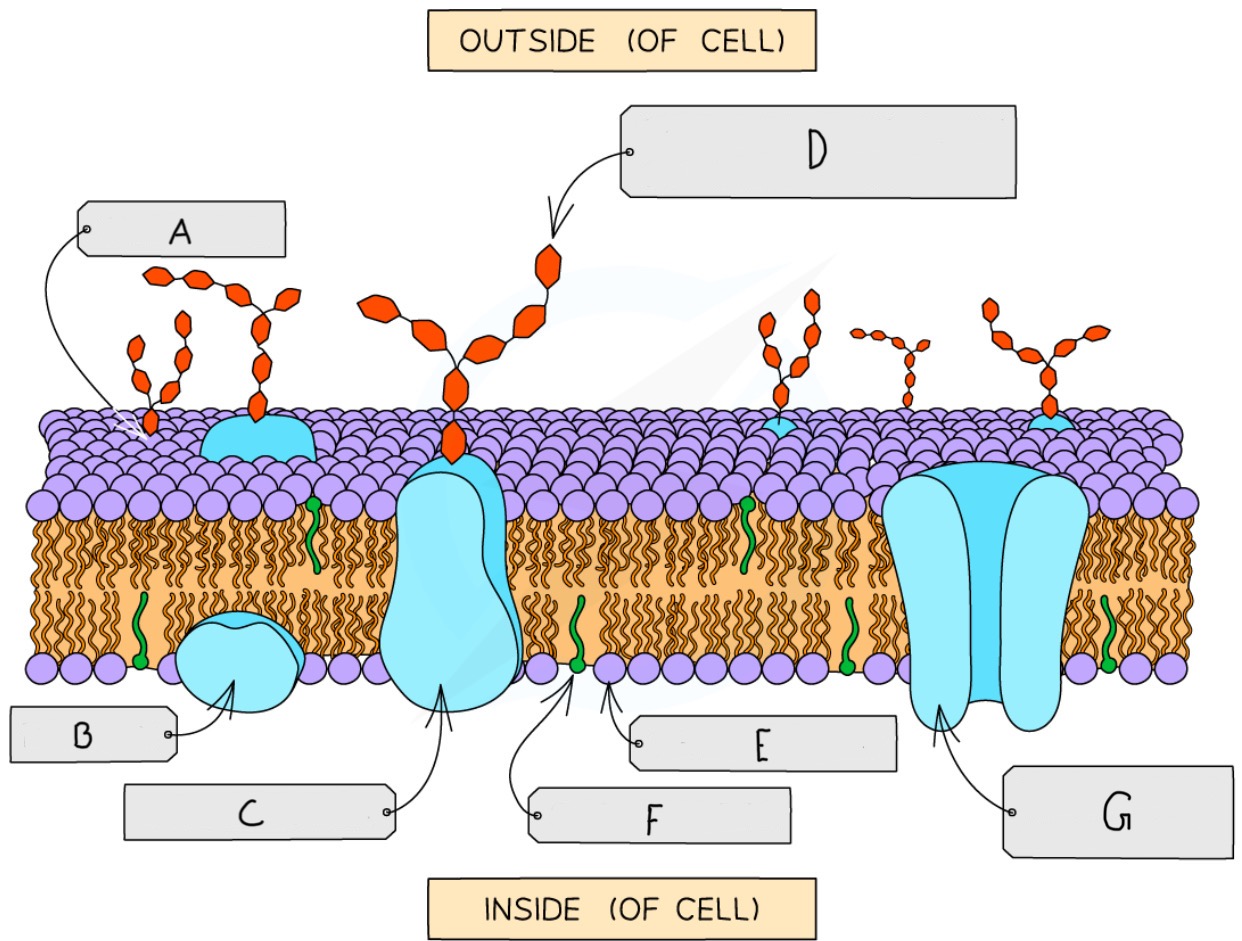
Name the parts of the phospholipid bi-layer protein
A = Glycolipid
B = Extrinsic/peripheral protein
C = Glycoprotein
D = Carbohydrate part of the glycoprotein
E = Phospholipid
F = Cholesterol
G = Transport/Intrinsic/Integral Protein
What is cholesterols role in the phospholipid bi layer
Regulates the fluidity of the membrane by being between the phospholipids
They prevent phospholipids from packing to closely together and crystallising
Also allows membrane to be impermeable to ions, to increase strength & stability
What is the structure of cholesterol
Lipid with a hydrophilic end and a hydrophobic end
What makes membranes less fluid
More saturated fatty acid chains, pack together tightly, high number of intermolecular forces between the chains
This is due to the double bonds of the saturated fatty acid chains having a double bond, meaning there’s less space and therefore less movement
Lower temperatures, molecules have less energy, not moving as freely, structure becomes more closely packed
What makes membranes more fluid
More unsaturated fatty acid chains, pack tether less tightly, less molecular forces between the chains
Higher temperatures, molecules have more energy, move freely, structure becomes more fluid
What are the roles of glycolipds and glycoproteins in the membrane
Can act as receptor molecules for hormones and neurotransmitters
Can act as receptor molecules for signalling
Can act as antigens
Can be used for recognition/identification of cells
Can act as receptor/binding site on transport proteins
Can be used for cell adhesion
Attaches to water to stabilise the cell
What is the structure of a glycoprotein
Intrinsic proteins embedded in the cell surface membrane
Carbohydrate chains of varying lengths and shapes are attached
What is the structure of a glycolipid
Lipids with attached carbohydrate chains
What are the roles of intrinsic proteins
Channel (pore) proteins: Create hydrophilic channels which allow ions and polar molecules to travel through membranes
Carrier proteins - the protein changes shape to allow this to happen
Each transport protein is specific to what it is transporting
The more intrinsic proteins inside a membrane, the faster the rate of diffusion
They are embedded through both layers of a membrane
How do membranes act as a site of chemical reactions
The enzymes of photosynthesis are found on membrane stacks within the chloroplasts
The proteins must be in particular positions for this to work
For example, the electron carriers and the enzyme ATP must be in the correct positions within the cristae for the production of ATP in respiration
What is the purpose of a centriole
They help to move chromosomes during cell division
What is diffusion
The net movement of a substance from a region of its higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration
Why does diffusion happen
Molecules move down a concentration gradient caused by natural kinetic energy
Eventually particles become evenly spread due to random movement of particles
What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion
Steepness of the concentration gradient
Temperature
Surface area
Properties of molecules/ions (size, charge)
The presence of carrier/channel proteins
How do the properties of molecules or ions affect the rate of diffusion
Large molecules diffuse slower than smaller ones as they require more energy to move
Uncharged and non-polar molecules diffuse directly across the phospholipid bi-layer
Non-polar molecules diffuse quicker then polar molecules as they are soluble in the non-polar phospholipid bi-layer
What is facilitated diffusion
Diffusion that uses Chanel and carrier proteins to assist certain substances that can’t use standard diffusion
These include
large polar molecules like glucose and amino acids
ions like sodium and chloride
What is osmosis
The et movement of water molecules from a region of high water potential to a region of low water potential
How does osmosis of water into a plant cell work
Plants placed in a dilute solution - water enters the plant cells cytoplasm & vacuole by osmosis - volume of cell increases
Plant cells have protoplasts (living portion of a plant cell)
These push up against the cell wall Which increases pressure which makes the cell become turgid
Turgidity provides support and strength for a plant - e.g. allows them to stand up straight
How does osmosis of water out of a plant cell work
Plant cell placed in a concentrated solution
Water leaves the plant cell’s cytoplasm and vacuole by osmosis - volume of cell decreases
Protoplast shrinks and pulls away from cell wall - decreases pressure - cell eventually becomes plasmolysed
How does having no cell wall affect animals cells during osmosis
They feel the effects more severely
What is a hypertonic solution
The outside solution is more concentrated with solutes
The net movement of water inwards
Cells swell - and may burst
What is a hypotonic solution
The outside solution is more diluted with water
Net movement of water out of cell
The cell shrivels
What is an isotonic solution
Outside solution and cytoplasm a similar solute concentration
No movement
What is active transport
The movement of molecules and ions through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration using energy from respiration
How does active transport work
The process required specific carrier proteins
The energy is required to make the protein change shape
So that molecules/ions can transfer across the membrane
It is used in:
Réabsorption in the kidney tubules
Absorption in digestion
Loading sugar and inorganic ions into phloem and root hair cells
What is co-transport
The coupled movement of substances across a cell membrane via a carrier protein (facilitated diffusion and active transport combined)
E.g.
NA & glucose ions are transported into epithelial cells via diffusion (Facilitated)
NA is then actively transported out of the cell, into the blood (which helps maintain a conc. gradient for sodium)
Glucose exits the cell and enters the blood again via facilitated diffusion
What organelles are adapted for faster transport
Neurone & muscle cells - Cell membrane read have specific channel proteins for sodium, potassium and calcium ions
Kidney cells - Contain very high number of Aquaporins
Aquaporins = specific channel proteins that allow facilitated diffusion