Final Review (In Progress)
1/150
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Probably a lot of duplicates I just need to delete. Text me if you see any duplicate terms.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Protein Synthesis
The process by which proteins are made in cells.
Biomolecules
Molecules needed for protein synthesis, including proteins and nucleic acids.
Proteins
Long chains of amino acids that perform various functions in the body.
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins that come from the food we eat.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, a type of nucleic acid that provides the sequence for protein synthesis.
Nucleic Acid
Long chains of nucleotides, including DNA and RNA.
Nucleotide
The subunits of nucleic acids, consisting of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogenous base.
Nitrogenous Bases
Cytosine, guanine, adenine, and thymine (in DNA) or uracil (in RNA).
Double Stranded
DNA is double stranded, meaning it consists of two complementary strands.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, a type of nucleic acid that plays a role in protein synthesis.
Single Stranded
RNA is single stranded, meaning it consists of a single strand of nucleotides.
Types of RNA
mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA, which play different roles in protein synthesis.
Organelles
Structures within cells that carry out specific functions.
Ribosomes
Organelles where protein synthesis occurs by linking amino acids together.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Organelle that transports the amino acid chain to the Golgi apparatus.
Golgi Apparatus
Organelle that folds, modifies, and packages proteins for transport.
Steps of Protein Synthesis
Transcription (DNA to mRNA) and Translation (mRNA to protein).
Transcription
Process of copying DNA into mRNA, which occurs in the nucleus.
Translation
Process of converting mRNA into a protein, which occurs in the cytoplasm.
Transcription Steps
Initiation, elongation, termination, and modification of pre-mRNA.
Translation Steps
Initiation, elongation, termination, and modification of the amino acid chain.
Mutations
Changes in the DNA sequence that can affect protein synthesis and function.
Photosynthesis
Process by which producers convert sunlight into the chemical energy of glucose.
Law of Conservation
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed.
Chloroplast
Organelle where photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria.
Thylakoids
Flat sacs in the chloroplast where the light reaction of photosynthesis takes place.
Stroma
Fluid space around the thylakoids where the dark reaction of photosynthesis occurs.
Light Absorption
Process by which pigments absorb sunlight energy to excite electrons.
Electron Transport Chain
Transfer of high-energy electrons through carrier proteins.
Oxygen Formation
Byproduct of splitting water during photosynthesis.
ATP Production
Process of generating ATP using the energy from hydrogen ions.
Carbon Fixation
Process of converting CO2 into organic molecules during the dark reaction.
Krebs Cycle
Series of reactions that harvest hydrogens from organic molecules.
Electron Transport Chain
Process of transferring electrons to generate ATP.
Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration without oxygen, resulting in fermentation.
Alcoholic Fermentation
Type of anaerobic respiration that produces ethanol and CO2.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Type of anaerobic respiration that produces lactic acid.
Cell Cycle
Series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide.
DNA Replication
The process in which each strand of DNA serves as a template to add DNA nucleotides.
Sister Chromatids
The replicated copies of a chromosome that are held together by a centromere.
G2 Phase
The phase of the cell cycle characterized by continued growth and replication of cell organelles.
Prophase
The stage of mitosis where chromatin condenses into chromosomes in their replicated sister chromatid state and the nuclear membrane breaks down.
Centrosomes
Structures that produce spindle fibers during cell division and attach them to the centromere of chromosomes.
Metaphase
The stage of mitosis where the spindle fibers move the sister chromatids to the center of the cell.
Anaphase
The stage of mitosis where the spindle fibers shorten, pulling the sister chromatids apart to opposite sides of the cell.
Telophase
The stage of mitosis where the spindle fibers breakdown, the nuclear membrane rebuilds around the chromosomes, and the chromosomes uncoil into chromatin.
Cytokinesis (Animal)
The process in animal cells where the cell membrane pinches inward, separating the cytoplasm and cell into two identical cells.
Cytokinesis (Plant)
The process in plant cells where a new cell wall is built along the center of the cell to separate the cytoplasm and cell into two identical cells.
What are the characteristics of living things?
Organization: Living things are made up of cells, tissues, organs, and systems.
Growth and Development: Living things grow and change throughout their lifespan.
Reproduction: Living things can produce offspring through sexual or asexual reproduction.
Response to Stimuli: Living things can respond to their environment and adjust their behavior accordingly.
Homeostasis: Living things can maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes.
Metabolism: Living things obtain and use energy to carry out life processes.
Adaptation: Living things can adapt to their surroundings through evolution.
Life Span: Living things have a limited lifespan and eventually die.
cell theory
The scientific principle stating that all living organisms are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living organisms, and cells arise from pre-existing cells.
prokaryote cells
Simple cells lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Found in bacteria and archaea.
Eukaryote cells
Cells that contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are more complex than prokaryote cells and can be found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. _____ cells allow for specialized functions and compartmentalization of cellular processes.
Cells of prokaryote bacteria
Cell Wall: Made of peptidoglycan: uses for support (difference between a Gram + and Gram -
Cell Membrane: Regulates what enters and leaves the cell (homeostasis)
Ribosomes: Site of protein synthesis
(no membrane), Different size than eukaryotes
Nucleoid: Region of the cell that the DNA is located
Plasmids: small circular piece of DNA that bacteria can exchange
Pili: Connect to other Bacteria to exchange plasmids
Flagella: Long tail that aids in movement.
cell wall
A rigid layer surrounding plant cells, providing support and protection. It is composed of cellulose fibers and helps maintain cell shape and prevent excessive water uptake.
cell membrane
A thin, flexible barrier that surrounds and protects the contents of a cell. It regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell, allowing essential nutrients to enter and waste products to exit. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance found inside cells, surrounding the organelles. It holds the cell's organelles in place and is involved in various cellular processes, such as metabolism and protein synthesis.
nucleus
Component of eukaryotic cells that contains DNA and serves as the control center for cellular activities.
nuleolus
"The _____ is a small, round structure found within the nucleus of a cell. It is involved in the production and assembly of ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis. The _____ contains DNA, RNA, and proteins. It plays a crucial role in cell growth and proliferation."
ribosome
Cellular organelle responsible for protein synthesis. Found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Consists of two subunits, large and small, that come together during protein synthesis. ______ read the genetic code from mRNA and assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains. Essential for cell function and growth.
endoplasmic reticulum
Network of membrane-bound tubes and sacs found in eukaryotic cells. Involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and calcium storage.
golgi apparatus
Stacked membrane-bound organelle involved in processing, modifying, and packaging proteins. Receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and sorts them for transport to their final destinations within or outside the cell.
chloroplast
A membrane-bound organelle found in plant cells responsible for photosynthesis. Contains chlorophyll, which captures sunlight and converts it into chemical energy.
mitochondria
Double-membraned organelles found in eukaryotic cells. Responsible for producing energy through cellular respiration. Contains its own DNA and can self-replicate."
Lysosome
Membrane-bound organelle containing digestive enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris in a cell.
vacuole
"Organelle found in plant and animal cells responsible for storing water, nutrients, and waste products. Helps maintain cell shape and turgor pressure. Plays a role in detoxification and cellular digestion."
Centrossomes
Organelles found in animal cells that play a crucial role in cell division. They contain a pair of centrioles and help in the formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division. ______ are involved in organizing and separating chromosomes, ensuring accurate distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.
phospholipids
Main component of cell membranes
Consists of a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails
Forms a bilayer structure
Controls the movement of molecules in and out of the cell
Provides structural support and flexibility to the cell membrane
Bilayer
A structure composed of two layers of molecules, typically lipids, arranged in a parallel manner. It forms the basic structure of cell membranes, with hydrophilic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails facing inward. The _____ provides a selective barrier that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
cholesterol
A waxy substance found in the body and certain foods. It is essential for cell function, hormone production, and digestion.
channel proteins
Proteins embedded in cell membranes that form channels allowing specific ions or molecules to pass through, facilitating the transport of substances across the cell membrane.
carrier proteins
Proteins that transport molecules across cell membranes by binding to them and facilitating their movement. They are specific to certain molecules and play a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
carbohydrates function in cell
Carbohydrates function in cell as a source of energy and structural support, aiding in cell recognition and communication.
What factors influence how molecules move across the cell membrane?
Concentration gradient, size of the molecule, charge of the molecule, and the presence of transport proteins.
passive transport
Type of cellular transport that does not require energy and moves molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Diffusion
The passive movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, resulting in the equal distribution of particles.
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive transport of molecules across a cell membrane with the help of transport proteins. It does not require energy and moves substances down their concentration gradient.
Osmosis
Facilitated diffusion of water only
Water moves toward solutes
Reach equilibrium
No energy
Hyperosmotic
Means more solute on the outside of the cell
Water move out of the cell
Cell shrinks
Also known as plasmolysis
hypoosmotic
Means less solute outside of the cell
More solute inside of the cell
Water moves in
Cell will expand
Also known as Turgor Pressure
Helps plants to stand tall
Turgor Pressure
Pressure exerted by the fluid inside plant cells against the cell wall, providing support and rigidity. Maintained by the influx of water through osmosis. Crucial for plant structure and function.
Isotonic
Equal amount of solute in and out of the cell
Equal movement of water in and out of the cell
No net loss or gain to cell size
Active Transport
Molecules move against the concentration gradient
Low concentration to High concentration
Never reach equilibrium-actively working AGAINST equilibrium
Requires a protein
Requires energy
sodium-potassium pump
used in nerve function and muscle cell contractions
electron transport chain
Used in photosynthesis and cell respiration
Endocytosis
Brings materials into the cell
Exocytosis
Removal of material from the cell
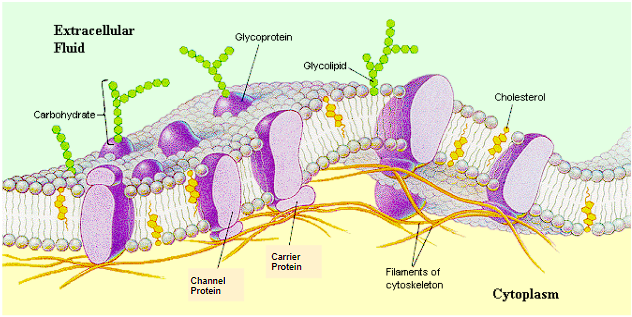
What organelle is this and where is it found?
Cell membrane, all cells
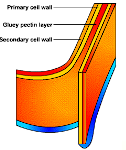
What organelle is this and where is it found?
Cell wall, all except animal cells
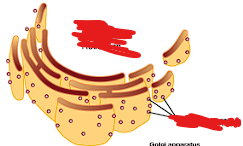
What organelle is on the outside of this and where is it found?
ribosomes, all cells
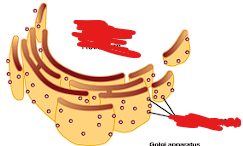
What organelle is this and where is it found?
endoplasmic reticulum, all cells except bacteria
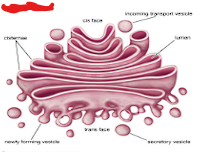
What organelle is this and where is it found?
Golgi apparatus, all cells except bacteria
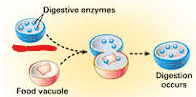
What organelle is this and where is it found?
lysosomes, all cells except bacteria

What organelle is this and where is it found?
Vacuole, all cells except bacteria
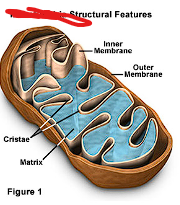
What organelle is this and where is it found?
Mitochondria, all cells except bacteria
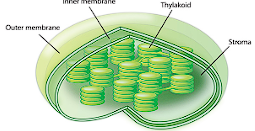
What organelle is this and where is it found?
Chloroplasts, plant cells
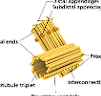
What organelle is this and where is it found?
Centrosome, animal cells
Compounds/Molecules
Combination of 2 or more atoms formed by bonds
Ionic Bond
Transfer of electrons from one element to another, between a metal and nonmetal
Covalent Bond
Sharing of electrons between nonmetals to fill their valence orbital
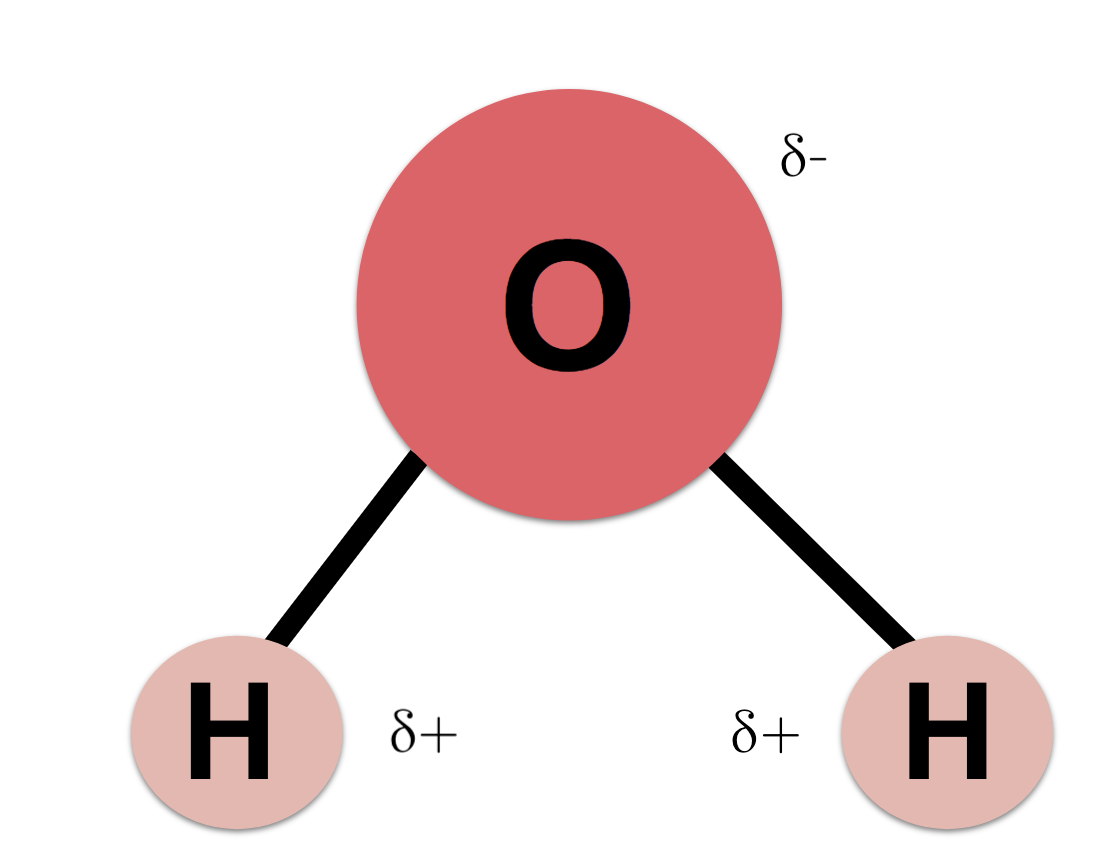
Water Structure
H2O, bent molecule with polarity and hydrogen bonds