VM 505 Pharmacology Final
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Acetaminophen, a weak acid, has a pKa of 9.5. At a pH of 6, what is the ratio of nonionized to ionized acetaminophen?
A. 0.003:1
B. 0.03:1
C. 33:1
D. 3162:1
D.
Polychlorinated biphenyls are persistent organic pollutants. You set up an experiment to determine the log P or (logKow) of a specific PCB congener 2,2’,4,4’,5,5’-hexachlorobiphenyl (PCB153). You measure a concentration of 37.77 mM in the octanol layer and a concentration of 3nM in the water layer. What is the experimentally determined logP? (Hint: remember to check the units)
LogP = 7.1
Hydroxychloroquine is an antimalarial drug that was briefly promoted as a putative treatment for COVID-19. The experimentally determined logP (or logKow) is 3. What would you expect the concentration ratio to be for hydroxychloroquine in octanol: hydroxychloroquine in water?
1000:1
Fipronil is a broad-use insecticide commonly used in flea control products for pets. The experimentally determined logP (or logKow) is 4. If this value was determined experimentally, what would you expect the concentration ratio to be for fipronil in octanol: fipronil in water? Is this compound fat soluble?
10,000:1
Fipronil has a logP of 4. Is Fipronil fat soluble?
Yes
Diazepam, a weak base, has a pKa of 3. At which pH will diazepam cross biological membranes more easily?
A. 6
B. 3.
C. 2
A.
In general, which of the following would be true of a drug that is a weak base (pKa = 8.4)?
A. This drug would be predominately unionized at rumen pH (5.5-6.5)
B. This drug would be predominately unionized in milk (6.5-6.8)
C. This drug would be predominately ionized at physiologic pH (approximately 7.4)
C.
The drug diazepam is given orally. It is a weak base with a pKa of 3. Assume the stomach has a pH of 3 and the small intestine has a pH of 6. Choose all explanations that account for variation in the absorption of Diazepam in the stomach and small intestine. (Select all that apply)
A. Ratio of ionized/unionized in the SI = 1000/1
B. Ratio of ionized/unionized in the SI = 3/1
C. GI tract has largest surface area to enhance absorption
D. Ratio of unionized/ionized in the stomach = 1/1
E. Ratio of unionized/ionized in the SI = 1000/1
C. D. E.
Drug X is a weak acid with a pKa of 4. Approximately what percent of the drug will be ionized in an environment with a pH of 4?
50%
A drug with an apparent volume of distribution that is greater than total body water implies:
A. The drug stays in the blood and plasma
B. The drug distributes to the extracellular fluid
C. The drug distributes into the body fat
C.
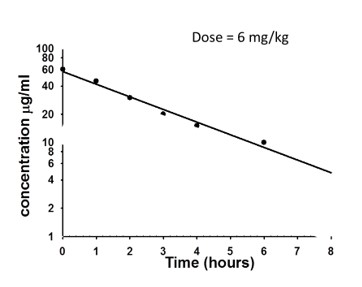
A drug is given at a dose of 6 mg/Kg. What will the volume of distribution be for a 75Kg person?
7.5 L
Name some properties that enhance the ability of a drug to cross cell membranes
Lipophilicity, ionization, size, solubility
What is the pH of a 10- 3M solution of HCl?
3
What is the hydrogen ion concentration [H+] of a solution labeled "Solution A",
whose pH is 5.60?
2.51 × 10^-6 M
A weak acid has a pKa of 4.5. At which pH will the acid have a greater fraction in the ionized form.
A. 3
B. 4.5
C. 6
C.
Acetaminophen has a pKa of 9.5. If the pH in the stomach ranges from 2-3, will acetaminophen be more in the ionized or unionized form when it is in the stomach.
Unionized
If a compound distributes equally into water and octanol, what is its logP value?
0
An acid is charged/ionized when its in the ___________ form
A base is charged/ionized when it is in the ___________ form
Deprotonated
Protonated
Define the term pharmacokinetics
The movement of drugs in the body or what the body does to the drug
Define the term pharmacodynamics
The effects of drugs and the mechanism of their action or what the drug does to the body
Define IP administration, where does it get injected into?
Direct injection into the abdominal cavity, peritoneal cavity
Which one of the following routes of administration does not have an absorption phase?
A. IV
B. Sublingual
C. Inhalation
D. Subcutaneous
E. Intramuscular
A.
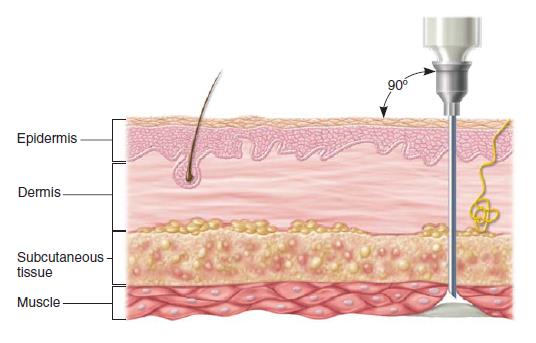
What route of administration is shown here?
IM
You are working for a large pharmaceutical company and are designing a new therapeutic for treating migraines (to be given orally). What physicochemical properties would increase bioavailability of the drug? Choose all that apply:
A. Increase lipid solubility
B. Increased water solubility
C. Hydrophobicity
D. Lipophobicity
A. C.
Fipronil has a logP of 4. For a person with total body water of 42L, would you expect the volume of distribution for fipronil to be less than, equal to, or greater than 42L?
VOD > 42L
If an identical formulation of a drug is given by injection IV, IM, and SQ, rank in order of quickest to slowest absorption into the bloodstream.
IV
IM
SQ
Which of the following routes of administration are subject to first pass metabolism? Select all that apply:
A. Oral through GI tract
B. IV
C. SQ
D. Intraperitoneal
A. D.
What is the most important determinant of absorption from the GI tract?
Surface area
Which of the following factors may alter the bioavailability of a drug? Select all that apply:
A. Drug-drug competition for transporters in GI tract
B. First pass metabolism
C. Plasma protein binding
D. Dose of drug given
A. B.
What is a beta blocker?
Beta blockers are a class of drug used in treated cardiovascular disorders
What is P(app)?
Apparent permeability in Caco-2 cells
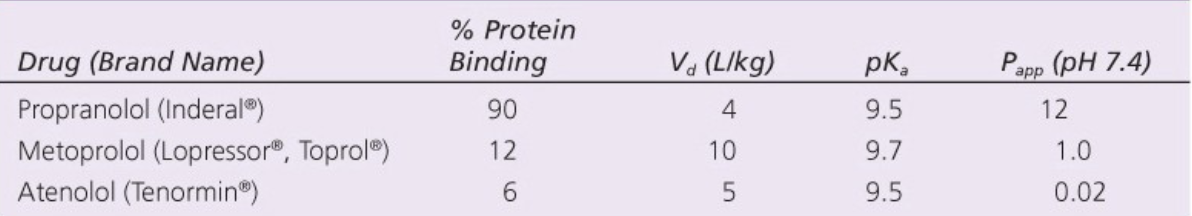
Which of these drugs is most likely to cross the blood brain barrier? Why?
Propranolol - highest P(app) at pH 7.4
T/F: Agents that are minimally protein bound diffuse/penetrate tissue better than those that are highly bound, but they are excrete much faster
True
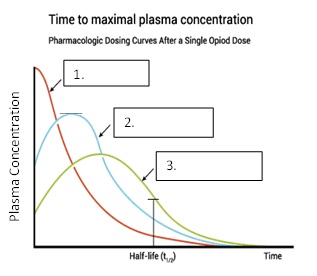
Label the different routes of absorption based on the plasma concentration curves from the figure below.
IV, IM (or SQ), Oral
Green - oral
Red - IV
Blue - IM or SQ
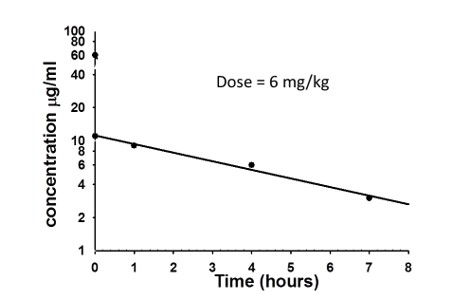
A drug is given at a dose of 6mg/kg. Based on this graph, what is the volume of distribution (L) for a 50Kg person?
30 L
Select all that apply to Phase I metabolism:
A. Substrates arise from phase II metabolism
B. Makes compounds more polar
C. Makes compound more biologically active
D. Requires co-substrate PAPS
E. Makes compounds less biologically active
B. C. E.
Which of the following will affect glomerular filtration of a drug? Select all that apply.
A. Afferent arteriole flow rate
B. Pressure inside the renal tubule
C. PH of the renal tubule
D. Presence of transporters in the tubular epithelial cells
E. Binding to plasma proteins
A. B. E.
Match the phase II enzyme with the corresponding cosubstrate :
Sulfotransferase →
Glucuronosyl transferase →
Glutathione transferase →
PAPS
UDP glucuronosyl
glutathione
Which factor of renal excretion is sensitive to drug ionization state?
Passive tubular reabsorption
Drugs that are weak acids are excreted faster in :
A. acidic urinary pH
B. No difference
C. Alkaline urinary pH
C.
Compounds that are neutral are excreted faster in:
A. acidic urinary pH
B. No difference
C. Alkaline urinary pH
B.
Select all that can apply to phase II metabolism:
A. Makes compounds less biologically active
B. Can be an oxidation, reduction or hydrolysis reaction
C. Requires a co-subtrate
D. Substrates can be parent compounds
E. Substrates can be products of phase I metabolism
A. C. D. E.
Which amino acid in glutathione contains the nucleophilic sulfur that reacts with the substrate to form a glutathione conjugate?
Cysteine
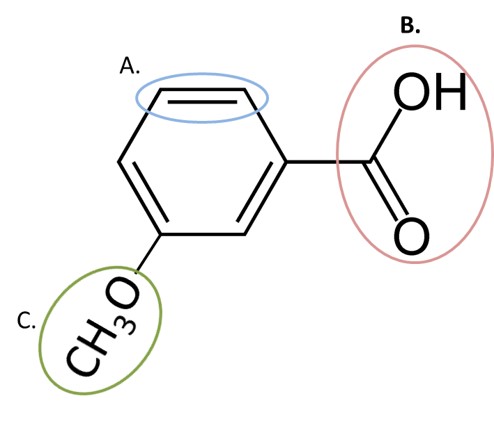
Given the structure below, match the letter of the functional group with the type of metabolic reaction likely to occur at that site.
Glucuronidation
O-dealkylation by P450
Epoxidation by P450
B
C
A
Drugs that are weak bases are excreted faster in:
A. acidic urinary pH
B. No difference
C. Alkaline urinary pH
A.
Which of the following will not affect glomerular filtration of a drug?
A. Binding to plasma proteins
B. Pressure inside the renal tubule
C. PH of the renal tubule
D. Afferent arteriole flow rate
C.
Buprenorphine is similar to codeine in structure and pain relief and commonly given to cats for pain control after surgeries. If you can only find a reported dose in mg/kg bodyweight for dogs, would you select a different dose to control pain in cats?
Lower dose in cats than in dogs
Codeine is metabolized to the more active form, morphine, through P450 catalyzed phase I metabolism. Which CYP2D6 phenotype will experience pain relief more quickly after taking codeine?
A. Poor metabolizer
B. Extensive metabolizer
B.
Match the following Phase I and Phase II metabolic enzymes with their required co-substrates/co-factors.
Sulfotransferases (SULTs)
Cytochrome P450s (CYPs)
UDP-glucuronosyl transferases (UGTs)
Glutathione transferases (GSTs)
PAPS
NADPH
UDP-glucuronic acid
Glutathione
What kinds of cellular changes can occur after a ligand triggers a signal? (select all that apply)
A. Changes in DNA transcription
B. Changes in intracellular calcium levels
C. Changes in protein levels
D. Changes in cAMP levels
All of the above
Receptors can be found (choose all that apply):
A. On cell membranes, and uclear membranes, but no in the cytosol
B. In various types depending on the tissue type
C. On cell membranes, on nuclear membranes and in the cytosol
D. Only in lung tissues
B. C.
T/F: A small molecule drug has a logP of 10. This drug is more likely to bind to a cytosolic receptor than a receptor on the plasma membrane.
True
Using the information below, match each drug with its appropriate classification: intrinsic activity 0, 0.5, 1
Buprenorphine
Morphine
Naloxone
0.5
1
0
A population dose response curve (select all that apply):
A. Determines the percentage of a population that exhibits a specific endpoint
B. Measures a graded response
C. Is the same as an individual dose response curve
D. Can be used to establish a LD50
A. D.
A ligand with a high Kd means it will bind _________ with a ________ ________ for a receptor
poorly
low affinity
Drugs can bind to receptors via different types of chemical bonds. Which of the following is the least common drug-receptor bond?
A. Hydrophobic
B. Van der Waals
C. Covalent
D. Hydrogen
E. Ionic
C.
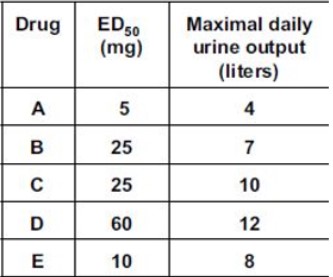
Five new diuretic drugs were tested in healthy volunteers. The results are given below: Which of the following drugs was the most effective?
D.
Which is not true: ion channels can be activated by
A. Chemical stimuli
B. Mechanical stimuli
C. Colorful stimuli
D. Voltage stimuli
C.
A 16-year-old girl suffering from seasonal rhinitis started a therapy with loratadine, a drug that binds to H1 histamine receptors. Which of the following terms best defines the intrinsic ability of a drug to bind to a receptor?
Affinity
A toxin targets IP3 receptors and releases large amounts of calcium into cardiac cells, causing arrhythmias. Which GPCR signaling pathway is this toxin mimicking?
Gq
Leaky ion channels that let potassium through are important because
they bring cells back to resting membrane potential
Most extracellular signal molecules act on cell-surface rather than intracellular receptors because they are
Either too large, too hydrophilic, or both to pass directly across the plasma membrane
RTKs can activate the enzyme phosphoinositide 3-kinase, which phosphorylates inositol phospholipids. These phospholipids then:
Serve as docking sites that recruit specific intracellular signaling proteins to the plasma membrane
Now that you know more about antagonistic and agonistic drugs and toxicants, let’s explore how to apply different types of drugs to the body. How can you overcome the effect of a competitive antagonist?
A. give same concentration
B. Not possible
C. Give lower concentration of agonist
D. Give higher concentration of agonist
D.
The term “Pharmacodynamics/Toxicodynamics” refers to
The biochemical effect of a toxin on the body and the biochemical effect of a drug on the body
Paracrine signals:
Short lives with local effects
Clinical potency is (select all that apply)
A. Determines by the hydrophobicity of a drug
B. The amount of drug needed to produce a certain level of therapeutic response
C. The amount of drug needed to produce lethal response
D. Determines by affinity of a drug for a receptor
B. D.
Which of the following terms best defines a drug with intrinsic activity higher than 0% and lower than 100%?
A. Chemical antagonists
B. Pharmacological antagonist
C. Functional antagonist
D. Partial agonist
E. Full agonist
Partial agonist
You determine that a tumor is proliferating uncontrollably by activating PKA. What G-protein would you want to inhibit?
Gs
RTKs are
membrane bound with an extracellular, transmembrane and intracellular domain
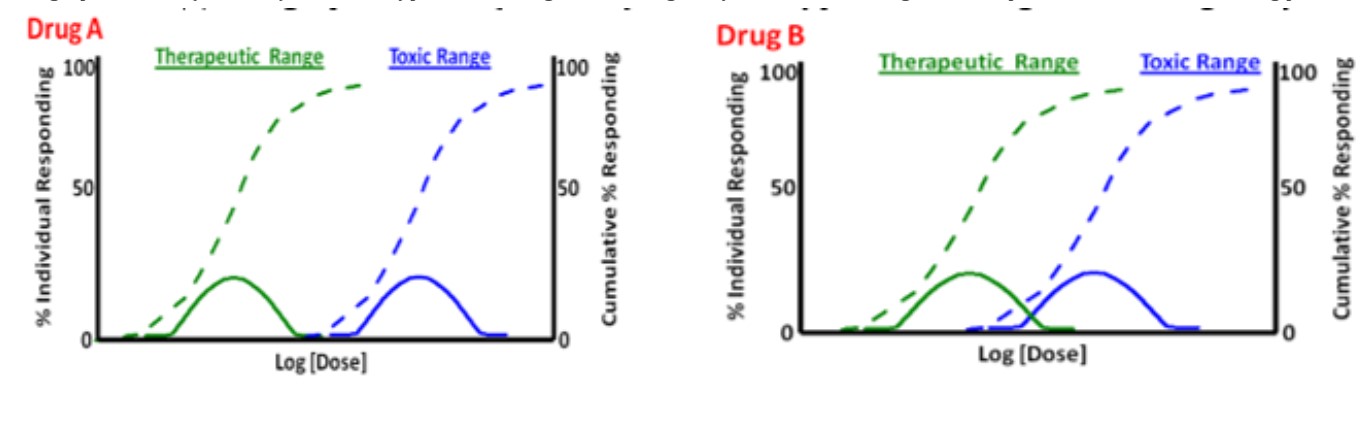
The graphical data (attached) is for two hypothetical drugs for treating tachycardia. Which drug would be preferred to be used treating patients?
Drug A, because the ED 90 and TD10 do not overlap
Matching:
RTKs
G proteins
Ion channels
GPCRs
Are important in the regulation of oncogenes and cell growth
Are heterotrimeric in structure
Form pores in the plasma membrane
Consist of a single polypeptide with 7 transmembrane domains
Many drugs act by binding to
Cell surface receptors
The phosphorylated tyrosines on activated RTKs (select all that apply):
A. Serve as binding sites for a variety of intracellular signaling proteins
B. Serve as binding sites for G proteins
C. Activate phospholipase C
D. Help activate the kinase activity of the receptor
A. D.
Buprenorphine is given by injection or oral mucosal [buccal] administration. It’s a cousin of morphine. It’s a weak base with a pKa of 8.24, small MW of 467.7 g/mol and a logP of 4.98. Explain whether buccal or oral administration results in a larger amount absorbed?
Buccal environment (pH 8-9) results in 50% of the compound to be unionized and favors absorption over the stomach (pH 1-2) or small intestine (pH 6-7). Oral mucosa is highly vascularized, drugs are absorbed through the oral mucosa enter systemic circulation directly
Where does phase I reactions take place?
Liver
What are phase I reactions?
Oxidation, reduction and hydrolysis
What is half-life (T1/2)?
The time it takes for the blood plasma concentration of a substance to have when circulating in the blood
Weak organic acids are well absorbed in the ______________ because they are ____________ at stomach pH.
Stomach
Uncharged
Drugs that alkalize the urine ____________ the clearance of weak acids though renal excretion
increase
Drugs that acidify the urine can ____________ the renal elimination of weak bases by keeping them in their __________ form
increase
charged
T/F: Cats lack UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes
True
What does the graded DRC relate?
Relates dose to intensity of effect
What factors help determine a ligand/receptor response? Select all that apply
A. Concentration of ligand
B. Affinity of the ligand to the receptor
C. Efficacy of the ligand to trigger a response
All of the above
Full agonists have (select all that apply)
A. High affinity and 100% intrinsic efficacy
B. Low affinity and 100% intrinsic efficacy
C. High affinity and 0% intrinsic efficacy
D. Low affinity and 0% intrinsic efficacy
A.
Antagonists have (select all that apply)
A. High affinity and 100% intrinsic efficacy
B. Low affinity and 100% intrinsic efficacy
C. High affinity and 0% intrinsic efficacy
D. Low affinity and 0% intrinsic efficacy
C. D.
If you want to look at a population response you should use a
Quantal response curve
It is better to transform graded dose-response data using ______ in order to get a sigmoidal curve with a linear dose-response relationship in the middle of the dose range
Log function
When evaluating a quantal dose-response relationship graph for dr, the bell curves for a therapeutic response and a toxic response should
A. Overlap at least 50%
B. Overlap as much as possible
C. Overlap as little as possible
D. Overlap at least 25%
C.
The dose response curve with a competitive antagonists shifts
To the right
How can you overcome the effect of non-competitive antagonist?
It is not possible
The dose response curve with a non-competitive antagonists shifts
down
A partial agonists activates receptor, but ___________
Does not elicit full response
Select all that apply to phase I metabolism
A. Can make a compound more biologically active
B. Can make a compound less biologically active
C. Can make a compound more polar
D. Requires NADPH
E. Catalyzed by cytochrome P450s
F. Typically an oxidation, reduction or hydrolysis reaction
All of the above