Chapter 6: Long-Run Economic Growth, sources, and policies
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are the two major factors that influence the level of labor productivity
the quantity of capital available to workers, and the level of technology
The Solow model of economic growth
The primary source of long run economic growth is technology
Per worker production function
shows the relationship between real gdp per hour worked (Y/L) and capital per hour worked (K/L)
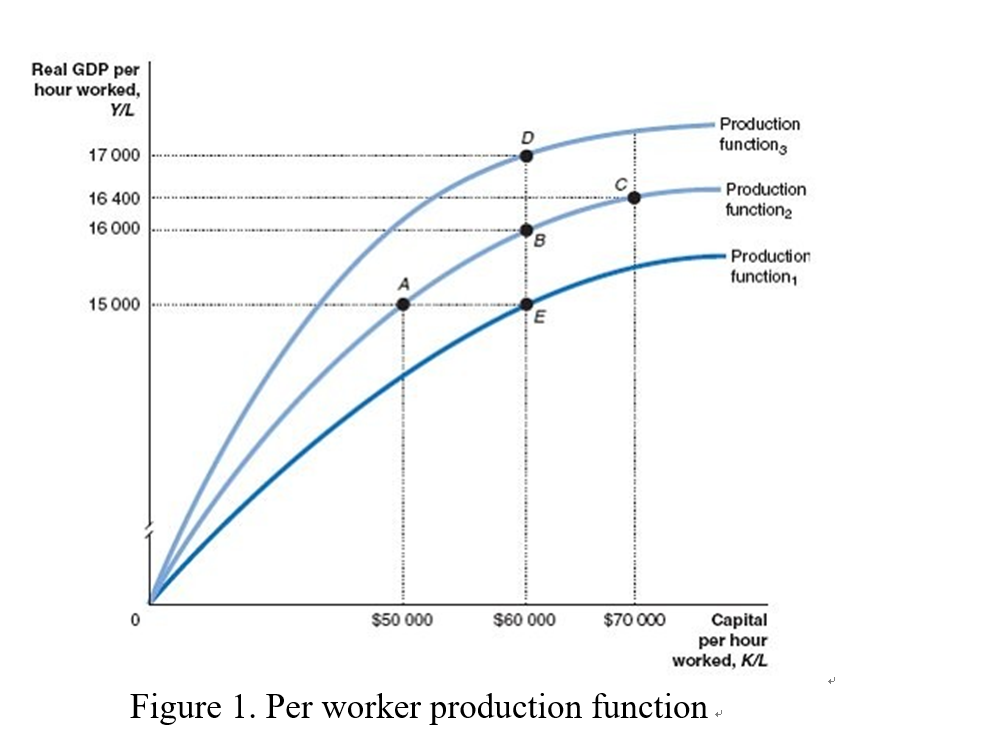
what shifts the production function
a change in technology
What happens to real gdp when capital per hours worked (k/l) increases
The increase in gdp becomes progressively smaller
diminishing returns
When we add more of an input (capital) to a fixed amount of another input (labor), so output increases by progressively smaller units
marginal product of capital
the increase in output that results from employing an additional unit of capital per worker
capital vs. technological change
capital is subject to diminishing returns while technological change can increase real output per hour worked
Why is the Solow growth model viewed as incomplete
It does not explain the factors that lead to technological change
The New Growth Theory
Knowledge capital is the primary source of economic growth in the long run, because it is the source of technological change
Knowledge capital at a firm vs. economic level
At a firm level, it is subject to diminishing returns while at an economic level, it is subject to increasing returns because it can be shared across firms
Market failure
when the free market doesn’t provide an efficient amount of a good or service
During market failure, how can the government help
protecting intellectual property, supporting research and development, and subsidizing education
why isn’t the whole world rich
catch-up hypothesis
catch up hypothesis
The idea that poorer countries can grow faster than richer ones due to existing research and development and technology
Growth policies for poorer counties to catch up
rule of law, protection of property rights, political freedoms
investment in health care and education
Investment in good physical capital (roads, airports)
Promoting innovation and technological progress
Promoting saving and investment