Ap Macro AP Test Review
1/145
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
scarcity
unlimited wants but limited recourses
opportunity cost
the most desirable alternative given up when making a choice
absolute advantage
the producer that can produce the most output or requires the least amount of input
comparative advantage
the producer with the lowest opportunity cost
PPC
shows differing options of how an economy could spend all their resources
productive efficiency
producing the largest number of products and services based on the available resources
allocative efficiency
the products being produced are the most desired by society
demand
different quantity of goods and services that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices
law of demand
there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
supply
different quantity of goods and services that businesses are willing and able to supply at different prices
law of supply
there is a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied
when demand goes up what happens to equilibrium price
PL goes up
when demand goes down what happens to equilibrium price
PL goes down
when supply goes up what happens to equilibrium price
PL goes down
when supply goes down what happens to equilibrium price
PL goes up
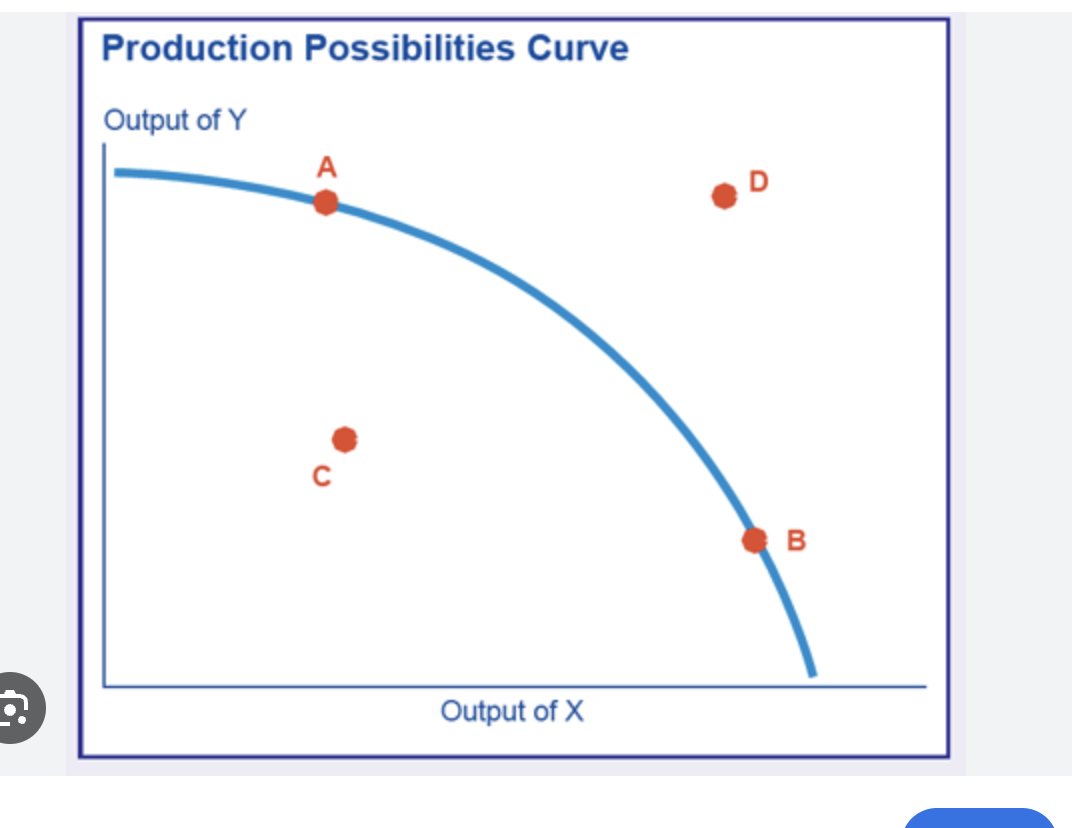
which is a PPC in a negative output gap
point C
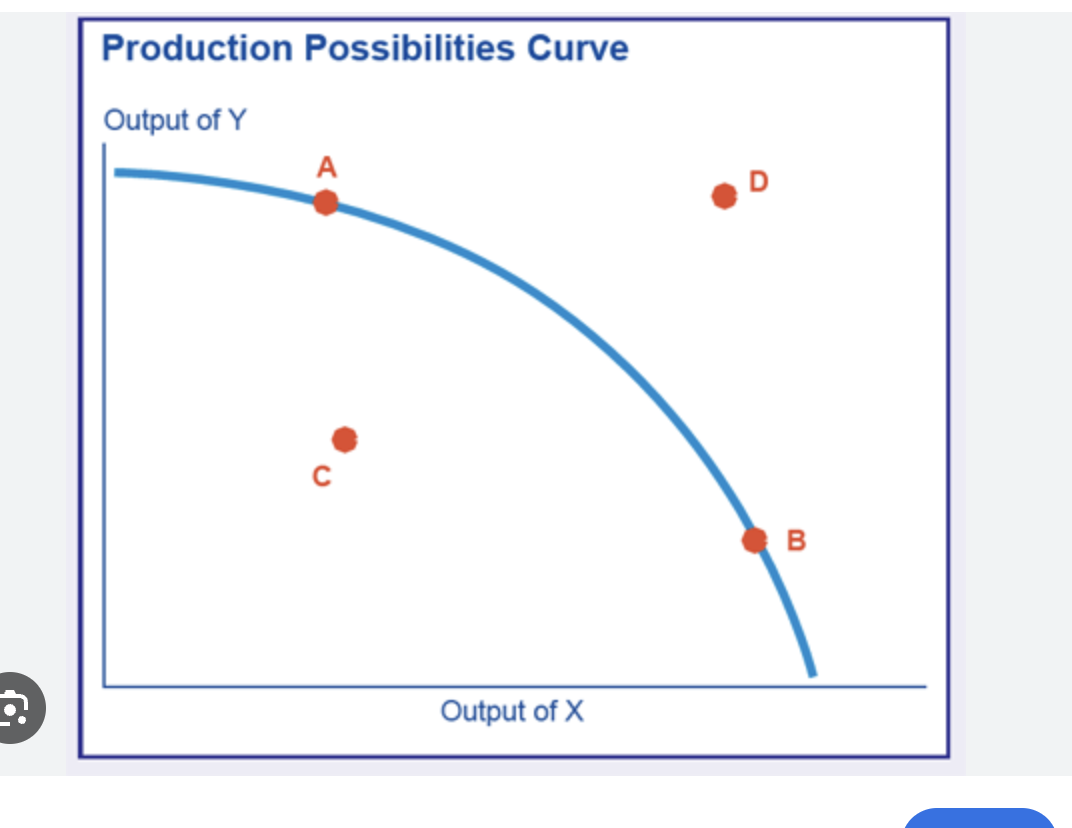
which is a PPC at full employment
point A or B
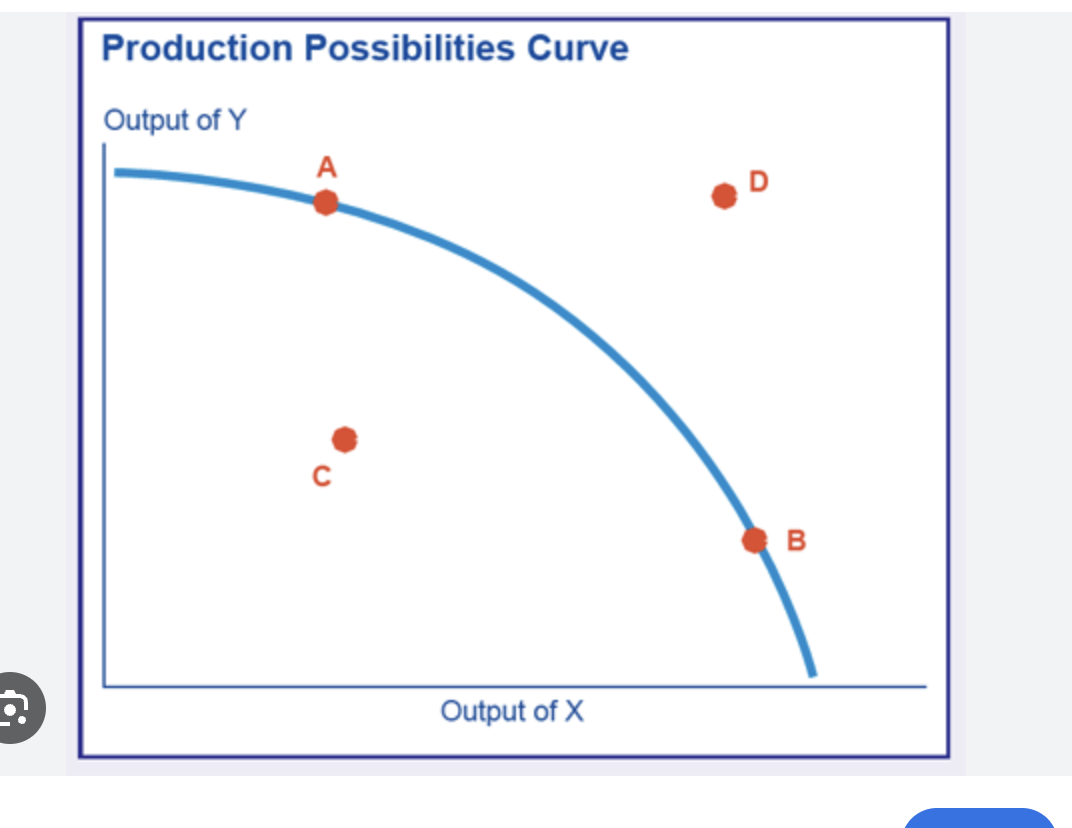
which is a PPC in a positive output gap
point D
the production of which good causes long run economic growth
capital goods because they are used to make consumer goods
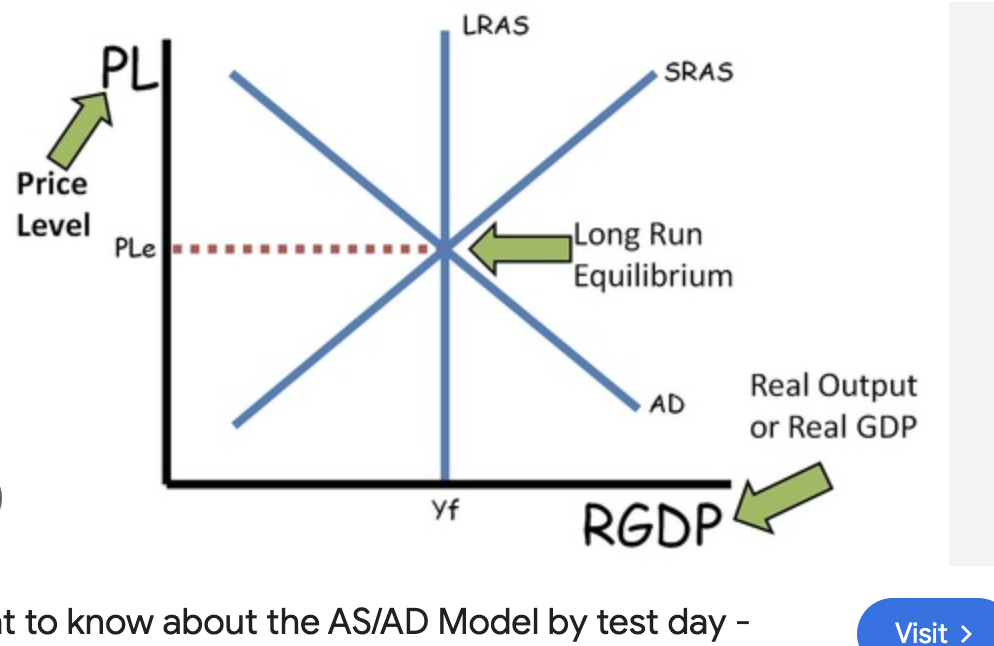
which is an AS/AD curve is in equilibrium
the circular flow model
demonstrates how money moves from producers to consumers and back in an endless loop
product market
where final goods and services are sold to households and foreign sector
factor market
resources that businesses use to purchase, rent or hire what they need to make goods and services
leakage
parts of income earned and currently spend on goods and services
gross domestic product
dollar value of all final goods and services produced in a ciuntry in a year
GDP per capita
GDP divided by the total population, it identifies on average how many products each person makes and it is the best measurement of quality of life)
standard of living
average quantity/quality of goods and services people in a country can afford to consume
factor payments
payments made by businesses for the factors for production
unemployment
people that are actively looking for a job but not working
natural rate of unemployment
frictional + structural unemployment
full employment
the r-GDP when there is no cyclical unemployment
inflation
rising general prices, reduces the purchasing power of money
inflation rate
% change in price level from year to year
price indices
index number assigned to each year to show how price level changes relative to specific base year
CPI
most commonly used measurement of inflation for consumers
labor force participation formula
civilian LF total/everyone x 100
unemployment rate formula
# unemployed/# in CLF x 100
% change in GDP formula
year 2- year 1/year 1 × 100
CPI formula
price of market basket/price of MB in base yr x 100
GDP deflator formula
nominal GDP/real GDP x 100
expenditures approach
C+I+G+(X-M)
C= consumer spending
I= investment spending
G= government spending
(X-M)= net exports
income approach
W+R+i+Pr
W= wages
R= rent
i= interest
Pr= profit
what are the 3 macroeconomic goals of all countries
promote economic growth
limit unemployment
keep prices stable (limit inflation)
what are the items not included in GDP calculations
intermediate goods
non production transactions
non market transactions
illegal transactions
frictional unemployment
temporary unemployment or being in between jobs
structural unemployment
changes in labor force make skills obsolete (technological unemployment)
cyclical unemployment
unemployment caused by a recession
who is helped by inflation
borrowers and businesses because the money they pay backs worth less than the money they borrow
who is hurt by inflation
lenders and savers because the money they get paid back has less purchasing power than the money they lent out
nominal GDP
GDP not adjusted for inflation
real GDP
GDP that is adjusted for inflation
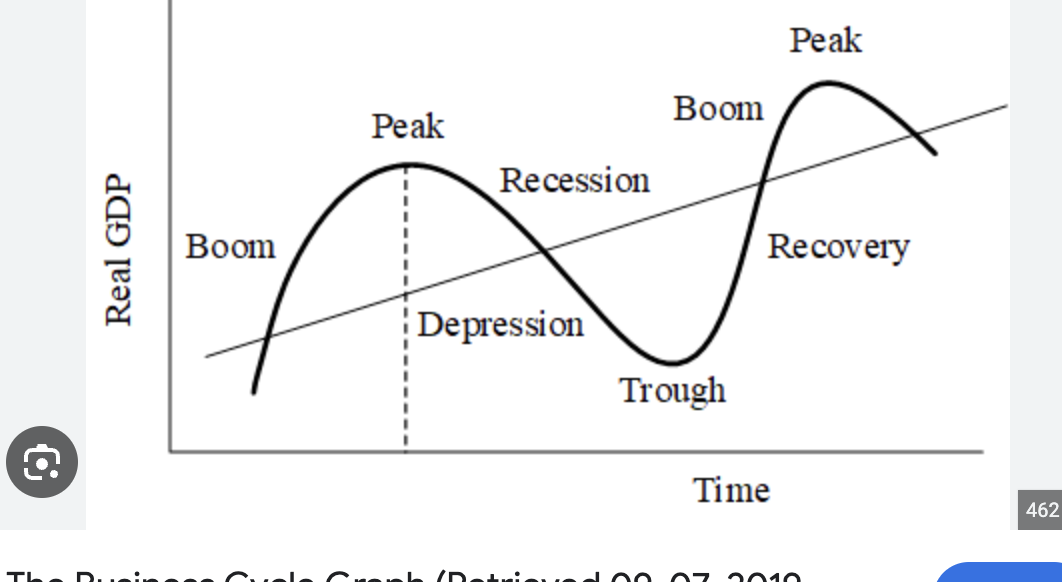
business cycle graph
aggregate demand
all the goods and services that buyers are willing and able to buy at differing price levels (same as GDP)
shifters of aggregate demand
C+I+G+Xn
C= consumer spending
I= investment spending
G= government spending
Xn= net exports
investment
an attempt to stimulate economic production by means of creating or acquiring capital goods
short-run aggregate supply
shows when wages and resource prices are sticky and WILL NOT change as price levels change
shifters of short run aggregate supply
RAP
change in resource prices
change in actions of the government
change in productivity
long run aggregate supply
shows when wages and resource prices are flexible and WILL change as price level changes
stagflation
the combination of high consumer price inflation with stagnant economic growth
the multiplier effect
says that an initial change in spending will set off a spending chain that is magnified in the economy
marginal propensity to consume
how much people consume rather than save when there is a change in their disposable income
marginal propensity to save
how much people save rather than consume there is a change in their disposable income
autonomous consumption
says consumers will spend a certain amount of money no matter what regardless of their income
fiscal policy
actions by the congress that stabilize the economy through government spending or taxation
automatic stabilizers
part of the government budget that offsets fluctuations in aggregate demand
discretionary fiscal policy
when congress creates a new bill that is designed to change the aggregate demand through government spending or taxation
non-discretionary fiscal policy
permanent spending and taxation laws enacted to work counter cyclically to stabilize the economy
MPC formula
1-MPS or change in consumption/change in disposable income
MPS formula
1-MPC or change in savings/change in disposable income
spending multiplier formula
1/MPS or 1/1-MPC
tax multiplier formula
MPC/MPS or the spending multiplier-1
when consumer spending increases what happens to real GDP
it increases
when interest rates increase what happens to investment
it decreases
when inflation increases what happens to real wages
they decrease
when aggregate demand increases what happens to price level
it increases
when short run aggregate supply increases what happens to price level
it decreases
when government spending increases what happens to real GDP
it increases
when taxes increase what happens to disposable income
it decreases
when MPC increases what happens to MPS
it decreases
shifters of long run aggregate supply
same as PPC shifters
change in resource quantity or quality
change in technology
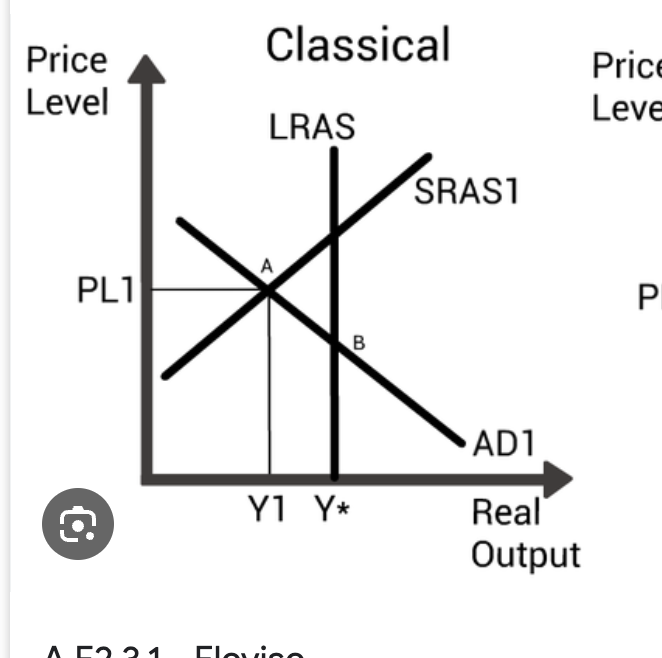
which shows negative output gap on AS/AD graph
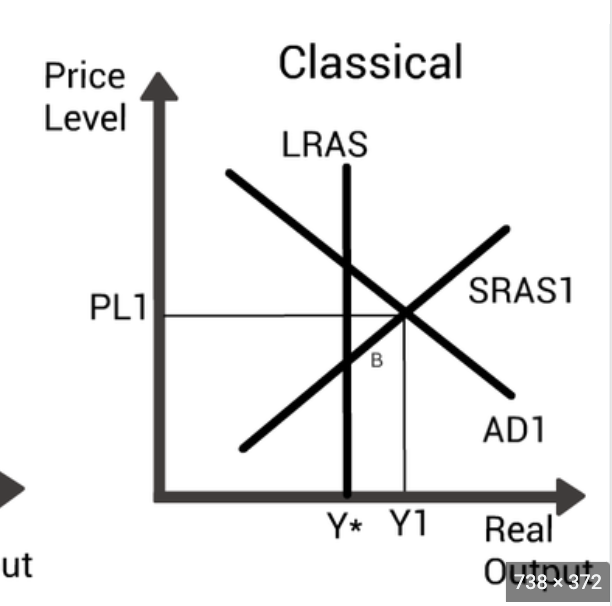
which shows positive output gap on AS/AD graph
demand pull inflation
when demand for goods and services rises faster than the supply
cost push inflation
when there is a decline in the supply of goods and services and the demand remains unchanged
what are the 3 main causes of inflation
demand pull
cost push
inflationary expectations
what are the 2 tools of fiscal policy
contractionary and expansionary fiscal policy
what are the 3 time lags of fiscal policy
recognition lag
administrative lag
operational lag
expansionary fiscal policy
laws that reduce inflation and decrease GDP by decreasing spending or increasing taxes
contractionary fiscal policy
laws that reduce unemployment and increase GDP by increasing spending or decreasing taxes
financial sector
network of institutions that link borrowers and lenders
assets
anything tangible or intangible that has value
liabilities
financial obligations that a bank must pay to a consumer and they must be repaid when requested
interest rates
the amount a lender charges a borrower for borrowing money
stocks
represent ownership of a corporation and the holder is often entitled to a portion of the profit
bonds
loans or IOUs that represent debt that the government, businesses, or an individual must repay to the lender
nominal interest rate
the percent increase in money that the borrower pays not adjusted for inflation
real interest rate
the percent increase in money that the borrower pays adjusted for inflation
commodity money
something that performs the function of money and has intrinsic value
fiat money
something that serves as money but has no other intrinsic value
purchasing power
amount of goods and services one unit of money can buy