Chemistry: Midterm Review
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What element is the most electronegative?
Fluorine
Where are protons located, what is their charge, and what is ther size?
nucleus, 1 AMU, positive
Where are neutrons located, what is their charge, and what is ther size?
nucleus, 1 AMU, neutral
Where are electrons located, what is their charge, and what is ther size?
electron cloud, 1/1836 AMU, negative
What is an isotope? What information do you need for isotope notation?
An isotope is a version of an element with a different number of neutrons. The atomic mass, and number are needed for isotope notation.
What element is the largest in group 13?
Nihonium
How many valence electrons does oxygen have? What about sulfur?
sulfur has 6 valence electrons, and so does oxygen.
What is the oxidation state of elements located in group 13?
-3
What type of metals have the greatest metallic charcter?
Alkalai metals
What is the electron configuration of Beryllium?
1s22s2 OR [He] 2s2
What is the electron configuration of Argon?
1s22s22p63s23p6 OR [Ne] 3s23p6
In what two blocks does the orbital number go down by one?
D and F
Which is larger phospherous or silicon?
silicon
Which is larger zirconium or xenon?
zirconium
What are the properties of metals?
Malleable (ductile), lusterous, conducts heat/electricity.
What are the properties of nonmetals?
Dull (not lusterous), brittle, poor conductor of heat/electricity?
What are the properties of metaloids?
Semi-conductive, brittle or malleable/ductile, sometimes lusterous
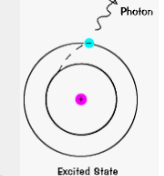
Explain how light is emitted when an element (sulfur) is expposed to a flame.
A photon is emitted.
Steps…
atom gains energy from outside source
energy causes atom to jump to excited state (higher energy orbital)
electrons eventually leave excited state and return to a ground state (starting orbital)
when electrons go back to a ground state, it emits a photon (energy exits) and its wavelength (related to energy) dtermines the color of the light seen
If the flame had a measured wavelength of 5.97 × 10 -7 m. What is the wavelength in nm?
597 nm
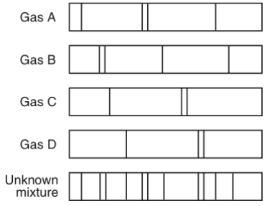
Using this emission spectcra, identify the gases located in the unkown mixture.
Gases A, B, and D are in the compound. The lines of those gases match up to the unkown mixture.
What kind of waves have the highest energy, and what kind of waves have the lowest?
Gamma rays have the highest, and radio waves have the lowest
What is the visible spectrum?
Photons (only radiation humans can see)
What is the visible spectrum from highest to lowest wavelengths?
-Wavelengths from 400nm to 750nm
Red: 750-620 Lowest Energy/Longest Wavelengths
Orange: 620-590
Yellow: 590-570
Green: 570-495
Blue: 495-450
Violet: 450-400 Highest Energy/Shortest Wavelength
What is a continuous emission spectrum?
a complete visible spectrum
What is an emmision line?
colored photons emitted by a substance (unique for every atom/element)
What is an absorption line?
opposite of emmision spectra
What is an emission spectra?
Wavelengths of the photon being emitted
As frequency increases, does energy increase or decrease?
increase
As wavelength decreases, does frequency increase or decrease?
increase
As energy increases, does wavelength increase or decrease?
decrease
Who created the first periodic table, and what was it organized by?
Medeleev, organized by atomic mass
Who created the current periodic table, and what is it organized by?
Mosley, organized by atomic number (protons in an element) and metals and nonemetals.
What is metallic character?
How pronounced metallic properties are in elements
What is atomic radius?
How large the atom is (size not mass)
distance from nucleus to outer-most orbital
What is electronegativity?
The atom’s potential to attract (gain) electrons from other atoms (How badly it wants to)
the larger the number to more potential
how likely the atom is going to gain electrons
What is ionization energy?
The energy required to remove an electron form an element (goes with electronegativity)
getting rid of electrons
for every electron lost - ionization energy increases (10 electrons = 10 energies)
Every time you lose one, the next is harder to lose
when there is a large increase the atom is done losing electrons
What does electron configuration show?
Shows where the electrons are in sub-orbitals if an atom (it is another layer to Bohr models)
What are the steps to drawing a L.D.S (Lewis Dot Structure)
Find the amount of valence electrons (don’t draw nucleus like a Bohr model)
Draw the chemical symbol
Pick 1 side first (NO CORNERS)
*remeber electrons hate pairing up unless it is needed (similar to seats on a bus). 4 spots (start top, go clockwise)
KEY: DOTS=VALENCE ELECTRONS (8 max)
What is an ion?
An atom that has gained a charge due to a change in the number of electrons.(result of ionic bonds/compounds)
What is a cation, and what is its charge?
A cation has a positive charge, it is the element losing valence electrons, and it is the metal in the ionic compound
What is an anion, what is its charge?
AN anion has a negative charge, it is the element gaining valence electrons, and it is the nonmetal in the ioic compound.
What is the exponent in ionic compounds?
The oxidation state.
How do you name an ionic compound?
metals →stay the same (normal)
nonmetals →change ending to -ide
What are the properties of ionic compounds?
Combination of metal and nonmetal properties (similar to metalloids)
Form crystals (rough shape) (ex. table salt)
Brittle
Soluble in water (dissolves)
Only conduct elecctricity when dissolved in water
High melting/boiling points
Are covalent compounds and molecular compounds the same thing?
Yes, covalent compounds create molecules.
What kind of elements do covalent compounds consist of?
Multiple nonmetals (2+)
How are covalent bonds formed?
Overlapping valence shells.
shared electrons (bonds)(complete valence shell)
paired eletrons (don’t touch)
What is the prefix for one?
mono
What is the prefix for two?
di
What is the prefix for three?
tri
What is the prefix for four?
tetra
What is the prefix for five?
penta
What is the prefix for six?
hexa
What is the prefix for seven?
septa
What is the prefix for eight?
octa
What is the prefix for ten?
deca
Which element does the negative dipole go on (*hint: looks like -S)
the more electronegative one
What is VSEPR?
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
What does VESPR declare?
covalent bonds and lone pairs space out as much as possible around the central atom
can be used to determine shape
What is electron domains?
Number of bonds + number of lone pairs
same thing as electron group