Cell Membranes and Transport
1/62
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are cell membranes made of?
A phospholipid bilayer

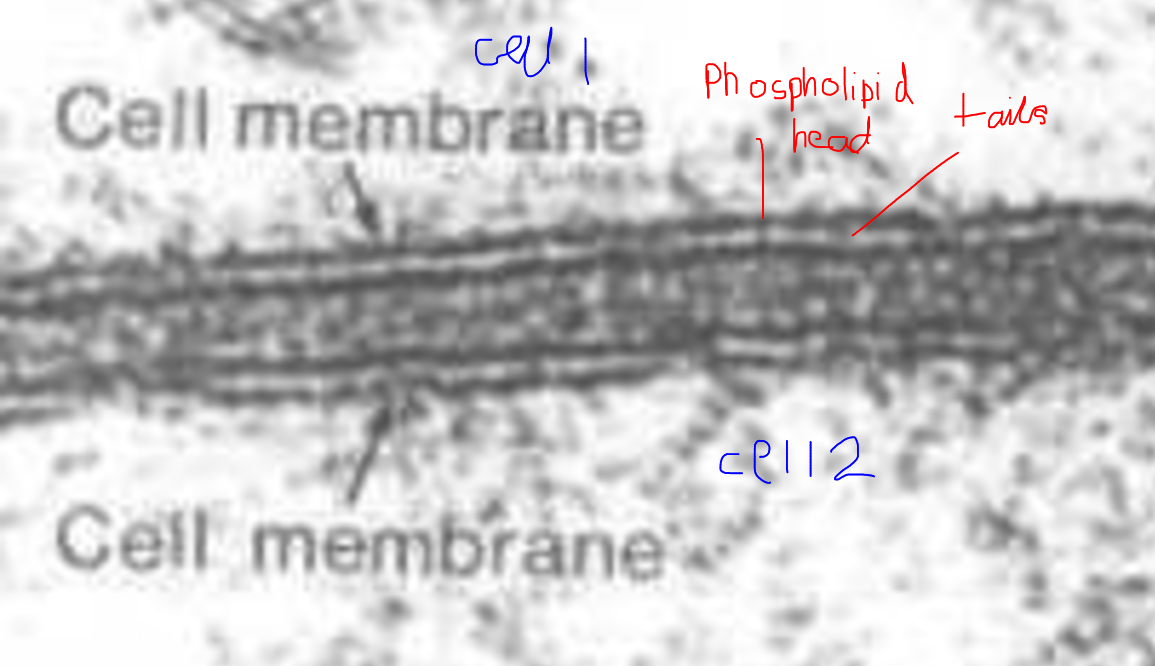
What are the main components of phospholipids?
Hydrophilic polar phosphate head, glycerol, hydrophobic non-polar hydrophobic fatty acid tails
What effect do phospholipids on their own have on hydrophobic and hydrophilic molecules?
Something hydrophilic can pass through the heads but not the tails so can not pass through (without help). Something hydrophobic is able to avoid the heads and pass through the tails so can pass through
What are the two types of protein molecules in phospholipid layers?
Extrinsic- partly embedded
Intrinsic- extend completely across the bilayer
These both have hydrophobic and hydrophilic sections.
What is the function of intrinsic protein molecules?
Transport through the membrane as Carrier Proteins or Protein Channels for molecules that would otherwise not be able to pass through.
The outside is hydrophilic/phobic and polar/nonpolar corresponding with the part of the membrane while the inside is polar for the molecules to pass through
What is the function of extrinsic protein molecules?
used for cell recognition, as enzymes or for cell recognition
What does a protein channel look like?
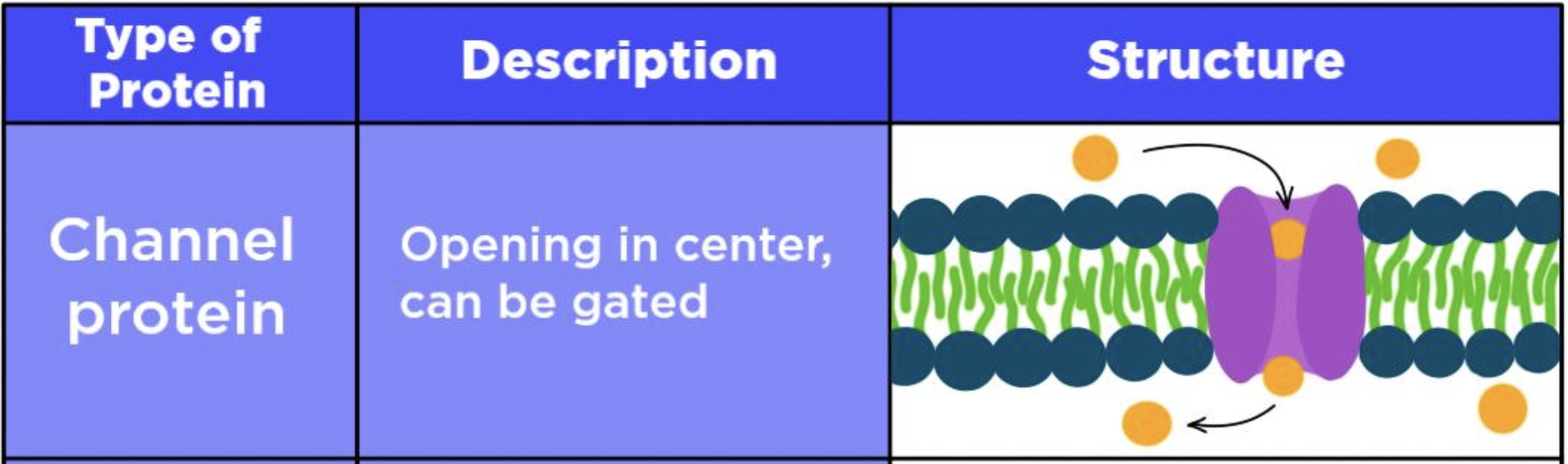
typically selective for certain molecules
they have hydrophilic R groups down the middle to allow charged proteins to pass
What does a carrier protein look like?
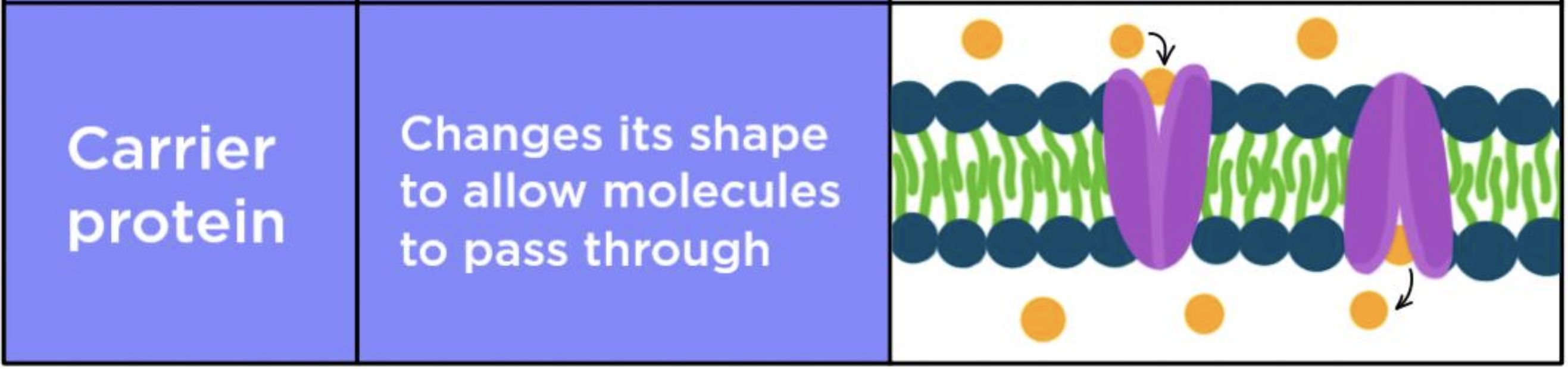
typically selective for certain molecules
What is it when a carbohydrate chain is attached to a phospholipid or protein?
It is a glycocalyx forming a glycolipid/ glycoprotein. It helps with the functions of the protein molecules.
What is the fluid mosaic model and who presented it?
It was presented by Singer and Nicholson. It means that the proteins and phospholipids can change places and move within the membrane and the proteins are randomly arranged
What does the cholesterol in ANIMAL membranes do?
bind the phospholipids together meaning there is less movement
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
regulating intake of nutrients and secretion of chemicals
cell recognition using glyco(proteins/lipids)
separating the inside and outside of the cell
separating one cell from another
How well do differently soluble substances pass through the membrane?
Lipid soluble substances move easily and quicky as they can move through the lipid bilayer. -non-polar
Water soluble substances move more slowly as they must move through protein channels. -polar
The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable, what things can diffuse across the bilayer?
small nonpolar molecules diffuse rapidly and so do uncharged polar molecules if they are small enough. HOWEVER the bilayer is highly impermeable to ALL charged molecules
Small= faster because it is easier for them to fit between phospholipid molecules + higher kinetic energy
What affects the permeability of the cell membrane?
Ethanol- dissolves the lipid components
Temp and pH- when they are above/ different ot the optimum the proteins denature
What is diffusion?
The net movement of molecules or ions from an area of high concentration to a region of low concentration until reached equilibrium. It is a passive process
What is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion?
simple diffusion occurs without a membrane while facilitated always happens across a membrane
Which factors increase rate of diffusion? (7)
a steeper concentration gradient
a higher temperature (as molecules have more kinetic energy)
a smaller molecule (can fit more easily through membranes and carriers
if they are lipid soluble (can pass straight through membrane)
shorter distance
larger surface area
more pores
What is meant by “net movement”?
there is still movement but there is no overall change in number of molecules on each side.
How does facilitated diffusion occur?
Carrier molecules in the membrane bind temporarily to the molecules allowing movement through protein channels. This is also passive and faster then simple diffusion.
What is cotransport?
a type of facilitated diffusion when two substances are simultaneously transported across a membrane by a carrier protein. It requires both of the molecules at the same time- one cannot pass through without the other
What are the two types of cotransport?
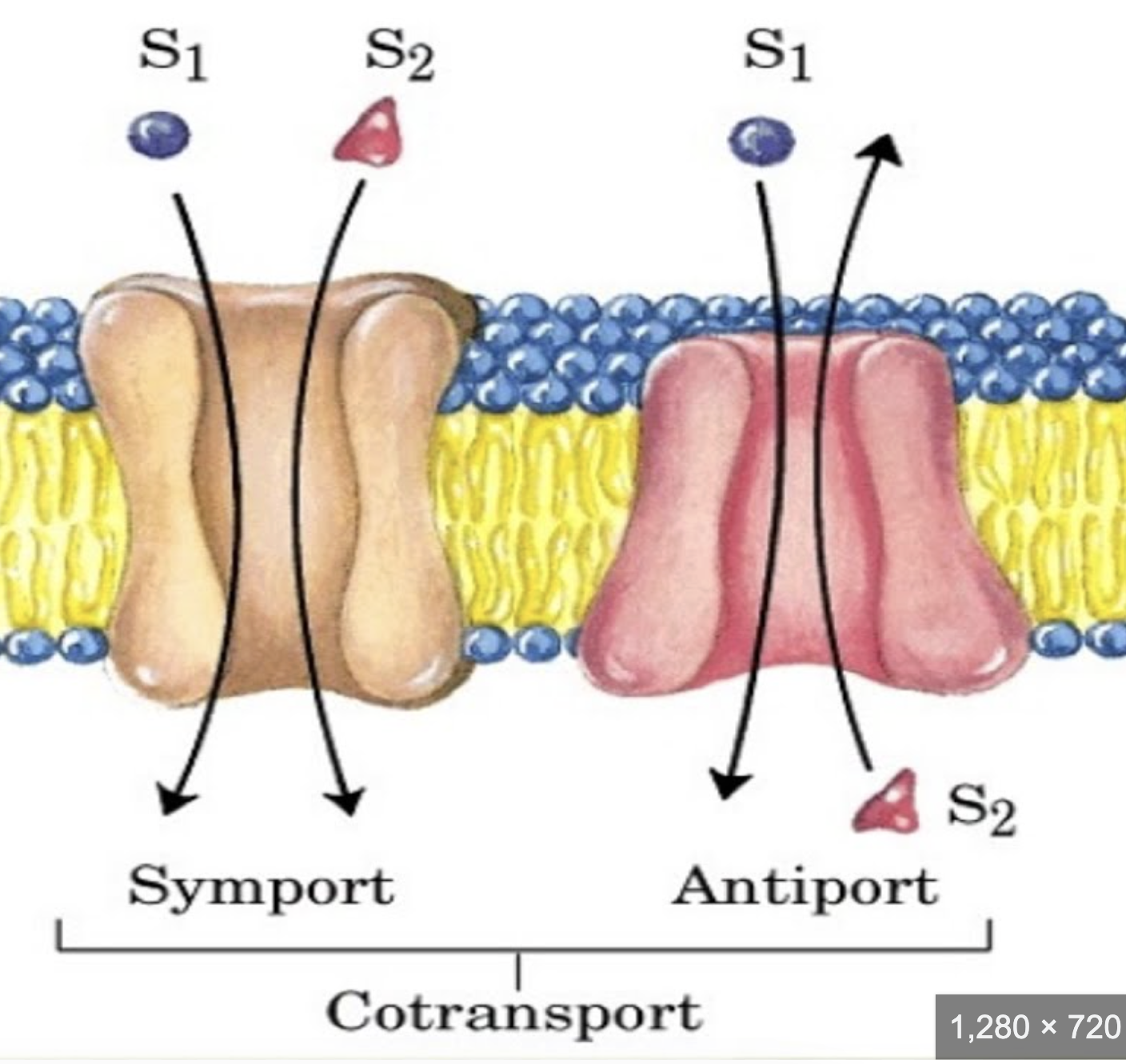
Why is transport across the membrane vital to the cell?
remove toxic substances and obtain nutrients
What is osmosis?
The passive movement of water molecules from a higher water potential to a lower water water potential across a selectively permeable membrane until equal
Down the water potential gradient
What does dilute mean simply?
MORE WATER
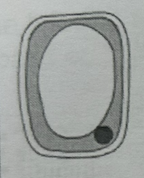
When a cell is in a hypotonic solution (less concentrated) there will be a net flow of water by osmosis into the cell making it turgid.
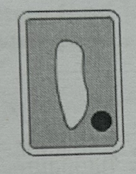
Cell is in an isotonic solution (conc is same in and out liquid)
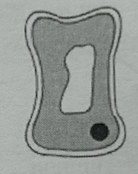
If a cell is placed in a hypertonic (more concentrated) solution then water will move by osmosis out of the cell and become flacid
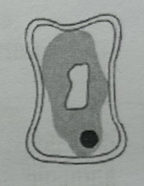
As more water osmosises out of the cell it becomes plasmolysed and the cytoplasm is pulled away from the wall
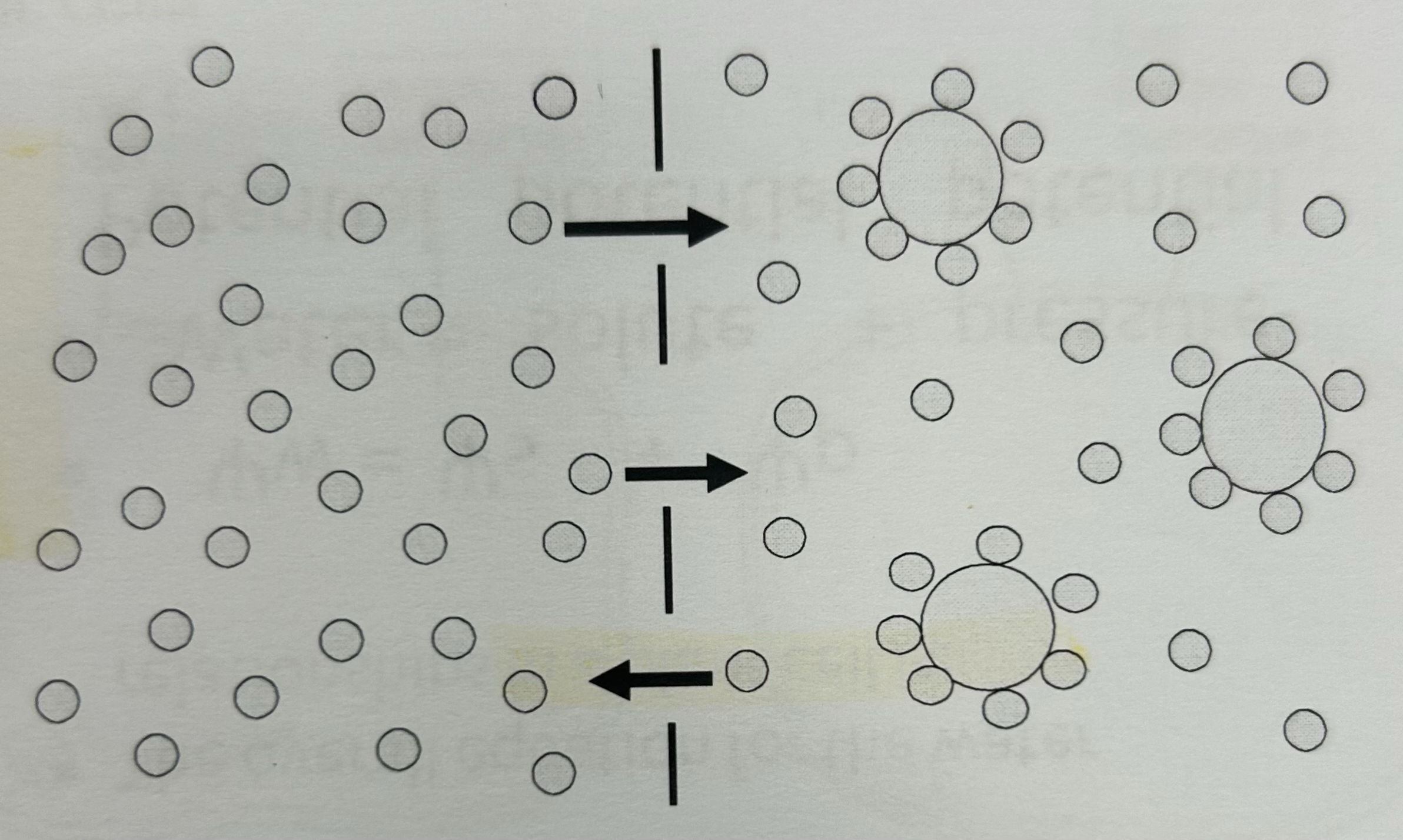
Describe this image
The number of water molecules are equal however, water is free to move until it is attracted to the solute. There are more free moving water molecules on the left than the right so it is more dilute so more move through the pores of the membrane to the right.
Tip for when talking about any kind of movement?
say how and what the conc. gradient is(eg. by osmosis down the conc. gradient)
if it requires energy (eg. passively)
and where energy comes from
What is water potential and its symbol and its unti?
The tendency for water molecules to move from a dilute to more concentrated solution/ out of a system. / the difference between the free energy of water molecules in a system and the free energy of molecules in pure water.
The pressure exerted by water on the membrane ψw, kPa
What is solute potential and the symbol?
is the amount by which the presence of a solute in pure water reduces the water potential. Ψs
More negative as solute concentration increases. less solute potential= less water potential
What is pressure potential and the symbol?
A measure of the pressure that developes inside a cell because of the inflow of water
ψp
What is the equation for the water relationships in plant cells?
Water potential= Ψs + Ψp
in pure water the water potential is 0. (closer to 0 higher water potential)
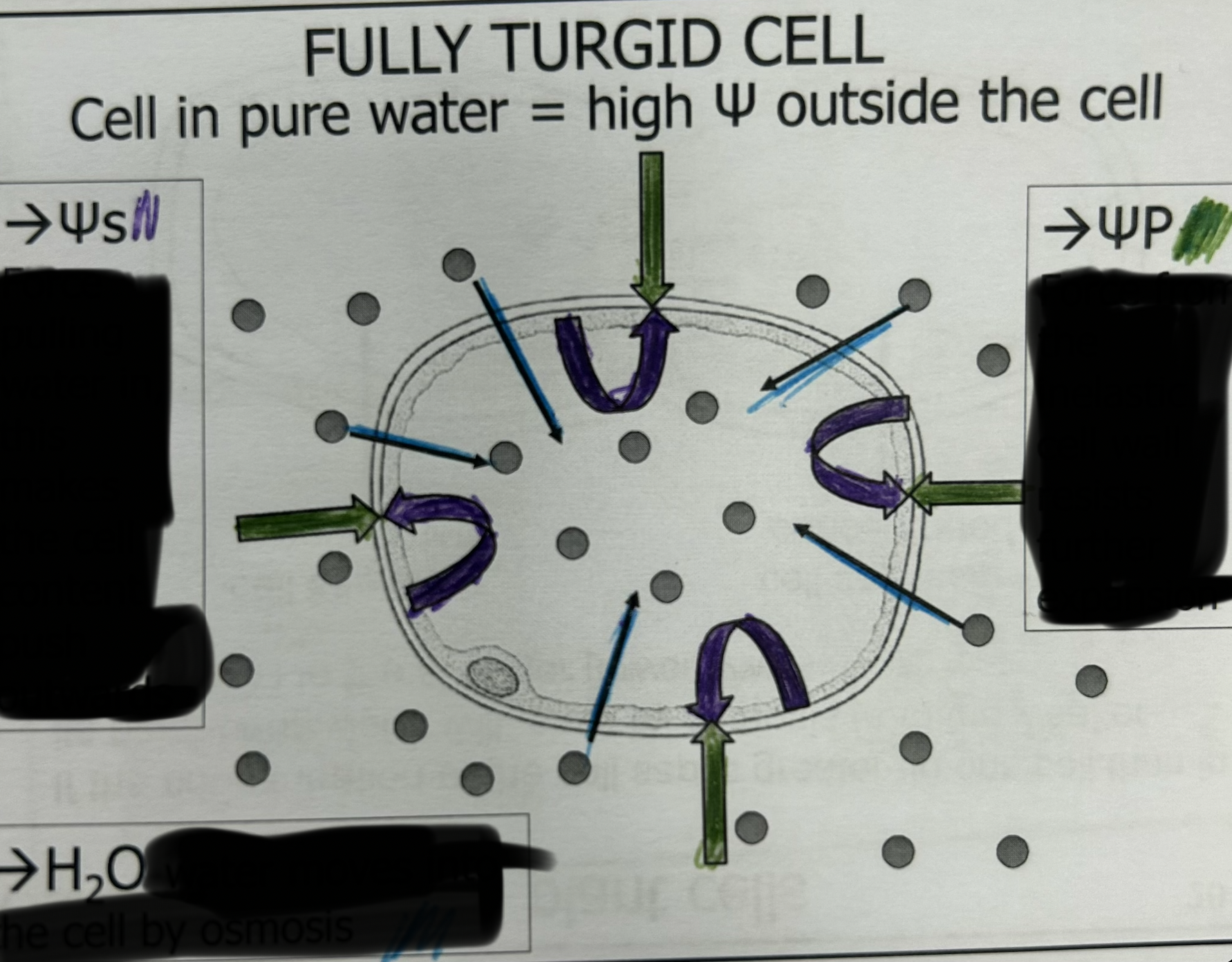
describe this of a turgid plant cell.
the solvent potential pulls water in and makes the cell content push outwardly. The Pressure potential of the cell wall pushes inwards, resisting further expansion. The solute potential is negative because there is some solutes
Water potential is 0 both in and out of the cell so there is so movement
0 = -5 + 5
What is the the water potential of a cell the same as in a isotonic solution?
The solute potential of the solution and vise versa
What is incipient plasmolysis?
The point at which the cell membrane/ cell content just pulls away from the cell wall- judged when about 50% of cells are showing signs of plasmolysis.
What is the pressure potential of a plasmolysed cell and why?
0- as the cell wall isn’t pushing back on anything
What is the equation for water potential in an animal cell?
Ψw= Ψs
There is no cell wall so no pressure potential
What is the effect of animals having no cell wall for osmosis?
There is nothing to stop the cells from bursting if too much water enters
What words are used to describe an animal cells’ shape in relation to water content/
Crenated = shrivelled and Lysed= burst
What is active transport?
The active passage movement of substances against the concentration gradient (low to high)
What is a feature of cells that carry out a lot of active transport?
rich in mitochondria and require large amounts of oxygen
How does active transport work?
Carrier proteins bind with a molecule or ion (on one side only) and go through a conformational change. This change requires ATP which binds to another part of the protein
How does cyanide impact active transport?
competitive inhibitor- inhibits respiration and in turn the release of energy
What is endocytosis and how does it happen?
The process of the cell surface membrane engulfs material (eg. bacteria/ liquid). This happens by the invagination (infolding) of the cell membrane around
What are the three types of endocytosis?
Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis
What is phagocytosis?
-intake of solid material- vacuole formed are phagocytic vacuoles
What is pinocytosis?
Intake of liquids
What is receptor mediated endocytosis?
receptor proteins on the surface of the cell membrane are used to capture specific molecules. When the receptors bind endocytosis is triggered and the recpetors and molecules are taken in a vesicle
What is exocytosis and how does it occur?
Material is transported out of cells. The substances (like enzymes) are taken to the membrane in vesicles and fuse with the membrane, releasing the substance
Give and example of a cotransport system and explain how it works?
A sodium potassium pump transports sodium out of the cell into the bloodstream and potassium in to the cell (active transport). This sets up a concentration gradient where inside the cell there is a low concentration of sodium. This makes the facilitated diffusion of the Sodium and Glucose cotransporter to occur quicker into the cell form the lumen of the small intestine. The glucose can then facilitated diffuse out of the cell into the bloodstream and reabsorb
Why is glucose absorption SECONDARY ACTIVE TRANSPORT?
If cyanide stops the production of ATP then the Na/K pump stops so there is no gradient set up for sodium and glucose to enter the cell (remember carrier proteins require both to bind for it to work) and so glucose can’t diffuse into the bloodstream and reabsorb (at all/ as quick)
beetroot experiment- explain this graph

Membrane proteins are stable at low temperatures. As temperature increases the colorimeter reader increases meaning more pigment has leaked out of the cell which means the cell membrane has been damages and the protein has denatured
Why will an active transport/ facilitated diffusion graph eventually platue when increasing the substance?
The concentration of substances will eventually outweigh the number of available protein carriers/ channels
Water potential by change in length or mass core practical
cut 15 cylinders of vegetables without skin and record each of their masses
prepare distilled water and gradually increasing concentrations of solution in test tubes. Place 3 cylinders into each tube
leave for 45 minutes. Take them out, blot them and re-weigh
?????
Incipient plasmolysis core practical?
set up 5 petri dishes, one with distilled water and rhe rest with increasingly concentrated sodium chloride
carefully peel off a layer of onion mesophyll. Place each into the distilled water and then into each of the petri dishes.
leave at room temp for 30 mins. Place each on a microscope slide and cut to 0.5 × 0.5cm. Add two drops of bathing solution and palce a cover slip
x400, count number of cells in each that are turgid and plasmolysed
make table and graph and find which conc. would allow for 50% plasmolysed
use the table from the previous experiment to find the solute potential of solution= solute potential of cell
Permeability of cell membrane with beetroot cells core practical?
Cut 5 1 cm length of beetroot from provided cylinders
Place a test tube with 5cm³ of distilled water into each water bath (15, 35, 45, 55, 65) and let equilibrate for 5 mins
place a beetroot into each and leave for 30 mins
shake each tube gently. Set a colorimeter to 530nm wavelenght or blue/green filter. Test it with distilled water then measure each coloured beetroot water and record results.
Rate of intake/ oxygen concentration graph
rate is proportional to oxygen concenration in diffusion
How is pressure potential built up in turgic cells?
water passes in by osmosis and CYTOPLASM expands. Cell becomes turgid as cytoplasm/ cell contents push against cell wall.
The wall is INELASTIC and resists further expansion
Effect on seedlings if their cells are plasmolysed?
-they will wilt