Fire Ecology Exam 4
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
Fire may regulate many ____ of the earth’s system
Aspects
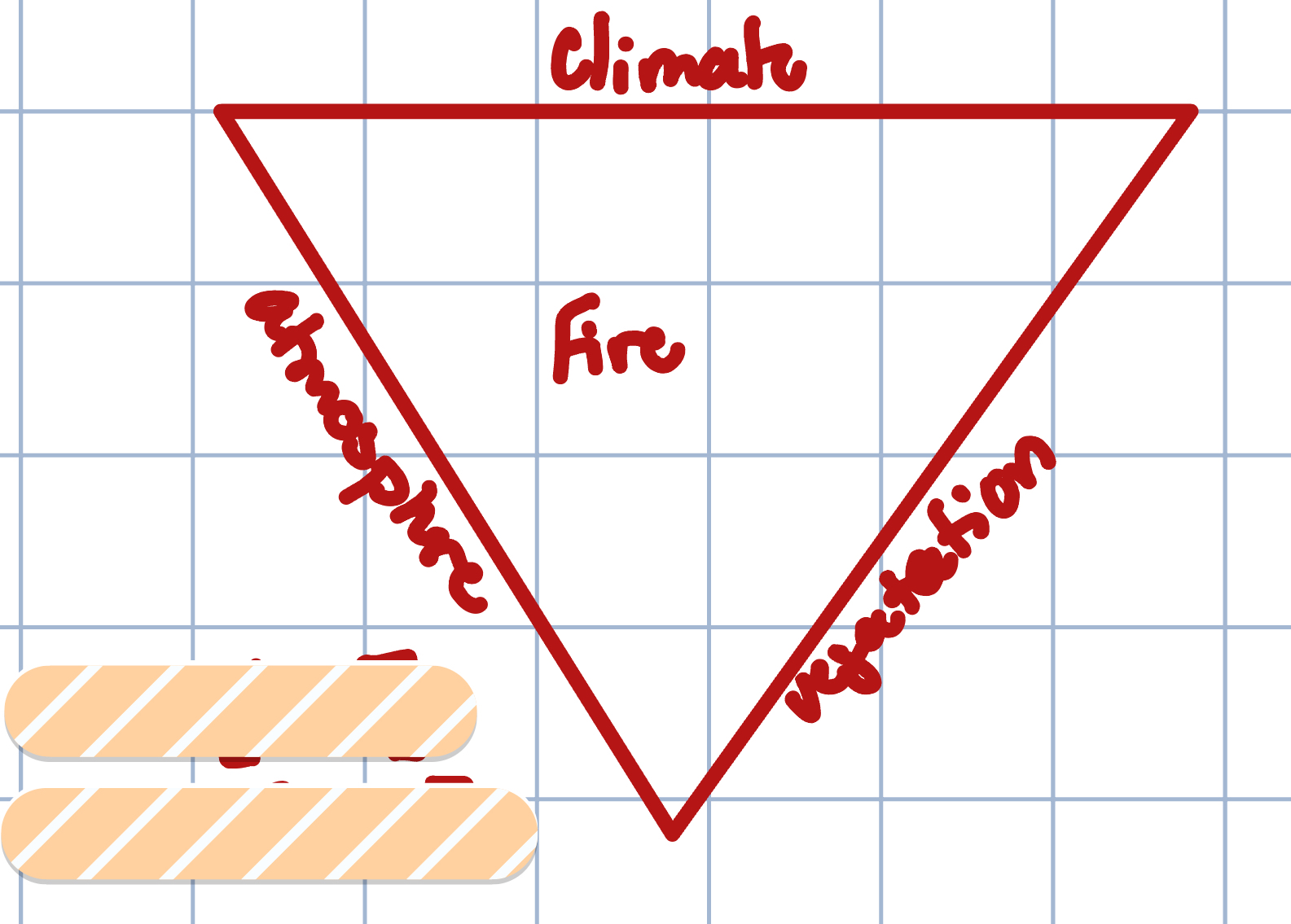
What do the three sides of the Paleofire Triangle consist of?
Climate, vegetation, atmosphere
What is the concentration of O2 in the atmosphere?
21 %
What is the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere?
0.04%
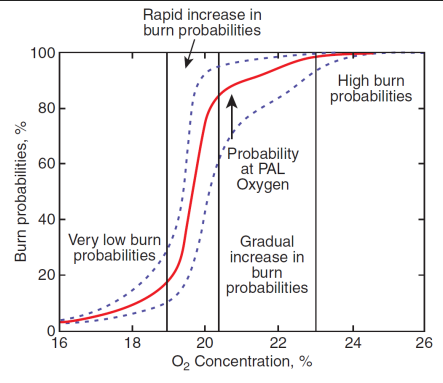
What is Fig 3.3 representing?
Burn probabilities are a function of atmospheric [O2]
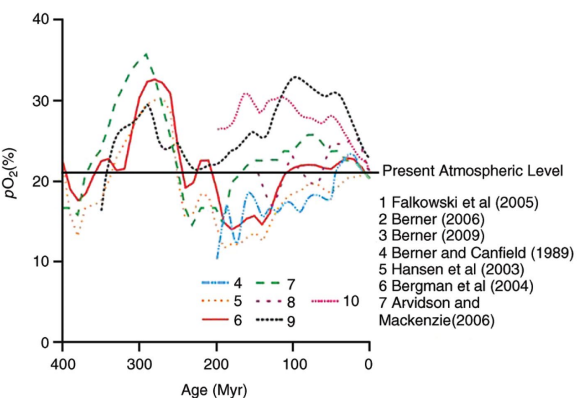
What is Fig 3.2 representing?
atmosphere [O2] over the past 400 M years
The late Paleozoic Era (300- 250 million years) was a period of what?
high [O2]
Coal of the late Paleozoic often contained up to _____ % charcoal
70
Finding charcoal in coal was a Palaeoecological indicator of ______?
[O2]
if [O2] < 15 % then
No charcoal should be present in coal
At present levels of O2 at 21%, how much charcoal should be in peat averages?
4 %
At what percentage max of [O2] can land plants exist at?
30-35%
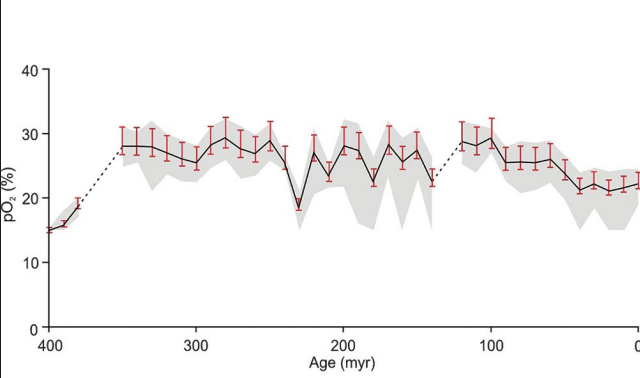
What is Fig 3.7 representing?
[O2] through time using charcoal approximants
During the Oxygen-Controlled World, what type of Fire feedback loops were present?
Positive, negative
Provide an example of a positive fire feedback loop

Provide an example of a negative fire feedback loop

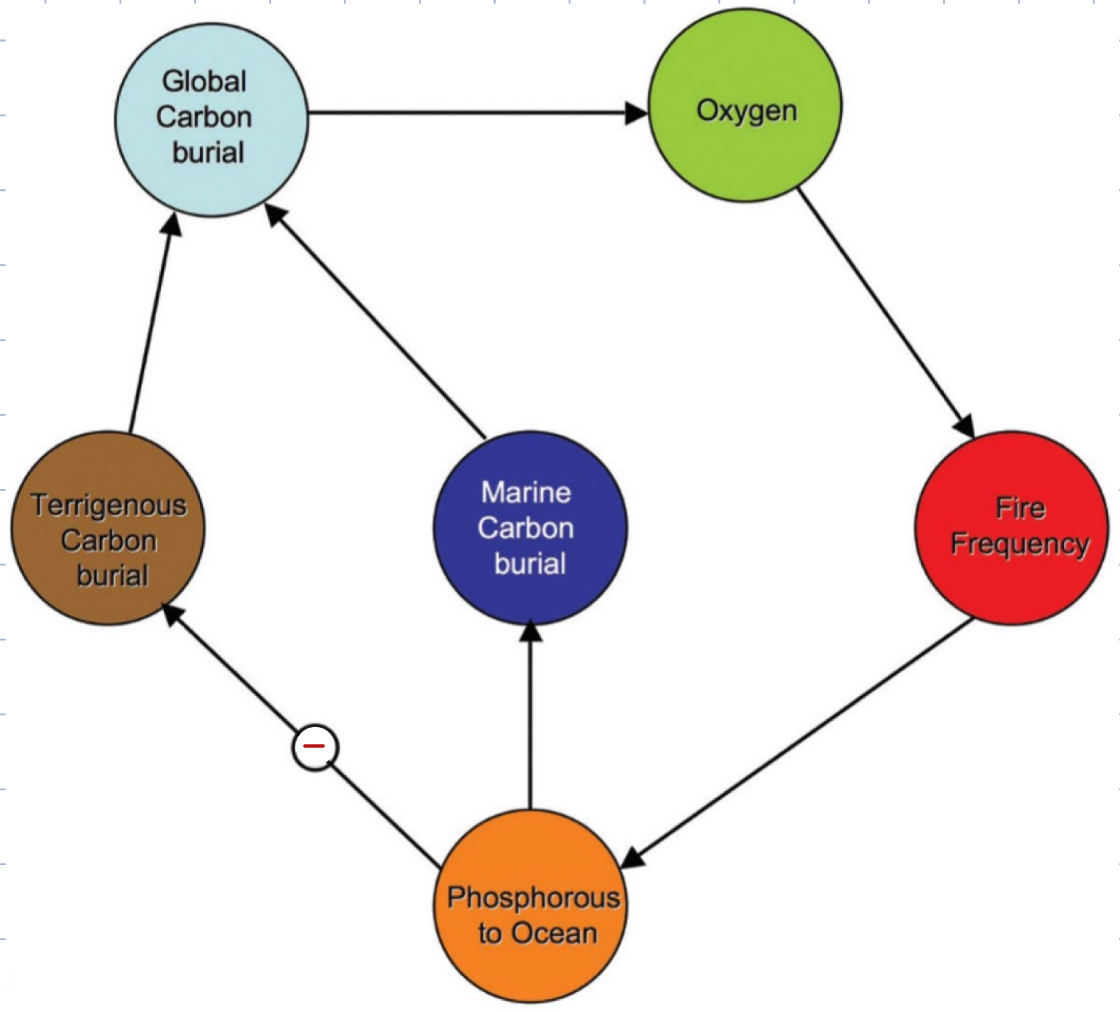
This diagram is an example of?
Fire through the production of ash is releasing P
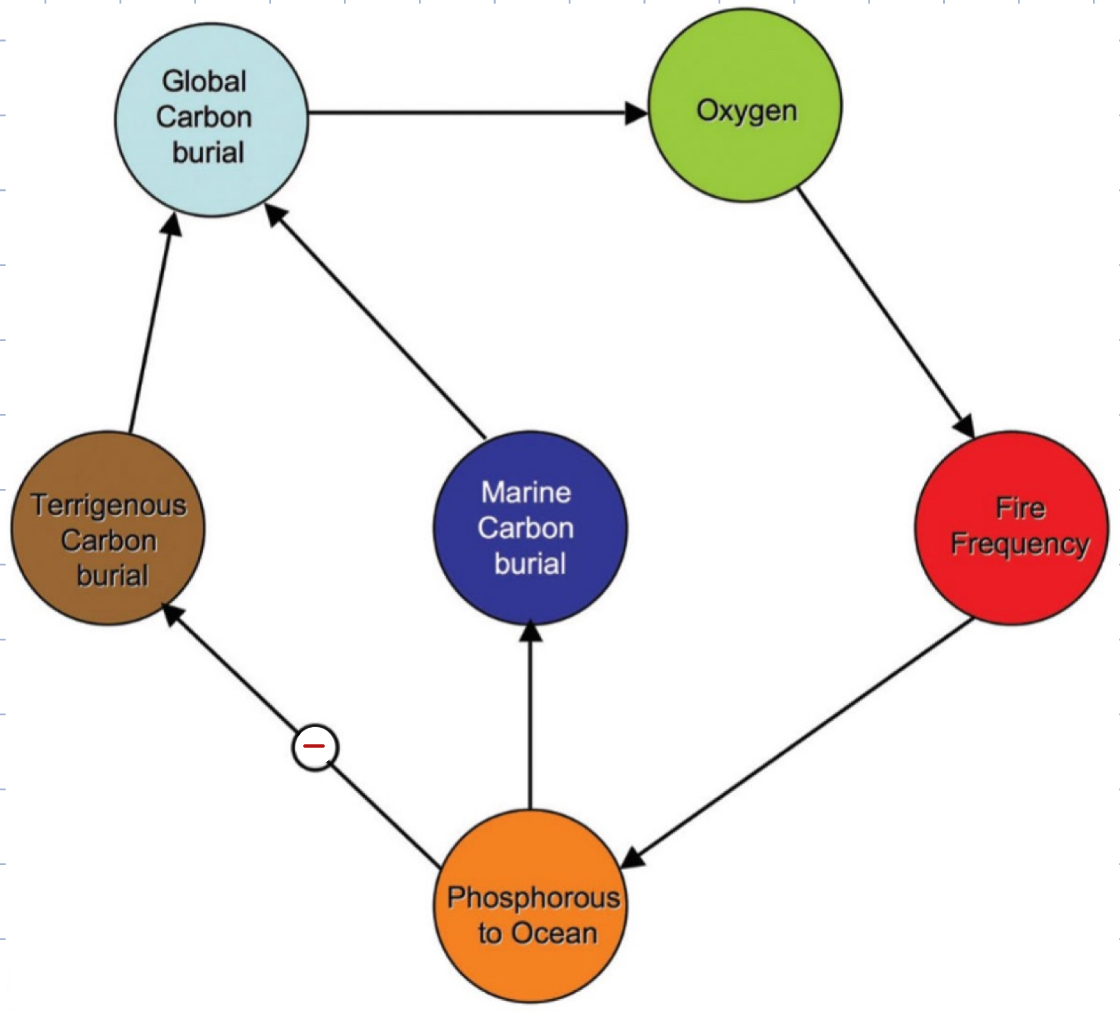
Why is the relationship from “Phosphorous in the ocean” → “Terrigenous Carbon Burial” negative?
because by sending phosphorous to the ocean it limits phosphorous for the land
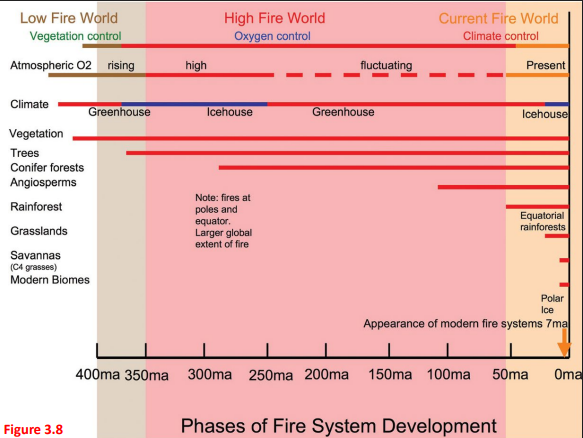
What does this diagram represent?
Evolution of plants and fire systems in relation to climate and O2
Between 480-420 mya what started to appear?
Non-vascular plants in damp habitats
What does non-vascular plants indicate?
No stems or tubes to transport water
During 480-420, with the appearance of non-vascular plants, how did it affect O2
increase vegetation with no fire= increase in O2
What did the years 420-360 mya indicate?
Diversification of land plants (fire not widespread; rare)
During the years 420-360 what were the first plants to have vasculature?
Lycopsids
Lycopsids with their vasculature indicated what type of environment?
Wet environments
During the years 420-360, ferns adapted to have what?
Spores
During the years 420-360, Gymnosperms adapted to have what?
seeds
Gymnosperms with their seeds indicated what type of environment?
Dry environment
360-300 mya indicated what period?
Carboniferous
In the Carboniferous period, what did we find first evidence of?
Coal deposits
What were coal deposits used for
Industrialization
in the Carboniferous period, land plants were _______?
widespread
In the Carboniferous period, O2 concentrations were (high or low)?
High
During the Carboniferous period, fires started to become ______
widespread
300-250 mya indicates what period?
Permian Period
During the Permian period fires were ______
widespread
During the Permian period [O2] were (high or low)
high
250 mya was known as the
Permian-Triassic Boundary
During the Permian-Triassic Boundary what happened to fire?
collapse of fire systems
How did Fire Systems collapse during the Permian-Triassic Boundary?
90% of species went extinct
Pangea formed
glaciers receded
volcanoes lead to increased CO2 and SO2
How many degrees of C increased when the volcanoes lead to an increase of CO2
8 degrees of C
Increased SO2 lead to
acid rain
During the Permian-Triassic Boundary, what percentage does O2 drop to?
15 %
Provide one reason why O2 dropped so low during the Permian-Triassic Boundary?
Lava may have burned huge coal deposits
What is the interaction between, fire, O2, vegetation and acid rain (draw it)?

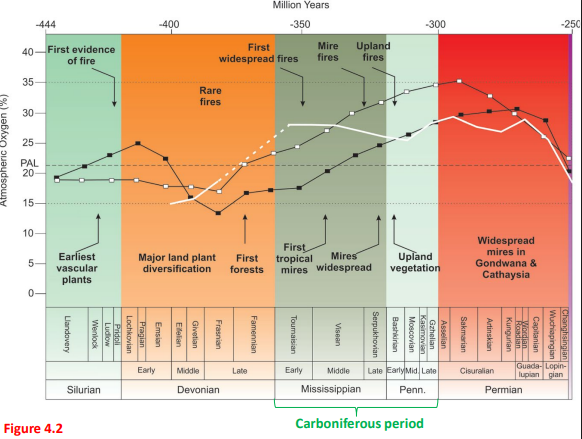
What does Fig. 4.2 represent?
Rise of fire during the Paleozoic
250-55 mya was known as the
Oxygen- Controlled World
What type of feedbacks did the Oxygen-Controlled World have?
Positive and Negative Feedbacks
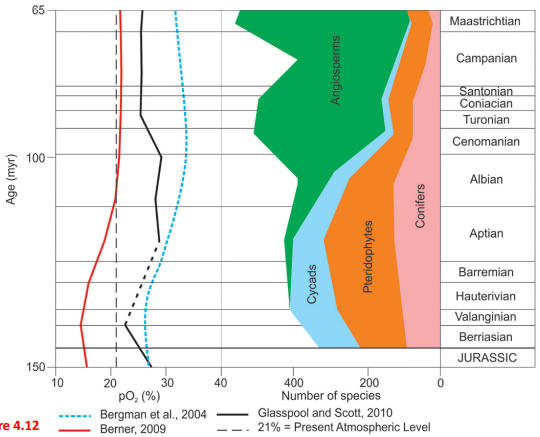
What can we gather from Fig 4.12?
O2 stabilizes at ~21% by 55 mya → O2 no longer the dominant control on fire
55 mya-Present is known as the
Climate Control of Global Fire
During the Climate Control of Global Fire what do we know about O2
it is stable at 21%
During the Climate Control of Global Fire what do we know about [CO2]
period of low [CO2]
From 55 mya to 7 mya what was there little of?
Fire
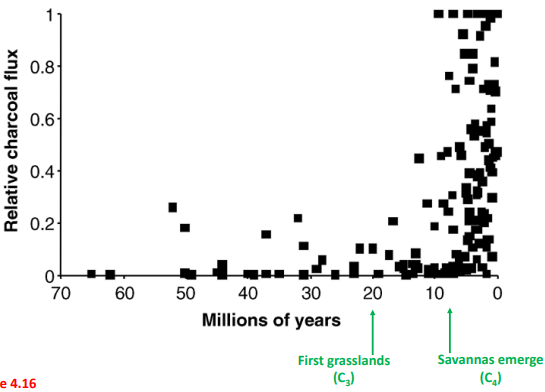
What can we infer happened around 7 mya Fig 4.16?
flammable savannas of C4 grasses spread
The spread of savannas continued through what period in time?
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene was between what years
2.6 mya-12 kya)
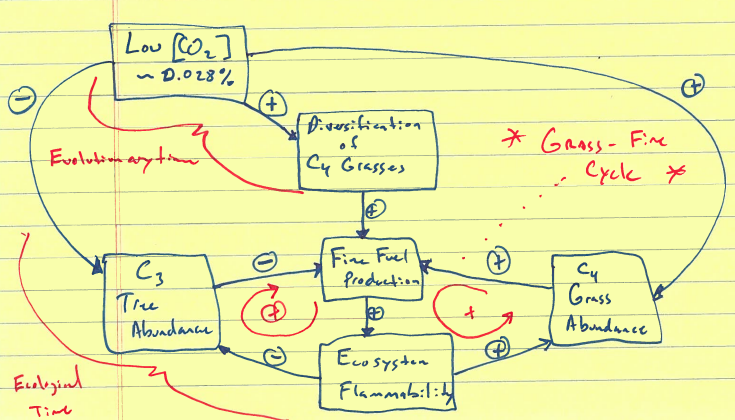
What does the Grass-Fire Cycle include
C4 grass abundance, Fire Fuel Production, Ecosystem Flammability
What does the Grass-Fire Cycle look like (draw it)?
Holocene Epoch in years
12 kya to present
What is the Holocene Epoch known for?
Most recent/current interglacial period
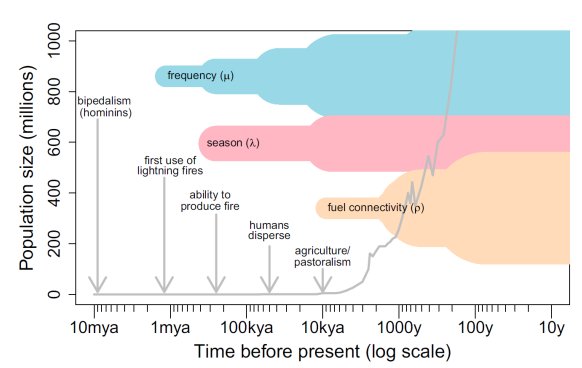
What does Fig 5.1 represent?
Fire and Human Activities
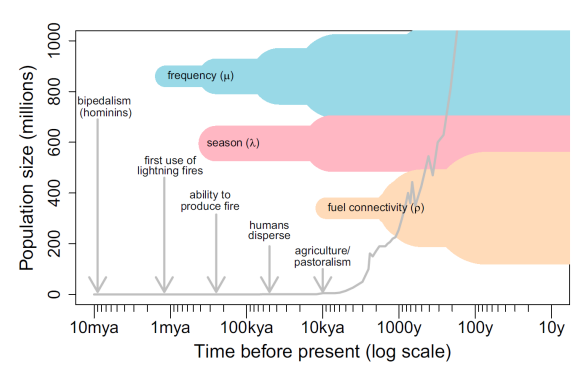
What do the thin portions and thick portions of this graph represent?
Thin portions: not much human influence
Thick portions: a lot of human influence
In places with no/few natural fires humans introduced fire as a part of what?
Agricultural activities
Where fire already existed what did humans change?
Extent, timing and frequency of fire
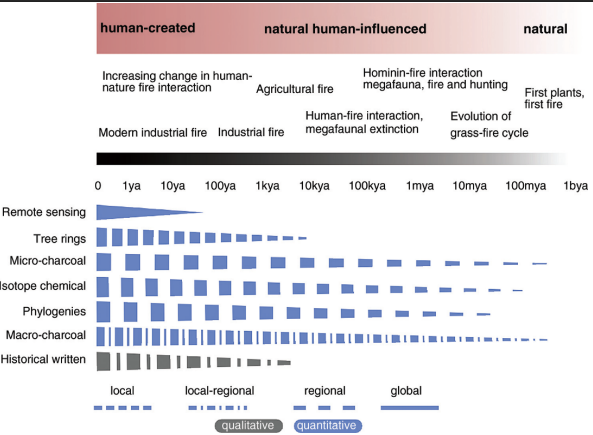
What does Fig 5.2 represent?
Evolution of fire and humans
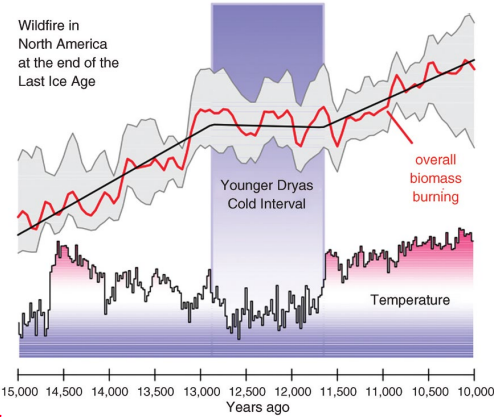
What does Fig 5.7 represent; be specific to area and year?
Temperature and Fire relationship in North America from 15-10 kya
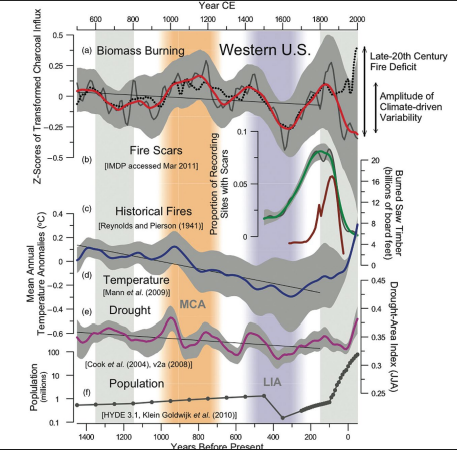
What does Fig 5.8 represent?
Population and Fire relationship
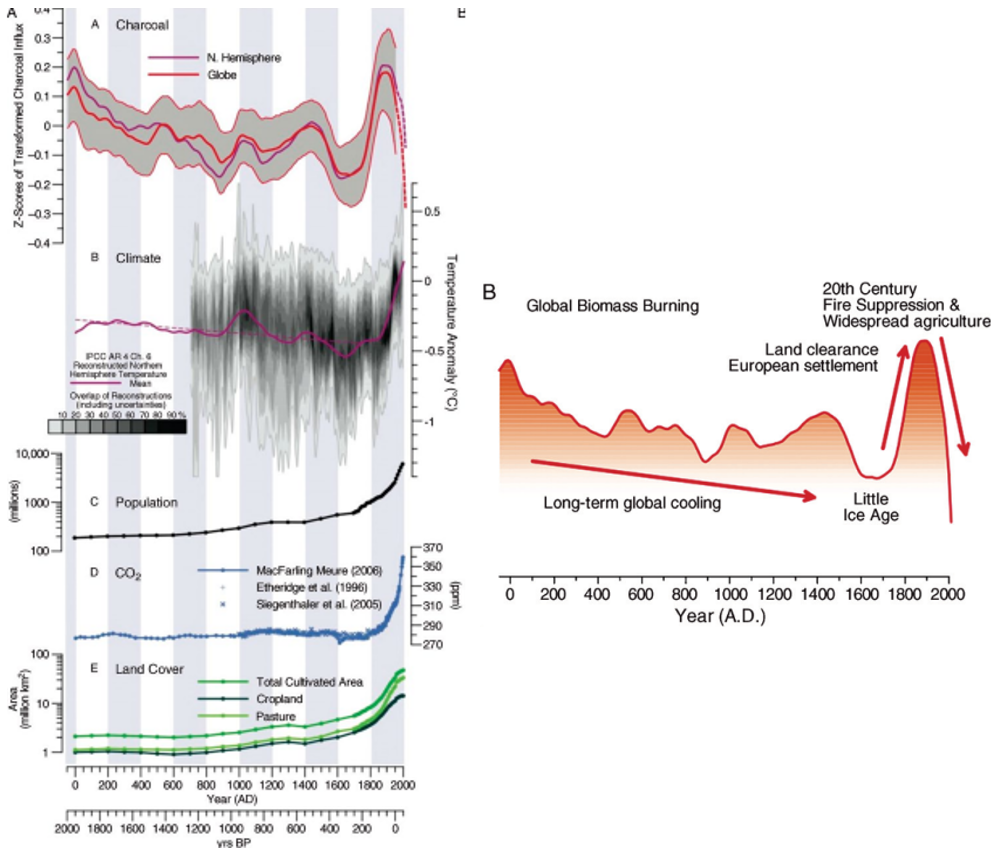
What can we indicate about the future of fire from Fig 5.9?
Agriculture has stopped fires where they use to ancestrally burn because fuels that had burned were removed
Define pyrogeography
Spatial & temporal patterns of fire
What does pyrogeography scale from?
Local to landscapes to regions to global
What is Extension of Biogeography the study of
spatial & temporal variation of life on earth
Define Classical Biogeography
Climate determines the distribution of Earth’s Biomes
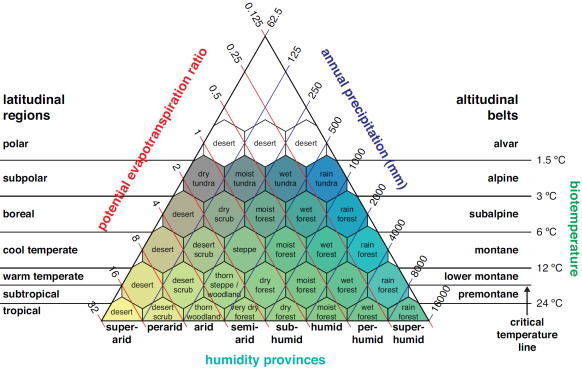
What does Fig. 6.2 represent?
Holdridge Life Zones
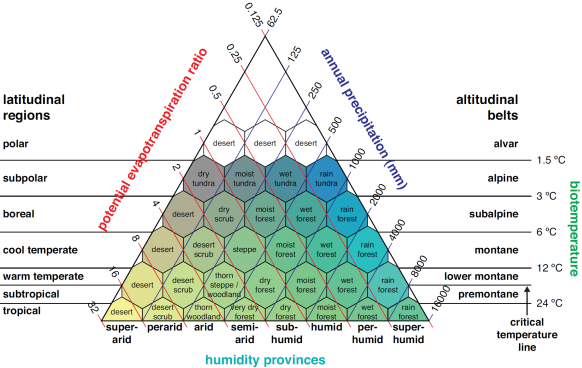
What can we take note of in the Holdridge Life Zones
Has no fire and no savannas
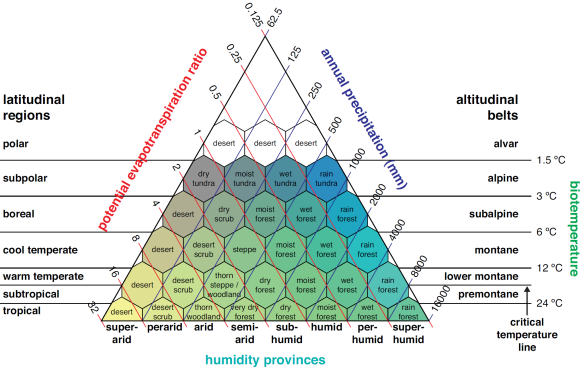
What is an emerging view that can be represented by Fig. 6.2?
Climate, vegetation, and fire interact to determine distributions of biomes (globally) and ecosystems (locally)
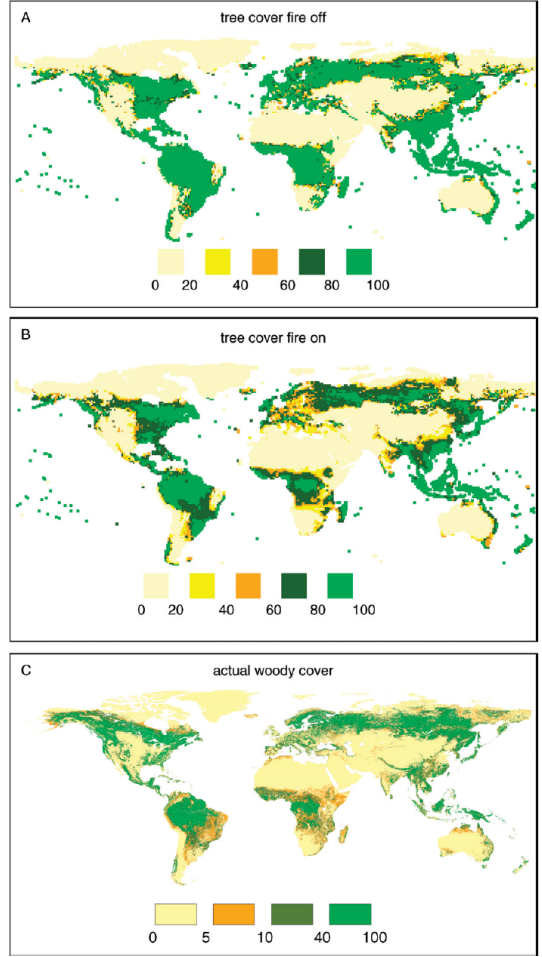
What does Fig 6.4, going from A→B→C→ indicate?
world without fire
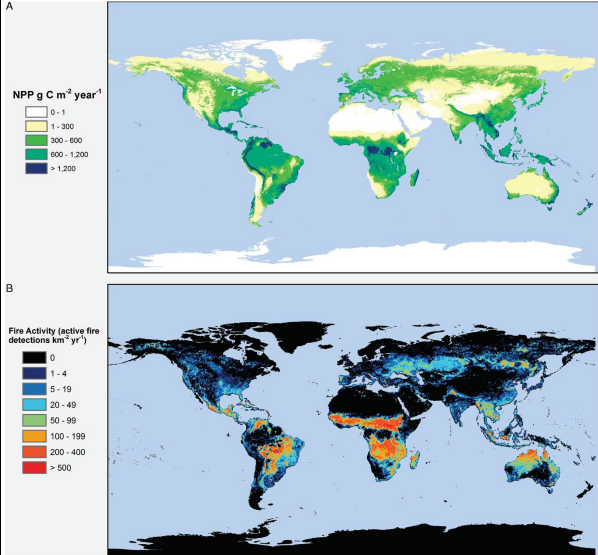
What does Fig 6.5 represent?
Fire at intermediate productivity
How can NPP (Net Primary Productivity) be related to fire?
NPP indicates the potential for an ecosystem to accumulate biomass aka fuel for fire
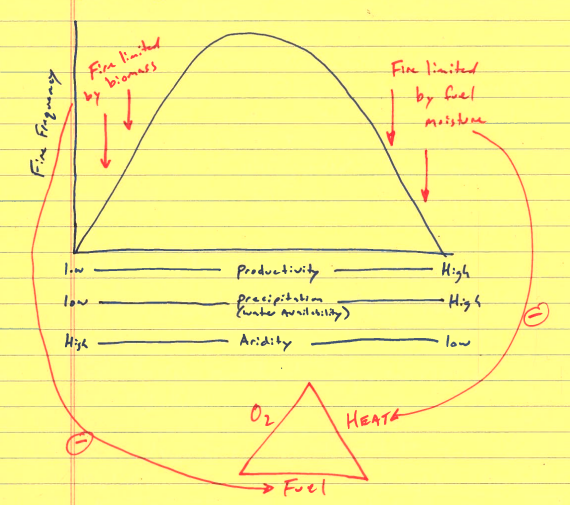
What should I understand from Fig 6.6?
How the amount of water, type of fuel, and location affects fire frequency
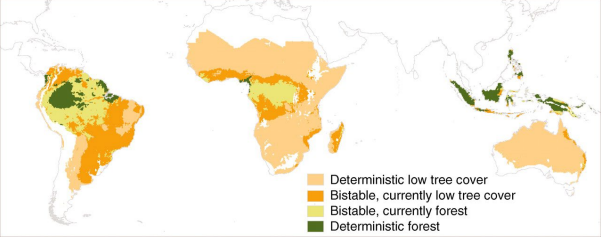
What does Fig 6.3 represent?
Alternative Biome States
Define deterministic
Climate dictates biome (High or low precipitation)
Define Bistable
Fire dictates the biome (occurring at intermediate precipitation)
What is considered an intermediate precipitation biome
Tropics
How much precipitation is in the Tropics
~500 to 2500 mm annual rainfall
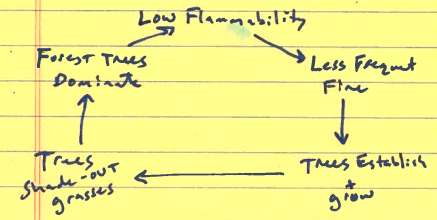
What does this drawing represent?
Fire Vegetation Feedback: Forest stabilizing
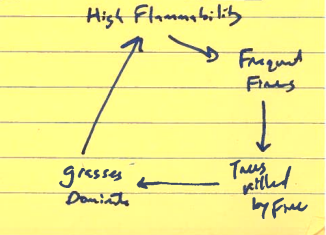
What does this drawing represent?
Fire Vegetation Feedback: Savanna Stabilizing Feedbacks
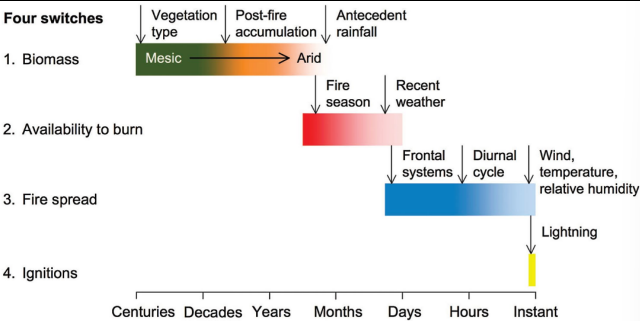
What does Fig 6.7 represent?
Four switch model of fire activity
What is Xylem?
tissue that carries water through a vascular plant from roots to leaves
What is phloem?
Tissue that transports sugars between leaves and roots
What is meristem?
Undifferentiated cells in areas of plant growth
What is vascular cambium?
Large tubular meristem, just below the stem surface that produces secondary growth (wood and bark)
What is secondary growth?
Process of increasing in girth through production of wood (secondary xylem) and bark (secondary phloem)
What are buds?
Embryonic shoots (often protected by modified leaves, bark or underground)
What do Dicots and Conifers produce?
Secondary growth i.e. “woody” species, trees and shrubs
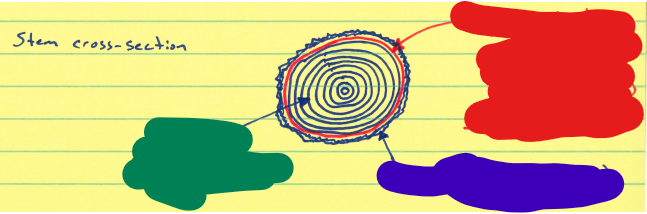
What is indicated by the red area of this stem cross-section?
Vascular Cambium
What does vascular cambium produce in a stem cross section?
Xylem (wood) on the inside and phloem (bark) on the outside