Production Possibilities Curve
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
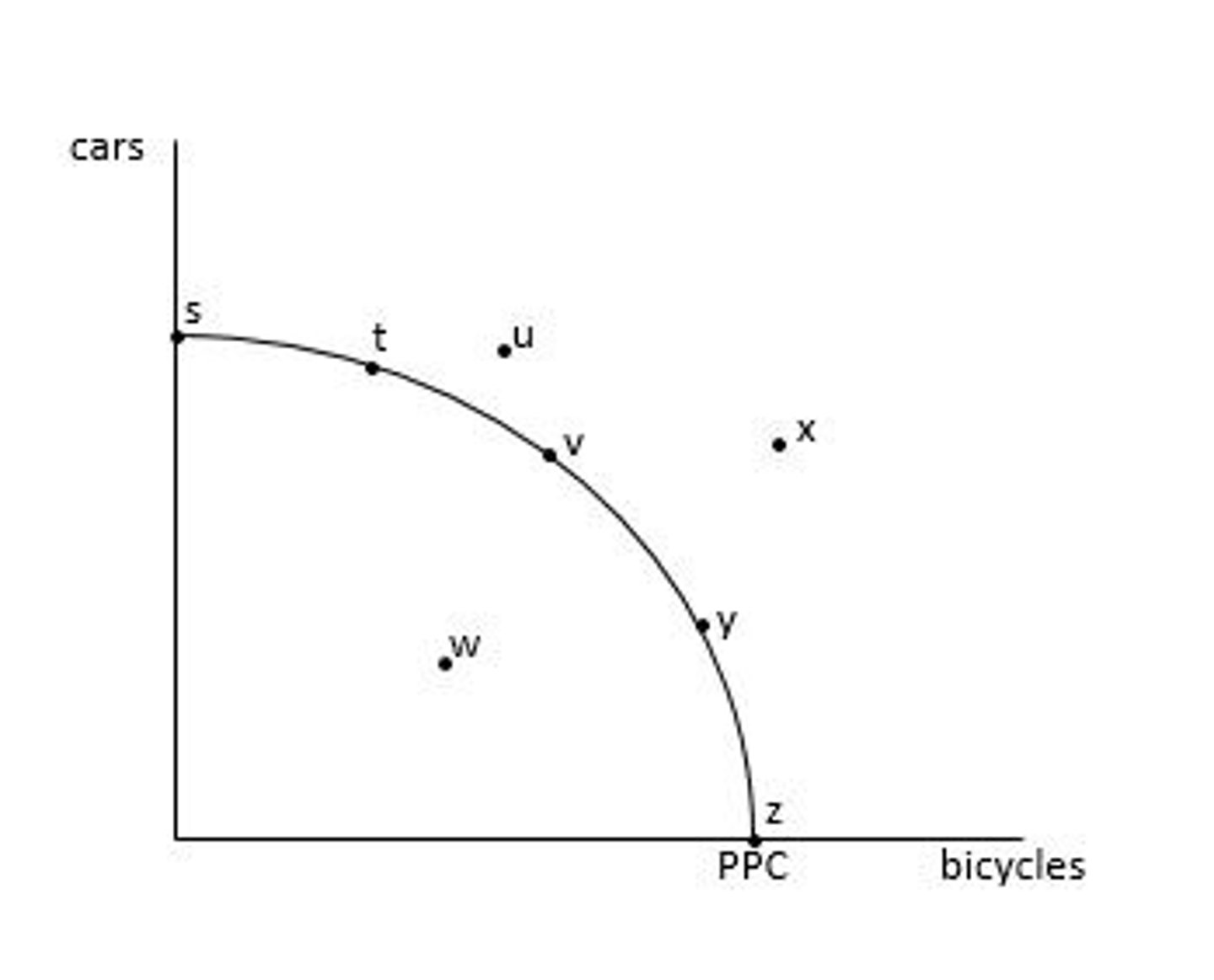
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
Graph that shows all possible combinations of two goods/services that an economy, firm, or individual can produce given a set amount of factors of production and technology.
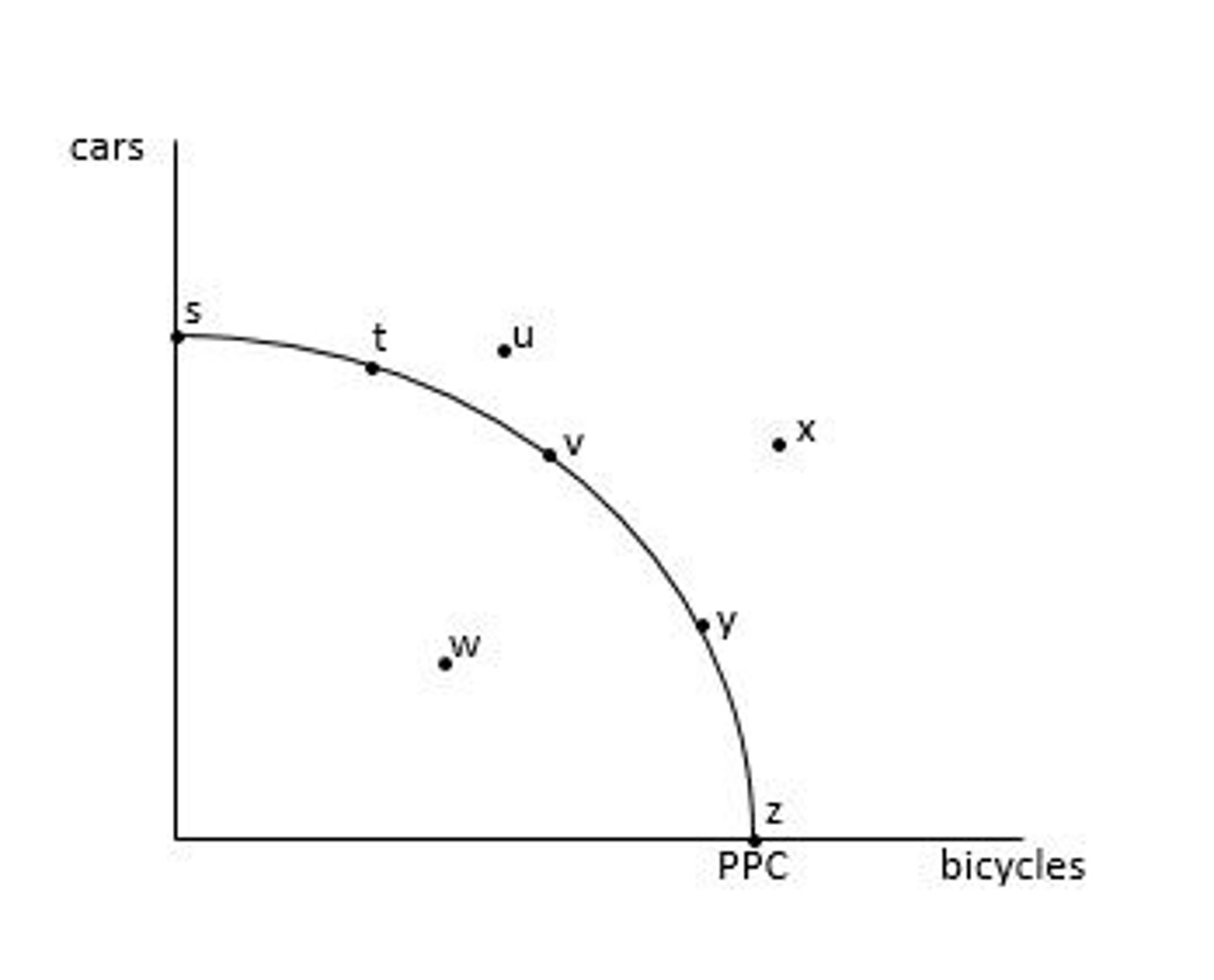
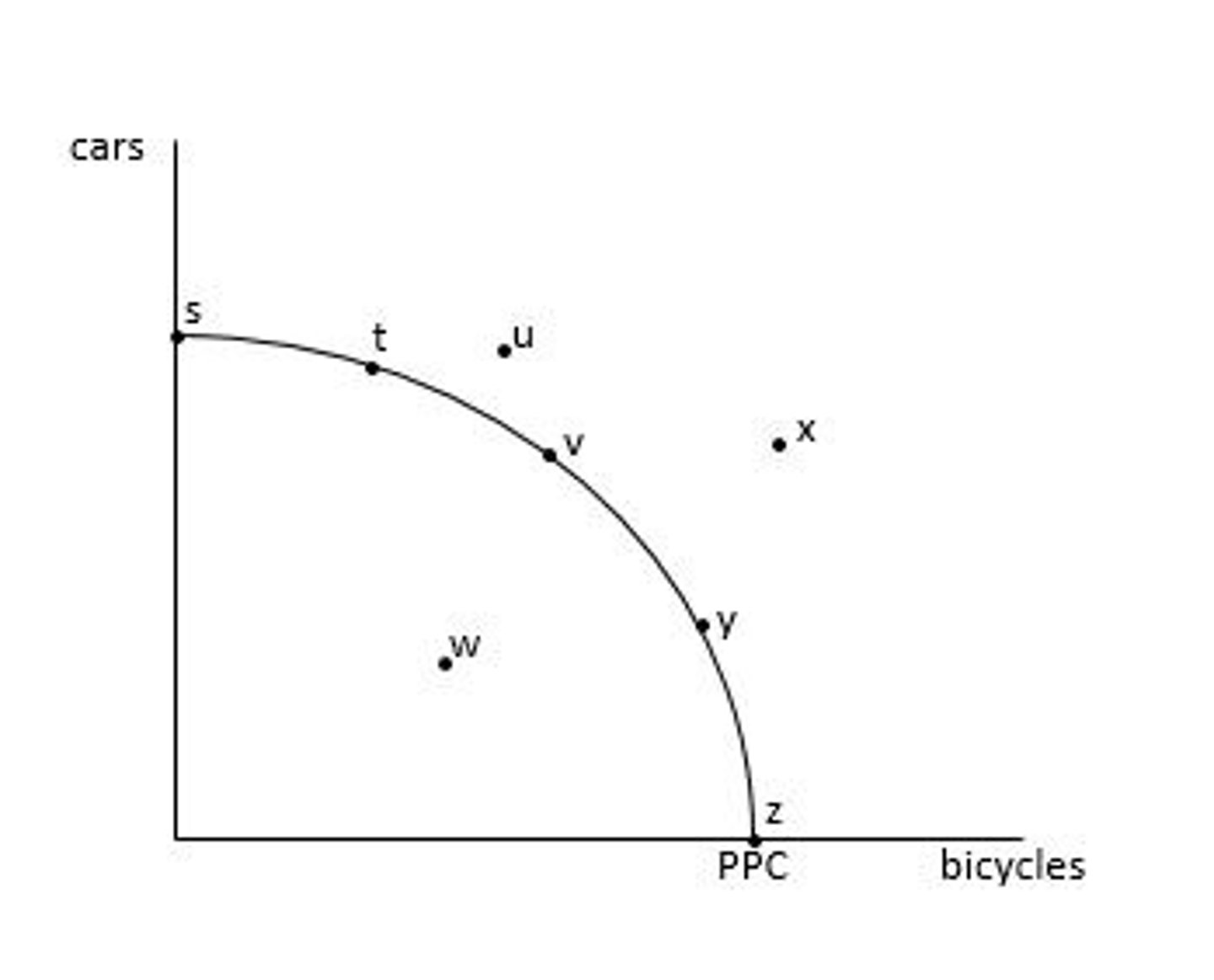
Attainable points: s, t, v, y, z, w
Attainable points = points on or inside the PPC
Attainable combinations are combinations of goods and services that the economy has enough resources to produce
What are the attainable points?
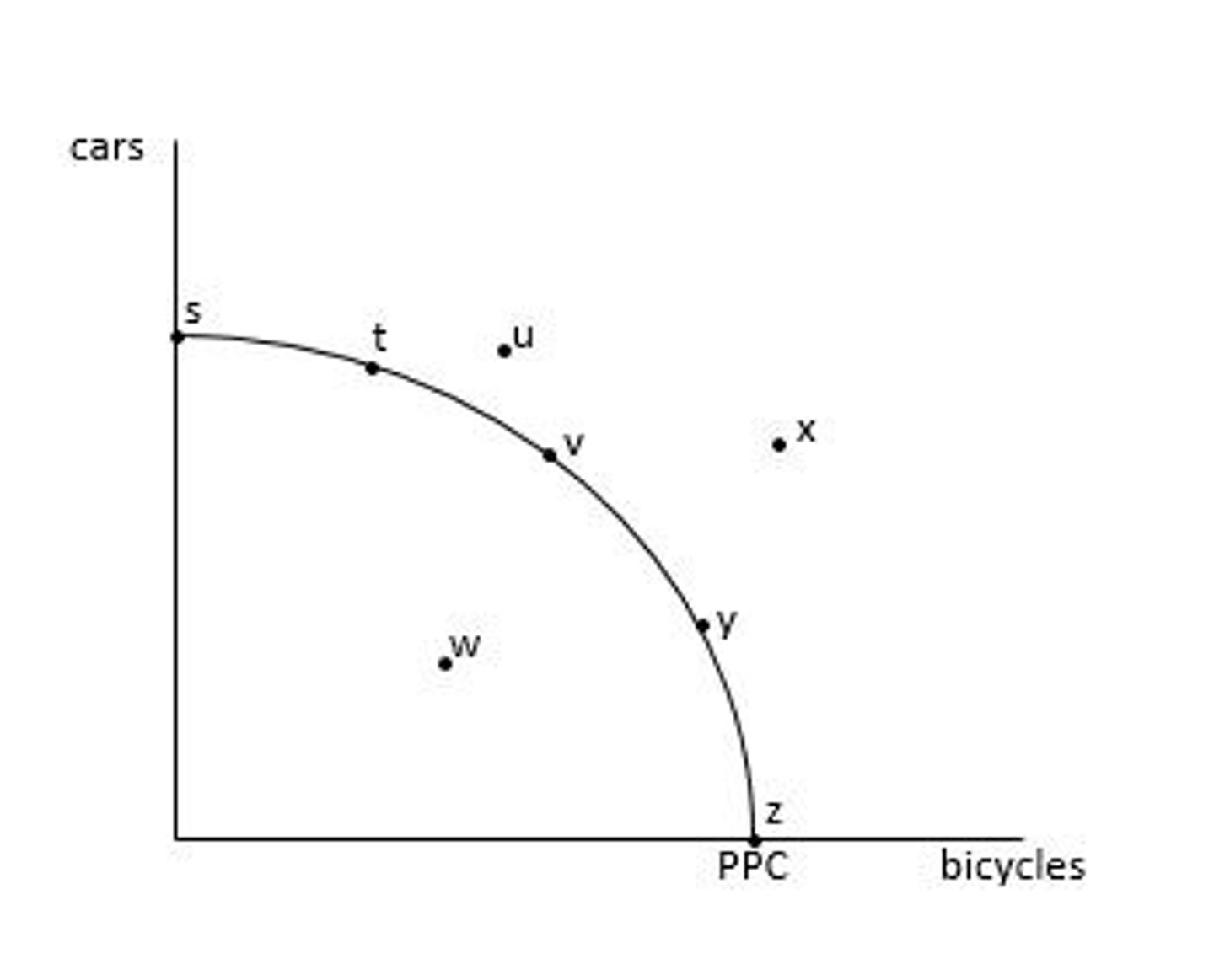
Unattainable points: u and x
Unattainable points = points outside the PPC
Unattainable combinations are the combinations of goods and services that the economy does NOT have enough resources to produce.
What are the unattainable points?
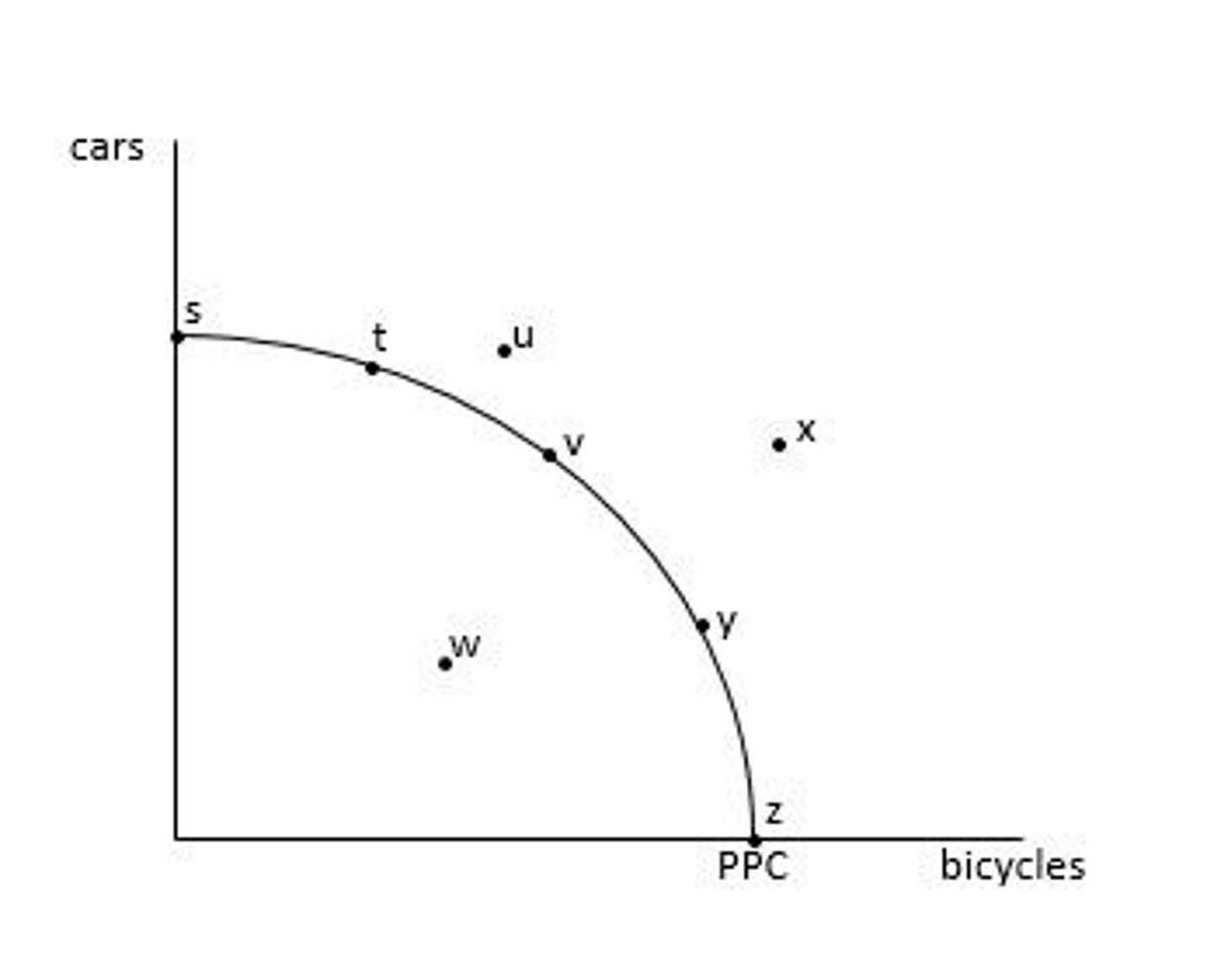
Productively efficient points: s, t, v, y, z
Any point on the PPC is productively efficient.
Productive efficiency is the amount of output an economy can produce when it is using the right amount of its factors of production. It is also known as "full employment" of the factors of production.
What points are productively efficient?
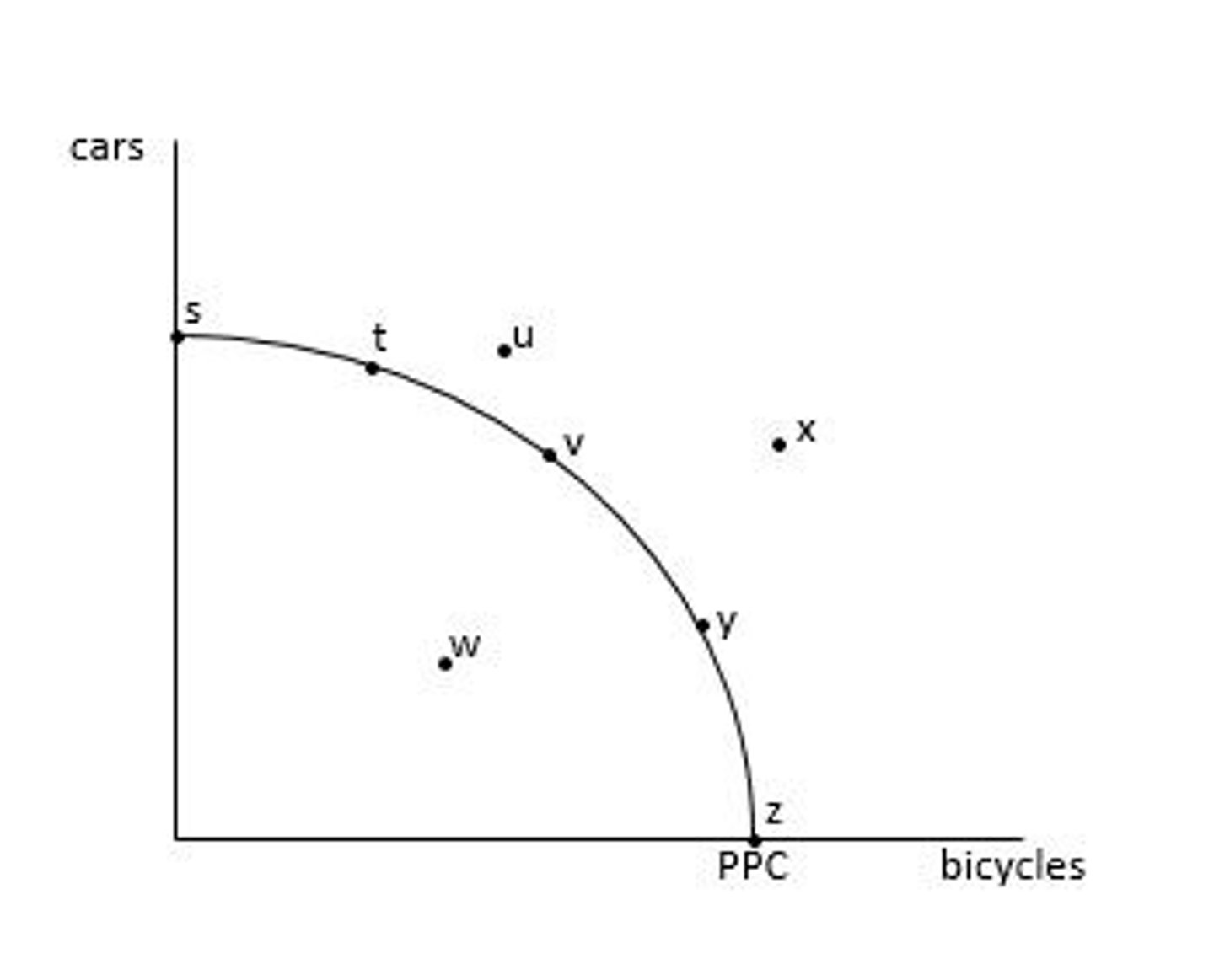
Productively inefficient points: w, u, x
Any point inside or outside the PPC is productively INefficient
Productive efficiency is the amount of output an economy can produce when it is using the right amount of ts factors of production. Thus, an economy is productively inefficient, when it is under utilizing its factors of production (points inside the PPC) or over utilizing its factors of production (points outside the PPC)
Note: multiple points can be productively efficient
What points are productively inefficient?
Indeterminate (i.e. it is impossible to tell which point is allocatively efficient without more information)
Allocatively efficiency is achieved when the the combination of goods and services being produced is the combination that society most desires.
Note: only 1 point can be allocatively efficient
What points are allocatively efficient?
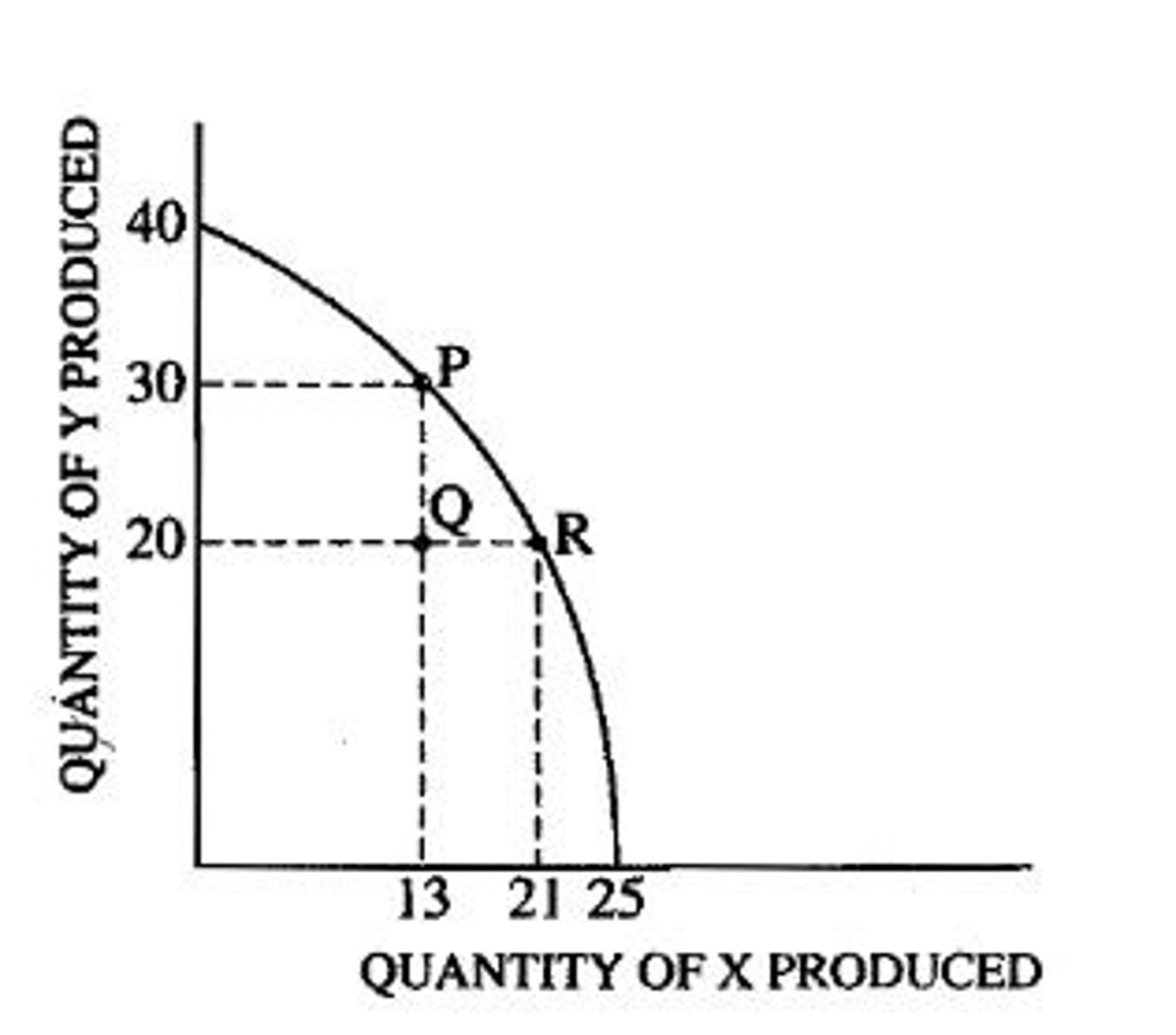
Moving from point P to point R, the economy gives up the production of 10 units of Y.
Economy was producing 30 units of Y at point P and at point R it is only producing 20.
What is the opportunity cost of moving from point P to point R?
Increasing opportunity costs
Any PPC that is bowed out from the origin exhibits increasing opportunity costs.
What type of opportunity costs does the PPC exhibit?
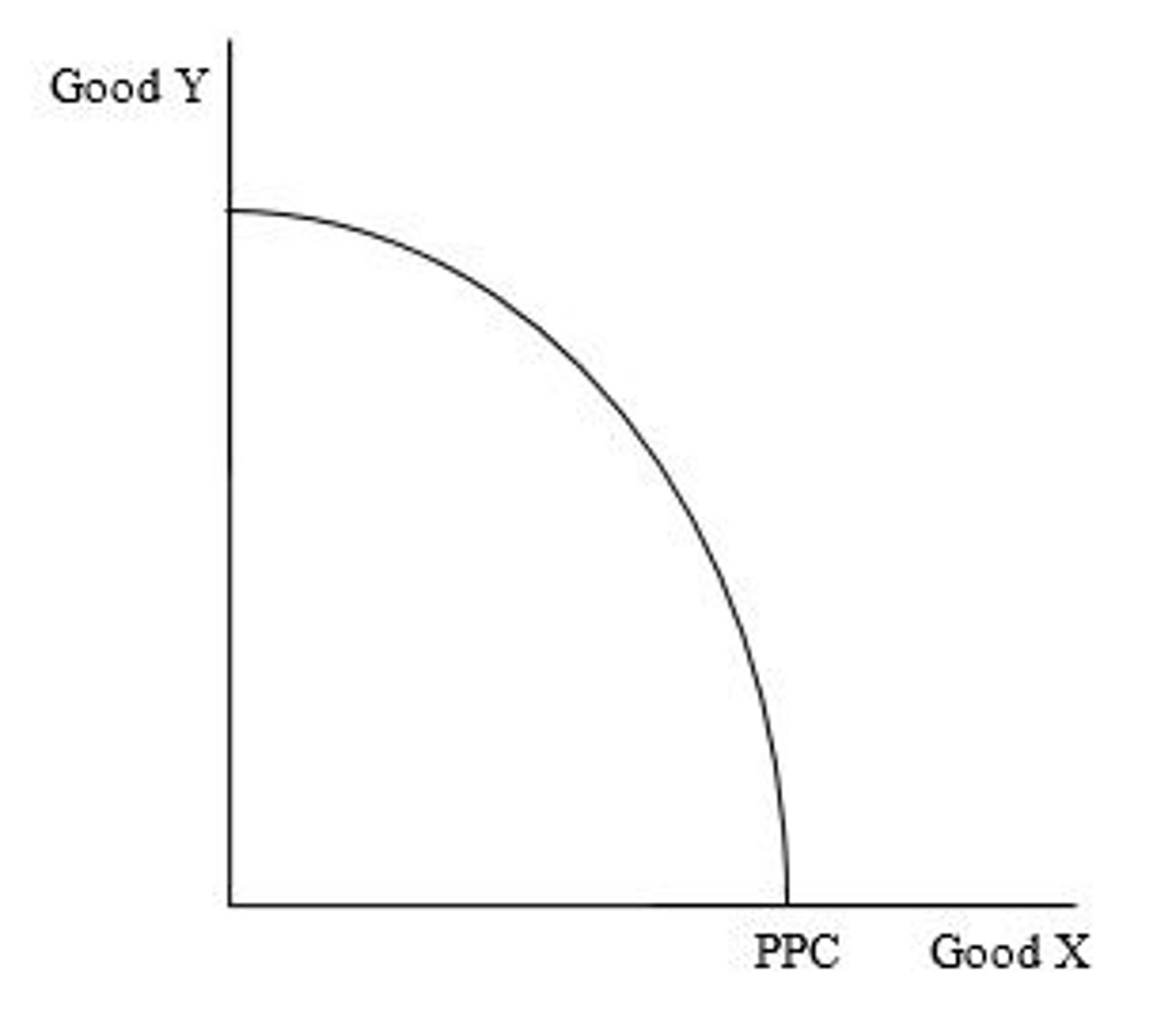
Increasing opportunity costs
The type of opportunity costs that exists when the opportunity cost of producing additional units of a good rises as more of the good is produced.
Resources are not equally suited to the production of both goods, and as we switch from making all of one of the goods to all of the other goods, the MOST efficient resources are moved first.
What causes increasing opportunity costs?
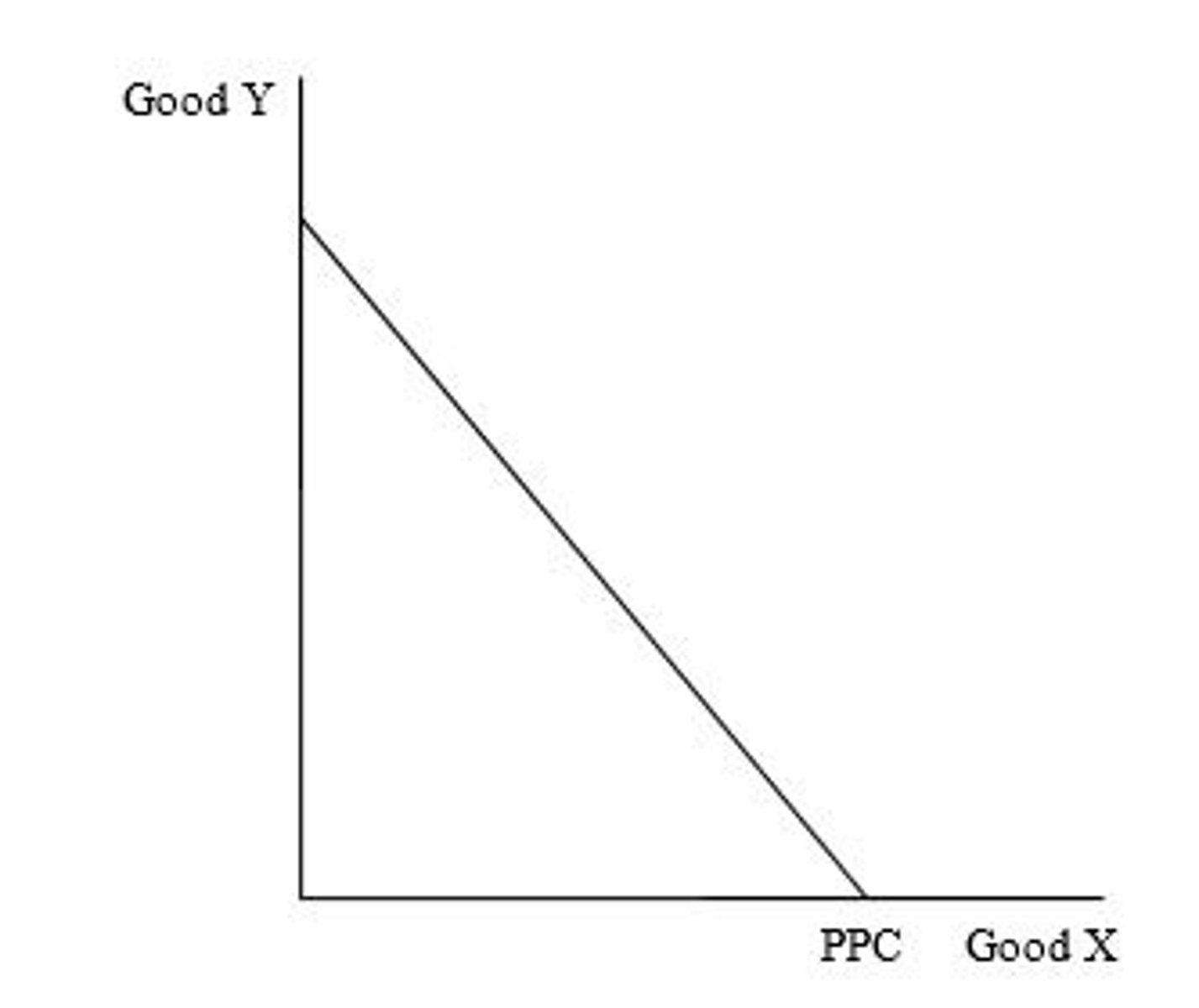
Constant opportunity costs
Any PPC that is a straight line has constant opportunity cost.
What type of opportunity costs does the PPC exhibit?
Decreasing opportunity costs
Any PPC that is bowed in towards the origin has decreasing opportunity cost.
What type of opportunity costs does the PPC exhibit?
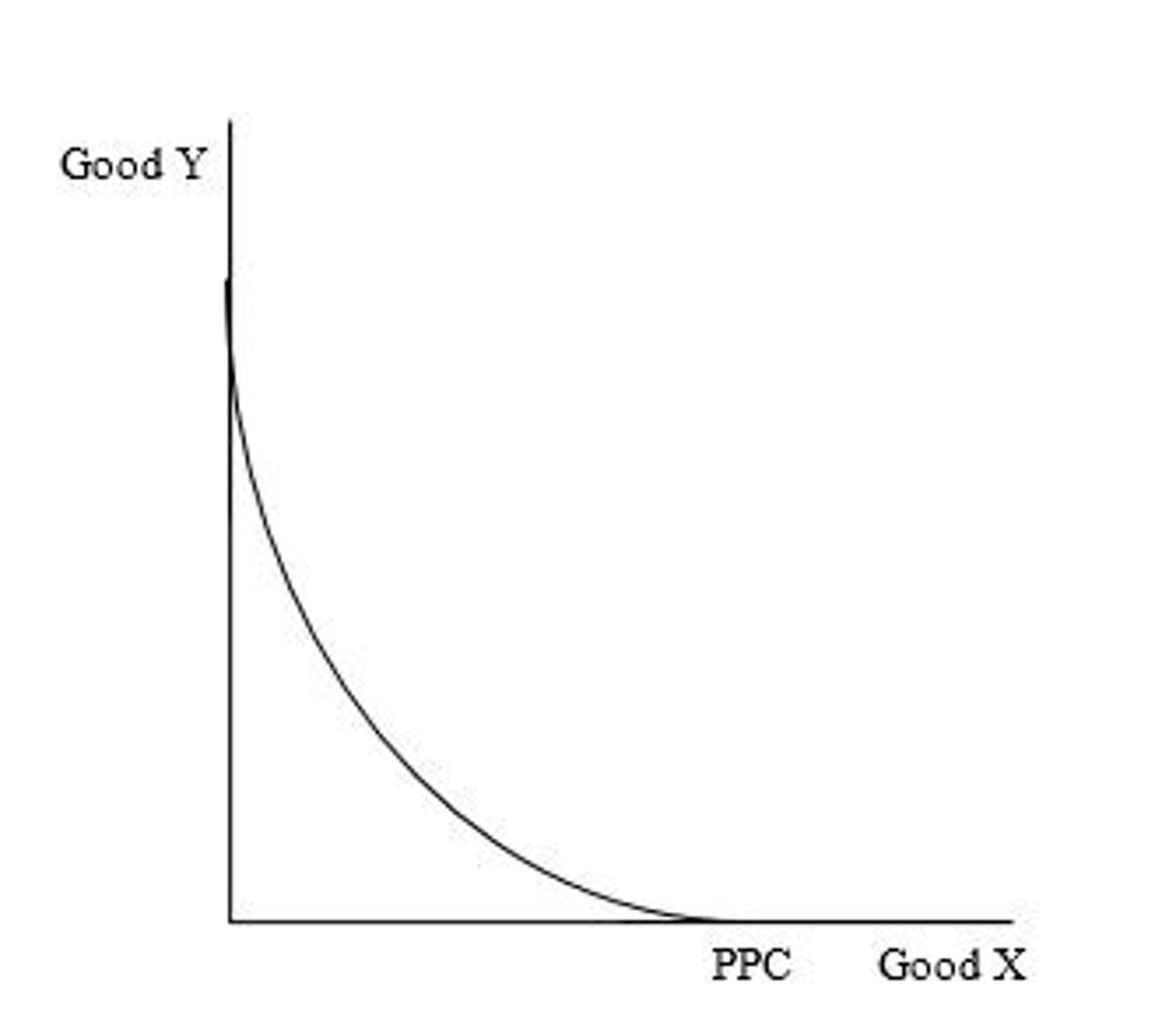
Decreasing opportunity cost
The type of opportunity cost that exists when the opportunity cost of producing additional units of the good decreases as more of the good is produced
Resources are not equally suited to the production processes of both goods, and as switch from making all of one good to all of the other good, the LEAST efficient resources are first moved first.
What causes decreasing opportunity costs?
point s
On an increasing opportunity cost PPC, the point of highest opportunity cost for making a good or service is when the economy is producing ONLY that good or service.
Why: because the inputs that were most efficient for making cars were switched from bicycle production first (i.e. switch involved lowest opportunity cost) and the least efficient resources for making cars were switched last (i.e. switch involved highest opportunity cost)
Point with the highest opportunity cost of producing cars?
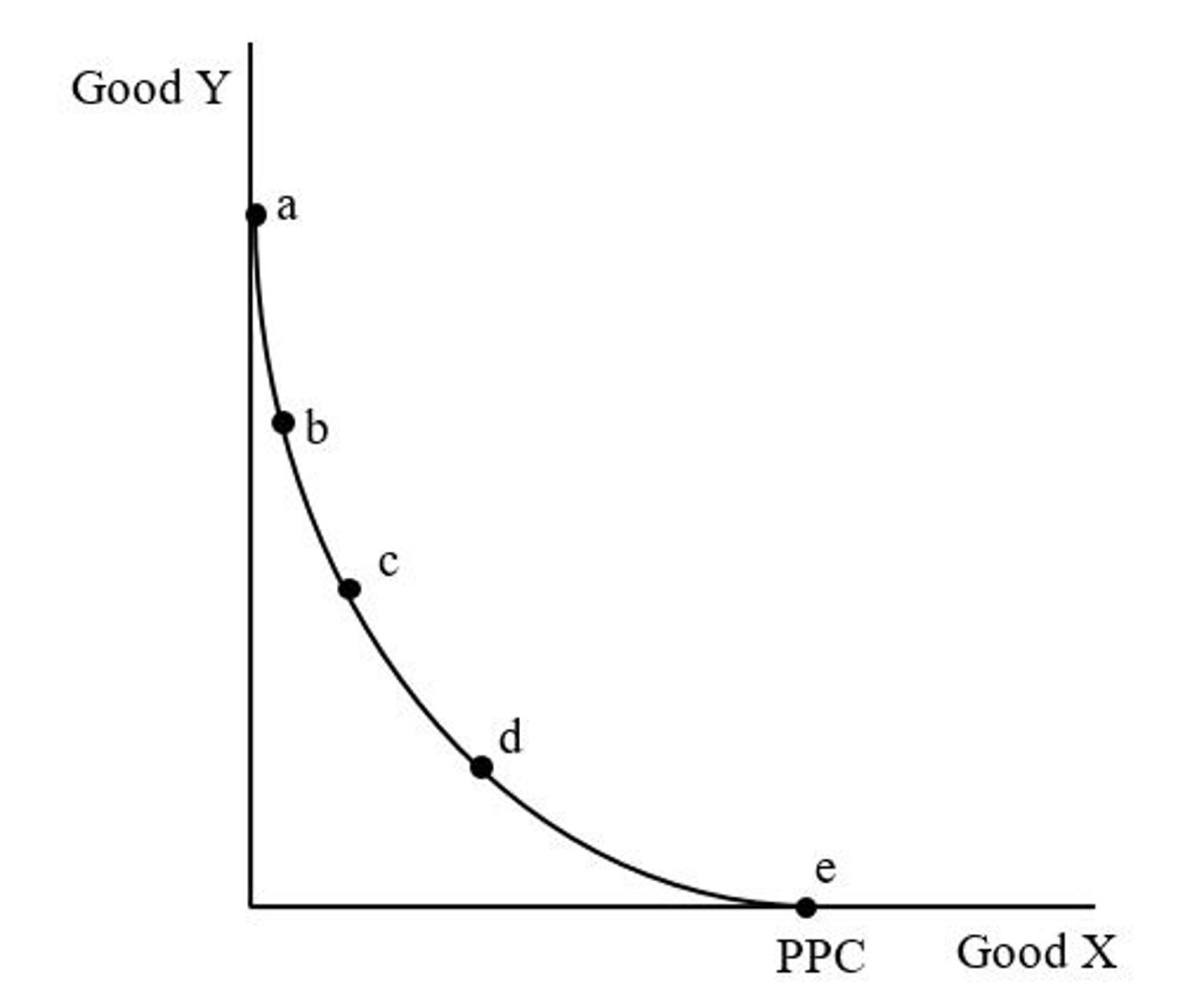
point d
On a decreasing opportunity cost PPC, the point of highest opportunity cost for making a good or service is when the country is producing 1 of that good or service.
Why: because the inputs that were least efficient for making good Y were switched from the production of good X first, this is the switch that would involve the highest opportunity cost.
Point with the highest opportunity cost of producing good Y?
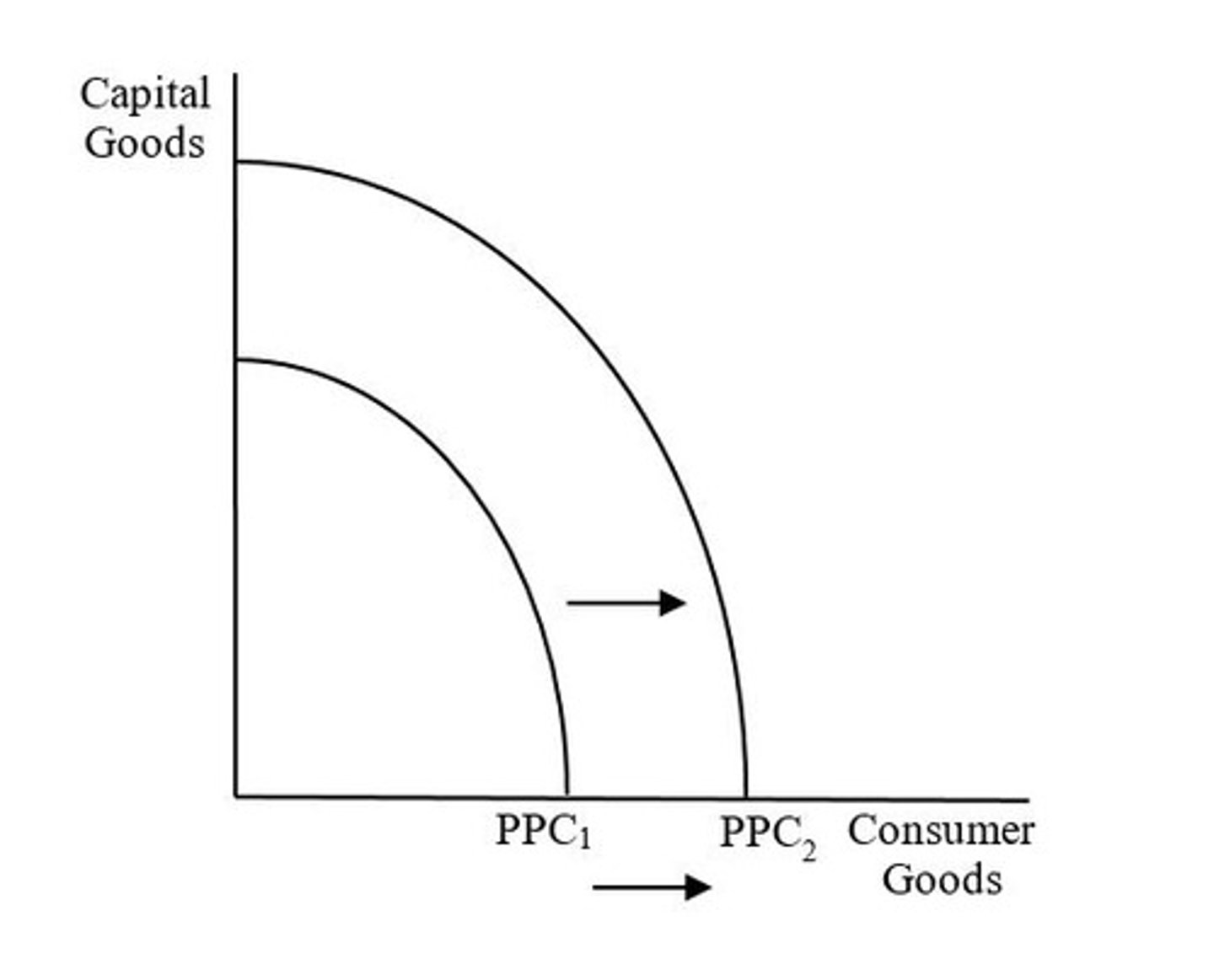
Rightward shift of PPC = economic growth
Meaning the country is now capable of producing more goods and services than before (i.e. its potential output has increased)
What does the shift from PPC1 to PPC2 indicate?
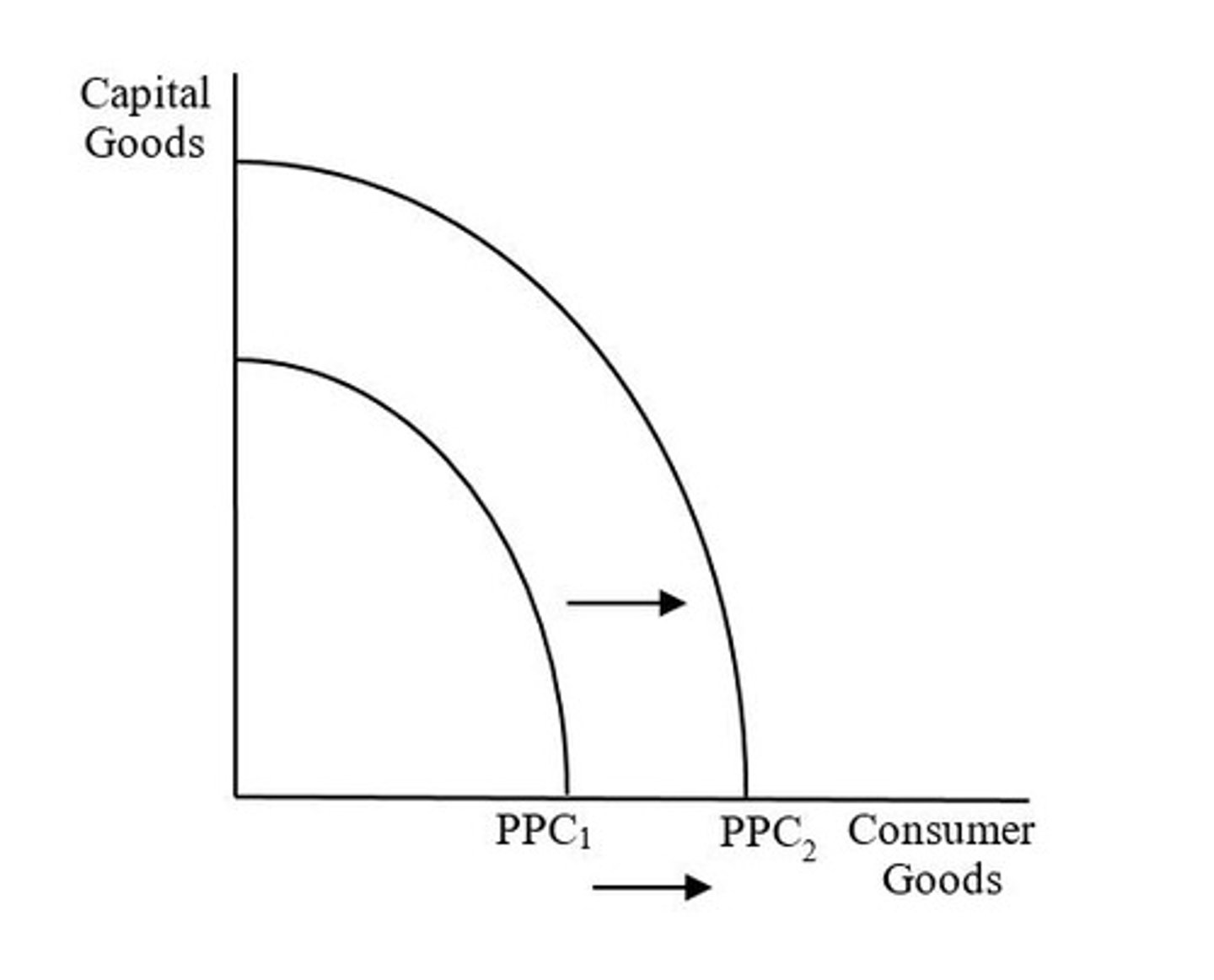
An increase in any type of input (i.e. land, labor, capital, or entrepreneurship) or an increase in productivity/technology.
What caused the shift from PPC1 to PPC2?
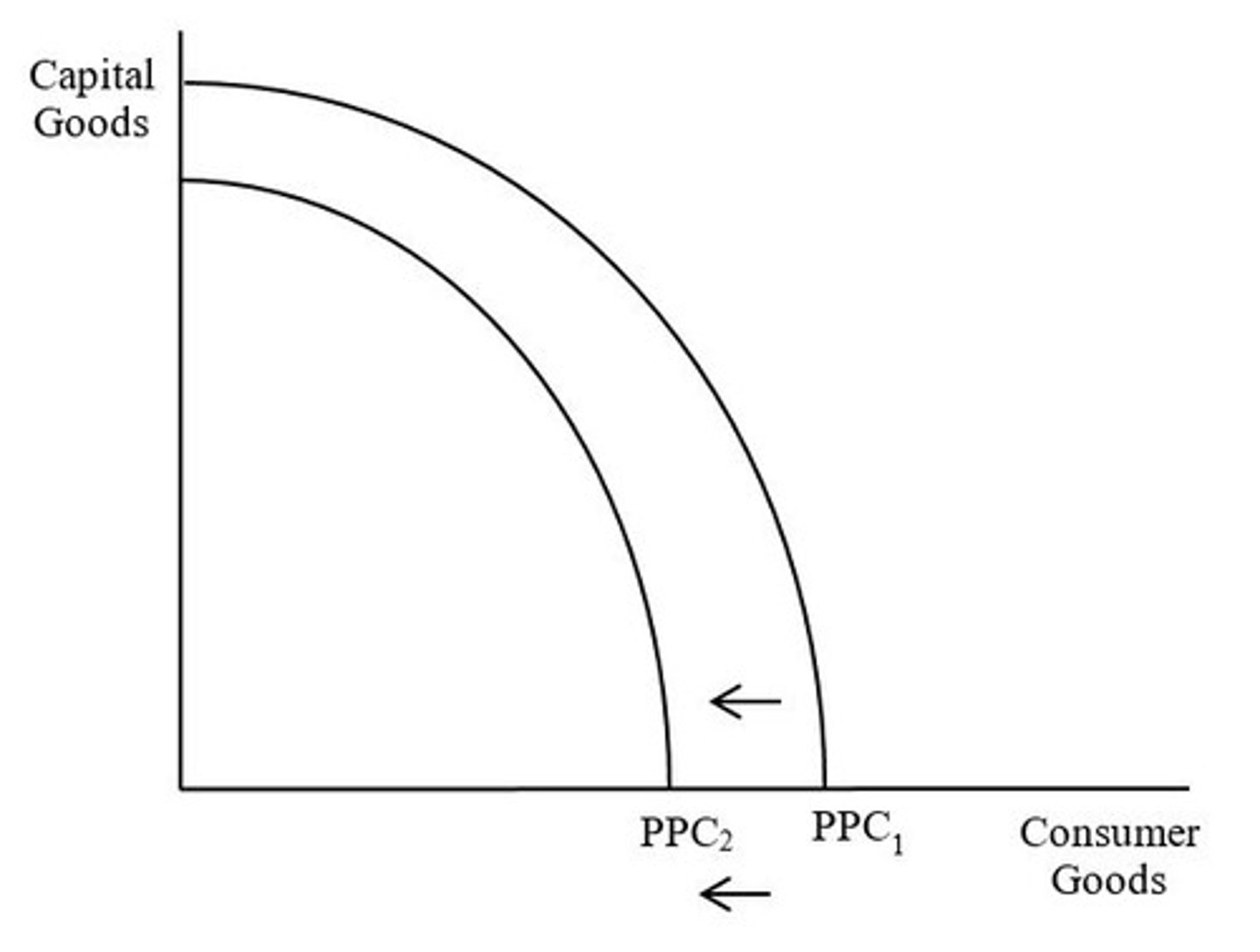
Rightward shift of PPC = economic contraction
Meaning the country is now capable of producing less goods and services than before (i.e. its potential output has decreased)
What does the shift from PPC1 to PPC2 indicate?
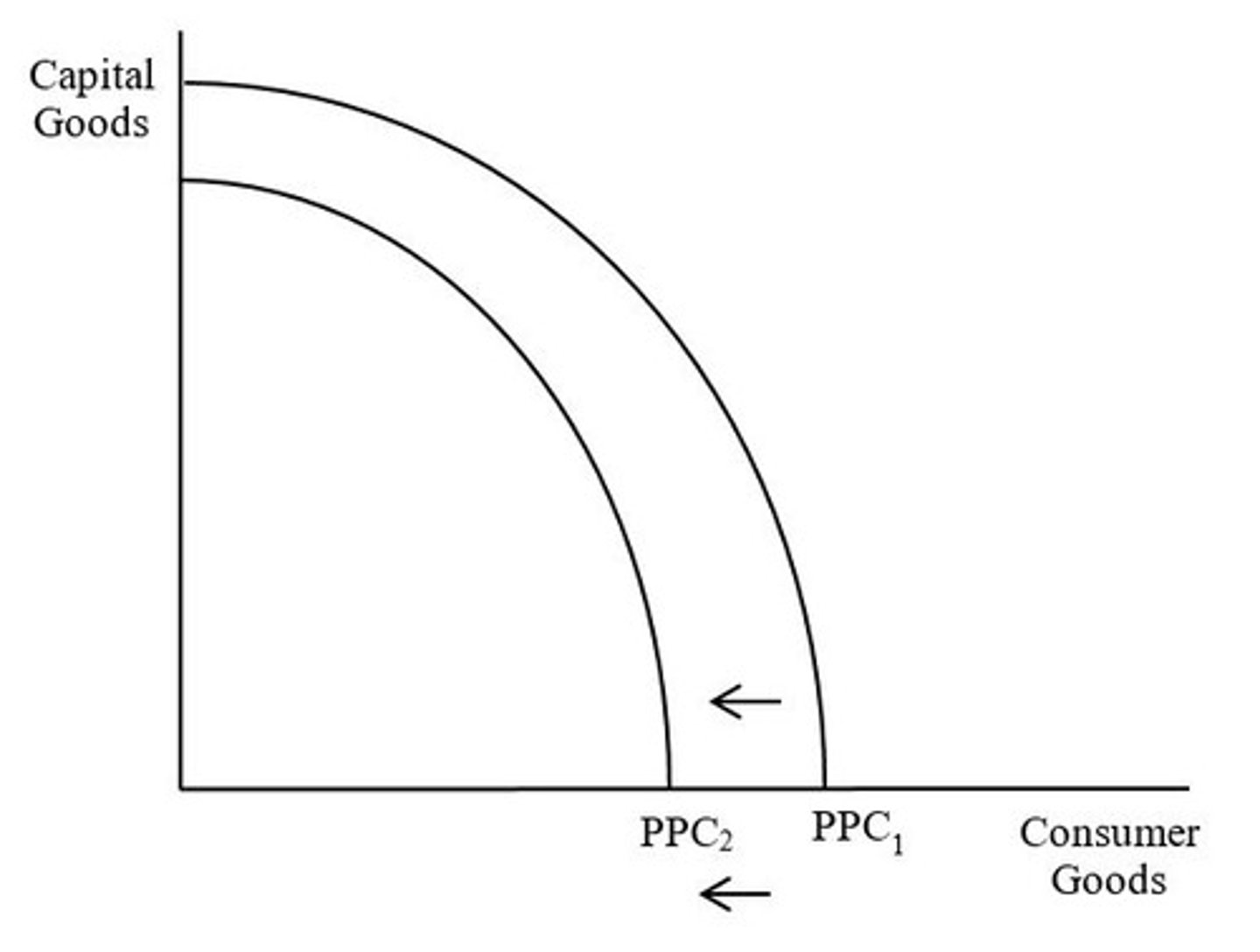
A decrease in any type of input (i.e. land, labor, capital, or entrepreneurship) and a decrease in productivity/technology.
What caused the shift from PPC 1 to PPC2?
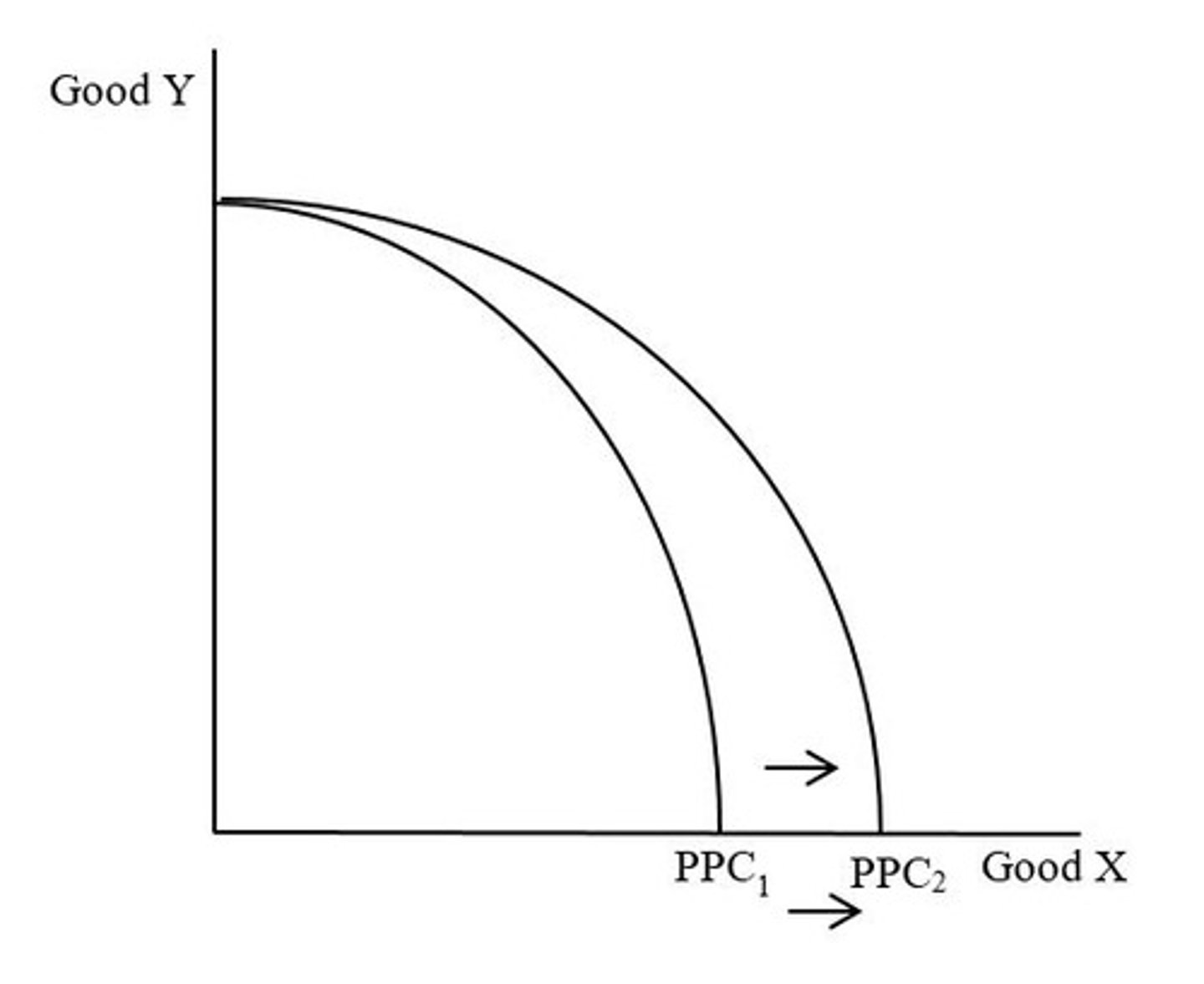
An increase in inputs or an increase in technology used only in the production of Good X.
Note: even though only inputs and technology used to produce good X increased, the economy can now produce more of good X and good Y than before.
What caused the shift from PPC1 to PPC2?
Potential output = PPC
Actual output = point (whether on PPC, inside PPC, or outside PPC)
What part of the graph represents potential output?
What part of the graph represents actual output?
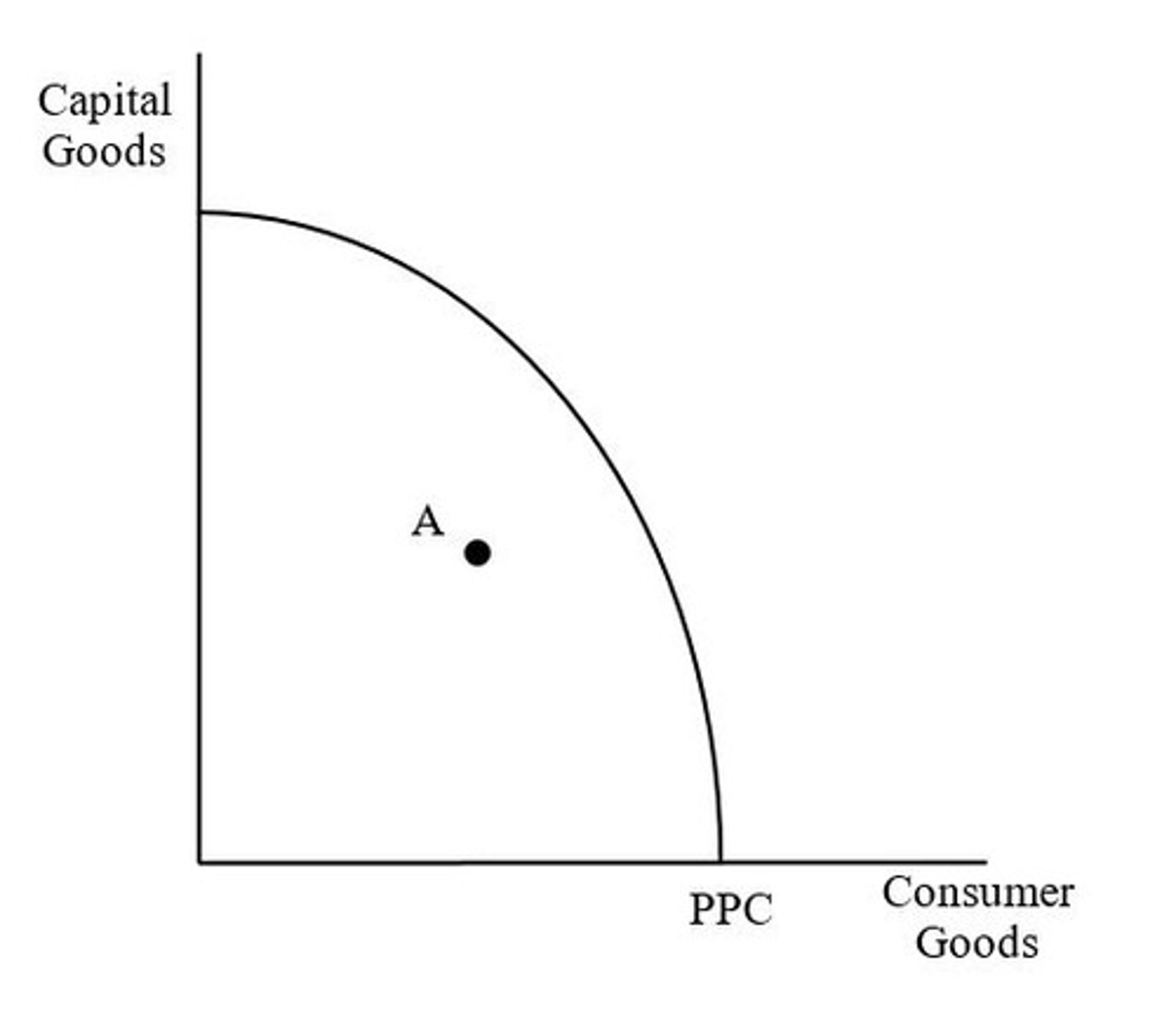
Point A would lead to more economic growth.
Why: point represents a higher production of capital goods than point B. Any additional inputs (like capital) grows the economy. Thus, since point A, means the economy is making more capital than at point B, point A will allow for more economic growth.
Which point would lead to more economic growth?
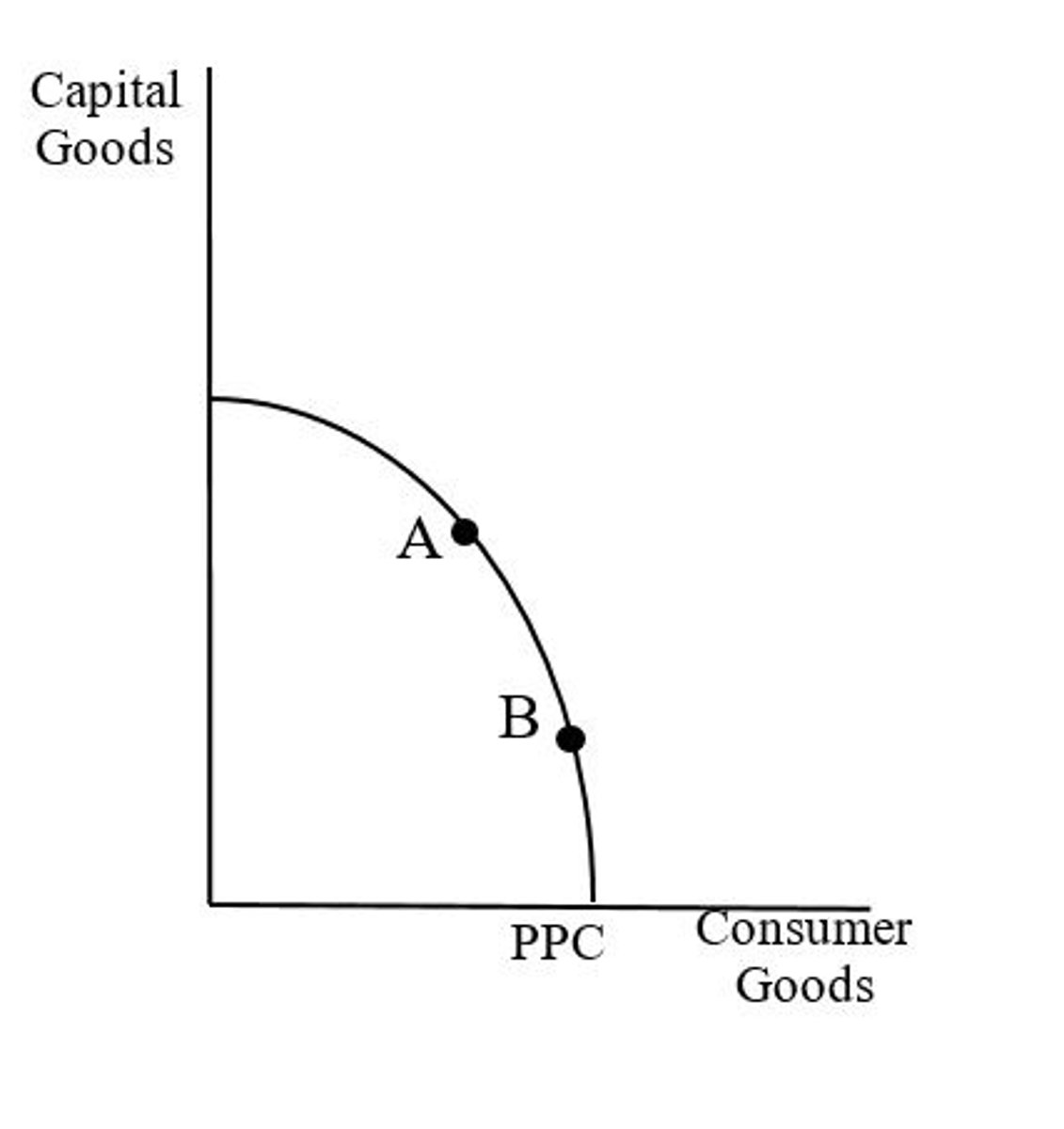
Point A
Because point A is inside the curve, that means that there are resources not being used ("idle resources). Those resources can be applied to making cars allowing for the production of more cars without decreasing the production of bicycles.
At point B, the country is employing all of its resources. In this situation, it can only produce more cars by giving up the production of some bicycles.
At which point can you increase the production of cars without giving up production of bicycles?
The production possibilities CURVE shows the maximum amount of two goods a country can make given its limited (i.e. scarce) inputs.
How does the PPC demonstrate the concept of scarcity?
Opportunity cost is what is given up when a choice is made.
On the production possibilities CURVE where an economy is using all of its resources, the economy can only produce more of one good by giving up some production of the other good.
How does the PPC demonstrate the concept of opportunity cost?