Microbiology Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:10 AM on 8/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
When was the Golden age of Microbiology?
1850-1915
2
New cards
Louis Pasteur
“Father of Microbiology”
\
Discovered/worked with fermentation + pasteurization
\
Domesticated yeast - bakers and brewers
*Saccharomyces cerevisiae*
\
Created Germ Theory of Disease in 1857
\
\
Discovered/worked with fermentation + pasteurization
\
Domesticated yeast - bakers and brewers
*Saccharomyces cerevisiae*
\
Created Germ Theory of Disease in 1857
\
3
New cards
BJ Palmer Germ Theory Quote
“If the Germ Theory of Disease were correct, there’d be no one living to believe it.” - BJ Pamer, As A Man Thinketh, 1921
4
New cards
Dr Drover Revised Germ Theory Quote
“If the Germ Theory of Disease were there *only* truth, there’s be no one living to believe it.” - Dr Drover
5
New cards
Preventing Infection and Disease
Semmelweis → Handwashing
\
Lister → Antiseptic technique
\
Snow → Infection control, field of epidemiology
\
Jenner → Smallpox vaccine, field of immunology
\
Lister → Antiseptic technique
\
Snow → Infection control, field of epidemiology
\
Jenner → Smallpox vaccine, field of immunology
6
New cards
Ignaz Semmelweis
Found that medical students had a 20x higher mortality rate than midwives in deliveries of babies.
\
Hypothesized “cadaver particles” from hands of medical students caused “puerperal fever”
\
Required washing hands, saw the mortality rate go down to less than 1%.
\
His views were considered radical, opposed, and he was driven out of the hospital.
\
Hypothesized “cadaver particles” from hands of medical students caused “puerperal fever”
\
Required washing hands, saw the mortality rate go down to less than 1%.
\
His views were considered radical, opposed, and he was driven out of the hospital.
7
New cards
Joseph Lister
Surgeon, noted problems with infection in wounds.
\
Began spraying wounds, incisions, and dressings with carbolic acid → decreased deaths by 2/3 among his patients
\
Known as antisepsis, the method was accepted into common practice.
\
Began spraying wounds, incisions, and dressings with carbolic acid → decreased deaths by 2/3 among his patients
\
Known as antisepsis, the method was accepted into common practice.
8
New cards
John Snow
Discovered cause of cholers transmission
\
Created first outbreak map, found it centered on a water supply.
\
Stopping access to source stopped cases.
\
Created first outbreak map, found it centered on a water supply.
\
Stopping access to source stopped cases.
9
New cards
Edward Jenner
Showed that vaccination with pus collected from cowpox lesions prevented smallpox.
\
Created field of immunology
\
Created field of immunology
10
New cards
Processes of Life
Growth
Reproduction
Responsiveness
Metabolism
Reproduction
Responsiveness
Metabolism
11
New cards
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotes →
No nucleus
Circular DNA
Smaller
Simple structure
Bacteria and archaea
\
Eukaryotes →
Nucleus
Linear DNA
Larger
Complex structure
Protozoa, fungi, animals, plants, algae
No nucleus
Circular DNA
Smaller
Simple structure
Bacteria and archaea
\
Eukaryotes →
Nucleus
Linear DNA
Larger
Complex structure
Protozoa, fungi, animals, plants, algae
12
New cards
Bacterial Cell Walls
Give bacterial cells structure, characteristic shape, and protection from osmotic forces
\
Assists some cells in attaching to other cells or resisting antimicrobial drugs
\
Composed of peptidoglycan
\
Most common types of bacterial cells walls: Gram + & Gram -
\
Assists some cells in attaching to other cells or resisting antimicrobial drugs
\
Composed of peptidoglycan
\
Most common types of bacterial cells walls: Gram + & Gram -
13
New cards
Categories of Bacteria
*See Image*
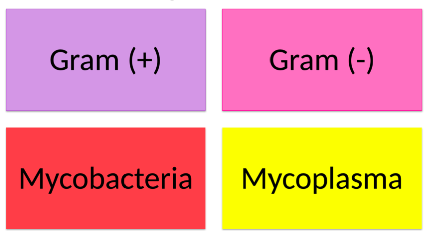
14
New cards
Gram (+) Bacteria
Cell wall
Thick layer of peptidoglycan
Appear *PURPLE* following Gram Stain
Thick layer of peptidoglycan
Appear *PURPLE* following Gram Stain
15
New cards
Gram (-) Bacteria
Cell Wall
Thin layer of peptidoglycan
Membrane contains Lipopolysaccharide known as Lipid A
\- Lipid A = endotoxin
*May trigger fever, vasodilation, inflammation, shock, and blood clotting. May be impediment to tx of disease.*
Appears *MAGENTA/RED* following Gram Stain
Thin layer of peptidoglycan
Membrane contains Lipopolysaccharide known as Lipid A
\- Lipid A = endotoxin
*May trigger fever, vasodilation, inflammation, shock, and blood clotting. May be impediment to tx of disease.*
Appears *MAGENTA/RED* following Gram Stain
16
New cards
Categories of Bacteria
Acid Fast Bacteria →
Cell Wall
Contains waxy, mycolic acid
Mycobacterium
\
No Cell Wall Bacteria →
Distinctive “fried egg” appearance when grown on media
Colonize osmotically protected habitats such as animals or the human body.
Mycoplasma
Cell Wall
Contains waxy, mycolic acid
Mycobacterium
\
No Cell Wall Bacteria →
Distinctive “fried egg” appearance when grown on media
Colonize osmotically protected habitats such as animals or the human body.
Mycoplasma
17
New cards
A typical bacterial cell (with a cell wall) which has a solute concentration of .85% NaCl is placed into a solution that has a .2% NaCl concentration, what will happen?
It will take on water but has no risk of bursting.
18
New cards
Effects of Solutions on Cells
*See Image*
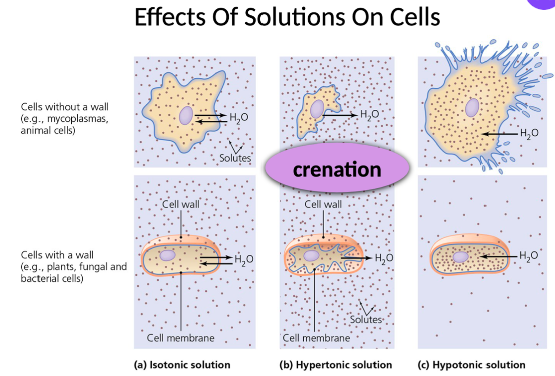
19
New cards
Other Important Features of Bacteria
Inclusions →
May include reserve deposits of chemicals
Stored when nutrients are in abundance, used when nutrients are scarce
\
Endospores →
Unique structures produced by some bacteria that are a defensive strategy against unfavorable conditions
Only produced by organisms in Genus Bacillus and Clostridium
May include reserve deposits of chemicals
Stored when nutrients are in abundance, used when nutrients are scarce
\
Endospores →
Unique structures produced by some bacteria that are a defensive strategy against unfavorable conditions
Only produced by organisms in Genus Bacillus and Clostridium
20
New cards
Non Membranous Organelles: Ribosomes
Sites of *protein synthesis* of a cell
Subunits size expressed in Svedbers (S)
\
Prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S (composed of 30S and 50S subunits)
*Yes, that’s not accurate math, it’s still the answer*
\
Eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S (composed of 40S and 60S subunits)
*BUT* mitochondria and chloroplasts have 70S ribosomes.
\
Why does this matter? -- Important target for antimicrobial drugs!
Subunits size expressed in Svedbers (S)
\
Prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S (composed of 30S and 50S subunits)
*Yes, that’s not accurate math, it’s still the answer*
\
Eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S (composed of 40S and 60S subunits)
*BUT* mitochondria and chloroplasts have 70S ribosomes.
\
Why does this matter? -- Important target for antimicrobial drugs!
21
New cards
General Principles of Microscopy
Resolution →
The shortest distance between two points on a specimen that can still be distinguished by the observer as separate entities
Ability of a lens to separate or distinguish small objects that are close together
\
Contrast →
Differences in intensity between two objects or between an object and background
\
Staining →
Increases contrast and resolution by coloring specimens with stains/dyes
The shortest distance between two points on a specimen that can still be distinguished by the observer as separate entities
Ability of a lens to separate or distinguish small objects that are close together
\
Contrast →
Differences in intensity between two objects or between an object and background
\
Staining →
Increases contrast and resolution by coloring specimens with stains/dyes
22
New cards
Staining
*See Image*
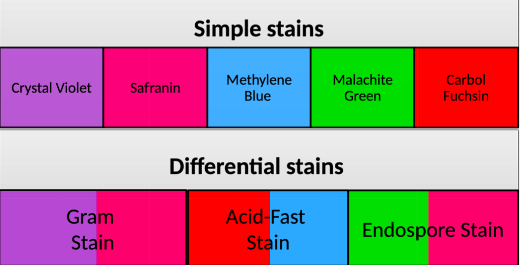
23
New cards
Gram Stain (Bacteria)
1. Crystal violet primary stain
2. Decolorize
1. Washes gram (-) cells of stain due to their thinner walls.
3. Counter stain (safranin)
1. Gram (-) cells take on magenta/red color
\
Results:
Purple - Gram (+) cells
Magenta (red) - Gram (-) cells
\
24
New cards
Mycobacteria
Group of bacteria that do not have the typical peptidoglycan cell walls
\
Their cell walls have a high, waxy, mycolic acid content, making them resistant to decolorization by acids during staining procedures such as the Gram stain.
\
Referred to as “Acid-Fact Bacteria”
\
Their cell walls have a high, waxy, mycolic acid content, making them resistant to decolorization by acids during staining procedures such as the Gram stain.
\
Referred to as “Acid-Fact Bacteria”
25
New cards
Acid-Fast Stain (Bacteria)
1. Carbol fuchsin primary stain
2. Decolorize (alcohol flush)
1. Acid-fast cells retain their red color because acid cannot penetrate the waxy wall
3. Counterstain (methylene blue)
1. Stains only bleached, non-acid-fast cells
\
Results:
Red Acid Fast cells
Blue Non-Acid Fast cells (including human cells and tissues)
26
New cards
Endospore Stain (Bacteria Bacillus and Clostridium)
1. Malachite Green Primary Stain
1. Use heat to drive into the endospore
2. Decolorize
1. Just uses water here
3. Counterstain (safranin)
\
Results:
Green endospores
Magenta (Red) vegetative cells
27
New cards
Classifying Prokaryotes
*Medically important groupings and genera of bacteria!*
\
Know the rules, memorize exceptions!
Genus name ends in -us or -um = Gram (+)
Genus name ends in -a or -er = Gram (-)
\
Know the rules, memorize exceptions!
Genus name ends in -us or -um = Gram (+)
Genus name ends in -a or -er = Gram (-)
28
New cards
Gram (+) Bacteria
*End in -us or -um*
\
Bacillus (anthrax)
Clostridium (tetanus, gas gangrene, botulism)
**Exeption** - Listeria (food poisoning)
Propionibacterium (acne)
Staphylococcus (abscesses, skin infections)
Streptococcus (strep throat, dental caries)
Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium (good bacteria)
\
Bacillus (anthrax)
Clostridium (tetanus, gas gangrene, botulism)
**Exeption** - Listeria (food poisoning)
Propionibacterium (acne)
Staphylococcus (abscesses, skin infections)
Streptococcus (strep throat, dental caries)
Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium (good bacteria)
29
New cards
Gram (-) Bacteria
*End in -a or -er*
\
Bartonella (cat scratch dx)
Bordetella (pertussis)
Borellia (lyme dx)
Brucella (brucellosis)
Campylobacter (food poisoning)
Chlamydia (chlamydia, trachoma)
Citrobacter (nosocomial catheter UTIs)
Escherichia (traveler’s diarrhea, UTIs)
Francisella (tularemia)
**Exception** - Haemophilus (meningitis, pinkeye, chancroid)
Klebsiella (pneumonia)
Legionella (lengionnaire’s dx)
Leptospira (kidney infection)
Neisseria (gonorrhea, meningitis)
**Exception** - Proteus (UTIs)
**Exception** - Pseudomonas (folliculitis, burns, infection)
Rickettsia (RM spotted fever)
Salmonella (food poisoning, Typhoid fever)
Serratia (nosocomial catheter UTIs)
Shigella (dysentery)
Treponema (syphilis)
**Exception** - Vibrio (cholera)
Yersinia (bubonic plague, food poisoning)
\
Bartonella (cat scratch dx)
Bordetella (pertussis)
Borellia (lyme dx)
Brucella (brucellosis)
Campylobacter (food poisoning)
Chlamydia (chlamydia, trachoma)
Citrobacter (nosocomial catheter UTIs)
Escherichia (traveler’s diarrhea, UTIs)
Francisella (tularemia)
**Exception** - Haemophilus (meningitis, pinkeye, chancroid)
Klebsiella (pneumonia)
Legionella (lengionnaire’s dx)
Leptospira (kidney infection)
Neisseria (gonorrhea, meningitis)
**Exception** - Proteus (UTIs)
**Exception** - Pseudomonas (folliculitis, burns, infection)
Rickettsia (RM spotted fever)
Salmonella (food poisoning, Typhoid fever)
Serratia (nosocomial catheter UTIs)
Shigella (dysentery)
Treponema (syphilis)
**Exception** - Vibrio (cholera)
Yersinia (bubonic plague, food poisoning)
30
New cards
Taxonomy: Linnaeus
System classified organisms based on characteristics in common
\
Used binomial nomenclature
*Genus Species*
\
Proposed only 2 kingdoms: Animals and Plants
\
\
\
Used binomial nomenclature
*Genus Species*
\
Proposed only 2 kingdoms: Animals and Plants
\
\
31
New cards
Taxonomy: Carl Woese
Compared nucleotide sequences of rRNA subunits
\
Proposed three domains as determined by ribosomal nucleotide sequences
*Eukarya, Bacteria, Archaea*
\
Cells within three domains differ with respect to many other characteristics
\
Proposed three domains as determined by ribosomal nucleotide sequences
*Eukarya, Bacteria, Archaea*
\
Cells within three domains differ with respect to many other characteristics
32
New cards
Microbial Growth
When speaking of reproductive activities of microbes, use the term growth to refer to an increase in the size of a population of microbes
\
Colony - An aggregation of cells arising from a single parent cell
\
Biofilm - A collection of microbes in a complex community
\
Colony - An aggregation of cells arising from a single parent cell
\
Biofilm - A collection of microbes in a complex community
33
New cards
Growth Styles
*See Chart*

34
New cards
7 Growth Requirements
Oxygen
\- Microorganisms vary widely in their oxygen requirements for growth
*Aerobe or Anaerobe*
\
Temperature
\- As a rule, temperature is the most important factor affecting the growth of microorganisms
*Organisms can grow within a range of temperatures*
Psychrophilic: Prefer cold temps
Mesophilic: Prefer moderate temps, near normal body temp, most pathogenic organisms
Hyper Thermophilic: Prefer higher temps
\
pH
\- Most microorganisms thrive in a pH range of 6-9
Most animal pathogens work best near a pH of 7
“Pickling” or preserving food may be accomplished in an acidic medium - vinegar
\
Moisture
\- Vegetative cell maintenance and growth requires water
Food and waste are transported through the cell wall in water solutions.
Water is a building material necessary in cell synthesis
\
Osmotic Pressure
\- Pressure created by osmosis
Cell in hypertonic environment: water is drawn out of cell
*Cell shrinks and may die - Crenation*
Cell in hypotonic environment: water is drawn into the cell
*Cell shrinks or may even burst - Lysis*
\
Light
\- Microbes also vary widely in their light requirements
In comparison, most pathogens are killed by direct sunlight
Both UV rays and warmth harm bacteria
Green and purple pigmented bacteria use light as an energy source
\
Food
\- Organisms require food for building cell components and proteins and for the energy necessary for cell survival
Microbial activity is limited when food supplies become exhausted
The amount and type of food available will have an impact on the organism’s survival and growth - Inclusions
\- Microorganisms vary widely in their oxygen requirements for growth
*Aerobe or Anaerobe*
\
Temperature
\- As a rule, temperature is the most important factor affecting the growth of microorganisms
*Organisms can grow within a range of temperatures*
Psychrophilic: Prefer cold temps
Mesophilic: Prefer moderate temps, near normal body temp, most pathogenic organisms
Hyper Thermophilic: Prefer higher temps
\
pH
\- Most microorganisms thrive in a pH range of 6-9
Most animal pathogens work best near a pH of 7
“Pickling” or preserving food may be accomplished in an acidic medium - vinegar
\
Moisture
\- Vegetative cell maintenance and growth requires water
Food and waste are transported through the cell wall in water solutions.
Water is a building material necessary in cell synthesis
\
Osmotic Pressure
\- Pressure created by osmosis
Cell in hypertonic environment: water is drawn out of cell
*Cell shrinks and may die - Crenation*
Cell in hypotonic environment: water is drawn into the cell
*Cell shrinks or may even burst - Lysis*
\
Light
\- Microbes also vary widely in their light requirements
In comparison, most pathogens are killed by direct sunlight
Both UV rays and warmth harm bacteria
Green and purple pigmented bacteria use light as an energy source
\
Food
\- Organisms require food for building cell components and proteins and for the energy necessary for cell survival
Microbial activity is limited when food supplies become exhausted
The amount and type of food available will have an impact on the organism’s survival and growth - Inclusions
35
New cards
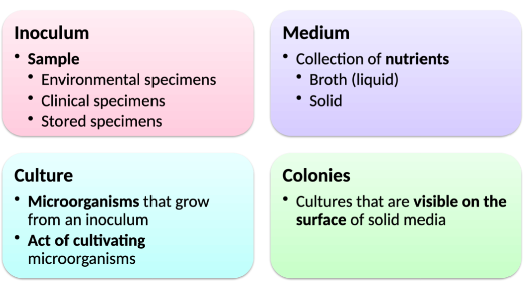
Culturing Microorganisms
Culture Media
\- Some microbes are not particular and cab be grown in a variety of media, others require specific nutrients
\
→ Selective Media
Contains substances that favor or inhibit the growth of particular organisms
Dyes or salts added, specific nutrients left out
Ex. Sabouraud detrose agar - Inhibits bacteria, selects for fungi
\
→ Differential Media
Presence of visible changes in medium or differences in the appearance of colonies help differentiate organisms
Ex. Blood agar - Streptococcus change appearance of blood
\
→ Both Selective and Differential Media
Will do both, will be selective but will also help differentiate between organisms
Ex. MacConkey agar - Selective for gram (-) bacteria and types within the negatives.
\- Some microbes are not particular and cab be grown in a variety of media, others require specific nutrients
\
→ Selective Media
Contains substances that favor or inhibit the growth of particular organisms
Dyes or salts added, specific nutrients left out
Ex. Sabouraud detrose agar - Inhibits bacteria, selects for fungi
\
→ Differential Media
Presence of visible changes in medium or differences in the appearance of colonies help differentiate organisms
Ex. Blood agar - Streptococcus change appearance of blood
\
→ Both Selective and Differential Media
Will do both, will be selective but will also help differentiate between organisms
Ex. MacConkey agar - Selective for gram (-) bacteria and types within the negatives.
36
New cards
The structure of Prokaryotic Genomes
Plasmids (aka Factors)
\
Small molecules of extra-chromosomal DNA that replicate independently
\
Not essential for normal metabolism, growth, or reproduction
\
Can confer survival advantages
\
Types:
\- Fertility factors (F plasmids)
*Carry instructions for conjugation*
\- Resistance factors (R Plasmids)
*Carry genes for resistance to abx*
\- Bacteriocin factors
*Carry genes for toxins called bacteriocins - can kill its competitors*
\- Virulence factors
*Carry instructions that enable bacterium to become pathogenic*
\
Small molecules of extra-chromosomal DNA that replicate independently
\
Not essential for normal metabolism, growth, or reproduction
\
Can confer survival advantages
\
Types:
\- Fertility factors (F plasmids)
*Carry instructions for conjugation*
\- Resistance factors (R Plasmids)
*Carry genes for resistance to abx*
\- Bacteriocin factors
*Carry genes for toxins called bacteriocins - can kill its competitors*
\- Virulence factors
*Carry instructions that enable bacterium to become pathogenic*
37
New cards
Genetic Transfer
Vertical Gene Transfer
\- Organisms replicate their genomes and provide copies to descendants
\- Normal process in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
\
Horizontal Gene Transfer
\- Aquire genes from other microbes of the same generations
\- Donor cell contributes part of genome to recipient cell
*May be different species*
3 Types:
1. Transformation
1. Recipient cell takes up DNA from environment can include DNA from dead organisms
2. Cells that take up DNA are called competent
3. Occurs in only a few types of bacteria
2. Transduction
1. Transfer of DNA from one cell to another via a replicating virus
2. Generalized - transducing phage carries random DNA segment from donor to recipient
3. Specialized - only certain donor DNA sequences are transferred
3. Bacterial conjugation
1. Transfer of DNA from one cell to another, mediated by conjugation pilli
2. Donor cell requires F plasmid (F+)
3. Recipient cell lacks F plasmid (F-)
\- Organisms replicate their genomes and provide copies to descendants
\- Normal process in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
\
Horizontal Gene Transfer
\- Aquire genes from other microbes of the same generations
\- Donor cell contributes part of genome to recipient cell
*May be different species*
3 Types:
1. Transformation
1. Recipient cell takes up DNA from environment can include DNA from dead organisms
2. Cells that take up DNA are called competent
3. Occurs in only a few types of bacteria
2. Transduction
1. Transfer of DNA from one cell to another via a replicating virus
2. Generalized - transducing phage carries random DNA segment from donor to recipient
3. Specialized - only certain donor DNA sequences are transferred
3. Bacterial conjugation
1. Transfer of DNA from one cell to another, mediated by conjugation pilli
2. Donor cell requires F plasmid (F+)
3. Recipient cell lacks F plasmid (F-)
38
New cards
Typical Prokaryote Morphologies
*See Image*
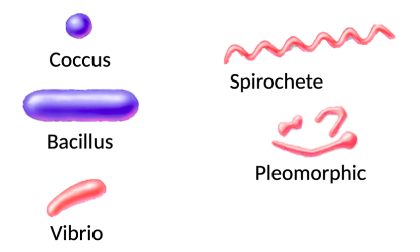
39
New cards
Reproduction of Prokaryotic Cells
All reproduce asexually
\
3 Main Methods:
1. Binary Fission (most common)
2. Snapping Division
1. Clostridium and Corynebacterium
3. Budding
\
3 Main Methods:
1. Binary Fission (most common)
2. Snapping Division
1. Clostridium and Corynebacterium
3. Budding
40
New cards
Eukaryotic Microbes of Clinical Interest
Fungi and Protozoa - Microscopic
Protozoa and Helminths - “parasites”
Protozoa and Helminths - “parasites”
41
New cards
Reproduction of Fungi
Budding, spore formation
\
*most also reproduce sexually*
\
*most also reproduce sexually*
42
New cards
Protozoa
Typically lack a cell wall
Require moist environments (waterborne illnesses)
Very few are pathogens!
Characterized by great morphological diversity
Most reproduce asexually only
\
All have trophozoite
*Motile feeding stage*
\
Some have cysts form, many pathogens are in cyst like forms that we ingest
*Hardy resting stage*
\
Some have contractile vacuoles
*Actively pump water from the cells, protecting them from osmotic lysis*
Require moist environments (waterborne illnesses)
Very few are pathogens!
Characterized by great morphological diversity
Most reproduce asexually only
\
All have trophozoite
*Motile feeding stage*
\
Some have cysts form, many pathogens are in cyst like forms that we ingest
*Hardy resting stage*
\
Some have contractile vacuoles
*Actively pump water from the cells, protecting them from osmotic lysis*
43
New cards
Effects of Solution on Cells
*See Image*
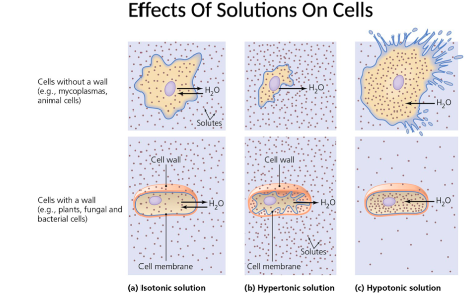
44
New cards
Characteristics of Viruses
Miniscule, acellular (no presence of life)
Infectious agent having either DNA or RNA
Cause infections of humans, animals, plants, and bacteria
Cause most of the diseases that plague the industrialized world
\
Extracellular State →
\- Called a viron
Protein coat (capsid) surrounding a nucleic acid core
Together the capsid and nucleic acid are called the nucleocapsid
Some have a phospholipid envelope
*Provide protection for viral nucleic acid and means of attachment to host cell*
Envelope virus versus non envelope virus
\
Intracellular State →
\- Once the virus is inside the host, the capsid is removed
*Virus exists simply as nucleic acid*
Infectious agent having either DNA or RNA
Cause infections of humans, animals, plants, and bacteria
Cause most of the diseases that plague the industrialized world
\
Extracellular State →
\- Called a viron
Protein coat (capsid) surrounding a nucleic acid core
Together the capsid and nucleic acid are called the nucleocapsid
Some have a phospholipid envelope
*Provide protection for viral nucleic acid and means of attachment to host cell*
Envelope virus versus non envelope virus
\
Intracellular State →
\- Once the virus is inside the host, the capsid is removed
*Virus exists simply as nucleic acid*
45
New cards
Hosts of Viruses
Specific →
HIV specifically attacks helper T lymphocytes in humans
*Has no effect on human muscles or bone cells*
\
Generalist →
West Nile Virus
*Can infect most species of birds, several mammalian species (including humans), and some reptiles*
\
**ALL types of organisms are susceptible to some sort of viral attack**
HIV specifically attacks helper T lymphocytes in humans
*Has no effect on human muscles or bone cells*
\
Generalist →
West Nile Virus
*Can infect most species of birds, several mammalian species (including humans), and some reptiles*
\
**ALL types of organisms are susceptible to some sort of viral attack**
46
New cards
Viral Capsid Shapes
Polyhedral
\- Geodesic dome
\- Most common viral shape → icosahedron(20 sides)
\
Complex
\- Capsids of many shapes
\
Helical
\- Spiral
\
\
\- Geodesic dome
\- Most common viral shape → icosahedron(20 sides)
\
Complex
\- Capsids of many shapes
\
Helical
\- Spiral
\
\
47
New cards
Viral Replication
Lytic Replication →
\- Synthesis of new nucleic acids and viral proteins by host cell
\- Assembly of new virions within host cell
\- Release of new virions from host cell, typically lyse the host cell
\
Lysogeny → Modified Replication Cycle
Infected host cells grow and reproduce normally for generations before they lyse.
*Prophages - inactive phages*
\
Lysogenic Conversion → When phages carry genes that alter phenotype of a bacterium
Can turn bacterium from harmless to pathogen
Can happen with animal/human cells too
\- Synthesis of new nucleic acids and viral proteins by host cell
\- Assembly of new virions within host cell
\- Release of new virions from host cell, typically lyse the host cell
\
Lysogeny → Modified Replication Cycle
Infected host cells grow and reproduce normally for generations before they lyse.
*Prophages - inactive phages*
\
Lysogenic Conversion → When phages carry genes that alter phenotype of a bacterium
Can turn bacterium from harmless to pathogen
Can happen with animal/human cells too
48
New cards
Latency of Animal Viruses
When animal viruses remain dormant in the host cells
\
Called Latent Viruses
\
May go years with no viral activity
\
Some latent viruses never become incorporated into host chromosome
\
If it happens, incorporation of latent virus into host DNA is permanent
\
Called Latent Viruses
\
May go years with no viral activity
\
Some latent viruses never become incorporated into host chromosome
\
If it happens, incorporation of latent virus into host DNA is permanent
49
New cards
Prions
Prions → Proteinaceous infectious agents, lack nucleic acid
\
Prion PrP converts cellular PrP into prion PrP
\- By inducing conformational change
\- Cellular PrP made by all mammals and has a-helices
\- Prion PrP is disease causing form with b-sheets
\
Prions only destroyed by:
1. Incineration
2. Autoclaving in sodium hydroxide
\
Prion PrP converts cellular PrP into prion PrP
\- By inducing conformational change
\- Cellular PrP made by all mammals and has a-helices
\- Prion PrP is disease causing form with b-sheets
\
Prions only destroyed by:
1. Incineration
2. Autoclaving in sodium hydroxide
50
New cards
Prion Diseases
Most prominent in Nervous System tissues
Large vacuoles form in brain
\- Characteristic spongy appearance
Spongiform Encephalopathy
\- Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE)
\- Variant Creutzfeldt Jacob Disease (vCJD)
\
*Prions composed of different proteins may lie behind other muscular and neuronal degenerative diseases*
Alzheimers, Parkinsons, ALS
Large vacuoles form in brain
\- Characteristic spongy appearance
Spongiform Encephalopathy
\- Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE)
\- Variant Creutzfeldt Jacob Disease (vCJD)
\
*Prions composed of different proteins may lie behind other muscular and neuronal degenerative diseases*
Alzheimers, Parkinsons, ALS
51
New cards
Foodborne Illnesses
Symptoms:
\- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, fatigue, muscle cramps
\
2 Types:
1. Food Infections
1. Consuming living microorganisms
2. Food Intoxications
1. Consume microbial toxins, NOT the microbe
\- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, fatigue, muscle cramps
\
2 Types:
1. Food Infections
1. Consuming living microorganisms
2. Food Intoxications
1. Consume microbial toxins, NOT the microbe
52
New cards
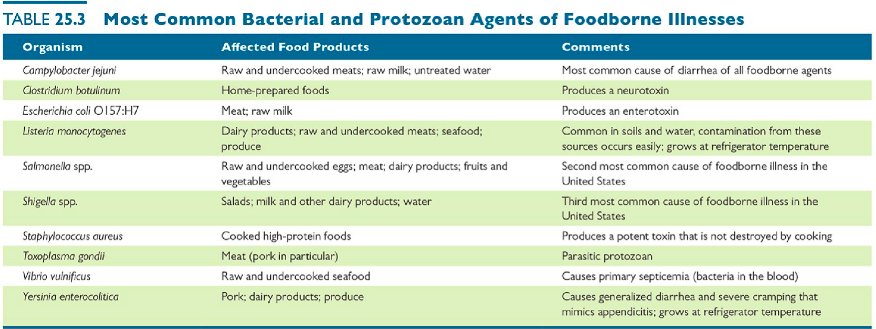
Top Germs Causing Illness
*See chart*
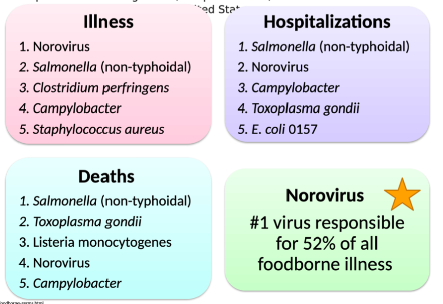
53
New cards
Waterborne Illnesses
Consuming contaminated water can cause various diseases
*Diarrheal dx occur worldwide*
\
Water treatment removes most waterborne pathogens
\
*See chart for diseases caused*
*Diarrheal dx occur worldwide*
\
Water treatment removes most waterborne pathogens
\
*See chart for diseases caused*
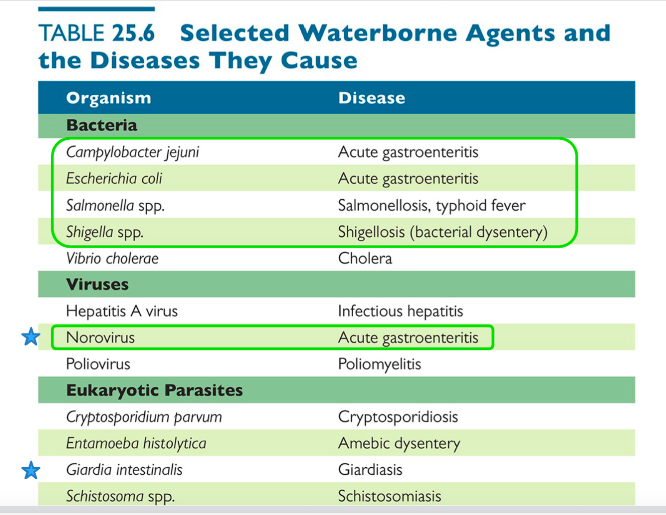
54
New cards
Water Treatment
Potable Water → water considered safe to drink
\- Water is not devoid of microorganisms and chemicals
\- Levels are low enough that it is not a health concern
\
Coliform Bacteria → Indicator of sanitary quality
\- Coliforms not normally causes of serious illness, but they are easy to culture and the presence of coliforms indicates fecal contamination.
*Increased likelihood that disease-causing microbes are present*
\
Treatment of Water →
\- Municipal water treatment
aka drinking water - clean water that is used in homes and businesses
\- Wastewater treatment
aka sewage - water that leaves homes or businesses after use
\- Water is not devoid of microorganisms and chemicals
\- Levels are low enough that it is not a health concern
\
Coliform Bacteria → Indicator of sanitary quality
\- Coliforms not normally causes of serious illness, but they are easy to culture and the presence of coliforms indicates fecal contamination.
*Increased likelihood that disease-causing microbes are present*
\
Treatment of Water →
\- Municipal water treatment
aka drinking water - clean water that is used in homes and businesses
\- Wastewater treatment
aka sewage - water that leaves homes or businesses after use
55
New cards
Bioremediation
Remediate - To solve a problem
\
Bio-remediate - to use biological organisms to solve an environmental problem such as contaminated soil or groundwater
\
Use organisms to clean up toxic, hazardous, or recalcitrant compounds by degrading them to harmless compounds.
\
Bio-remediate - to use biological organisms to solve an environmental problem such as contaminated soil or groundwater
\
Use organisms to clean up toxic, hazardous, or recalcitrant compounds by degrading them to harmless compounds.
56
New cards
Biological Warefare and Bioterrorism
Bioterrorism →
Uses microbes or their toxins to terrorize human populations
\
Agroterrorism →
Uses microbes to terrorize human populations by destroying the food supply
Uses microbes or their toxins to terrorize human populations
\
Agroterrorism →
Uses microbes to terrorize human populations by destroying the food supply
57
New cards
Criteria for Assessing Biological Threats to Humans
Public Health Impact
\- Ability of hospitals and clinics to handle the casualties
\
Delivery Potential
\- How easily agent can be introduced into the population
\
Public Perception
\- Effect of public fear on ability to control an outbreak
\
Public Health Preparedness
\- Existing response measures
\- Ability of hospitals and clinics to handle the casualties
\
Delivery Potential
\- How easily agent can be introduced into the population
\
Public Perception
\- Effect of public fear on ability to control an outbreak
\
Public Health Preparedness
\- Existing response measures
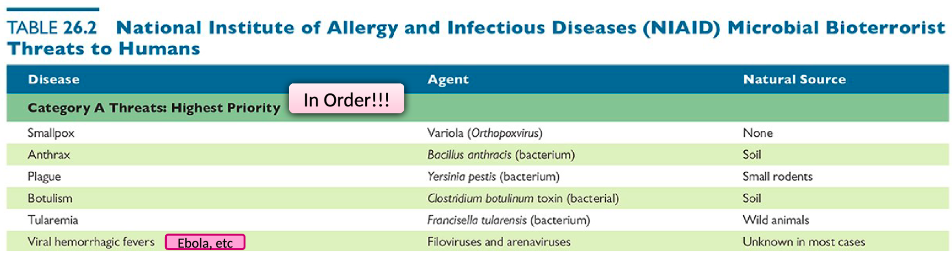
58
New cards
Biosafety Levels
(by CDC)
(by CDC)
Biosafety Level 1
\- Handling pathogens that do not cause disease in healthy humans
\
Biosafety Level 2
\- Handling of moderately hazardous agents
\
Biosafety Level 3
\- Handling of microbes in safety cabinets
\- May cause serious or potentially lethal disease after inhalation
\
Biosafety Level 4
\- Handling of microbes that cause severe or fatal disease
\- Handling pathogens that do not cause disease in healthy humans
\
Biosafety Level 2
\- Handling of moderately hazardous agents
\
Biosafety Level 3
\- Handling of microbes in safety cabinets
\- May cause serious or potentially lethal disease after inhalation
\
Biosafety Level 4
\- Handling of microbes that cause severe or fatal disease
59
New cards
Normal Microbiota
aka normal flora or indigenous microbiota
aka normal flora or indigenous microbiota
Organisms that colonize the body’s surfaces without normally causing disease
\
Resident Microbiota →
Remain part of normal microbiota of a person for life
\
Transient Microbiota →
Remain in body for few hours, days, months before disappearing
\
Acquisition of Normal Microbiota
Axenic: Sites that are free of any microbes and are not supposed to be colonized by normal flora:
\- Alveoil of lungs
\- Central Nervous System
\- Circulatory System
\- Upper Urogenital Regions
\- Uterus
\
In Utero → No exposure to microbiota (uterus is axenic)
Begin to develop during birthing process
\- Mouth and nose through birth canal
\- First breath
\- handling by staff, family, people
\
Much of one’s resident microbiota established during first months of life.
\
Resident Microbiota →
Remain part of normal microbiota of a person for life
\
Transient Microbiota →
Remain in body for few hours, days, months before disappearing
\
Acquisition of Normal Microbiota
Axenic: Sites that are free of any microbes and are not supposed to be colonized by normal flora:
\- Alveoil of lungs
\- Central Nervous System
\- Circulatory System
\- Upper Urogenital Regions
\- Uterus
\
In Utero → No exposure to microbiota (uterus is axenic)
Begin to develop during birthing process
\- Mouth and nose through birth canal
\- First breath
\- handling by staff, family, people
\
Much of one’s resident microbiota established during first months of life.
60
New cards
Opportunistic Pathogens
Normal microbiota that cause disease under certain circumstances
\
Conditions that provide opportunities:
\- Induction into unusual site in body
*E. coli mutualistic in colon, but if it enters the urethra becomes opportunistic*
\- Immune suppression
*AIDS and cancer from patients often die from opportunistic infections*
\- Changes in the normal microbiota
*Take antibiotics, kills normal flora also, allows opportunistic yeast infection*
\- Stressful conditions
*Anything that strains a person’s normal metabolism or emotional state*
\
Conditions that provide opportunities:
\- Induction into unusual site in body
*E. coli mutualistic in colon, but if it enters the urethra becomes opportunistic*
\- Immune suppression
*AIDS and cancer from patients often die from opportunistic infections*
\- Changes in the normal microbiota
*Take antibiotics, kills normal flora also, allows opportunistic yeast infection*
\- Stressful conditions
*Anything that strains a person’s normal metabolism or emotional state*
61
New cards
Reservoirs of Infectious Diseases
The habitat in which an organism normally lives, grows, and multiplies
\
3 Types:
1. Animal Reservoirs
1. Zoonoses - diseases naturally spread from animal host to humans
1. Acquired through direct contact with animal or it’s waste, eating animals, bloodsucking arthropods
2. Humans are usually a dead end host - humans get dieases from animals, animals do not get diseases from humans
2. Human Carriers
3. Nonliving Reservoirs
\
3 Types:
1. Animal Reservoirs
1. Zoonoses - diseases naturally spread from animal host to humans
1. Acquired through direct contact with animal or it’s waste, eating animals, bloodsucking arthropods
2. Humans are usually a dead end host - humans get dieases from animals, animals do not get diseases from humans
2. Human Carriers
3. Nonliving Reservoirs

62
New cards
Strategies to Limit the Spread of Disease
Isolation →
Used to separate and restrict the movement of ill persons who have an infectious disease
\
Quarantine →
Used to separate and restrict the movement of well persons who may have been exposed to an infectious disease
Used to separate and restrict the movement of ill persons who have an infectious disease
\
Quarantine →
Used to separate and restrict the movement of well persons who may have been exposed to an infectious disease
63
New cards
Non living Reservoirs
Soil, water, and food can be reservoirs of infection
\
Sometimes the environment is conducive to growth of microbe
\
Sometimes the presence of microorganisms is due to contamination by feces or urine
\
Sometimes the environment is conducive to growth of microbe
\
Sometimes the presence of microorganisms is due to contamination by feces or urine
64
New cards
Exposure to Microbes
Contamination →
The mere presence of microbes in or on the body
\
Infection →
When a pathogenic organism successfully evades body’s external defenses and becomes established in the body.
*May or may not result in disease*
The mere presence of microbes in or on the body
\
Infection →
When a pathogenic organism successfully evades body’s external defenses and becomes established in the body.
*May or may not result in disease*
65
New cards
Portals of Entry
Sites through which pathogens enter the body
\
3 Major Paths:
1. Skin
1. Openings or cuts
2. Hair follicules or sweat glands
3. Burrowing into or digesting outer layers of skin
2. Mucous Membranes
1. Line the body cavities that are open to the environment
2. Provide a moist, warm environment hospitable to pathogens
3. Respiratory tract is the most common site of entry (nose, mouth, eyes)
4. GIT *MAY* be route of entry… must survive pH of stomach.
3. Placenta
1. Typically forms effective barrier to pathogens
1. Pathogens may cross the placenta and infect the fetus
2. Can cause spontaneous abortion, birth defects, premature birth.
*Parenteral Route is technically NOT a portal of entry, but a way to circumvent the usual portals of entry*
\- Not a true portal of entry, pathogens deposited directly into tissues beneath the skin or mucous membranes.
\
3 Major Paths:
1. Skin
1. Openings or cuts
2. Hair follicules or sweat glands
3. Burrowing into or digesting outer layers of skin
2. Mucous Membranes
1. Line the body cavities that are open to the environment
2. Provide a moist, warm environment hospitable to pathogens
3. Respiratory tract is the most common site of entry (nose, mouth, eyes)
4. GIT *MAY* be route of entry… must survive pH of stomach.
3. Placenta
1. Typically forms effective barrier to pathogens
1. Pathogens may cross the placenta and infect the fetus
2. Can cause spontaneous abortion, birth defects, premature birth.
*Parenteral Route is technically NOT a portal of entry, but a way to circumvent the usual portals of entry*
\- Not a true portal of entry, pathogens deposited directly into tissues beneath the skin or mucous membranes.
66
New cards
Symptoms
Subjective characteristics of disease felt only by the patient
67
New cards
Signs
Objective manifestations of disease observed or measured by others
68
New cards
Syndrome
Group of symptoms and signs that characterize a disease or abnormal condition.
69
New cards
Terminology of Disease
*See Image*
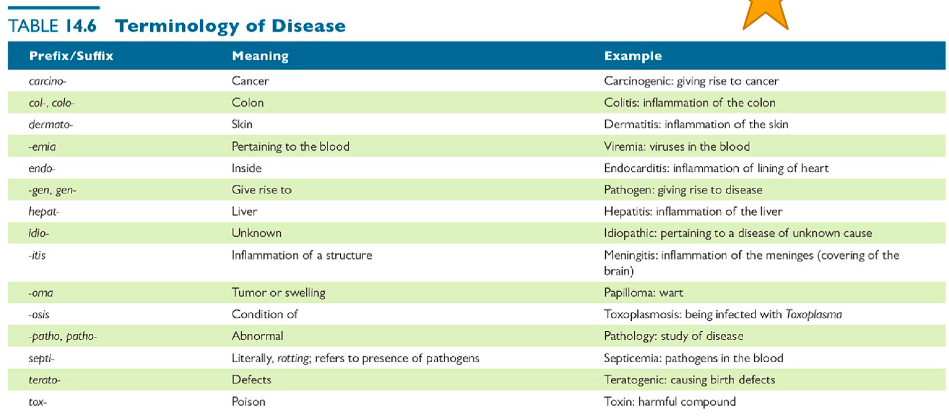
70
New cards
Triad or Triangle of Health
When these 3 are in normal balance health results.
When out of balance, disease results.
\
Host → Environment → Agent
\
*Infectious disease transmission occurs when a susceptible host and a pathogenic agent exist in an environment conducive to disease transmission.*
When out of balance, disease results.
\
Host → Environment → Agent
\
*Infectious disease transmission occurs when a susceptible host and a pathogenic agent exist in an environment conducive to disease transmission.*
71
New cards
The Nature of Infectious Disease
Disease →
Results if the invading pathogen alters normal body functions (aka morbidity)
\
Virulence →
Degree of pathogenicity (how easy is it for the organism to cause disease)
\
Severity →
The extent of organ system derangement or physiologic decompensation for a patient (how harmful is the disease)
Results if the invading pathogen alters normal body functions (aka morbidity)
\
Virulence →
Degree of pathogenicity (how easy is it for the organism to cause disease)
\
Severity →
The extent of organ system derangement or physiologic decompensation for a patient (how harmful is the disease)
72
New cards
Virulence Factors
Contribute to Virulence
\
Adhesion factors/Biofils
Extracellular enzymes
Toxins
Antiphagocytic factors
\
Adhesion factors/Biofils
Extracellular enzymes
Toxins
Antiphagocytic factors
73
New cards
Stages of Infectious Disease
Incubation Period
Prodromal Period
Illness
Decline
Convalescence
\
*See image for details*
Prodromal Period
Illness
Decline
Convalescence
\
*See image for details*
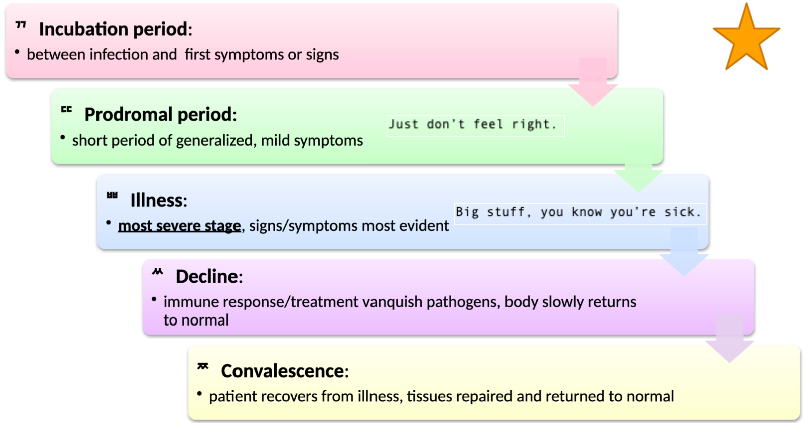
74
New cards
Portals of Exit
How pathogens leave the host - Many are the same as portals of entry
\
Bodily secretions
*Earwax, tears, nasal secretions, saliva, sputum, respiratory droplets*
Blood
Vaginal secretions or semen
Breastmilk
Bodily wastes
*Urine, excrement, sweat*
\
Bodily secretions
*Earwax, tears, nasal secretions, saliva, sputum, respiratory droplets*
Blood
Vaginal secretions or semen
Breastmilk
Bodily wastes
*Urine, excrement, sweat*
75
New cards
Modes of Transmission
Contact →
DIrect, indirect (fomites), droplets
*Fomites = inanimate object involved in indirect transmission*
\
Vehicle →
Airborne, waterborne, foodborne, fecal-oral, bodily fluids
\
Vector →
Arachid, insect
\
Preinatal →
Mom to baby
DIrect, indirect (fomites), droplets
*Fomites = inanimate object involved in indirect transmission*
\
Vehicle →
Airborne, waterborne, foodborne, fecal-oral, bodily fluids
\
Vector →
Arachid, insect
\
Preinatal →
Mom to baby
76
New cards
Disease Vectors
Vectors are Arthropods that transmit pathogens
\- Insects, arachnids
\
Mechanical vectors: passively carry the pathogens only
\- Flies, cockroaches
\
Biological vectors: serve as host for pathogen
\- Mosquitoes (most common of all vectors)
\- Ticks, fleas, lice, tse tse flies, sand flies, reduviid bug, mites
\- Insects, arachnids
\
Mechanical vectors: passively carry the pathogens only
\- Flies, cockroaches
\
Biological vectors: serve as host for pathogen
\- Mosquitoes (most common of all vectors)
\- Ticks, fleas, lice, tse tse flies, sand flies, reduviid bug, mites
77
New cards
Epidemiology
Frequency or occurrence of disease
Frequency or occurrence of disease
Incidence →
Number of new cases of a disease in a given area/population during a given period of time
\
Prevalence →
Number of total cases of a disease in a given area/population during a given period of time
Number of new cases of a disease in a given area/population during a given period of time
\
Prevalence →
Number of total cases of a disease in a given area/population during a given period of time
78
New cards
Case Fatality Rate
Number of fatalities divided by the number of confirmed cases
79
New cards
Crude (population) Mortality (fatality) Rate
Number of fatalities divided by the total population
80
New cards
Epidemiology
Frequency/Geography of Disease
Frequency/Geography of Disease
Endemic →
Disease that typically occurs at regular intervals at a relatively stable incidence within a given population or geographical area
\
Sporadic →
Only a few scattered cases within an area or population
\
Epidemic →
Occurs at a greater frequency than is usual for an area or population
\
Pandemic →
An epidemic that occurs simultaneously on more than one continent
Disease that typically occurs at regular intervals at a relatively stable incidence within a given population or geographical area
\
Sporadic →
Only a few scattered cases within an area or population
\
Epidemic →
Occurs at a greater frequency than is usual for an area or population
\
Pandemic →
An epidemic that occurs simultaneously on more than one continent
81
New cards
Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs)
aka Nosocomial infections
aka Nosocomial infections
Exogenous →
Pathogen acquired from the HC environment
\
Endogenous →
Normal microbiota within the patient become pathogenic due to factors in the HC setting
\
Iatrogenic →
Results from modern medical procedures
\
*Control = Hand washing! → Most effective way to reduce nosocomial infections*
Pathogen acquired from the HC environment
\
Endogenous →
Normal microbiota within the patient become pathogenic due to factors in the HC setting
\
Iatrogenic →
Results from modern medical procedures
\
*Control = Hand washing! → Most effective way to reduce nosocomial infections*
82
New cards
Notifiable Diseases
*See image*
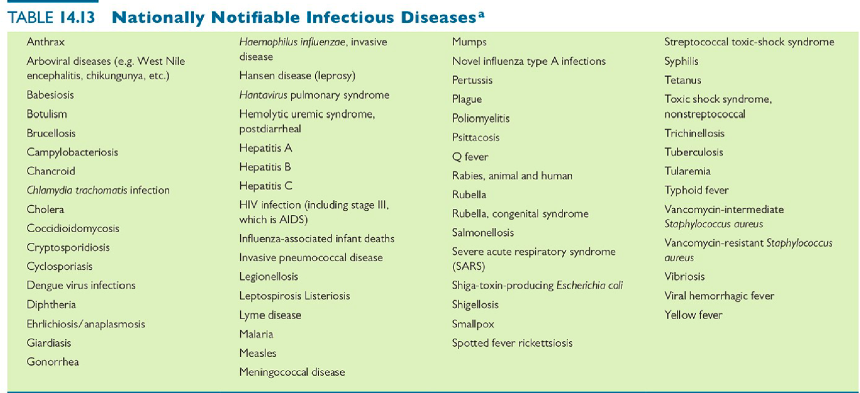
83
New cards
Basic Principles of Microbial Control
Sterilization →
Removal or destruction of all microbes, including viruses and bacterial endospores, in or on an object
\
Aseptic →
An environment or procedure that is free of contamination by pathogens
\
Disinfection →
Use of physical or chemical agents known as disinfectants to inhibit or destroy microorganisms
*Does not guarantee that all pathogens are eliminated*
\
Antisepsis →
When a chemical used on skin or other tissue (human tissue), the process is called antisepsis and the chemical is called an antiseptic
\
Degerming →
Removal of microbes from a surface by scrubbing
\
Sanitization →
Process of disinfecting places and utensils used by the public to reduce the number of pathogenic microbes to meet accepted health standards
\
Pasteurization →
Use of heat to kill pathogens and reduce the number of spoilage microorganisms in food and beverages
\
\-stasis/-static →
Suffixes to indicate that a chemical or physical agent inhibits microbial metabolism and growth
\
\-cide/-cidal →
Refers to agents that destroy or permanently inactivate a particular type of microbe
Removal or destruction of all microbes, including viruses and bacterial endospores, in or on an object
\
Aseptic →
An environment or procedure that is free of contamination by pathogens
\
Disinfection →
Use of physical or chemical agents known as disinfectants to inhibit or destroy microorganisms
*Does not guarantee that all pathogens are eliminated*
\
Antisepsis →
When a chemical used on skin or other tissue (human tissue), the process is called antisepsis and the chemical is called an antiseptic
\
Degerming →
Removal of microbes from a surface by scrubbing
\
Sanitization →
Process of disinfecting places and utensils used by the public to reduce the number of pathogenic microbes to meet accepted health standards
\
Pasteurization →
Use of heat to kill pathogens and reduce the number of spoilage microorganisms in food and beverages
\
\-stasis/-static →
Suffixes to indicate that a chemical or physical agent inhibits microbial metabolism and growth
\
\-cide/-cidal →
Refers to agents that destroy or permanently inactivate a particular type of microbe
84
New cards
Relative susceptibility of microorganisms
Prions, endospores = most resistant
\
Gram (+) bacteria, enveloped viruses = least resistant
\
Gram (+) bacteria, enveloped viruses = least resistant
85
New cards
Why are Gram (-) bacteria more resistant to antimicrobials?
They have a double phospholipid bilayer and lipid A in cell wall
\
They tend to have more R plasmids
\
They tend to have more R plasmids
86
New cards
Physical Methods of Microbial Control
*See Image*

87
New cards
10 Major Categories: Chemical methods of microbial control
*See Image*
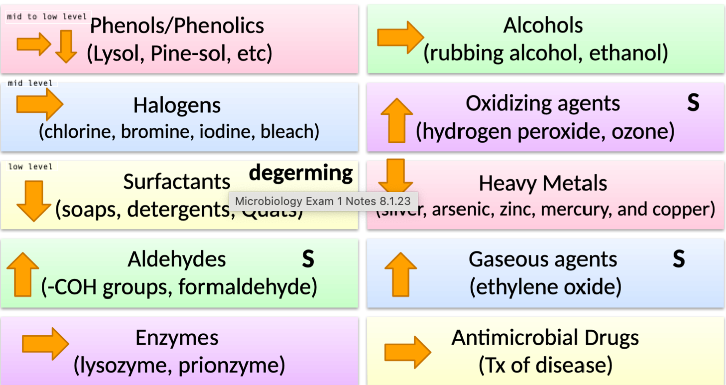
88
New cards
After performing the gram stain, you notice that the cells under the microscope are purple. What is the type of bacteria?
Gram +
89
New cards
Which of the following is used in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes
90
New cards
Which one of the following is a differential stain?
Gram stain
91
New cards
A cell would swell in what type of solution?
Hypotonic
92
New cards
Which one of the following would be most sensitive to antibiotics that interfere with peptidoglycan formation?
Gram +
93
New cards
Which one of the following would be most sensitive to change in tonicity?
Mycoplasma → Wall-less
94
New cards
Endospores are produced primarily by which of the following genera
Clostridium and bacillus
95
New cards
When performing an endospore stain the endospores will appear
Green
96
New cards
Plasmids that carry antibiotic resistance genes are called
R Factors
97
New cards
A rod bacterial cell shape is called what?
Bacillus
98
New cards
Bacteria that have a cell arrangement in a chain is called?
Strepto-
99
New cards
A square of four bacterial cells could be called what?
Tetrad
100
New cards
What is the most common type of bacterial cell division?
Binary fission