materials test 2
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
3 Stages of Fatigue
Initiation
Propagation
Final Fracture
Cyclic Loading
Application of repeated or fluctuating stresses and strains to a component
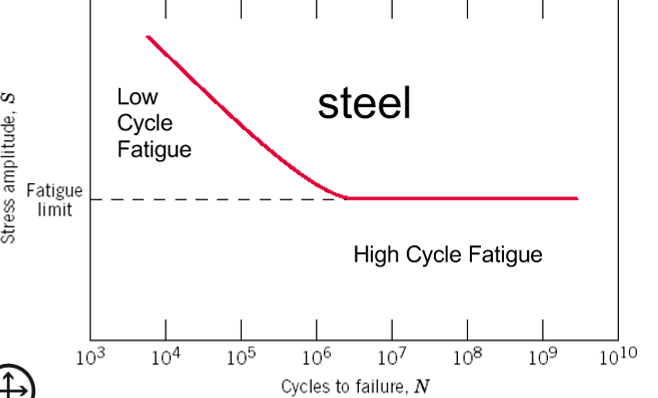
Fatigue Limit
the stress amplitude below which fatigue failure will not occur
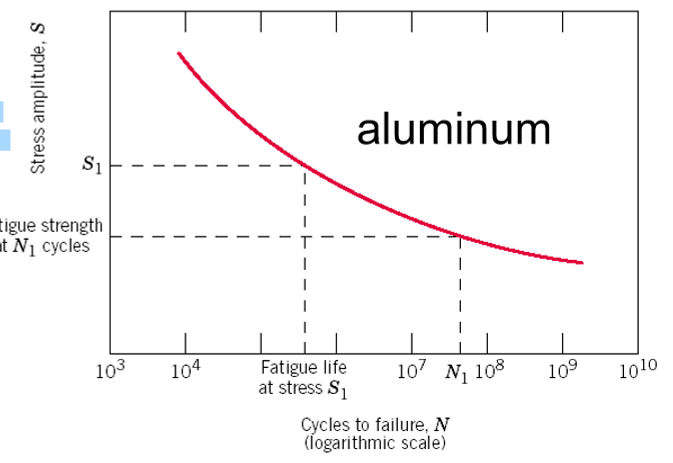
Fatigue Strength
The stress amplitude value for failure to occur in a specified number of cycles
Striations
micro-scale features indicating crack origin and growth characteristics
Beachmarks
macro-scale features visible by the eye, usually associated with periodic start-up and shut-down operation (one line per start-up and shut down). Does NOT reflect load cycles
Tensile stress is needed for crack growth
FALSE. Cracks will not grow if only compressive stresses are present.
3 Factors affecting Fatigue Life
Mean Stress
Surface Treatments
Design Factors (reduce stress concentration areas)
Surface Treatments
Case Hardening
Shot Peening
Case Hardening
Material maintains toughness but has a harder (wear resistant) surface
Shot Peening
Compressive surface stresses to delay crack initiation
Creep
time dependent plastic deformation at high homologous temperatures
Creep Strain
Primary
Strain which occurs after the first instantaneous change ( ɛ = ε_c + ε_E+ε_P)