6: Ohm's law
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
remember to
demonstrate understanding that the temperature of the wire is kept constant using a switch and small currents;
recall that this shows that the current and voltage are proportional for a metal wire at constant temperature, and that this is known as Ohm’s law.
apparatus
1m length of constantan wire, a metre rule, a low voltage power pack, a variable resistor, a voltmeter, an ammeter, connecting leads, a switch, 2 crocodile clips, Sellotape.
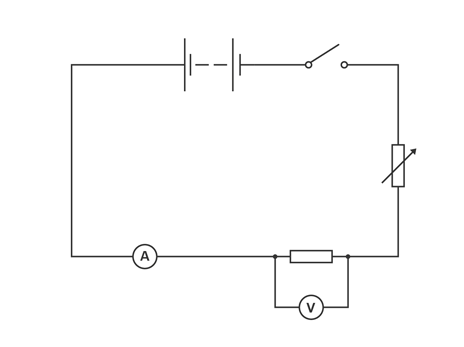
Method
Set up the circuit,
Adjust the variable resistor until the current on the Ammeter is 0.1 A. Record the current in a suitable table.
Read the corresponding value of voltage across the wire on the voltmeter and record in the table.
Turn the switch off between all readings to prevent the temperature of the wire rising.
Turn on again. Ensure that the current is still 0.1 A and repeat the voltage reading. Calculate the average voltage.
Repeat the procedure for six values of current up to 0.7 A.
Avoiding errors
The temperature of the wire must be kept constant.
To ensure the temperature of the wire does not increase, switch off between readings and keep the current as small as possible.
Read the ammeter and voltmeter accurately by reading the scale from directly above the pointer or use digital instruments
independent variable
electric current
dependent variable
voltage
controlled variable
material , length, cross section area and temperature of the wire
risks
hazard | Consequence | Control measures |
Water | Electric shock | Do not set up the experiment near taps, sinks etc. |
Wire gets hot | Minor burns | Do not handle the wire. Switch off between readings. |
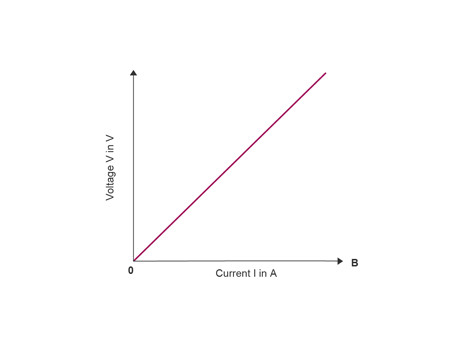
conclusion
as the current increases the voltage also increases.
its directly proportional provided all physical conditions such as temperature remain cosntant
ohms law equation
voltage V = current I x resistance R
V= IR
V = voltage in V
I = current in A
R = resistance in Ω (ohms)