Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
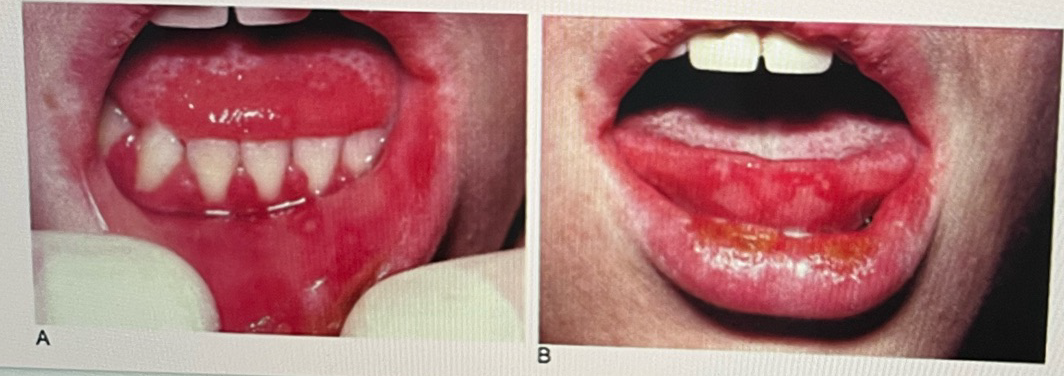
Determine the disease
Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
Common oral disease which develops in both children and young adult
Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis develops in both [?] and [?]
children
young adult
Who suggested that the primary form is probably more common in older adults? (HSV1)
sheridans and hermann
Sheridans and hermann suggested that primary form is probably more common in [?], (?)
older adults
HSV1
Clinical features of Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis (x7)
Develops in both children and young adults
Rarely occurs before 6 months because of the circulating antibodies in the infant derived from the mother
The disease occurring in children is frequently the primary attack and is characterized by development of fever, irritability, headache, pain upon swallowing and regional lymphadenopathy
Within few days mouth become painful and the gingiva intensely inflamed
The lips, tongue, buccal mucosa, pharynx, and tonsils may also be involved, Shortly, yellowish fluid filled vesicle develop. These ruptures and form shallow, ragged extremely painful ulcers covered by fray membrane and covered by an erythematous halo
The gingival inflammation precedes the formation of ulcers by several days. The ulcers vary in size, from tiny to several millimeter in diameter
They spontaneously within 7-14 days and leave no scar
Could be isolated from facial, labial, and oral herpetic lesions for 2-6 days
HSV1
Could be isolated from genital lesions for 2-14 days
HSV2
HSV1 could be isolated from [?] for 2-6 days
facial, labial, and oral herpetic lesion
HSV1 could be isolated from facial, labial, and oral herpetic lesions for [?]
2-6 days
HSV2 could be isolated from [?]s for 2-14 days
genital lesions
HSV2 Could be isolated from genital lesions for[?]
2-14 days
Could be isolated from patients suffering from a gingivostomatitis with particular clinical configuration
herpes simplex virus
histologic features of primary herpetic ginginvostomatitis
Herpetic vesicle is an intraepithelial blister filled with fluid
Degenerating cells show “ballooning degeneration”
Other cells contains intranuclear inclusions called lipschutz bodies
The subjacent connective tissue is usually infiltrated by inflammatory cell
When the vesicle ruptures the surface of the tissue is covered by an exudate filled fibrin, PMNL and degenerated cells
Herpetic virus may be recovered from [?] of patient during the course of the disease
saliva
Mode of transmission of Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
Transmission may occur by droplet infection
Direct contact with affected person
Commonly associated with pneumonia, meningitis and common cold
Incubation period range from 2-20 days
Occasional epidemics in an orphanage nursery
Treatment Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
Treatment is unsatisfactory because of the disease is unalterable
Antibiotic therapy to prevent secondary infection