Long bone and osteos
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Long bone
Humerus, femur, tibia, phalanges
Short bones
Carpels and tarsals
Flat bone
Cranial, sternum
Irregular bones
Coral, vertebrae, scapula
Sesamoid bones (round bones)
Patella
Osteoblasts
These are the bone forming cells
Secrete the college in ground substance constitudes unmineralized bone
Responsible for classification of the matrix
Osteocytes
Mature bone cell
Synthesize in breakdown the matrix to maintain homostasis
Each osteocytes occupies a space of the lacuna
Osteoclasts
Large multinucleated cells
Function is to reabsorb or eat bone or break down bone
Dissolves matrix with acids and hydrolytic enzymes phagocytes
When do osteoclasts and osteoblasts turn into osteocytes
When you mature around the age 25
What happen to the osteoblasts and osteoclasts when you mature
They popped back up to help with repair
Osteocytes do both jobs of what
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts
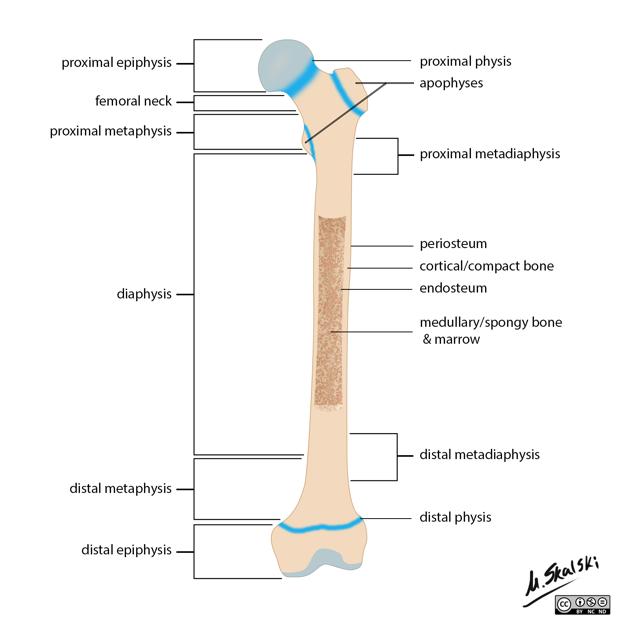
Diaphysis
Shaft with contact bone and medullary cavity.
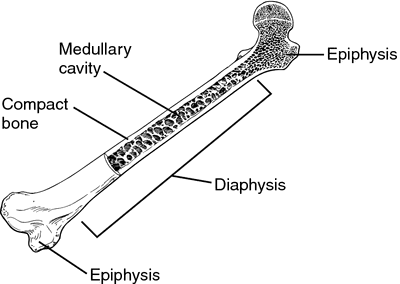
Epiphysis
Ends articular cartilage and compact bone covering cancellous bone
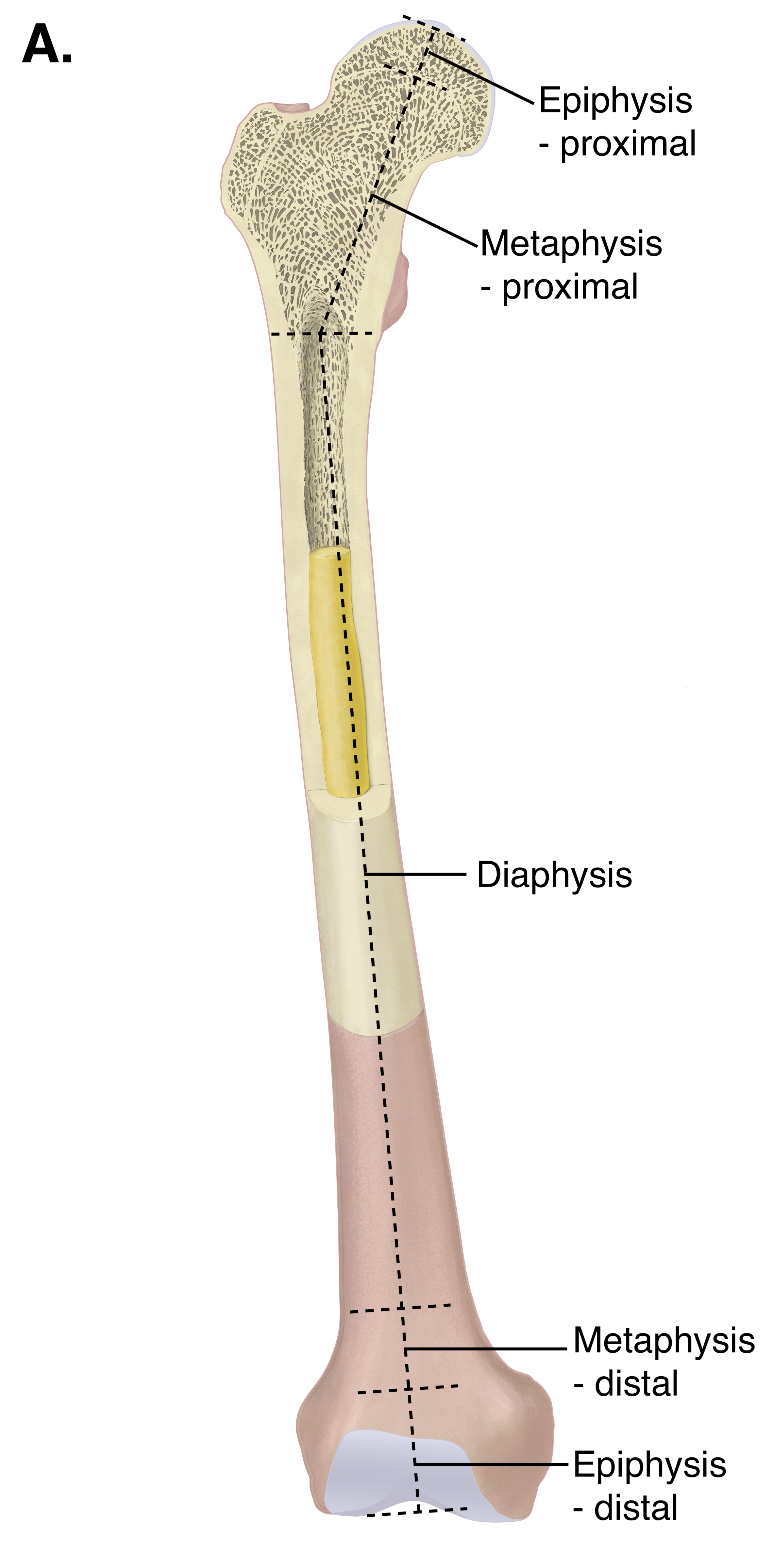
epiphyseal line
Between epiphysis and diaphysis - Region of bone growth
Also known as epiphyseal plate or growth plate

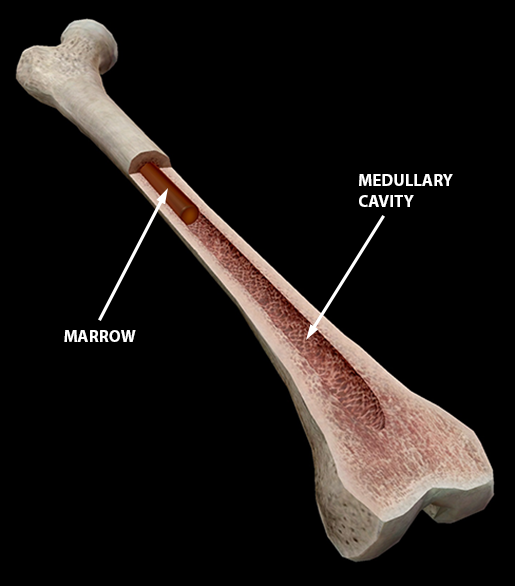
Medullary cavity
Filled with yellow bone marrow
Articular cartilage
Hyaline cartilage on the ends of longbones
Periosteum
Vascular covering of fibrous tissue
Completely enclosed outside of the bone
Rich supply of nerves and blood vessels
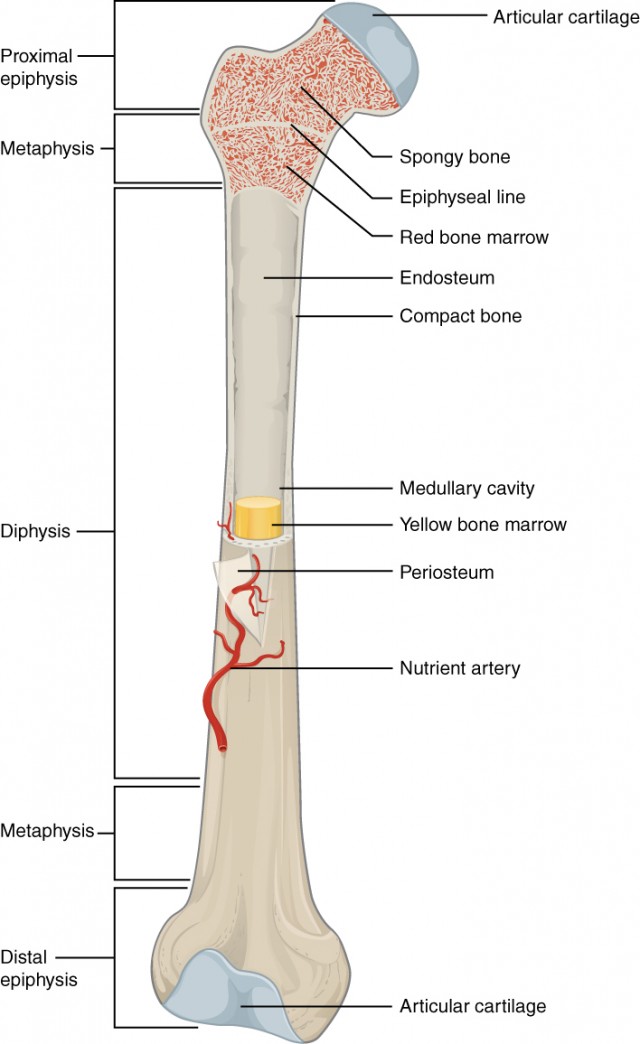
Endosteum
Cellular layer contains cytes, clasts and blast.
Covering trabeculae and lines inner shafts of bones
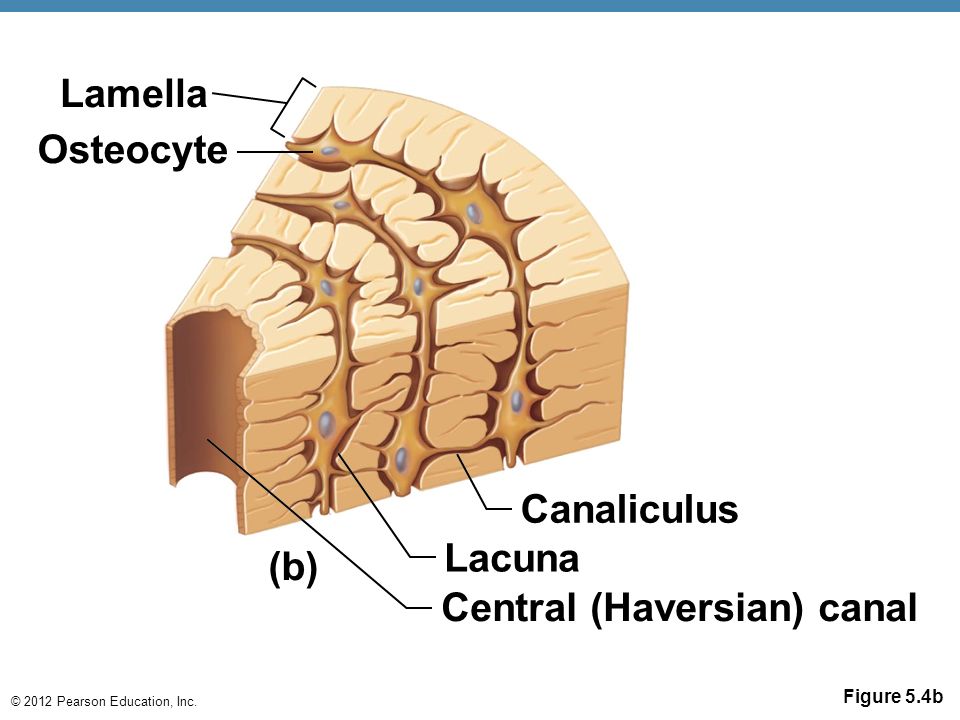
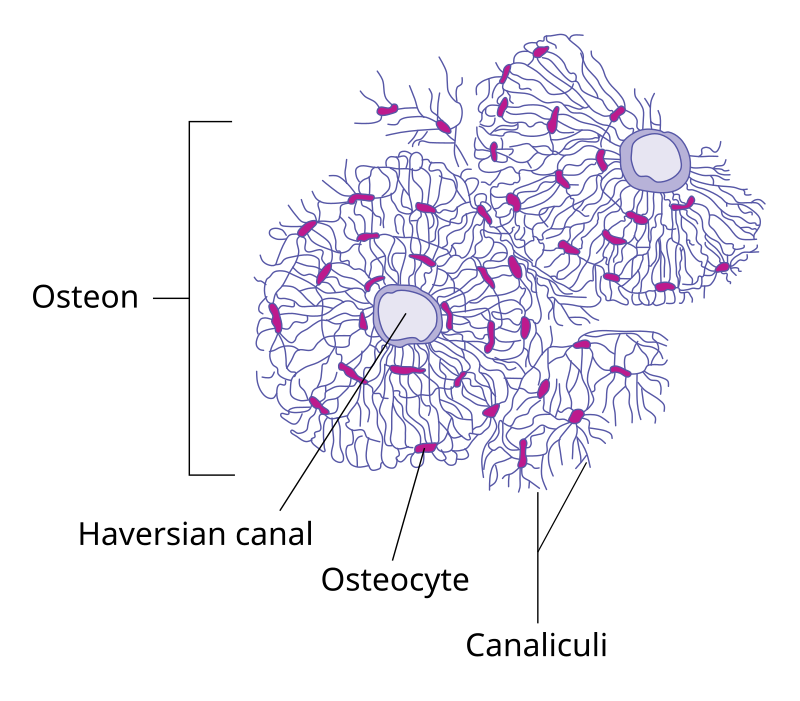
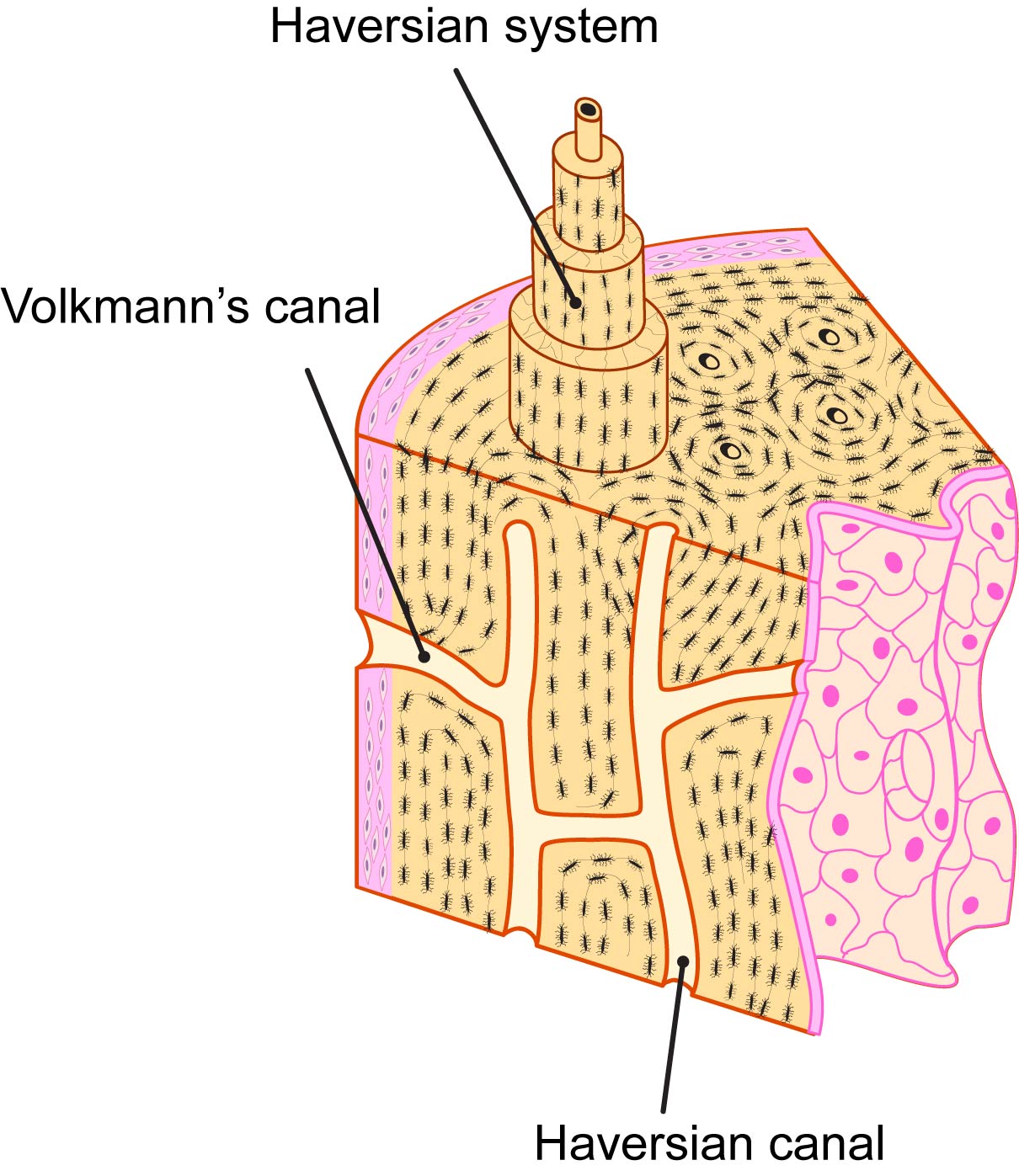
Haversian system is also known as
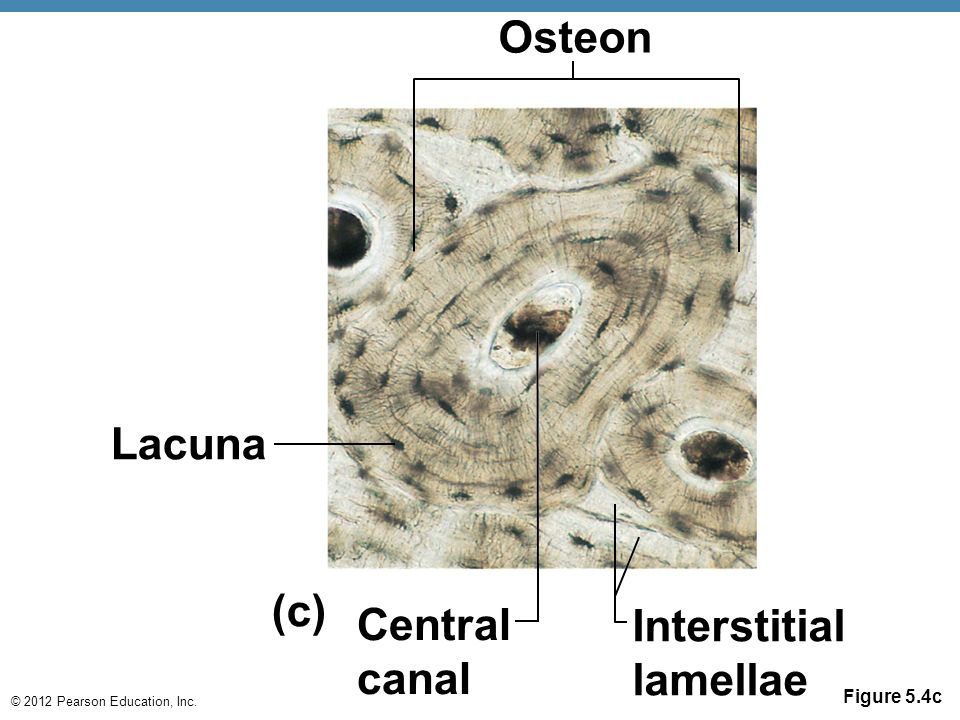
Osteon
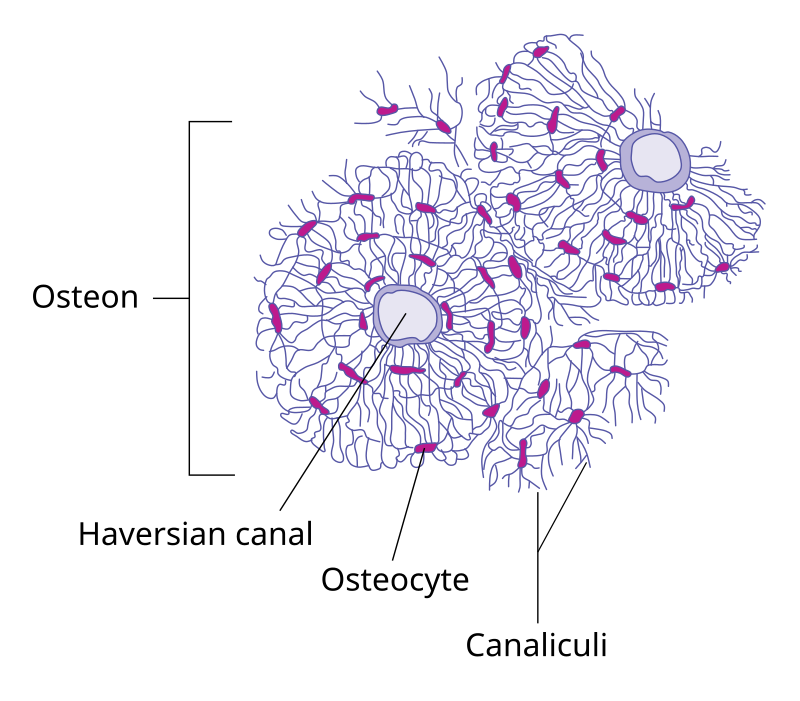
Central Haversian canal or osteonic canal
Pathway for blood vessels and nerves
Volkmann's canals or preforating canal
Right angle to central canal connects Haversian canal to another Haversian canal. Communication
Osteocytes in lacuna
Between lamellar layers
Canaliculi
Communicate - connects lacunae - lacunae and Haversian canal
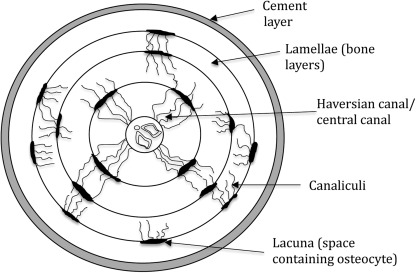
Lamella
Concentric rings