Social influence
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
How are norms different to beliefs?
They exist externally (are extrinsic) and result in an individual forming an intrinsic belief.
What study can we use to demonstrate the effects of social norms on individual beliefs?
The Auto-Kinetic Illusion (AKI) (Sherif, 1935)
Where do social norms come from?
Socialisation processes
Who challenged the idea that human cooperation is due to socialisation processes^?
(Warneken & Tomasello, 2006)
What did they show instead^?
That human children are capable of helping others achieve their goals, even when they receive no immediate benefit, suggesting that human cooperation (social norms) may have some level of innateness.
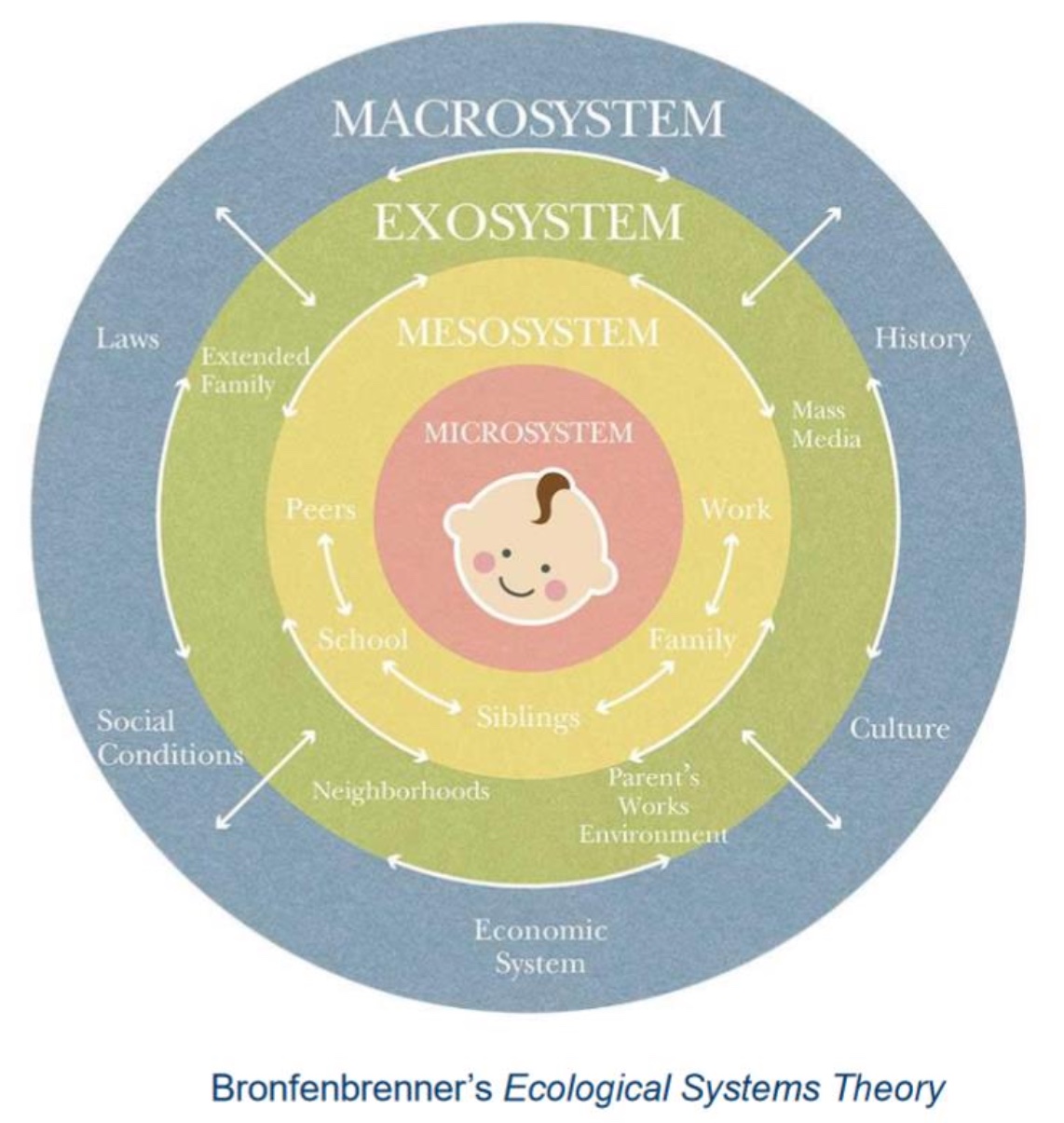
What is the ecological systems theory?
The idea that human development is influenced by a complex set of nested environments, ranging from immediate surroundings like family and school (microsystem) to broader societal factors like culture and government (macrosystem).
Is social conformity psychologically rewarding?
(Campbell-Meiklejohn, 2010) found that, using fMRI, when participants agreed with expert reviewers about the value of a piece of music, it activated the ventral striatum, a brain region involved in processing rewards
(Klucharev, 2009) showed that when individuals' judgments of facial attractiveness conflicted with group opinions, it triggered a "prediction error" response in the ventral striatum and the strength of this neural response predicted how much individuals would adjust their behavior to conform
What is conformity?
Everybody does something, and you follow
What is compliance?
Somebody requests that you do something, and you choose to comply.
What is obedience?
You are being ordered to do something, and you obey.
Who came up with the return potential model (RPM)?
(Jackson, 1965)
What is the RPM?
The representation of a social norm as the distribution of potential approval and disapproval by others for various alternatives of a person’s behavior along a continuum.
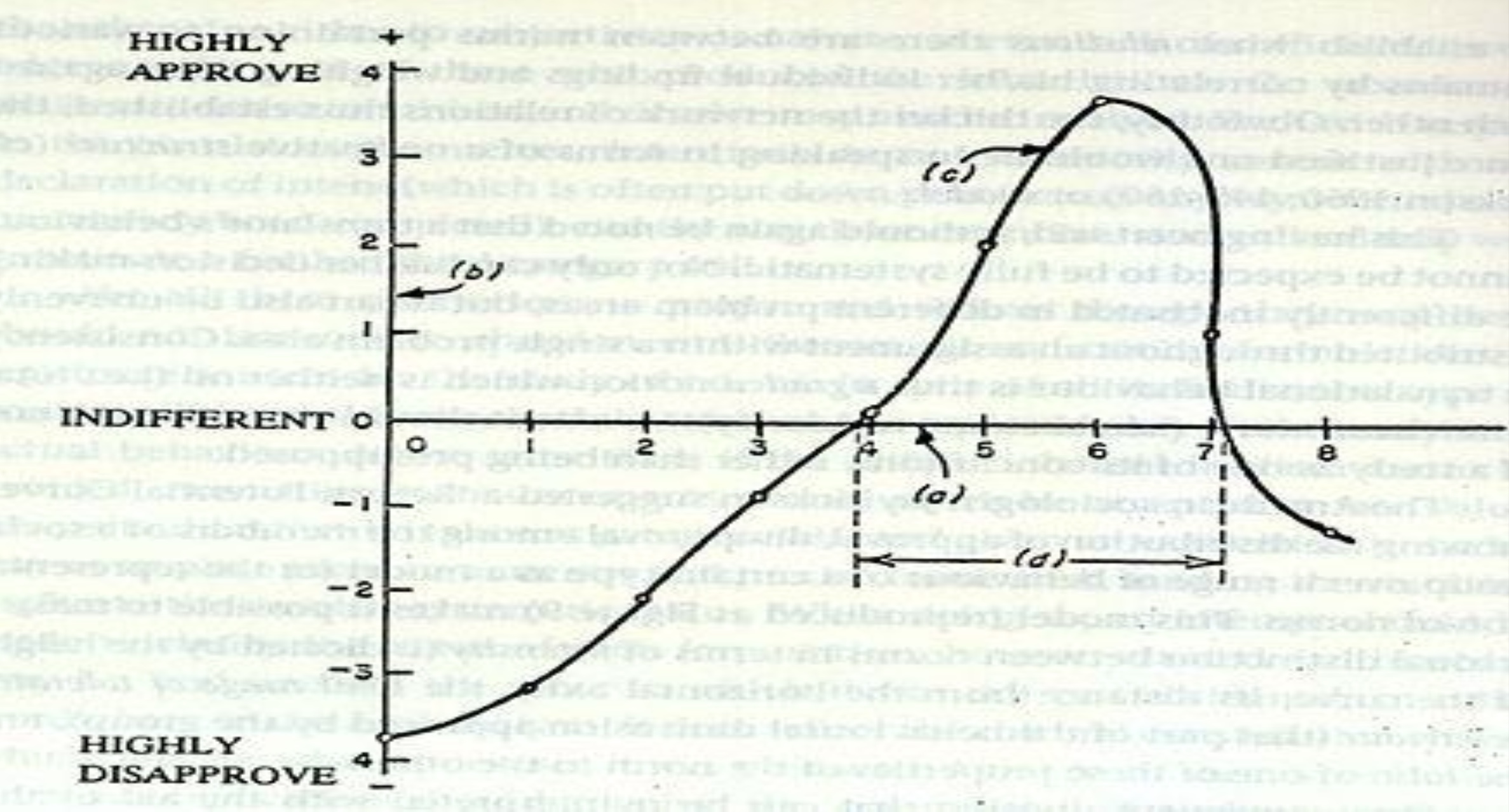
What are the structural characteristics of norms (according to the RPM)?
Point of maximum return
Range of tolerable behaviour
Norm intensity
Norm crystallisation
Normative power
It assumes that norms are static and are shared uniformly
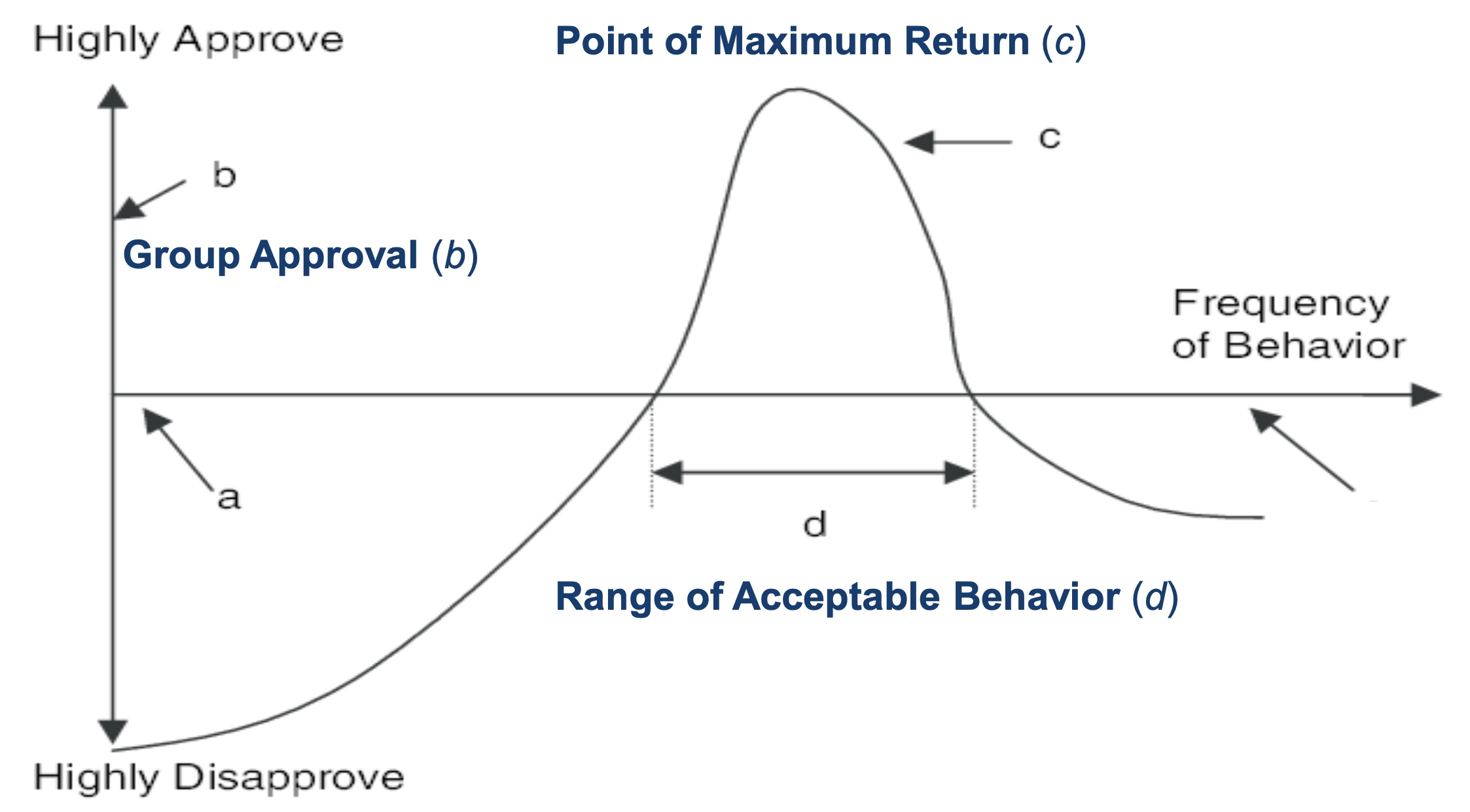
What is the point of maximum return?
The greatest y coordinate and the desirable norm (maximum social approval).
What is the range of tolerable behaviour?
The area under the curve, the range of behaviour that the group find acceptable.
What is norm intensity?
The total area of the curve (positive and negative) - how much the group cares about the norm.
What is norm crystallisation?
The degree of variance within the curve - the degree of agreement (group consensus) about the approval or disapproval of a behaviour.
Measured by the spread of the curve (narrower spread = more crystallised)
What is normative power?
Norm intensity x norm crystallisation
^Demonstrates pressure to conform
Who conducted research using the RPM and what did they show?
(Glynn & Huge, 2007) analysed telephone survey data and found that people’s opinions can influence how often they talk about certain topics
What is informational social influence?
When individuals conform to others' behaviors or opinions because they believe those others have accurate information. It is driven by the desire to be correct or make accurate judgments.
What is normative social influence?
When individuals conform to others' behaviors or opinions in order to be liked, accepted, or avoid social rejection. It is driven by the desire to fit in with a group or adhere to social norms.
What are descriptive and prescriptive (injunctive) norms?
Descriptive = informational influence
Prescriptive = normative influence
What is the focus theory of normative conduct?
It suggests that individuals' behaviors are influenced by social norms primarily when these norms are made focal or salient in a given context.
Who studied this idea and what was their experiment^?
(Cialdini, 1990) explored how injunctive norm-focus procedures promote socially desirable behavior, specifically the norm against littering. In the experiment, participants conformed to this norm only when the norm was made salient.
A heavily littered environment, made littering more common (made descriptive norms salient)
Who replicated this study and what were their conclusions^?
(Bergquist, 2021)
Clean environments lead to less littering (agrees with original study)
Adding a single piece of litter to a clean environment did not reduce littering as expected, and instead it led to more littering (disagrees)
Adding a single piece of litter made people more aware of the rule against littering. However, as more litter built up, the pressure to follow the anti-littering rule became weaker, suggesting that people's behavior is influenced by both the presence of litter and the social norms around it, and that these influences can change as the situation develops
How can we explain the influence of norms on behaviour?
Socio-cognitive processes (whether they are salient for a given behaviour in a specific situation)
What type of norm is made salient (descriptive, prescriptive, etc.)
When are norms most likely to influence behaviour?
Norms are intense
Norms are crystallized (high consensus)
Norms are focal to the behavior in question
Norms are active/salient in consciousness
Norms are expressed by a valued referent (in)-group
Norms are internalized over time
What can we use consensus to do?
To create and change social norms
What is the advantage of following social norms?
It is often adaptive because it reduces the cost of individual learning, allowing much of human social behavior to become automated (it helps us learn from others rather than figuring it out ourselves).
What was (Milgram, 1969) study?
It showed that, with an increasing crowd size, a greater proportion of pedestrians also adopted the behavior of looking up (social conformity).
Who investigated the idea of norms as a decision-heuristic and what did they show?
(Cai, 2009) showed that when customers were provided with rankings of the five most popular dishes, the demand for those dishes increased by 13% to 20%. However, no significant saliency effect was found (simply making the dishes more prominent did not have a strong or meaningful impact on customer behavior).
What is the bias-variance dilemma?
Individuals can either make overly simplistic assumptions about situations (bias) or be overly sensitive to small changes and inconsistencies (variance), and the challenge is to find a balance where behaviors are flexible enough to adapt to new situations without being too rigid or too erratic.
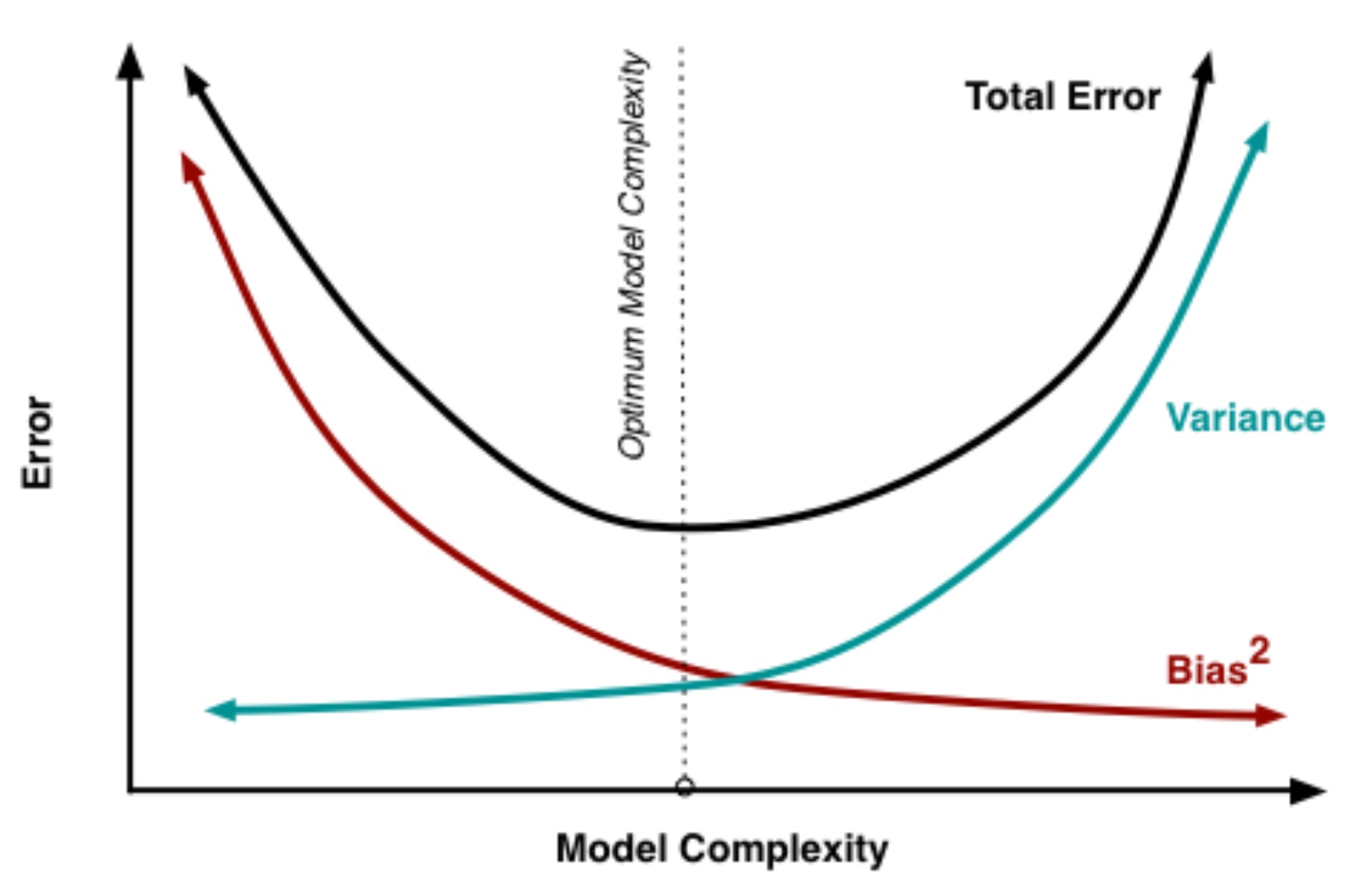
What is total judgement error?
Variance + bias
Use of heuristics can result in…
…lower total error (low variance and high bias)
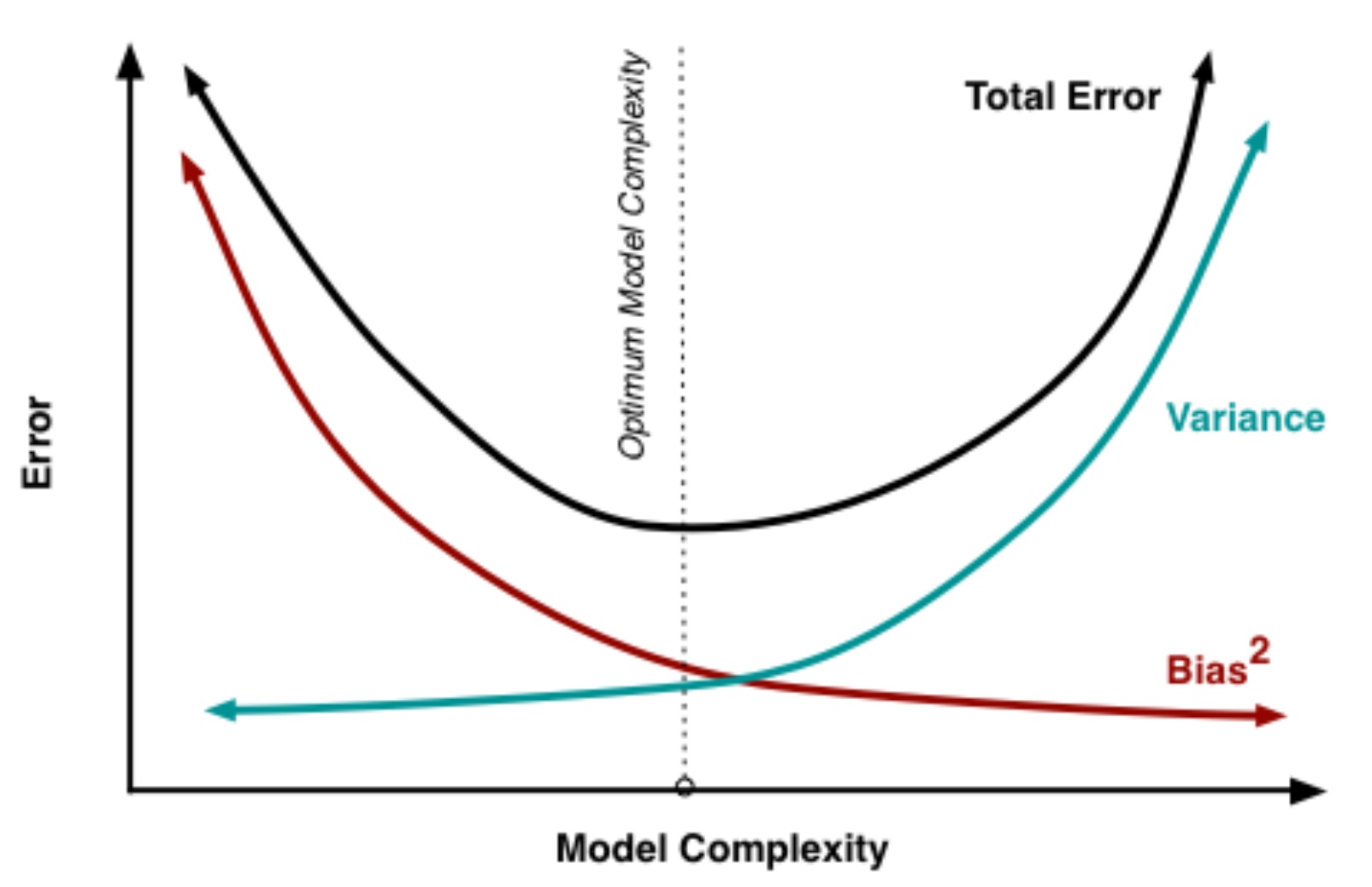
Why is low variance and low bias not possible?
Because in order to achieve low bias you need to take into account all relevant information (big comprehensive decision-model) which means you are increasing the variance in your estimates.
What happens when the bias is too large?
Low variance doesn’t compensate sufficiently
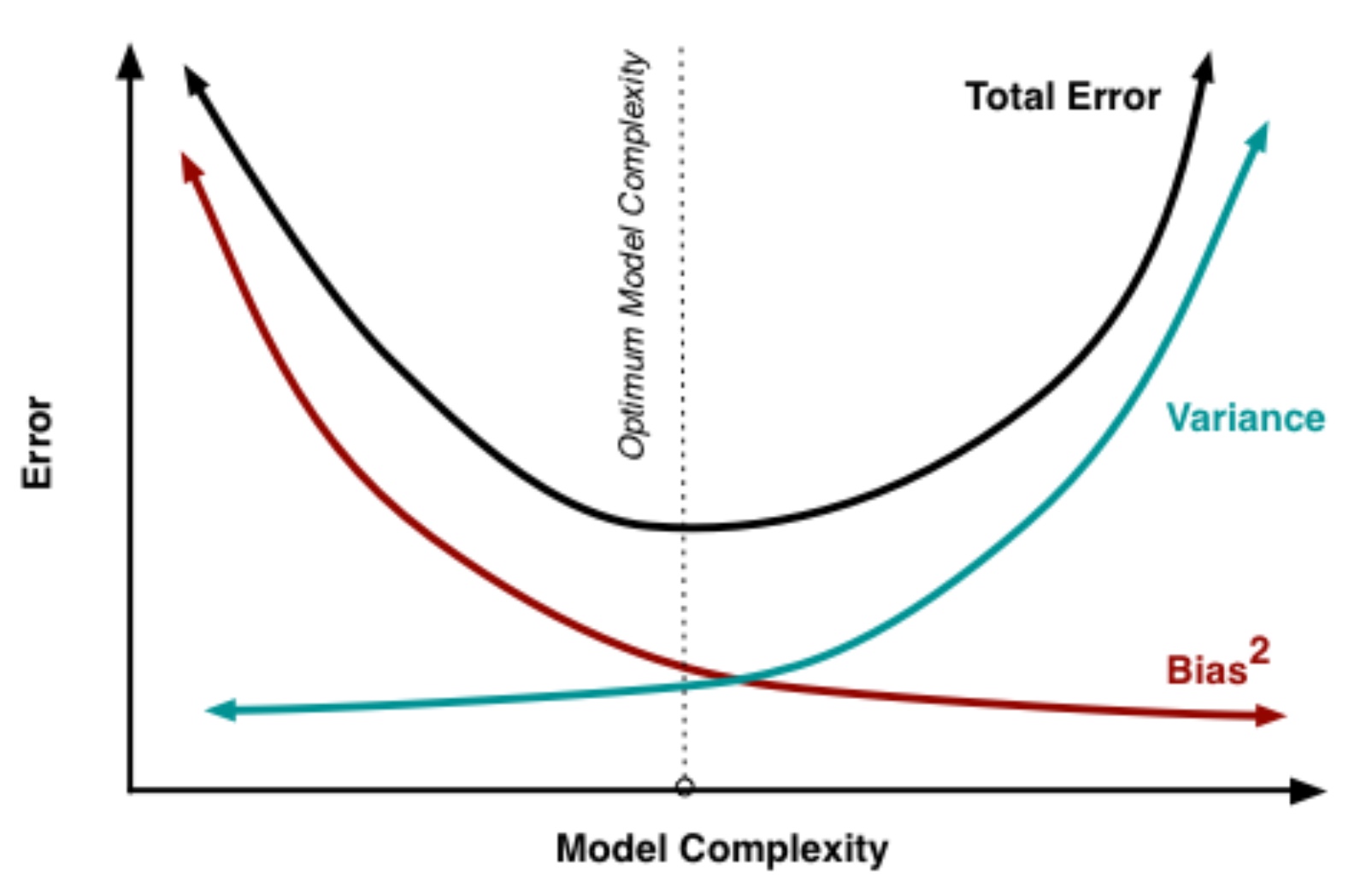
Where would we place stereotypes on this graph?
Low variance (they apply an exaggerated average to an individual)
High bias (aren’t accurate)
What is the wisdom of the crowd?
The idea that the collective judgment or decision-making of a large group of people is often more accurate or reliable than that of an individual expert, as long as the group is diverse and independent in its thinking.
What is Condorcet’s Jury Theorem?
It suggests if each member of a jury (or group) has a better-than-even chance of making the correct decision, then as the size of the jury increases, the probability of the group making the correct decision approaches 1 (or certainty).

What are the four conditions for wisdom of the crowd?
Diversity of opinion
Independence
Decentralisation
Aggregation
Who studied decentralisation and what did they show^?
(Becker, 2017)
In decentralised communication networks, where individuals interact without central control, social influence can actually improve the accuracy of group estimates
Shows how network structure affects group accuracy: in centralized networks, where a few individuals dominate, group estimates are more likely to become less accurate
Who looked at alcohol use^?
(Baer & Carney, 1993) - Students overestimate how much alcohol their peers are drinking compared to themselves.
What did (Prentice & Miller, 1993) study show?
Evidence of pluralistic ignorance, where students believed they were more uncomfortable with campus alcohol practices than the average student.
What was the best way to combat drinking problems in college?
(Haines & Spear, 1996)
Initially, a traditional intervention with educational presentations was unsuccessful
The intervention was followed by a media campaign, including display advertisements and weekly classified ads in the campus newspaper. This led to an 18.5% decrease in students who perceived binge drinking as the norm
The results suggest that altering students' perceptions of drinking norms can reduce binge drinking behaviors
What might we call this type of intervention^?
Social norm intervention
What is the Gateway Belief Model (GBM) (Van der Linden, 2017)?
It suggests that individuals' beliefs about the social norms and behaviors of others serve as a ‘gateway’ influencing their own behaviors.
Who studied the gateway belief model and what did this study show^?
(Van der Linden, 2017) - found that when people learn that most scientists agree on something, it can actually reduce bias and help people become less extreme in their views - showing that sharing facts the right way can make a positive difference.
Who came up with social judgement theory?
(Hovland & Sherif, 1980)
What is social judgement theory?
It suggests that people evaluate new information based on their existing attitudes and beliefs, categorizing it as acceptable, objectionable, or neutral, and that these evaluations are influenced by the perceived discrepancy between the new information and their current views.
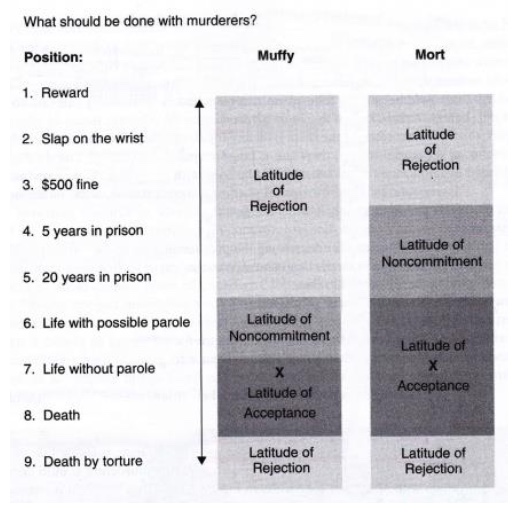
What is the spread-activation model?
It assumes that people's knowledge of the world is organized into a network of ideas based on their experiences. When a word is activated, it spreads to related words in the network, making them more likely to be recalled.
Who conducted an experiment investigating the spread-activation model and what did they show^?
(Keizer, 2008)
It suggests that visible signs of disorder, like graffiti and litter, can trigger more disorderly behavior
They found that when people observe others violating social norms or rules, they are more likely to engage in similar violations, causing disorder to spread
This suggests that the presence of minor violations can encourage further misconduct
What about prosocial norms?
(Nook, 2016)
Participants who observed generous donations to charities were more likely to donate themselves and later engage in supportive behaviors, such as writing encouraging notes
Observing empathic group responses not only increased participants' own empathic feelings but also influenced their subsequent donations to a homeless shelter
What are social tipping points?
The point where a vicious cycle turns into a virtuous one or vice versa (e.g. if there are more men than women in top leadership positions, it’s more likely that men will be hired and serve on subsequent hiring committees, leading to more men in top positions and even fewer women).
They show how norms can change quickly
Who looked at conformity in collectivist and individualist cultures?
(Smith & Bond, 1996) - That collectivist cultures had a significantly higher rate of conformity than cultures classified as individualistic.
X Who else experimented with the idea of social tipping points and what did they show?
(Centola, 2018)
Shows how minority groups can initiate social change and establish new social conventions by reaching a "critical mass" in a system of social coordination
Once a minority group reaches the critical size needed to trigger change, they can successfully overturn established behaviors
The required critical mass varies depending on the specific features of the social context
What about conformity to norms in other animals?
(Whiten, 2005)
Researchers trained female chimpanzees in two groups to use different techniques for obtaining food
When reintroduced, other chimps copied the method used by the expert in their own group
Over time, each group kept using their own method, showing that chimps can develop and pass on their own group traditions
What is the norm-activation model of prosociality (Schwartz, 1977)?
It suggests that prosocial behavior is activated when individuals become aware of a personal responsibility to help others, which is triggered by the salience of social norms and a sense of moral obligation.
What is the theory of normative conduct?
It suggests that individuals' behaviors are largely influenced by the social norms and expectations within their group, with people striving to align their actions with what is considered acceptable or appropriate in a given social context.
X Who explored the difference between social and moral norms and what did they find?
(Van der Linden, 2021)
Investigated how personal and contextual factors influence the effectiveness of social norm interventions in promoting pro-environmental behavior
The strength of personal moral norms did not influence the effectiveness of social norm messages, but activating moral norms—regardless of their strength—eliminated the effect of social norms on making a pro-environmental pledge
Can social and personal norms change?
(Tankard, 2017)
Found that when people saw the Supreme Court’s same-sex marriage ruling as likely, they were more likely to think support for gay marriage was a common social norm
This shift didn’t change their personal beliefs but did increase their perception of what others believed
Big institutional decisions can shape how we think society feels (perceptions of social norms), even if our own views stay the same
How else might norms change over time?
(Sparkman, 2017)
Found that showing people how behavior is changing over time could encourage them to change their own actions
For example, when people were told that more and more people were eating less meat, they were more likely to want to eat less meat themselves and even order more meatless options at a cafe
The study showed that if people already saw a positive current behavior (like saving water), then showing that this behavior was improving over time made them even more likely to take action
Changing norms over time can motivate people to adopt better behaviors, even if current behaviors are already good