11 urine screening for Metabolic disorders
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Overflow disorders
Caused by an inborn error of metabolism (IEM)
disruption of metabolic pathway causing plasma concentration of specific metabolite to rise
Metabolite surpass renal threshold and appear in urine
Now screened via Tandem mass spec new born screen
Inborn error of metabolism (IEM)
failure to inherit gene that produces necessary enzyme in a metabolic pathway
Renal disorders
Malfunction in tubular reabsorption causing metabolites to enter urine
Amino acid disorder catagories
phenylalanine-tyrosine disorder
branched chain amino acid disorder
tryptophan disorder
cystine disorder
Phenylalanine tyrosine disorders
phenylketonuria
tyrosyluria
alkaptonuria
melanuria
Branched chain amino acid disorders (2 catagories)
Accumilation of early amino acid metabolism products:
maple syrup urine disease
Accumulation of later amino acid metabolism products:
organic acidemias
Typtophan disorder
indicanuria
5-hydroxyindoleacitic acid
cystine disorders
cystinuria
cystinosis
homocystinuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Phenylalanine tyrosine disorder
cannot convert phenylalanine → tyrosine
No melanin bc tyrosine is needed to produce melanin
→ albinism common
Can cause neurological symptoms if phenylalanine builds up too much
Treatment
decreased food intake of phenylalanine and aspartame
aspartame converts into phenylalanine
Babies need special milk!
Children can form alternative pathways to metabolize phenylalanine
Phenylketonuria (PKU) UA
Mousy urine smell
increased keto acids
Ferric chloride test
nonspecific reaction with amino acids
Permanent blue green color
Not used for diagnosis bc screen is used
used for monitoring dietary control
follow up if screen is questionable

Phenylketonuria Blood testing
Tandem mass spec for phenylalanine
can have high false negatives if heel stick screen is too early. best taken after ingestion of milk (containing pheylalanine)
Required by all 50 states, included in all newborn screens
Can also do bacterial inhibition test (Guthrie test)
Guthrie test
Bacterial inhibition test to detect high phenylalanine in blood
heel stick blood is absorbed on paper
paper is incubated on plate with bacillus subtitles and inhibitor in media
If enough phenylalanine is in the blood, the bacteria can overcome the inhibitor and grow around blood disk
can detect serum phenylalanine levels of 180 - 240μmol/L
normal is under 120μmol/L
Tyrosyluria
Phenylalanine tyrosine disorder
excess tyrosine, hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid, hydroxypheylacitic acid
IEM or transient or aquired
transient in premature babies bc liver not mature enough to make enzymes to metabolize tyrosine
aquired liver disease from cirrhosis, alcohol damage, etc can also cause
Tyrosyluria UA
tyrosine and leucine crystal
if cause is liver damage
Ferric chloride test
fading green
Nitroso-napthol test
orange red
Melanuria
Phenylalanine tyrosine disorder
overproduction of melanogin → oxidized into melanin
black urine
overproliferation of melanocytes: usually melanoma
Melanuria UA
Ferric chloride
grey or black precipitate
sodium nitroprusside
red
Ehrlich reagent
red
Alkaptonuria
Phenylalanine tyrosine disorder
accumulation of homogentisic acid in blood, tissue, urine
children: brown, black stained diapers
adults: pigment deposits on body, ear and hands. arthritis from deposits
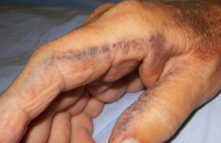
Alkaptonuria UA
ferric chloride
blue
clintitest
yellow precipitate
alkalization of urine → dark color
add silver nitrate, ammonium hydroxide → black urine
Maple Syrup Urine Disease
Branched chain amino acid disorder
IEM
Leucine, isoleucine, valine converted into keto acid
unable to decarboxylate the ketoacid
accumulation of ketoacids
Must detect before d11 birth and restrict diet or else the newborn will fail to thrive
Maple syrup urine disease UA
maple syrup smell
High ketones
DNPH (2,4- dinitrophenylhydrazine)
yellow precipitate
Amino acid chromatography
Organic acidemias
Branched amino acid disorder
symptoms: vomiting, metabolic acidosis, hypoglycemia, ketonuria, increased serum ammonia
IEM, with later metabolite accumilation
Common disorders
isovaleric acedemia
propinoic acedimia
methylmalonic acidemia
Isovaleric acedemia
organic acedemia
branched chain amino acid disorder
urine smells like sweaty feet
Indicanuria
Tryptophan disorder
Intestinal disorders disrupt tryptophan metabolism
normal: tryptophan converted to indole by intestinal bacteria and excreted
Abnormal: obstruction, increased bacteria, malabsorption, IEM can cause excess conversion of tryptophan to indole
Indole reabsorbed → converted to indican in liver → increased indican in blood → indican in urine
Indican colorless → oxidizes to indigo blue
blue diaper sydrome
Hartnup disease
Indicanuria - tryptophan disorder
IEM that effects intestinal reabsorption of tryptophan
Causes abnormalities of renal tubules
Acquired Fanconi syndrome (other aa affected)
Dry red scaly rash, as it oxidized will turn blueish
Muscular incoordination
Treatment with niacin, eat less tryptophan
5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5HIAA)
Tryptophan disorder - carcinoid tumor
malignant tumor can convert tryptophan into seratonin
seratonin broken down into 5HIAA
Increased 5HIAA seen in urine of patients with carcinoid tumors
Cystinuria
cystine disorder
elevated cystine in urine from inability of renal tubules to reabsorb cystine
NOT IEM
Renal disorder
Lysine, arginine, ornathine also not reabsorbed
Cystinuria UA
cystine crystal
renal calculi (most common cause in children)
cyanide nitroprusside
red purple
Amino acid chromatography for lysine, arginine, ornathine
Cystinosis
Cystine disorder
IEM - OVERFLOW DISORDER
Crystalline cystine deposits in cornea (blindness), bone marrow, lymph node, RTE (acquired fanconi)
Bad prognosis compared to cystinuria
renal failure possible
Cystinosis UA
polyuria (decreased reabsorption)
aminoaciduria (decreased reabsorption)
Decreased urine concentration
Homocystinuria
IEM, increase in homocystine
Cataracts, mental retardation, thromboembolic problems, death
Homocystinuria UA
screen: cyanide nitroprusside test
red
Confirmatory: silver nitroprusside test
red
not red for cystinuria
Porphyrins
intermediate compounds in heme production
3 main porphyrins
uroporphyrin
coproporphyrin
protoporphyrin
Porphyria
porphyrin metabolism disorder
IEM or acquired (RBC dysfunction, liver dysfunction, toxins)
symptoms: neurologic, psychiatric, cutaneous photosensitivity
Port red wine colored urine
Porphyria UA
Ehrlich reaction: porphobilinogen
Hoesch test: porphobilinogen
Fluorescence screen
blue - NEG
purple, pink red - POS
Mucopolysacchride disorders
Glycosaminoglycan metabolism issue - IEM
accumulation of GAG in lysosome of connective tissue and excreted in urine
Hurler’s syndrome
Mucopolysacchride disorder
gargoylism
usually fatal in childhood
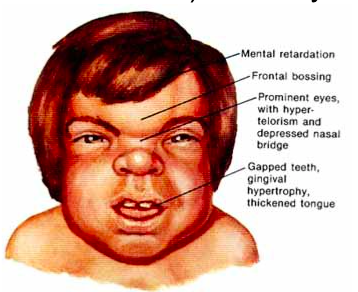
Hunter’s syndrome
Mucopolysaccharide disorder
affects skeleton structure and causes mental retardation
Usually fatal in childhood
Sanfilippo’s syndrome
Mucopolysaccharide disorder
causes mental retardation
not as fatal as others
Mucopolysaccharide disorder UA
CTAB (cety-trimethyl-ammonium bromide)
forms white turbidity
Acid-albumin turbidity test
forms white turbidity
Metachromatic staining spot test
blue spot
Lesch Nyhan disease
Purine disorder
IEM
Increased uric acid
severe motor defects, mental retardation, mental dysfunction, self destruction, gout, and renal calculi
Lesch Nyhan disease UA
orange sand in diaper
uric acid crystals HIGH
renal calculi
Melituria
Increase of any urinary sugar, usually IEM
Galactosuria
Melituria
IEM, deficient in enzyme to convert galactose to glucose
galactosemia
liver disorder, cataracts, severe mental retardation in babies
Treatment
remove galactose and lactose(breaks down into galactose) from diet
Galactosuria UA
screen
clintitiest + glucose strip =
chromatographt