CH 23:Evolution of Populations: Mechanisms, Natural Selection, and Genetic Variation
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Microevolution
Small-scale changes in allele frequencies within a population over time.
Natural selection
A mechanism of evolution where individuals with favorable traits are more likely to reproduce.
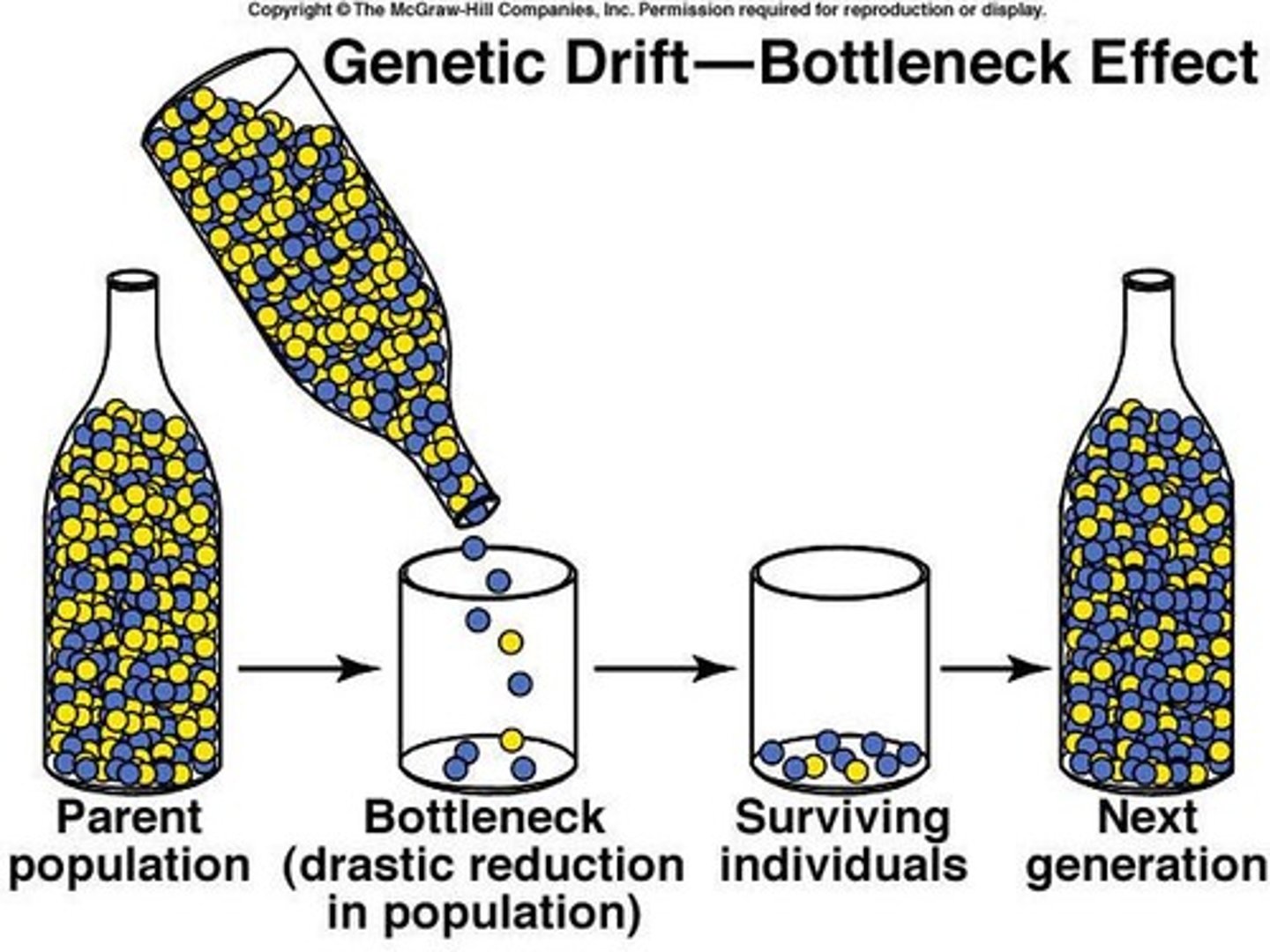
Genetic drift
Random changes in allele frequencies in a population, often having a more significant effect in smaller populations.
Gene flow
The transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another.
Genetic variation
Differences in alleles among individuals in a population.
Mutations
Formation of new alleles, introducing variation into a population.
Gene duplication
Duplications of large chromosome segments, usually harmful, but smaller DNA piece duplications can play a major role in evolution.
Olfactory genes
Genes that enable mammals to distinguish among many different chemicals, enhanced by gene duplication.
Rapid Reproduction
Shorter generation times allow mutations to accumulate rapidly.
Clostridium
A bacterium that reproduces every 20 minutes.
Locus
The specific location of a gene on a chromosome.
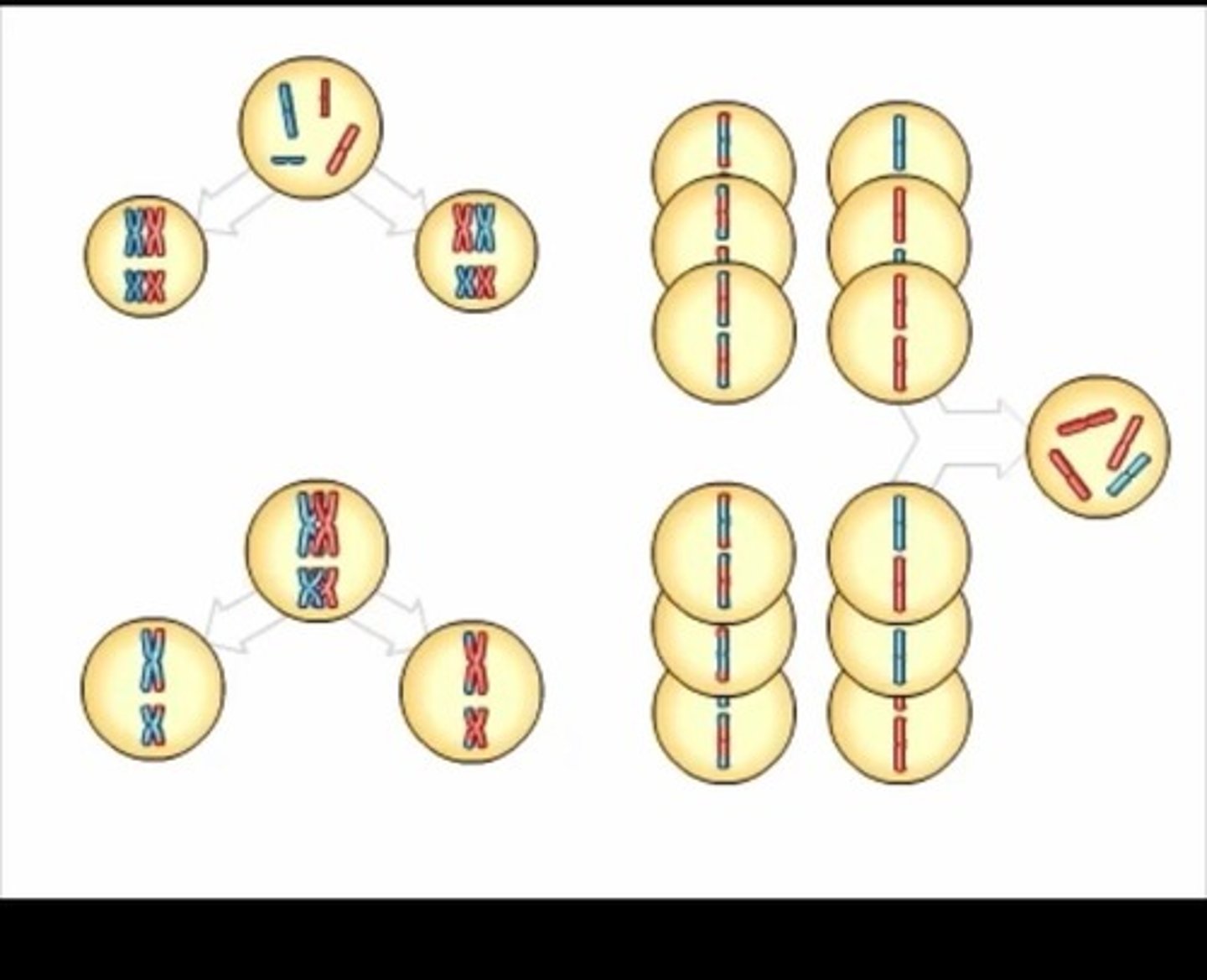
Diploid
A cell or organism with two sets of chromosomes.
Haploid
A cell or organism with one set of chromosomes.
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an individual.
Phenotype
The observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an individual.
Alleles
Versions of genes.
Population
All of the individuals of the same species that live in a particular place at the same time.
Gene Pool
All copies of every allele at every locus in the whole population, characterized by allelic frequencies.
Allele frequency
Percentage of a specific allele of a given gene locus in the population.
Genetic equilibrium
Condition where allele and genotype frequencies remain constant across generations.
Hardy-Weinberg Equation
Provides a baseline for comparing actual populations to determine if they are evolving.
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
A state where a population is not changing, requiring no mutations, random mating, no gene flow, extremely large populations, and no natural selection.
Ancestral population
The original population from which later populations descend.
Allele frequencies
The proportion of different alleles of a gene in a population.
Mutation
A new genetic variant that appears in a population.
Nonrandom Mating
A mating pattern that affects genotype frequency but does not change allele frequencies.
Migration
The physical flow of alleles between populations, also known as gene flow.
Founder Effect
The establishment of a new population by a small number of individuals from a larger population.
Genotype frequency
The proportion of different genotypes in a population.
Random mating
A mating pattern where individuals pair by chance, not influenced by genotype or phenotype.
Inbreeding
Mating between closely related individuals, which can lead to reduced genetic diversity.
Allele
A variant form of a gene.
Isolation
Separation of populations that can lead to reduced gene flow.
Adaptation
The process by which a species becomes better suited to its environment.
Chance event
An occurrence that can randomly affect allele frequencies in a population.
Small populations
Populations that have a limited number of individuals, which can lead to genetic drift.
Pollutant
A substance that can harm organisms, affecting allele frequencies by selectively killing certain genotypes.
Hardy-Weinberg condition
A set of conditions under which allele frequencies in a population remain constant over generations.
Allele frequencies change
Alterations in the proportion of different alleles in a population due to evolutionary mechanisms.
Culex pipiens
A species of mosquito that has shown global spread of insecticide resistance alleles.
Banded patterns
A physical trait observed in mainland snakes that is favored by natural selection.
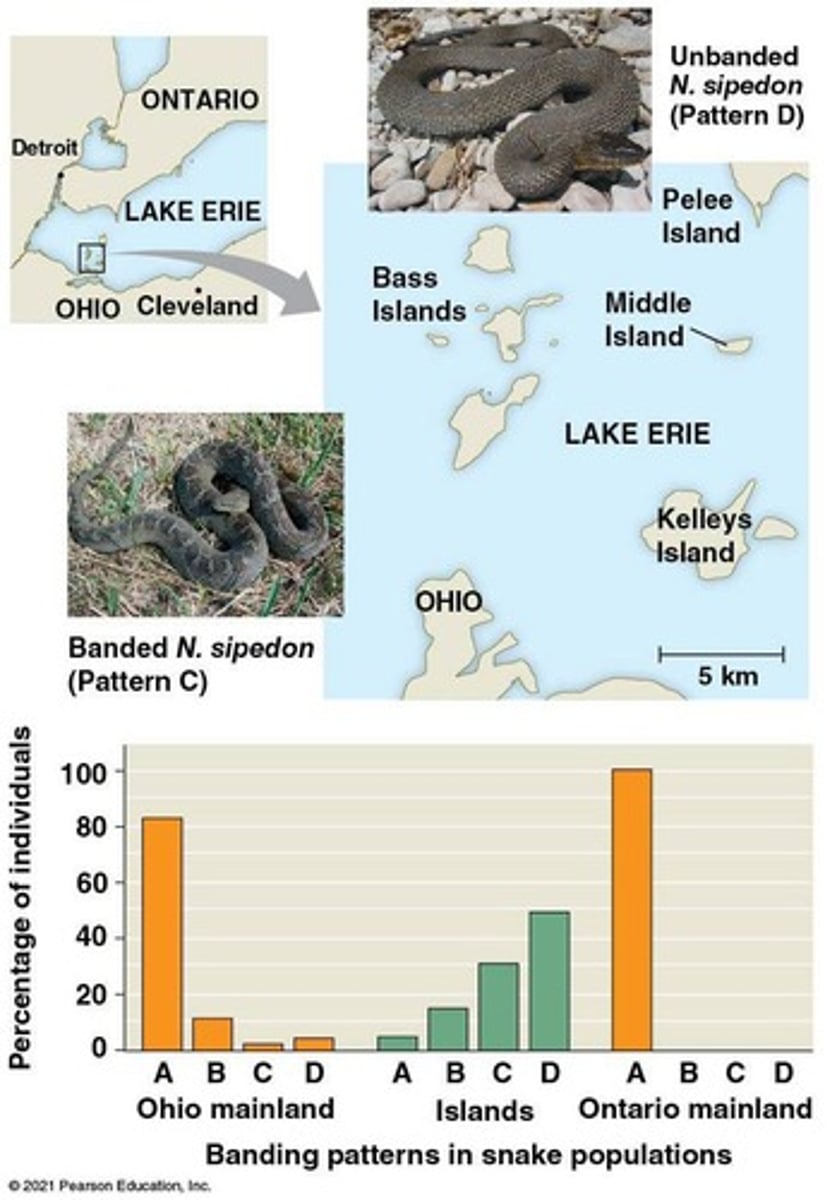
Modification of Prevailing Conditions
Environmental change that affects natural selection.
Overproduction
Excess progeny produced by a population.
Relative Fitness
The success of an individual in passing on its genes compared to others in the population.
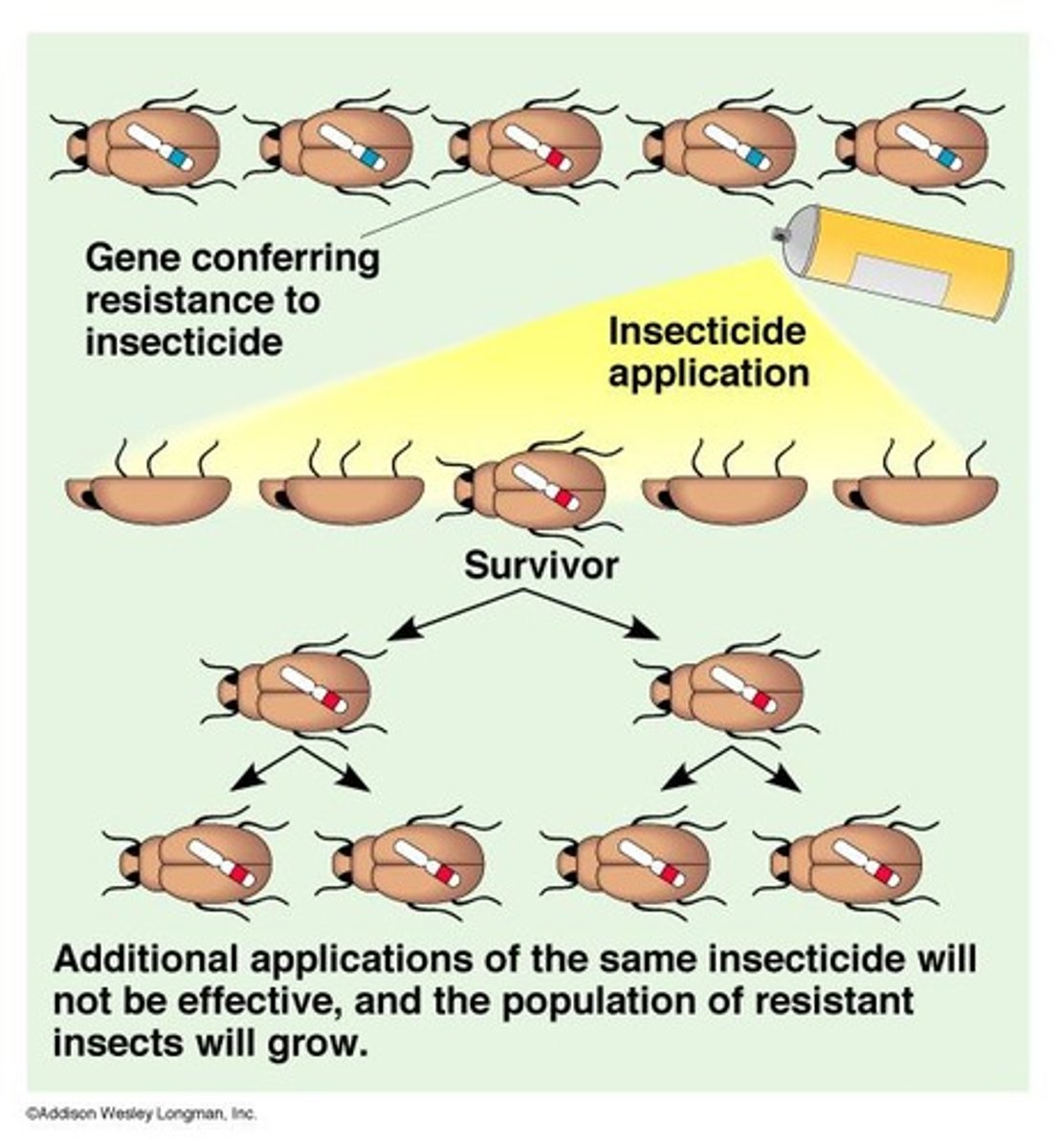
Directional Selection
A type of selection that favors one extreme phenotype over others.
Resistance
An example of directional selection.
Beak Morphology Shift
The evolution of longer and larger beaks in Anna's Hummingbirds due to environmental changes.
Mechanism of Selection
The process by which certain traits are favored in a population due to selective pressures.
Sexual Selection Component
The selection of traits based on their role in courtship and competition for mates.
Thermoregulatory Trade-Offs
Adaptations in beak morphology to conserve heat in colder regions.
Rapid Evolution
Evolutionary changes that occur quickly in response to environmental changes.
Stabilizing Selection
Selection that favors intermediate phenotypes and acts against extremes.
Disruptive Selection
Selection that favors extreme phenotypes over intermediate ones.
Sexual Selection
The process by which individuals select mates based on desirable traits.
Courtship Displays
Behavioral displays used by individuals to attract mates.
Greater Prairie Chicken Male Dance and Behavior
A specific courtship display used by male Greater Prairie Chickens.
Elaborate Decoration of Males
Physical traits developed in males to attract females.
Male vs Female Bees
Differences in physical traits between male and female bees.
Anna's Hummingbird
A species studied for its evolutionary changes in beak morphology.
Environmental Change
Alterations in the environment that can affect natural selection.
Selective Pressure
Factors that influence the survival and reproduction of individuals in a population.
Genetic Characteristics
The inherited traits that define a population.