Unit 3- Aortic Regurgitation
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 3- Aortic Regurgitation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What is the “Method of choice” for evaluation and etiology
Echo and Doppler
Aortic Regurgitation Etiology (4)
Valve Degeneration
Infective Endocarditis
Genetic
Trauma
AR Etiology: Valve Degeneration
Calcification
Fibrosis
AR Etiology: Infective Endocarditis
Leaflet Destruction
AR Etiology: Genetic
Connective Tissue Disorders
(Marfan syndrome, Ehlers Danlos, Loeys-Dietz)
Causes Connective Tissue Disorders to occur (3)
Dilation
Aneurysm
Dissection
Marfan’s syndrome
Effacement of S-T Junction
(giant aortic root and ascending aorta)
AR Etiology: Trauma
Aortic valve rupture
Leaflet tear
Non-coaptation
Likelihood of “physiologic” regurgitation: MR
70 – 80%
Likelihood of “physiologic” regurgitation: TR
80 – 90%
Likelihood of “physiologic” regurgitation: PR
70 – 80%
Likelihood of “physiologic” regurgitation: AR
5%
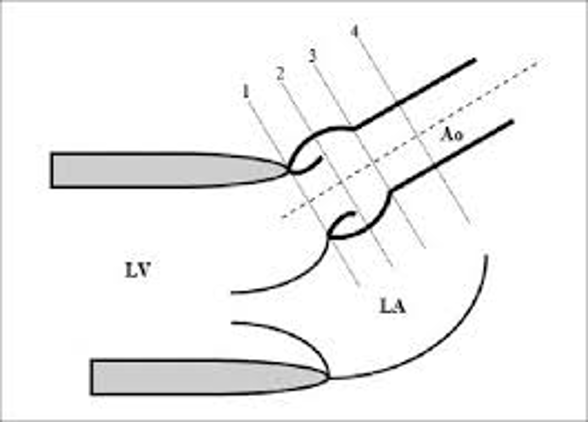
1.
1.1.7 – 2.2cm
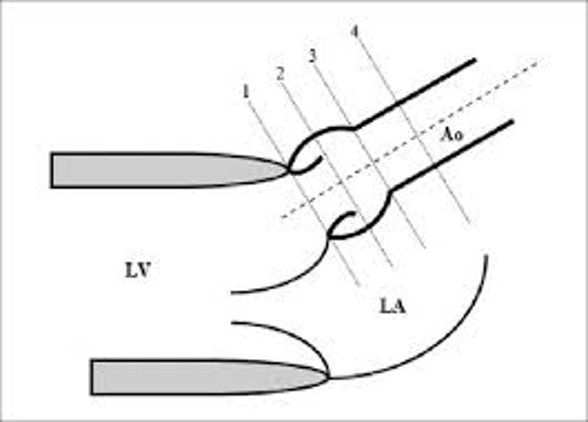
2.
2.0 – 3.7cm
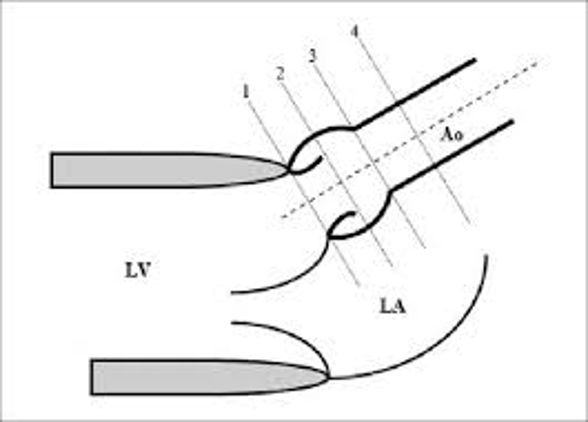
3.
2.0 – 3.6cm
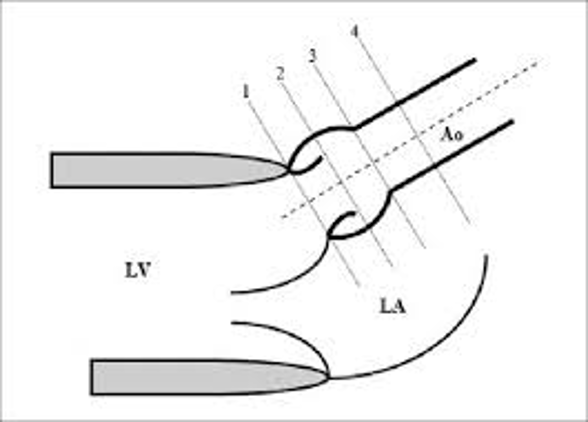
4.
2.0 – 3.4cm
Wall Stress
Force on myocardial fibers that pulls them apart; energy is expended in opposing that force.
Wall Stress Equation or “Law of La Place”
pressure x radius / 2 x thickness
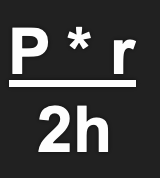
wall stress and O2 demand
Increase; Increase
Wall stress is proportional to:_____ & _____
pressure and radius
Wall stress is inversely proportional to: ______
thickness
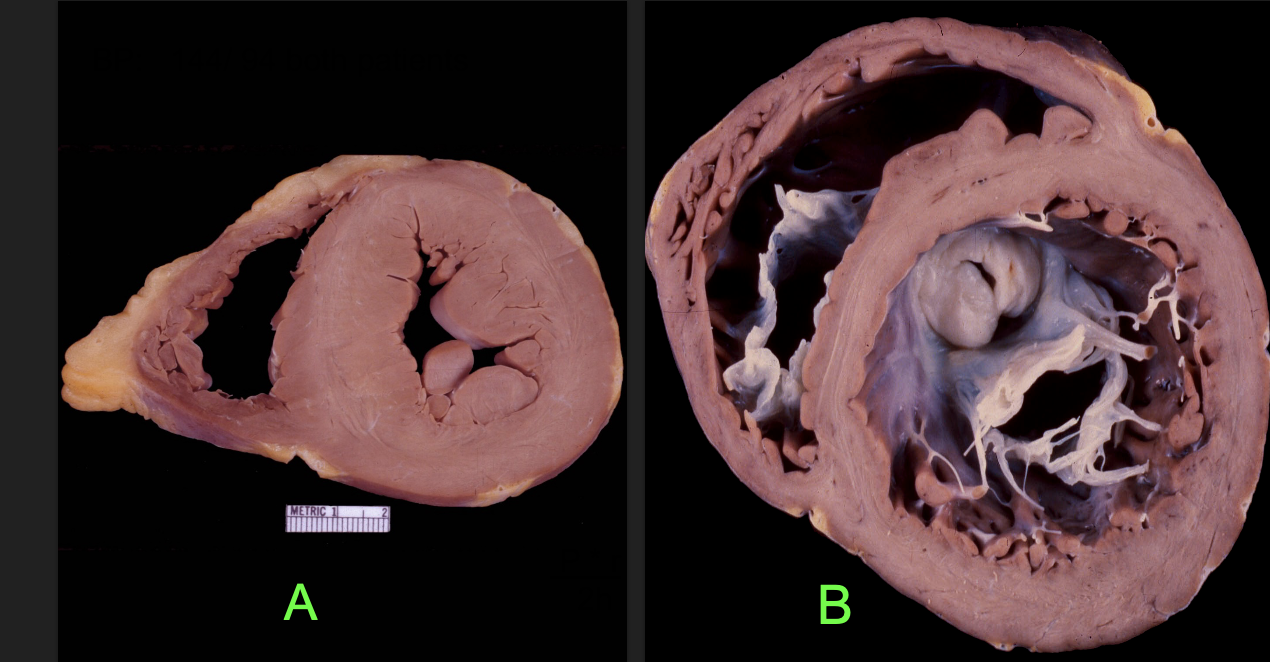
Is wall stress GREATER in specimen “A” or “B”?
B
Chronic AR
Progressive LV volume overload
Causes of Chronic AR
congenital, valve degeneration, infections
Acute AR
Sudden, short, severe course
Causes of Acute AR
infective endocarditis, aortic dissection, trauma
Acute AR:
Abrupt LV volume overload in an LV that has not had time to adapt. Excessive preload
Acute rise in , and end diastolic pressure
LVEDP; LA
Acute AR: May lead to: (2)
Pulmonary edema
Cardiogenic shock
Pulmonary Edema
Condition where excessive fluid accumulates in the lungs, interfering with gas exchange and breathing.
Cardiogenic Shock
Heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Typically caused by a severe heart attack (myocardial infarction).
Acute AR: Treatment
Surgical intervention frequently needed
Chronic AR:
LVE, Increase in LV compliance
SV includes regurgitant volume
Chronic AR: SV includes regurgitant volume:
Increases systolic BP --This does help maintain a proper CO.
Some hypertrophy
LVED volume can be 3 – 4 times normal, leads to failure
AR Complications
Coronary arteries perfuse myocardium in diastole.
AR Complications:
LVEDP increase, -symptoms of fatigue, dyspnea
Angina with normal coronaries arteries
LVE can result in MR, further volume overload
LV systolic dysfunction, SV decreases, HR increase, reduction in filling time….
*** Patients can remain asymptomatic until far along in the course.***
Define “BNP”
B-type natriuretic peptide
“BNP”
Bio marker for heart failure
Ventricles produce B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) in response to increased wall stress. BNP protects heart from adverse consequences of overload by increasing natriuresis and diuresis, relaxing vascular smooth muscle, and by counteracting cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis.
Normal BNP
Less than 100 picograms per milliliter (pg/mL) for adults
Patient presentation:
_______ ________ Murmur;
_______ ________ Pressure
Austin Flint;
Wide Pulse
What is Wide Pulse Pressure?
Large difference of 100 mmHg or more between systolic (top number) and diastolic (bottom number) blood pressures
Wide Pulse Pressure Example: 170/60
difference is 110; 170-60=110 mmHg
Sensitive Tools to Detect AR
Spectral doppler and Color doppler
Diagnosing “AR”
Qualitative & Quantitative parameters
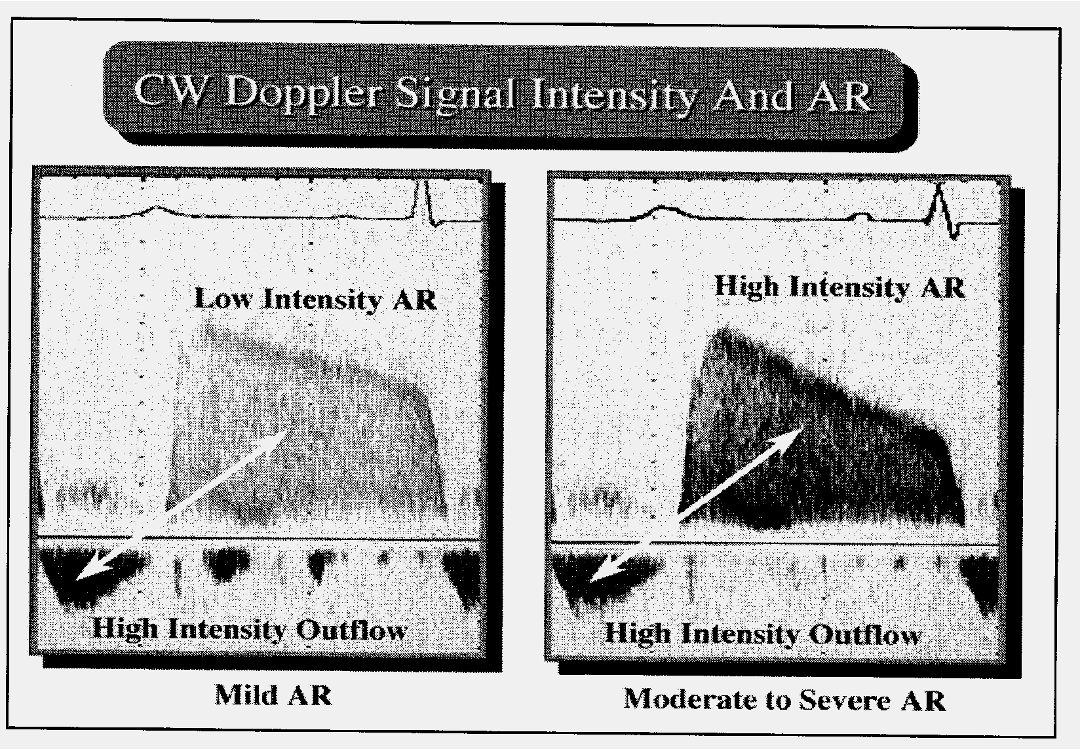
What does the slope (diastolic decay) indicate?
Pressure difference between aorta and LV
The steeper the Decel time the more significant
More regurg=fast pressure equalizes=steep slope
AR peak velocity at least m/sec. -severe
4
What does severe AR do to diastolic function?
produce diastolic dysfunction
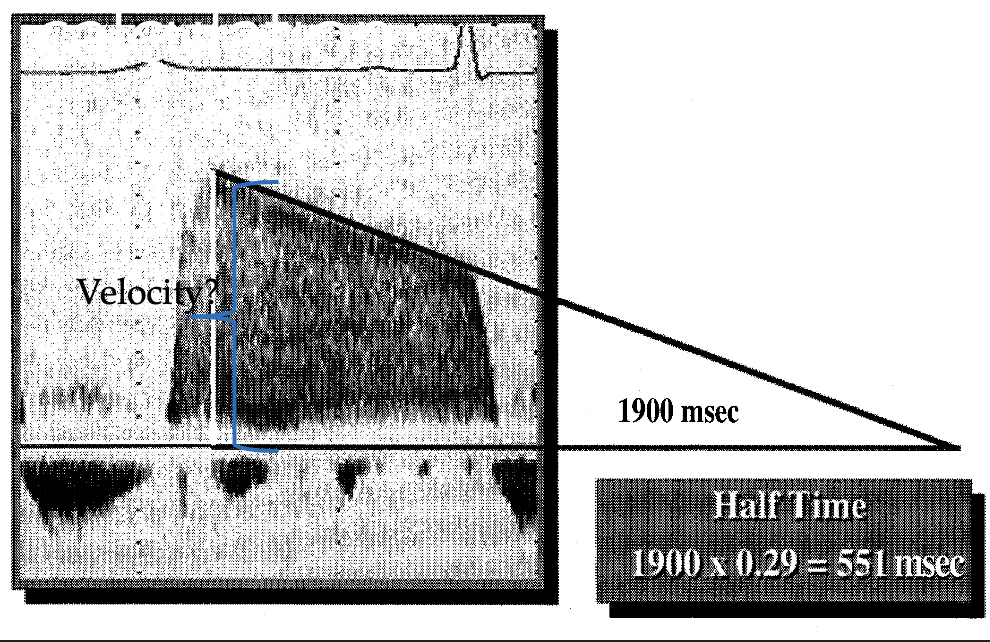
Pressure ½ time calculation
Decel time x 0.29
Pressure ½ time also known as what? (2)
P 1/2 t or PHT
PHT: Mild
>500 msec
PHT: Moderate
200-500 msec
PHT: Severe
< 200 msec
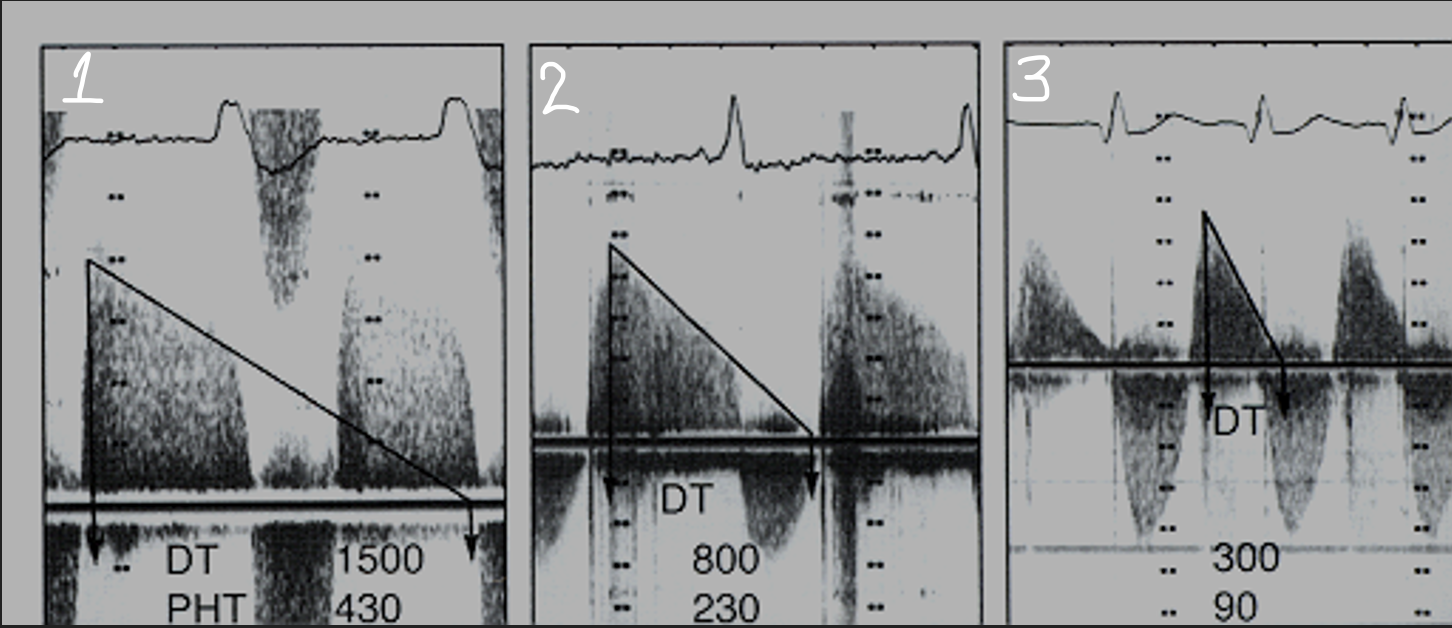
Who’s got it bad?
3; steeper and higher PHT
Standard practice to measure waveforms; if pt has an arrhythmia
3; 5
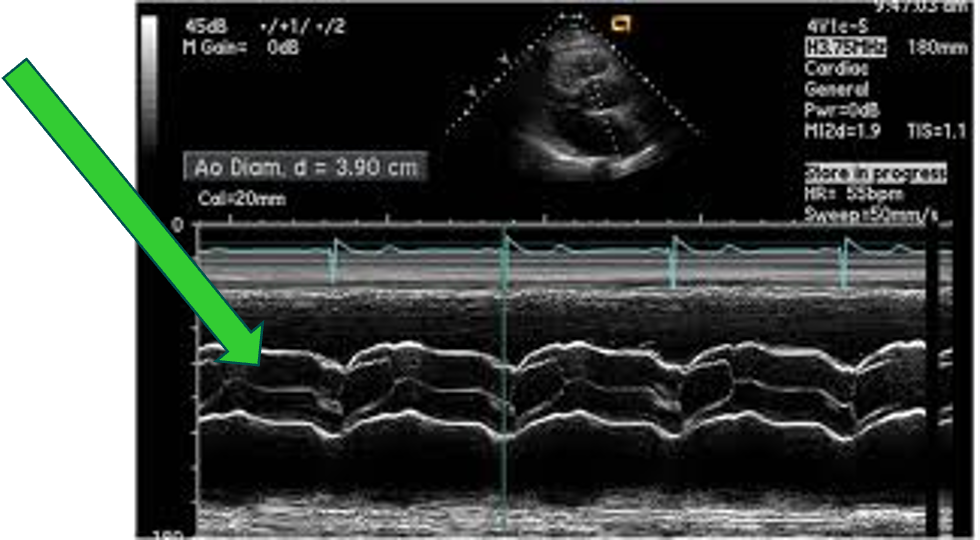
“AR” ON M-Mode; Green Arrow
“Fluttering” with closure line
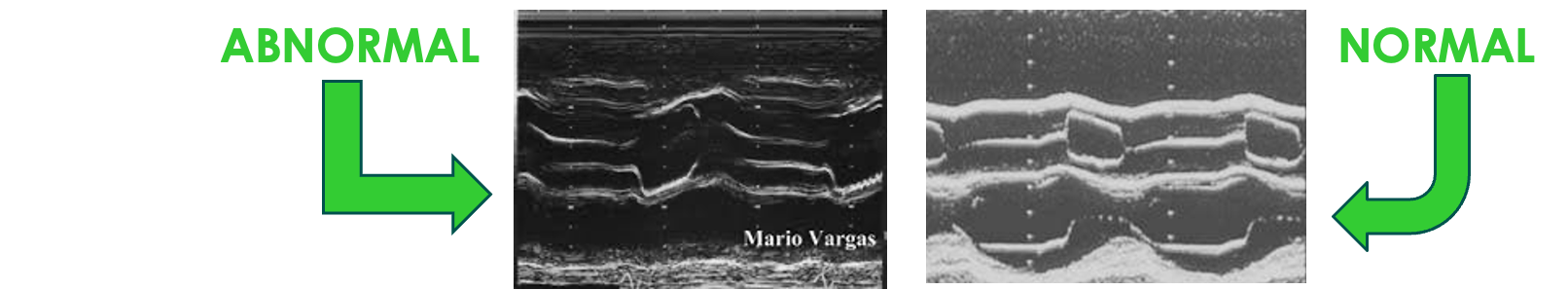
“AR” ON M-Mode: Abnormal; Green Arrow
Incomplete closure of valve leaflets during diastole
DIASTOLIC FLUTTERING OF THE “AMVL”
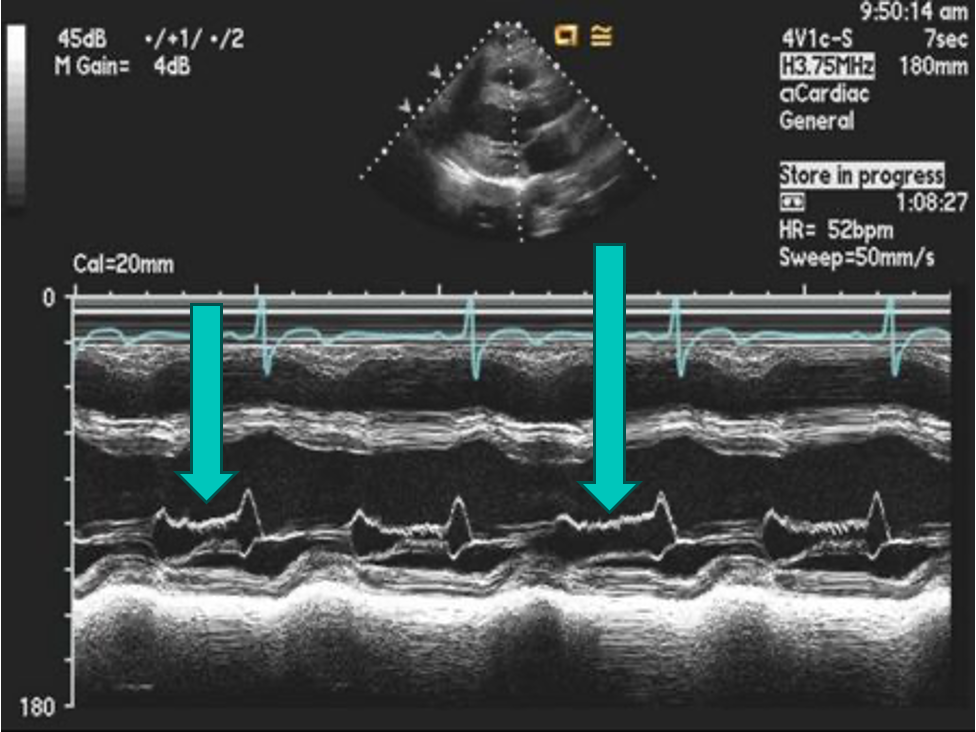
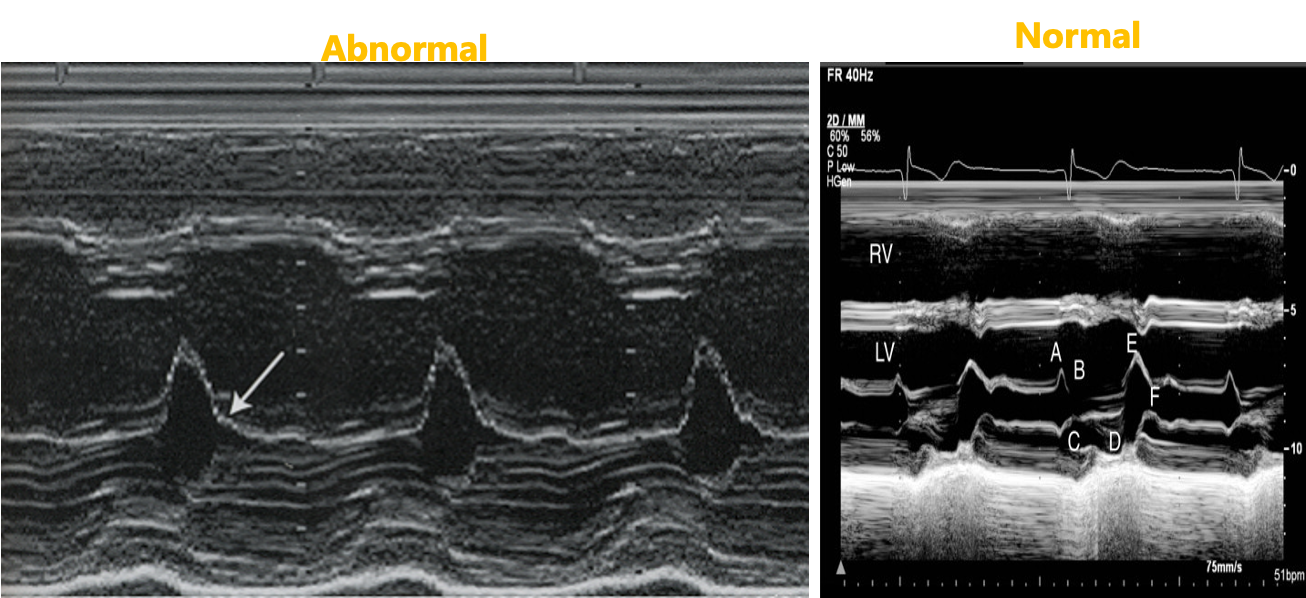
Severe AR
Early diastolic closure of the MV results in No “A” wave
Review: How does high LVEDP affect P1/2t in AR?
shortens it
Review: What is Wide Pulse Pressure?
difference between your systolic and diastolic blood pressure; greater than 100 mmHg
Review: A dilated LV will have more/less wall stress?
more
Review: Relationship of wall stress to wall thickness?
inverse
Review: Greater risk of pulmonary edema? Acute or chronic AR?
acute
Review: AR etiology:
degenerative, endocarditis, congenital or genetic connective tissue disorders, trauma
Review: Acute, severe AR may cause abnormal MV M-mode. What does it look like?
fluttering or no A wave
Review: P ½ time less than __________ is SEVERE AR.
200 m/sec