Human bio revision
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Complication of human bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Name the organelles in an animal cell? (10)
Nucleus → Nucleolus
Ribosomes
Mitochondria
Endoplasmic reticulum → RER + SER
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Cell membrane
Centroiles
Cytoplasm → cytosol
vesicle
What are the organelles used for protein making?
Nuceluolus - creates the ribosomes, This process is essential for cell function and communication.
Nucleus - where RNA is created.
Ribosomes - site of protein synthesis
Rough endoplasmic reticulum - adds and takes things from the sequence of the protein and folds it up. Makes it ready
Golgi apparatus - Packages the proteins for export.
Label the cell memebrane.
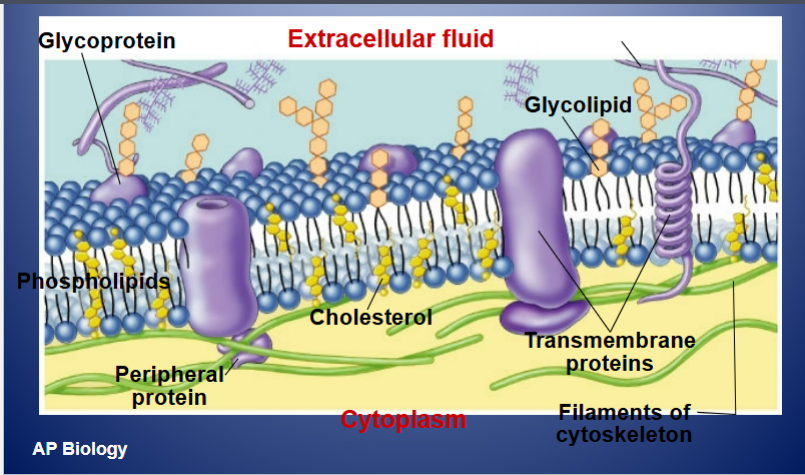
State and describe what the cell membrane is made of.
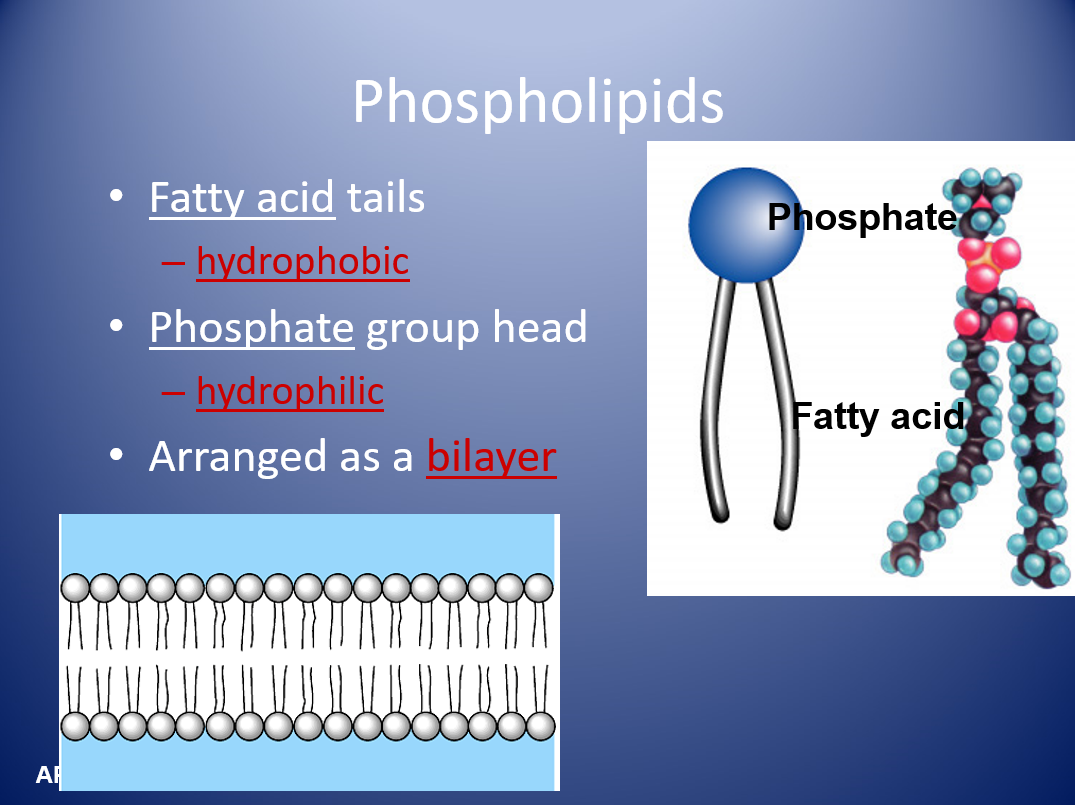
The cell membrane consists of a collage of proteins in a phospholipids bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer contains phosphate heads and fatty acide tails. The tails are hyrdophobic and the heads are hydrophillic.
What type of proteins can be found in the cell membrane?
peripheral proteins - loosely bound to the surface of the cell.
intergral proteins - penetrate the lipid bilayer e.g transmembrane proteins - channels.
What can effect the cell membrane?
The amount of fat in the membrane effects its flexility. The membrane needs to be fluid so that proteins and other subtances can bidn to it and so it can allow transport.
The percentage of unsaturated fat effects is viscousity. Less unsaturated fat keeps the membrane fluid whereas the more unsatrurated fat makes the lipid more viscous.
→ We need the Lipid to be viscous so that the membrane can be selectively permeable membrane. As well as being fluid (fluid osaic model) but keep its structural integrity.
How are substances transported into/out of the cell?
Through transport proteins. Substances are diffused from a high concentration to a low concentration (follows concentration gradient).
What are the different types of transportation?
Passive transport - follows the concentration gradient and not much energy is used. e.g Simple Diffusion
Active Transport - particles go against the concentration gradient.
Faciliated diffusion is where the particle uses a carrier or channel to transport it.
What are some inputs and outputs of a cell?
inputs: nutrients, food, oxygen, salts, sugars, lipids, proteins
outputs: Waste, C02, hormones(proteins), water(sweat), ammonia
How do you move large molceules in and out the cell?
Endocytosis is the process where large particles use vacuoles and vesicle to be transported across the cell membrane (into and out of the cell)
Phagocytosis - membrnae engulfs solid particles and produces a vesicle inside th cytoplasm
Exocytosis - vesicle/vacuole re-connencts with the cell membrane and releases the solid/liquid molceules to the outside of the cell.
Pinocyctosis - cell membrne engulfs liquide molceules and produces a vacuole in the cytoplasm
What is the equation for cellular respiration?
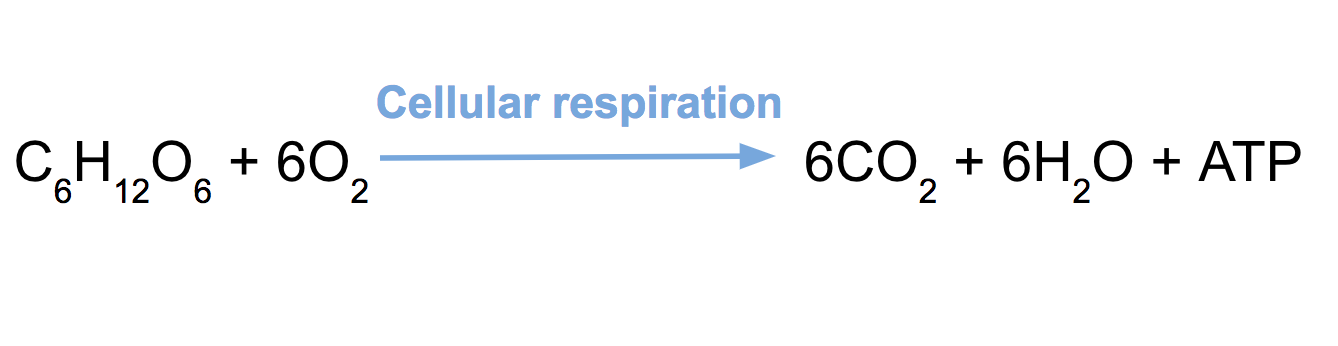
What is anaerobic respiration?
anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen. It turn gluclose into pyruvate in a process called glycolysis, proudcing 2 ATP. It takes place in the cytoplasm.
What is aerobic respiration?
It uses oxygen and turns gluclose into pyruvate (2ATP)and then pyruvate into CO2(2ATP), O2 and H2O. The O2 makes H2O in the redox reaction of the elelectron transport chain. This produces 34 ATP. Overall ATP produces is 38.
How does the ATP cycle work?
ATP stars off as ADP (adenosine di-phosphate). A phosphate bonds to the last phosphate group and energy from glucose is trapped in the bond between them. When the ATP is used the phosphate snaps of and the energy held in the bond is release, it then become ADP again. The process repeats itself.
what are the 4 types of tissue?
connective - fibre like. loosedy oganises and separated by a non-cellular matrix
Muscle - able to contract and relax. Structure is different my compisition is the same.
Nervous - sends messages to and from the brain and spinal chord used for movement, senses and breathing.
Epithelial - cover inner and outler layer of organs, protecting the organs and varys in shape. Closely packed together to secrete and aborb specific things.
Carbohydrates nutrient
H,C,O
Monosaccharides - simple sugars e.g glucose and fructose
Source of energy, cell recognition and cellular respiration
e.g gluclose (monosaccharides), sucrose (diasaccharides), starch (complex)
Lipids (fats)
H,C,O
triglyceride
source of energy, basis of steroid hormones, mane ingredient in the cell membrane
e.g fats and oils. (saturated and unsaturated forms in the body)
Proteins
H,C,O
amine acids
transport proteins, receptors, hormones, enzymes, antibodies
e.g amylase, insulin, membrane protein channels, haemoglobin
nucleic acids
H,C,O,N,P
nucleotide
contains the instuctions for the synthesis of proteins
e.g RNA, DNA
What is an enzyme?
A biological catalyst. Proteins that control all reactions in your body that require a catalyst.
what is activation energy?
The certain amount of energy needed to cause a reaction.
What are some factor effecting enzyme catalysed reactions?
Temperature - increase in kinetic energy. Particles are moving faster so they are most likely to hit eachother. However excess vibrations will destroy the shape of the protein. *Enzyme will de-naturate
Enzyme concentration - more enzymes for the subtrates to react with ina given volume → R.R increases
Substrate concentration - more subtrate to compliment the enzymes, however too mcuh saturates the reaction with substrate.They can’t work faster than they can.
Product concentration - decreases R.R because it is more difficult for enzymes and substrates to collide
pH (acidity) - Acidic and basic are both bad. protiens hav ions. Chemicals determine their strucutre, extra H+ or OH- effects its shape and hence its function. - Papsin like acidity. Works at an optimum pH.
What are co-factors?
Substances that bind to the enzymes to make them the correct shape for substrates. This allows only specifci substrates to bind to them. this would be good in cases where a specific reaction has to occur more than another.
What are inhibitors?
Binds to the active site of the enzyme preventing a substrate from binding.
What is metabolism?
all the enzyme controlled reactions that occur in the cell abd hence the human body.
must maitain a balance between energy releasea and utilised.
What is anabolic metabolism?
reactions in which smaller molecules are built into larger ones. This requires energy. e.g protein synthesis
What is catablic metabolism?
reaction where larger molecules are broken down into smaller molecules. THis releases energy. e.g digection.
articular capsule
surrounds and enlcoses the joints
made of a fiborous and synovial membrane
provides support
Fiborous capsule
firm outer layer of the synovial membrane
It is dense fiborous connective tissue attached to the periosteum
Synovial membrane
lines the inner capsule
makes synovial fluid
without the fiborous capsule the synovial membrane might break (infection of fluid)
Articular cartilage
Made of connective tissue and hyaline cartilage.
Protects the bone, also absorbs shock and provides non-friction movement
Collects nutrients from synovial fluid because it doesn’t have any blood vessls
Articular disc (menisci)
Made of fibrocartilage
divides and directs synovial fluid to reduce friction
Bursae
Sac of fluid surrounding the knee
Prevents friction between bone and ligaments, tendon and bone.
Accesory Ligament
holds bone to bone together in many joints
extra support, additonal strength
What are the types of synovial joints?
Ball and socket
Hinge
Pivot
Gliding
Saddle
Condyloid
Explain a ball and socket joint
Circumduction
most flexible, hence most easy to brake
e.g shoulder, hip joints
Explaine a hinge joint
moves up and down (like a door on its side)
movement on one plane only
e.g mandible, carpal; metacarpals and phalanges
Explain pivot joint
Allows rotation on a longitudional axis
e.g neck, radius-ulna
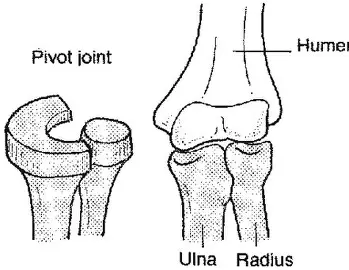
Explain gliding joint
Side-to-side (A.G) movement
small movement that allows for flexing
e.g intercarpal (wrist), intercarsal (ankles)
Explain saddle joint.
Allows free movement on two planes
allows circumduction and pinching
e.g only in the thumb
Explain condyloid joint
Allows free movement on two planes
allows the rotation of the wrist
e.g knuckles (metacarpasl and phalanges), joints of wrists
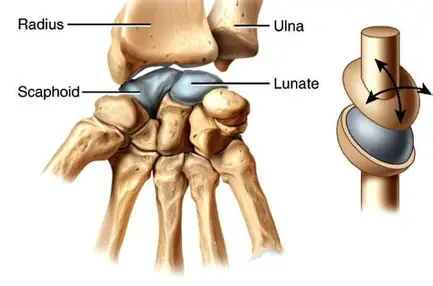
What are the movement of joints
Flexion
Extension
Abduction
Adduction
Rotation
Circumduction
Supination
Pronation
Inversion
Eversion
What is felxion and extension?
Flexion is reducing the angle between two bones (bending the joint)
Extension is straightening the angle between the bones (engles between the bone increases)
What is abduction and adduction?
Abduction is moving the bone away from the body
Adduction in the moving the bone towards the body
What is rotation and circumduction?
Rotation is like twisting, it is rotation on the longitudal axis.
Circumduction is 360 degrees rotation. circular motion of the limb
What is supination and pronation
supination rotation of the hand so the forearm and palm is facing up.
pronation is the rotatioin of the hand so the forearm and arm are facing down.
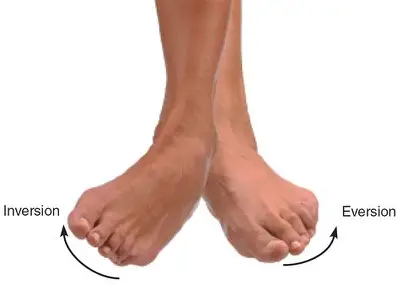
What is inversion and eversion
Inversion is movement of the feet so the soles are facing inwards.
eversion is movement of the feet so the soles are facing outwards.
what is the band of fiborous tissue that connects muscle to bone?
tendon
What is the fixed end of the muscle
origin.
the muscle that causes the desired action by contracting
agonist
muscle that relaxes whislt the agonist contracts
antagonist.
smaller muscle that assits the primary agonst muscle
synergist
synergist that immoboilize a joint preventing movement.
fixators
the muscle that causes bending when it contracts
flexer/ abductor
the muscles that cause extension when contracting
extensor/adductor
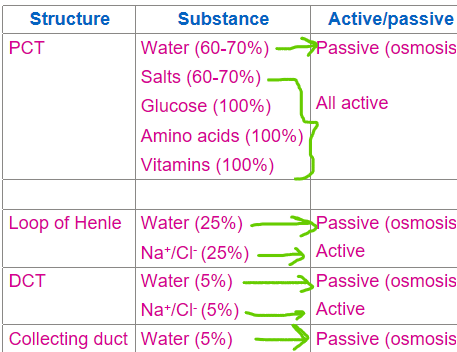
what is reabsorbed where in the nephron?