Threats to biodiversity
1/20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Over-exploitation
This causes the numbers of a population to become dangerously low
Example: over-exploitation
Overfishing - as the development of bigger nets and more sophisticated sonar increases, the populations of fish species has started to deplete to such a low level that the continued exploitation of these species is no longer sustainable
What five things can be done to stop the depletion of fish stocks and recover their populations?
Control the number of boats
Quotas
Reduce hours at sea
Restrict areas where fishing is permitted
Strict regulations
Use nets with larger holes to allow smaller fish to swim through
Bottleneck effect
When a significant percentage of a population has been wiped out the surviving small population may have lost some of its genetic variation
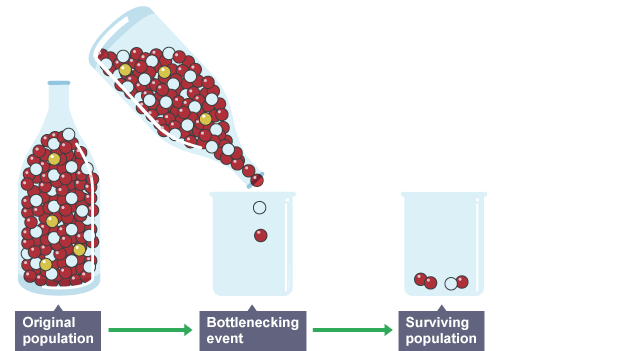
Diagram: bottleneck effect
What two things can cause a population to be wiped out?
Natural disasters like a fire or a flood, or human activity like deforestation or over-hunting
What two problems can occur when there is a loss of genetic diversity?
Inbreeding and poor reproductive rates, and the population might not survive environmental changes
What causes habitat loss by fragmentation?
The clearing of habitats (deforestation)
What does the process of fragmentation of a habitat result in?
The formation of several habitat fragments whose total surface area is less than that of the original habitat
What do habitat fragments suffer from?
Degradation at their edges which may further reduce the habitats size
What does habitat loss by fragmentation result in?
An increase in competition between species, causing a decrease in biodiversity as more isolated fragments and smaller fragments exhibit a lower species diversity
What is one way of helping habitat loss by fragmentation?
Habitat corridors
In what three ways do habitat corridors help habitat loss by fragmentation?
Increased access to a choice in mate
Increased access to food
Increased chance of recolonisation of small fragments after local extinctions
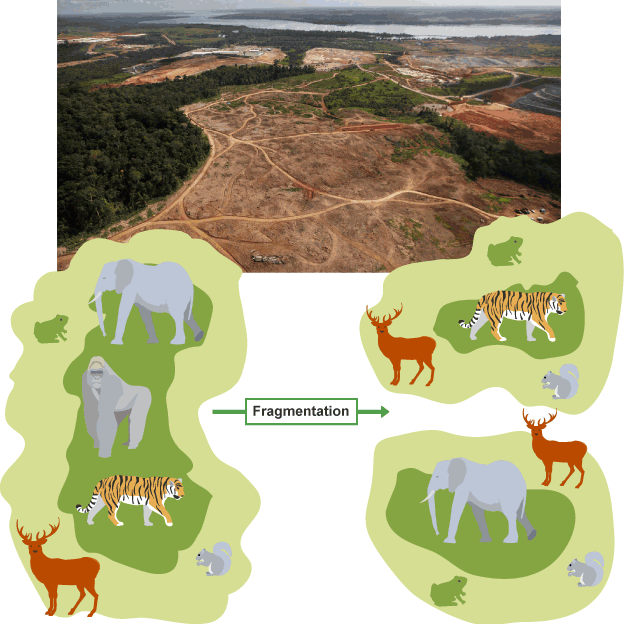
Diagram: habitat fragmentation
Example: habitat loss by fragmentaiton
Tigers - 95% of tigers were wiped out due to over-hunting and to combat this habitat corridors have been introduced to encourage breeding
Introduced species
Non-native species that humans have moved, accidentally or intentionally, to a new geographical location
Naturalised species
Introduced species that have become established in wild communities
Invasive species
Naturalised species that have spread rapidly and eliminated native species, therefore reducing species diversity
Why are some invasive species successful?
They are free of their natural enemy/pathogen/parasite and competitors which limited their population in their native habitat
What three things might invasive species do to native species?
Hybridise with them
Prey on them
Out-compete with them for resources
Example: an invasive species
Giant hogweed - their sap is poisonous, causing blistering and burning of the skin