Cestoda
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
platyhelminthes
Phylum known as flatworms
– Have solid bodies with no cavity
– Internal organs are embedded in tissue
(parenchyma)
– No respiratory or vascular system
– No mouth or digestive tract
– At least one intermediate host is
required to support life cycle
two classes of platyhelminthes
– Trematodes (Digenea)
• the flukes
• flukes have a rudimentary alimentary canal
– Cestodes
• contains the flatworms (tape worms)
• must absorb all nutrients through the tegument
(external surface)
all platyehelminthes are ? (with the exception of the blood flukes)
hermaphroditic
cestoda
Commonly called tapeworms
4Long, ribbon-like and are flattened in
cross-section
4Adults may range from a few
millimeters to 20 meters
4Adults lives in the intestinal tract of
definitive host
4Larval stages inhabit the tissues of
intermediate host
morphology
Scolex: head-like
anterior end
– Sometimes hooked for
attachment to host
Strobila: entire body
following the scolex
Proglottid: Segments
of the body
2 orders that infect humans
Cyclophyllidae and Pseudophyllidea
Cyclophyllidae typically have a scolex with 4
suckers
4 Pseudophyllidea typically have a scolex with 2
opposing sucking grooves
4 Another important point of differentiation is that
Cyclophyllidae has 2 hosts in its life cycle whereas
Pseudophyllidea requires 3
cestoda anatomy
Anterior end of the worm (scolex)
4is modified for attachment
– Equipped with four cup-shaped suckers
– May contain Rostellum
• Some species may have a hooks (armed)
– Scolex is usually less than 2 mm long
The body is termed the strobila
– Can be up to 20 m in length
– Worms have no vascular, mouth or digestive
system
– All nutrients are absorbed through the
tegument
– Waste products are released through the
tegument
4Body segments known as Proglottids
– Differ species by uterine branches
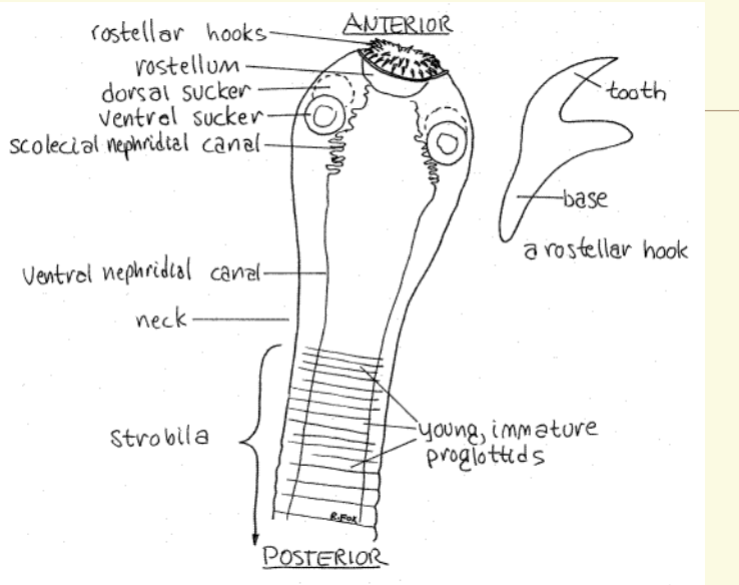
proglottids
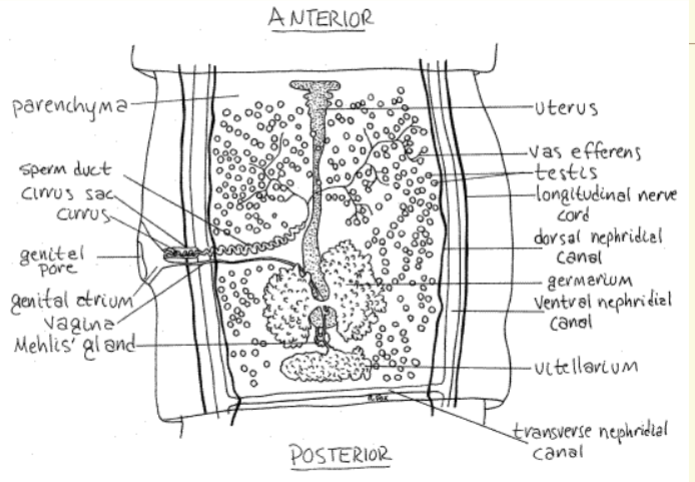
reproduction of cestoda
Each tapeworm is
hermaphroditic
4 Mature Proglottids contain both male and
female reproductive organs
4 Sex organs mature gradually
4 Proglottids at the terminus contain fully
matured reproductive organs
4 Uterus is filled with fertilized eggs
4 The shape of the Proglottids and uterus is
distinctive for each species (diagnostic
tool)
Posterior segments are termed gravid
Proglottids
4Can be found singly or in short chains
– Break off and are expelled in feces
– Are distinct for given species
– used as a diagnostic tool
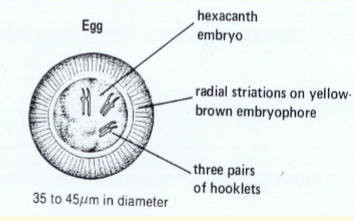
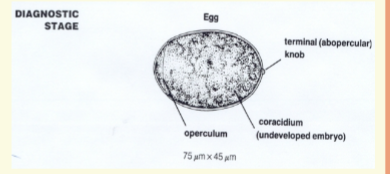
embryo
Onchosphere
– or hexacanth embryo
4Bears six tiny hooklets (3 pairs)
4Facilitates attachment onto intestinal
mucosa after hatching
4Eggs are passed in the feces
4Eggs are distinct for species
– Use as a diagnostic tool
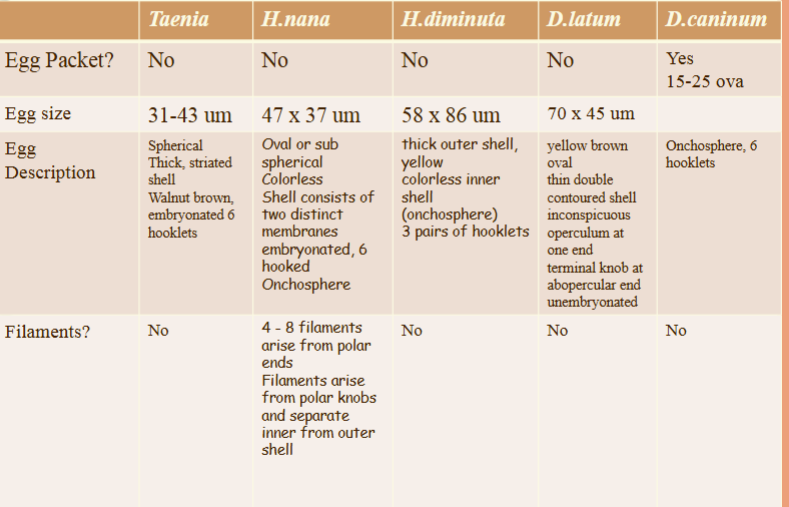
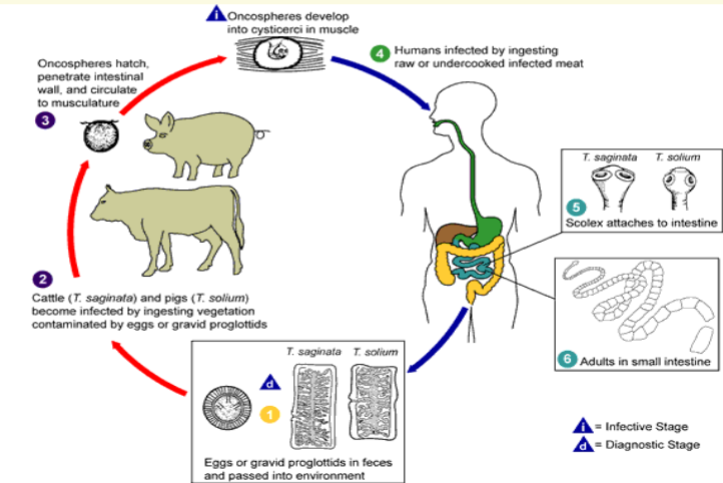
Taenia spp.
Two Species
–Taenia saginata (beef tape worm)
–Taenia solium (pork tape worm)
Infection: Cysticercosis
Taenia saginata
Beef tapeworm
4 Distribution:
– Cosmopolitan
4 Adults live in small
intestines
4 2-10 m
4 Agent ofCysticercosis bovis
4 Transmitted by eating
undercooked beef
containing larva

Taenia solium
Pork tapeworm
4 Worldwide
– (rare in the U.S.)
4 Agent of Cysticercus
cellulosae
4 Transmitted by
ingestion of larva in
undercooked pork
4 Adults live in the small
intestine
4 2 - 4 m
Taenia major pathology
Most people infected are asymptomatic
4 Abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss
4 Moderate eosinophilia
4 Humans can serve an intermediate host forT. solium
4 If eggs of
T. solium are ingested, can hatch
in intestines and larvae migrate causing
Cysticercosis in organs or CNS
4 Epilepsy, headache, vomiting
Taenia spp life cycle
Taenia lab diagnosis
Recovery of ova,
Proglottids, or scolices
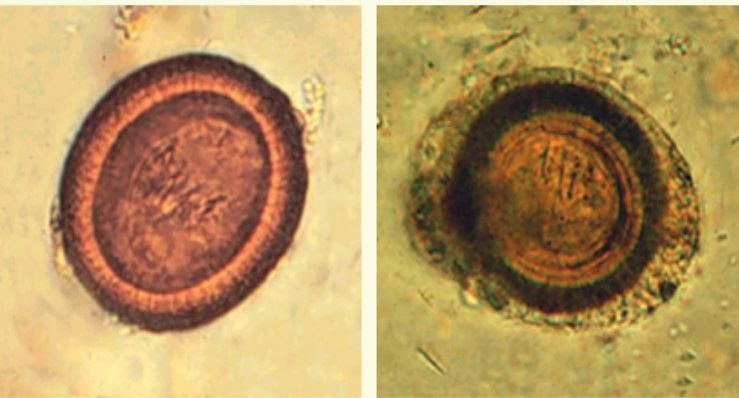
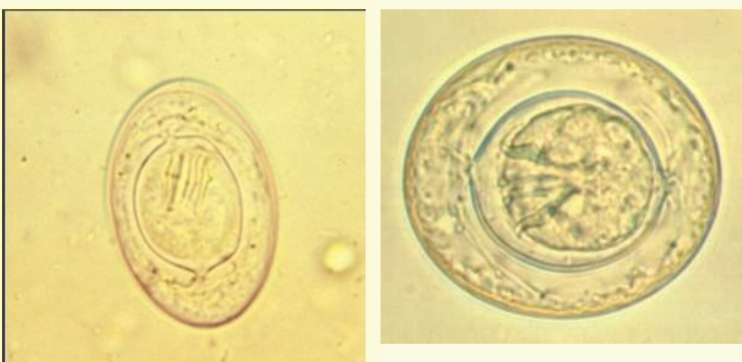
4 Taenia Ova:
– 31-43 um
– Spherical
– T hick, striated shell
– Walnut brown
– Embryonated,
4 Onchosphere
– 3 pairs of hooklets
4
T. saginata and T.
solium ova are
indistinguishable
Taenia spp ova
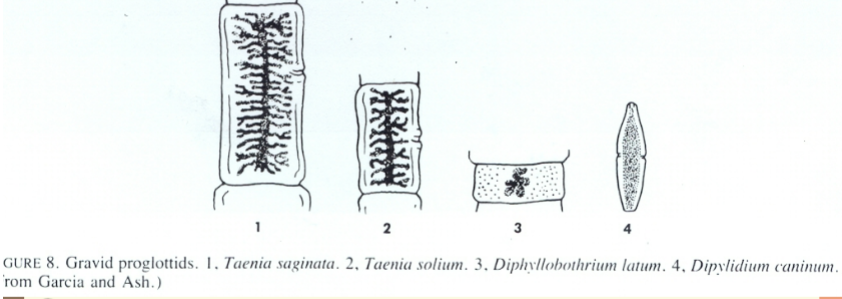
Taenia gravid proglottids
T. saginata
– 16-20 mm long, 5-7 mm wide
– central stem with 15-30 uterine
branches on each side
– usually on surface of fecal material
4
T. solium
– 12 mm long, 5-7 mm wide
– central stem with 7-13 uterine branches
– usually on surface of fecal material
Taenia spp proglottids

Different gravid proglottids
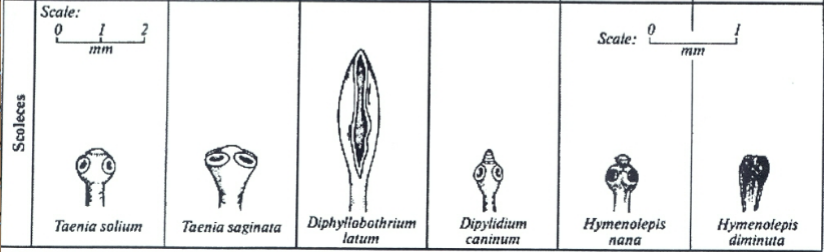
Taenia scolices
T. saginata
– rounded, 1-2 mm in size
– 4 sucking disks
– no rostellum or attachment hooks (unarmed)
T. solium
– 4 sucking disks
– Rostellum with hooks (armed)
– double row of 25-30 chitinous hooks (armed)
– hooks arranged around the rostellum
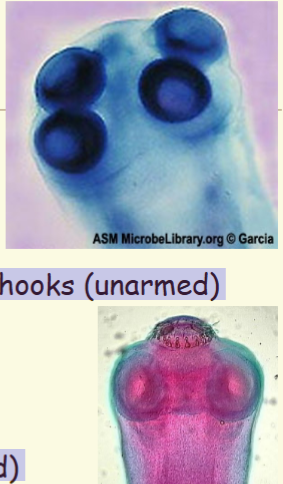
All scolices among species
T. saginata vs T. solium

Taenia treatment
Praziquantel
– For Cysticercosis
4Albendazole
4Anticonvulsants for neuro-
cysticercosis
4Surgery
definitive host of Taenia
humans
Adults may live for many years and
usually only one worm is present
4Human cysticercosis is common in
locations where undercooked pork or
beef is consumed
4Also found in communities where pigs
and people live in close contact
order: cyclophyllidea genus: Hymenolepis
Two species
– H. nana
– H.diminuta
4Fleas and beetles can serve as transport
hosts
– Cysticercoid larvae develop and are infective to
humans or rodents
Hymenolepis nana
Dwarf Tapeworm
4Agent of Hymenolepiasis
4The smallest Cestode
4Only species that parasitizes without
requiring an intermediate host
H. nana distribution
Worldwide, tropics and subtropics
4Especially in children and
institutionalized persons
4Most common human tapeworm in the
U.S.
4Greater prevalence in the Southeast
4Infection rate of 3%
H. nana morphology
Adult length: 15 -
40 mm
4 Scolex:
– has a retractile
rostellum
– single row of 20-30
hooks
4 Proglottids:
– usually disintegrate
– not seen in stool
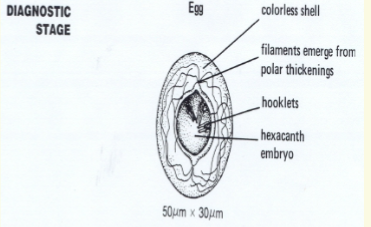
H. nana ova
The diagnostic stage
4 Oval or sub spherical
4 Colorless
4 47 x 37 um
4 Shell consists of two distinct membranes
4 Contains embryonated, 6 hooked
Onchosphere
4 4 - 8 filaments arise from polar ends
4 Filaments arise from polar knobs
4 Filaments separate inner from outer shell
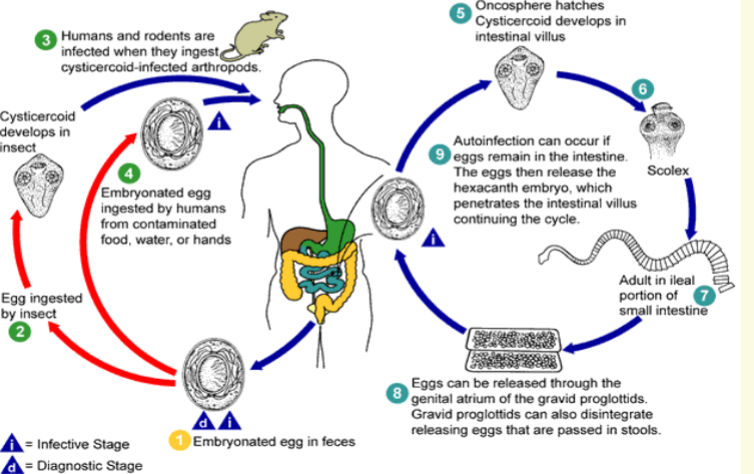
H. nana transmission
Ingestion of infective ova
4 Requires no intermediate host
4 Common in house mice, fleas, beetles serve
as transport host
4 Larvae develops in body cavity of insects
4 Insects are infective to humans or rodents
if ingested
4 Eggs in rodent feces are common source of
human infection
H. nana pathology
Light Infections: asymptomatic
4Heavy infections:
– intestinal enteritis
– abdominal pain
– diarrhea
– headache
– dizziness
– anorexia
multiple infections are common
Hymenolepis life cycle
H. nana lab diagnosis
Recovery and
identification of ova in
feces
4 50 x 30
um
4 thin, colorless shell
4 filaments emerge from
polar thickenings
4 contains hexacanth
embryo
– six tiny hooklets (3
pair)
H. nana ova
H. nana treatment
Praziquantel
– Increases membrane permeability to Calcium
– Causes spastic contraction and paralysis of
worm musculature
– Causing worms to detach and disintegrate
4 Niclosamide
– Interrupts phosphorylation of mitochondria
– Induces complete muscular paralysis
– Complete detachment of scolex
– Not available in the U.S.
Hymenolepis diminuta
Rat tapeworm
4 Distribution: Worldwide
4 Disease: Cysticercosis
4 Adults live in the intestines of rat
4 Humans are accidental host
– ingests larvae in flea or grain beetle (IM host)
4 Pathology: Mild symptoms
– tapeworms are lost spontaneously
– eggs in feces are diagnostic
H. diminuta ova
Similar to
H. nana ova
4 58 x 86 um
4 has thick outer shell,
yellow
4 colorless inner shell
(onchosphere)
4 3 pairs of hooklets
present
4 no polar filaments
from inner membrane.
– Distinguishes it form
H.
nana
Dyphyllobothrium latum
Fish Tapeworm
4 Disease: Diphyllobothriasis, fish tapeworm
infection
4 Distribution: temperate regions where
freshwater fish are common in diet
– Circumpolar regions
Full-grown Worm
– vary in size from 1-15 m
– is the longest human tapeworm
– It consists of up to 3000-4000 Proglottids
4 The scolex, as mentioned, has 2 sucking
grooves, also called bothria
4 Proglottids
– typically wider than they are long
– is why
D latum is called the broad tapeworm
4 In the gravid state,
– the proglottids have a distinctive rosette-like
uterus in the center
D. latum infection and treatment
Diphyllobothriasis
4 long lasting (decades)
4 most infections are asymptomatic
4 abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, vomiting,
weight loss
4 Macrocytic anemia
– vitamin B12 deficiency and pernicious anemia
(utilization of up to 100%)
4 Nervous system disturbances
4 Treatment: Niclosamide or Praziquantel
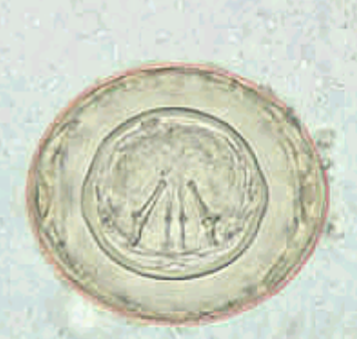
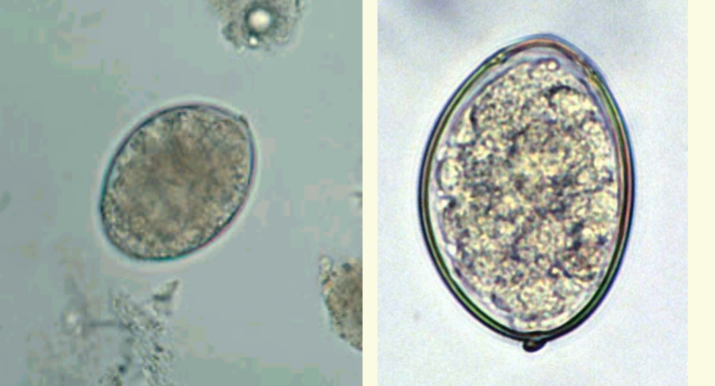
D. latum lab diagnosis
Recovery of ova or
Proglottids in feces
4 Ova:
– yellow brown
– 70 x 45 um, oval
– thin double contoured
shell
– inconspicuous operculum at
one end
– terminal knob at
abopercular end (may see)
4 unembryonated
4 may be confused with
Paragonamus ova
D. latum ova
D. latum adults
Adult worms measure 3-20 m
4scolex: flat, almond shaped, spatulate
– longitudinal groove
– no hooklets or rostellum
D. latum proglottids
Proglottids:
– broader than long
– central, rosette
shaped
– genital pore, middle
of flat surface
T. saginata, T. solium vs. D.
latum

D. latum life cycle
Definitive host...Man, dog, cat, other
mammals
4 Intermediate host...copepod, then fish
– pikes and pickerels
4 Infective form: plerocercoid larvae
4 Stages in human: adult
– Inhabits small intestine
4 Treatment: Praziquantel or Niclosamide

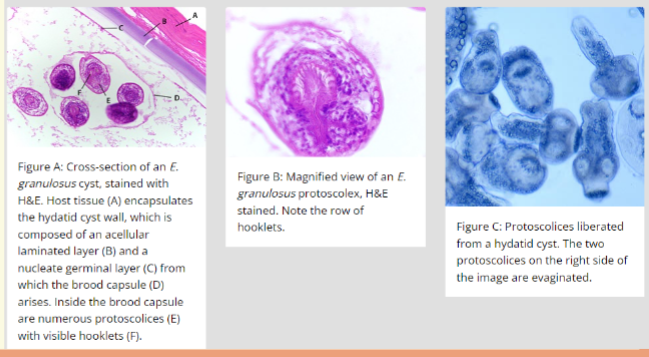
Echinococcus granulosus
Disease: Echinococcosis: Hydatid Cyst
disease or Hydatidosis
4Distribution
– Worldwide in sheep raising areas
– where domestic dogs are used in herding
E. granulosus major pathology
E. granulosus - Major
Pathology
4 Hydatid Cyst Disease
4 Varies according to size and location of cyst
– No symptoms until cyst gets larger
4 Expanding cyst causes pressure, necrosis of
surrounding tissue: liver, lung, brain
– liver (most common), portal hypertension,
– lung, SOB, chest pain
4 Cyst growth and rupture can result in death
4 Anaphylactic shock if cyst ruptures
4 Eosinophilia, uticaria, bronchospasms
E. granulosus characteristics
Adults: 3 - 8.5 mm
4 Scolex: 4 suckers
– armed w/30-36
hooklets
– Rostellum: Present
4 Proglottids:
– only 3 present
– longer than broad
– loose coil in
terminal Proglottids
– lateral genital pore
ova: resemble
Taenia spp.
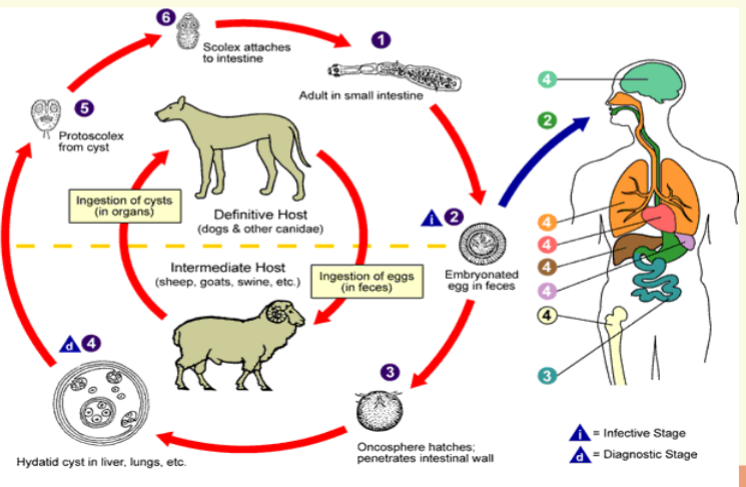
4infective larval form: ingested eggs
4definitive host: dog and wolves
4intermediate host: Man, sheep,
horses, hogs
4stage in man: larval
4location in man: various organs
E. granulosus lab diagnosis
x-rays, ultrasound or CT scan
4 serology tests, ELISA
4 presence of scolices, Hydatid sand or daughter
cysts
E. granulosus life cyle
E. granulosus treatment
Surgery
4Chemotherapy
4PAIR: percutaneous aspiration,
injection of chemicals and re-aspiration
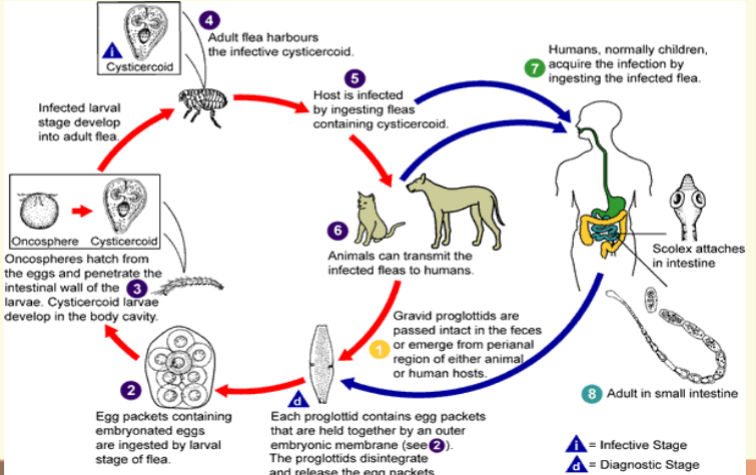
Dipylidium caninum
The double pore dog tapeworm
4mainly infects dogs, cats and
occasionally humans
4Geographic distribution:
– Worldwide
– infections reported in Europe, China-
Japan, Argentina, and the U.S.
D. caninum life cycle
D. caninum clincal features
Most infections in humans are
asymptomatic
4Pets exhibit behavior to relieve anal
pruritus
lab diagnosis of D. caninum
Most infections in humans are
asymptomatic
4Pets exhibit behavior to relieve anal
pruritus
size comparison chart

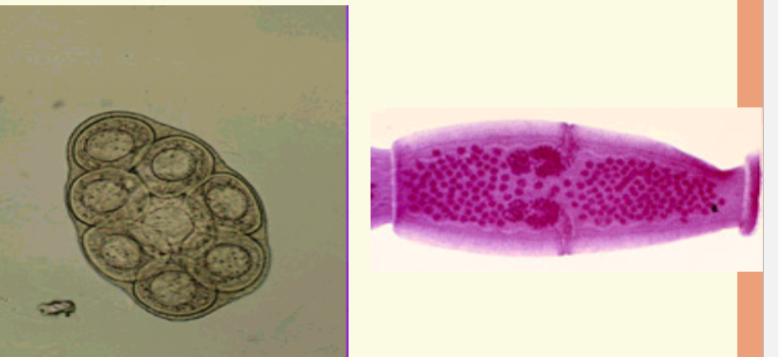
cestode ova comparison