Urinary systems + Electrolyte balance
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the osmotic pressure of capillaries?
osmotic pressure of blood plasma = ~300mOsm
isosmotic with interstitial fluid as only 1.5mOsm difference
What causes net filtration + net reaborption from capillaries?
net filtration = hydrostatic pressure > osmotic pressure
net reabsorption = osmotic pressure > hydrostatic pressure
solute levels in capillary higher than outside = net movement
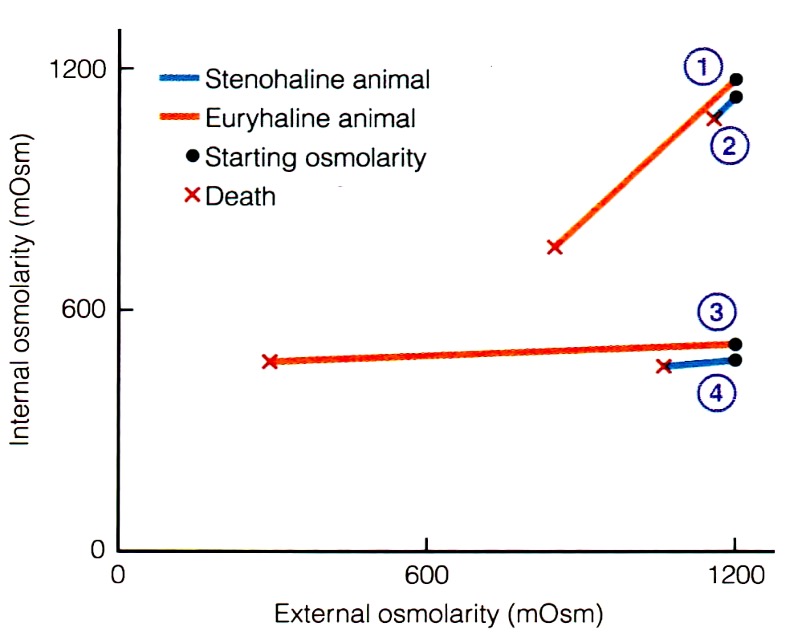
How does sea water affect extracellular fluid ion concentrations?
↑ external solute concentration = ↑ internal solute concentration
What are the major sites of ion + water exchange?
skin, respiratory systems, digestive systems + excretory systems
How does bulk flow osmoregulation work?
each cell has direct contact with fluid
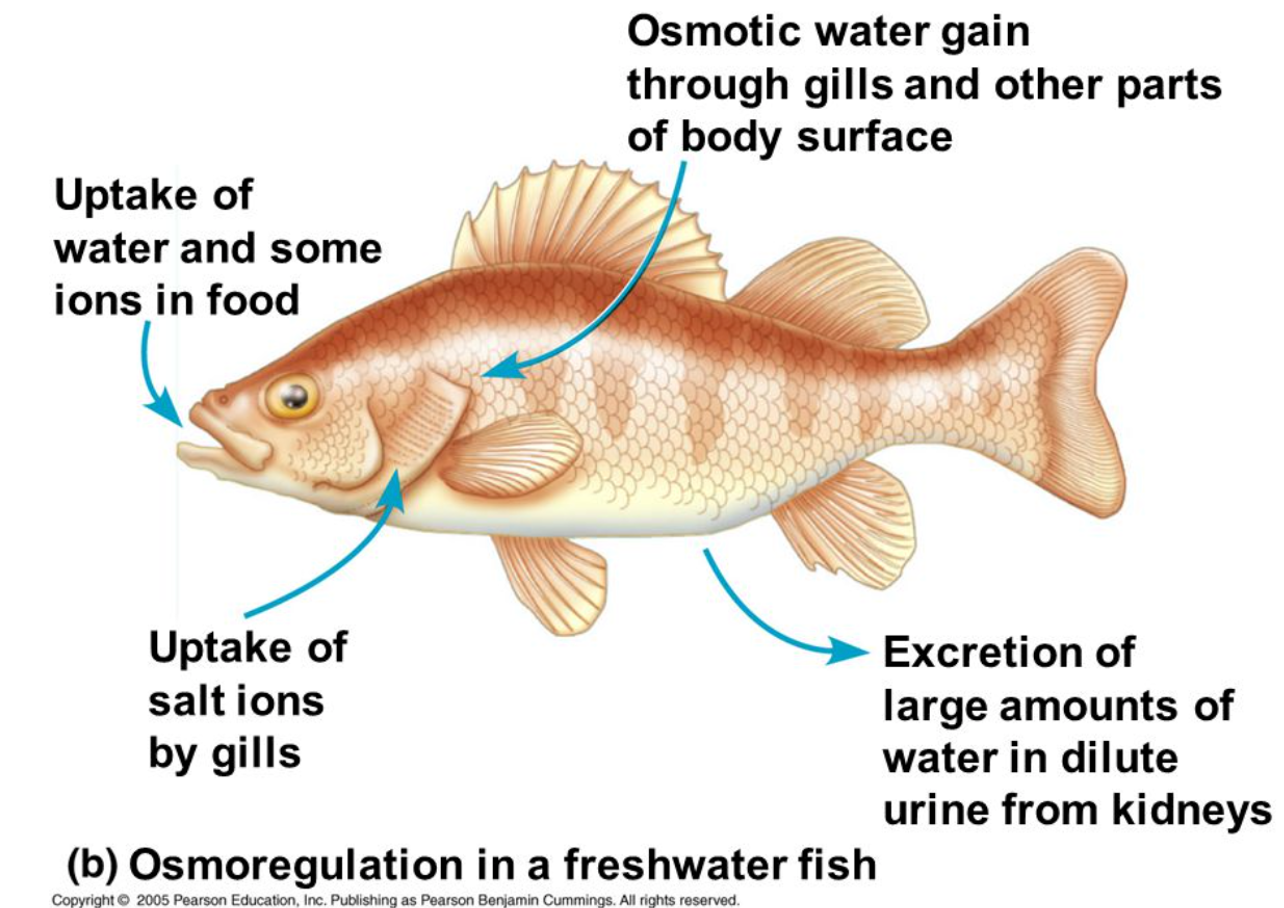
How does osmoregulation occur in freshwater fish?
High ion conc in fish = water enters by osmosis
water + some ion uptake in food
uptake of salt ions by gills
osmotic water gain through gills
extretion of large amounts of water in dilute urine
What are aquaporins?
tetramers that allow movement of water passively. Can be used both transcellularly (through cell membranes + in/out of cell) or paracellularly (between cells)
How does osmotic regulation change cell volume?
too much water entry = cells swell + burst - high ion conc inside cell
too much water loss = cells shrink + die - high ion conc outside cell
Whats the difference between metabolic water + ingested water?
ingested = preformed water
metabolic = used and produced by metabolic reactions
How is water lost by respiration?
when animals breathe, they lose water by evaporation. Magnitude of loss depends on breathing physiology + humidity of air
How is water lost in urine?
protein catabolism produces nitrogenous waste (urea) that needs excreting - requires water
How is water lost in faeces?
preformed water from digested food
What types of regulation in blood plasma can occur?
osmotic regulation - osmostic pressure
ionic regulation - amount of solute
volume regulation - water movement
What is the difference between obligatory + regulated ion/water exchange?
obligatory = response to factors beyond physiological control
regulated = physiologically controlled + required for maintaining homeostasis
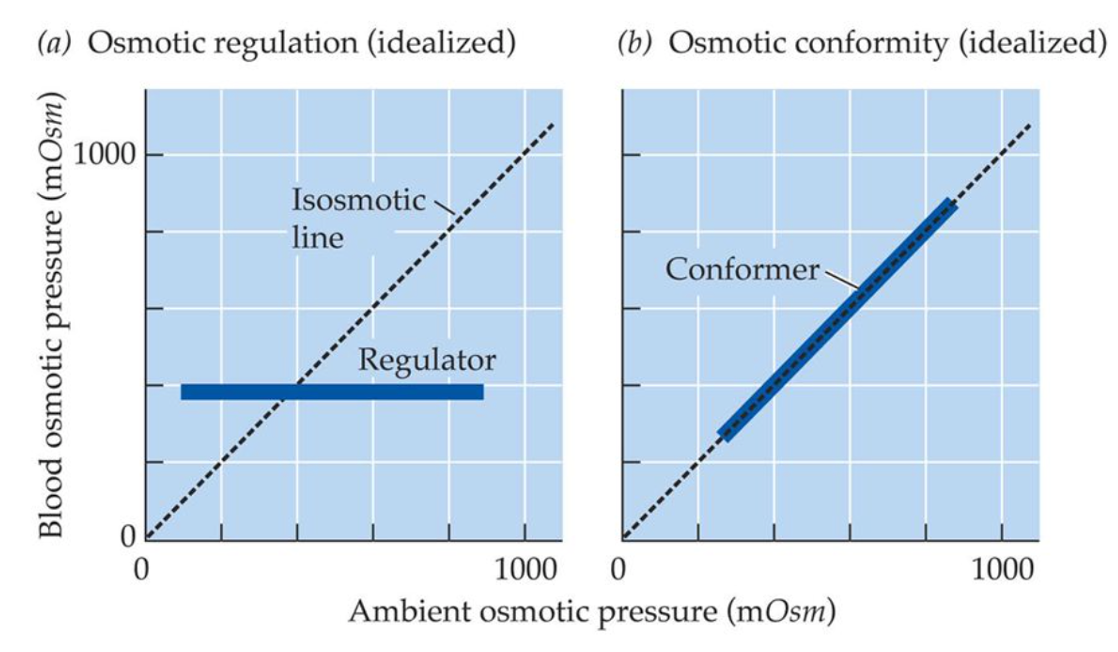
What are osmotic regulators or conformers?
conformers = aquatic animals that have osmolarity + ion composition similar to surrounding water even if that changes
regulators = regulate osmolarity + ion compositoon to keep constant independent of changes to external environment
animals often have mixture of osmotic regulation + conformity
How do crabs regulate volumes of body fluids?
amount of water gained by osmosis = amount of urine excreted by kidneys
hemolymph is highly hyperosmotic to surrounding water
urine is isosmotic to hemolymph
Why are freshwater animals described as hyperosmotic regulators?
regulate their blood osmotic pressure at levels hyperosmotic to freshwater
What challenges do freshwater fish face?
volume regulation = water constantly entering from dilute environment (osmotic gradient)
osmotic regulation = water entering decreases osmotic pressure of extracellular fluid
ionic regulation = ions moving from extracellular fluid to water
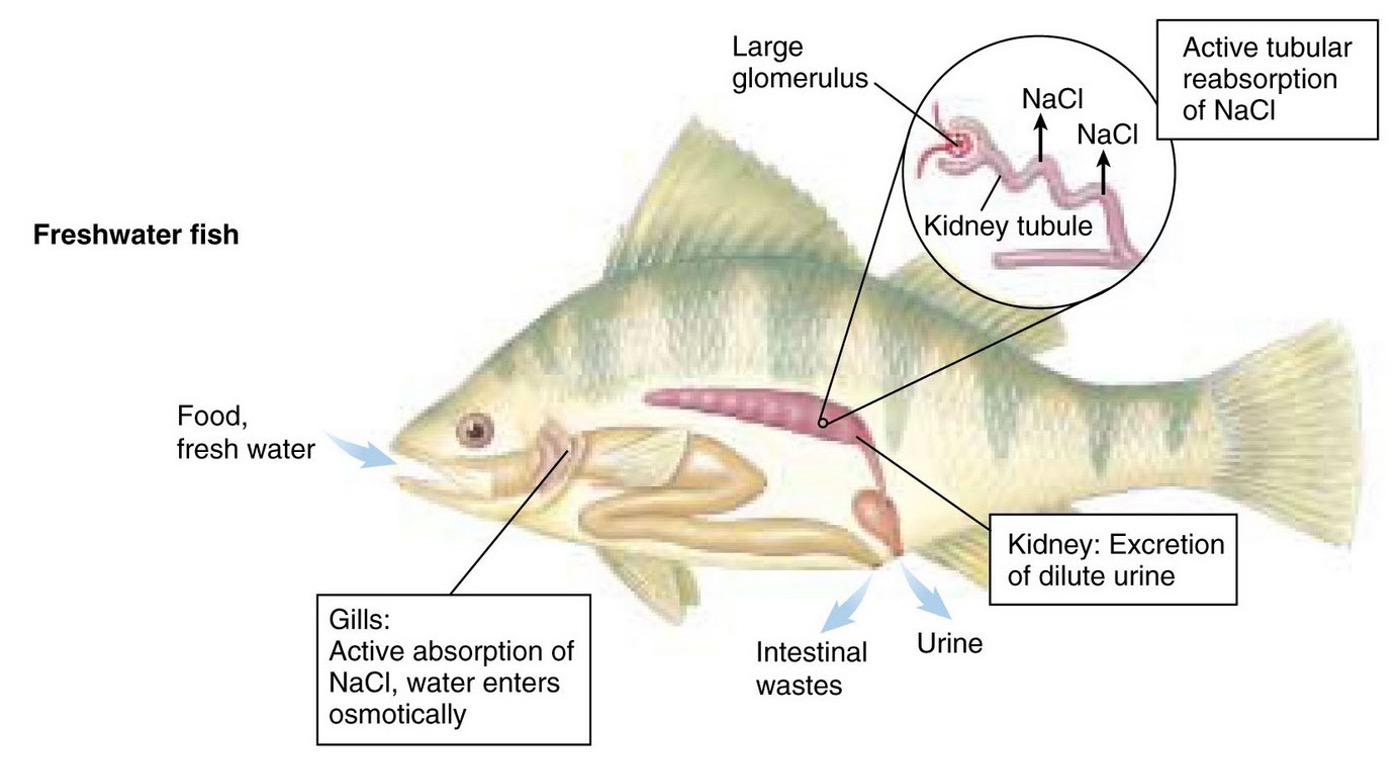
How do freshwater fish gain ions?
kidneys - regulate volume, water + ion balance. Produce large amounts of hyposmotic urine to prevent loss of ions
gills - active uptake of ions
gut - active uptake of ions from food
How do marine fish lose ions?
glomerulus absent + short nephrons = reduce water loss in urine
gills = active secretion of NaCl + water loss
Stomach = passive reabsorption of ions + water
urine = concentrated
What is the role of the kidney in marine fish?
epithelia of marine fish poorly penetrable to water
drink water + absorb via gut epithelia - co-absorption of monovalent ions
kidneys produce small amounts of isosmotic urine
main role of kidneys is excretion of divalent ions
gills = excretion of Na, Cl + products of metabolism
How do different animals tolerate water salinity?
differ to degree of tolerance to changes in water salinity
stenohaline = tolerate only narrow ranges of NaCl
euryhaline = tolerate wide varience in NaCl
What is the function of the urinary system?
removal of waste
regulation of volume + solute concentration of blood plasma
elimination of waste products
What are the components of urinary system?
kidneys = urine production, extretion + regulation
ureters = urine transfer to bladder
bladder = urine storage + elimination
urethra = urine release + elimination
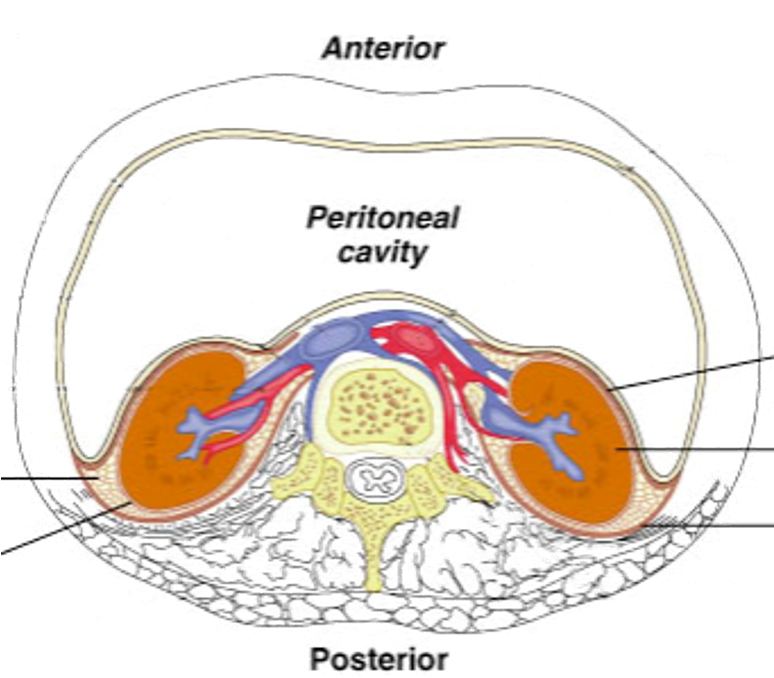
Where are the kidneys located?
Either side of midline on posterior abdominal wall. Left is slightly higher than right due to the liver. Between T12 - L3 of spine
What are the characteristics of the adrenal glands?
on superior pole (above) kidney
right = pyramidal shape, left = concentric shape
cortex - corticosteroids, sodium + water retention, ↑BP + volume
medulla - adrenaline + noradrenaline ‘fight or flight’ response
What is the relationship between kidneys + peritoneum?
lie behind the parietal peritoneum - surrounded by fat
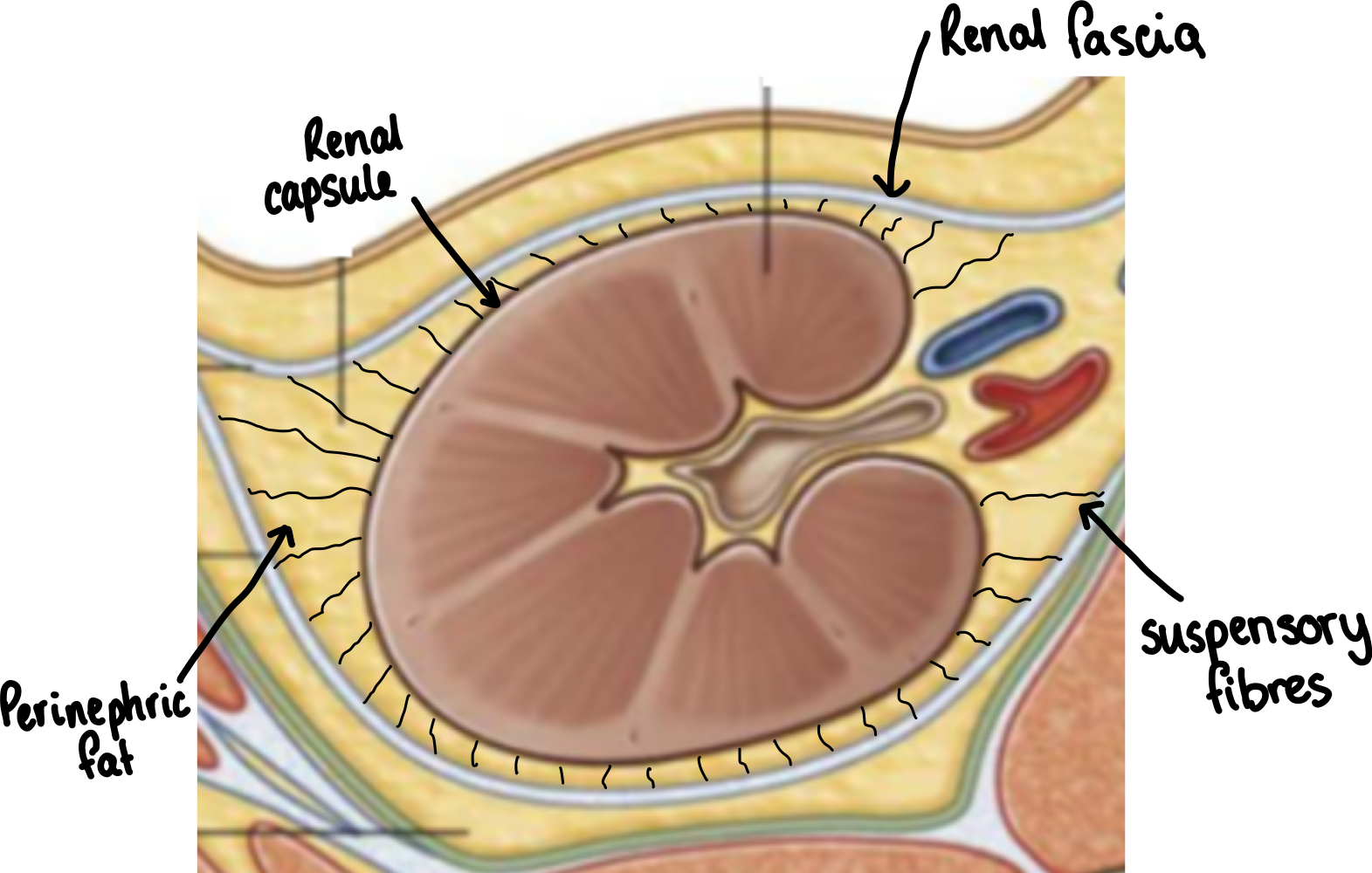
What is the external structure of the kidneys?
renal capsule - collagen rich, firmly adhered to kidney
renal fascia - collagenous membrane
perinephric fat - adipose tissue
suspensory fibres - prevent kidney moving
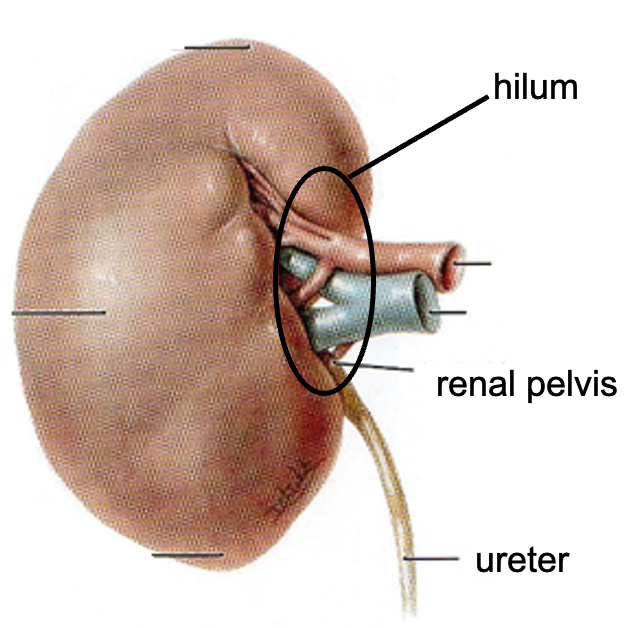
What is the overall structure of the kidney?
indented ovoid (bean) shaped
hilium = structures enter + leave kidney - renal artery, renal vein, ureter
What is the structure of the renal lobe?
renal cortex - proximal + distal parts of nephron + collecting ducts
renal medulla - loops of Henle + collecting ducts
renal papilla

What is the structure of the kidney
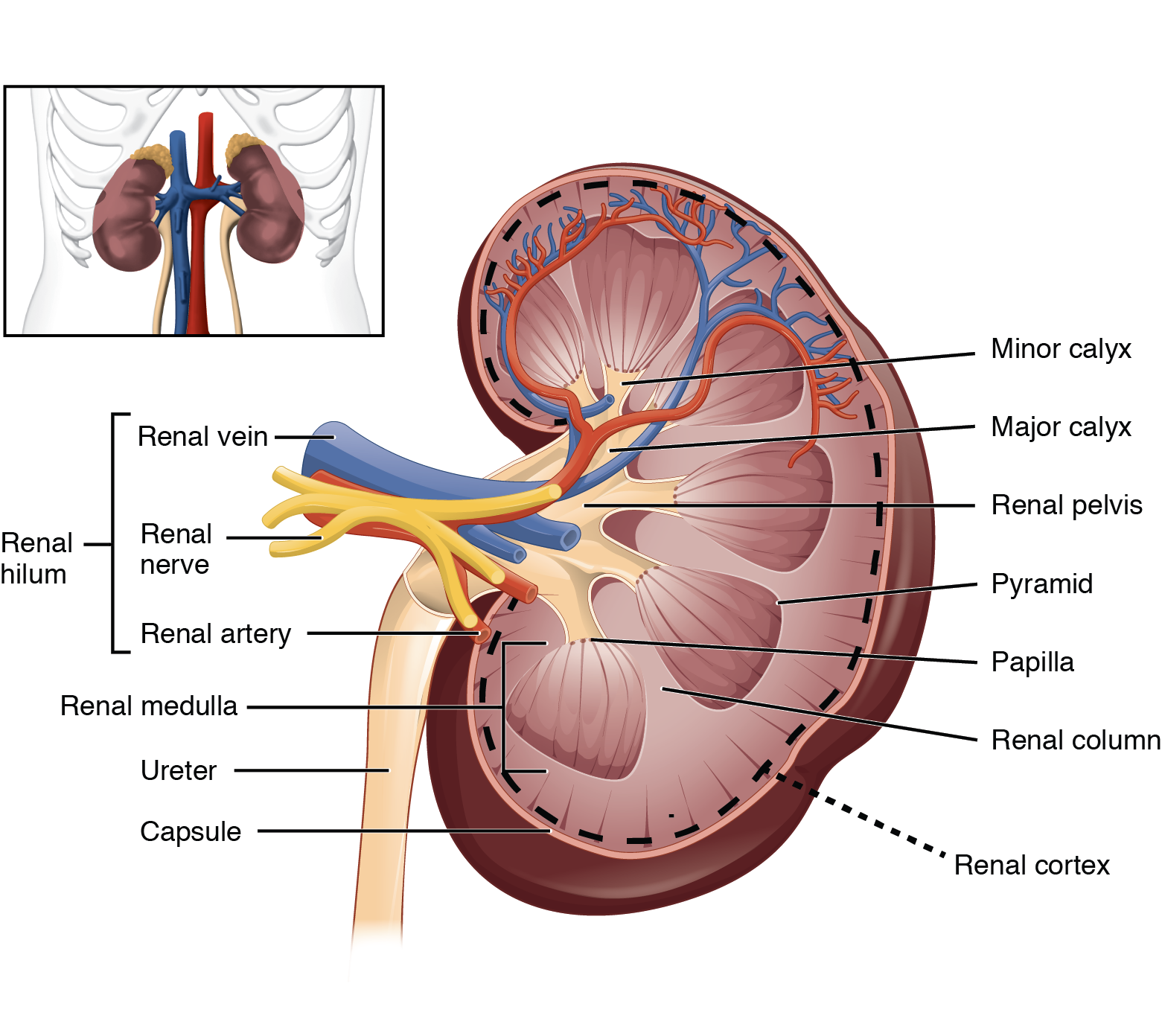
What is the function of the ureters?
hollow muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to bladder
~30cm long
enter bladder obliquely
when bladder is full prevent backflow of urine = compression closes off ureters acting as valves
What is the exterior structure of bladder?
apex = points towards pubic symphysis
fundus = opposite apex and formed by posterior wall
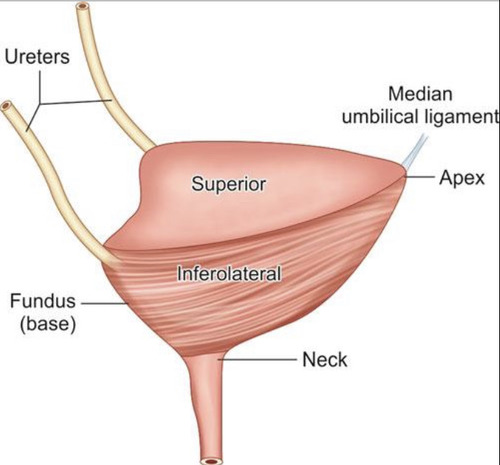
What is the internal structure of the bladder?
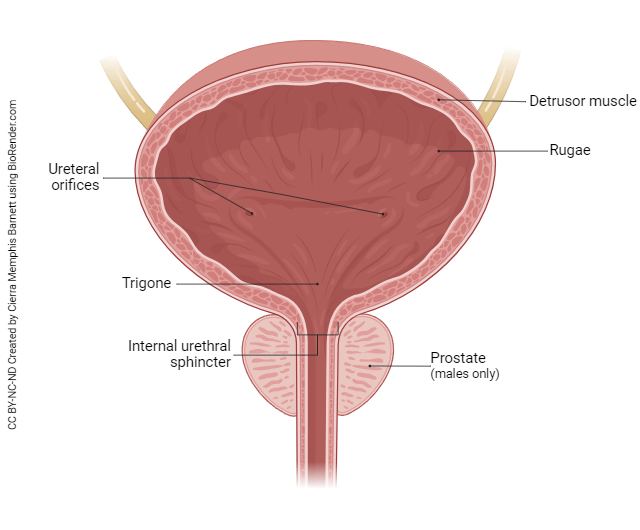
What is the main difference between female + male urethras?
Female urethral sphincters are immediately inferior to one another. In males, internal urethral sphincter = between bladder and urethra (prevents semen in bladder) but external sphincter = inferior to prostate
What are the functions of kidney?
water balance (volume)
osmotic balance
ion balance
pH balance
excretion of waste
hormone production
regulation of blood pressure
What are the 4 principle processes of kidney?
filtration
reabsorption
secretion
excretion
What are the 3 layers of the glomerulus filtration barrier?
lumen of blood vessel, endothelial cells, basement membrane + podocytes. Keep blood + protein in body but allow fluid + small molecules to pass through.
What is the structure of the glomerulus?
blood flows in via afferent arteriole + leaves via efferent arteriole. Inside there is a capillary tuft (or glomerula tuft) = network of capillaries with thin cell walls.
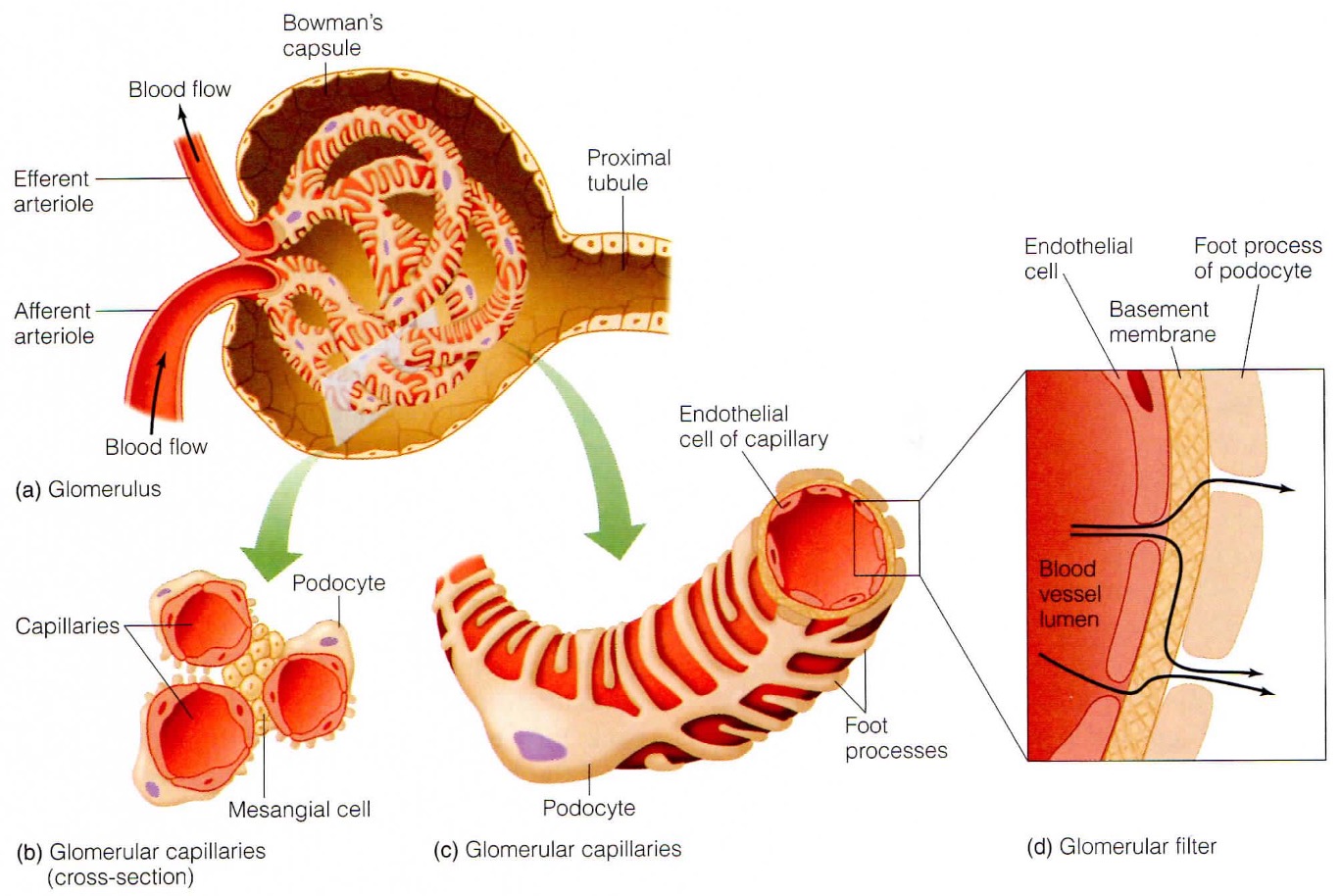
What does the charge + size selectivity of the basement membrane determine?
What will cross. It also enables capillary tuft to resist high pressure + acts as scaffold.
What is clearance in the kidney?
the ability of the kidneys to totally clear blood of a certain substance
What is Starlings principle of fluid exchange?
the direction of fluid flow across capillary wall is result of Net Filtration pressure = balance between osmotic + hydrostatic pressure
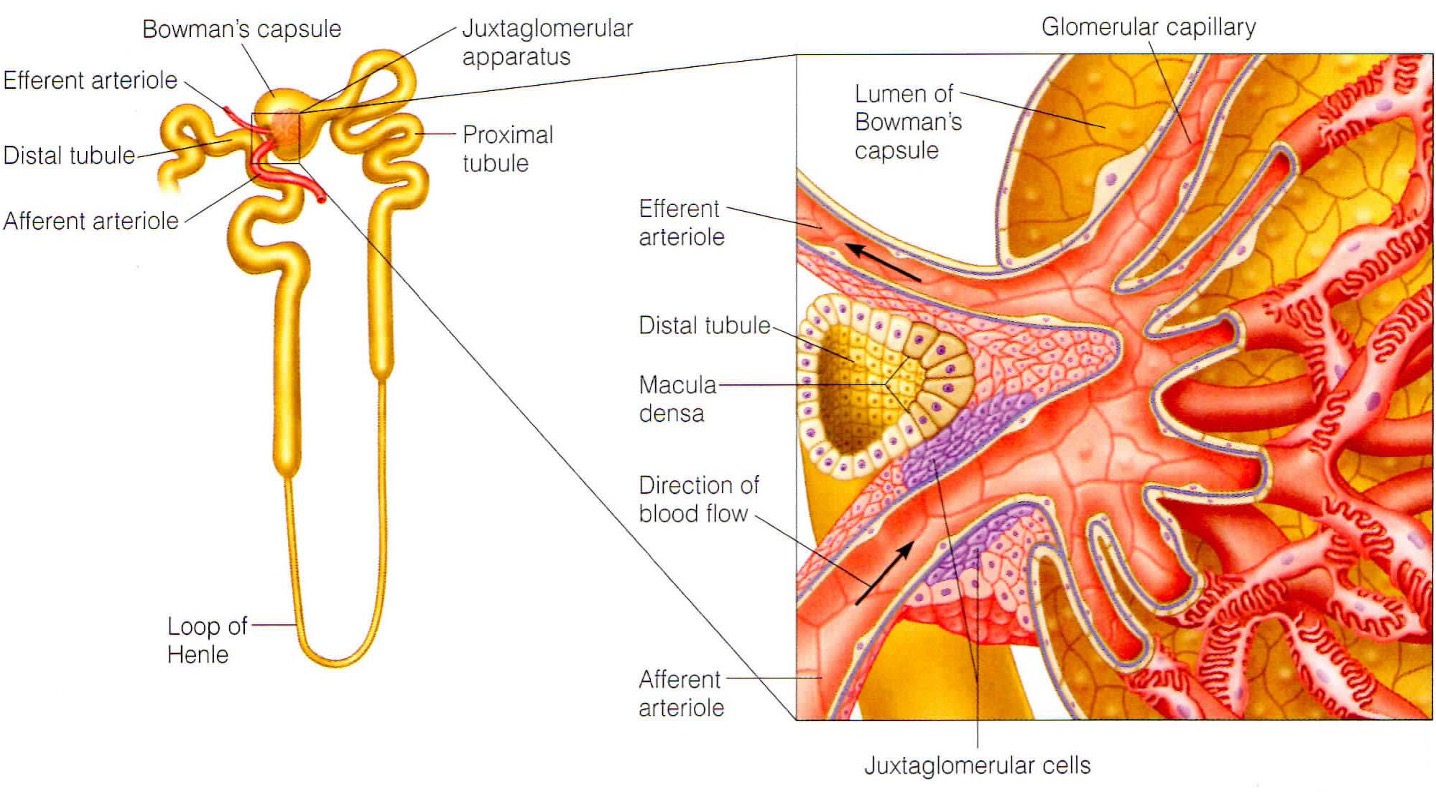
What is the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
specialised region that is important for sensing flow into kidney + producing hormones susch as renin
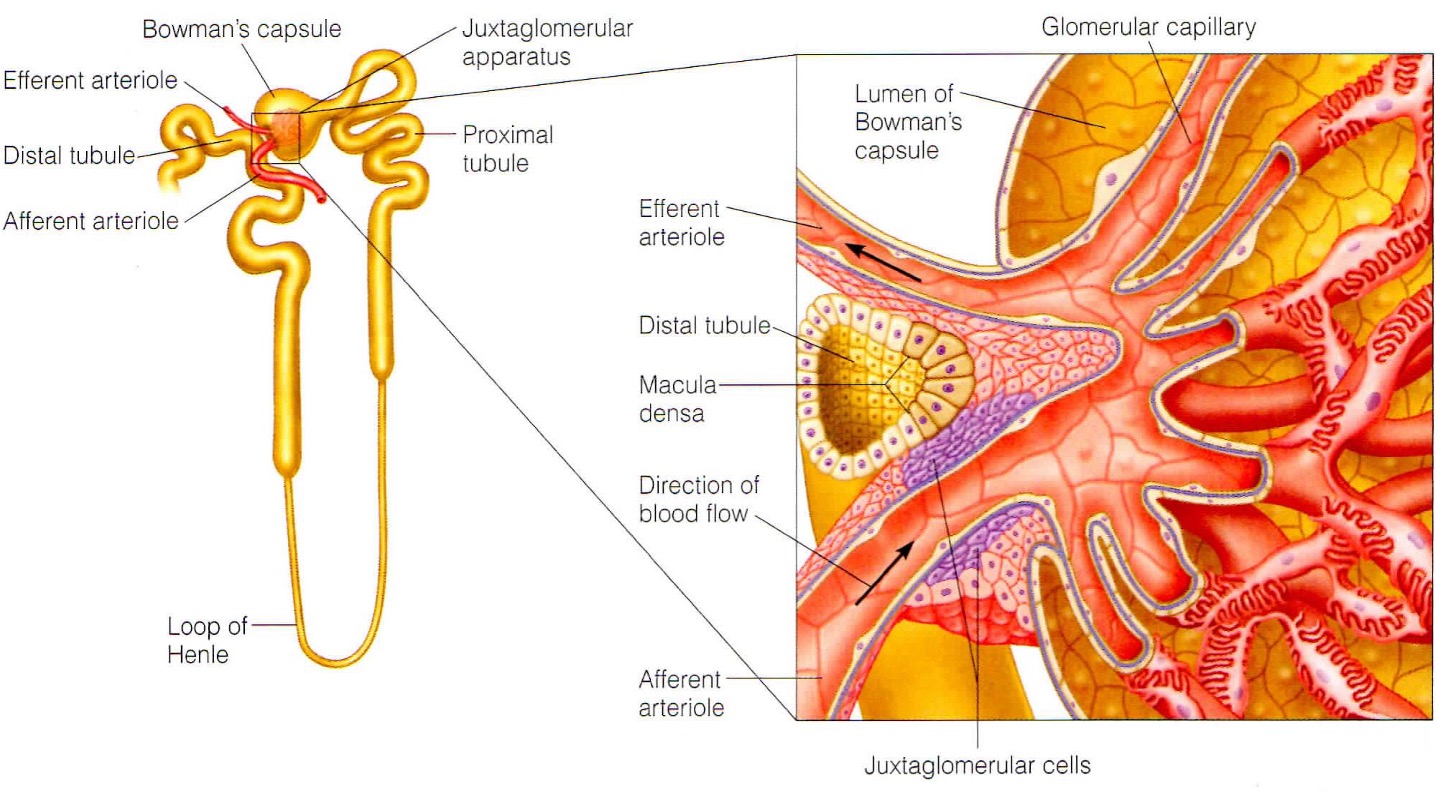
What do the smooth muscles in the JGA sense?
smooth muscle in walls of afferent arterioles sense stretching and respond bu constriction/dilation to modify blood flow + filtration rate
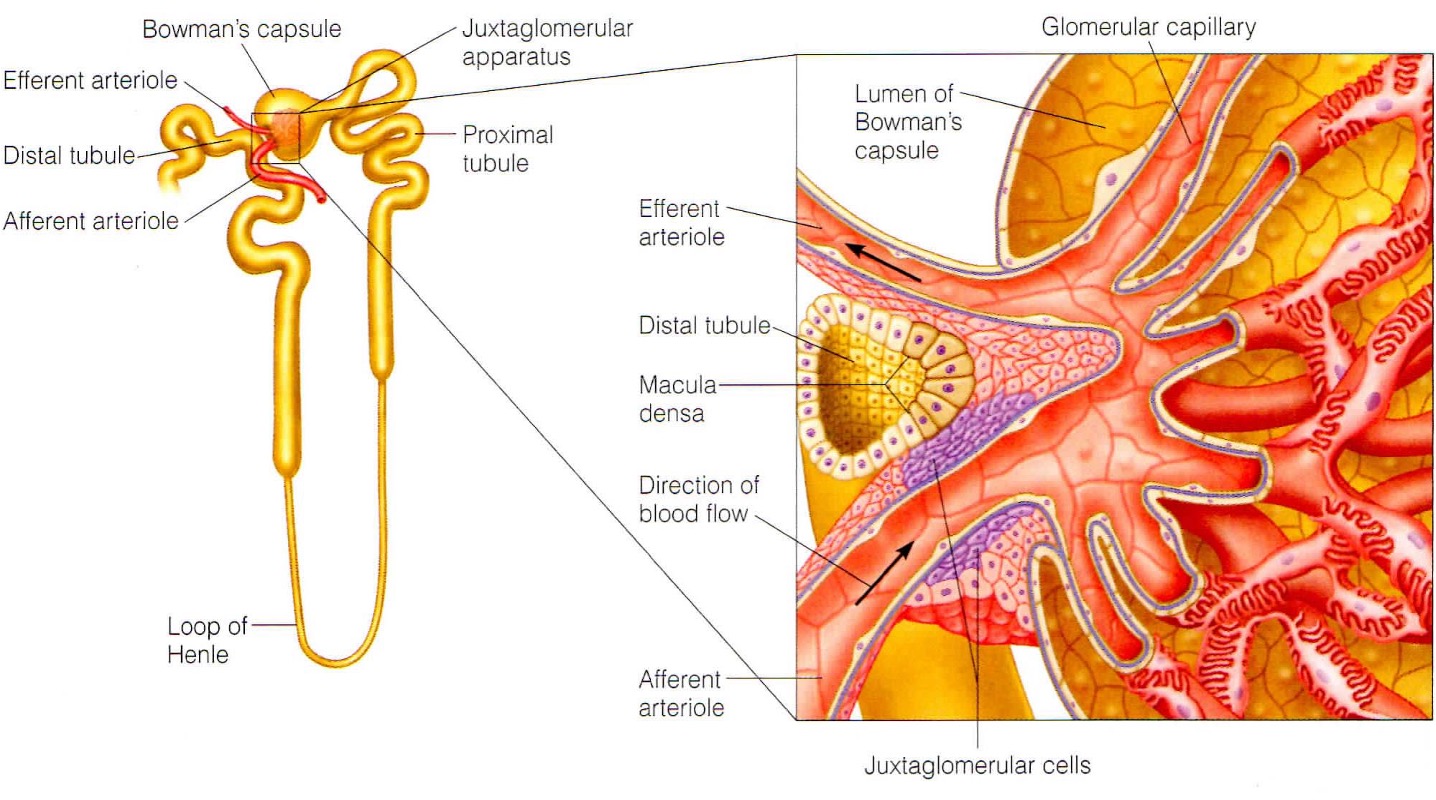
What does the macular densa in the JGA sense?
they are modified cells in distal tubule that sense changes in flow + increase in osmolarity of intertubular fluid. They send chemical signals to afferent capillaries to constrict.
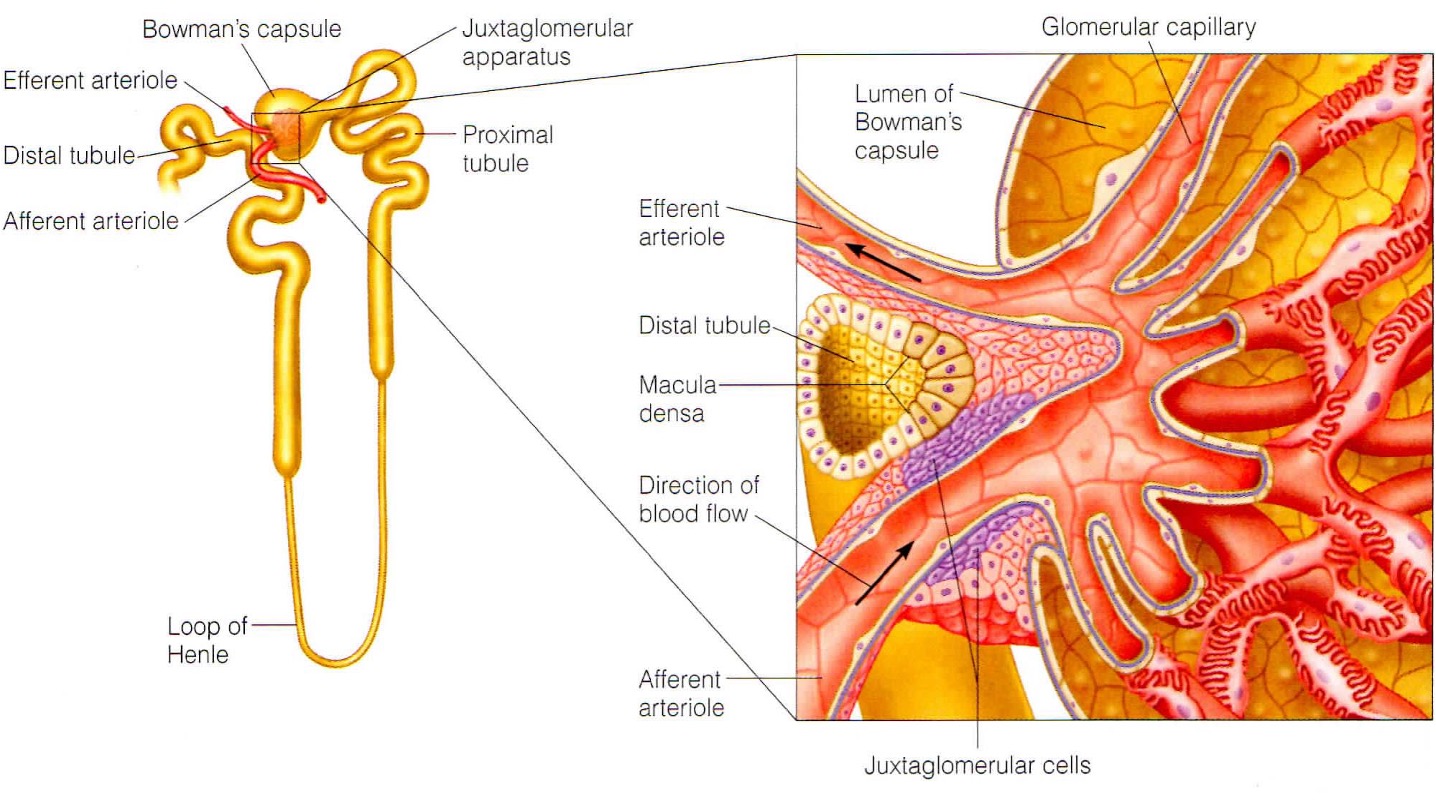
What is the function of the smooth muscle like juxtaglomerular cells?
Signals are received from the macula densa when the osmolarity of intertubular fluid drops. Baroreceptors also sense a decrease in arterial pressure. Signals stimulate the cells to secrete renin into the bloodstream.
How do podocytes respond to stretching capillaries?
increase permeability of glomerular filter and total surface area available for filtration
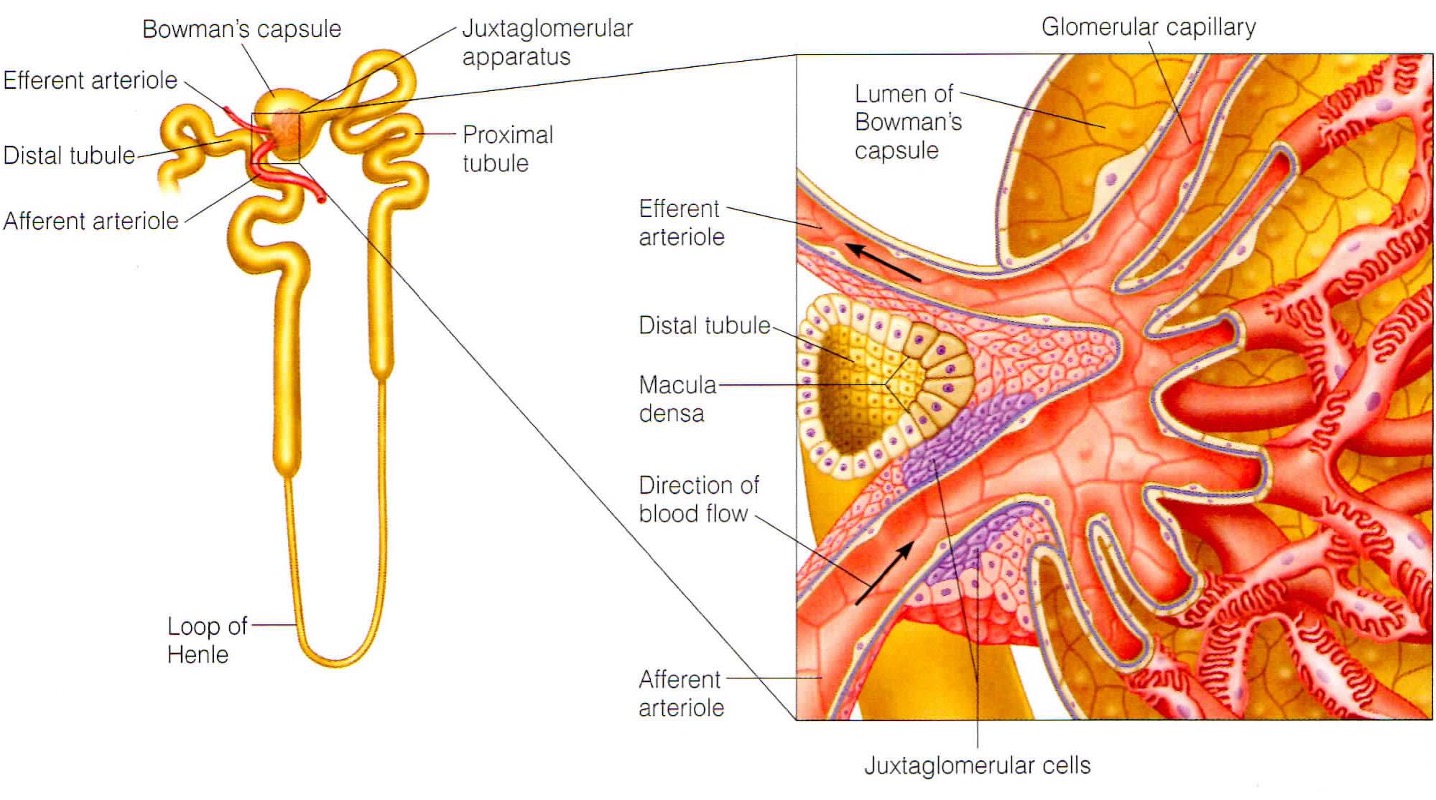
In summary what is the response to decreased osmolarity?
reduction in osmolarity of filtrate - vasodilation - macula densa cells sense - release of renin - blood pressure returns to normal
In summary what is the response to increased osmolarity?
increase in osmolarity - vasoconstriction - blood pressure returns to normal
What are the characteristics of tubule epithelial cells?
relatively impermeable
tight junctions - prevent paracellular transport
polarity - enabling unidirectional flow of certain substances
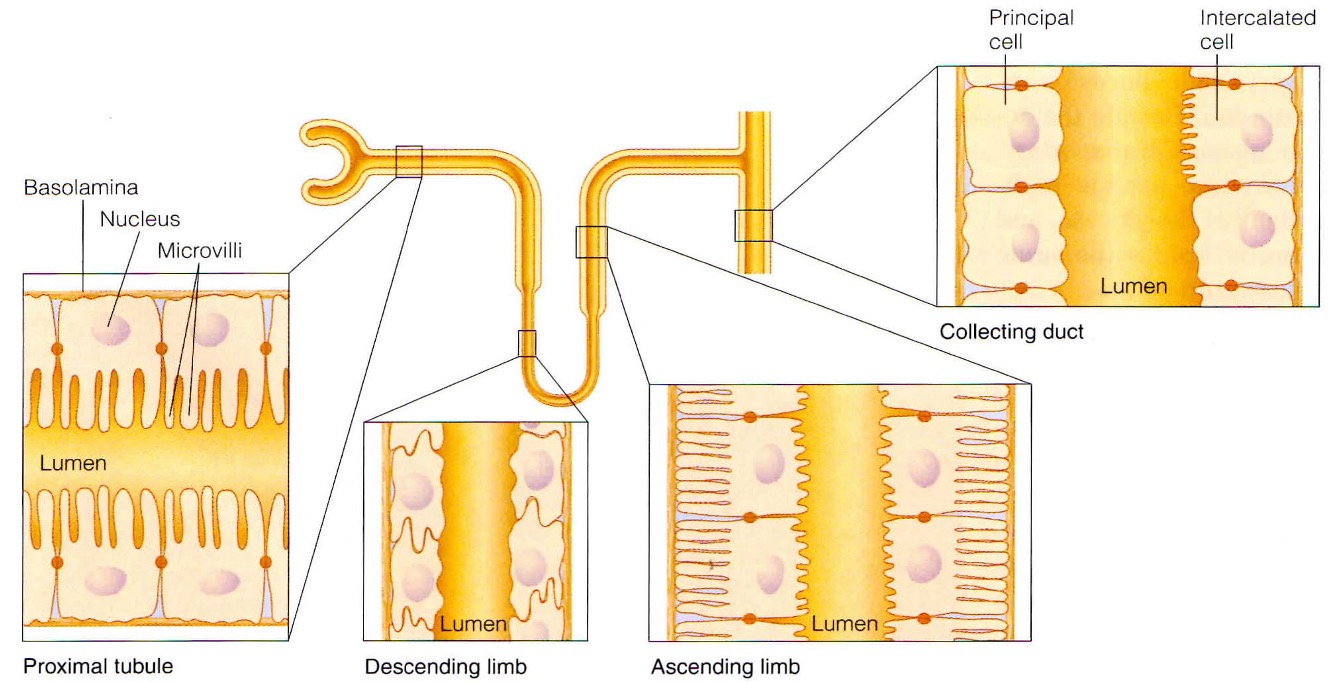
What are the adaptations of epithelial cells in each section of the kidney?
proximal tubule
microvilli to increase SA
lots of mitochondria - reclamation of particles = energy dependent
Loop of Henle
thin descending limb
thick descending limb
lots of mitochondria = pump ions against conc gradient
lots of tight junctions
Collecting duct
lots of tight junctions
sensitive to hormonal stimuli
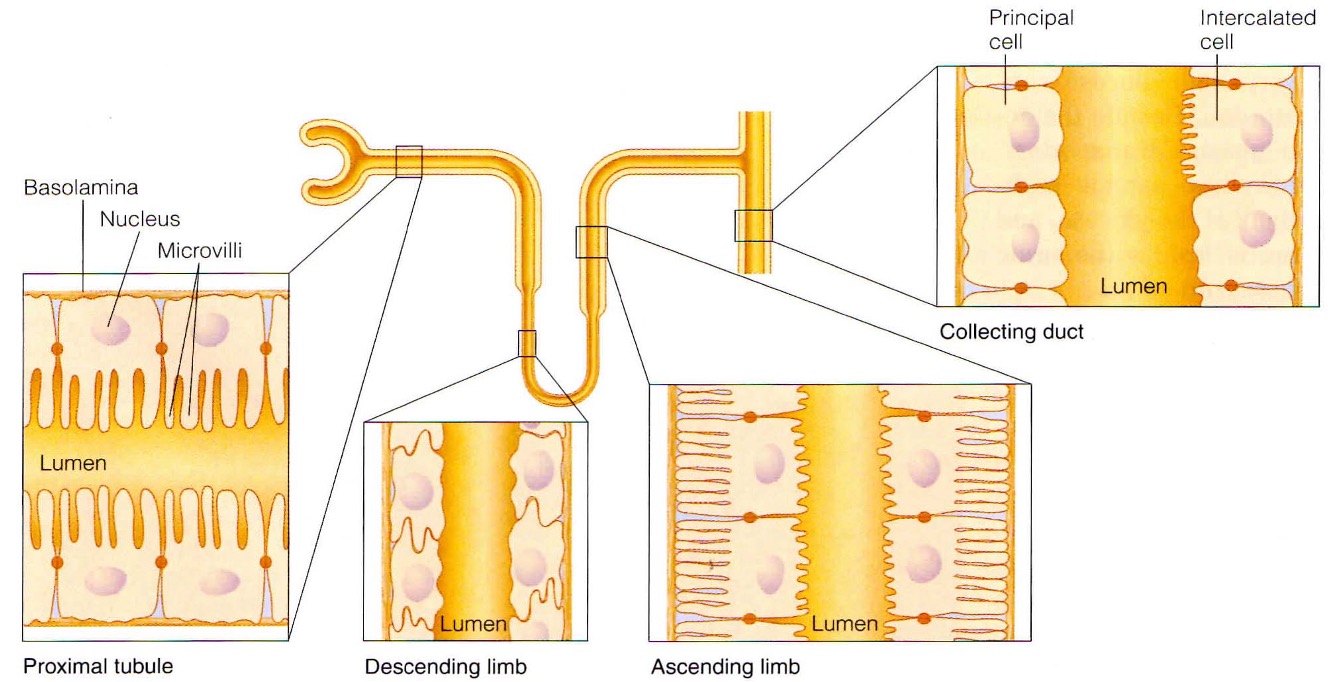
What is the function of each section of the kidney tubule?

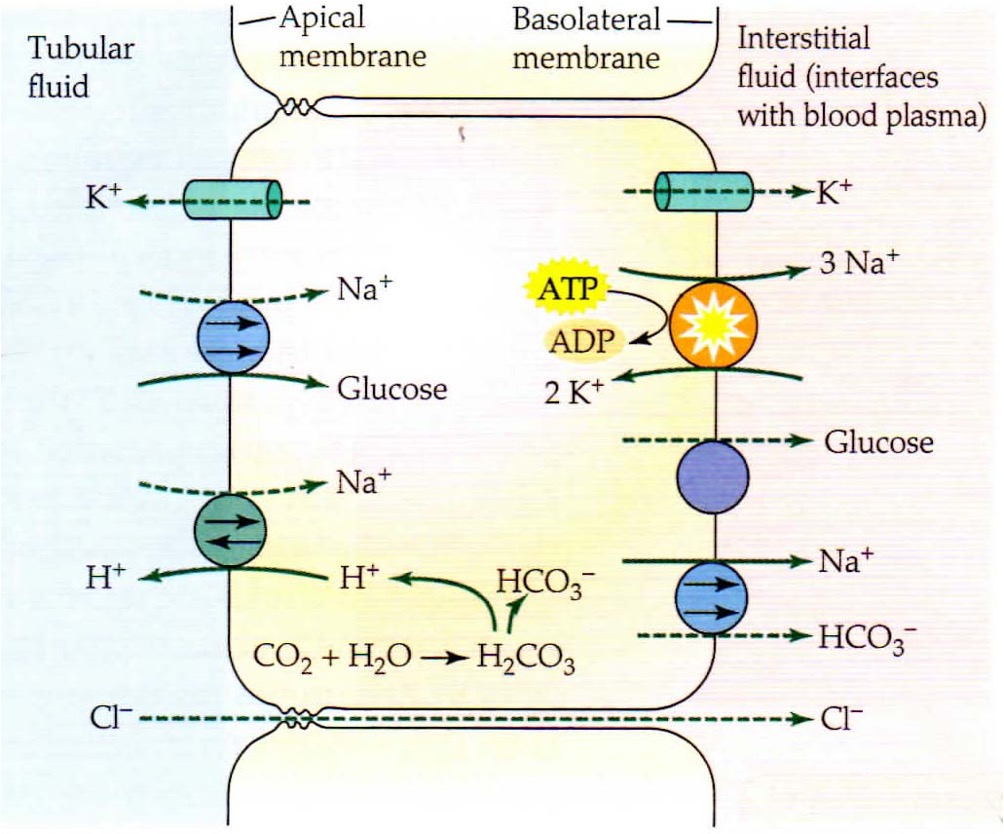
What is the function of the proximal convoluted tubule?
Reabsorption of 75% of water, sodium + chloride ions. At end of PCT, tubular fluid is isosmic to surrounding interstitial fluid + blood plasma. Some active secretion of cetain ions/toxins
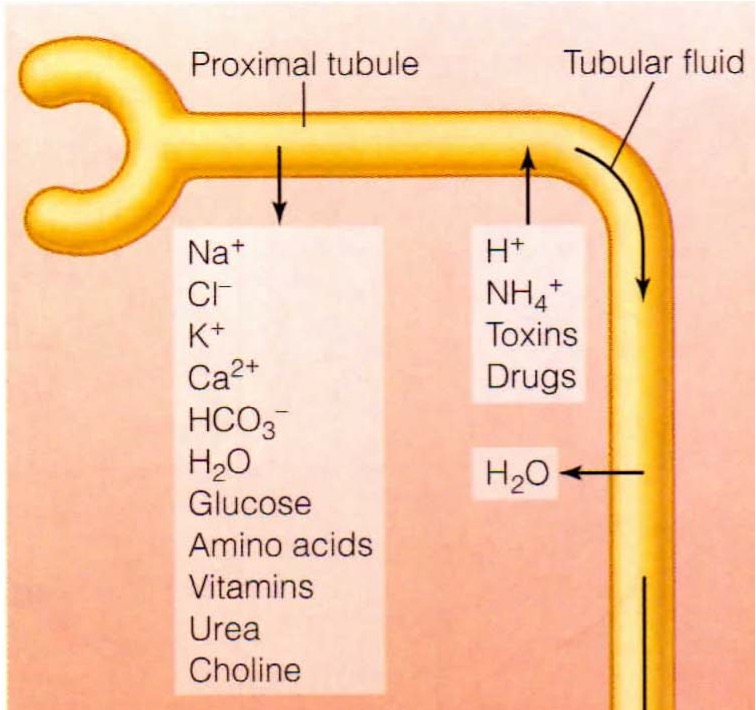
What are the main cellular mechanisms that occur in the proximal convoluted tubule?
reabsorption of Na+ though apical membrane with co-transport with glucose or exchange with H ions. Na+ then transported across basolateral membrane using co-transport with bicarbonate + active transport in exchange for K+. Osmotic gradient allows movement of water through aquaporins.
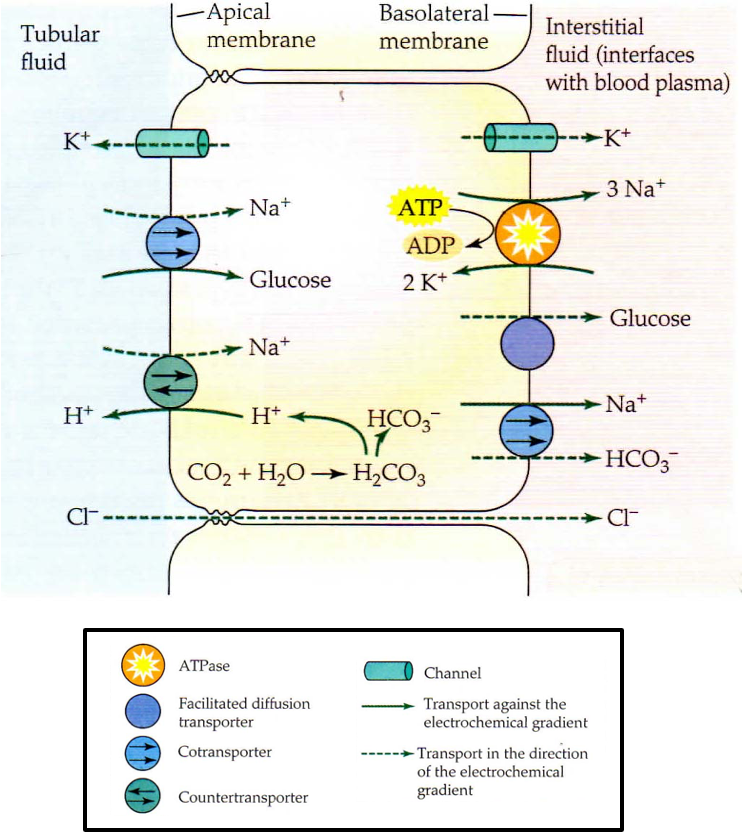
What is the function of the Loop of Henle?
reabsorption of water. Descending limb is very permeable to water + doesnt have tight junctions. No active transport of solutes. Ascending limb is impermeable to water, no active transport of solutes + permeable to ions.
Only water reabsorption in descending + only ion reabsorption in ascending(passive diffusion in thin segment + active transport in thick)
What is the function of the distal convoluted tubule?
reabsorption + secretion
reabsorption of sodium, chloride, calcium, magnesium + other inorganic ions
secretion of protons, potassium + ammonium ions
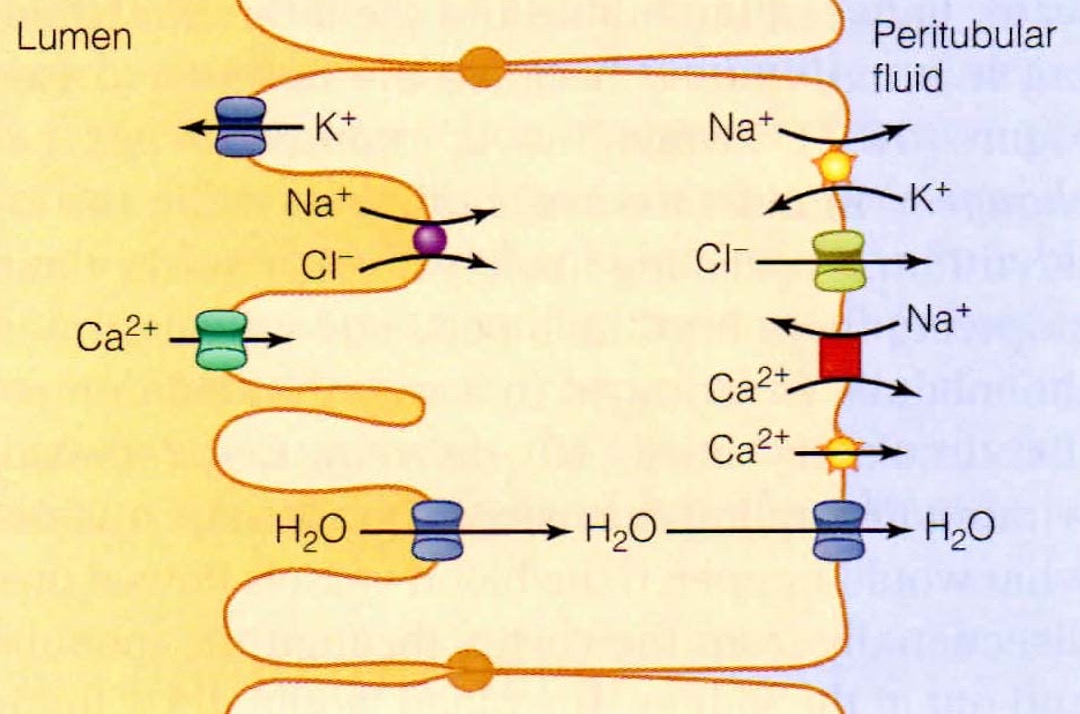
What is the function of the collecting duct?
final stage of reabsorption + secretion.
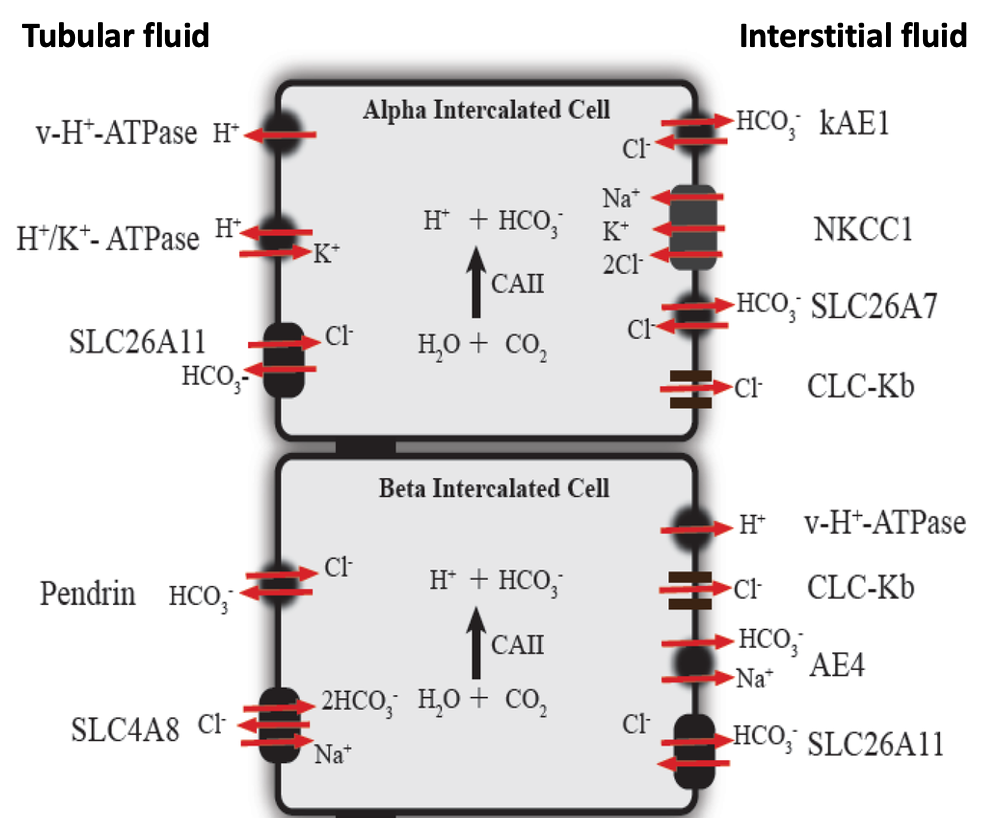
How is acid-base (pH) balance maintained?
occurs in distal tubule + collecting duct
Alpha intercalated cells (acid secreting) and beta intercalated cells (base secreting) possess sensors for biocarbonate, CO2 or proton conc
signals from sensors modulate, expression, abundance or activity of these cells under hormonal control.
What is net filtration pressure?
pressure favouring filtration - pressures opposing filtration = net filtration pressure
glomerular capillary pressure (hydrostatic pressure within capillaries) minus intercapsular pressure (hydrostatic pressure within lumen of bowmans capsule) = net hydrostatic pressure
net hydrostaic pressure - colloid osmotic pressure (oncotic pressure) = net filtration pressure