Infectious Diseases of the GI System
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
G- vs G+
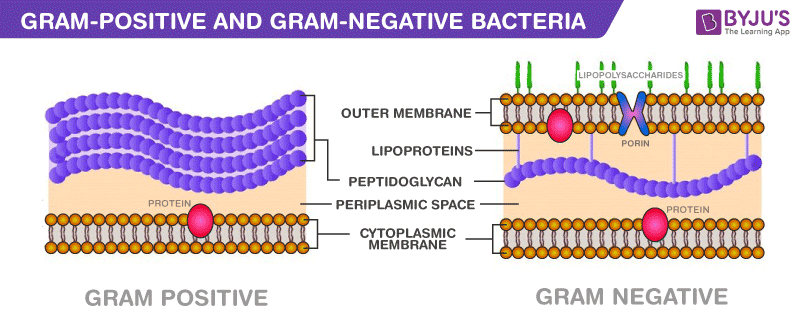
G+ = more susceptible, endospores
G- = more resistant - outer membr. blocks antibiotics
Dental Caries
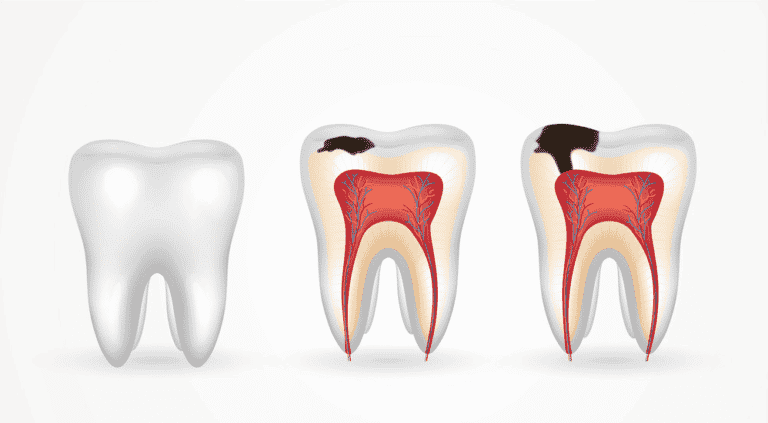
tooth decay
Streptococcus & Lactobacillus families
Virulence: fermentation of sugars → acid → demineralization of enamel → biofilm (plaque) → cavities
Key Features: plaque, cavities
Diagnosis: clinical
Treatment: dental hygiene, restoration
Endodontic Infections (Pulpitis → Necrosis)
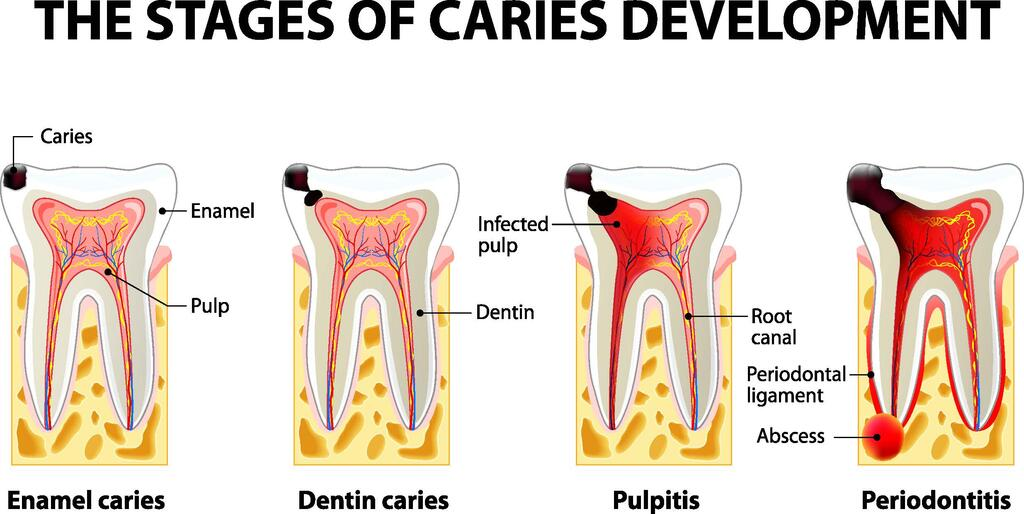
bacterial invasion of pulp (innermost layer - deep tissue)
Multiple types of anaerobic bac.
Virulence: fermentation acids & proteolytic enzymes (break down proteins)
Key Features:
reversible pulpitis = cold sensivity
irreversible pulpitis = spontaneous, intense pain
necrosis → abscess
Possible cellulitis (deep tissue spread)
Diagnosis: clinical + x-ray
Treatment: root canal
Periodontium
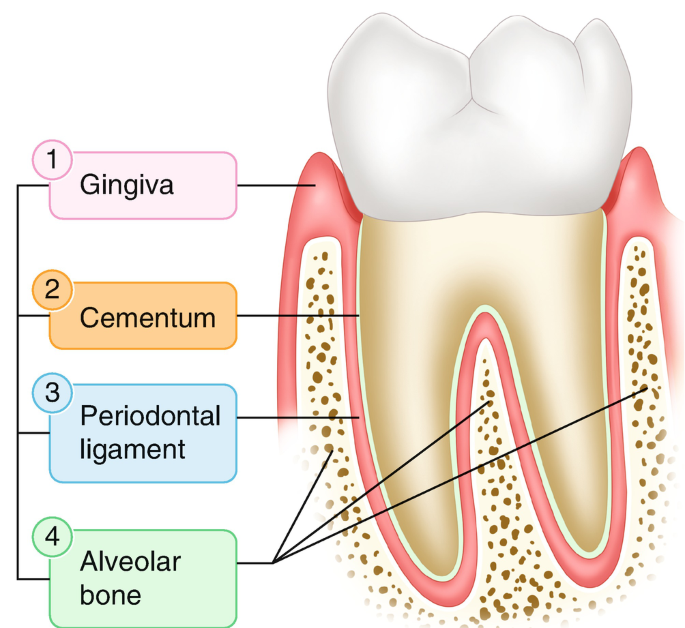
tissues that support/surround teeth
Periodontal Diseases
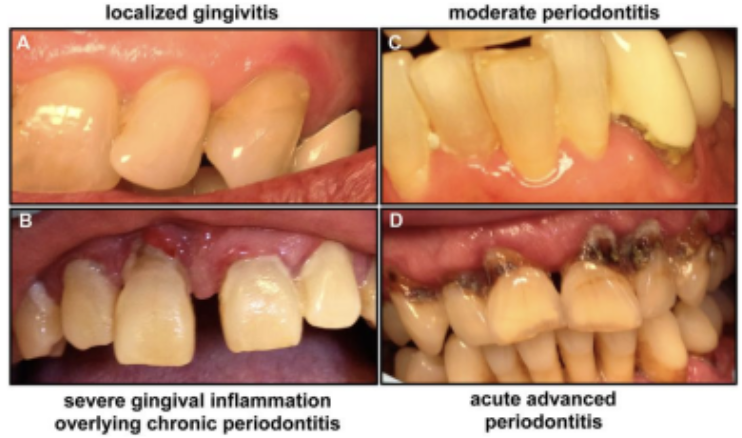
G- anaerobes
Virulence: catabolic enzymes, inflammation, biofilm
Key Features:
Gingivitis - reversible
Periodontitis - tissue destruction
Diagnosis: clinical (look at depth + bone loss)
Treatment: deep teeth cleaning, hygiene
Enteric
Relating to the intestines
Enteritis
Small Intestine Infections
Colitis
Large Intestine Infections
Gastroenteritis
Acute Infectious Inflammation of the Stomach and Small Intestine
Main Symptoms: diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever
Virulence:
Invasion of mucosa
Adhesion + toxin production
Enterocyte destruction
Preformed toxins (no invasion)
Campylobacter jejuni
G-, microaerophilic (grows at avian body temp)
Virulence: cytotoxins, mucosal invasion (has flagella → motile)
Reservoir & Transmission: zoonotic = undercooked poultry
Key Features: watery + bloody diarrhea, fever, ab cramps
Diagnosis: stool PCR/culture
Treatment: supportive, antibiotics if severe
Notes: associated w/ Guillain-Barrè syndrome (autoimmune nerve damage)
Salmonella enteria (non-typhoidal)
G-, motile
Virulence: mucosal invasion, survives in macrophages
Reservoir & Transmission: zoonotic = poultry, eggs, reptiles, livestock
Key Features: watery diarrhea (sometimes mucus or bloody), fever
Diagnosis: stool PCR/culture
Treatment: supportive, avoid antibiotics
Notes: high bac load to infect, survives well in environment
Shigella spp.
G-
Virulence: Shiga toxin (cytotoxin), invasion plasmid for epithelial invasion, motile inside cells
bac inject proteins that damage host cell cytoskeleton, host cell engulf bac, bac reproduce, bac use host cell actin to move & invade other cells
Reservoir & Transmission: human only, fecal-oral
Key Features: dysentery (bloody, mucous diarrhea), tenesmus (constant urge to poop)
Diagnosis: stool PCR/culture + Shiga toxin detection
Treatment: supportive, antibiotics shorten duration of symptoms
Notes: low infectious dose → outbreaks, acid-resistant (survives GI tract)
Pathogenic E. coli
G-
ETEC, EPEC, EIEC, EAEC, STEC
Virulence:
ETEC: heat-labile & heat-stable toxins
EPEC: attaching & effacing lesions
EIEC: Shigella-like invasion
EAEC: biofilm
STEC: Shiga toxin
Reservoir & Transmission: depends on pathotype (ex: cont. food/water, fecal-oral)
Key Features:
ETEC/EPEC: watery diarrhea
EIEC/STEC: bloody diarrhea
EAEC/EPEC: chronic diarrhea
ETEC: traveler’s diarrhea
STEC: HUS (hemolytic uremic syndrome - blood vessel damage → kidney failure) risk
Diagnosis: stool PCR + Shiga toxin test
Treatment: rehydration. avoid antibiotics (unless severe)
Notes: avoid antibiotics in STEC due to HUS risk
ETEC
Enterotoxigenic
traveler’s diarrhea
Symptoms: watery diarrhea, ab cramps, no fever
Virulence: heat-labile & heat-stable toxins (cause diarrhea)
EPEC
Enteropathogenic
infants - diarrhea, vomiting
attaching & effacing (A/E) lesions on microvilli
EIEC
Enteroinvasive
dysentery-like
Symptoms: bloody/mucous stools, tenesmus, cramps, fever
Virulence: invasion like Shigella
EAEC
Enteroaggregative
Biofilm
Persistent diarrhea
STEC
Shiga-toxin producing
Hemorrhagic colitis + HUS risk
^^^bloody diarrhea + cramping
Clostridium perfringens (foodborne)
G+, anaerobic, spore-forming
Virulence: enterotoxin produced while spore-forming in intestine
Reservoir & Transmission: foodborne - soil, animal intestines, raw meat, poultry
Key Features: watery diarrhea, no fever
Diagnosis: clinical + stool culture for toxin
Treatment: hydration only
Notes: reheated meat dishes, short disease duration
vibrio cholerae
G-
Virulence: bacteriophage encodes Cholera Toxin, toxin-coregulated pili allow colonization of S.I. (non-invasive, but toxin-releasing)
Cholera toxin causes massive water loss
Reservoir & Transmission: water & food cont. w/ poop
Key Features: “rice-water stools”, dehydration
Diagnosis: stool PCR/culture
Treatment: immediate oral or IV rehydration, antibiotics shorten symptom duration
Notes: life-threatening, endemic, water sanitation essential
Yersinia enterocolitica
G-
Virulence: Yops proteins prevent phagocytosis (immune evasion)
Reservoir & Transmission: Pigs (undercooked pork)
Key Features: pseudoappendicitis (mimics appendicitis) + diarrhea
Diagnosis: stool PCR/culture
Treatment: supportive (hydration), antibiotics only if severe
Notes: grows at refrigeration temps
Bacillus cereus
G+, spore-forming
Virulence:
Emetic Type: emetic (vomit-causing) toxin called cereulide
Diarrheal Type: diarrheal enterotoxins produced in intestine
Reservoir & Transmission: cooked food - rice
Key Features:
Emetic: nausea & vomiting (less diarrhea)
Diarrheal: watery diarrhea, ab cramps
Diagnosis: clinical
Treatment: supportive
Staphylococcus aureus (food poisoning)
G+, heat-stable
Virulence: preformed enterotoxins (disease will happen even if bac killed in cooking)
Reservoir & Transmission: zoonotic, creamy foods
Key Features: rapid vomiting, mild diarrhea, no fever
Diagnosis: clinical
Treatment: supportive (hydration), antibiotics don’t work
Notes: short duration, toxin not infection (bc disease caused by the toxins bac produce, not the bac themselves)
Clostridioides difficile
G+, anaerobic, spore-forming
caused by disruption of microbiota (antibiotic use)
Virulence: toxins A & B cause colitis
Reservoir & Transmission: normal gut microbiota
Key Features: antibiotic-associated diarrhea, pseudomembranous colitis (severe colon infl.)
Diagnosis: stool PCR + toxin EIA
Treatment: oral vancomycin. fecal transplant if reccurent
Notes: spores resist disinfectants
Listeria monocytogenes
G+, motile
Virulence:
Listeriolysin → escapes phagosomes
actin-based motility
epithelial invasion
Reservoir & Transmission: soft cheeses, ready-to-eat food, meats
Key Features: severe disease in pregnancy/neonates/elderly (possible meningitis)
Diagnosis: blood/CSF culture
Treatment: antibiotics (ampicillin)
Notes: survives in cold temps (refrigerated foods), avoid soft cheeses during pregnancy
Enteric Viruses
Rotavirus, Norovirus, Astrovirus, Adenovirus 40/41
RNA viruses (except Adenovirus - dsDNA)
Virulence: epithelial destruction → malabsorption
Key Features: vomiting, watery diarrhea
Diagnosis: stool PCR
Notes:
Rotavirus - vaccine helpful
Norovirus: low infectious dose + resistant to disinfectants = outbreaks
Protozoa
Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Entamoeba
Virulence:
Attachment - Giardia
Chlorine resistance - Cryptosporidium
Tissue invasion - Entamoeba
Key Features:
Giardia - greasy diarrhea (steatorrhea)
Cryptosporidium - watery diarrhea
Entamoeba - bloody diarrhea (dysentery)
Diagnosis: stool antigen/PCR
Notes: waterborne + travel related
PCR
amplifies & detects DNA sequences
faster, comprehensive, used for viruses
Stool culture
grow microorgs. from sample in lab
can test for antibiotic susceptibility
takes longer