serology unit 6
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
List some immune defenses that protect us from viral infection?
skin, mucus barriers, immune cells, antibodies, type 1 interferons, NK cells
What will antibodies do when they find a virus
bind to it and prevent it from penetrating host cells
How do viruses escape host defenses?
1. genetic variation
2. can avoid immune response
3. can inhibit the immune response
4. can remain latent in the body
A patients serum has IgM present for a virus, what does that mean?
the patient has a current or recent viral infection
A patients serum has IgG present for a virus, what does that mean?
The patient has a current or past infection and could have built up viral immunity
How can current infections be detected
through immunoassays for viral antigens in serum, or the presence of viral nucleic acids
Hepatitis infections mainly affect which organ?
Liver
Early Hepatitis symptoms
Flu like symptoms, and pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen
Hepatitis can progress to
hepatomegaly, tenderness, jaundice, DARK URINE, LIGHT FECES
What initial laboratory findings suggest a hepatitis infection?
elevated bilirubin and liver enzymes, notably Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
NOTE: these are nonspecific and further testing will be needed
Hepatitis A is transferred by
fecal-oral route, close person contact, ingestion of contaminated food/water, or rarely transfused blood
When testing for anti-HAV antibodies it is important to remember to
test individuals with active symptoms, asymptomatic patients will give a false pos
A positive anti-HAV and a negative IgM indicates
A patient has developed immunity to the hep A virus
Which Hepatitis is DNA based instead of RNA
Hep B
Which hepatitis variants are spread through parenteral, sexual or perinatally
Hep B, Hep C, Hep D*
*requires a hbv infection
In an infant what would suggest an infection?
the presence of IgM
In an infant where would they get IgG
their mother
HbeAG is a ___
Hepatitis B e antigen
How is CMV/cytomegalovirus transmitted
contact with bodily fluid, sexual contact, organ transplants, and perinatal exposure
How would you test for CMV?
-CMV specific IgM and IgG serology
- PCR for immunocomp. and newborns
EBV/Epstein Barr virus
mononucleosis aka mono
How would you test for EBV?
heterophile antibody test
How would you test for VZV?
-serological tests for VZV-specific IgM and IgG
- PCR for DNA from skin lesions is the most sensitive
How would you test for rubella, rubeola and mumps?
-serological tests for IgM and IgG
- RT-PCR recommended for confirmation
How would you test for HTLV-1?
initial screening with an antibody test, confirming with western blot
What is the clinical significance of heterophile antibodies?
strong indicator of acute infectious mononucleosis caused by EBV
Anti-HB
Hep B surface antibody, indicates recovery from HBV infection or successful vaccination, providing immunity
heterophile antibodies
non-specific IgM antibodies produced during acute EBV infection and detected by the monospot test
Parenteral
Administration or transmission that does not involve the digestive tract
ex: transmissions through needles and blood
VZV stands for ___
Varicella-zoster virus
TORCH tests for
Toxoplasmosis
Other infections- syphilis, hep, HIV
Rubella
Cytomegalovirus
Herpes simplex
When would you use TORCH
screening pregnant women and newborns for infections that can cause serious birth defects and miscarriage
interferons are
proteins released by infected cells that inhibit viral replication in neighboring cells
Which cell can detect and kill viruses without prior sensitization?
NK cells
Phagocytes can
engulf and digest virions and infected cells
What can the complement system do for viral infections?
lyse enveloped viruses and virus-infected cells and enhance phagocytosis
Which cells produce cytokines
t helper cells
Immunological memory
after an infection memory b and t cells provide a stronger immune response upon re-exposure
Latent phase
viruses can enter a latency and integrate their genetic material into the host cell and produce no markers to become invisible
antigenic variation
viruses can mutate surface proteins allowing them to evade antibodies and t cell recognition
NAAT or nucleic acid amplification tests detect what
viral genetic material directly
- highly sensitive and specific GOLD STANDARD FOR HEP
- tests like RT-PCR
How is hepatitis monitored
quantitative molecular tests to measure the viral load in a patients sample
- effectiveness of treatment and disease progression
core window is
a gap during the acute hep b, disappearance of HBsAg but before the appearance of protective HB antibodies
IgM anti HBc
Confirms a recent or acute Hep B
Which disease testing uses heterophile antibodies
EBV/mononucleosis
Which diseases are diagnosed by (disease) specific IgM and IgG serology
CMV, VZV, Rubella, Rubeola and Mumps
Which disease uses antibody test (ELISA)
HTLV-1
Which HIV form is more virulent
HIV-1
Which HIV-1 group is responsible for the global pandemic
group M (main)
- group n, o, and P are rarer
Recombinant forms are
when a person is infected with 2 different HIV subtypes and a new hybrid can be created
Circulating recombinant forms (CRF)
become widespread in a population
Unique recombinant forms (URF)
Hybrid viruses found in only one person
What does HIV transmission require
direct contact with bodily fluids containing the virus, and a mucous membrane, damaged tissue or the bloodstream
How does HIV transmit
sexual contact, shared needles/syringe, perinatal
What increases the risk of HIV transmission
High viral loa, untreated STI
HIV envelope contains which glycoprotiens
gp120 and gp41
Gp120
External protein that binds to CD4 receptor
Gp41
anchors gp120 to the envelope and facilitates fusion with the host cell membrane
What's inside the HIV core
RNA and enzymes
what does reverse transcriptase do
converts viral RNA into DNA
Protease does what
cleaves precursor polypeptides during viral maturation
What does integrase do
integrates viral DNA into the host cells DNA
Replication cycle of HIV
1. binding
2. fusion
3. reverse transcription
4. integration
5. replication
6. assembly
7. budding and maturation
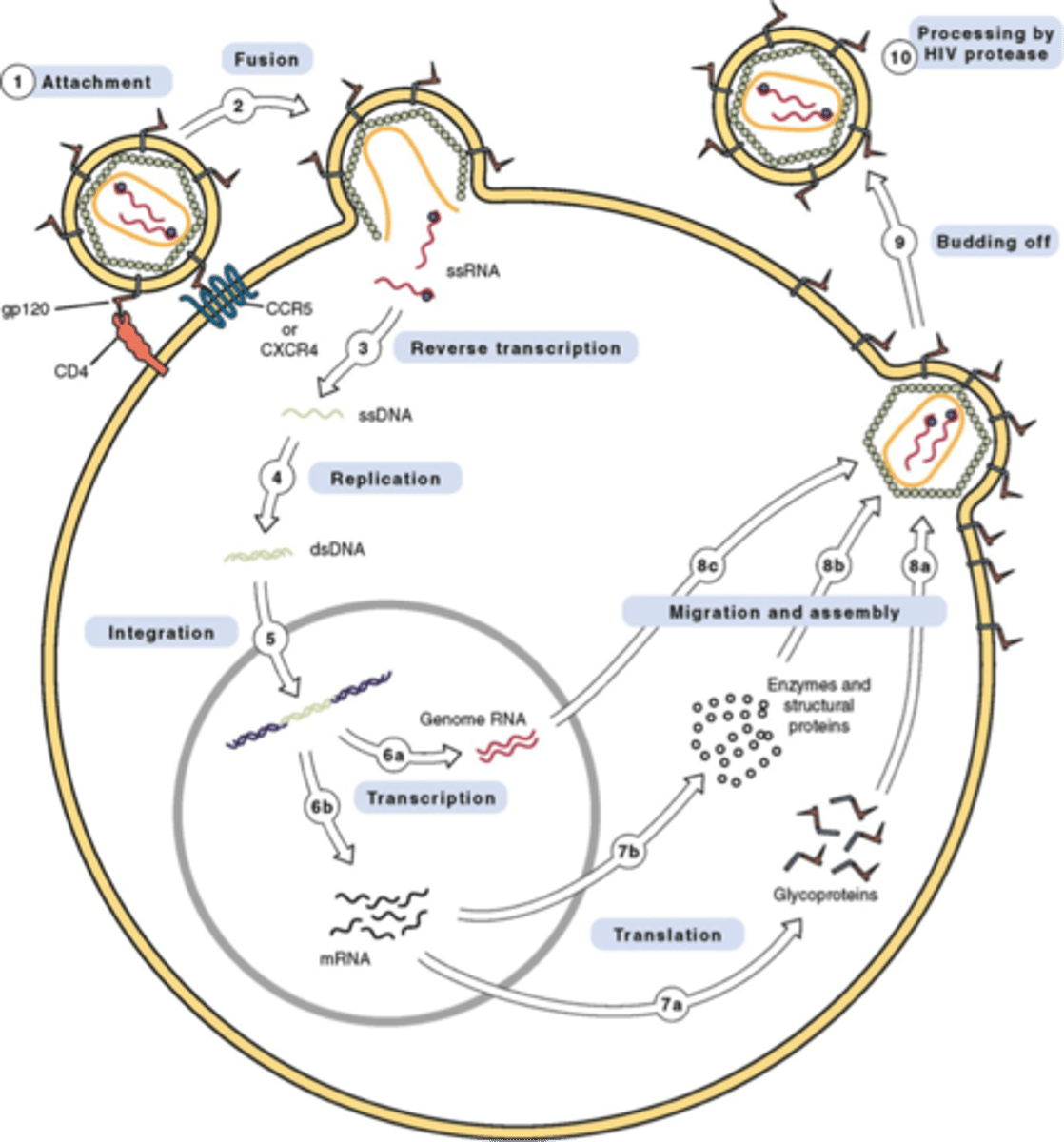
HIV binding
Gp120 binds to CD4
fusion
gp41 enables the viral envelope to fuse with the host cell membrane, viral core will enter the cell
reverse transcription
inside the cell single stranded viral RNA is converted to double stranded DNA
integration
HIV integrase enzyme integrates the HIV DNA into the host DNA
replication
host cell is used to produce new HIV RNA and HIV proteins
Assembly
New HIV RNA + proteins move to cell surface where they become an immature virion
budding and maturation
immature virion pushes out the cell; it will steal the cell membrane with it. HIV protease will cleave the protein chains allowing it to mature
How does the immune system initially respond to an HIV infection?
1. Killer t cells recognize and destroy HIV cells however, are easily evaded through mutation
2. antibodies are produced, but they can be ineffective
HIV primarily infects and destroys
CD4 t cells
What will HIV infection lead to
Chronic generalized immune activation which will cause a snowball effect
(more immune cells to infect, worse disease)
What tissue does HIV effect
Lymphoid tissue, it will damage it directly effecting the immune system since its where the cells reside
What can HIV develop into
AIDS
What defines the progression into AIDS
when CD4 cells fall below a critical threshold (200 cells ul), causes the immune system to be severely compromised
Primary/acute stage of HIV
2-4 weeks, flu like illness (ARS) or asymptomatic
Clinical latency of HIV
Happens after ARS the spread/multiplication slows and can remain latent for years
still causes immune damage
symptomatic HIV infection
The immune system will weaken causing milder infections and chronic symptoms including: persistent fatigue, fever, swollen lymph, diarrhea, and oral thrush
AIDS leaves room for
other infections and cancers including pneumocystis pneumonia, Kaposi's sarcoma, and cytomegalovirus
Stage 0
early HIV infections, inferred from a negative or indeterminate test w/i 6 months of a confirmed positive
Stage 1
Cd4 cell count is above or equal to 500 cells/ul and no AIDS defining symptoms
Stage 2
Cd4 t cell count from 200-499 cells and no aids defining conditions
stage 3
Cd4 count less than 200, or the presence of an AIDS defining condition
stage unknown
when there is insufficient info on the CD4 cell count or AIDS conditions to classify the person
What is the major structural protien (core) of the HIV-1 virus
p24
Another name for ART
Antiretroviral treatments
3 bodily fluids that will not transmit HIV
saliva, tears, urine, and saliva
What does the p24 protein encode?
Group specific antigen (GAG)
Toxoplasmosis is clinically significant because
It causes congenital deformities

Ig cannot cross the placenta
IgM
Zoonotically transmitted by eating undercooked meat from infected animals
Hep E
Gene that encodes the precursor protein for the internal structural proteins of HIV such as the capsid (p24) and matrix (p17)
GAG
Primary transmission route for Hep A
fecal oral route
Increase AST and ALT plus anti-HAV antibodies, recently drinking from a forest lake
Hep A
IgM vs IgG
IgM: current or recent infection
IgG: past infection or immunity
serological marker indicating a recent hep B infection
IgM and anti-HBc
Which antibody is the first produced in response to a viral infection
IgM
Herpesvirus responsible for causing chickenpox and shingles
varicella zoster virus (VZV)
Which test would be most reliable in detecting HIV in an infant younger than 18 months
DNA PCR testing