Kidney 3
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
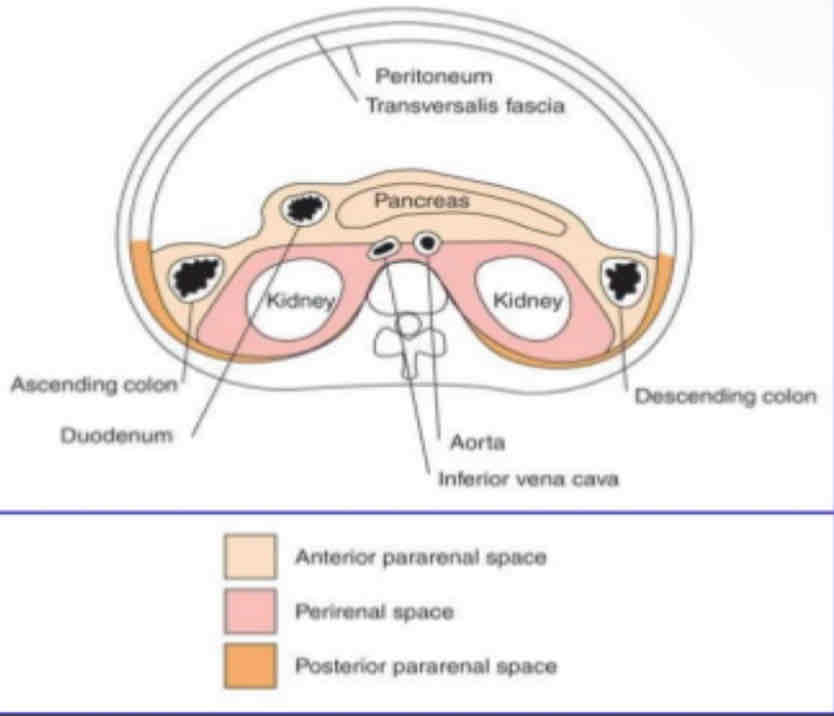
What is the following picture?
compartments of the retroperitoneum
What is impairment of kidney function resulting in the inability of the kidney(s) to maintain normal function. It is also called as Acute kidney injury (AKI).
acute renal failure
What are the three mechanisms of AKI?
prerenal failure
intrarenal (intrinsic)
postrenal failure
What is renal hypoperfusion secondary to a systemic cause
– Acute bilateral renal artery occlusion
– Heart failure
– Hypotension
– Hypovolemia (dehydration, hemorrhage
– Salt depletion
– Septicemia
Prerenal Failure
What is the result of medical disease
– Acute tubular necrosis Ischemic disorders
– Nephrotoxicity—glomerular membrane injury from exposure to nephrotoxic
wastes (aminoglycosides, heavy metals, radiographic opaque materials,
organic solvents, pesticides or fungicides, antibiotics)
– Cortical necrosis
– Acute Glomerulonephritis
Intrarenal (intrinsic)
What is the result of outflow obstruction
– Acute bilateral renal vein thrombosis
– Acute urinary tract obstruction (calculi, tumors, prostatic hypertrophy,
urethral strictures) ,Bladder outlet obstruction
Postrenal Failure
What are the laboratory findings for renal failure?
Elevated BUN and creatinine, Proteinuria
What is the sonographic findings of renal failure?
1. Normal appearing kidneys in early stages
2. Hydronephrosis with post renal obstructive processes
3. Enlarged kidneys with inflammatory processes
4. End-stage--- Small kidneys with parenchymal thinning , Increased
cortical echogenicity and Loss of corticomedullary differentiation
What is the role of ultrasound in diagnosing the cause of acute Kidney injury is to
determine?
a. Hydronephrosis(indicates post renal failure)
b. Abnormal resistive index (suggest intrinsic)
What is enlarged kidney and increased resistive index (RI)
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
What does the following describe?
• is the most common cause of medical renal disease or intrinsic (intra-renal) acute renal failure.
• results from prolonged ischemia or nephrotoxins causing damage to the tubular epithelium of the nephron leading to acute renal failure.
• The renal insufficiency that occurs in this can be reversible .
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
What is a rare cause of acute renal failure secondary to ischemic necrosis of the renal cortex?
Renal cortical necrosis (ACN)
What are the sonographic findings for renal cortical necrosis (ACN)?
The sonographic findings are of bilateral, normal sized kidneys. Initially, the renal cortex appears hypoechoic, and there is a loss of normal cortico-medullary definition.
What does the following describe?
• Increased amounts of myoglobin(is an iron and oxygen binding protein found in muscles tissue) are released into the tissues and bloodstream following rhabdomyolysis (an acute, sometimes fatal disease characterized by destruction of skeletal muscle)
• A result of other causes, including alcohol and drug addiction, crush injuries, strokes, toxins, fever, or myositis.
• Ranging from completely normal kidneys in ATN to enlarged, echogenic kidneys in cases where changes reflect cellular interstitial infiltration.
• With enlarged, distended medullary vessels, the pyramids may be prominent and hypoechoic.
• In end-stage fibrosis, the kidneys may be shrunken and echogenic.
myoglobinuria

What does the following describe?
• Dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces due to obstruction of outflow of urine from either a congenital, intrinsic, or extrinsic cause.
• Separation of the normal sinus echogenicity by anechoic urine collection
• If untreated can lead to hypertension, loss of renal function and sepsis
• Pregnancy causes-- Mechanical compression of ureter at pelvic brim during
the third trimester.
• Overdistention of urinary bladder.
Hydronephrosis
Three common areas of obstruction by a stone are
– Ureterovesicle junction (most common)
– Ureteropelvic junction
– Pelvic brim
Obstruction produces hemodynamic changes with intrarenal vasoconstriction and elevation in renal arterial resistance, what suggests obstructive hydronephrosis?
Threshold RI > 0.7
Classification of hydronephrosis in grade I–IV: dilation of the renal pelvis without dilatation of the calices
Grade I
Classification of hydronephrosis in grade I–IV: dilation of the renal pevis and calices, that
become convex; no signs of cortical thinning
Grade II
Classification of hydronephrosis in grade I–IV: presence of cortical thinning
Grade III
Classification of hydronephrosis in grade I–IV: massive dilation of the real pelvis and calices, severe cortical thinning
Grade IV
False-positive diagnoses for Hydronephrosis include
– extrarenal pelvis
– vesicoureteral reflux
– Full or overdistended bladder (pseudohydronephrosis)
– Post surgical dilatation
– high urine flow as seen with overhydration and furosemide use
– parapelvic or peripelvic cysts
• The severity of hydronephrosis postnatally is determined by a sonogram performed after _______ of life in a full term infant and is based on the anterior posterior renal pelvic
diameter as
• Normal <7mm
• Mild 7 to 8 mm
• Moderate 9 to 15 mm
• Severe >15 mm
48 hours
Most pediatric patients with moderate hydronephrosis have resolution by
18 months of age
What obstruction is by far the most common cause of pediatric hydronephrosis, it occurs more common in males on left kidney?
Ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction
What does the following describe?
• It’s a wide ureter greater than 7 mm in diameter.
• Primary ______ is classified according to the
presence or absence of reflux and obstruction
megaureter
What does the following describe?
lt’s a leakage of urine from the UPJ or UVJ. Occurs as a post operative complication . Usually presents 1-2 weeks post-transplant. It may cause hydronephrosis due to ureter compression.
Sonographic Appearance: Cystic collection adjacent to kidney, may see debris .
Urinoma
What does the following describe?
It’s encapsulated collection of lymph.
It also occurs as a post operative complication. It can have delayed
presentation of up to 2-6 months after surgery .Sonographic Appearance: Cystic structure between kidney and
bladder
Lymphocele
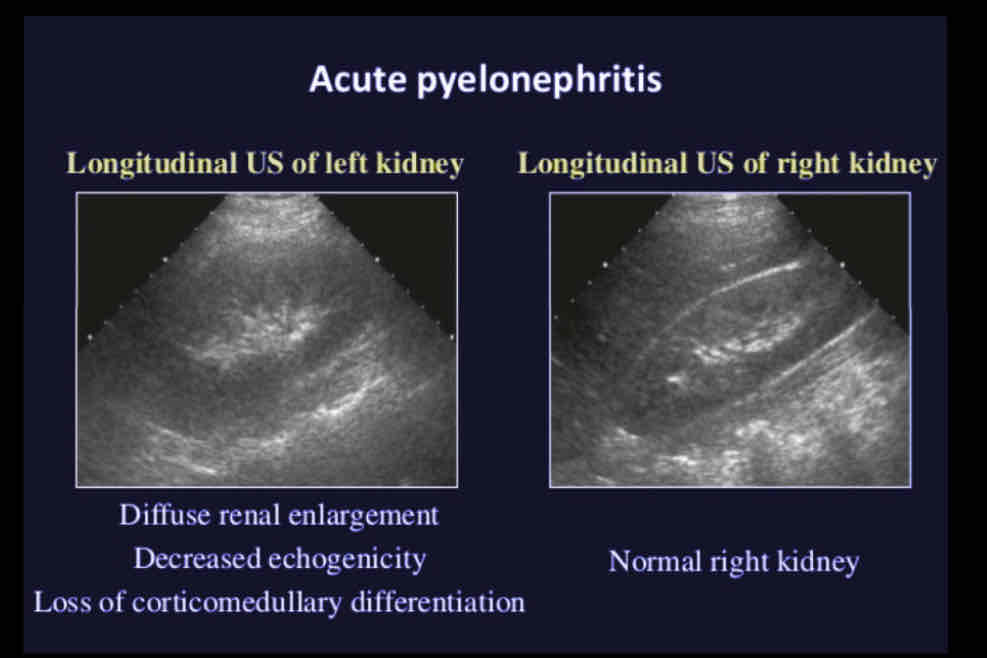
What does the following describe?
• Most renal infections occur via ascending route from bladder. Usually results from bacterial invasion. Imaging studies often not ordered because patient diagnosed by clinical
symptoms
Clinical presentation
– Flank pain
– Fever and chills
Laboratory results
– Elevated WBC
– Pyuria
– Bacteremia
– Microscopic hematuria
Acute pyelonephritis
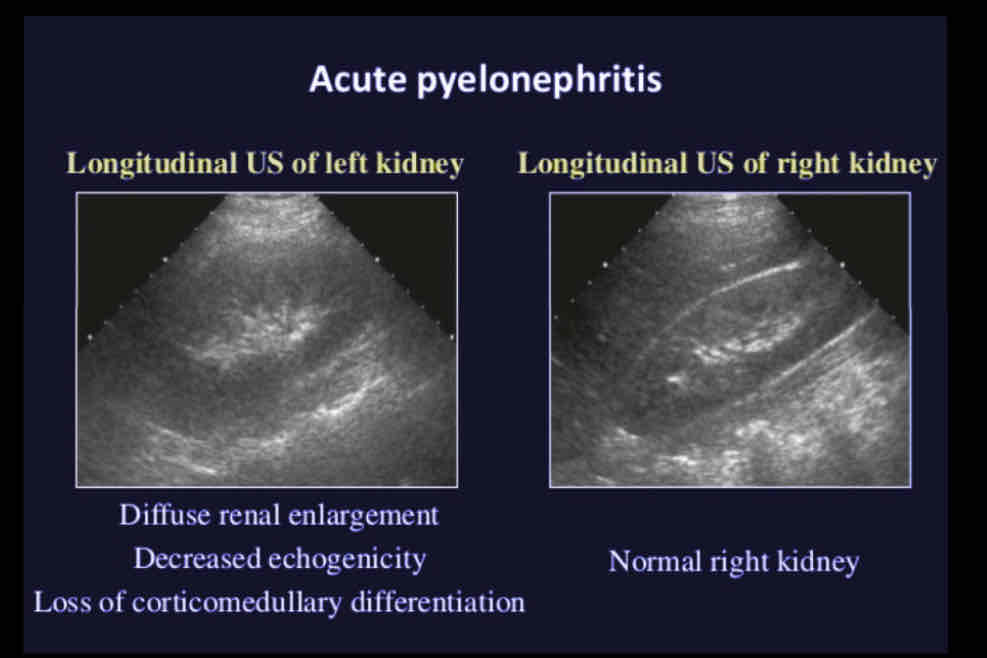
Sonographic Appearance
• Varied appearance, most patients have normal kidneys on ultrasound
• Diffuse - Unilateral or bilateral renal enlargement with diffuse swelling; loss of
corticomedulary definition
• Focal - Normal renal size with a focal, indistinct, hypoechoic wedge shaped segment of parenchyma; similar in appearance to renal infarct
• Loss of distinction between the renal cortex and medulla
• Diminished sinus echoes in affected kidney/segment
Acute pyelonephritis
True/False: Emphysematous Pyelonephritis is not a life-threatening condition.
false, it a life threatening condition. Nephrectomy is usually required.
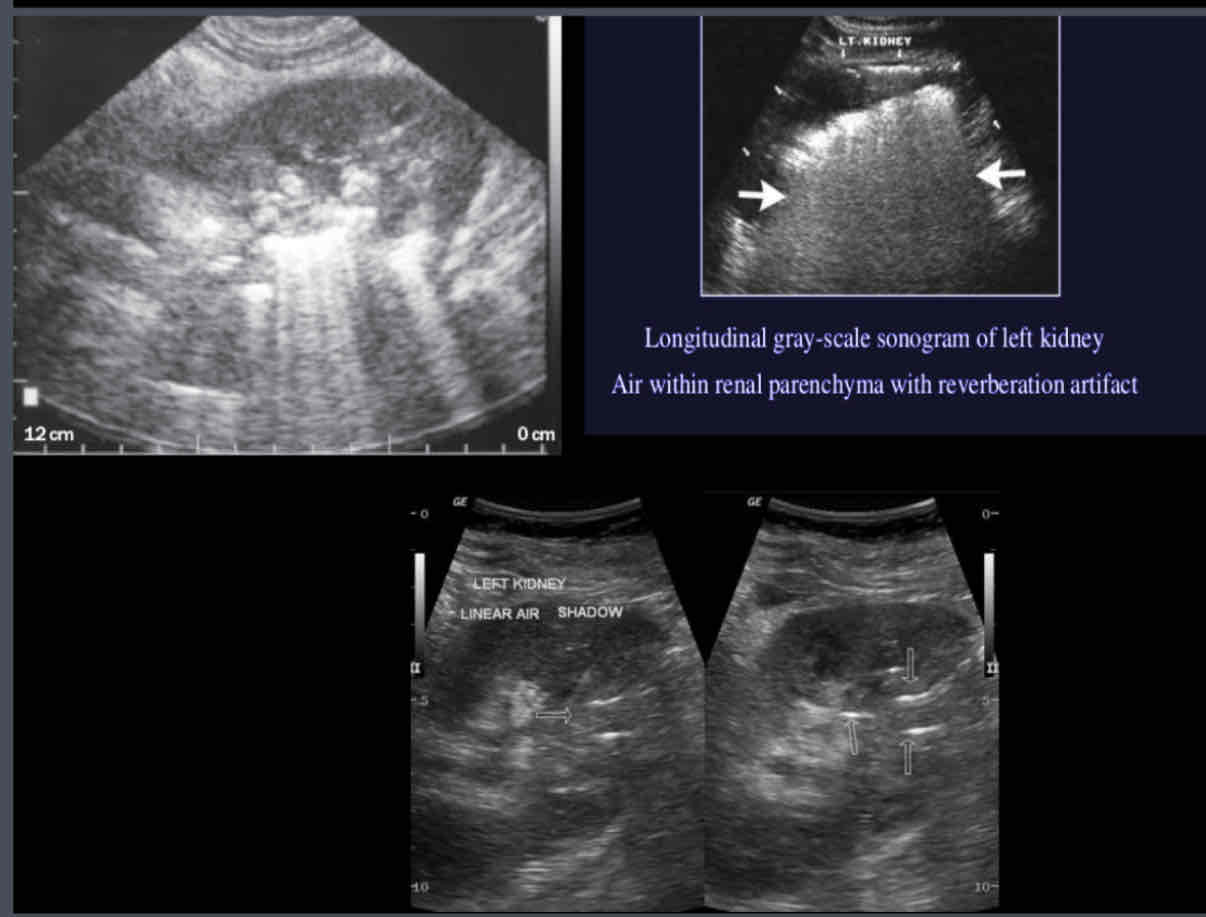
What does the following describe?
• Bacterial Infection of renal parenchyma associated with renal ischemia
• Most common in diabetics, immunosuppressed, and patients with urinary tract obstructions
• Anaerobic bacteria produce intra-renal gas causing reverberation, comet-tail, artifacts
Emphysematous Pyelonephritis
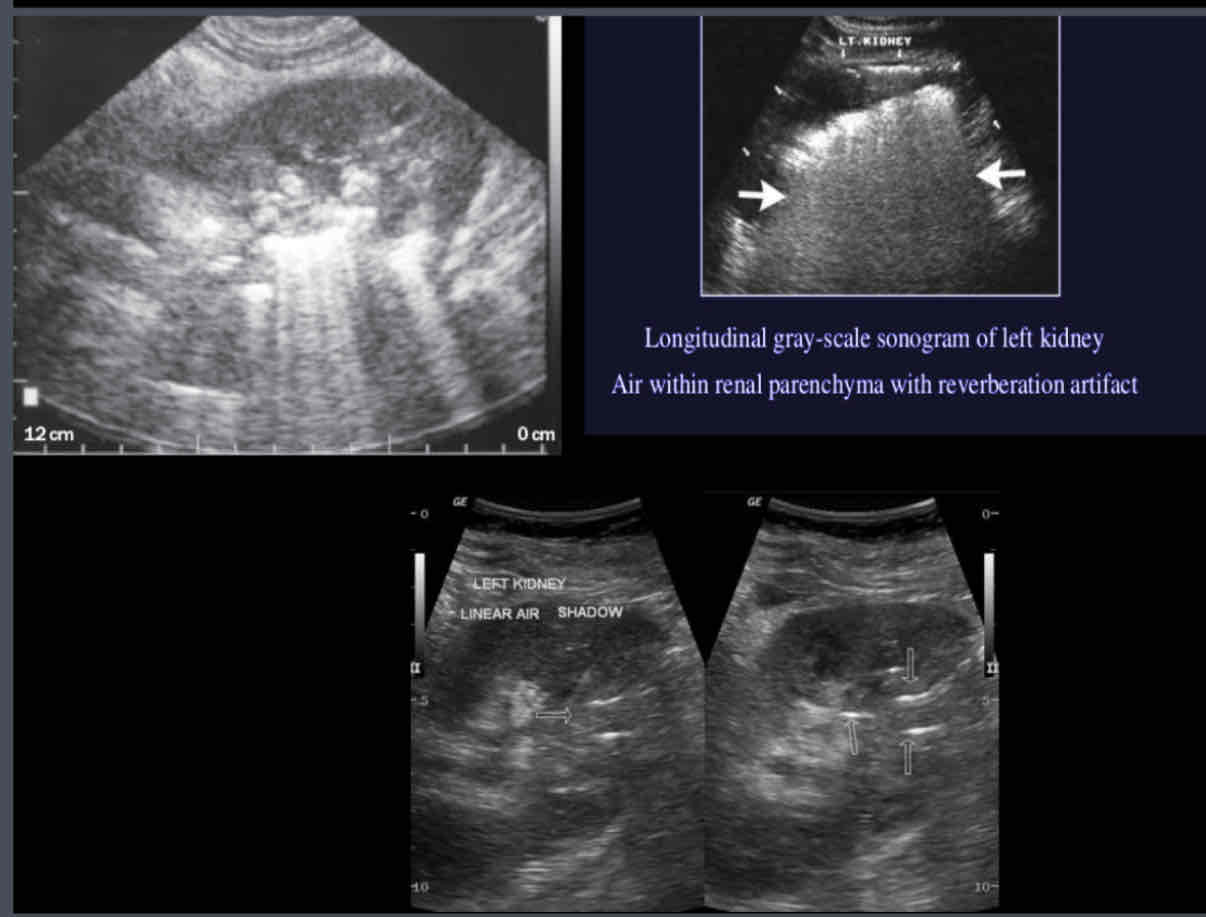
What does the following sonographic appearance describe?
1. Multiple echogenic foci with reverberation/comet tail artifact in the sinus
or parenchyma
2.May demonstrate areas of echogenicity with dirty posterior shadowing
3.Gas within parenchyma and/or collecting system
Emphysematous Pyelonephritis
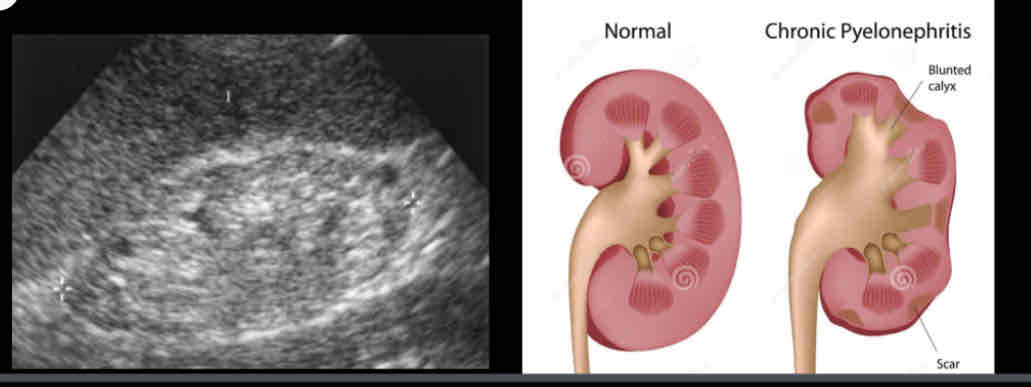
What does the following describe?
• Constant injury to kidney due to recurrent infection, from anomalies, obstructive lesions and ureteral reflux
• Nephritis resulting from ongoing or recurring UTIs.
chronic pyelonephritis
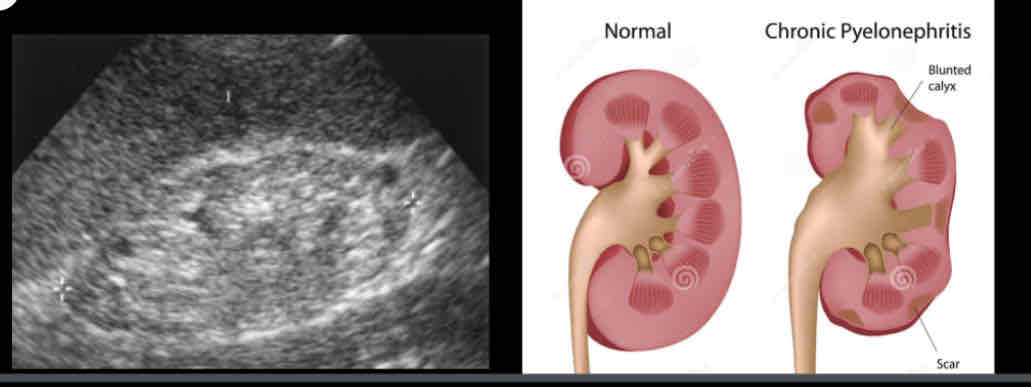
What does the following sonographic appearance describe?
• Decreased renal size
• Unilateral or bilateral focal areas of cortical thinning and increased echogenicity.Overlying cortical atrophy/scarring
• hypertrophy of contralateral kidney
chronic pyelonephritis
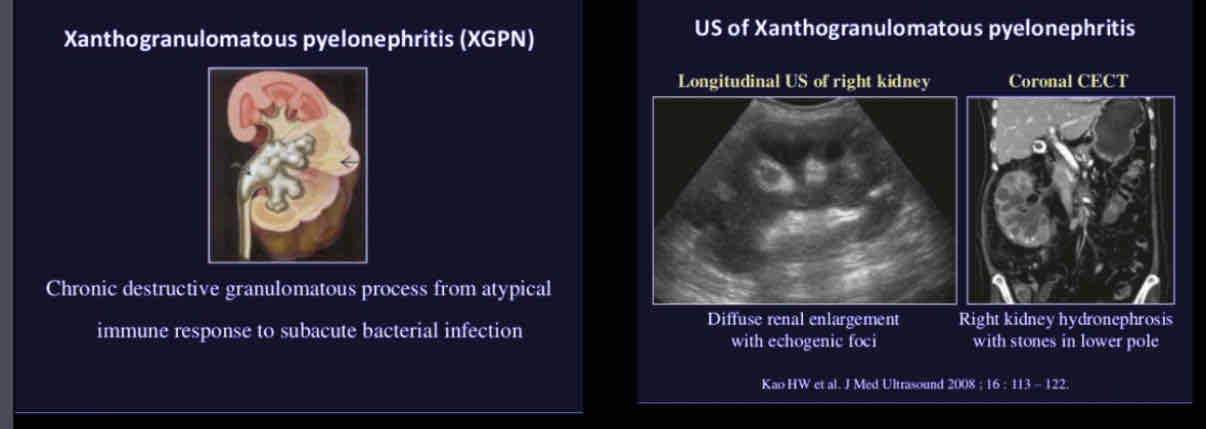
What does the following describe?
• Type of chronic pyelonephritis from a long term obstruction which leads to destruction of parenchyma and replacement with lipid laden macrophages
• Unable to depict a normal kidney,associated with staghorn calculi
• Associated findings: kidney enlargement, parenchymal abscesses, staghorn calculi, papillary necrosis, hydronephrosis, pyonephrosis, loss of cortical-medullary boundary, cortical thinning.
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (XGPN)
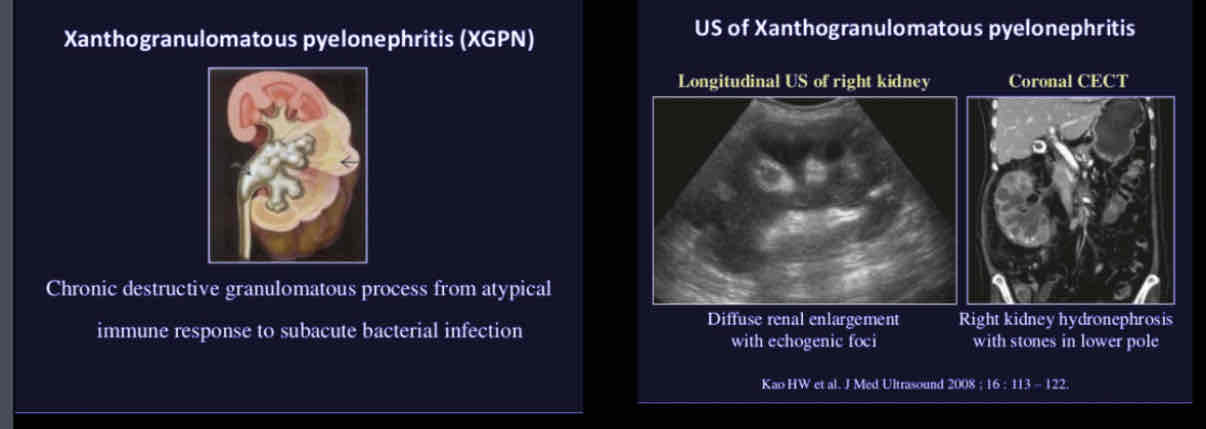
What does the following describe?
Most commonly found in middle aged women
and diabetics
Typically unilateral
Associated with nephrolithiasis (70%) and
obstructive nephropathy
Can be diffuse, segmental or focal
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (XGPN)
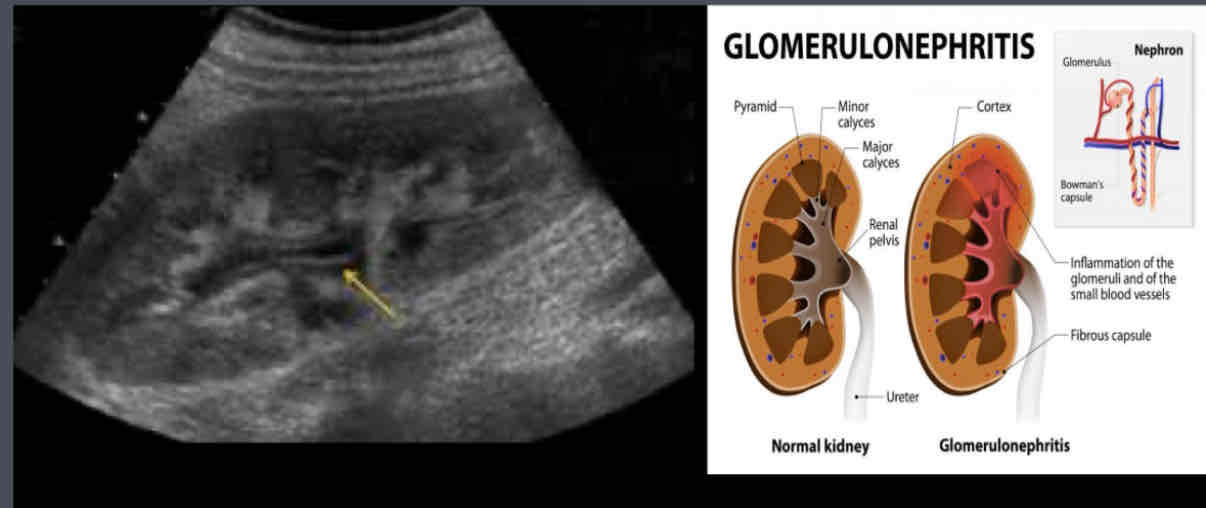
What is an Inflammation of glomeruli, caused by infection, autoimmune response, medications, toxins (can be acute or chronic)?
Glomerulonephritis
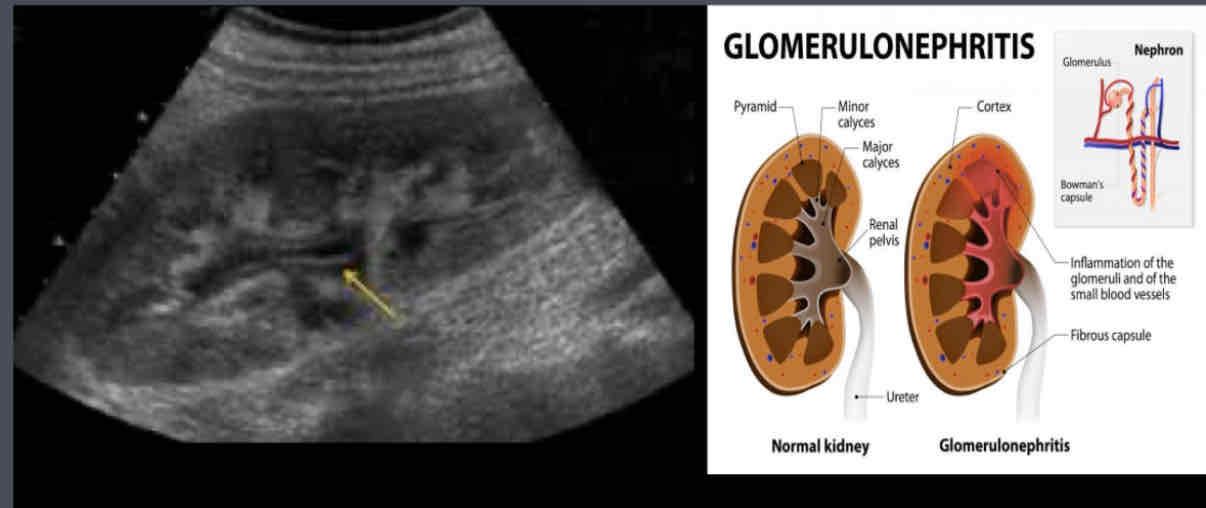
What does the following describe?
Lab Testing:
– Increased BUN and creatinine
– Can lead to significant proteinuria, if chronic
Symptoms---
– sudden onset of hematuria
– Proteinuria
Glomerulonephritis
Acute glomerulonephritis (AGN) is a renal inflammation that may be categorized as…
(1) a renal inflammatory response caused by an autoimmune reaction resulting in glomerular damage
(2) interstitial inflammation due to infection (by gram-negative bacilli), exposure to toxins and drugs, or infiltration of inflammatory cells into the renal interstitium.
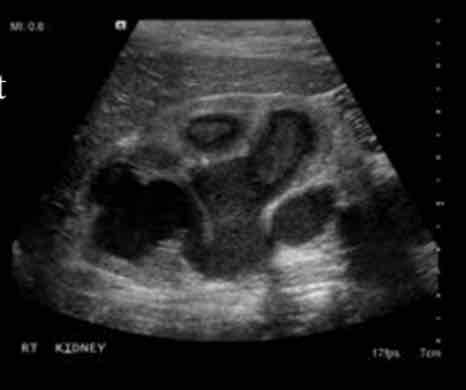
What is the presence of pus in collection system, associated with infection secondary to renal obstruction?
Sonographic appearance
• hyperechoic debris in dilated renal collecting system
• Drainage required for treatmen
pyonephrosis
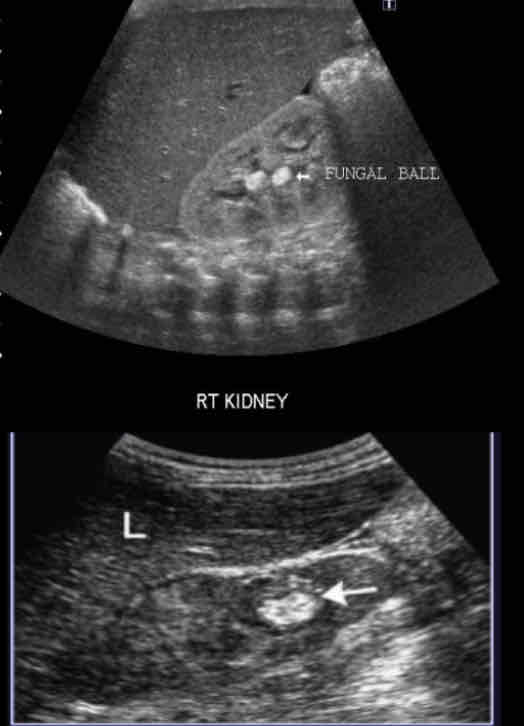
What is a fungal infection of urinary tract that occurs in drainage structure instead of renal
parenchyma?
Mycetoma (Fungal ball)
true/false: In patients with systemic candidiasis, the kidney is vulnerable to the formation of corticle abscesses or obstructive intrarenal masses(fungal masses),usually at the uretropelvic junction
true
What are renal stones called?
Nephrolithiasis
What is focal concentration of calcium, uric acid or cystine in the renal parenchyma or collecting system?
urolithiasis
What is a stone filling the entire renal
pelvis, is almost always associated with urinary tract infection, persistent alkaline urine, or both?
Staghorn calculus
What are the two main types of stones?
Calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate
True/False: Calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, or a combination of the two (80%–90%), usually associated with increased blood and urinary concentration of calcium predisposed by excessive bone reabsorption
true
What is a color Doppler artifact that appears as a rapidly alternating mixture of red and blue Doppler signals distal to a strongly reflective surface such as a stone?
Twinkle sign
What does the following describe?
• Atherosclerosis in cortical vessels
• Punctuate calcifications
• May or may not shadow depending on the size
• Not related to hydronephrosis or urinary
obstruction
Renal Vascular Calcifications
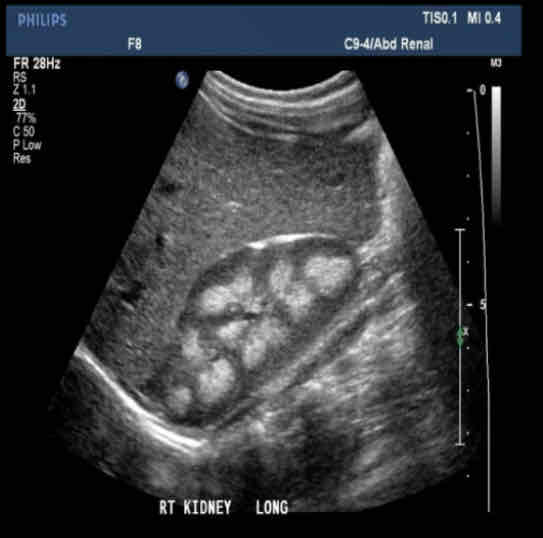
What is the formation of aggregates of calcium
in distal convoluted tubules and loops of Henle?
Medullary Nephrocalcinosis
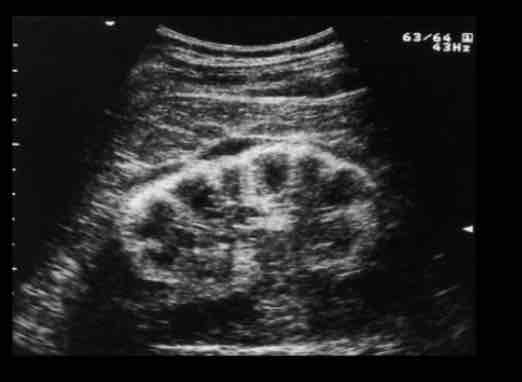
What is a diffuse or focal calcium deposition in the renal cortex?
• Risk factors--- Acute cortical necrosis, Chronic glomerulonephritis, Rejected renal
transplant.
Cortical Nephrocalcinosis
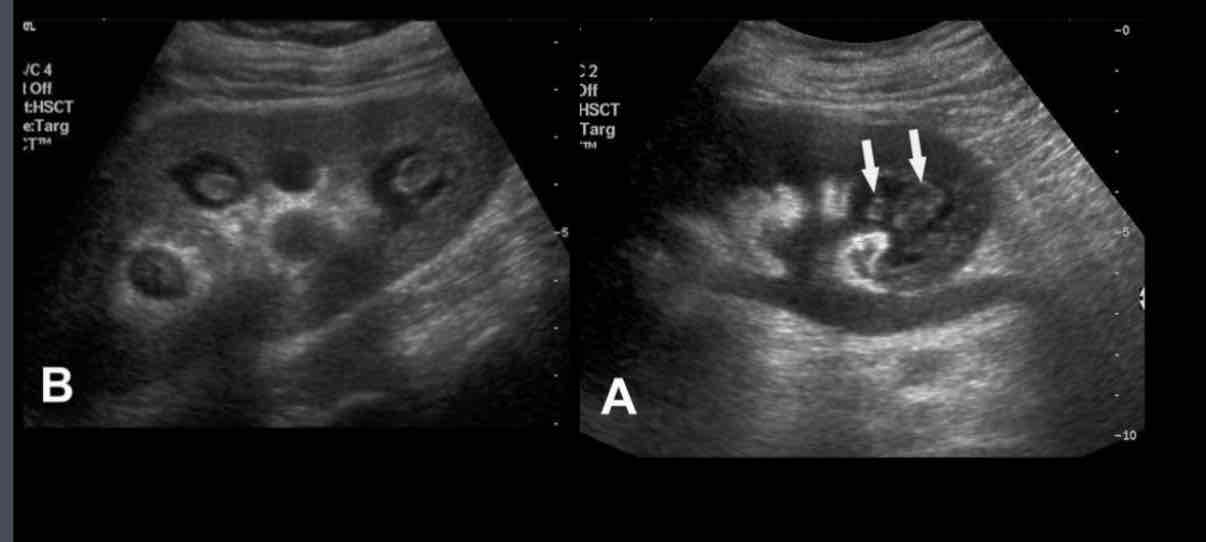
What does the following describe?
• Ischemia of medullary pyramids
• Sloughed papilla in urine may be painful and cause ureteric obstruction, but makes clinical diagnosis
papillary necrosis
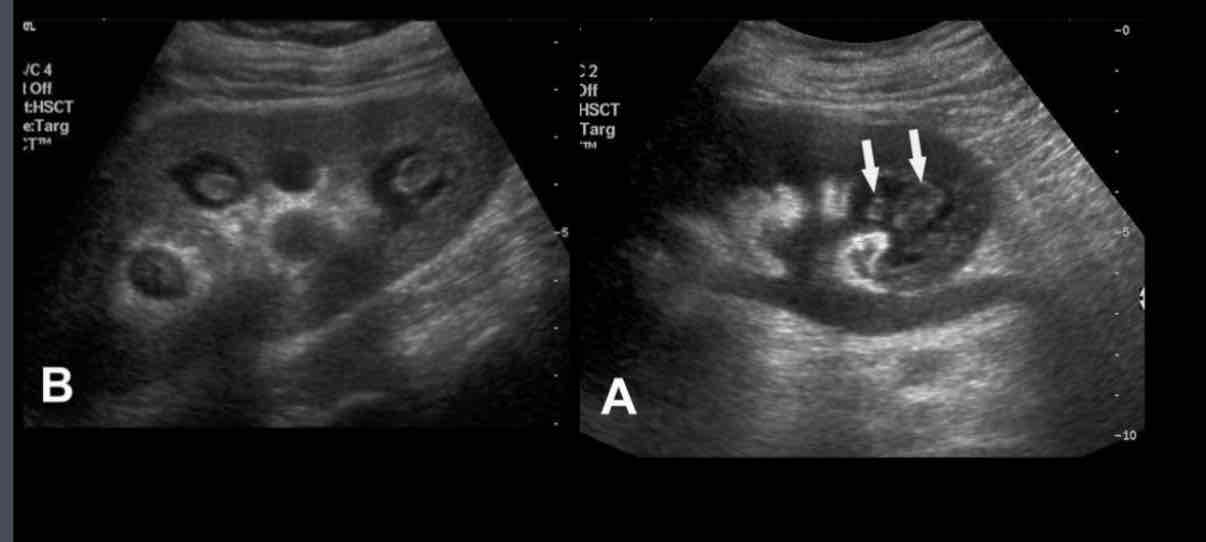
What is associated with analgesic abuse (most common), DM, UTIs, renal vein thrombosis, sickle cell disease, chronic heart failure and cirrhosis?
papillary necrosis
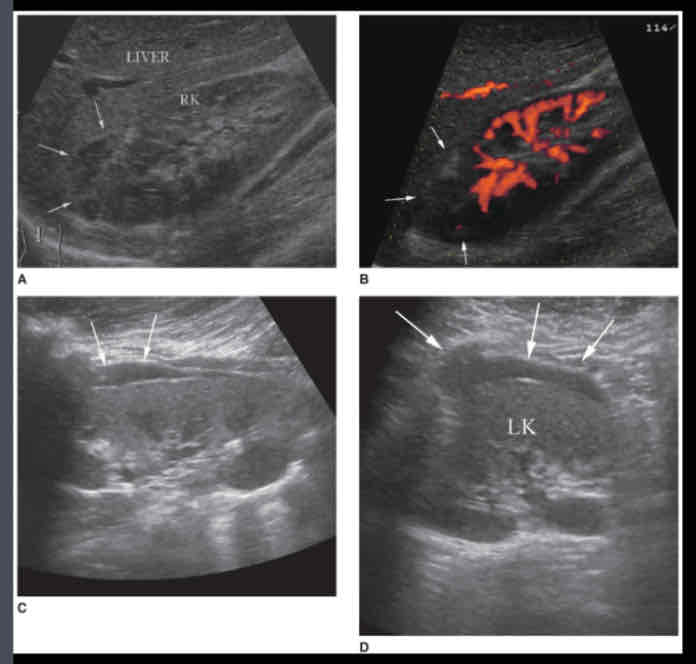
What does the following describe?
• It’s a Collection of blood outside the kidney
• Due to trauma, anticoagulant therapy
• Mass may be palpable; unilateral flank pain
• Decreased hematocrit value
Sonographic appearance-- depending on stage of the bleeding process, varying echo patterns from anechoic to complex masses, with both cystic and solid components
hematoma
Chronic hematoma may develop what?
calcifications with characteristic acoustic shadowing
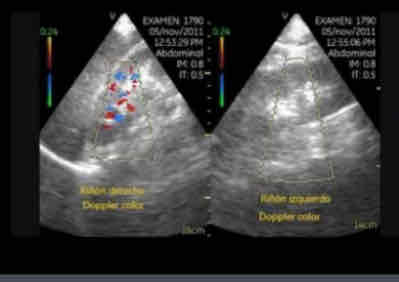
What does the following describe?
• Obstruction of blood supply or drainage
• Hypertension; lower extremity pulses absent
• Elevated LDH, hematuria
• Depending on the time frame following occlusion, renal parenchyma appears normal,
hypoechoic, or hyperechoic
infarction
What is used to evaluate renal transplant rejection, access suspected hydronephrosis and to evaluate medical renal disease?
Resistive index
The normal renal artery shows….
continuous forward flow during diastole, typical of low resistance perfusion
Renal dysfunctions results in loss of…
diastolic flow and thus increases renal arterial resistance
What does hemodynamically significant renal artery stenosis demonstrates---(Direct)
• Peak systolic velocity of greater than 150 cm/sec.
• Peak systolic velocity ratio of renal artery: aorta (RAR) greater than 3.5.
• When stenosis is completely obstructing, no detectable flow within the renal artery.
• Loss of diastolic flow
What does hemodynamically significant renal artery stenosis demonstrates---(Indirect evaluation)
• Parvus tardus(small slow pulse)
• Absent early systolic peak
What is hemodynamically significant luminal narrowing of renal artery?
Renal artery stenosis (RAS)
What is the presence of obstructive or non-obstructive thrombus in the renal vein?
Renal vein thrombosis
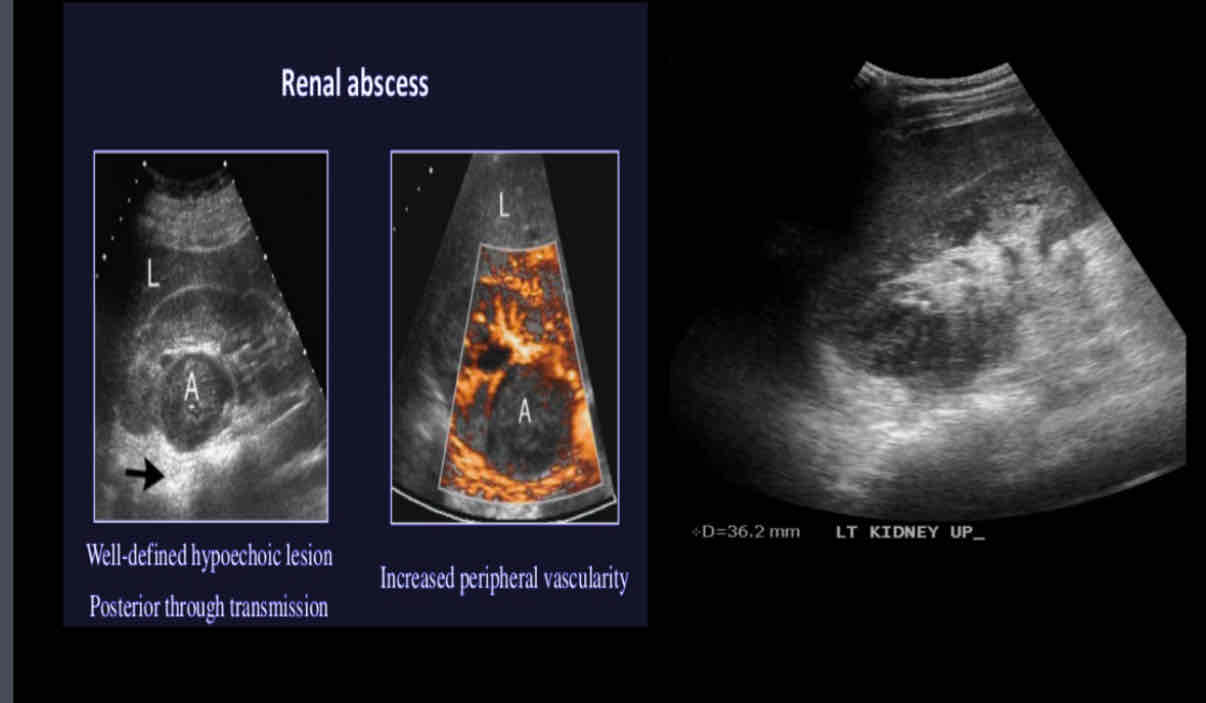
What is caused by ascending spread of bacteria in the urinary tract?
renal abscess