topic 1: biochem
1/42
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
atom
basic unit of matter, cant be broken down by oridnary means
elements vs atoms
an element is a specific type of atom while an atom is just a plain old atom with the possibility to be something else
what do atoms consist of?
nucleus: positive protons, neutral neutrons
electron cloud: negative electrons
what are the rules for the rings in the electron cloud?
1st ring can hold 2
2nd ring can hold 8
3rd ring can hold 8
valence number
the number of vacancies an element has in its outer most ring (ex. carbon has 4 electrons in its 3rd ring so its valence number is 4)
atomic number
the number of protons an element has (ex. carbon has six protons in its nucleus so its atomic number is 6)
atomic mass
the number of protons + the number of neutrons
why do we only count protons and neutrons in the atomic mass?
because each proton and neutron has 1 mass unit, electrons barely weigh anything
what is atomic mass in grams?
1 mole of protons/neutrons = 1 gram, so 1 mole of element xyz atoms = the atomic mass of element xyz
what is the variation in hydrogens atomic structure?
hydrogen usually has no neutron so 99% of hydrogen is H-1, but 1% is H-2
ions
an atom that has more/less electrons than normal which gives them a net charge (H+, Na+, Cl-, Mg2+)
how many essential elements are there?
25, but only 6/CHNOPS are required in bulk
CHNOPS
Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorous Sulfur
which elements are required in trace amounts?
iodine for the thyroid gland, iron for the hemoglobin, fluoride for our enamel
covalent bonds
bonds formed by sharing electrons between atoms, covalent bonds are stronger and more common than ionic bonds
polar covalent bonds
the electrons are being shared unequally because atom 1 has more electronegativity than the other; so, the electrons are more attracted to atom 1’s nucleus than atom 2’s nucleus
this creates a slighty -/+ charge on each atom since the one with more electronegativity has the electrons more (its -) and the other has the electrons less (its +)
ex. H2O, H’s are + O is -
nonpolar covalent bonds
electrons are shared equally between atoms because the atoms are the about the same size or same electronegativity
no charge is created since all the atoms are sharing the electrons the same amount all the time
ex. CH4
ionic bonds
occurs between ions of opposite charges when atoms are at opposite ends of the electronegativity spectrum
ex. NaCl, Na is a cation Cl is an anion
cation
positive ions that form by losing electrons
anion
negative ions that form by gaining electrons
hydrogen bonds
arise from polar bonds because that contain a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative another atom
iondipole bonds
occurs between an atom with a partial charge and an ion (full charge)
hydrophobic forces
the force that occurs between water/polar molecule and a nonpolar molecule
ex. oil and water do not mix because water is extremely polar and wants to stick to itself, so it pushes the oil out of the way
chemical/molecular formula
tells you what is in a molecule
ex. C2H5NO2
structual formula
tells you where teh atoms are bonded together
ex. O
/ \
H H
how do you show a chemical reaction in a chemcial equaiton?
reactants → products
ex. 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
cohesion
thing that says molecules with hydrogen bonds want to stick together, allows for surface tension, very hydrophobic
adhesion
says opposites attract because of electronegativity, very hydrophyllic
hydrocarbons
organic molecules consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen, these are usually gases of sorts
ex. CH4 (methane), 2 H6 (ethane)
organic functional gorups
groups of atoms that occur within molecules and made specific chemical properties
Hydroxyl OH
Methyl CH3
Carboxyl COOH
Amino NH2
Phosphate PO4
monomer
smallest unit of a larger molecules that are polymers
what is the function of proteins?
they aid in transport, storage, and membranes
what are proteins made of?
amino acids
what does a protein need to function?
at least 1 polypeptide
what is the amino acid for proteins?
R = anything else, is specific to the type of protein
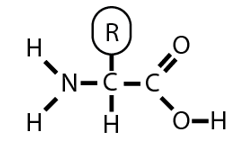
what are the three main types of proteins?
collagen + keratin (structural) and enzyme (enzymatic)
what are carbohydrates made of?
sugars
what is the empirical formula for carbohydrates?
(CH2O)n, n = # of carbons in the molecule that represents carbohydrates
whata re all the “-ides” of carbohydrates?
monosaccharides = sugars
disaccharides = table sugar
polysaccharides = starches, complex carbohydrates
what re lipids?
a diverse group of compounds that are mostly nonpolar and hydrophobic; they contain a polar head gorup, a phosphate, a glycerol backbone, and two fatty acid chains
ex. estrildid, testosterone, cholesterol,
what is the purpose of a nucleic acid?
to carry the cells genetic blueprint anf instructions for the cells functioning (DNA + RNA)
dehydration
reaction that links monomer molecules and releases a water molecule for every bond that is formed AKA smaller stuff is used to make bigger stuff and each time that happens water appears
ex. condensation
hydrolosis
opposite of dehydration, uses water to breka down larger molecules