AQA GCSE Physics Paper 2
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
vectors
forces with magnitude and direction
scalars
forces with magnitude but no direction
contact forces
requires contact eg friction
non contact forces
doesnt require contact eg gravity
mass and weigth
directly proportional
weight
mass x gravitational field strength
gravitational field strength on earth
9.81
resultant force
the overal force acting on an object
if a resultant force moves and object
work is done
scale drawings
triangular drawings, finding the hypotenuse usually using pythagoras or trigonometry
object in equilibrium
when to forces acting on the object are balanced
extension
directly proportional to force
(spring) force
spring constant x extension
limit of proportionality/elasticity
when an elastic object gets stretched too much and it become plastic
moment of a force
force x perpendicular distance from pivot to the line of action of the force
levers
make it easier to do work and increase the distance form a pivot
gears
transmit rotational effects
pressure of an obeject
force ÷ area
pressure in fluids
height above point X density of fluid X gravitational field strength
pressure of a fluid
a force is exerted at right angles to any surface in contact with the fluid
a floating object
weight + upthrust
objects in water
experience upthrust
atmospheric pressure
decreases with height
an object will sink...
if it displaces a volume of water less than the objects weight
an object will float...
if it displaces a volume of water more or equal to the objects weight
distance
is scalar
displacement
is a vector
speed
how fast something is going
velocity
how fast youre going in a particular direction
distance travelled
speed x time
acceleration
change in velocity ÷ time
distance time graph
gradient = speed
velocity time graph
gradient = acceleration
drag increases...
as speed increases
friction
slows things down
objects falling through fluids (gas or liquid)
can reach a terminal velocity
newtons first law
objects with balanced forces acting on them will stay at rest, or in constant motion.
newtons second law
force + mass x acceleration
inertia
the tendency for motion to remain unchanged
newtons third law
when two objects interact the forces the exert on each other are equal and opposite
stopping distance
thinking distance + braking distance
thinking distance variants
speed, reaction times
reaction time inhibitants
drowsiness, alcohol/drug influences, concentration/distraction
braking distance variants
speed, weather, tread on wheels, brakes condition
braking
relies on the friction between tires and road
momentum
mass x velocity
total momentum laws in a closed system
total momentum before collision will be the same as the total momentum after collision
force (momentum)
change in momentum ÷ change in time
waves
transfer energy in the direction they are travelling
amplitude of a wave
height between undisturbed position and crest
wavelength
distance between crests or troughs
crests
top point
trough
bottom point
transverse waves
have sideways vibration eg electromagnetic waves
longitudinal waves
parallel vibrations eg sound
wave speed
frequency x wavelength
period of a wave
1/frequency
measuring sound
using an oscilloscope
angle of incidence in a reflection
= angle of reflection
specular reflection
uniform incoming rays reflect uniformly at 90 degrees off a shiny/smooth surface
diffuse reflection
uniform incoming rays reflect and scatter in all directions off a rough surface
refraction
waves changing direction at a boundary eg surface of water
the electromagnetic spectrum
radio waves, micro waves, infra-red radiation, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays
radio waves
made by oscillating changes, has lowest frequency
uses of radio waves
carrying TV, radio and phone signals
uses of microwaves
communications - satellites TV an phone signals
cooking - ovens create microwaves that are absorbed by water and causes heat
infrared radiation
used to increase or monitor temperature
uses of infrared radiation
toasters, night vision
infrasound
sounds lower than the human hearing range (20Hz)
a suntan is created by...
ultraviolet radiation
used in medicine
x rays and gamma rays
uses of ultrasound
scanning unborn babies, navigation under water
ultrasound
sounds higher than the human hearing range (20,000Hz)
uses of x-rays
used in the detection of broken bones and internal cracks
uses of ultraviolet light
forgery detection, sunbeds
uses of gamma rays
killing bacteria, sterilising equipment
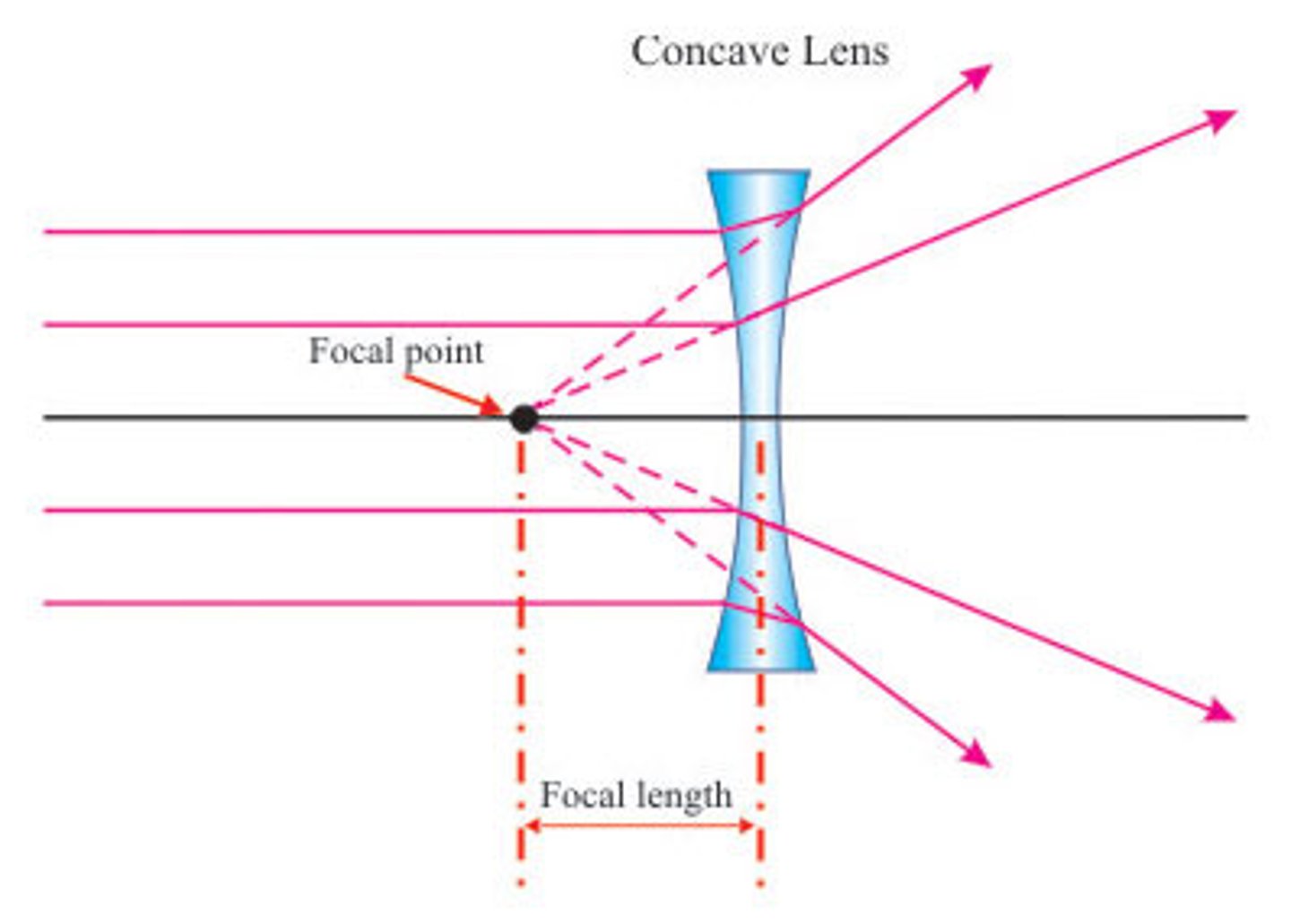
concave lens
causes light to diverge
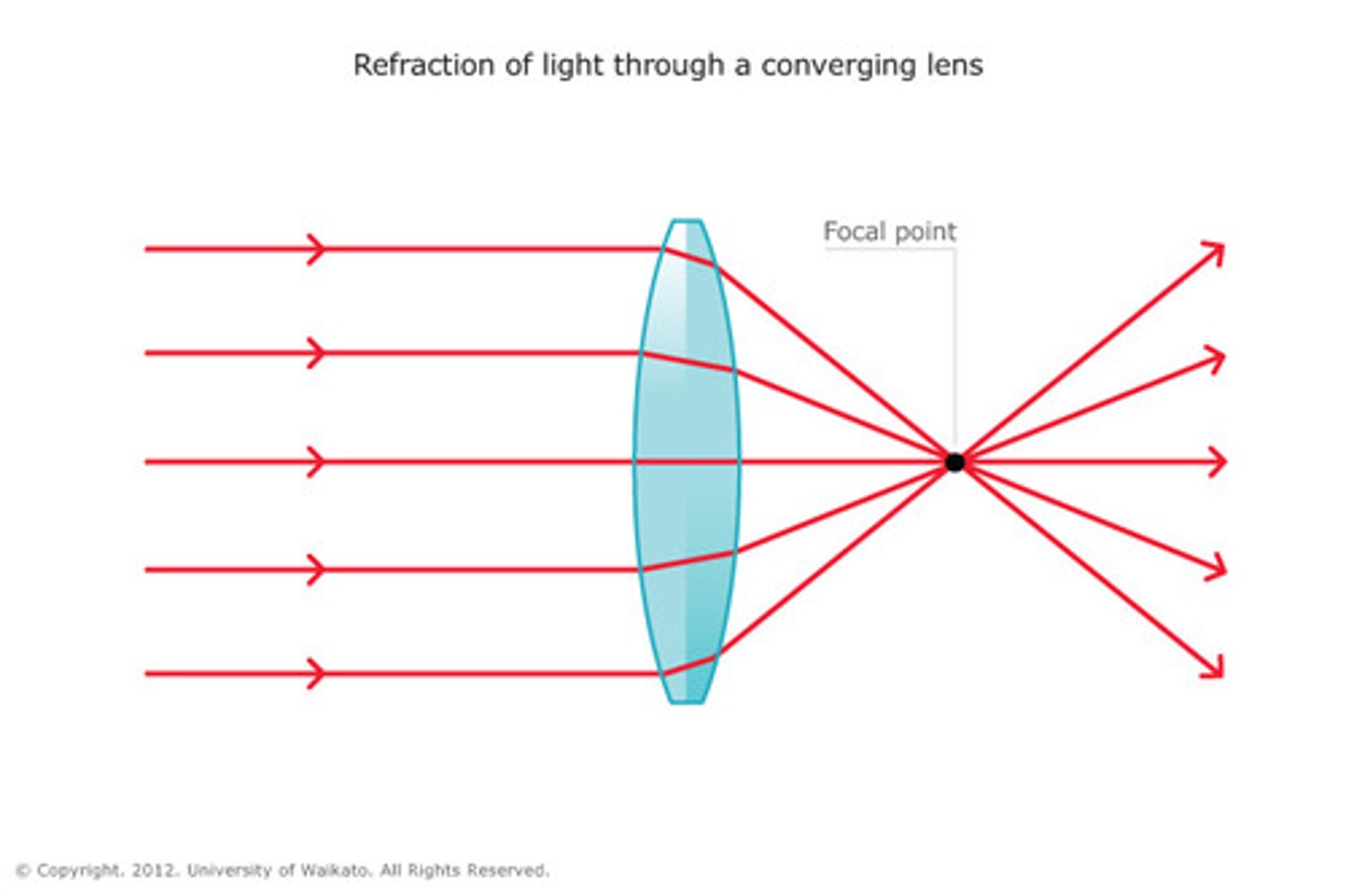
convex lens
light rays meet after passing through lens
rules of refraction in lenses
incident ray parallel to the axis refracts through the lens and passes through the principal focus on the other side
an incident ray passing through the principal focus refracts through the lens and travels parallel to the axis
an incident ray travelling through the axis continues in that direction
distance from the convex lens
affects the image size
magnifying glasses
use convex lenses
visible light
made of a rage of colours
white
all colours
black
absence of colour
how colour is seen
an object absorbs all coloured light except the colour of the light that the object is which is then reflected into our eyes
colour filters
if a coloured object is covered by a colour filter that is a different colour then the object will appear black
leslie cube
investigates emission with different coloured and textured sides
every object emits and absorbs...
infrared radiation
radiation within the atmosphere and space
affects the earths temperature
compression in sound waves
a collection of sound particles in a sound wave
rarefaction in sound waves
sparser sound particles in a sound wave
how sound is heard
ear drum vibrates
how an ultrasound works
the transmitter/receiver transmits particles that hit the foetus (for example) and are then reflected back showing the size. or submarines do the same to find the bottom of the ocean, like echolocation
seismic waves
caused by earthquakes and explosions
p waves
primary longitudinal waves that travel through liquids
s waves
secondary transverse waves that cannot travel through liquids
the focus of an earthquake
where the fracture occured
the epicentre of an earthquake
the place on earth where the fracture is closest to
what is the combine point?
where 2 waves interact
permanent magnets
produce their own magnetic fields