Unit 5: Heredity
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Examples of Asexual Reproducion
Mitosis
Produces exact copies
Single-celled eukaryotes
Simple multicellular eukaryotes, the example below is a simple animal animal Hydra species. It clones itself by budding.
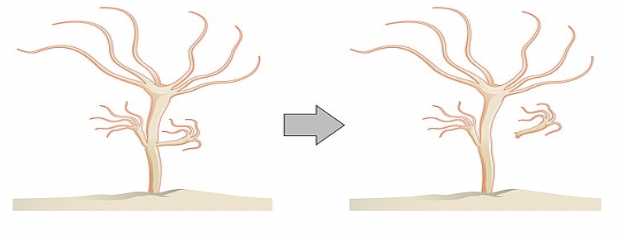
Examples of Sexual Reproduction
Reproduction in complex multicellular organisms
Variation in offspring is the point
Reproductive cells are produced by meiosis.
Outcome of Meiosis
Produces gametes (reproductive cells)
Two cell divisions
Reduces the number of chromosomes by half
The cells that are produced are different from each other and from the original cell
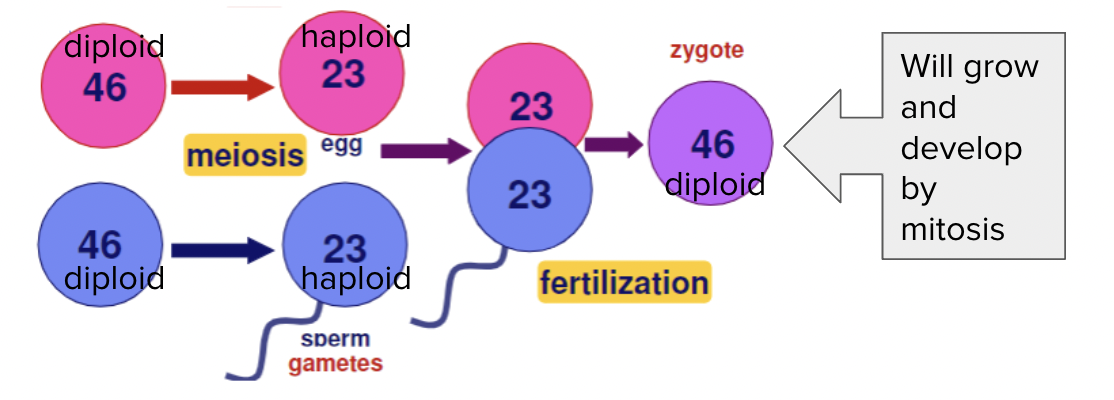
How can a change in ploidy be expressed in terms of n? When does it occur?
(ploidy reduces in Metaphase 1)
Diploid 2n→ haploid n (other species can be 4n - 6n!)
Draw a general diagram of meiosis
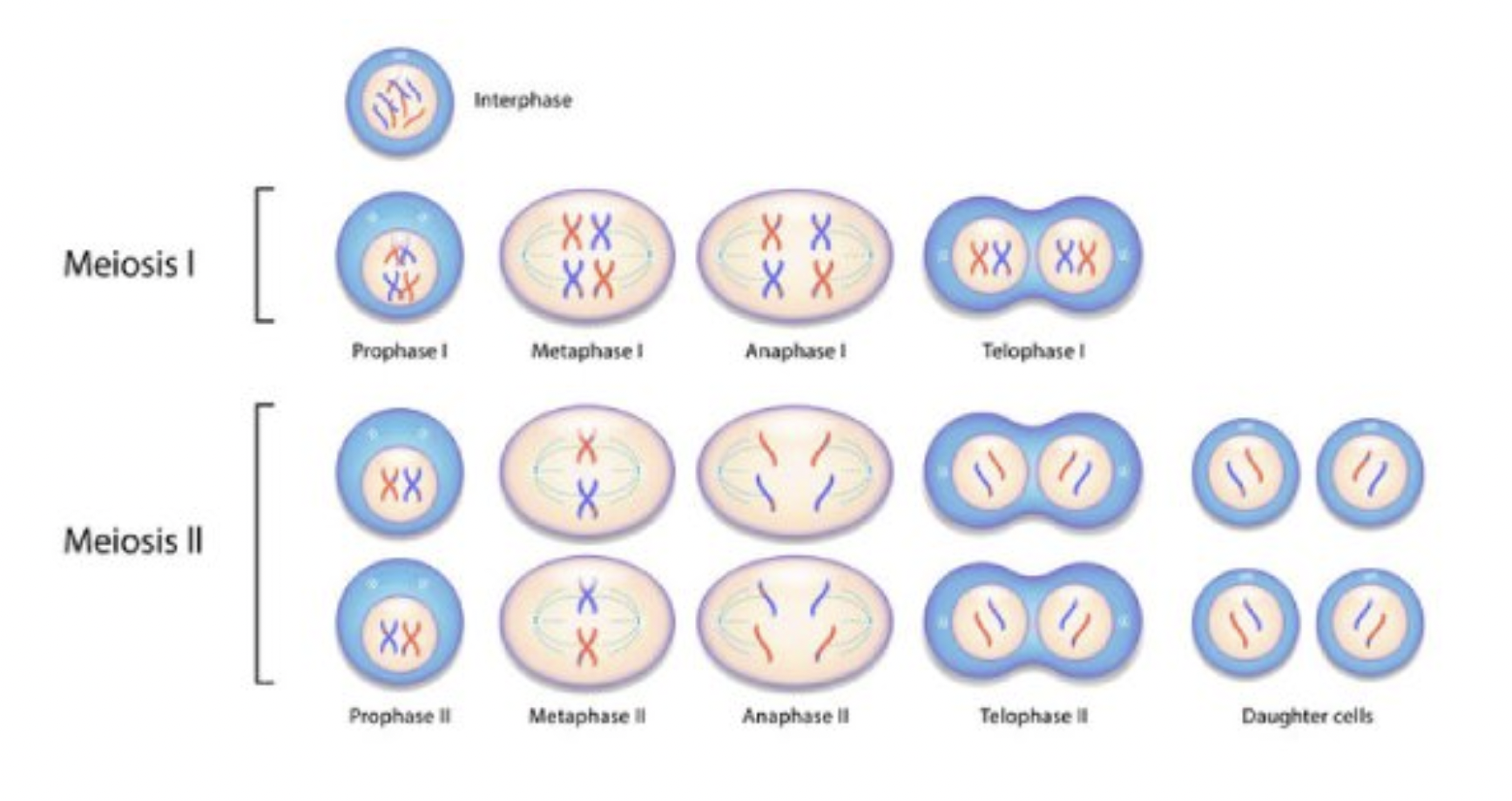
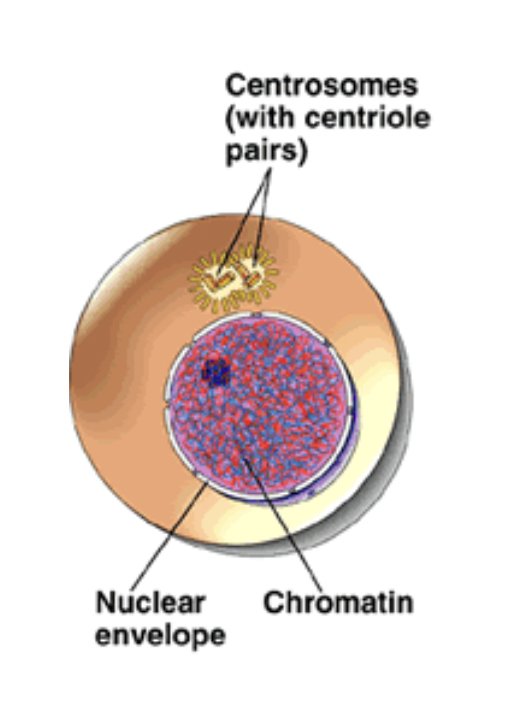
Interphase
DNA is replicated
The cell prepares for division
Interphase only happens once
Prophase 1
Homologous pairs can exchange segments during crossing over (increasing variation and driving evolution faster)
Metaphase 1
Homologous pairs line up in the middle of the cell - opposite each other (not above each other as in mitosis)
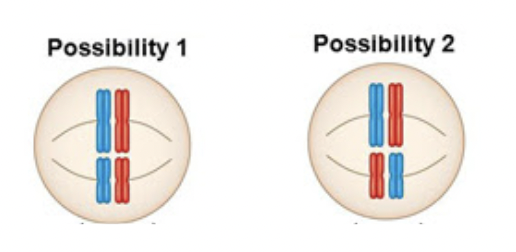
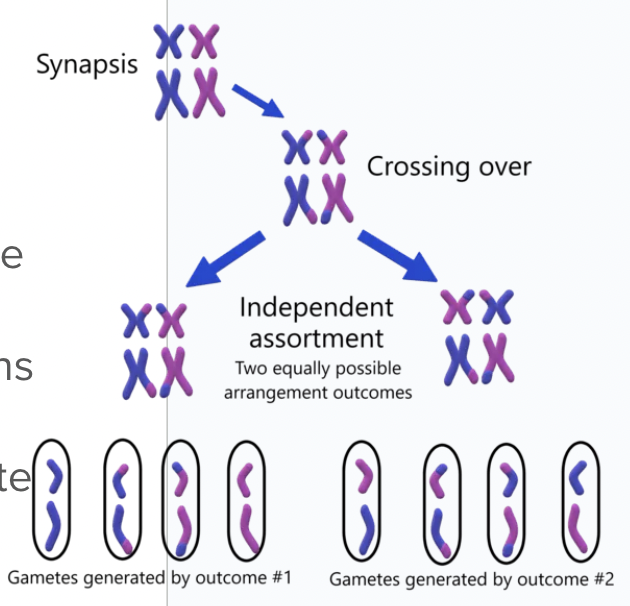
Independent assortment
Independent assortment
Pairs randomly line up in the middle (Mendel’s 1st Law)
Anaphase 1
Homologous pairs are separated; ploidy reduced
Telophase 1
Two nuclei form and the cell splits into two
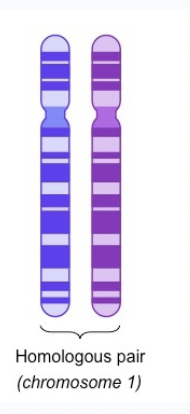
In each pair, one chromosome is from each?
Parent
The chromosomes contain genes for the same trait (ex. hair color).
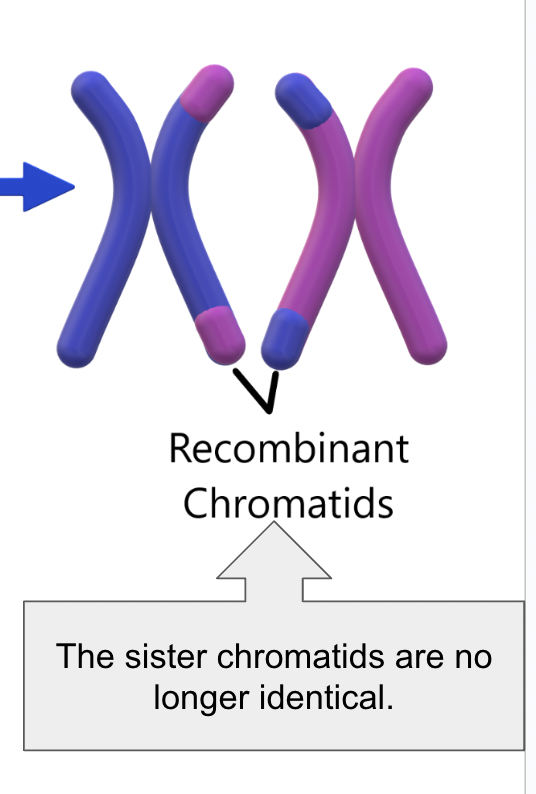
Draw a diagram of crossing over
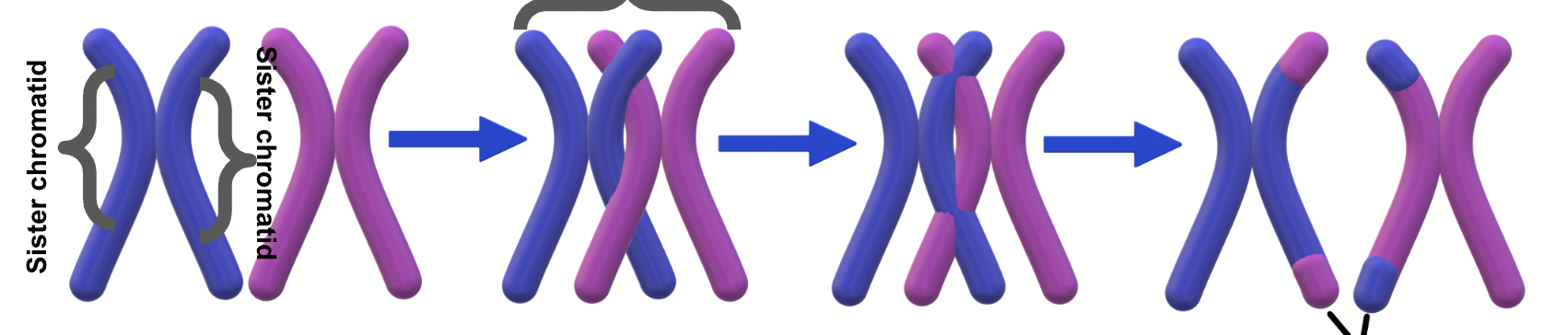
Tetrad
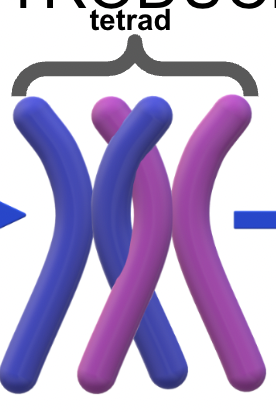
Name the steps of crossing over
Homologous pair, synapsis, crossing over, recombinant chromosomes
Homologous pair
These are replicated chromosomes, so each side (sister chromatid) is identical.
Recombinants
Genetic combinations that did not previously exist
Meiosis 1
Homologous pairs are separated
Meiosis 2
Sister chromatids are separated
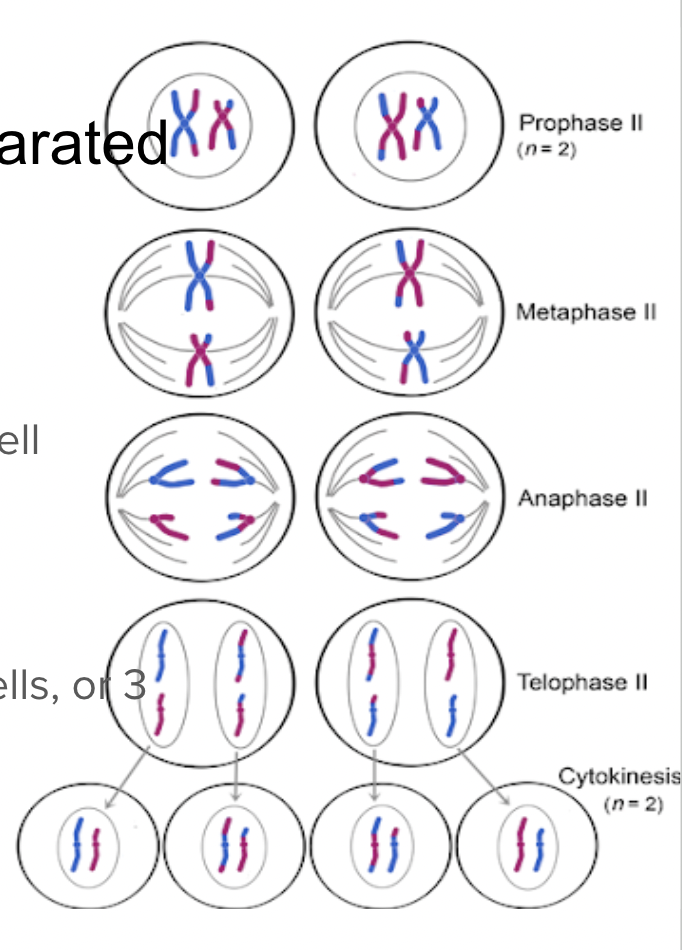
Prophase 2
Crossing over does not occur
Metaphse 2
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase 2
Sister chromatids are separated
Telophase 2
Nuclei form and cells split (either 4 sperm cells, or 3 polar bodies and and egg)
Variation is an advantage, why?
It increases the likelihood that some members of a population will survive disease, disaster, etc. (driving natural selection)
What increases variation in a population
Sexual reproduction
Crossing over
During meiosis mixes alleles across homologous chromosomes, creating new combinations of traits on each chromosome
Independent assortment outcome
During metaphase I of meiosis results in the formation of gametes that are different from each other (223 combinations in gametes)
Random fertilization
Of an egg cell (any two parents will produce a zygote with 223 x 223 possible diploid combinations)
When done correctly, meiosis should result in? What would the zygote have?
Gametes with 23 chromosomes each.
That way, the zygote has 46 chromosomes - 44 of which are autosomes and 2 of which are sex chromosomes (in humans, the X & Y).
What errors can occur in meiosis?
Nondisjunction or breaking of chromosomes
Nondisjunction, possible cause?
Chromosomes don’t separate properly during meiosis
Problems with the meiotic spindle cause daughter cells to have too many or too few chromosomes
Breaking of chromosomes
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Translocation
Nondisjunction 1
Homologous pairs do not separate properly during Meiosis 1
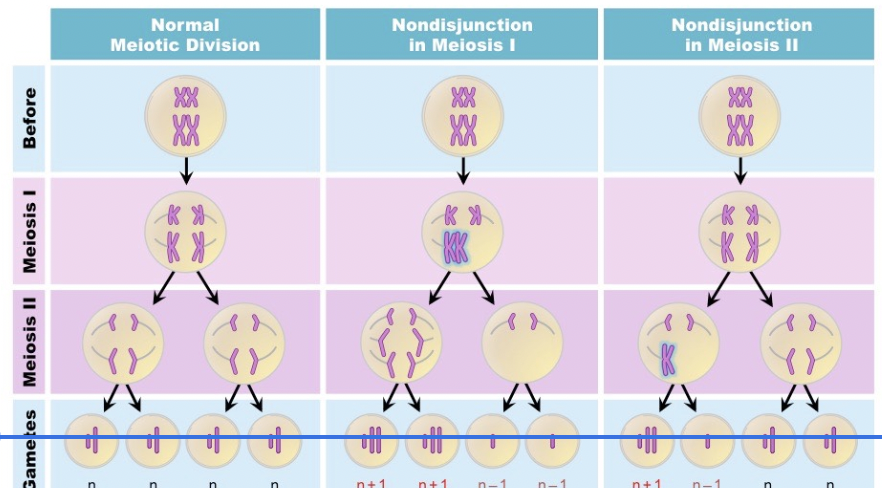
Nondisjunction 2
Sister chromatids do not separate during Meiosis 2
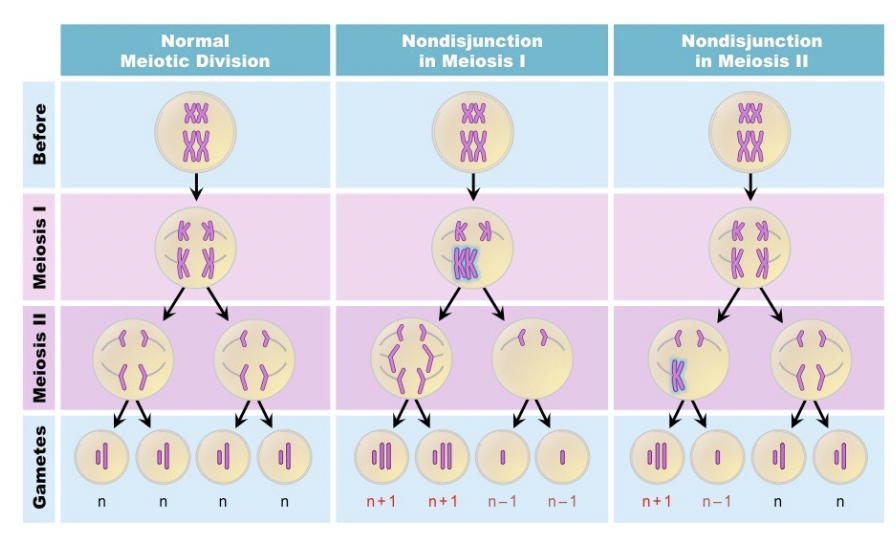
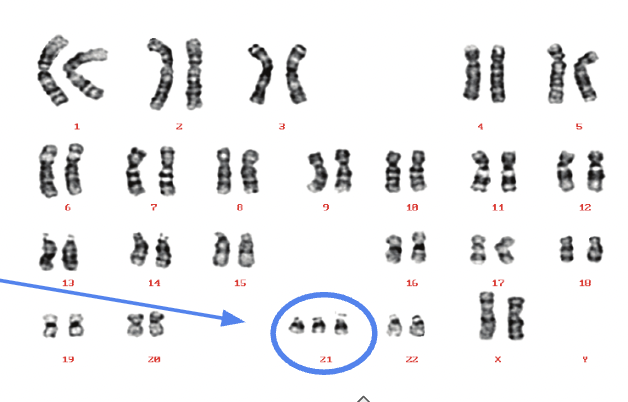
Results of nondisjunction
Zygotes with 3 copies of a chromosome (trisomy) or 1 copy (monosomy) instead of 2 copies of each chromosome
Most of the time nondisjuncition results in?
Miscarriage
What are some examples of nondisjunction when a miscarriage does not happen?
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
Klinefelter’s Syndrome (XXY male)
Turner’s Syndrome (XO)
Jacob’s Syndrome (XYY)

Karyotype
Picture of chromosomes
Changes in Chromosome Structure
Deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation
Deletion
Removes a chromosomal segment
Duplication
Repeats a segment
Inversion
Reverses a segment within a chromosome
Translocation
Move a segment from one chromosome to another, nonhomologous one
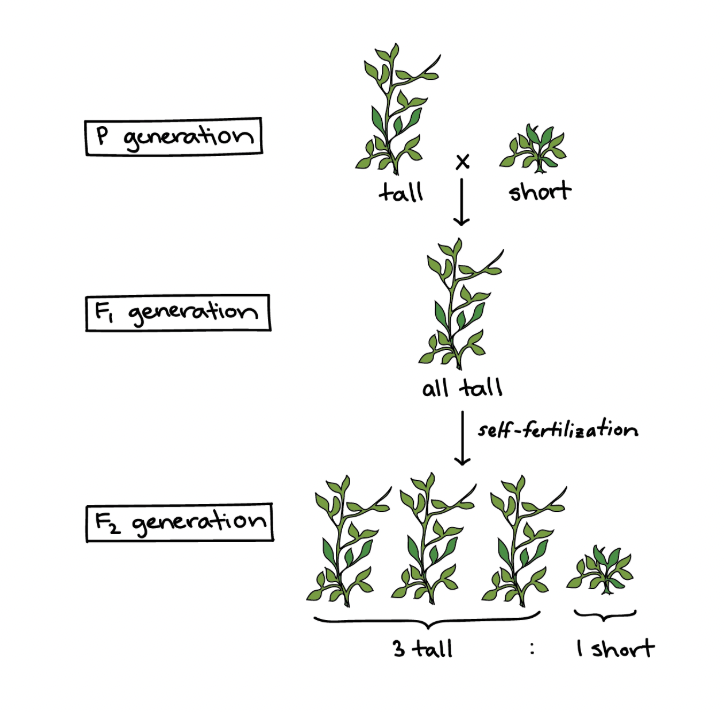
Gregor Mendel
Documened the inheritance of peas
Mendel’s findings
Traits come in alternate versions (alleles)
For each characteristic, an organism inherits 2 alleles, 1 from each parent
Some traits mask others (dominant masks recessive)
Phenotype
Physical appearance of a trait
eg. purple or white
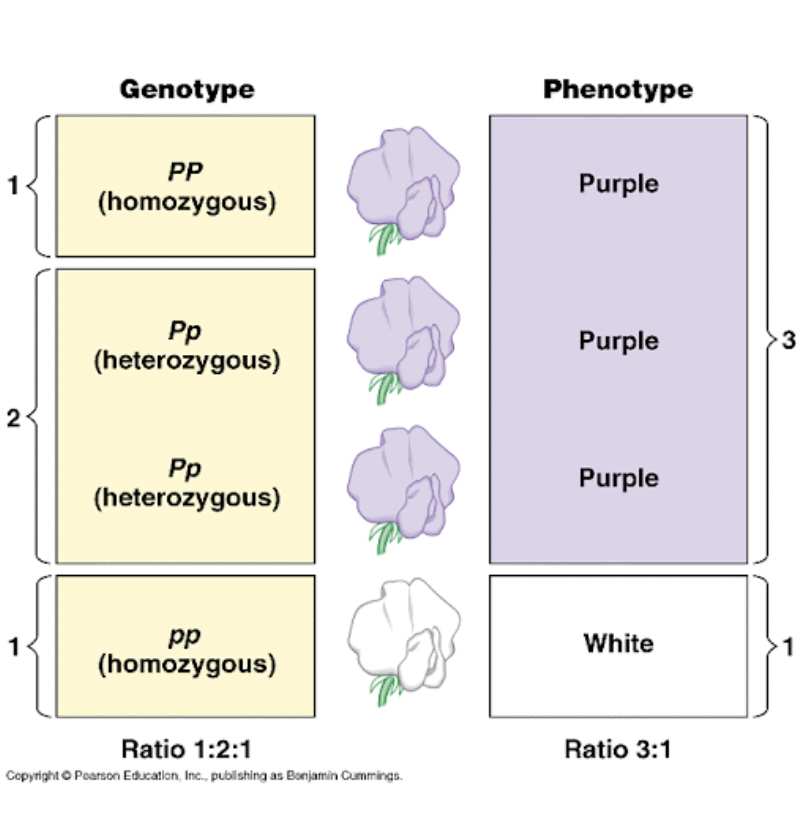
Genotype
an organism’s genetic makeup
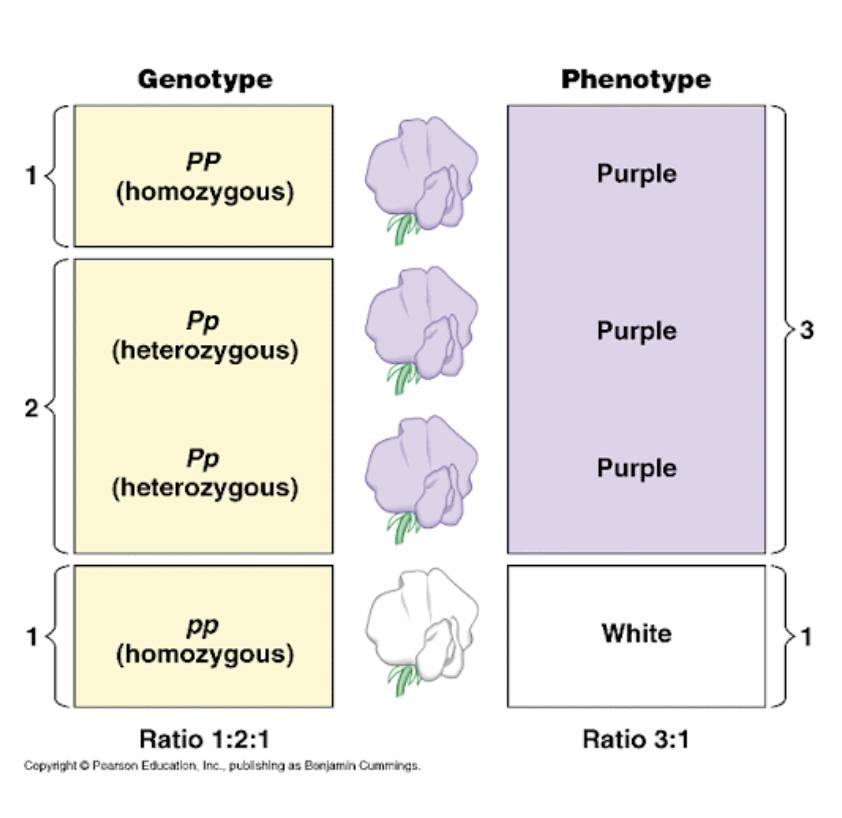
Homozygous
Same alleles; PP or pp
Heterozygous
Different alleles; Pp
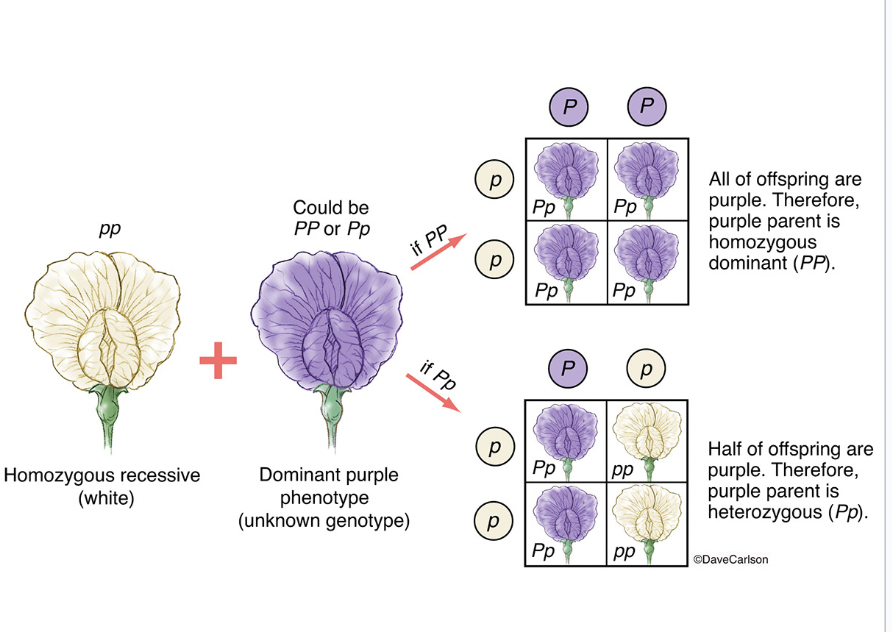
Test cross
A visible, low tech test for genotype
An organism has the dominant phenotype but an unknown genotype could be?
Homozygous dominant or heterozygous)
How would the cross test go for the organism with an unknown genotype but dominant phenotype?
Cross the organism with one that is homozygous recessive - the ‘test’
If some of the offspring have the recessive phenotype → organism was heterozygous
If none of the offspring have the recessive phenotype → organism was homozygous dominant
Mendel’s first law
Law of segregation (coming apart)
Law of segregation
During meiosis, alleles segregate (separate)
Homologous chromosomes separate during anaphase I
Each allele for a trait is packaged into a separate gamete.
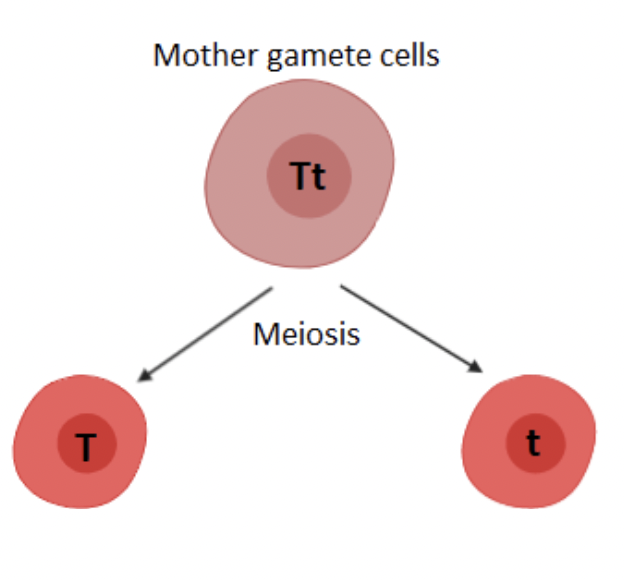
Mendel’s 2nd Law
Law of independent assortment
Law of independent assortment
Different chromosomes separate into gametes independently
In this diagram, you can have multiple combinations of red and blue chromosomes in each gamete
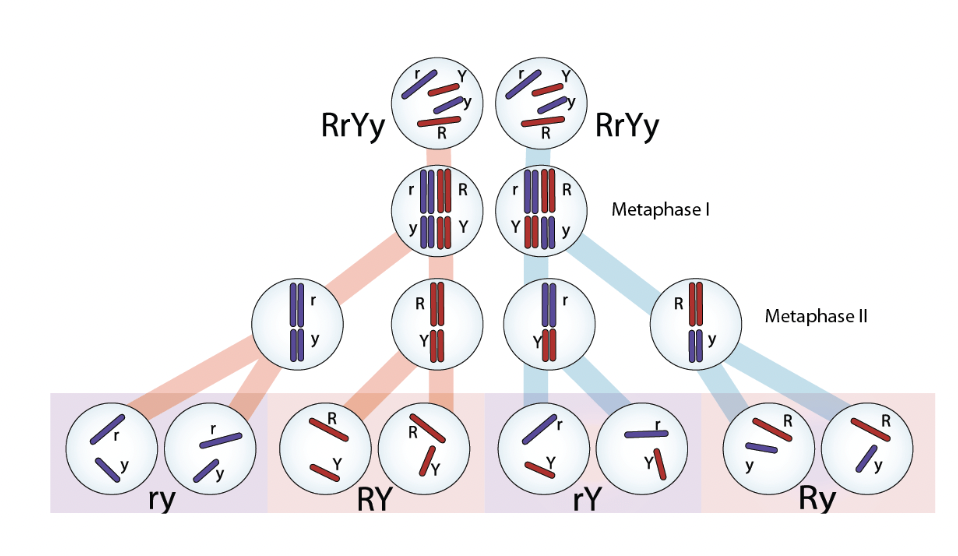
When does independent assortment occur?
Non-homologous chromosomes align independently during metaphase I
For which genes is independent assortment true?
Only true for genes on separate chromosomes or on same chromosome but far apart so that crossing over happens frequently
Autosomal dominant disease example
Huntington’s
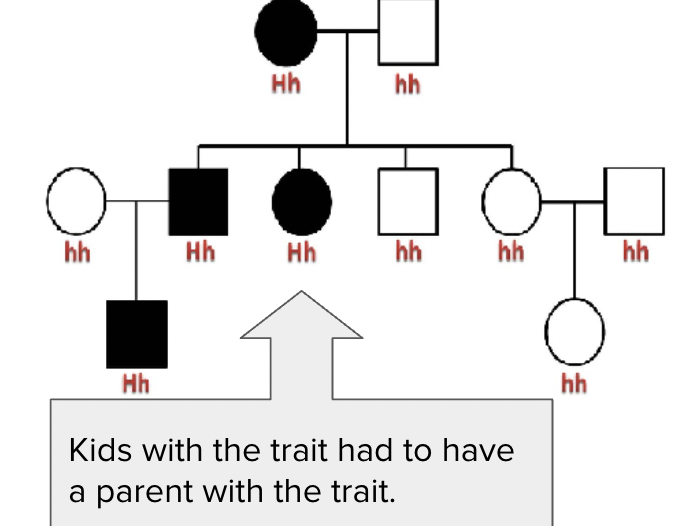
Autosomal recessive disease example
Cystic fibrosis
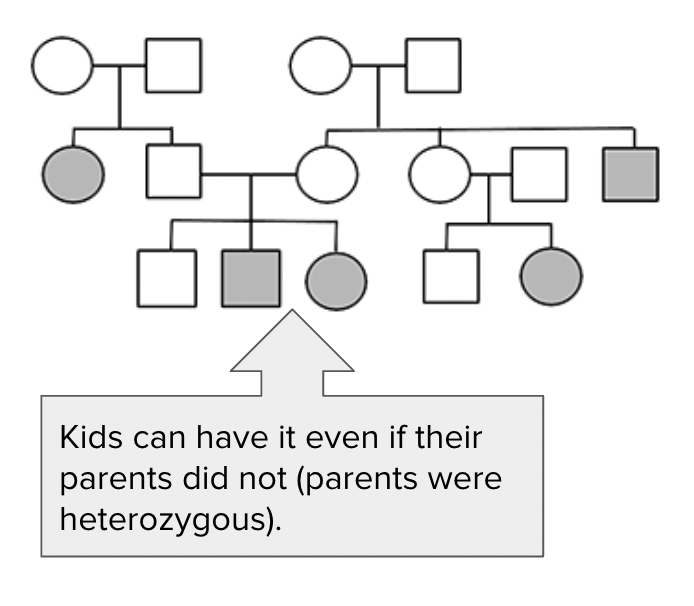
Draw a key for pedigrees
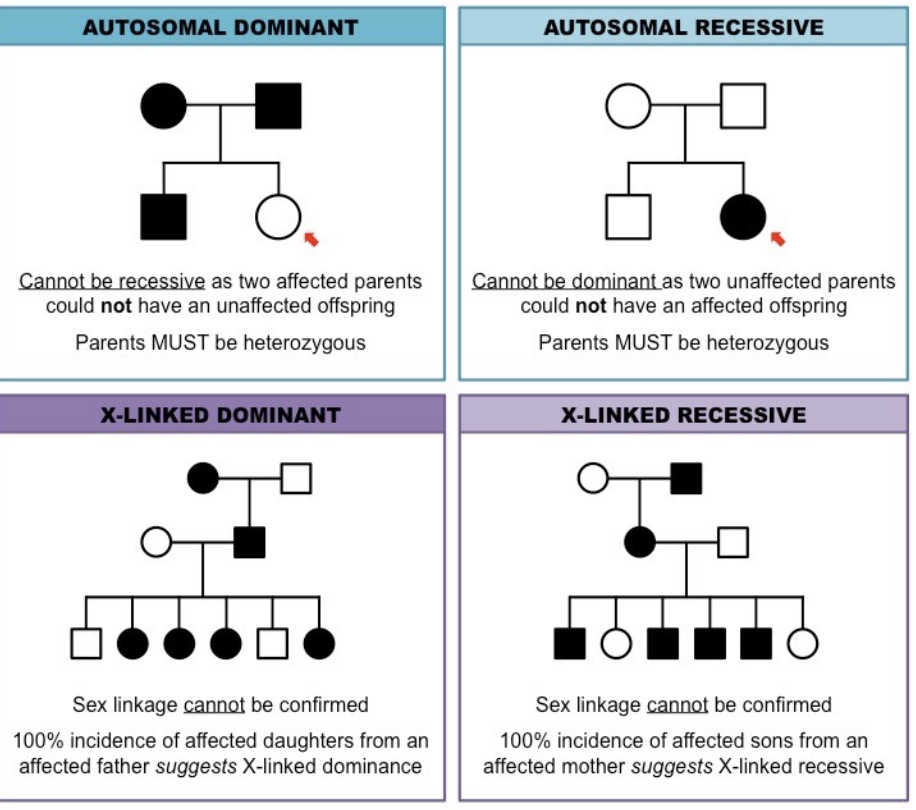
Pedigrees Autosomal, X-linked, dominant and recessive patterns of inheritance: provide a brief indication of each
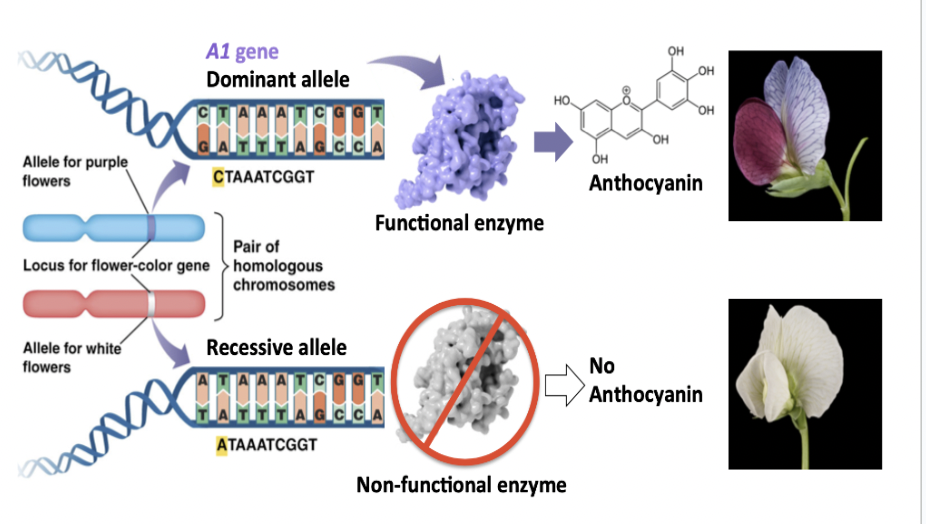
What causes dominance vs. recessive?
Dominant and recessive alleles code for two different proteins because their nucleotide sequences are different. (Mendel’s 3rd Law)
For a gene coding an enzyme: what if it is homozygous dominant?
100% functional protein produced

For a gene coding an ezyme: what if it is heterozygous?
Only 50% functional protein produced
50% may enough to accomplish the cellular function
The dominant allele may be up-regulated to compensate for the lack of function due to the recessive allele
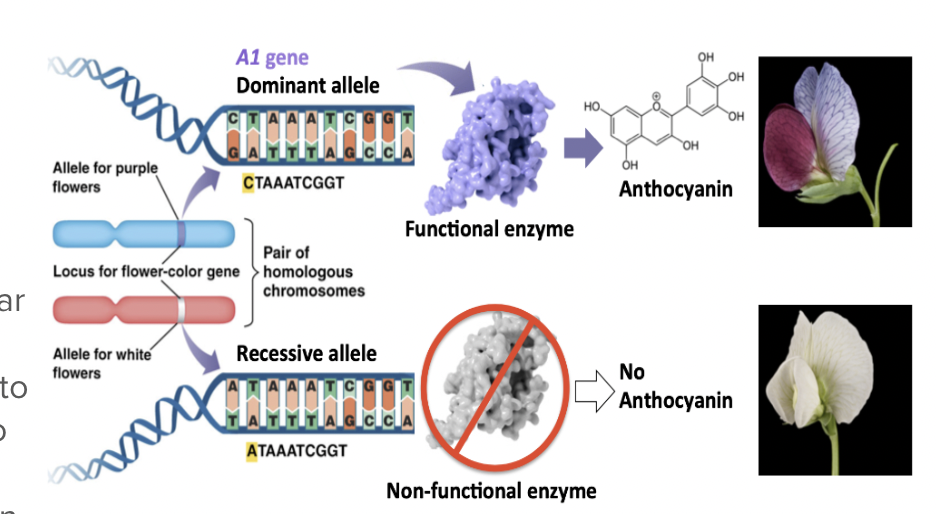
For a gene coding an enzyme: what if it is homozygous recessive?
0% functional protein produced
Genetics & Probability
Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment reflect the same laws of probability that apply to tossing coins or rolling dice.
What is the probability of passing on B in a gamete in a heterozygous combination? What is this similar to?
50%
Tossing heads
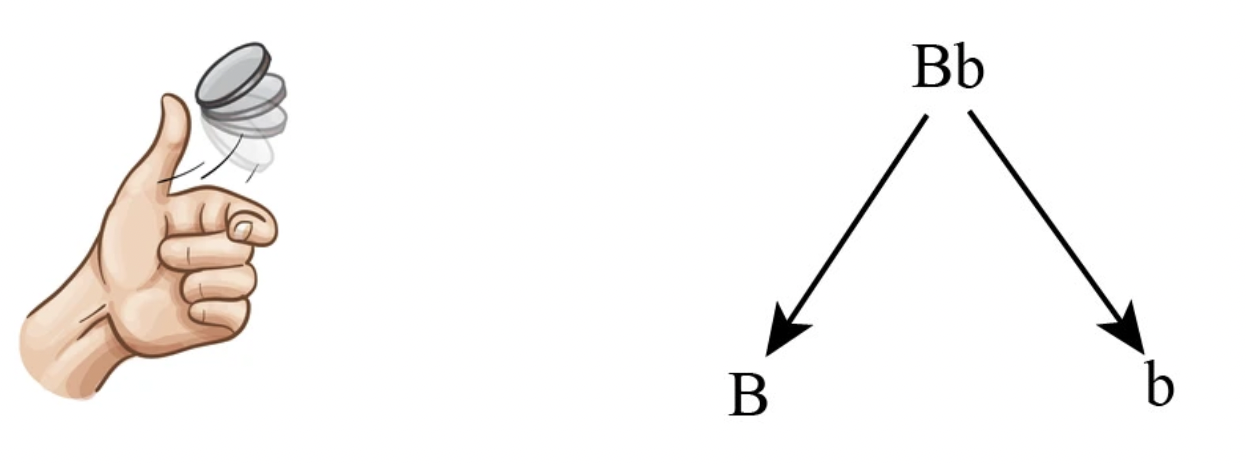
Rule of Multiplication
Chance that 2 or more independent events will occur together
Provide an example of the rule of multiplication
Probability that 2 coins tossed at the same time will land heads up: ½ x ½ = ¼
Probability of Pp x Pp having offspring pp: ½ x ½ = ¼
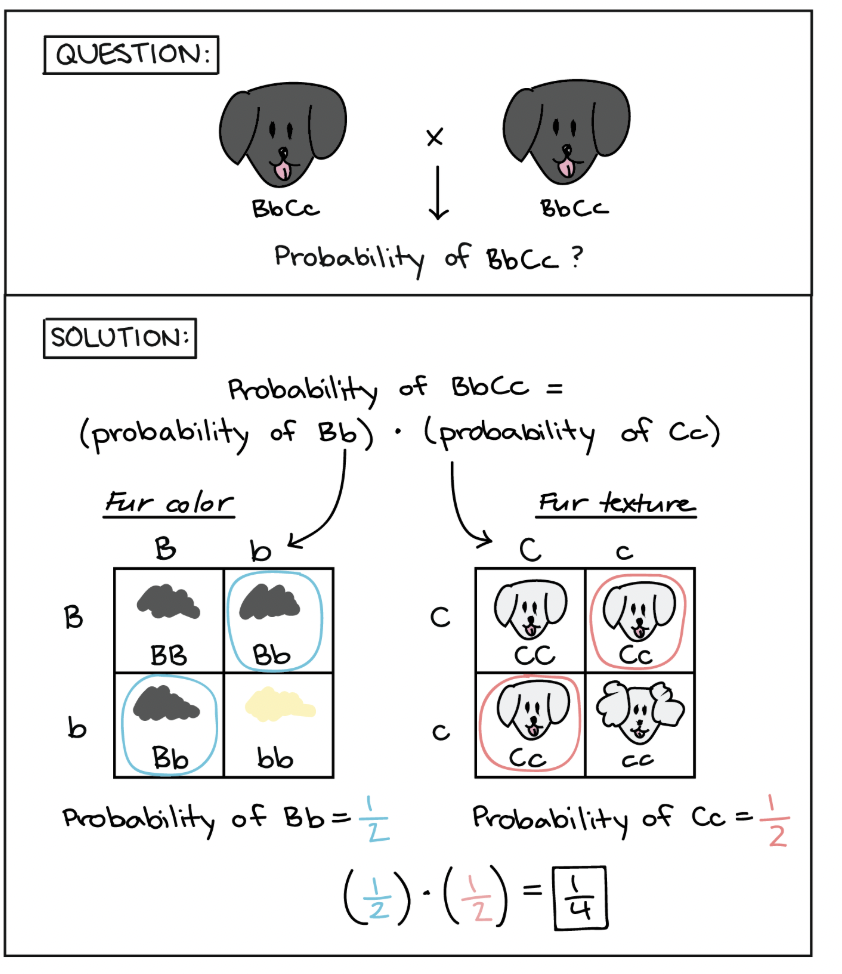
Given the cross AABbccDdEEFf x AaBbccDdeeFf, what is the probability offspring will have the genotype AabbccDdEeFF?
1/64
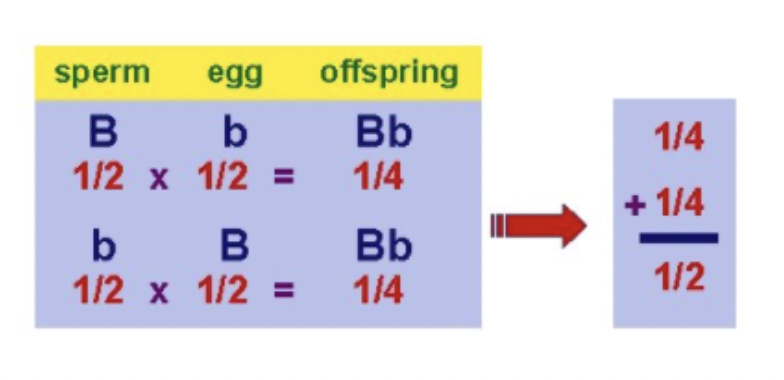
Rule of Addition
Chance that an event can occur 2 or more different ways
Probability of Bb x Bb → Bb?
1/2
Chi square
An analysis to determine if the results of a cross fit the expected ratio.
Outcomes of a Chi Square
If calculated value > critical value → reject null hypothesis
If calculated value < critical value → accept null hypothesis
Why might you reject the null hypothesis?
You have a small sample size.
Your sample is not representative of the larger sample.
The genes do not show independent assortment - non-mendelian genetics.
May be linked (close together on the same chromosome)
May be sex-linked (on one of the sex chromosomes)
Chi Square formula
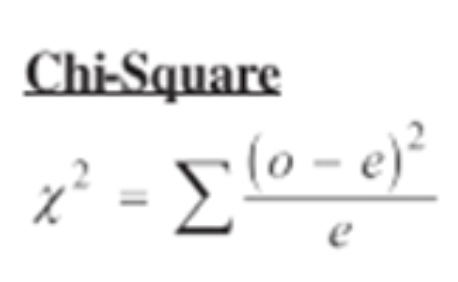
Degrees of freedom
Number of phenotypes - 1
Mendel worked with a simple system following what principles?
Peas are genetically simple
Most traits are controlled by a single gene
Each gene has only 2 alleles, 1 of which is completely dominant to the other
What did Mendel not consider?
The relationship between genotype and phenotype is rarely that simple:
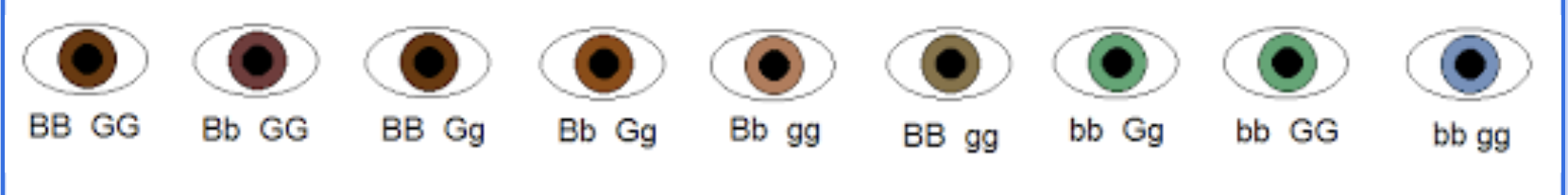
Mnemonic for dihybrid crosses
FOIL (first, outside, inside, last)
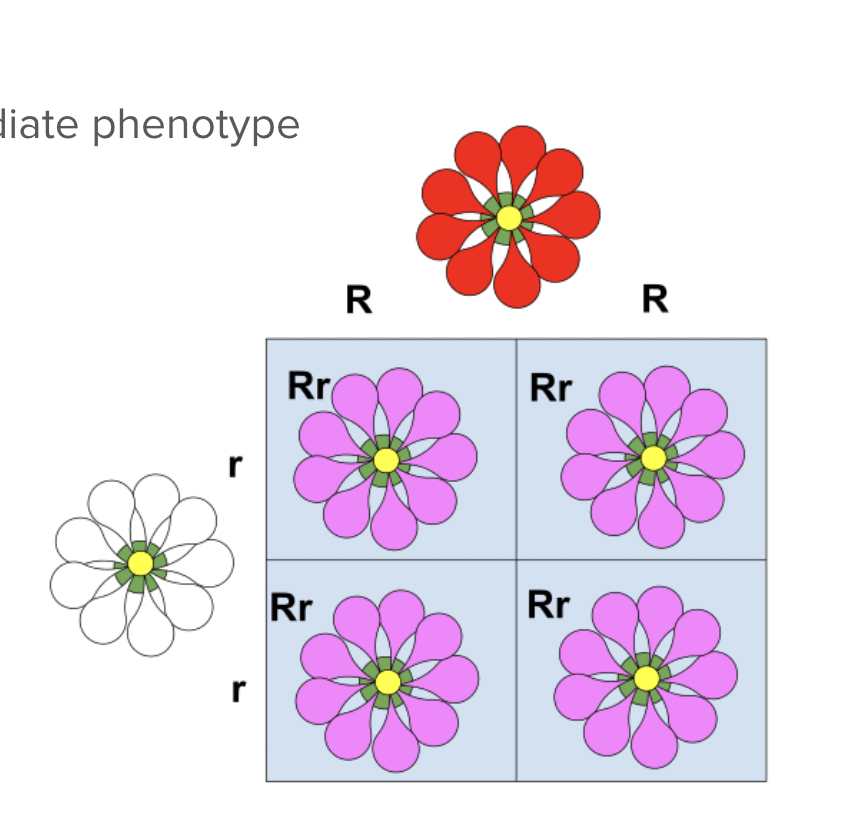
Incomplete dominance
Heterozygotes show an intermediate phenotype
Example of incomplete dominance
RR = red flowers
Rr = pink flowers
rr = white flowers
Null hypothesis
No relationship between two variables; the finding probably occured by chance
Alternative hypothesis
States the opposite of a null; there is a relationship between two varibales; the finding did not occur by chance
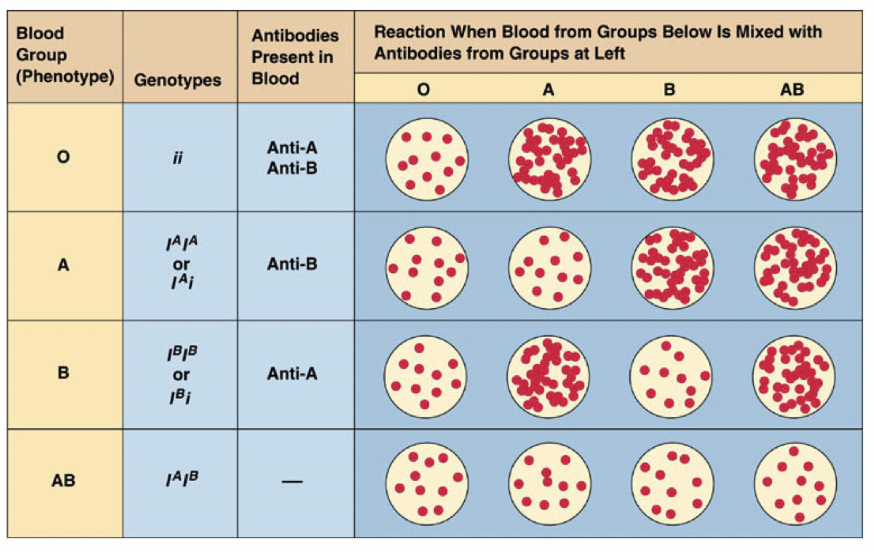
Codominance
2 alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishabl
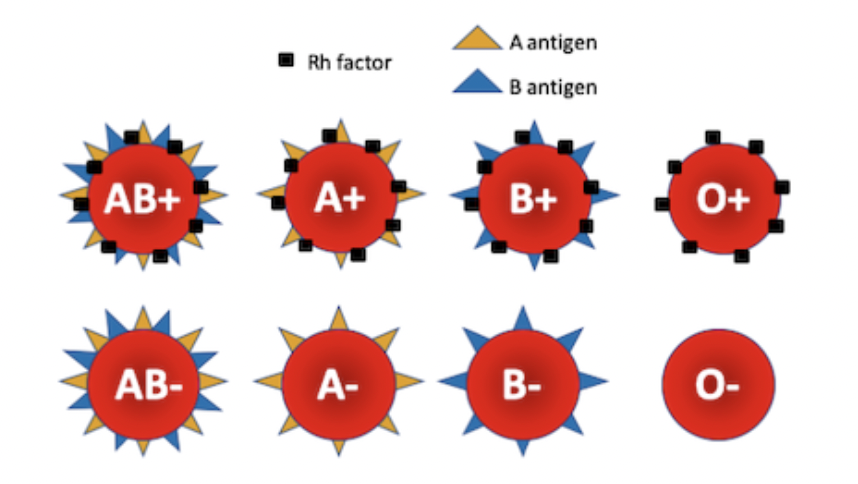
Example of codomniance
ABO blood types - A and B are codominant, so people with type AB blood have A and B antigens on their blood cells
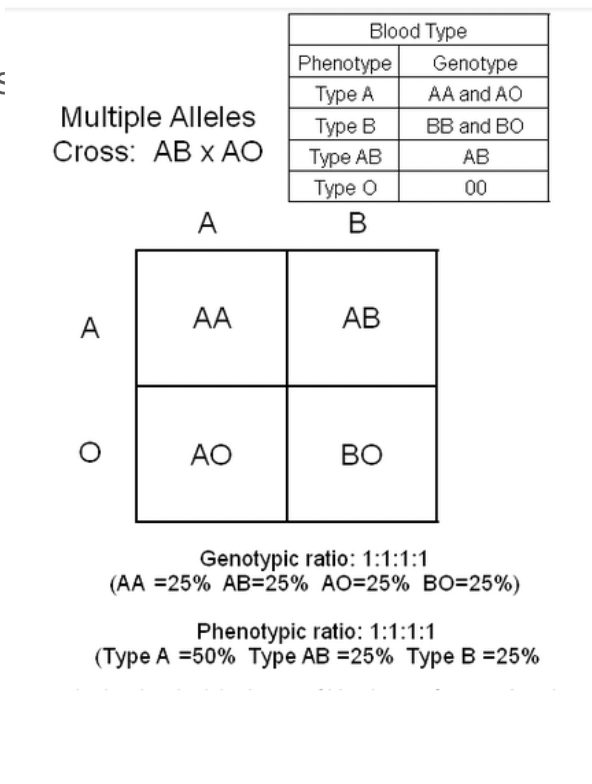
Blood compatibility
Matching compatible blood groups is important for blood transfusions
What in a person’s blood affects blood compatibility?
A person produces antibodies in their blood plasma against the antigens on foreign blood cells
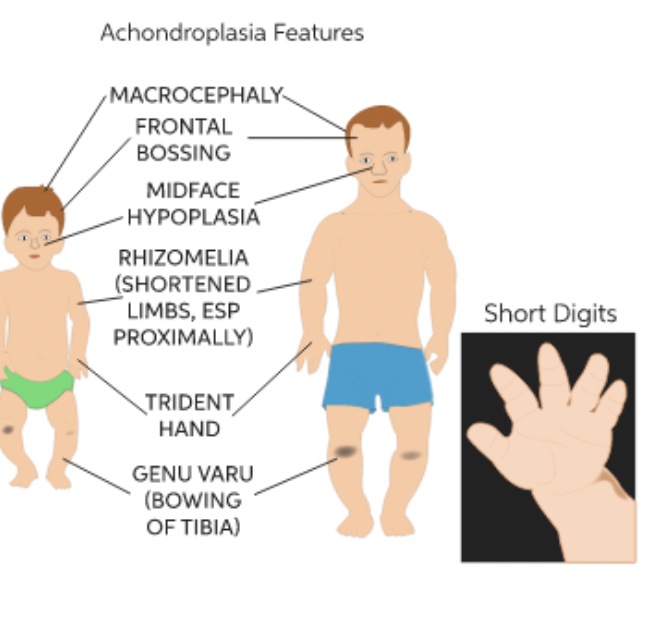
Pleiotropy
Most genes are pleiotropic - affect more than one phenotypic character
Wide-ranging effects due to a single gene
Examples of pleiotropy
Ex. dwarfism (achondroplasia)
Ex. gigantism (acromegaly)
Epistasis
One gene masks another
Example of epistasis :)
Ex. coat color in mice
Pigment (C) is dominant to no pigment (c)
Black pigment (B) is dominant to brown pigment (b)
cc is albino, regardless of the B allele
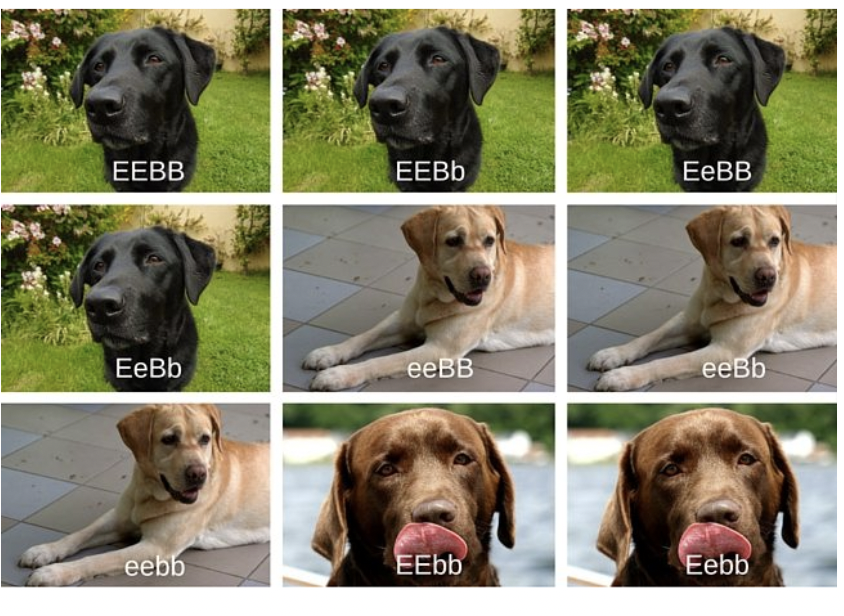
Ex. coat color in Labrador retrievers
Pigment (E) or no pigment (e)
Black pigment (B) or brown pigment (b)

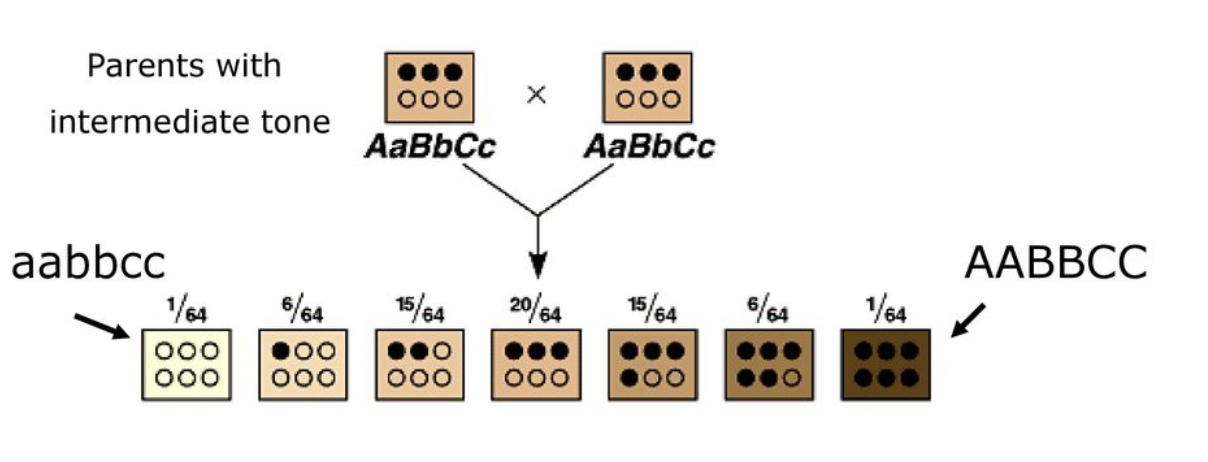
Polygenic inheritance
Some phenotypes are determined by the additive effects of 2 or more genes on a single character
Examples of polygenic inheritance
Many human traits - skin color, height, eye color, etc.
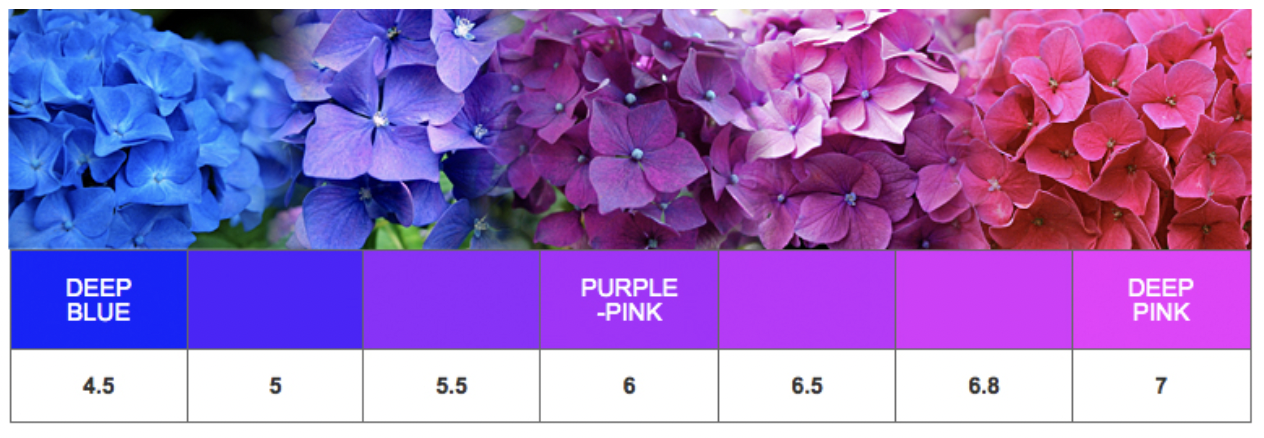
Nature vs. Nurture (Phenotypic Plasticity)
Phenotype is controlled by the environment and genes
Examples of phenotypic plasticity
Ex. coat color in Himalayan rabbits influenced by heat sensitive alleles
Ex. color of Hydrangea flowers influenced by soil pH
Ex. human skin color influenced by UV radiation
Sex-linked traits
Human sex chromosomes: X and Y
Female
2X chromosomes
Male
XY